9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-1
Page 9B-1
Section 9B
Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to Section 2
Precautions in this Supplement and Section 00 Warnings, Cautions and Notes in the MY2005 VZ Service
Information for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and/or property damage.
The structure of the body shell has been
developed using complex design and
development techniques. In addition to
meeting all required standards, the vehicle
body is also a critical part of the overall safety
systems. It is therefore imperative the repair
procedures described here are adhered to
during all vehicle body repairs.
1 General Description ...............................................................................................................................2
1.1 Roof Components.................................................................................................................................................. 2
Wagon..................................................................................................................................................................... 3
Wagon, with Sunroof............................................................................................................................................. 3
2 Service Operations.................................................................................................................................4
2.1 Roof Panel – Replace ............................................................................................................................................ 4
Remove................................................................................................................................................................... 4
Replace................................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.2 Roof Front Header Panel – Replace ..................................................................................................................... 8
2.3 Roof Bow Panels – Replace.................................................................................................................................. 9
Roof Bow Panel No. 1............................................................................................................................................9
Roof Bow Panel No. 3.......................................................................................................................................... 10
Roof Bow Panel No. 2 and 4................................................................................................................................ 10
2.4 Roof Rear Panel – Replace ................................................................................................................................. 11
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-2
Page 9B-2
1 General Description
This Section describes the replacement procedures for the roof structure. The componen t s covered include the roof
panel and the roof header, bo w and re ar panels.
Removal of trim and bolt-on components is not covered. Reference must be made to the appropriate Sections of the MY
2005 VZ Service Information.
The roof panel is both spot welded and glued in place with structural adhesive. Heating or other normal means cannot
soften this adhesive and the panel can o nly be removed by cutting and/or grinding.
A sunroof is fitted on the production line to High Level AW D Wagon vehicles and as an o ption on Low Level AWD Wagon
vehicles. To cater for this option, a new roof structure has been introduced which features a housing assembly in place of
several roof bow panels. A stainless steel front drain tube is also fitted within the hinge pillar cavity which affects the
service procedures for the hinge pillar, refer to Section 7G Body Side – AWD Wagon. Despite these differences, the
service procedures for the roof panel with sunroof carry over from roof panel without sunroof, noting the subframe
assembly replaces several of the roof bow panels and must be removed with the roof panel.
When repairing the roof structure, care must be taken to ensure it is returned to its original prod uction configuration.
NOTE
It is imperative that the correct body adhesives,
sealers, deadeners and cavity waxes are used
when repairing the body structure. Refer to
Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon for
details of the correct materials and their
commercially available equivalents.
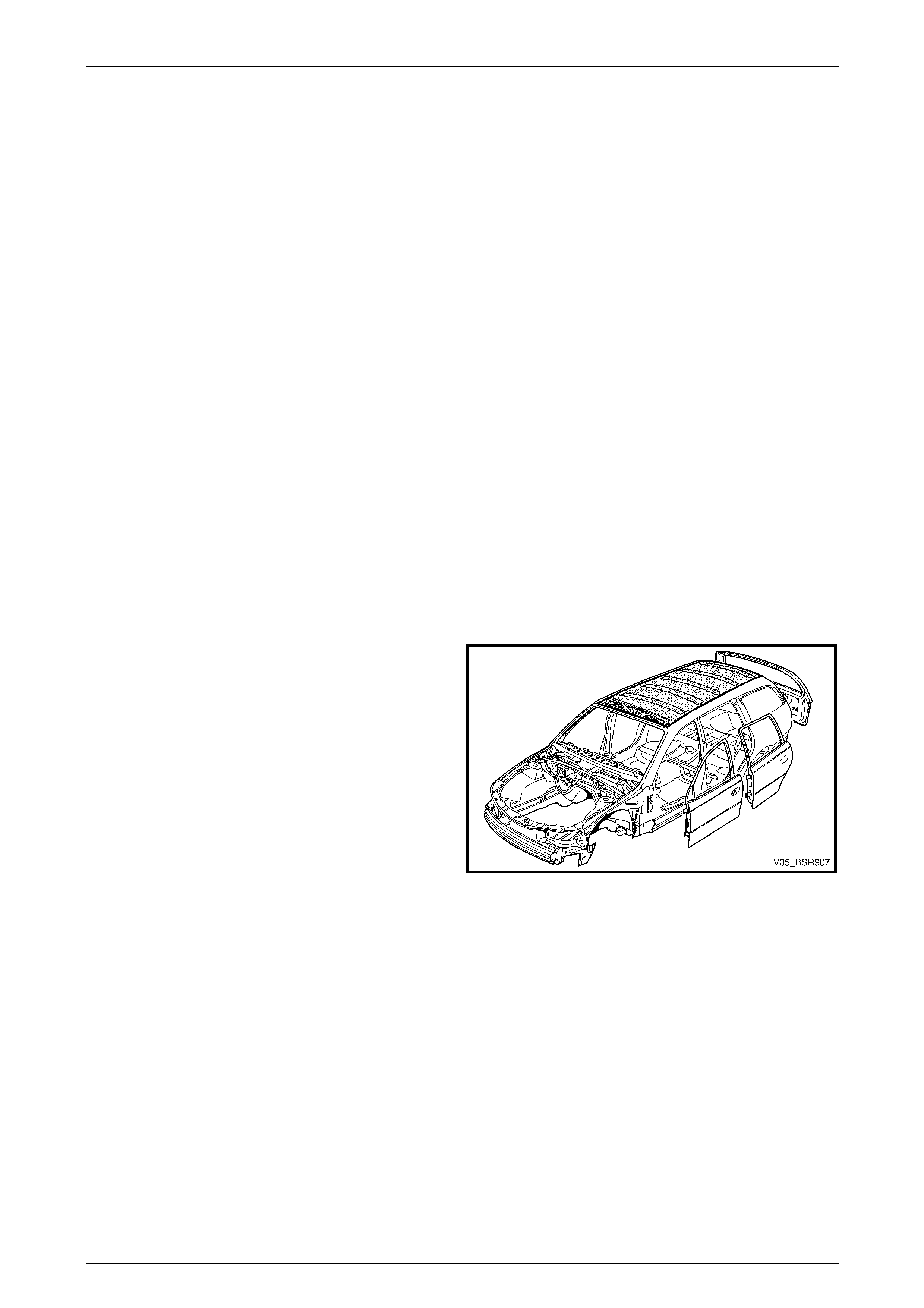
1.1 Roof Components
The shaded components in Figure 9B – 1 are those dealt
with in this Section.
The components and assemblies shown
below are the serviceable parts that form the basis of the
repair procedures in this Section.
For a detailed view of the body components, refer to
Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
NOTE
Always refer to an Authorised Retailer for spare
parts availability configurations.
Figure 9B – 1
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-3
Page 9B-3
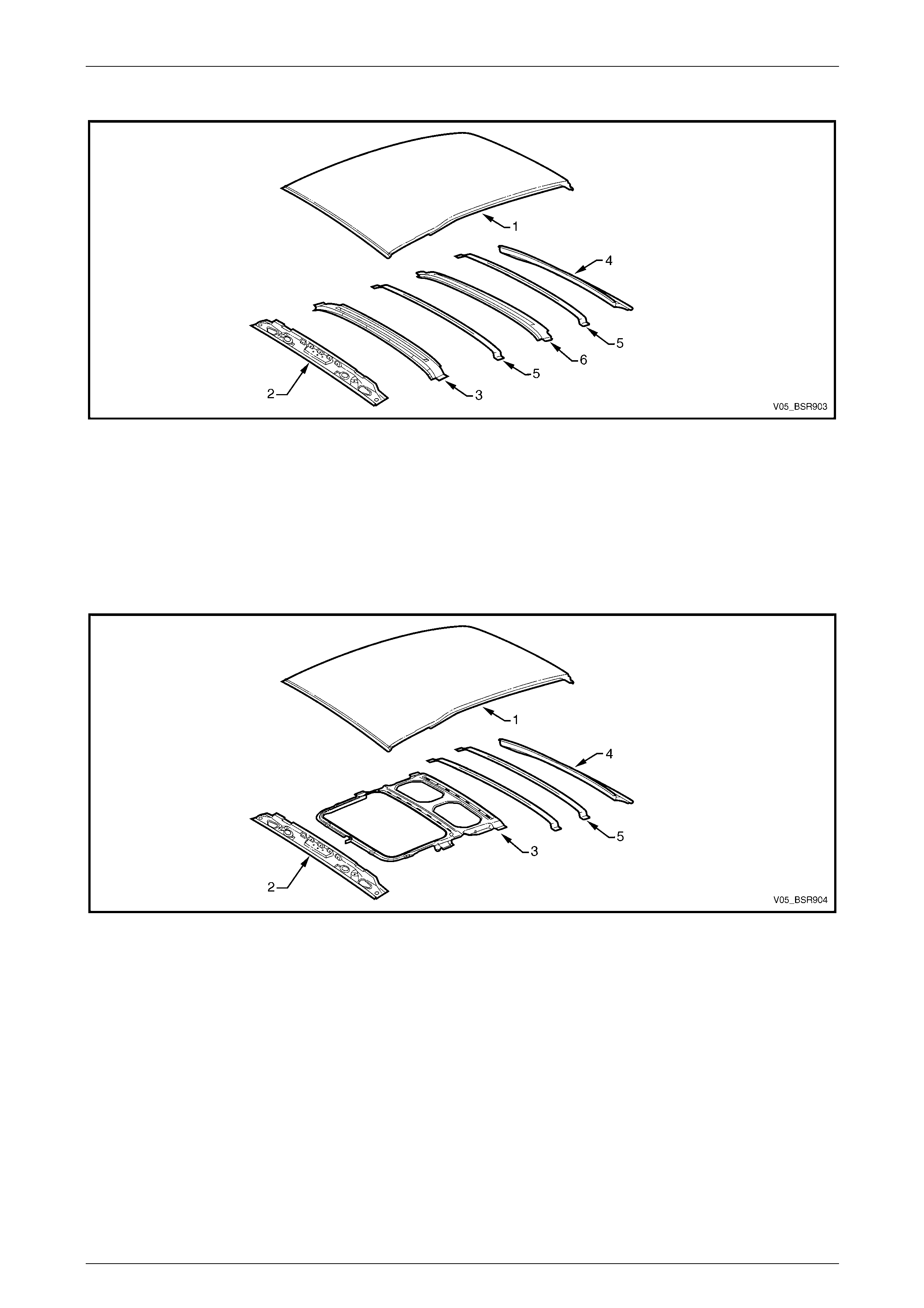
Wagon
Figure 9B – 2
Legend
1 Roof Panel
2 Roof Front Header Panel
3 Roof Bow Panel No. 1
4 Roof Rear Panel
5 Roof Bow Panel No. 2
6 Roof Bow Panel No. 3
Wagon, with Sunroof
Figure 9B – 3
Legend
1 Roof Panel Assembly
2 Roof Front Header Panel
3 Sunroof Housing Assembly
4 Roof Rear Panel
5 Roof Bow Panel No. 2
NOTE
The roof panel assembly includes a housing
assembly that is not serviced separately.
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-4
Page 9B-4
2 Service Operations
2.1 Roof Panel – Replace
Remove
1 Remove the adjacent trim and components as described in the appropriate Section of the MY 2005 VZ Service
Information.
2 Remove the windshield, refer to Section 1A6 Stationary Windo ws in the MY 2005 VZ Service Information.
3 Remove the liftgate, refer to Section 8 Doors, Liftgate and Endg ate .
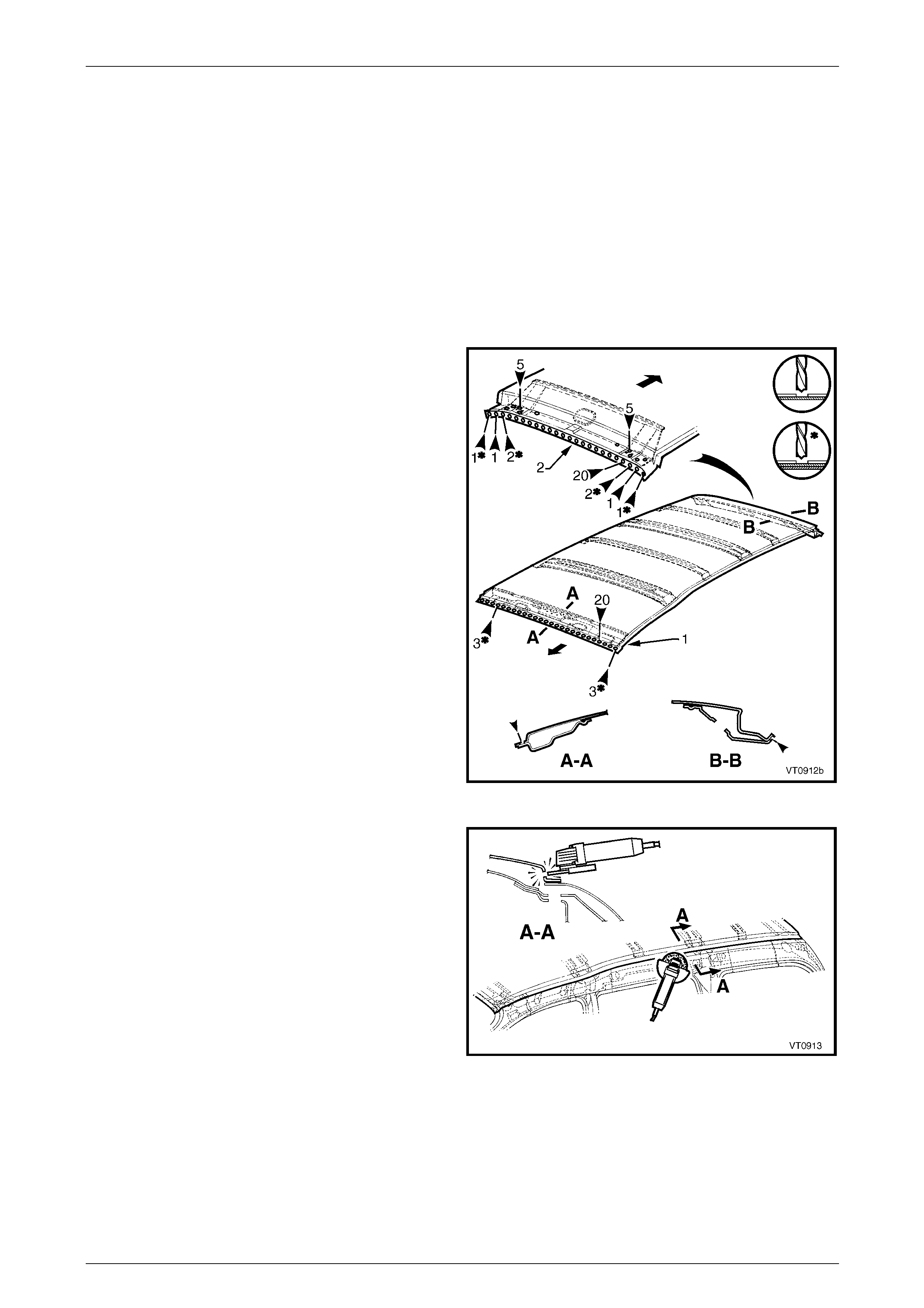
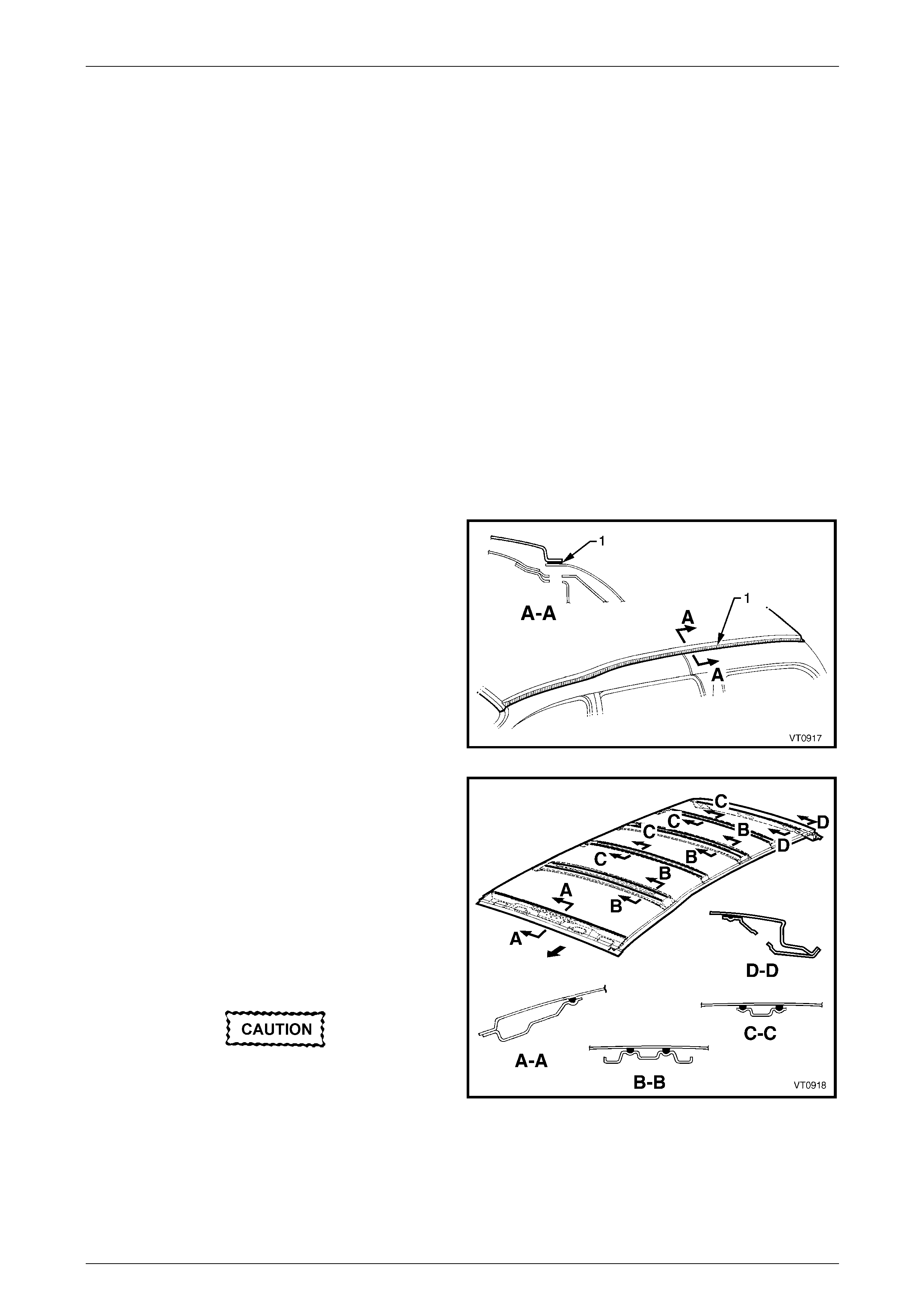
4 Spot cut the welds attaching the roof panel to the roof
front header panel (1) and roof rear panel (2).
Figure 9B – 4
5 Using a cutting tool such as an air chisel or a ngle
grinder, cut through the roof panel along the side of
the roof channel.
NOTE
• As the roof panel is securely glued to the
body side panel along the channel it cannot
be removed by simply spot cutting the welds.
• If the roof front header panel, roof bow
panels and roof rear pan el are to be reta ined,
take care not to cut them off with the roof
panel. Alternatively, if one or all are to be
replaced, it is easier to cut those being
replaced off with the roof panel. Figure 9B – 5
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-5
Page 9B-5
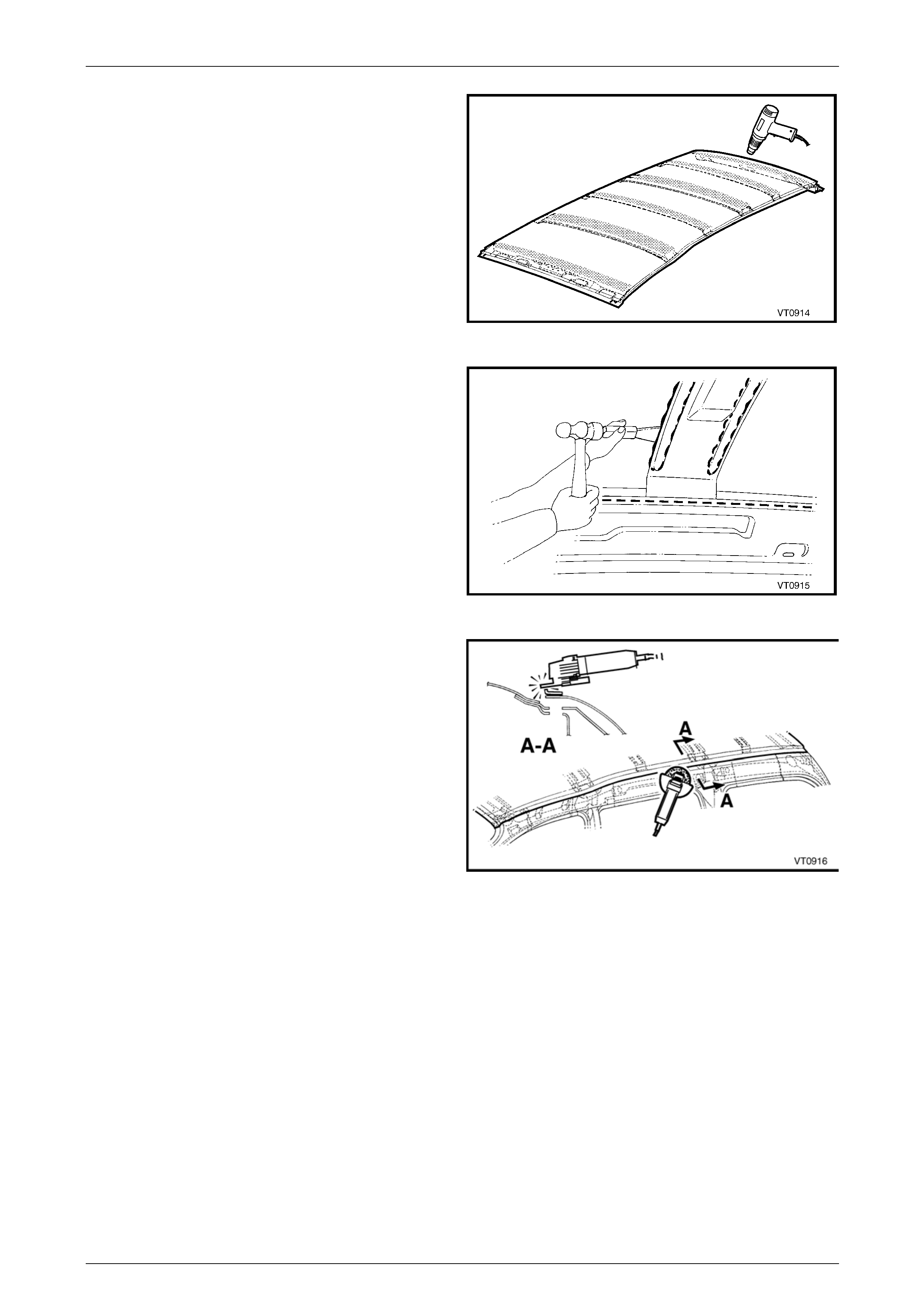
6 Use a heat gun to soften the Anti-flutter adhesive
between the roof front header panel, roof bo w panels
and roof rear panel by heating the areas shown.
Figure 9B – 6
7 Cut through the softened adhesive between the roof
panel and roof front header panel, roof bow panels
and roof rear panel using a suitable tool.
8 Remove the roof panel from the vehicle.
Figure 9B – 7
9 Using an angle grind er, air chi s el or other suitable tool,
remove the remaining strip of roof panel from the body
side panel, along with the adhesive ben eath the strip.
10 Repair any damage to adjacent parts.
11 Check and rectify the alignme nt of
the body as equired, refer to
Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
Figure 9B – 8
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-6
Page 9B-6
Replace
NOTE
• Spot welding is the preferred method for
attaching of panels and should be used
whenever possible. Where the spot welding
equipment available will not access the
required weld position, a plug weld should be
performed.
• The same number and position of spot welds
(or plug welds) should be used when
replacing the panel, as was used during
manufacture, in order to maintain the original
structural strength of the vehicle.
• When welding a relatively flat panel such as
the roof panel, due care must be taken to
minimise the heat absorbed by the panel
which could lead to panel distortion.
1 Clean any remaining Anti-fl utter adh esive from the surface of the roof front header panel, roof bow panels and roof
rear panel.
2 Prepare the mating areas for welding. Dress the channel flange ar ea, the roof front header panel, roof bow panels
and roof rear panel. These areas should be flat and free from imperfections.
3 As required, mark the new panel with drilling locations in preparation for plug welding. Drill holes as required.
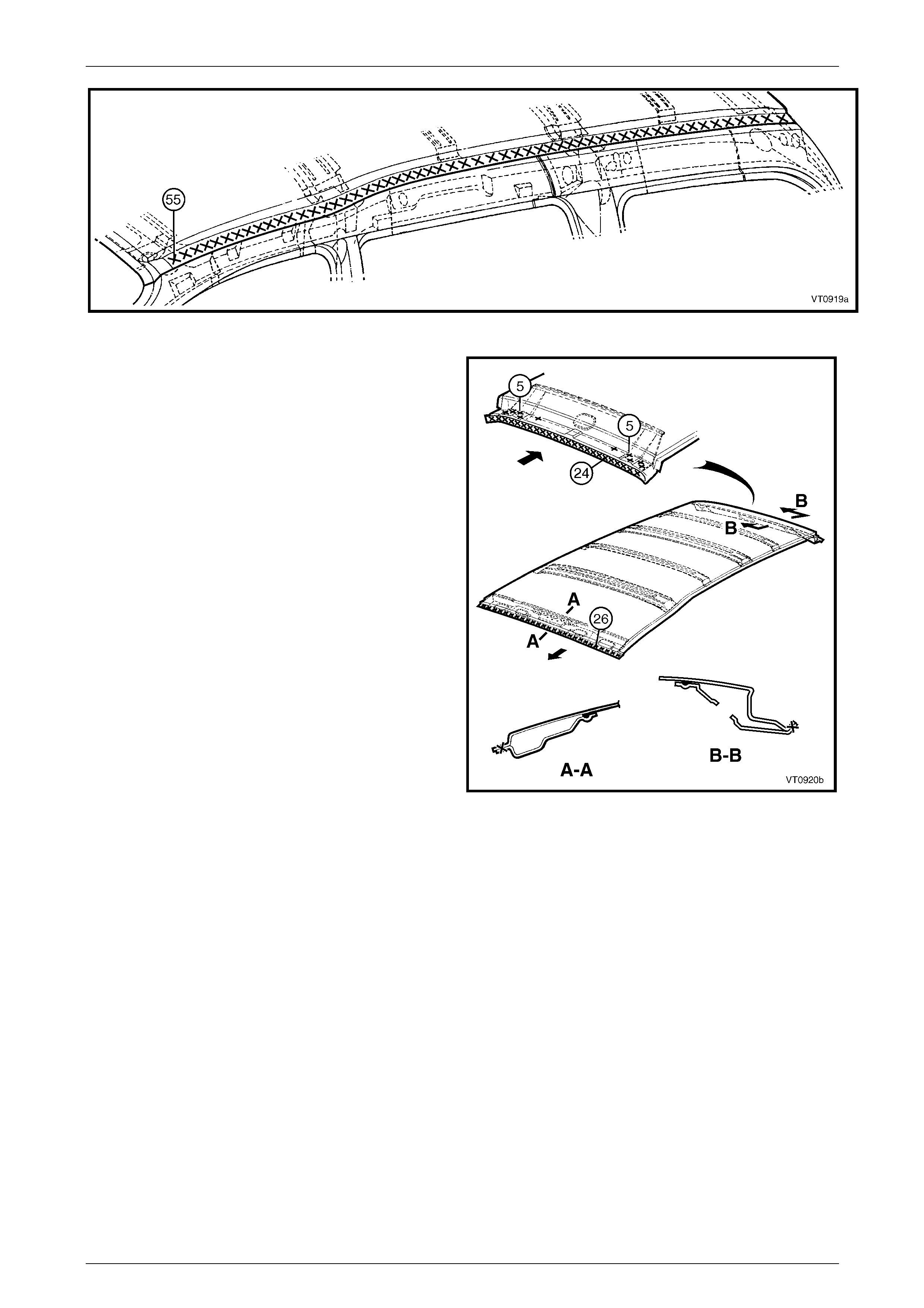
4 Apply Structural Adhesive (1) (Item 6), refer to
Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
Figure 9B – 9
5 Apply a bead of Anti-flutter Adhesiv e (Item 5)
to the full length of the groove in the roof
front panel and roof rear panel. Refer to
Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
6 Apply two full length bea ds of Anti-flutter adhesive to
the grooves in the roof bow panels.
7 Position the roof panel on the vehicle and clamp in
place.
8 Spot or plug weld the roof panel to the door opening
frame on both sides of the vehicle using the same
number of welds as the original production build.
Refer to Figure 9B – 11.
• Take care to minimise the heat absorbed
by the panel in order to reduce heat
distortion.
• In some cases it may be advantageous to
begin welding from the middle of the run
and weld alternatively to the front and
rear. This may reduce panel distortion.
Figure 9B – 10
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-7
Page 9B-7
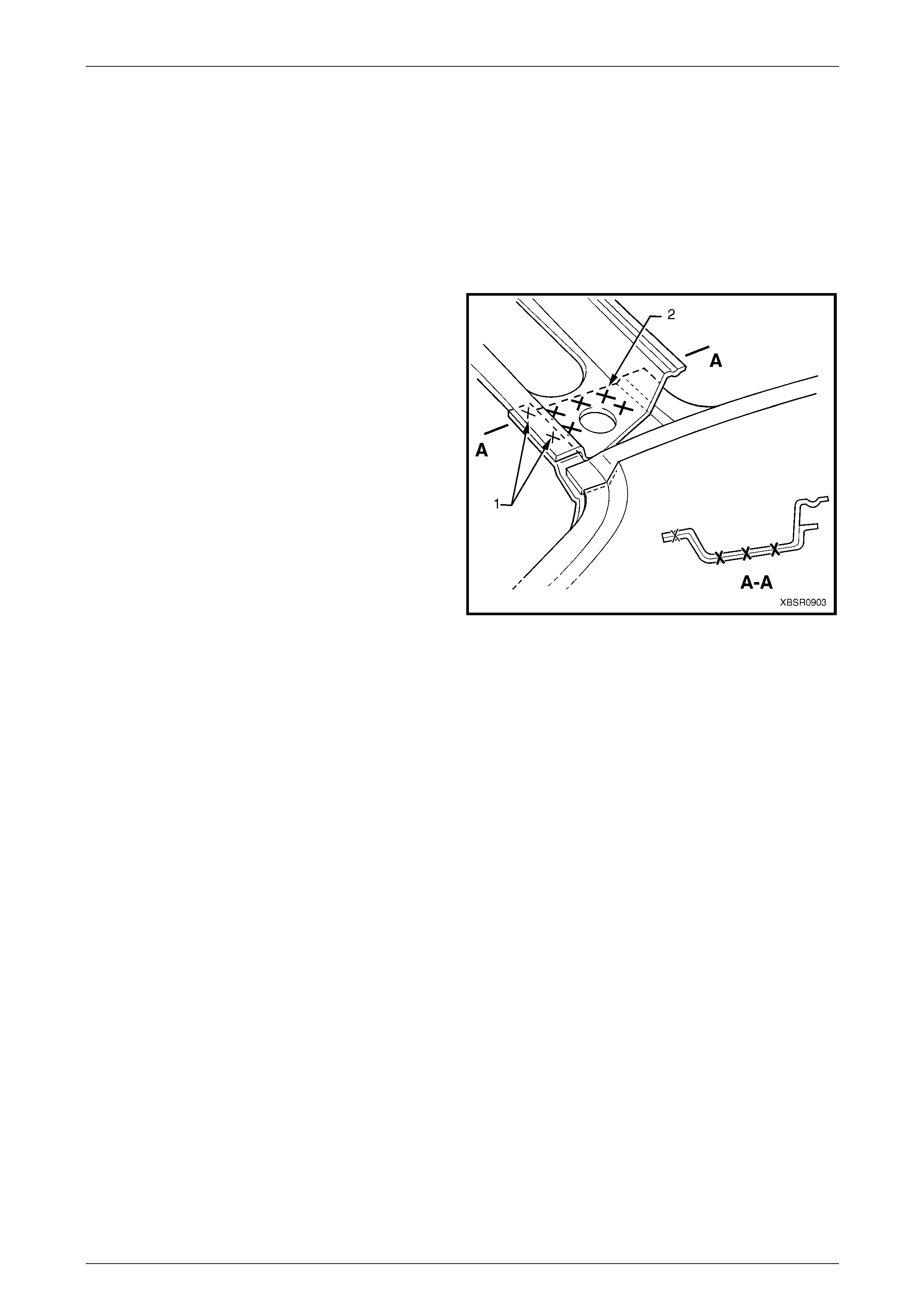
Figure 9B – 11
9 Spot or plug weld the roof panel to the roof front
header panel and roof rear panel using the same
number of welds as per original build.
10 Refinish and paint panels and other components as
required. Refer to Section 3 Body Construction .
11 Apply Joint Sealer (Item 3) as required.
Refer to Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
12 Apply Cavity Wax (Item 8) as required to the inside of
any box sections or areas inaccessible to paint,
refer to Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or
Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
13 Replace the windshield, refer to
Section 1A6 Stationary Windows in the MY 2 005 VZ
Service Information.
14 Install the liftgate,
refer to Section 8 Doors, Liftgate and Endgat e.
15 Install the remaining components as described in the
appropriate Section of the MY 2005 VZ Servic e
Information.
Figure 9B – 12
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-8
Page 9B-8
2.2 Roof Front Header Panel – Replace
Following removal of the roof panel, as required spot cut the welds attaching the roof front header panel as shown in the
following diagram.
When installing a roof front header p an el, eit her spot weld the part to the vehicle or mark and drill the new part with holes
in preparation for plug welding. The number of spot or plug welds must match the number shown in the appropriate
diagram.
Before fitting the part, prepare the mating surfaces and treat with Weld Through Primer (Item 1) as required,
refer to, Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
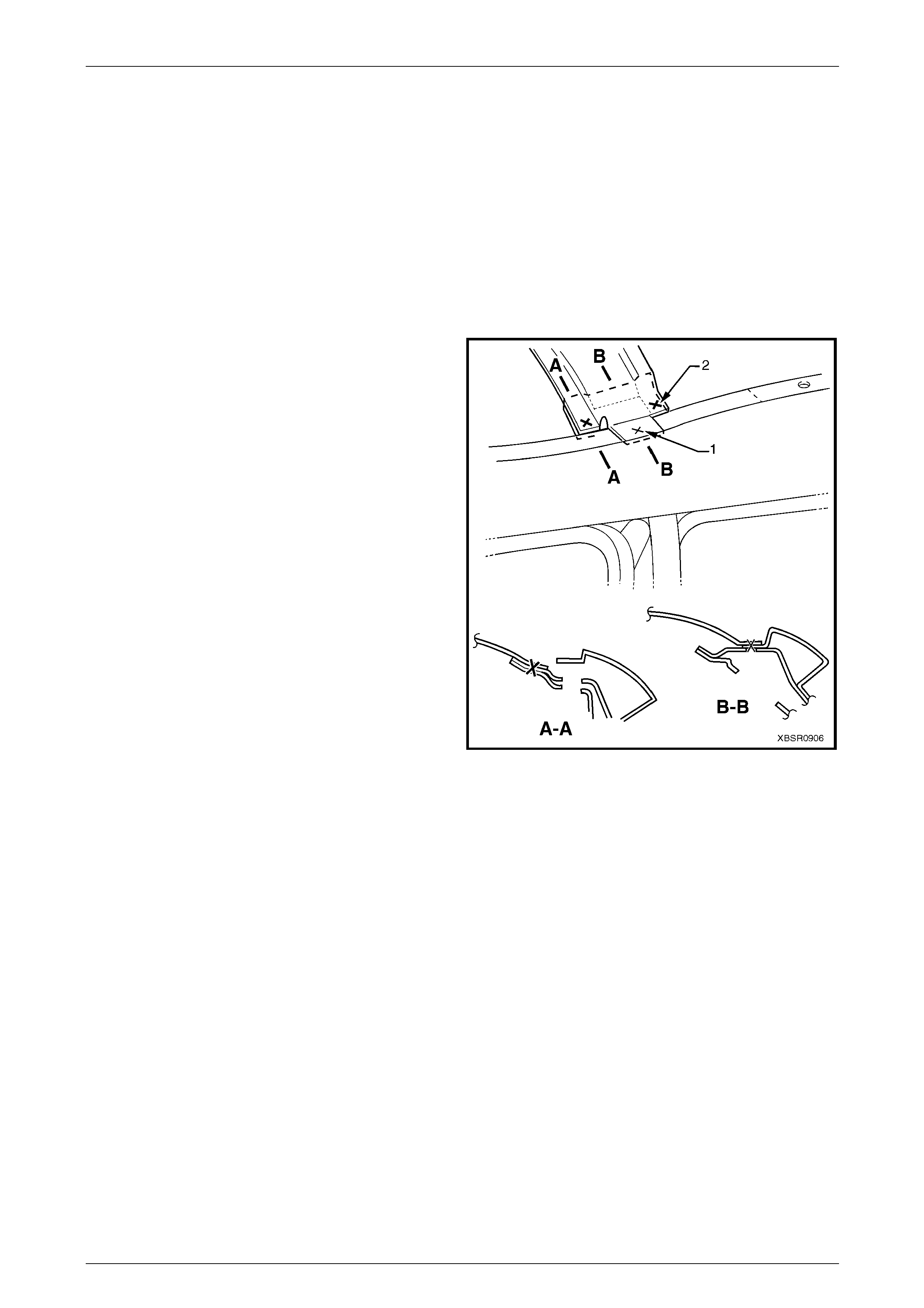
The two spot welds (1) are removed with the roof panel.
Remove the five spot welds (2) from each side of the vehicle
to remove the roof front header panel.
Figure 9B – 13
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-9
Page 9B-9
2.3 Roof Bow Panels – Replace
Following removal of the roof panel, as required spot cut the welds attaching the roof bow panels as sh own in the
following diagrams.
When installing a roof bow panel, either spot weld the part to the vehicle or mark and drill the new part with holes in
preparation for plug welding. The number of spot or plug welds must match the number shown in the appropriate
diagram.
Before fitting the part, prepare the mating surfaces and treat with Weld Through Primer (Item 1) as required,
Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
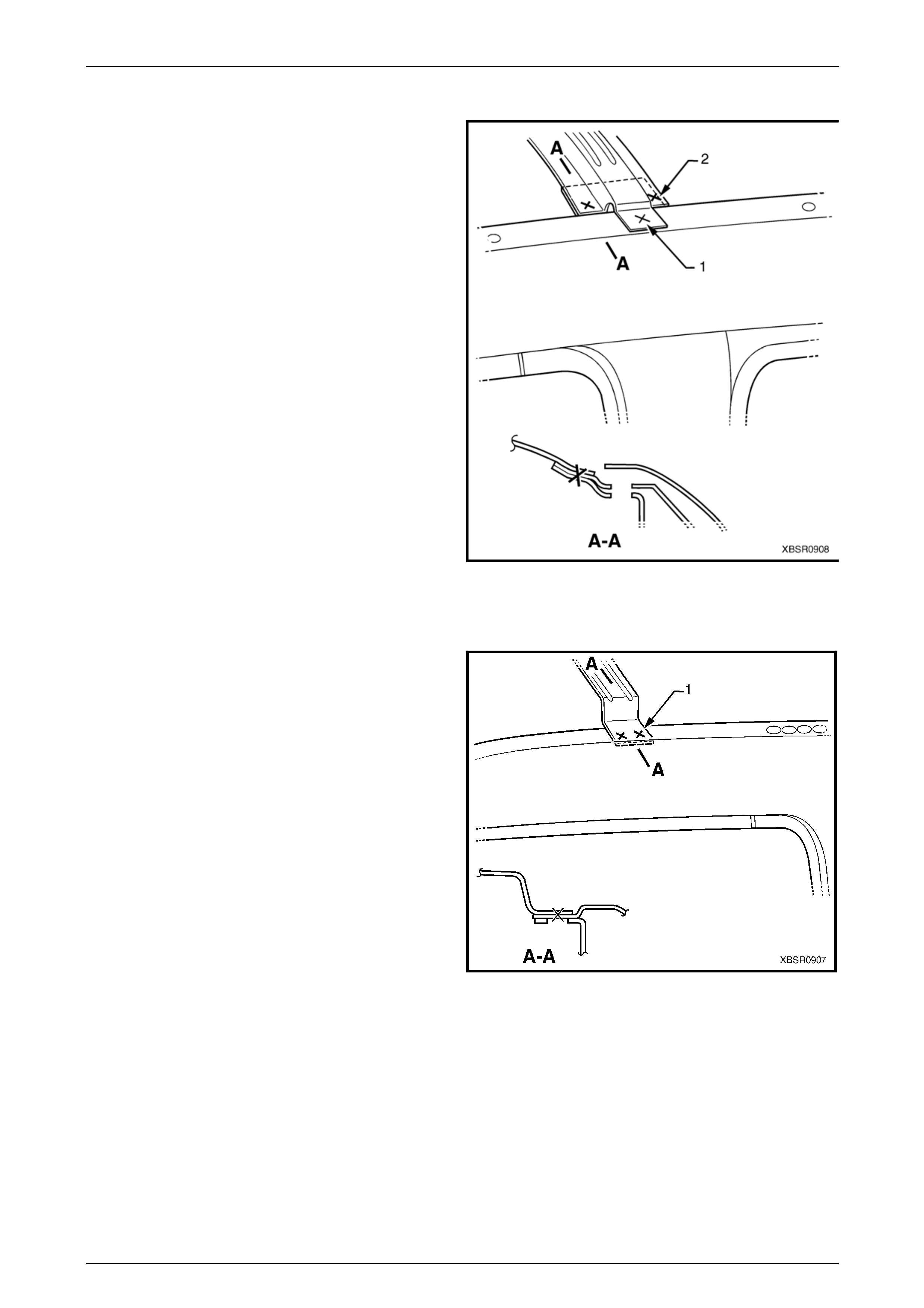
Roof Bow Panel No. 1
The spot weld (1) is removed with the roof panel.
Remove the two spot welds (2) from each side of the vehicle
to remove the roof bow panel No. 1.
Figure 9B – 14
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-10
Page 9B-10
Roof Bow Panel No. 3
The spot weld (1) is removed with the roof panel.
Remove the two spot welds (2) from each side of the vehicle
to remove the roof bow panel No. 3.
Figure 9B – 15
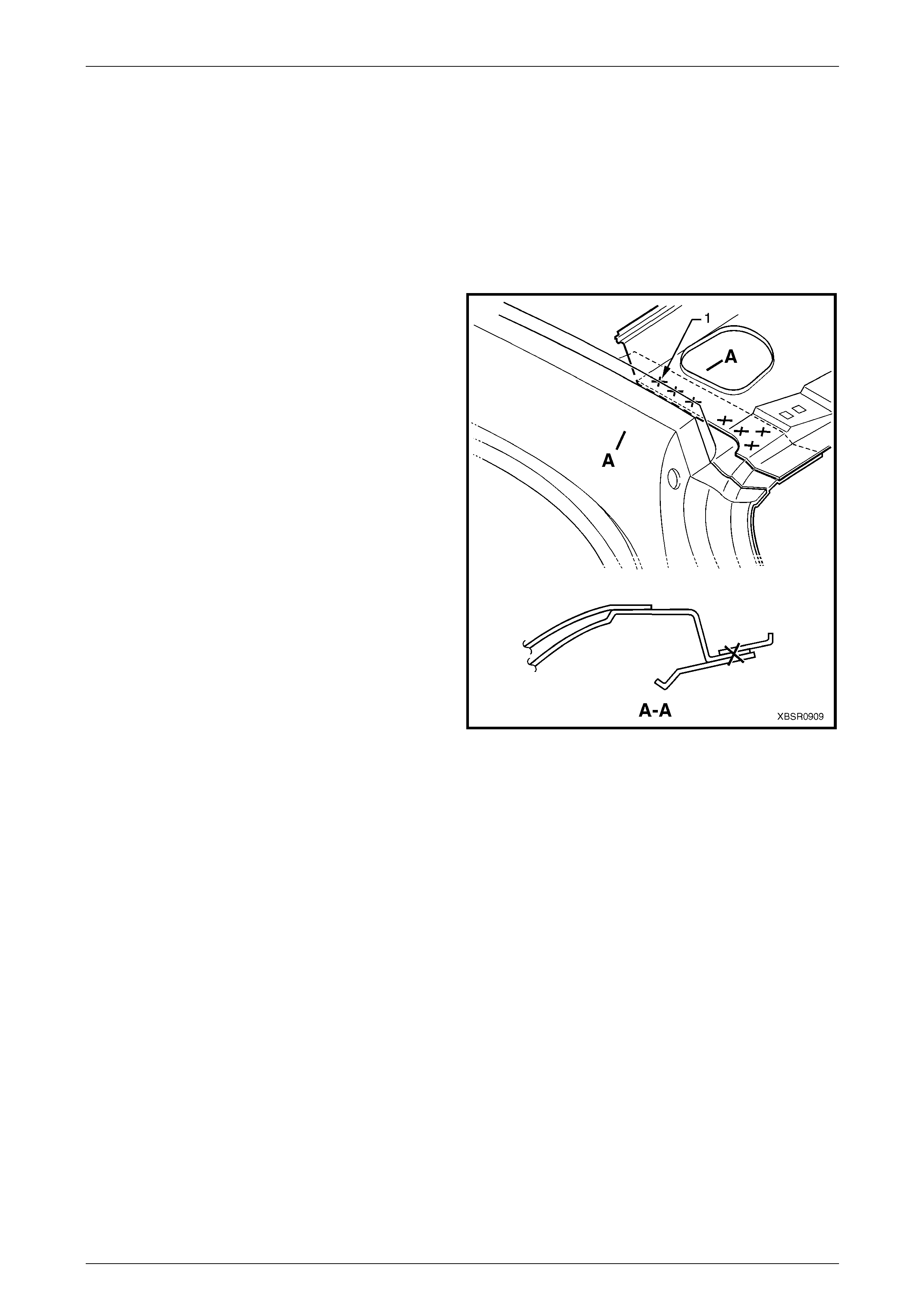
Roof Bow Panel No. 2 and 4
The two spot welds (1) are removed with the roof panel.
Figure 9B – 16
9B Roof – Wagon and AWD Wagon Page 9B-11
Page 9B-11
2.4 Roof Rear Panel – Replace
Following removal of the roof panel, as required spot cut the welds attaching the roof rea r panel as shown in the
following diagram.
When installing a roof rear panel, eith er spot weld the part to the vehicle or mark and drill the new part with holes in
preparation for plug welding. The number of spot or plug welds must match the number shown in the appropriate
diagram.
Before fitting the part, prepare the mating surfaces and treat with Weld Through Primer (Item 1) as required,
refer to Section 3B Body Construction – Wagon or Section 3G Body Construction – AWD Wagon.
Remove the seven spot welds (1) from each side of the
vehicle to remove the roof rear panel.
Figure 9B – 17