
SECTION 5C - POWER-ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM (MY2002)
Service Precaution
General Description
Diagnosis
General Diagnosis
Hydraulic Brakes
Filling Master Cylinder Reservoir
Deterioration of Brake Fluid
Leakage of Brake Fluid
Bleeding Brake Hydraulic System
Flushing Brake Hydraulic System
Brake Pipes and Hoses
Brake Hose Inspection
Front Caliper Brake Hose
Front Caliper Brake Hose and
Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Rear Axle Brake Hose
Rear Axle Brake Hose and Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Brake Pipe
Removal
Installation
P & B (Proportioning and Bypass) Valve
P & B (Proportioning and Bypass) Valve
Sectional View
Removal
Installation
Main Data and Specifications
Brake Pedal
Checking Pedal Height
Checking Pedal Travel
Brake Pedal and Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Stoplight Switch
Parts Location
Removal
Installation
Main Data and Specifications
Master Cylinder Assembly
Master Cylinder Assembly and
Associated Parts
Removal
Inspection and Repair
Main Data and Specifications
Master Cylinder Assembly
Master Cylinder Assembly
Disassembled View
Disassembly
Inspection
Reassembly
Installation
Vacuum Booster Assembly
Vacuum Booster Assembly and
Associated Parts
Removal
Inspection and Repair
Installation
Exterior Components
Exterior Components and Associated Parts
Removal
Inspection and Repair
Installation
Vacuum Booster Overhaul
Vacuum Booster
Main Data and Specifications
Front Disc Brake Pads
Front Disc Brake Pads Inspection
Front Disc Brake Pads and Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Inspection
Replacing Brake Rotors
Refinishing Brake Rotors
Front Disc Brake Caliper Assembly
Front Disc Brake Caliper Assembly and
Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Front Disc Brake Caliper
Front Disc Brake Caliper Disassembled View
Disassembly
Inspection and Repair
Reassembly
Main Data and Specifications
Rear Disc Brake Pads
Brake Pads Inspection
Brake Pads and Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Inspection
Replacing Brake Rotors
Refinishing Brake Rotors
Rear Drum (In Disc) Inside Diameter Check
Rear Disc Brake Caliper Assembly
Rear Disc Brake Caliper Assembly and
Associated Parts
Removal
Installation
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
Rear Disc Brake Caliper Disassembled View
Disassembly
Inspection and Repair
Reassembly
Main Data and Specifications
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE
SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER
TO THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE
AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
HOLDEN will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. HOLDEN will also call
out the fasteners that require thread lockers or
thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED,
do not use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases,
or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners
or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such
coatings adversely affect the fastener torque and
the joint clamping force, and may damage the
fastener. When you install fasteners, use the correct
tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to
parts and systems.
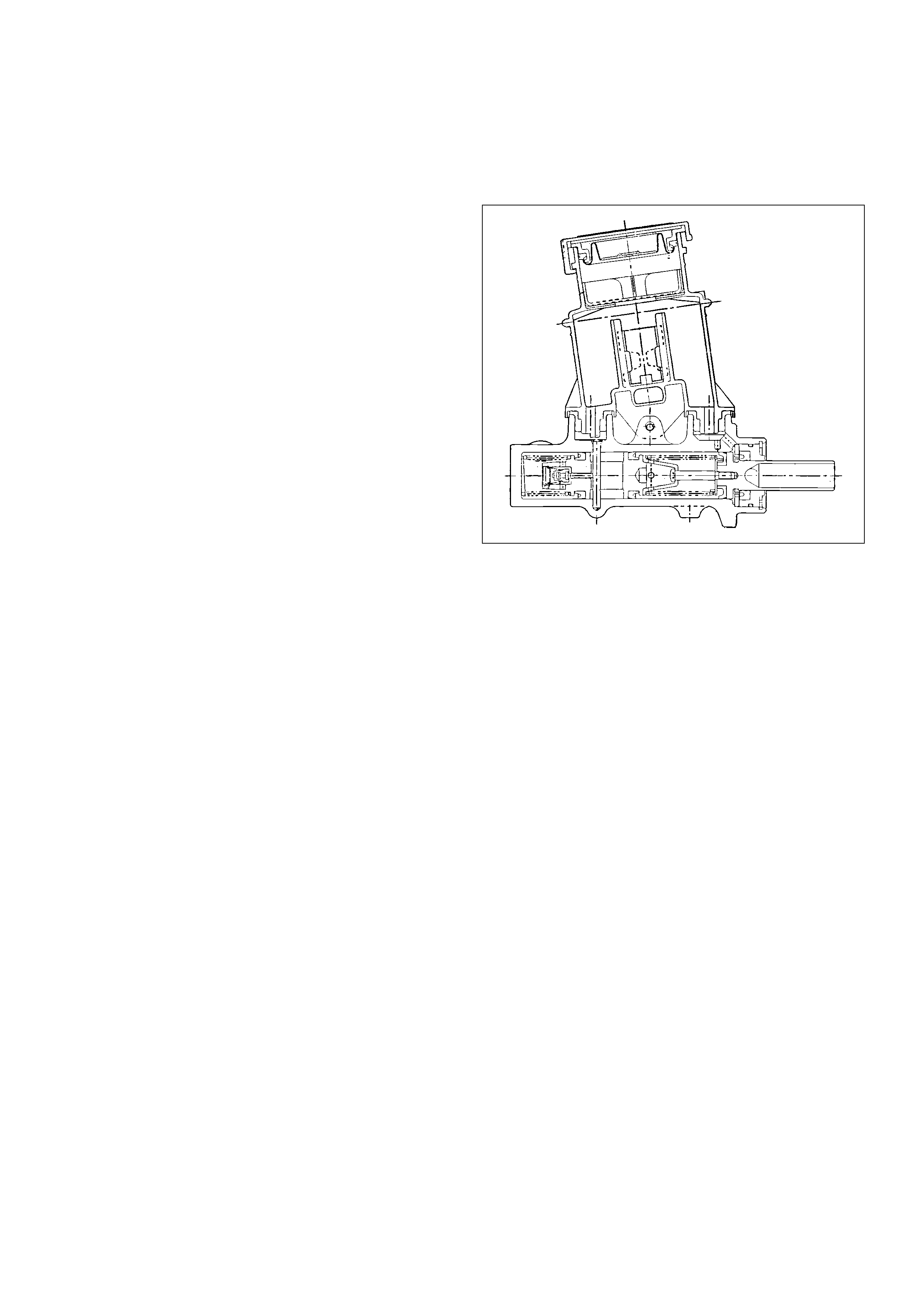
General Description
Master Cylinder Assembly
330R200002
The master cylinder contains two pistons that supply the
hydraulic pressure for a dual–circuit braking system.
The primary piston provides the fluid pressure to the
front brakes, while the secondary piston provides the
fluid pressure to the rear brakes. If the pressure is lost
from either system, the remaining system will function to
stop the vehicle.
CAUTION:
1.The master cylinder is not repairable. If found
defective, it must be replaced as a complete
assembly.
2.If any hydraulic component is removed or
disconnected, it may be necessary to bleed all
or part of the brake system. (Refer to “Bleeding
Brake Hydraulic System" in this section.)
3.The torque values specified are for dry,
unlubricated fasteners.
4.Perform service operations on a clean bench
free from all mineral oil materials.
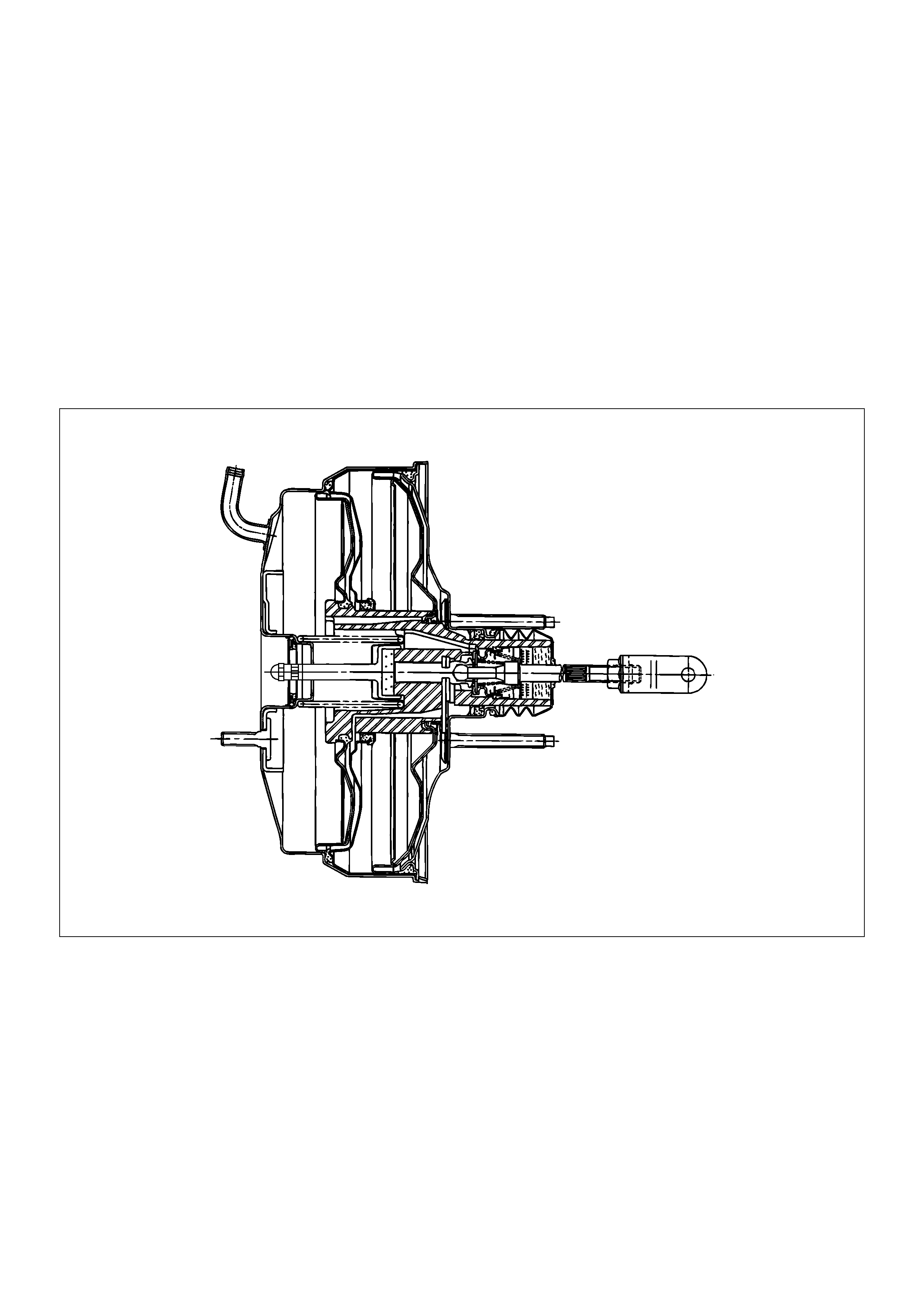
Brake Booster
331R200001
This booster is a tandem vacuum unit with a diaphragm
effective diameter 205mm + 230mm (8.07in + 9.06in). In
normal operating mode, with the service brakes in the
released position, the tandem vacuum booster operates
with vacuum on both sides of its diaphragms. When the
brakes are applied, air at atmospheric pressure is
admitted to one side of each diaphragm to provide the
power assist. When the service brake is released, the
atmospheric air is shut off from the one side of each
diaphragm. The air is then drawn from the booster
through the vacuum check valve to the vacuum source.
CAUTION:
1. If any hydraulic component is removed or
disconnected, it may be necessary to bleed all
or part of the brake system.
2. The torque values specified are for dry,
unlubricated fasteners.
3. The vacuum booster is not repairable and must
be replaced as complete assembly.
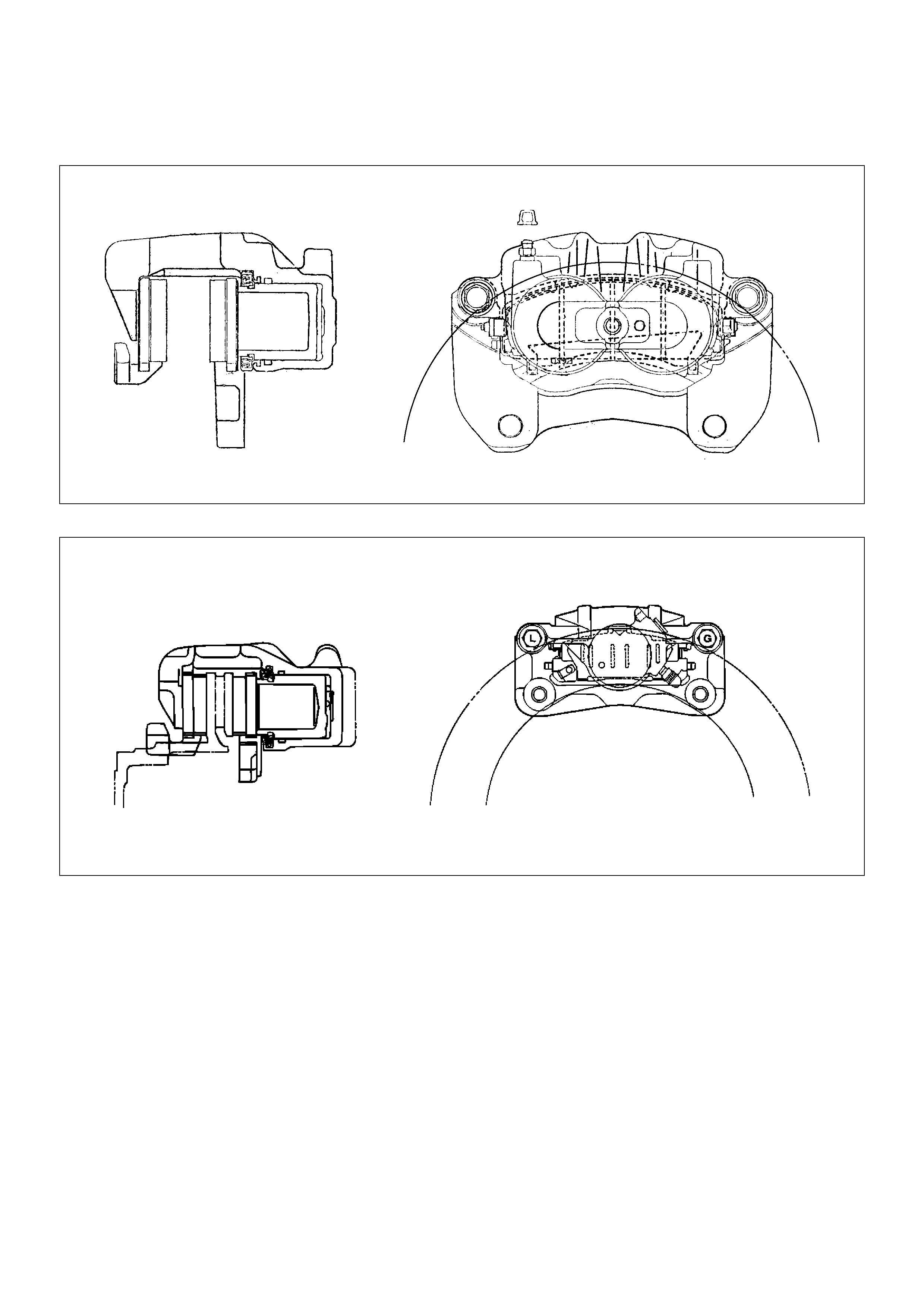
Disc Brake
Front Disc Brake
A05R200001
Rear Disc Brake
A05RW002
The disc brake assembly consists of a caliper, piston,
rotor, pad assembly and support bracket. The caliper
assembly has a single bore and is mounted to the
support bracket with two mounting bolts. The support
bracket allows the caliper to move laterally against the
rotor. The caliper is a one–piece casting with the
inboard side containing the piston bore. A square cut
rubber seal is located in a groove in the piston bore
which provides the hydraulic seal between the piston
and the cylinder wall.
NOTE:
1. Replace all components included in repair kits used
to service this caliper.
2. Lubricate rubber parts with clean brake fluid to ease
assembly.
3. If any hydraulic component is removed or
disconnected, it may be necessary to bleed all or
part of the brake system.
4. Replace pads in axle sets only.
5. The torque values specified are for dry, unlubricated
fasteners.
6. Perform the service operation on a clean bench free
from all mineral oil materials.
Operation
Hydraulic pressure, created by applying the brake
pedal, is converted by the caliper to a stopping force.
This force acts equally against the piston and the
bottom of the caliper bore to move the piston outward
and to move (slide) the caliper inward resulting in a
clamping action on the rotor. This clamping action
forces the linings against the rotor, creating friction to
stop the vehicle.

Diagnosis
Road Testing The Brakes
Brake Test
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake
performance cannot be made if the roadway is wet,
greasy or covered with loose dirt so that all tyres do not
grip the road equally. Testing will also be adversely
affected if the roadway is crowned so as to throw the
weight of the vehicle toward wheels on one side or if the
roadway is so rough that wheels tend to bounce. Test
the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both light and
heavy pedal pressure; however, avoid locking the
wheels and sliding the tyres. Locked wheels and sliding
tyres do not indicate brake efficiency, since heavily
braked but turning wheels will stop the vehicle in less
distance than locked wheels. More tyre–to–road friction
is present with a heavily braked turning tyre then with a
sliding tyre.
The standard brake system is designed and balanced to
avoid locking the wheels except at very high
deceleration levels.
It is designed this way because the shortest stopping
distance and best control is achieved without brake
lock–up.
Because of high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
External Conditions That Affect Brake Performance
1.Tyres: Tyres having unequal contact and grip on the
road will cause unequal braking. Tyres must be
equally inflated, identical in size, and the thread
pattern of right and left tyres must be approximately
equal.
2.Vehicle Loading: A heavily loaded vehicle requires
more braking effort.
3.Wheel Alignment: Misalignment of the wheels,
particularly in regard to excessive camber and
caster, will cause the brakes to pull to one side.
Brake Fluid Leaks
With engine running at idle and the transmission in
“Neutral", depress the brake pedal and hold a constant
foot pressure on the pedal. If pedal gradually falls away
with the constant pressure, the hydraulic system may be
leaking.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight drop
in the reservoir level will result from normal lining wear,
an abnormally low level in reservoir indicates a leak in
the system. The hydraulic system may be leaking
internally as well as externally. Refer to “Master Cylinder
Inspection". Also, the system may appear to pass this
test but still have slight leakage. If fluid level is normal,
check the vacuum booster push rod length. If an
incorrect length push rod is found, adjust or replace the
push rod. Check the brake pedal travel and the parking
brake adjustment.
When checking the fluid level, the master cylinder fluid
level may be low from the “MAX" mark if the front and
rear linings are worn. This is not abnormal.
Warning Light Operation
When the ignition switch is in the START position, the
“BRAKE" warning light should turn on and go off when
the ignition switch returns to the ON position.
The following conditions will activate the “BRAKE" light:
1. Parking brake applied. The light should be on
whenever the parking brake is applied and the
ignition switch is on.
2. Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master
cylinder will turn the “BRAKE" light on.
3. During engine cranking the “BRAKE" light should
remain on. This notifies the driver that the warning
circuit is operating properly.
General Diagnosis
Condition Possible cause Correction
Brake Pull Tyre inflation pressure is unequal. Adjust
Front wheel alignment is incorrect. Adjust
Unmatched tyres on same axle. Tyres with approx. the same amount
of tread should be used on the same
axle.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses. Check for soft hoses and damaged
lines. Replace with new hoses and
new double“walled steel brake
piping.
Water or oil on the brake pads. Clean or replace.
Brake pads hardened. Replace
Brake pads worn excessively. Replace
Brake rotor worn or scored. Grind or replace.
Disc brake caliper malfunctioning. Clean or replace.
Front hub bearing preload incorrect. Adjust or replace.
Loose suspension parts. Check all suspension mountings.
Loose calipers. Check and tighten the bolts to
specifications.
Brake Roughness or Chatter
(Pulsates)
Excessive lateral runout. Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine
the rotor.
Parallelism not within specifications. Check per instructions. If not within
specifications, replace or machine
the rotor.
Wheel bearings not adjusted. Adjust wheel bearings to correct
specifications
Pad reversed (steel against iron). Replace the brake pad and machine
rotor to within specifications.
Excessive Pedal Effort Malfunctioning vacuum booster. Check the vacuum booster
operation and repair, if necessary.
Partial system failure. Check the front and rear brake
system for failure and repair. Also,
check the brake warning light. If a
failed system is found, the light
should indicate failure.
Excessively worn pad. Check and replace pads in sets.
Piston in caliper stuck or sluggish. Remove caliper and rebuild.
Fading brakes due to incorrect pad. Remove and replace with original
equipment pad or equivalent.
Vacuum leak to vacuum booster. Check for ruptured or loose hose.
Check the direction of check valve
within vacuum hose.
Correct vacuum hose direction.
Grease on the brake pads. Replace or clean.
Excessive Brake Pedal Travel Air in hydraulic circuit. Bleed the hydraulic circuit.
Level of brake fluid in the reservoir
too low.
Replenish brake fluid reservoir to
specified level and bleed hydraulic
circuit as necessary.
Master cylinder push rod clearance
excessive.
Adjust
Leakage in hydraulic system. Correct or replace defective parts.
Brake Drag Master cylinder pistons not returning
correctly.
Adjust the stop light switch and
vacuum booster push rod. If
necessary, rebuild.
Restricted brake pipes or hoses. Check for soft hoses or damaged
pipes, and replace with new hoses
and new double–walled steel brake
piping.
Parking brake maladjusted. Adjust
Parking brake lining clearance
insufficient.
Adjust
Brake pedal free play insufficient. Adjust the brake pedal height or
power cylinder operating rod.
Piston in the master cylinder
sticking.
Replace
Piston in the disc brake caliper
sticking.
Replace piston seals.
Brake pads sticking in caliper. Clean
Return spring weakened. Replace
Parking brake binding. Overhaul the parking brakes and
correct.
Front hub bearing preload incorrect. Adjust or replace.
Parking brake shoes not returning. Correct or replace the brake back
plate and brake shoe as necessary.
Obstructions in hydraulic circuit. Clean
Rotor warped excessively. Grind or replace.
Rear brake drum distorted. Grind or replace.
Parking cable sticking. Grind or replace.
Grabbing or Uneven Braking Action
(All conditions listed under “Pulls")
Malfunctioning vacuum booster. Check operation and correct as
necessary.
Binding brake pedal mechanism. Check and lubricate, if necessary.
Corroded caliper assembly. Clean and lubricate.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Brake Noisy Brake pads are worn. Replace
Brake pads are hardened. Replace
Brake pads are in poor contact with
rotor.
Correct
Brake disc(s) warped, worn or
damaged.
Grind or replace.
Disc brake anti–squeak shims
fatigued.
Replace
Front hub bearings are loose or
preload is incorrect.
Adjust or replace.
Brake disc is rusted. Grind or replace.
Poor Brake Action Master cylinder faulty. Correct or replace.
Vacuum booster faulty. Correct or replace.
Level of brake fluid in reservoir too
low.
Replenish and bleed.
Air in hydraulic circuit. Bleed
Disc brake caliper faulty. Clean or replace.
Water or oil on brake pads. Clean or replace.
Brake pads in poor contact with the
rotor.
Correct
Brake pads worn. Replace
Brake disc rusted. Grind or replace.
Check valve in vacuum hose faulty. Correct or replace.
Condition Possible cause Correction

Hydraulic Brakes
Filling Master Cylinder Reservoir
CAUTION: Use only specified brake fluid. Do not
use any fluid which contains a petroleum base. Do
not use a container which has been used for
petroleum based fluids or a container which is wet
with water. Petroleum based fluid will cause
swelling and distortion of rubber parts in the
hydraulic brake system. Water mixed with brake
fluid lowers the fluid boiling point. Keep all fluid
containers capped to prevent contamination.
Always fill the master cylinder reservoir when the
engine is cold.
Never allow the brake fluid to come in contact with
the painted surfaces.
The master cylinder reservoir must be kept properly
filled to ensure adequate reserve and to prevent air
and moisture from entering the hydraulic system.
However, because of expansion due to heat
absorbed from the brakes and the engine, the
reservoir must not be overfilled. The brake fluid
reservoir is on the master cylinder, which is located
under the hood on the left side of the cowl.
Thoroughly clean reservoir cap before removal to
avoid getting dirt into reservoir. Remove the
diaphragm. Add fluid as required to bring level to
the “MAX" mark on the reservoir tank. Use “DOT 3"
Hydraulic Brake Fluid. If the fluid cap diaphragm is
stretched, return it to the original position before
installing.
Deterioration of Brake Fluid
Using any other brake fluid than specified or brake fluid
with mineral oil or water mixed in will drop the boiling
point of brake fluid. It may, in turn, result in vapor lock or
deteriorated rubber parts of the hydraulic system. Be
sure to change the brake fluid at specified intervals.
If the rubber parts are deteriorated, remove all the
system parts and clean them with alcohol. Prior to
reassembly, dry the cleaned parts with air to remove the
alcohol. Replace all the hoses and rubber parts of the
system.
Leakage of Brake Fluid
With engine idling, set shift lever in the neutral position
and continue to depress brake pedal at a constant pedal
application force.
Should the pedal stroke become deeper gradually,
leakage from the hydraulic pressure system is possible.
Make sure by visual check that there is no leak.
Bleeding Brake Hydraulic System
A bleeding operation is necessary to remove air from
the hydraulic brake system whenever air is introduced
into the hydraulic system. It may be necessary to bleed
the hydraulic system at all four brakes if air has been
introduced through a low fluid level or by disconnecting
brake pipes at the master cylinder. If a brake pipe is
disconnected at one wheel, only that wheel cylinder/
caliper needs to be bled. If the pipes are disconnected
at any fitting located between the master cylinder and
brakes, then the brake system served by the
disconnected pipe must be bled.
1. For 4–Wheel Antilock Brake System (ABS)
equipped vehicle, be sure to remove the ABS main
fuse 60A located at the relay and fuse box before
bleeding air. If you attempt to bleed air without
removing the main fuse, air cannot be let out
thoroughly, and this may cause damage to the
hydraulic unit. After bleeding air, be sure to replace
the ABS main fuse back to its original position.
2. Set the parking brake completely, then start the
engine.
NOTE: The vacuum booster will be damaged if the
bleeding operation is performed with the engine off.
3. Remove the master cylinder reservoir cap.
4. Fill the master cylinder reservoir with brake fluid.
Keep the reservoir at least half full during the air
bleeding operation
5. Always use new brake fluid for replenishment.
6. In replenishing brake fluid, take care that air bubbles
do not enter the brake fluid.
When the master cylinder is replaced or overhauled,
first bleed the air from the master cylinder, then from
each wheel cylinder and caliper following the
procedures described below.
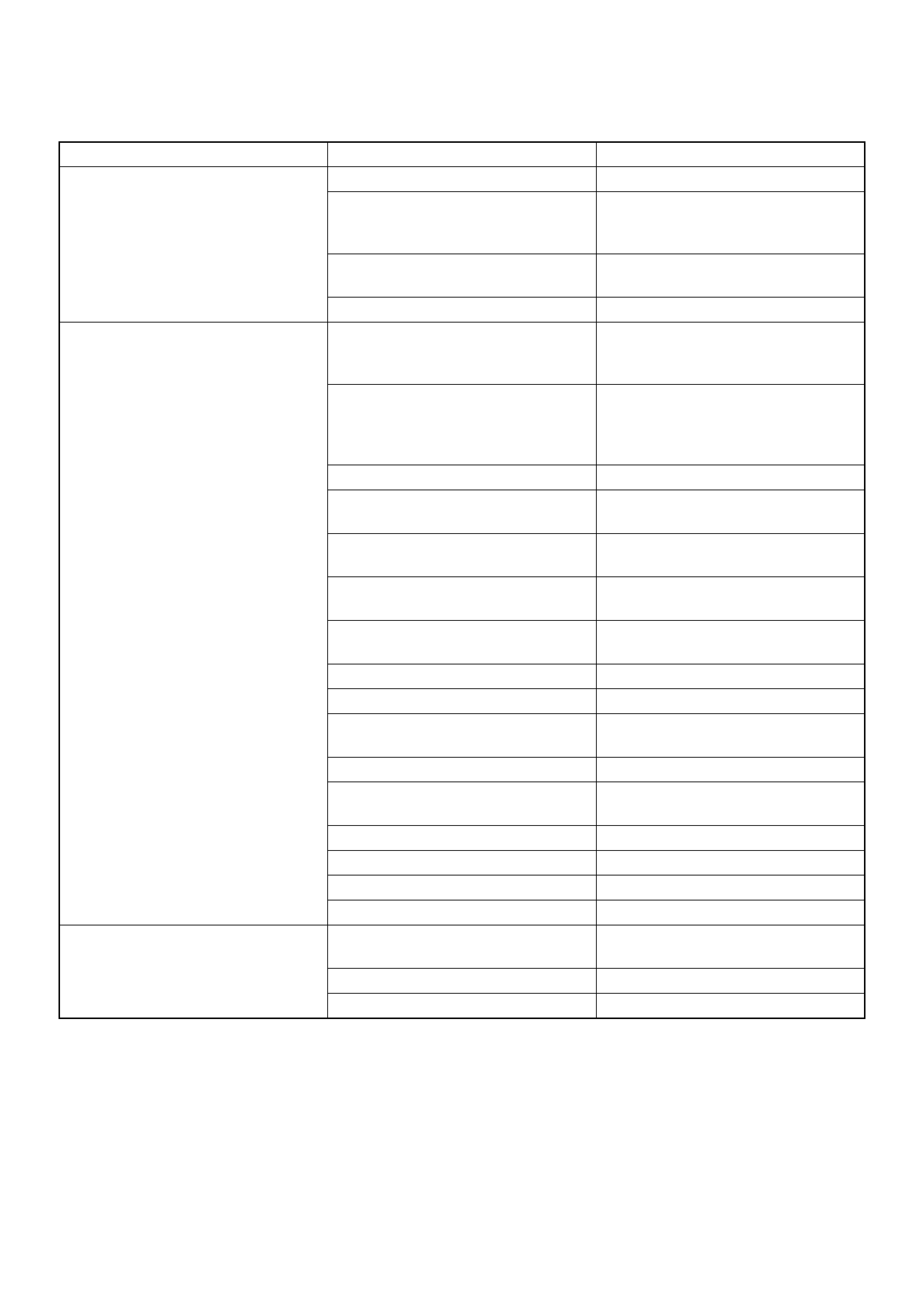
Bleeding the Master Cylinder
7. Disconnect the rear wheel brake pipe (1) from the
master cylinder.
Check the fluid level and replenish as necessary. If
replenished, leave the system for at least one
minute.
8. Depress the brake pedal slowly once and hold it
depressed.
9. Completely seal the delivery port of the master
cylinder with your finger, where the pipe was
disconnected then release the brake pedal slowly.
10. Release your finger from the delivery port when the
brake pedal returns completely.
11. Repeat steps 8 through 10 until the brake fluid
comes out of the delivery port during step 8.
NOTE: Do not allow the fluid level in the reservoir to go
below the half–way mark.
12. Reconnect the brake pipe (1) to the master cylinder
and tighten the pipe.
13. Depress the brake pedal slowly once and hold it
depressed.
14. Loosen the rear wheel brake pipe (1) at the master
cylinder.
15. Retighten the brake pipe, then release the brake
pedal slowly.
16.Repeat steps 13 through 15 until no air comes out of
the port when the brake pipe is loosened
NOTE: Be very careful not to allow the brake fluid to
come in contact with painted surfaces.
330R200004
17.Bleed the air from the front wheel brake pipe
connection (2) by repeating steps 7 through 16.
Bleeding the Caliper
18.Bleed the air from each wheel in the order listed
below:
•Right rear caliper or wheel cylinder
•Left rear caliper or wheel cylinder
•Right front caliper
•Left front caliper
Conduct air bleeding from the wheels in the above
order. If no brake fluid comes out, it suggests that air
is mixed in the master cylinder. In this case, bleed
air from the master cylinder. In this case, bleed air
from the master cylinder in accordance with steps 7
through 17, and then bleed air from the caliper or
wheel cylinder.
19.Place the proper size box end wrench over the
bleeder screw.
20.Cover the bleeder screw with a transparent tube,
and submerge the free end of the transparent tube
in a transparent container containing brake fluid.
21.Pump the brake pedal slowly three (3) times (once/
sec), then hold it depressed.
22.Loosen the bleeder screw until fluid flows through
the tube.
23.Retighten the bleeder screw.
24.Release the brake pedal slowly.
25.Repeat steps 21 through 24 until the air is
completely removed.
It may be necessary to repeat the bleeding
procedure 10 or more times for front wheels and 15
or more times for rear wheels.
26.Go to the next wheel in the sequence after each
wheel is bled.
Be sure to monitor reservoir fluid level.
27.Depress the brake pedal to check if you feel
“sponginess" after the air has been removed from
all wheel cylinders and calipers.
If the pedal feels “spongy", the entyre bleeding
procedure must be repeated.
28.After the bleeding operation is completed on the
each individual wheel, check the level of the brake
fluid in the reservoir and replenish up to the “MAX"
level as necessary.
29.Attach the reservoir cap.
If the diaphragm inside the cap is deformed, reform
it and install.
30.Stop the engine.
Flushing Brake Hydraulic System
It is recommended that the entyre hydraulic system be
thoroughly flushed with clean brake fluid whenever new
parts are installed in the hydraulic system.
Approximately one quart of fluid is required to flush the
hydraulic system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been used
which contains the slightest trace of mineral oil. All
rubber parts that have been subjected to a
contaminated fluid must be replaced.
Brake Pipes and Hoses
The hydraulic brake system components are
interconnected by special steel piping and flexible
hoses. Flexible hoses are used between the frame and
the front calipers, the frame and rear axle case and the
rear axle and the rear calipers.
When the hydraulic pipes have been disconnected for
any reason, the brake system must be bled after
reconnecting the pipe. Refer to “Bleeding the Brake
Hydraulic System" in this section.
Brake Hose Inspection
The brake hose should be inspected at least twice a
year. The brake hose assembly should be checked for
road hazard, cracks and chafing of the outer cover, and
for leaks and blisters. Inspect for proper routing and
mounting of the hose. A brake hose that rubs on
suspension components will wear and eventually fail. A
light and mirror may be needed for an adequate
inspection. If any of the above conditions are observed
on the brake hose, adjust or replace the hose as
necessary.
CAUTION: Never allow brake components such as
calipers to hang from the brake hoses, as damage
to the hoses may occur.
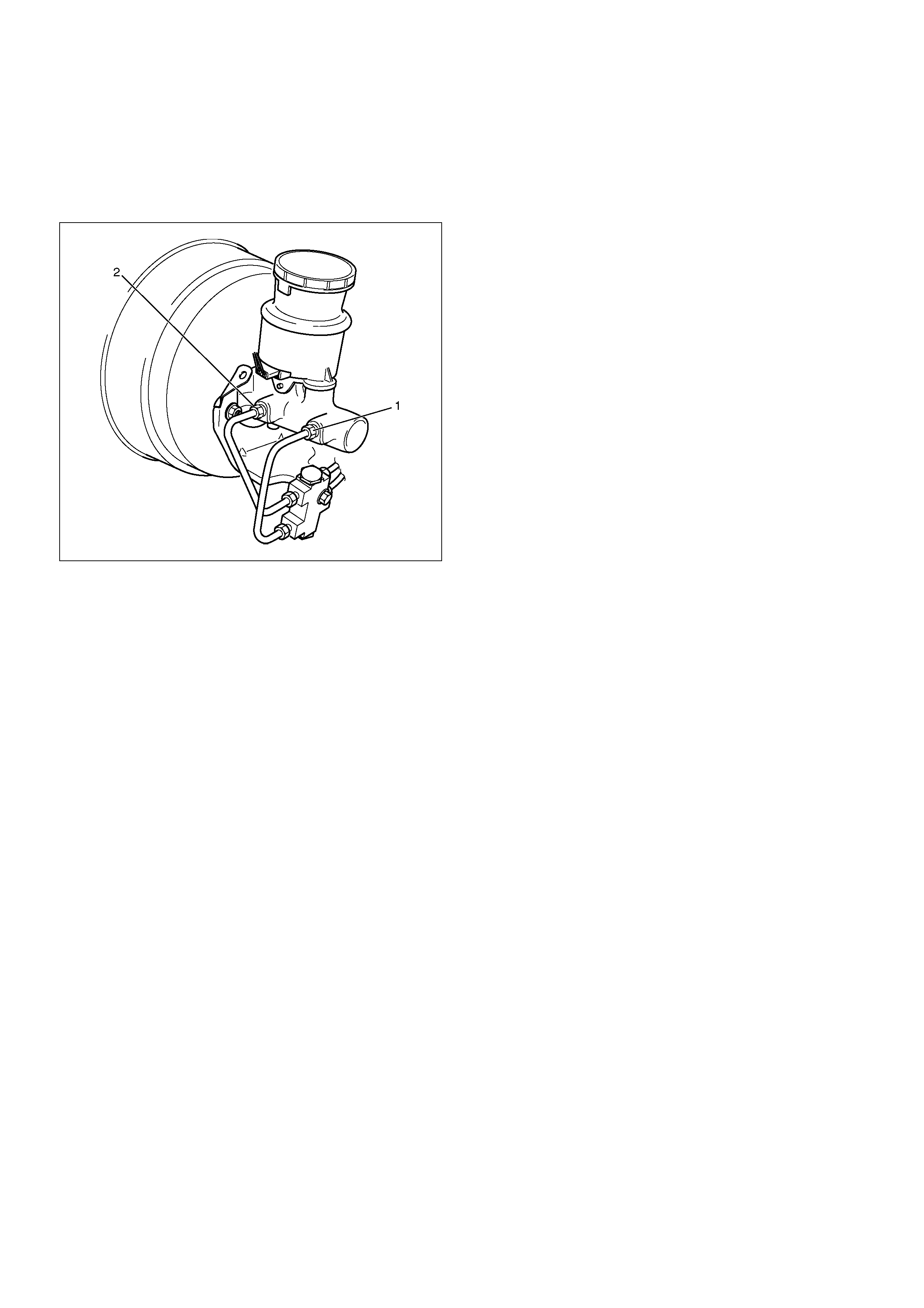
Front Caliper Brake Hose
Front Caliper Brake Hose and Associated
Parts
352RW001
EndOFCallout
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle and support it with suitable safety
stands.
2. Remove the wheel and tyre assembly.
3. Clean dirt, grease, and other foreign material off the
hose fittings at both ends.
4. Disconnect brake pipe.
5. Remove clip.
6. Remove bolt and gasket.
7. Remove hose.
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points.
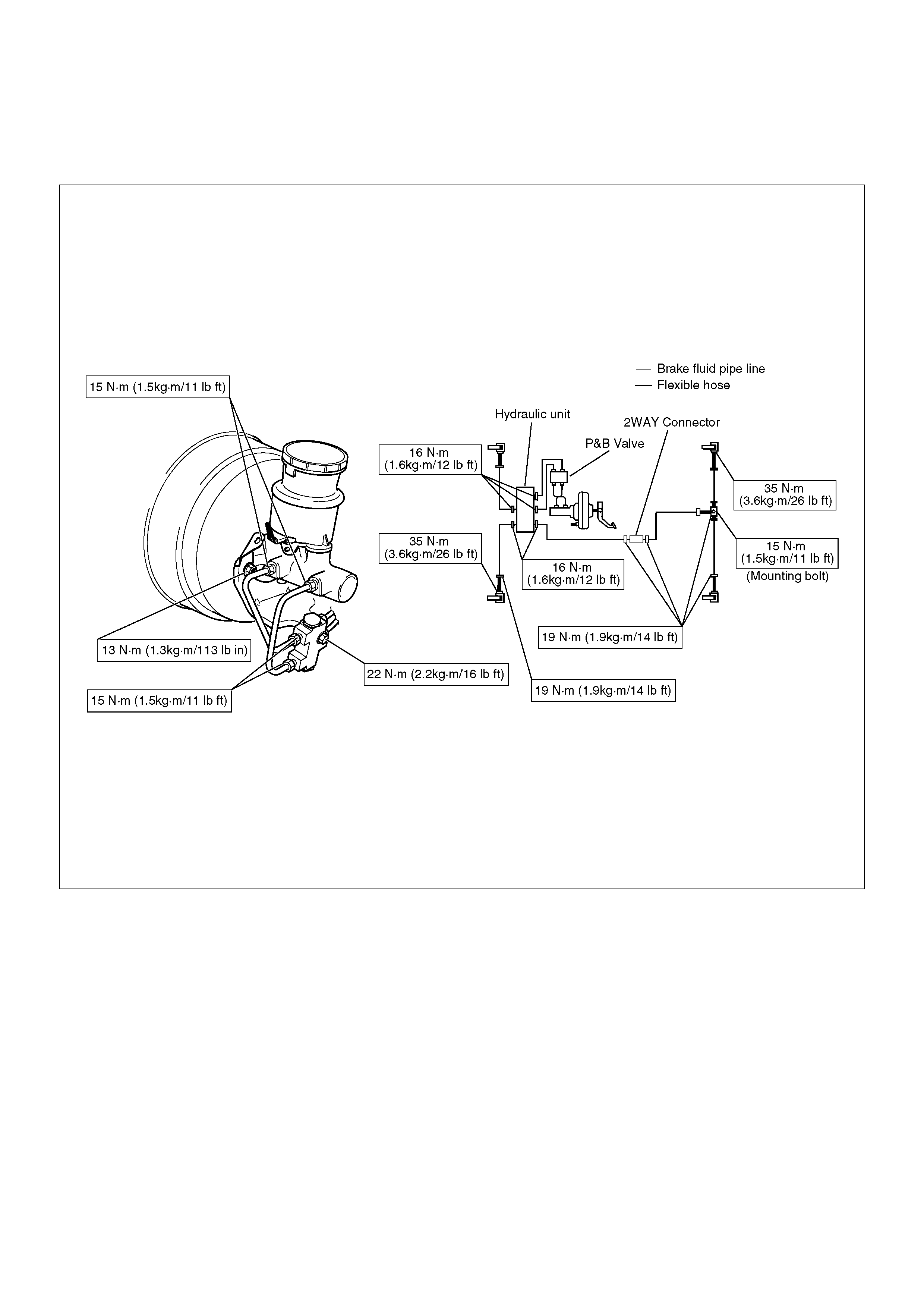
1. Tighten the brake pipes to the specified torque
Torque: 19 N·m (1.9 kg·m/14 lbft)
2. Tighten the bolt to the specified torque.
Torque: 34 N·m (3.5 kg·m/25 lbft)
NOTE: Always use new gaskets and be sure to put the
hooked edge of the flexible hose end into the anti–
rotation cavity.
After installing the brake hoses, bleed the brakes as
described in this section.
Legend
(1) Bolt and Gasket
(2) Clip
(3) Hose
(4) Brake Pipe
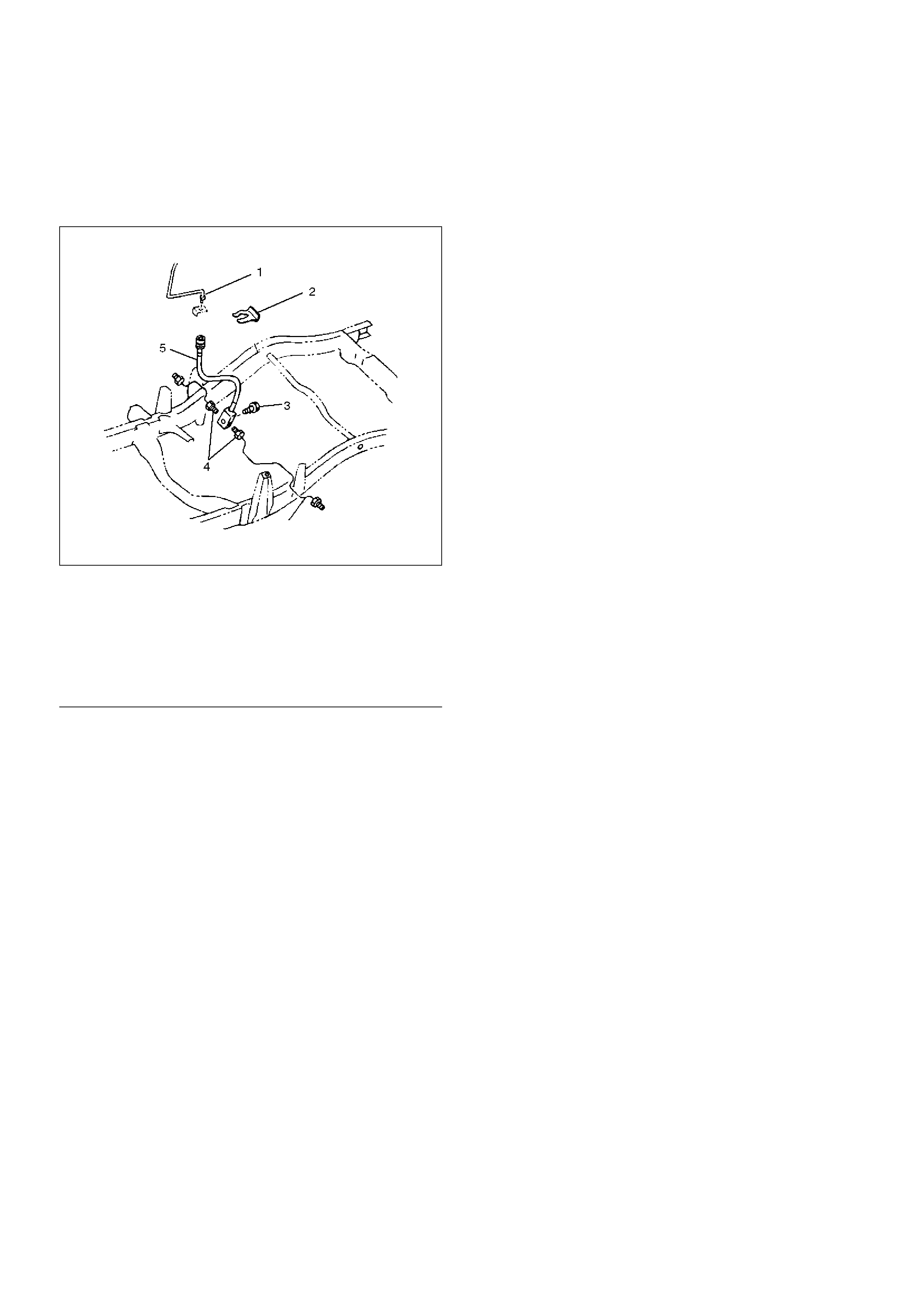
Rear Axle Brake Hose
Rear Axle Brake Hose and Associated
Parts
352RW002
EndOFCallout
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle and support it with suitable safety
stands.
2. Remove wheel and tyre assembly.
3. Clean dirt, grease, and other foreign material off the
hose fittings at both ends.
4. Disconnect brake pipe.
5. Remove clip.
6. Remove brake pipe.
7. Remove bolt.
8. Remove hose.
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points.
1. Tighten the brake pipes to the specified torque
Torque: 19 N·m (1.9 kg·m/14 lbft)
2. Tighten the bolt to the specified torque.
Torque: 15 N·m (1.5 kg·m/11 lbft)
After installing the brake hoses, bleed the brakes as
described in this section.
Legend
(1) Brake Pipe
(2) Clip
(3) Bolt
(4) Brake Pipe
(5) Hose
Brake Pipe
Removal
1. Raise the vehicle and support it with suitable safety
stands.
2. Remove wheel and tyre assembly as necessary.
3. Clean dirt, grease, and other foreign material off the
pipe fittings at both ends.
4. Remove brake pipe (1).
330R20000 3
5. Remove plastic clip (2).
330RW002
Installation
To install, follow the removal steps in the reverse order,
noting the following points.
1. Tighten the brake pipes to the specified torque.
Master cylinder and P&B valve sides
Torque: 15 N·m (1.5 kg·m/11 lbft)
Others
Torque: 16 N·m (1.6 kg·m/12 lbft)
After installing the brake pipes, bleed the brakes as
described in this section.
P & B (Proportioning and Bypass) Valve
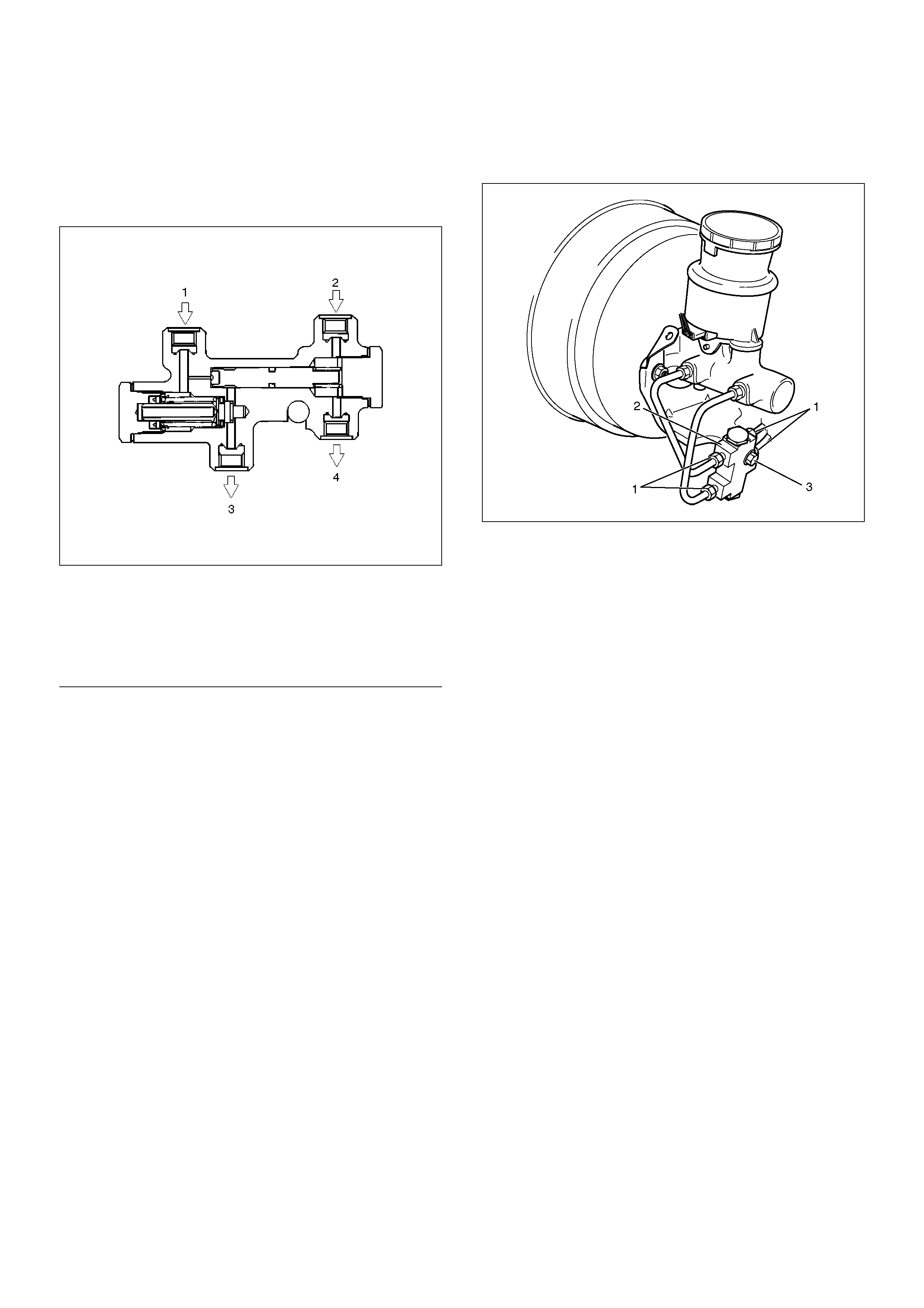
P & B (Proportioning and Bypass) Valve
Sectional View
350RW014
EndOFCallout
The P&B valve contains two sections, each serving a
different function.
The proportioning section of the P&B valve proportions
outlet pressure to the rear brakes after a predetermined
rear input pressure has been reached. This is done to
prevent rear wheel lock up on the vehicles with light rear
wheel loads. The valve has a by–pass feature which
assures full system pressure to the rear brakes in the
event of front brake system malfunction. Also full front
pressure is retained in the event of rear brake
malfunction.
The P&B valve is not repairable and must be replaced
as complete assembly.
Removal
1. The P&B valve is not repairable and must be
replaced as a complete assembly. Care must be
taken to prevent brake fluid from contacting any
painted surface.
2. Remove hydraulic pipes (1) and plug the pipes (1)
to prevent the loss of fluid or the entrance of dirt.
3. Remove bolt (3).
4. Remove P&B valve (2).
350R200003
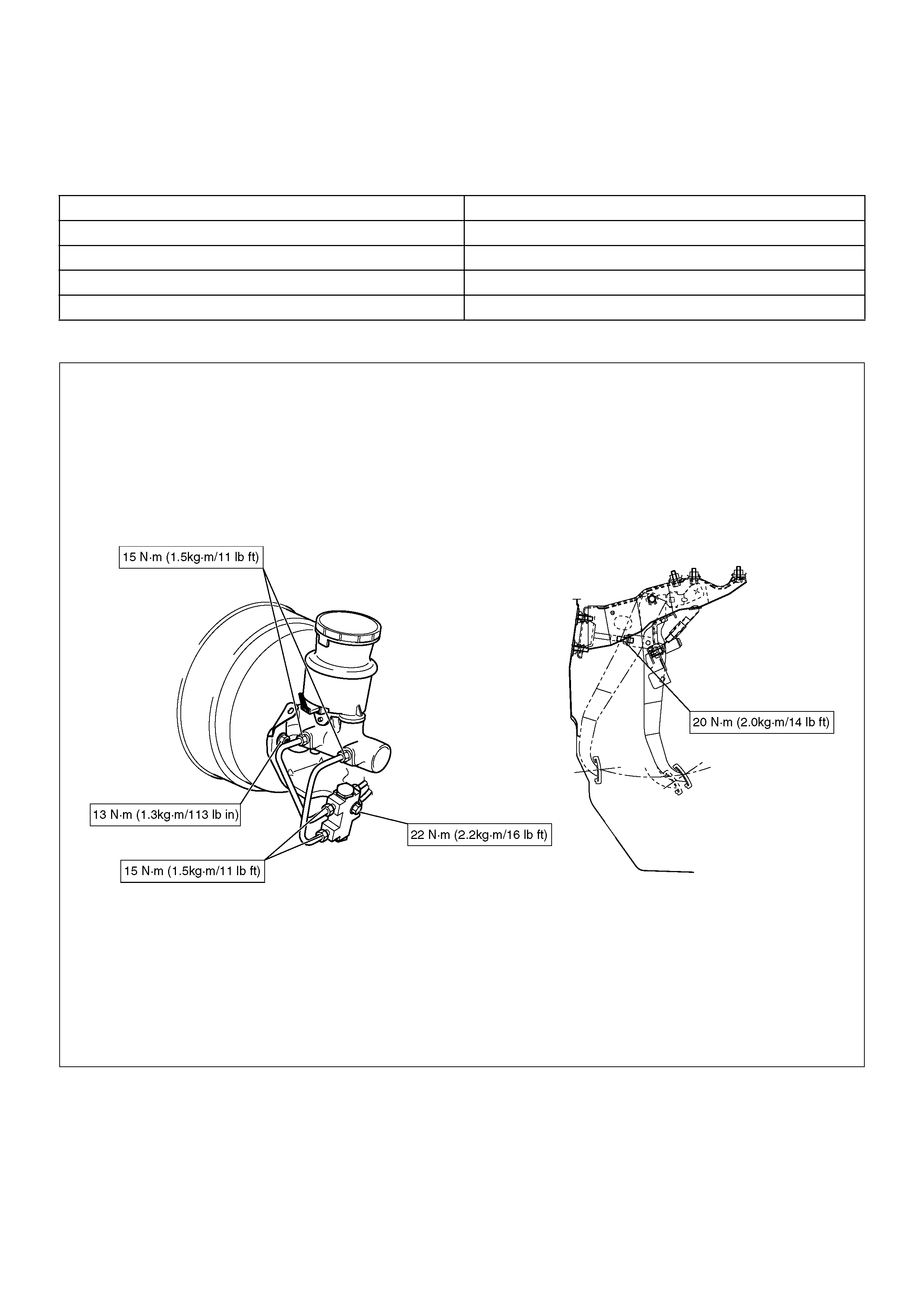
Installation
1. Install P&B valve (2).
2. Install bolt (3) and tighten the bolt to the specified
torque.
Torque: 22 N·m (2.2 kg·m/16 lbft)
3. Install hydraulic pipes (1) and tighten the bolt to the
specified torque.
Torque: 15 N·m (1.5 kg·m/11 lbft)
4. After installing the brake pipes, bleed the brakes as
described in Bleeding Brake Hydraulic System in
this section.
Legend
(1) Master Cylinder (Secondary)
(2) Master Cylinder (Primary)
(3) Rear Brake
(4) Front Brake
Main Data and Specifications
Torque Specifications
E05R200009
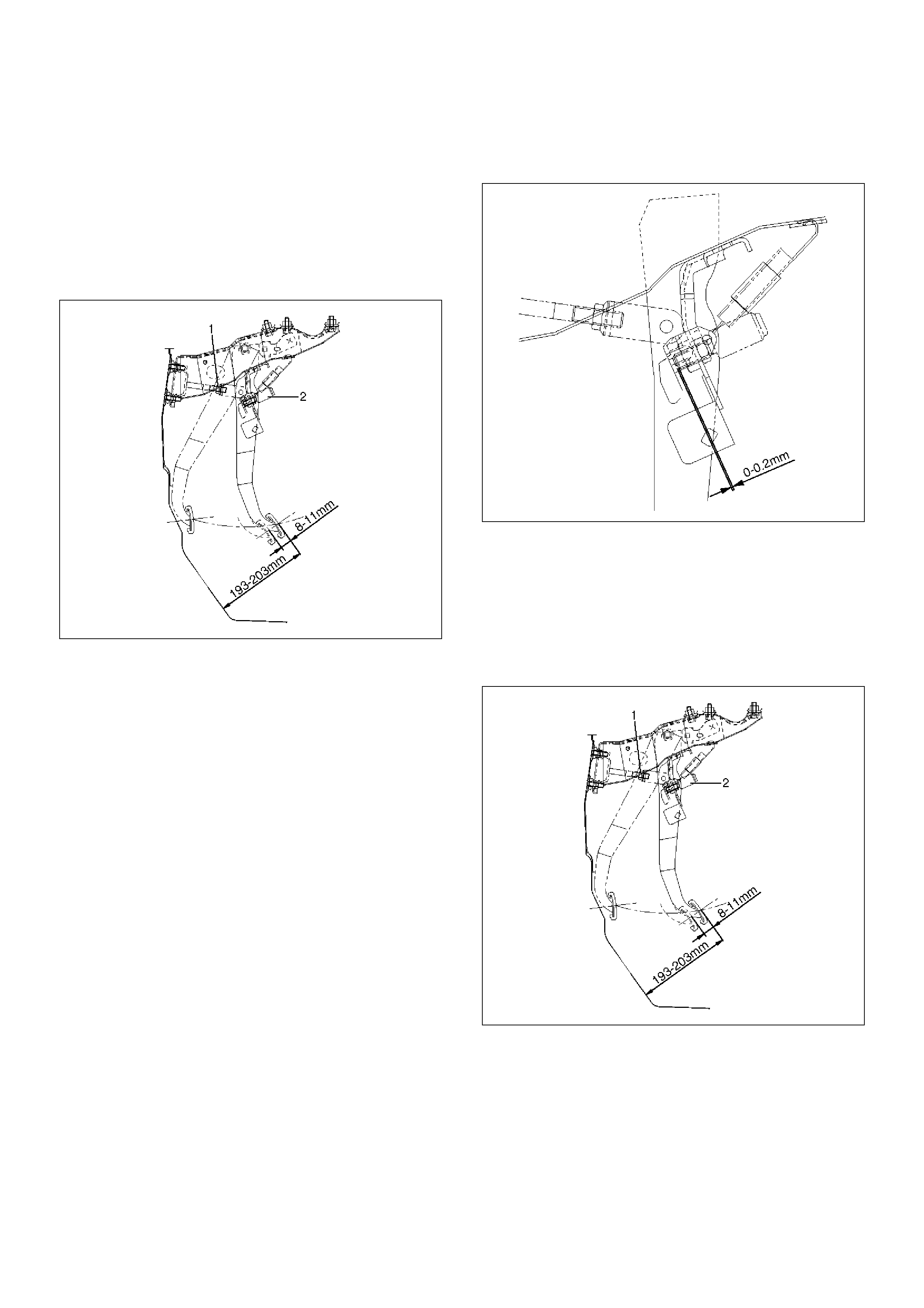
Brake Pedal
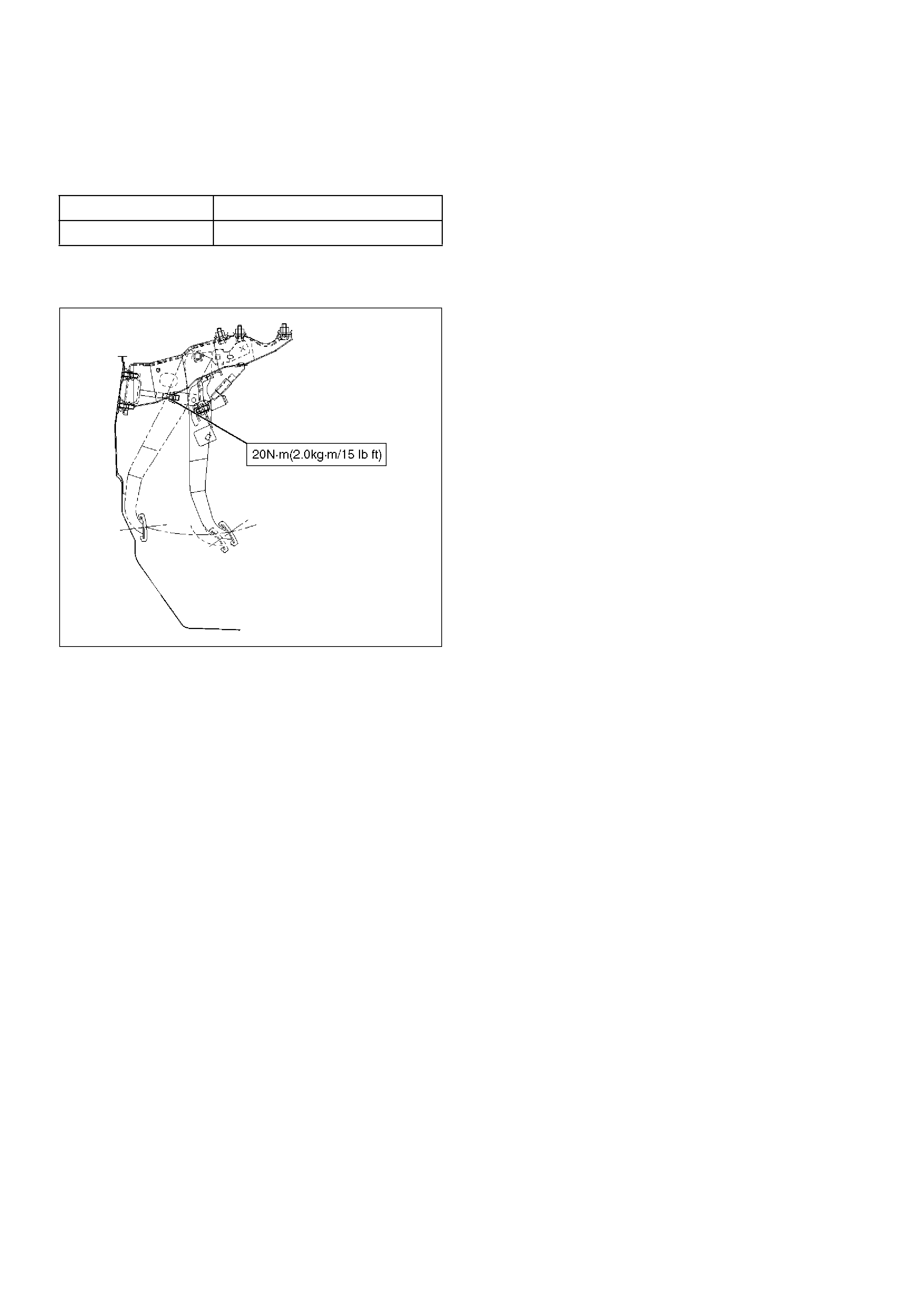
Checking Pedal Height
The push rod serves as the brake pedal stopper when
the pedal is fully released. Brake pedal height
adjustment should be performed as follows:
Adjust Brake Pedal
310RW021
1. Measure the brake pedal height after making sure
the pedal is fully returned by the pedal return spring.
Pedal height must be measured after starting the
engine and stepping on it several times.
Pedal Free Play: 8-11 mm (0.31-0.43 in)
Pedal Height: 193-203 mm (7.60-7.99 in)
NOTE: Pedal free play must be measured after turning
off the engine and stepping on the brake pedal firmly
five times or more.
2. If the measured value is not within the above range,
adjust the brake pedal as follows:
a Disconnect the stoplight switch connector.
b Loosen the stoplight switch lock nut.
c Rotate the stoplight switch so that it moves
away from the brake pedal.
d Loosen the lock nut (1) on the push rod.
e Adjust the brake pedal to the specified height by
rotating the push rod in the appropriate
direction.
f Tighten the lock nut to the specified torque.
Torque: 20 N·m(2.0 kg·m/15 lbft)
g Adjust the stoplight switch (2) to the specified
clearance (between the switch housing and the
brake pedal) by rotating the switch housing.
Clearance: 0–0.2 mm (0–0.008 in)
310RW022
NOTE: While adjusting the stoplight switch, make sure
that the threaded part of the stoplight switch does not
push the brake pedal.
h Tighten the stoplight switch lock nut.
i Connect the stoplight switch connector.
Checking Pedal Travel
310RW021
1. Pedal height must be measured after starting the
engine and revving it several times to apply vacuum
to the vacuum booster fully.
NOTE: Pedal height must be 50 mm (1.97 in) or more
when about 490N (50kg/110Ib) of stepping force is
applied.
2. If the measured value is lower than the above
range, air existing in the hydraulic system is
suspected. Perform the bleeding procedure.
Brake Pedal and Associated Parts
310RY00008
EndOFCallout
Removal
1.Disconnect the battery “–" terminal cable, and wait
at least 5 minutes.
2.Disconnect the yellow 3 way SRS connector located
under the steering column.
3.Remove the engine hood opening lever.
4.Remove lower cover (8).
5.Remove driver knee bolster (10).
6.Disconnect the stop light switch connector (3).
Disconnect the anti-theft control module connector.
f to Body and Accessories section.
7.Remove snap pin (4) and push rod pin (7).
8.Remove the steering column shaft fixing bolt and
nut (9) on the steering wheel side, and lower the
steering column shaft.
9.Remove the brake pedal bracket assembly (1).
10.Remove return spring (5).
11.Remove fulcrum pin and nut (2).
12.Remove pedal assembly (6).
Installation
1.Apply grease to the entyre circumference of the
fulcrum pin.
2.Install pedal assembly (6) and fulcrum pin and nut
(2).
Tighten the nut (2) to the specified torque.
Torque: 35 N·m (3.6 kg·m/26 lbft)
3.Install the brake pedal bracket assembly (1).
Tighten the bolts and nuts soecified torque.
Torque: 15 N·m (1.5 kg·m/11 lbft)
4.Install return spring (5).
5.Adjust pedal free travel.
Refer to Brake Pedal Adjustment in this section.
6. Tighten the steering column fixing bolt (9) (dash
panel) to the specified torque.
Torque: 20 N·m (2.0 kg·m/14 lbft)
7. Tighten the steering column fixing nut (9) (Cross
Beam) to the specified torque.
Torque: 17 N·m (1.7 kg·m/12 lbft)
Legend
(1) Brake Pedal Bracket Assembly
(2) Fulcrum Pin and Nut
(3) Connector
(4) Snap Pin
(5) Return Spring
(6) Pedal Assembly
(7) Push Rod Pin
(8) Lower Cover
(9) Bolts and Nut
(10) Driver Knee Bolster
8.Apply grease to the entyre circumference of the
Push rod pin (7).
9.Install push rod pin (7).
10.Install snap pin (4).
11.Connect the anti-theft control module connector.
Refer to Body and Accessories section.
12. Connect the stop light switch connector (3).
13. Install driver knee bolster (10) and lower cover (8).
14. Install the engine hood opening lever.
15. Connect the yellow 3 way SRS connector located
under the steering column.
16. Connect the battery “–" terminal cable.
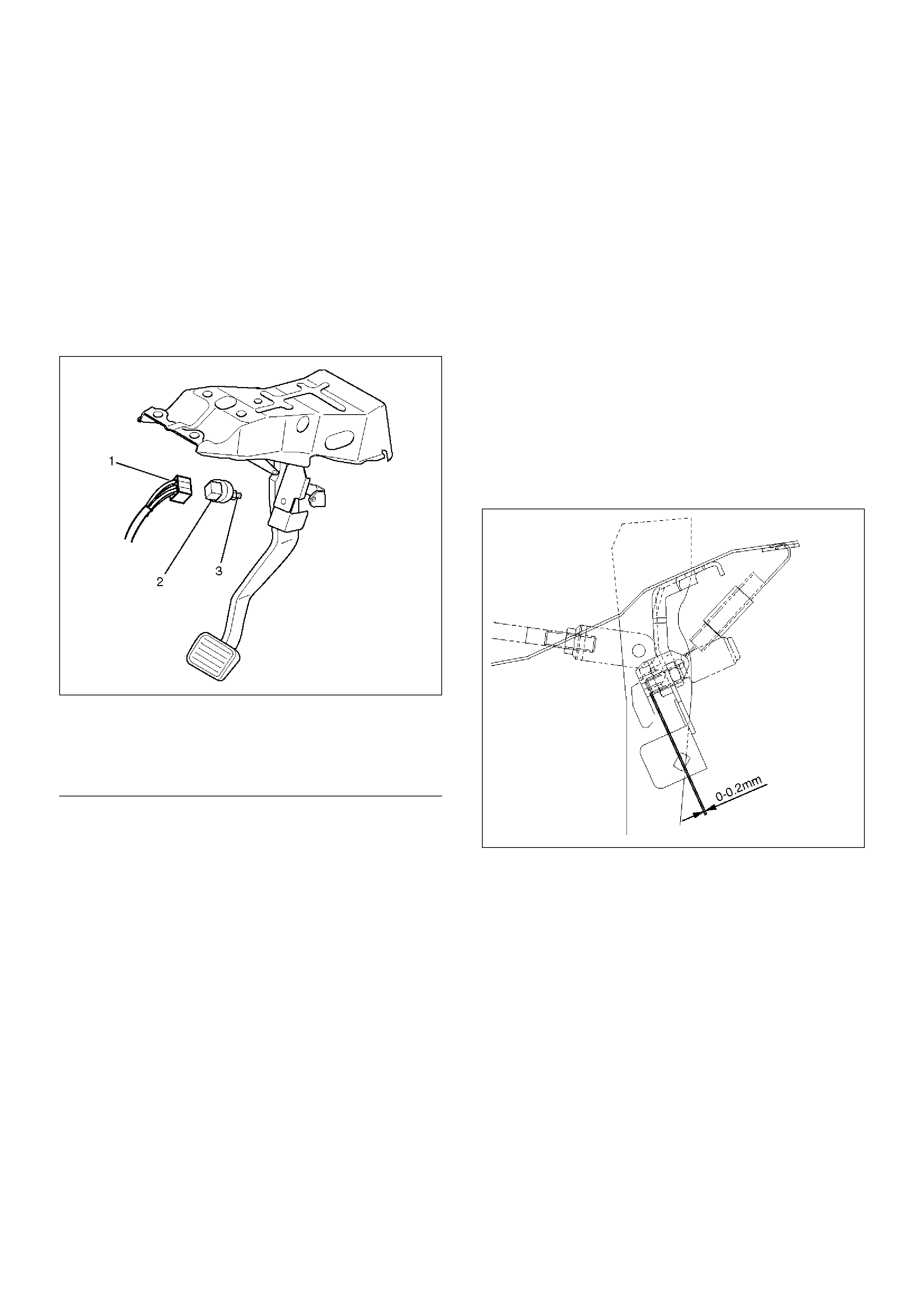
Stoplight Switch
Parts Location
310RW024
EndOFCallout
Removal
1. Disconnect connector (1)
2. Remove lock nut (3).
3. Remove switch (2).
Installation
1. Adjust the stop light switch to the specified
clearance (between switch housing and brake
pedal) by rotating the switch housing.
Clearance : 0-0.2 mm (0-0.008 in)
NOTE: Do not attempt to force the push rod into
position during the stop light switch installation and
adjustment procedure.
310RW022
2. Connect connector (1).
3. Install lock nut (3).
Legend
(1) Connector
(2) Switch
(3) Lock Nut
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Torque Specifications
E05RX006
Pedal free play 6–10 mm (0.23 –0.39 in)
Pedal Height 173–185 mm (6.81–7.28 in)
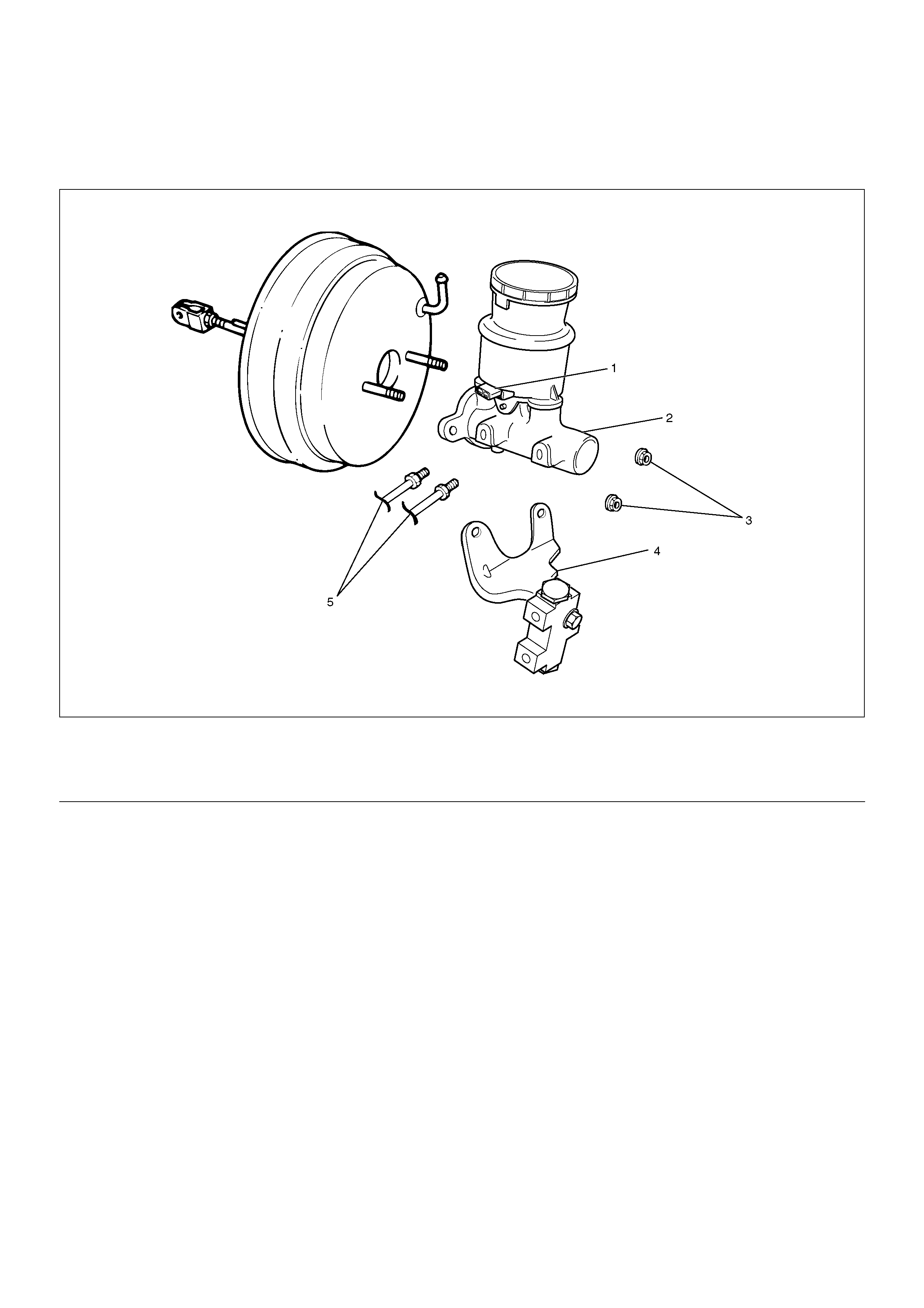
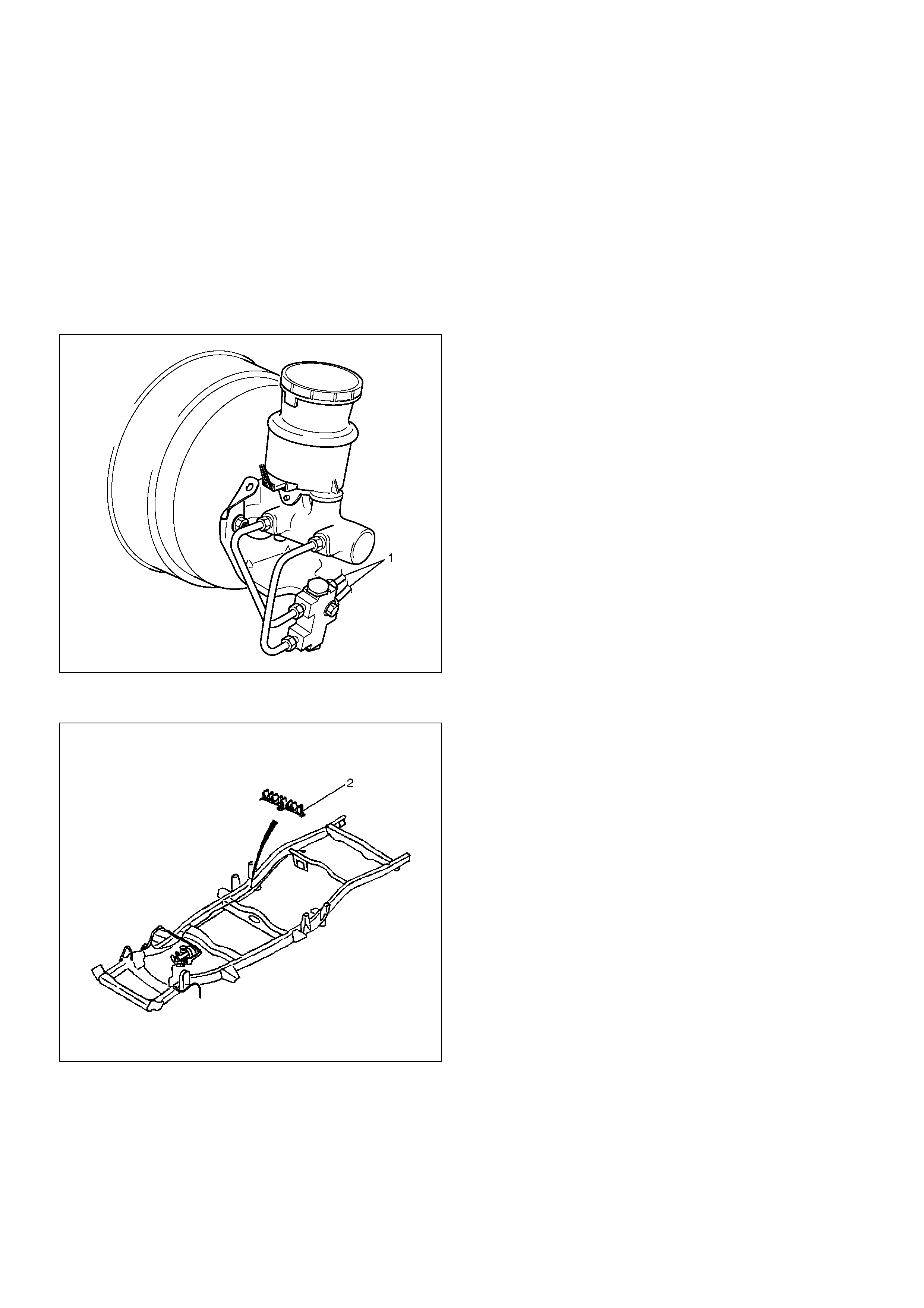
Master Cylinder Assembly
Master Cylinder Assembly and Associated Parts
330R200006
EndOFCallout
Removal
CAUTION: When removing the master cylinder
from the vacuum booster, be sure to get rid of the
internal negative pressure of the vacuum booster
(by, disconnecting the vacuum hose) in advance.
If any negative pressure remains in the vacuum
booster, the piston may possibly come out when the
master cylinder is being removed, letting the brake
fluid run out.
While removing the master cylinder, do not hold the
piston as it can be easily pulled out.
Outside surface of the piston is the surface on
which seals are to slide. Care should be taken to
keep the surface free of cuts and dents.
1. Disconnect electrical connector.
2. Remove brake pipes and after disconnecting the
brake pipe, cap or tape the openings of the brake
pipe to prevent the entry of foreign matter.
3. Remove 2 attaching nuts.
4. Remove P&B valve and bracket.
5. Remove master cylinder.
Inspection and Repair
Master Cylinder
The master cylinder is not repairable and must be
replaced as a complete assembly if found defective.
Inspection
Excessive brake pedal travel, malfunction or dragging
brake suggests that the master cylinder is defective. In
such cases perform the following visual check:
Visual Check
Make parts replacement as required if wear, distortion,
nicks, cuts, corrosion, or other abnormal conditions are
found through the following parts inspection:
• Master cylinder body
• Fluid reservoir
•O–ring
Legend
(1) Electrical Connector
(2) Master Cylinder
(3) 2 attaching Nuts
(4) P&B Valve and Bracket
(5) Brake Pipes

Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Torque Specifications
E05R200010
Type Dual–circuit
Piston bore
diameter
25.4 mm (1.000 in)
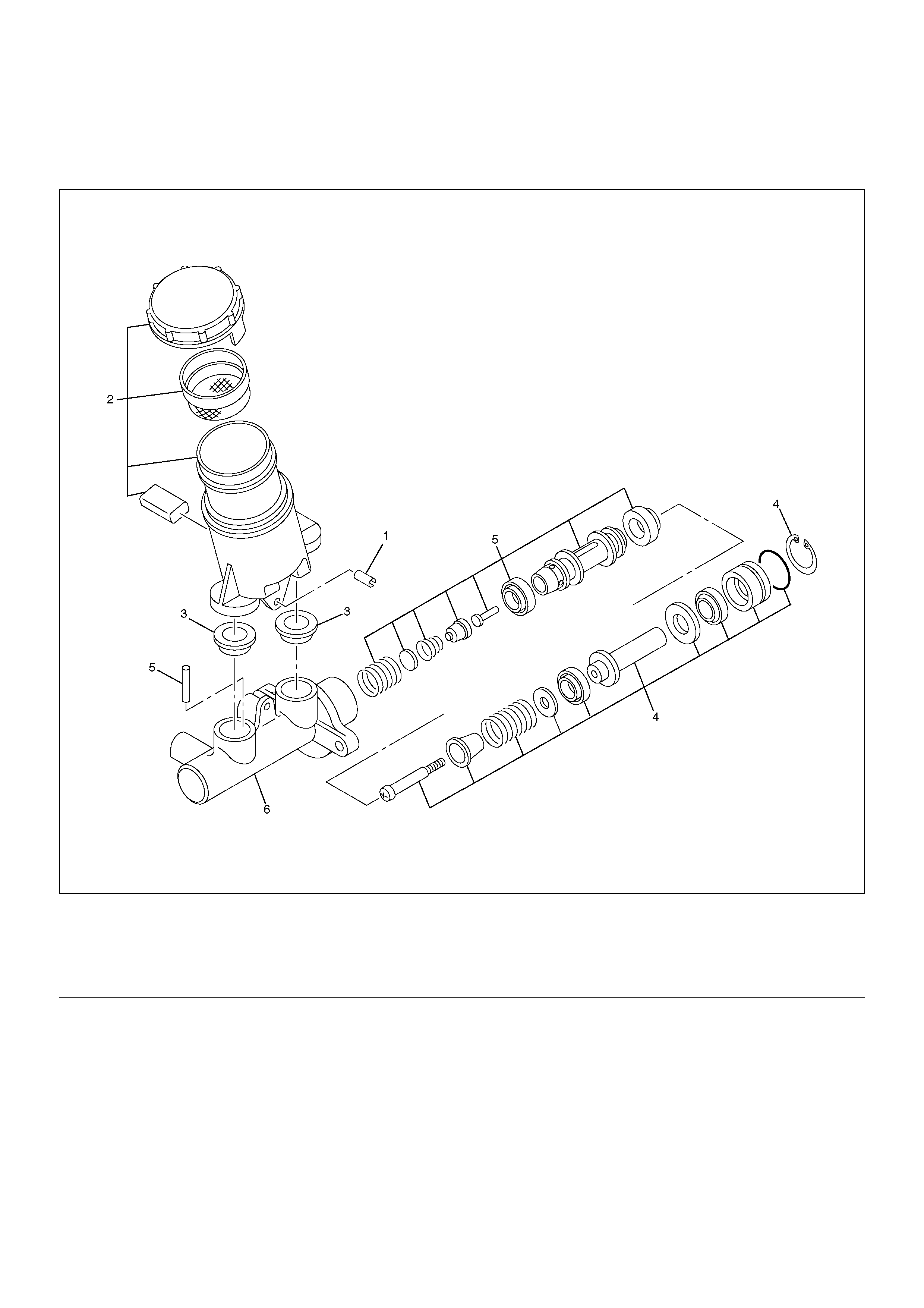
Master Cylinder Assembly
Master Cylinder Assembly Desassembled View
330R200005
EndOFCallout
Disassembly
1. Remove the spring pin.
2. Remove the reserve tank and the reserve tank cap.
The brake fulid level switch is built–in to the reserve
tank and cannot be removed.
3. Remove the O–ring.
4. Remove the snap ring.
5. Remove the primary piston assembly.
6. Invert the cylinder body and push on the secondary
piston until the pin falls free.
7. Remove the secondary piston assembly.
8. Remove the cylinder body.
Inspection
Excessive brake pedal travel, malfunction or dragging
brake suggests that the master cylinder is defective. In
such cases perform the following visual check:
Legend
(1) Spring Pin
(2) Reserve Tank and Reserve Tank Cap
(3) O–ring
(4) Primary Piston Assembly
(5) Secondary Piston Assembly
(6) Cylinder Body

Visual Check
Make parts replacement as required if wear, distortion,
nicks, cuts, corrosion, or other abnormal conditions are
found through the following parts inspection:
•Master cylinder body
•Fluid reservoir
•O–ring
•Wash each part in brake fluid before beginning the
inspection procedure.
•Check the inside surfaces of the master cylinder for
abrasion, corrosion, and other damage. Replace the
cylinder if necessary.
•Check the return port for clogging. Clean the port with
a wire and compressed air if nesessay.
•Check the piston and piston cup for abrasion,
damage, and wear. Replace the piston assembly if
any of these conditions exist.
•Check the return spring. Replace the spring if it is
weak.
•Check the snap ring. Replace the snap ring if it is
stretched or weak.
Reassembly
1.Wash each master cylinder internal part in brake
fluid before beginning installation.
2.Install the cylinder body.
3.Press the secondary piston assembly into the
cylinder body and hold it. Thread the pin through the
long hole of the piston to secure the piston
assembly.
4.Install the primary piston assembly.
5.Install the snap ring.
6.Install the O–ring
7.Install the reserve tank and the reserve tank cap.
8.Install the spring pin.
Installation
1.Install master cylinder.
When replacing the master cylinder or vacuum
booster or both, always measure the vacuum
booster push rod protrusion and adjust it as
necessary (Refer to Vacuum Booster in section).
2. Install P&B valve and bracket.
3. Install 2 attaching nuts and tighten the attaching
nuts to the specified torque.
Torque: 13 N·m (1.3 kg·m/113 lbin)
4. Install brake pipes and tighten the brake pipe to the
specified torque.
Master cylinder and P&B valve sides
Torque: 15 N·m (1.5 kg·m/11 lbin)
Others
Torque: 16 N·m (1.6 kg·m/12 lbin)
5. Connect electrical connector.
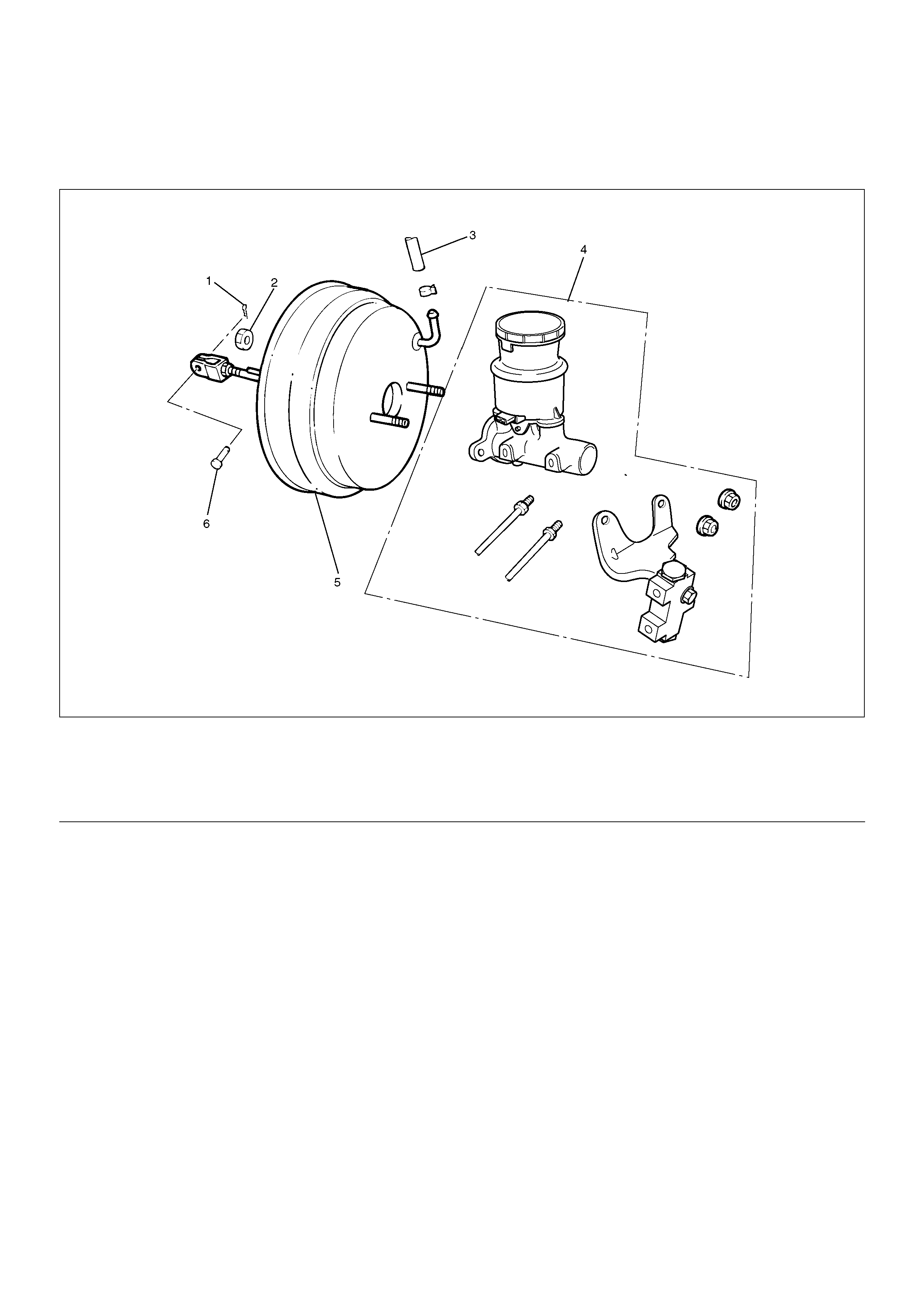
Vacuum Booster Assembly
Vacuum Booster Assembly and Associated Parts
331R200004
EndOFCallout
Removal
1.Before removing the vacuum booster assembly,
disconnect and remove the brake pipes.
2.Remove master cylinder, refer to “Master Cylinder
Removal" in this section.
CAUTION: When removing the master cylinder
from the vacuum booster, be sure to get rid of the
internal negative pressure of the vacuum booster
(by, disconnecting the vacuum hose) in advance.
If any negative pressure remains in the vacuum
booster, the piston may possibly come out when the
master cylinder is being removed, letting the brake
fluid run out.
Do not hold the piston while removing the master
cylinder, the piston can be easily pulled out.
Outside surface of the piston is the surface on
which seals are to slide. Care should be taken to
keep the surface free of cuts and dents.
3. Remove vacuum hose.
4. Disconnect the yoke clevis from the brake pedal.
5. Remove vacuum booster fixing nut.
6. Remove vacuum booster.
Inspection and Repair
Vacuum Hose
1. Inspect the check valve (2), which is installed inside
the vacuum hose.
2. Air should pass freely from the vacuum booster (3)
to the engine (1).
Legend
(1) Snap Pin
(2) Vacuum Booster Fixing Nut
(3) Vacuum Hose
(4) Master Cylinder
(5) Vacuum Booster
(6) Pin
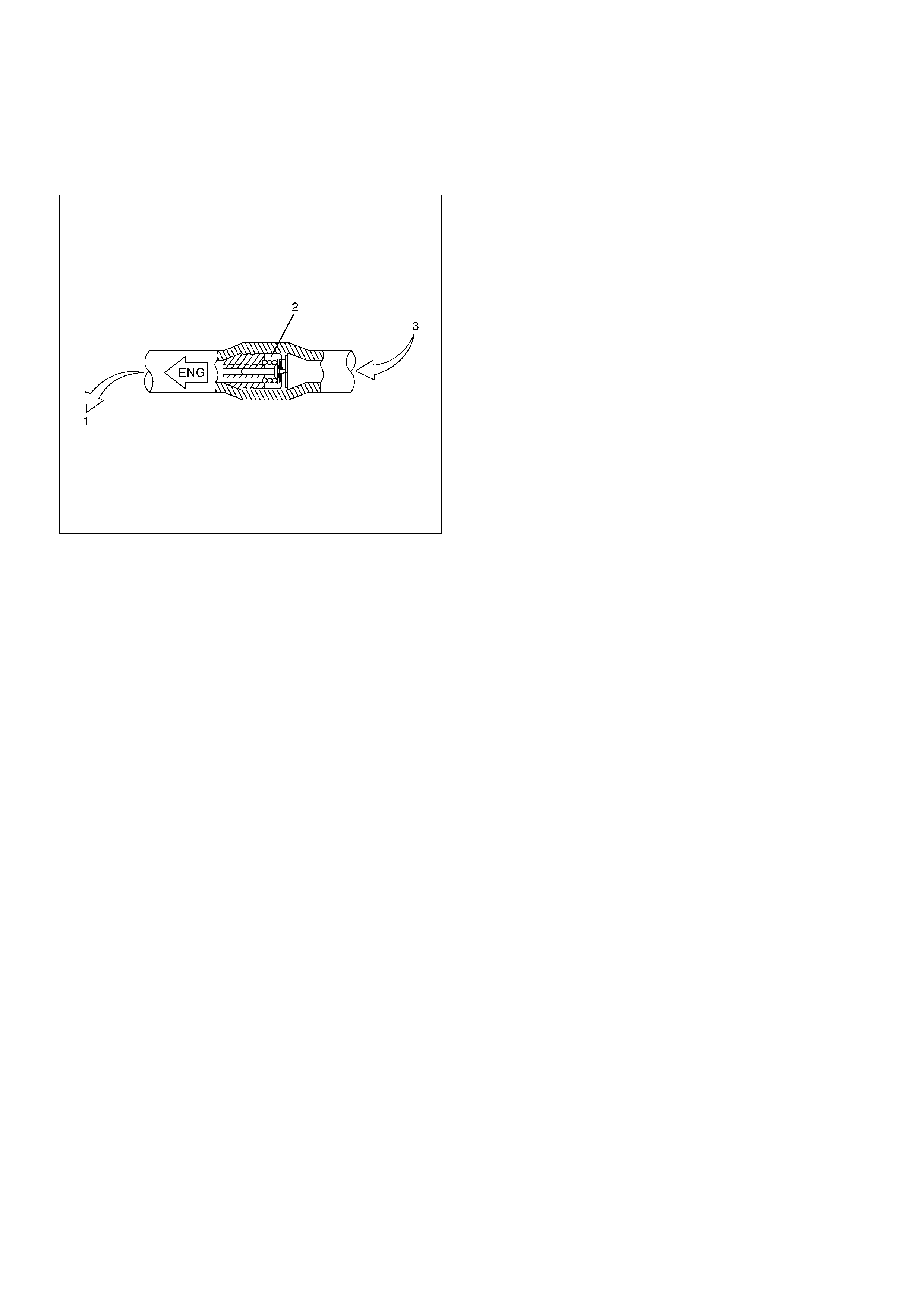
3.Air should not pass from the engine (1) to the
vacuum booster (3). If it does, the check valve is
inoperative and must be replaced.
360RY00004
Installation
1.Install vacuum booster fixing nut and tighten the
specified torque.
Torque: 15 N·m (1.5 kg·m/11 lbft)
2.Install yoke clevis.
3.Connect vacuum hose and make sure that the
arrow on the hose points in the direction of the
engine.
4.Install master cylinder, refer to “Master Cylinder
Installation" in this section.

Exterior Components
Exterior Components and Associated Parts
331R200006
EndOFCallout
Removal
1.Remove master cylinder. Refer to “Master Cylinder"
in this section.
2.Remove vacuum booster. Refer to “Vacuum
Booster" in this section.
3. Remove 2 gaskets and spacer.
4. Remove retainer, plate and seal assembly.
331RS003
Legend
(1) 2 Gaskets and Spacer
(2) Vacuum Booster
(3) Plate and Seal Assembly
(4) Retainer
(5) Master Cylinder

Inspection and Repair
Visual Check
Make necessary parts replacement if cuts, nicks,
excessive wear, or other abnormal conditions are found
through inspection.
NOTE: The parts listed below must be replaced with
new ones whenever the master cylinder is removed.
1.Plate and seal assembly
2.Retainer
Installation
1.Install plate and seal assembly.
2.Install retainer.
3.Install vacuum booster, refer to “Vacuum Booster" in
this section.
4.Install master cylinder, refer to “Master Cylinder" in
this section and after installation, perform brake
pedal check and adjustment. Refer to “Brake Pedal"
in this section.
Vacuum Booster Overhaul
Vacuum Booster
The vacuum booster cannot be disassembled for repair.
Replace a defective vacuum booster with a new one.
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Torque Specifications
E05R200011
Vacuum booster diaphragm diameter (Front) 205 mm (8.07 in)
Vacuum booster diaphragm diameter (Rear) 230 mm (9.06 in)
Push rod stroke More than 32.0 mm (1.26 in)
Plunger diameter 10.25 mm (0.40 in)
Push rod diameter 27.4 mm (1.08 in)
Front Disc Brake Pads
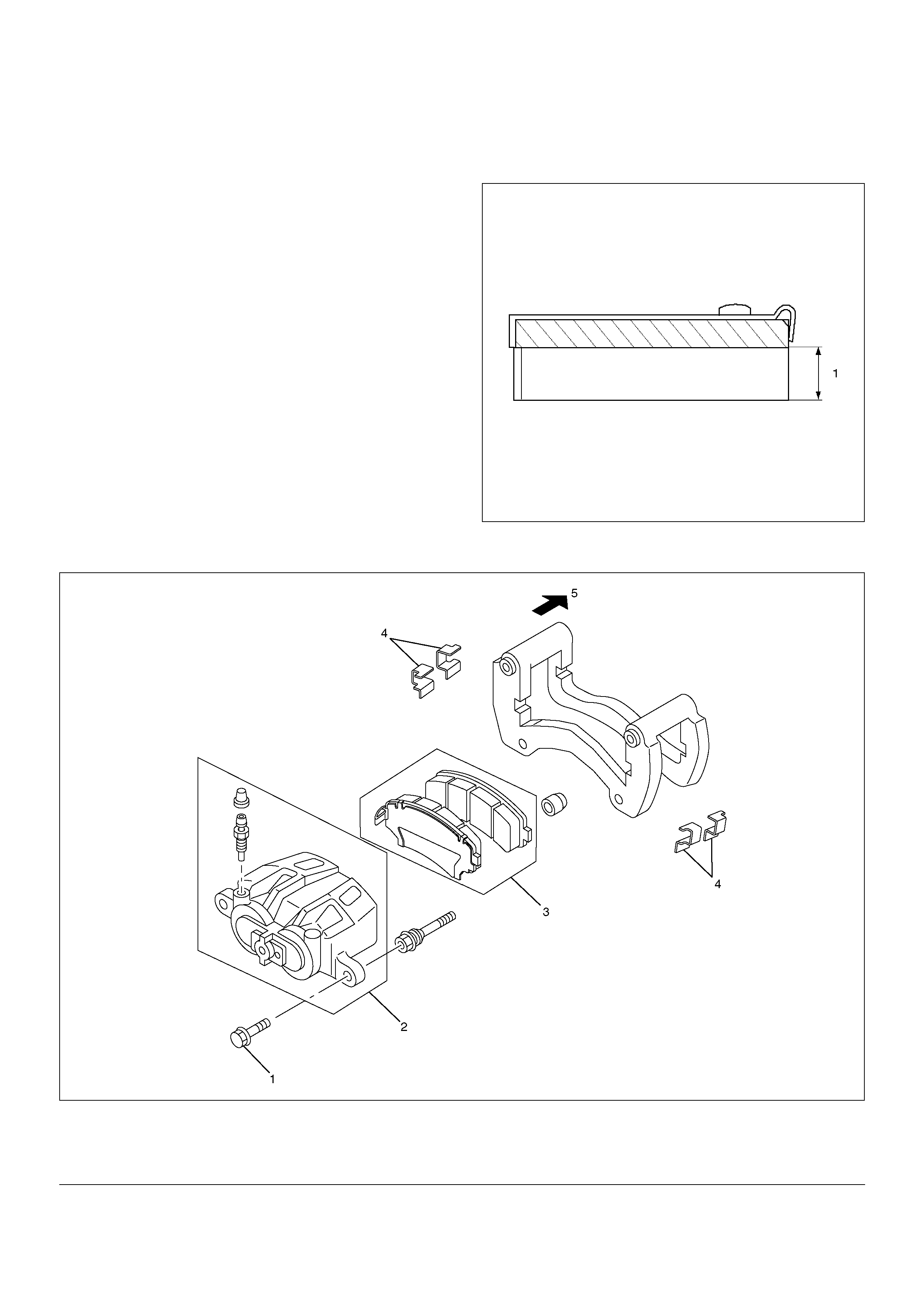
Front Disc Brake Pads Inspection
Check the outer pad by looking at each caliper from
above. Check the thickness on the inner pad by looking
down through the inspection hole in the top of the
caliper. Whenever the pad is worn to about the
thickness of the pad base, the pad should be removed
for further measurements. The pad should be replaced
anytime the pad thickness (1) is worn to within 1.00 mm
(0.039 in) of the pad itself.
Wear indicators are installed on disc brake pads, disc
brake pads need replacement when the wear
indicator is heard.
Minimum limit (1): 1.0 mm (0.039 in)
302RS002
Front Disc Brake Pads and Associated Parts
302R200026
EndOFCallout
Legend
(1) Pin Bolt
(2) Caliper Assembly
(3) Pad Assembly
(4) Clip
(5) Outer Side
Removal
NOTE: If a squealing noise occurs from the front brake
while driving, check the pad wear indicator plate. If the
indicator plate contacts the rotor, the disc pad assembly
should be replaced.
•Draw out two–thirds of the brake fluid from the
reservoir.
•Raise the vehicle and support it with suitable safety
stands.
1.Remove wheel and tyre assembly, refer to Wheels
and Tyres System in Section 10.
2. Remove pin bolt (1).
302R20002 8
3. Rotate caliper assembly and support the caliper
assembly so that the brake hose is not stretched or
damaged.
4. Remove pad assembly with shim.
5. Remove Clip.
Installation
1. Install clip.
302R200023
2. Apply special grease (approximately 0.2g) to both
contacting surfaces of the inner shims (2). Wipe
off extruded grease after installing. Install pad
assembly with shim.
302R200024
EndOFCallout
Legend
(2) Inner Shim
(3) Wear Indicator
(4) Inner Side
3.Carefyully use adjustable pliers to bottom the piston
into the caliper bore. Do not pull or twist the flexible
hose or damage will occur.
Install caliper assembly.
Set caliper assembly in place.
4.Install lock bolt (5) and tighten the bolt to the
specified torque.
Torque: 45 N·m (4.6 kg·m/33 lbft)
302R200008
5.Install wheel and tyre assembly, refer to Wheels and
Tyres System in Section 10.
6. Pump the brake pedal several times to make sure
that the pedal is firm. Check the brake fluid level in
the reservoir after pumping the brakes.
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Inspection
In the manufacturing of the brake rotor, all the
tolerances regarding surface finish, parallelism and
lateral runout are held very closely. Maintaining these
tolerances provides the surface necessary to assure
smooth brake operation.
Lateral Runout
Lateral runout is the movement of the rotor from side to
side as it rotates on the spindle. This could also be
referred to as “rotor wobble".
This movement causes the piston to be knocked back
into its bore. This results in additional pedal travel and a
vibration during braking.
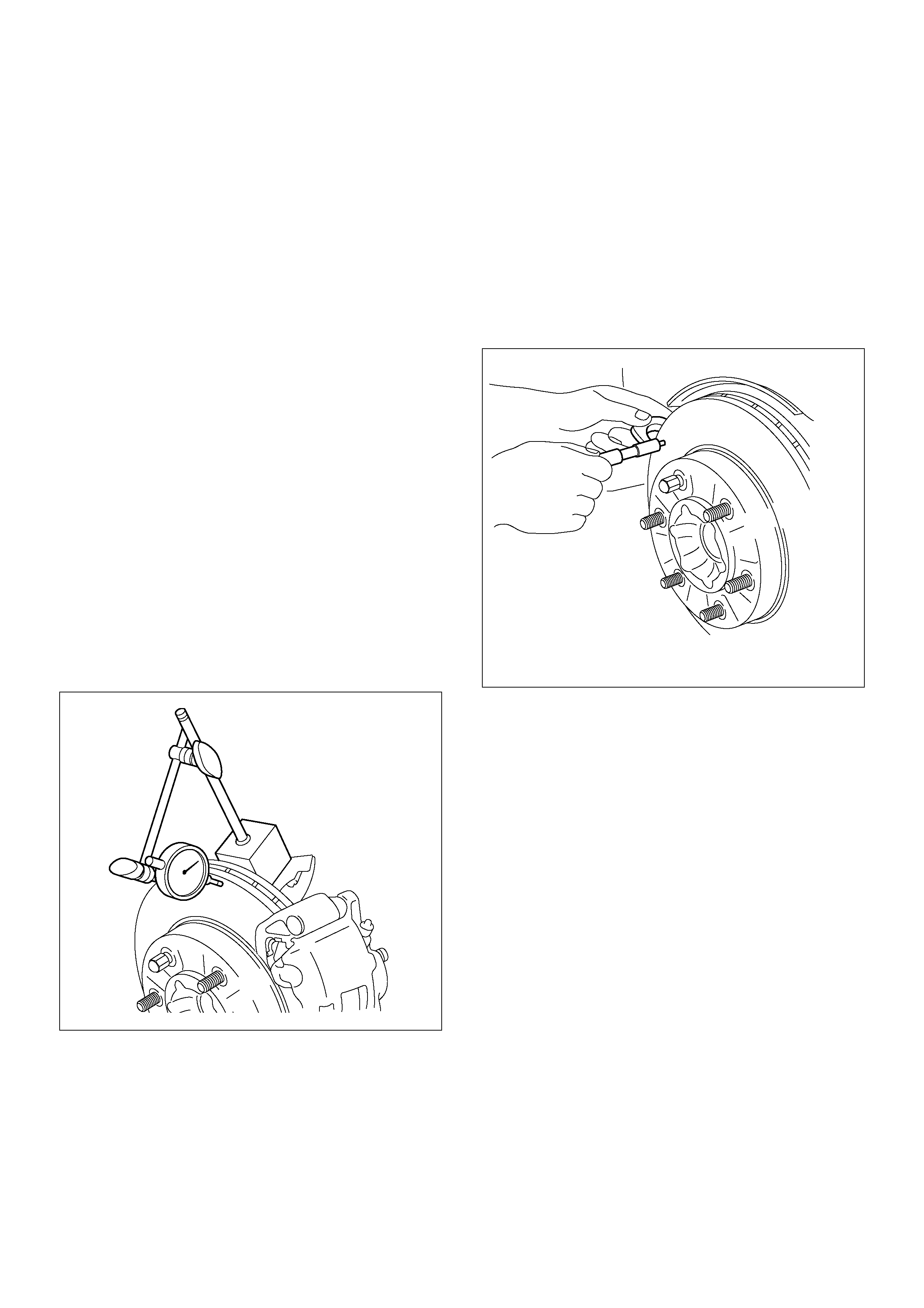
Checking Lateral Runout
1.Adjust the wheel bearing correctly, refer to
Differential in Section 4A.
2. Attach the dial indicator accordingly so that the stem
contacts the rotor surface to approximately
29mm (1.14 in) from the rotor edge.
3. Rotate the rotor one complete turn and inspect for
signs of lateral runout. Lateral runout should
not exceed 0.13 mm (0.005 in).
Maximum runout: 0.13 mm (0.005 in)
411R200008
Parallelism
Parallelism is the measurement of thickness of the rotor
at four or more points around the circumference of the
rotor. All measurement must be made at 29 mm (1.14
in) from the edge of the rotor.
The rotor thickness must not vary more than 0.010 mm
(0.0004 in) from point to point.
Maximum runout: 0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
411R200007
Replacing Brake Rotors
When installing new brake rotors, do not refinish the
surfaces. These parts are at the correct level of surface
finish.
Refinishing Brake Rotors
Accurate control of the rotor tolerances is necessary for
proper performance of the disc brakes. Machining of the
rotor should be done only with precision equipment. All
brake rotors have a minimum thickness dimension cast
into them. This dimension is the minimum wear
dimension and not a refinish dimension. The minimum
wear dimension is 24.60 mm (0.969 in). The minimum
refinish dimension is 26.00 mm (1.024 in).
When refinishing rotors, always use sharp cutting tools
or bits. Dull or worn tools leave a poor surface finish
which will affect initial braking performance. Vibration
dampening attachments should always be used when
refinishing braking surfaces. These attachments
eliminate tool chatter and will result in better surface
finish.
After refinishing, replace any rotor that does not meet
the minimum thickness of 26.00 mm (1.024 in). Do not
use a brake rotor that exceeds the manufacturers
specifications.
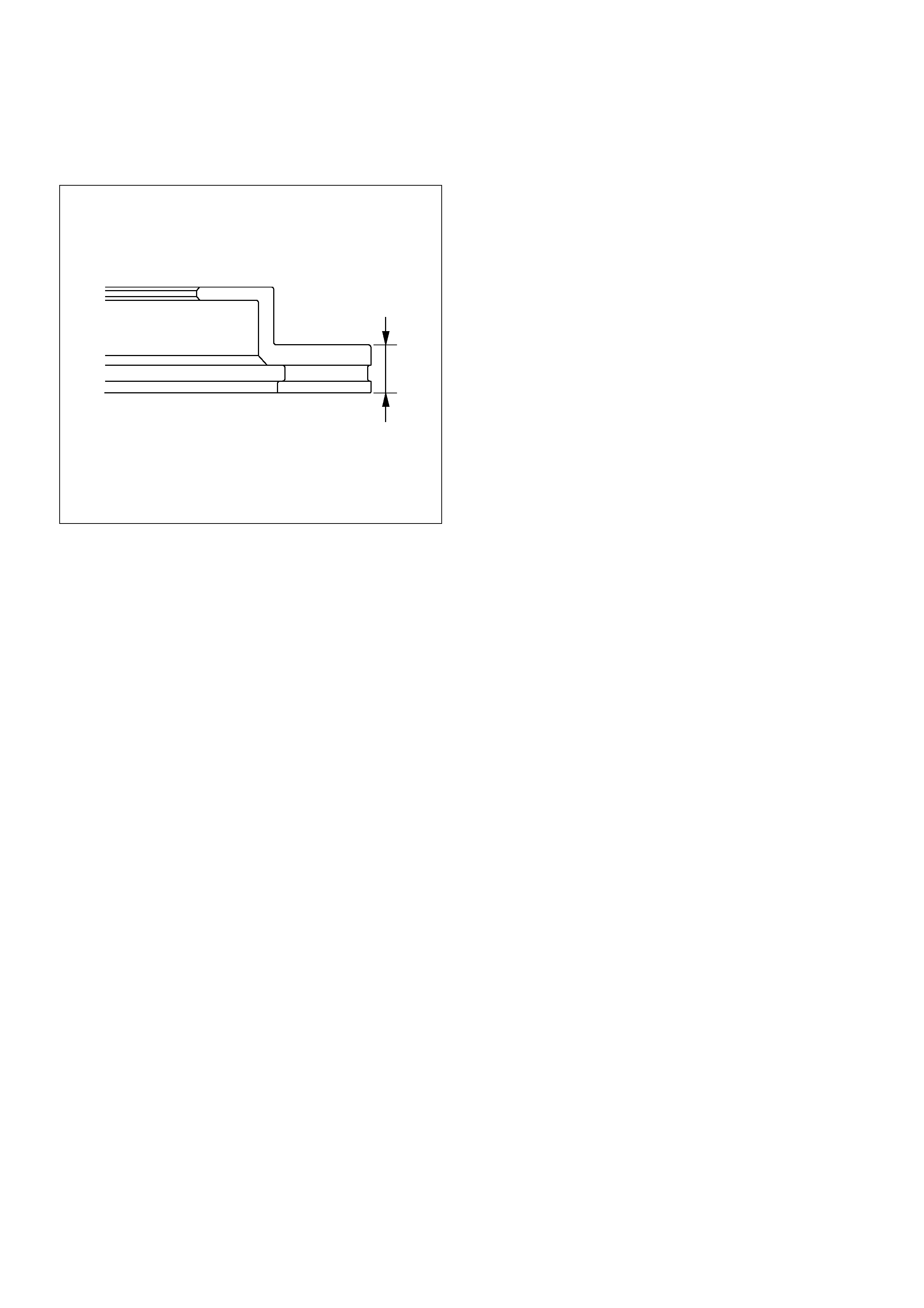
Minimum wear dimension: 24.60 mm (1.024 in)
Refinish dimension: 26.00 mm (1.024 in)
411R200009
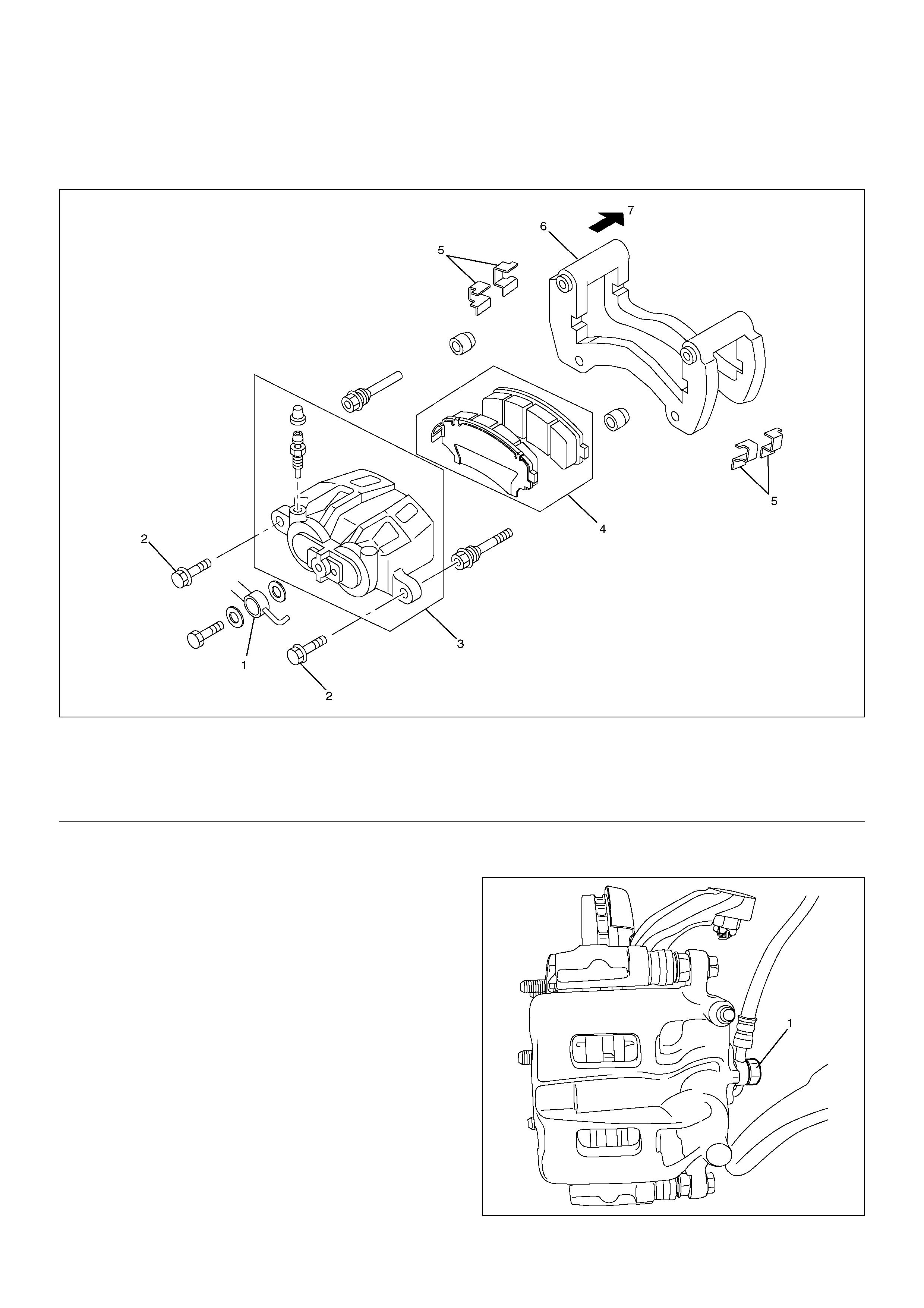
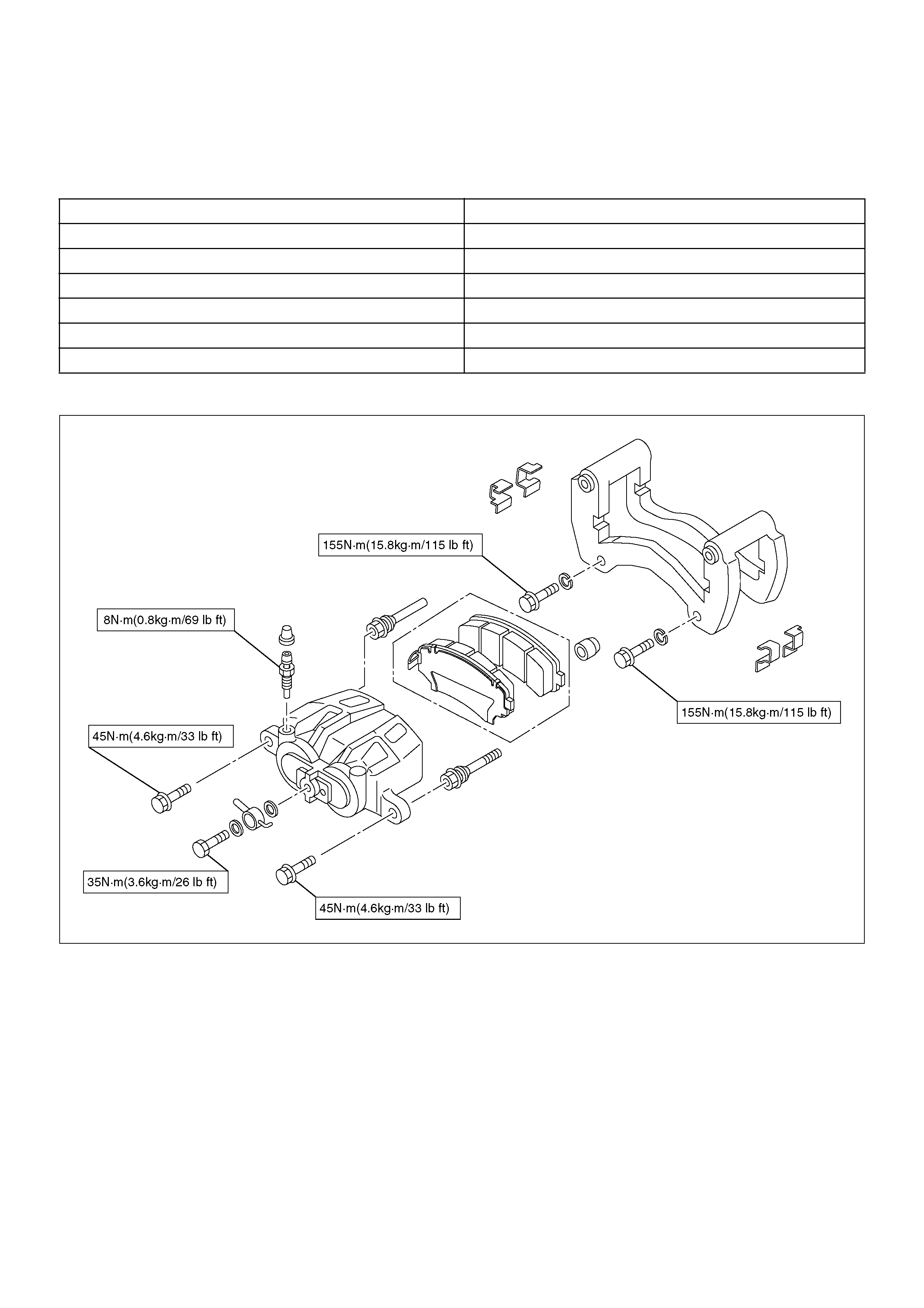
Front Disc Brake Caliper Assembly
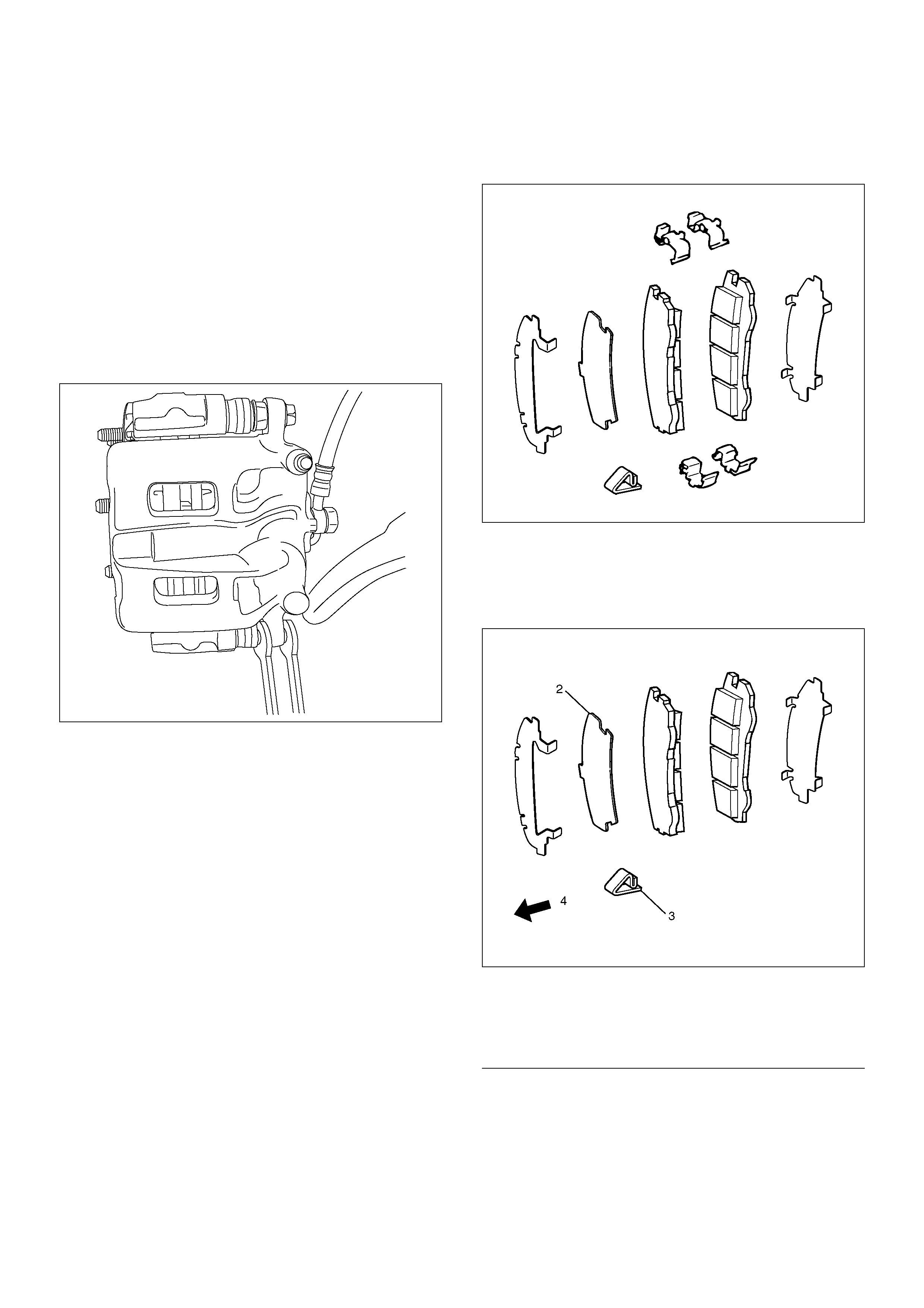
Front Disc Brake Caliper Assembly and Associated Parts
302R200027
EndOFCallout
Removal
1.Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stands.
2.Remove wheel and tyre assembly, refer to Wheels
and Tyres System in Section 10.
3. Remove the bolt and gaskets, then disconnect the
flexible hose from the caliper and after
disconnecting the flexible hose (1), cap or tape the
openings to prevent entry of foreign material.
302R200007
Legend
(1) Brake Flexible Hose
(2) Pin Bolt
(3) Caliper Assembly
(4) Pad Assembly
(5) Clip
(6) Support Bracket with Pad Assembly
(7) Outer Side
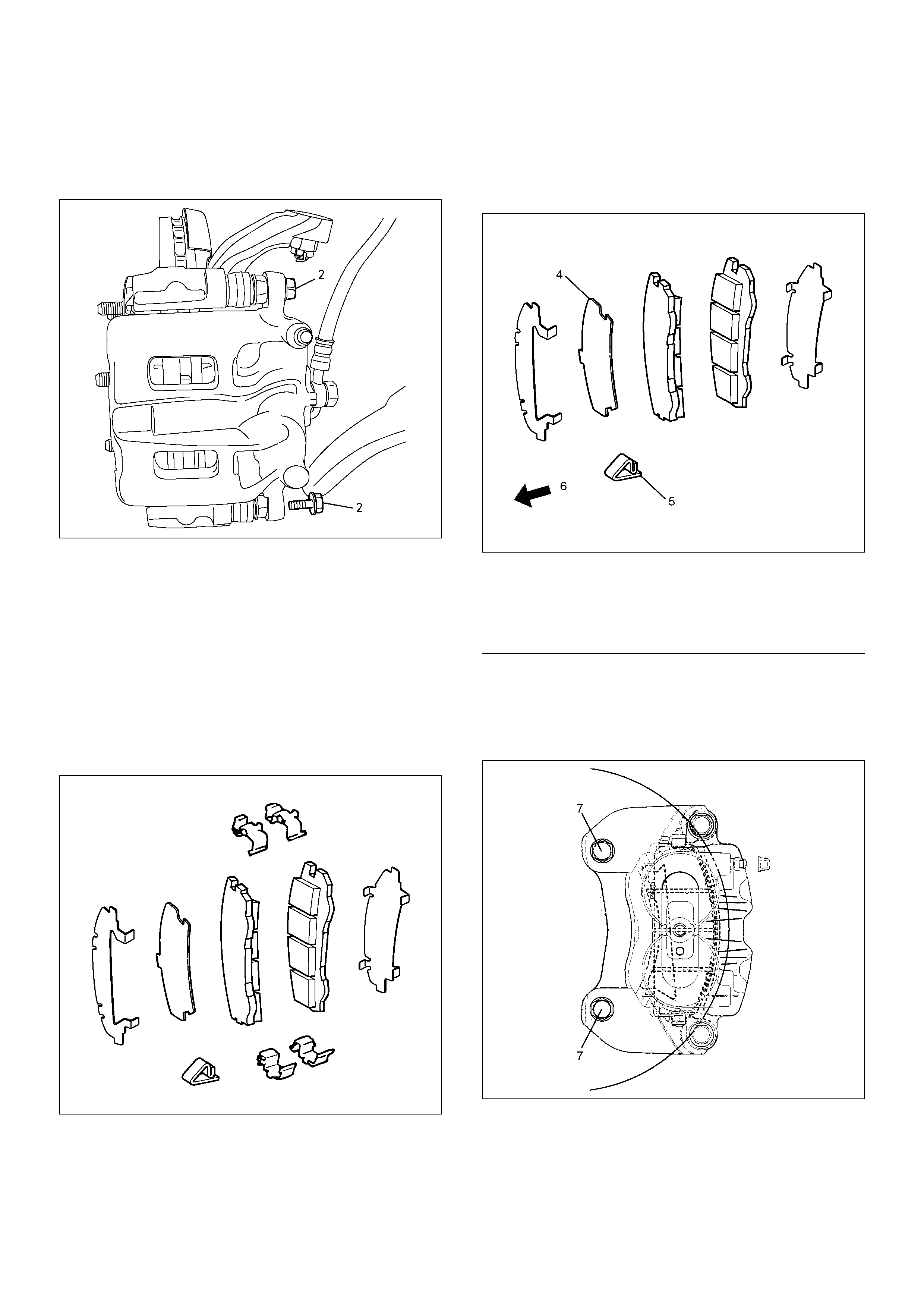
4. Since the brake fluid flows out from the connecting
coupler, place a drain pan under the vehicle.
5. Remove pin bolt (2).
302R20002 0
6. Remove caliper assembly.
7. Remove support bracket with pad assembly and
take care not to damage the flexible brake hose
when removing the support bracket.
8. Remove pad assembly with shim and mark the
lining locations if they are to be reinstalled.
9. Remove clip.
Installation
1. Install clip.
302R20002 3
2. Apply special grease (approximately 0.2 g) to both
contacting surfaces of the inner shims (4). Wipe off
extruded grease after installing. Install pad
assembly with shim.
302R200025
EndOFCallout
3. Install support bracket and tighten the bolt (7) to the
specified torque.
Torque: 155 N·m (15.8 kg·m/115 lbft)
302R200009
Legend
(4) Inner Shim
(5) Wear Indicator
(6) Inner Side
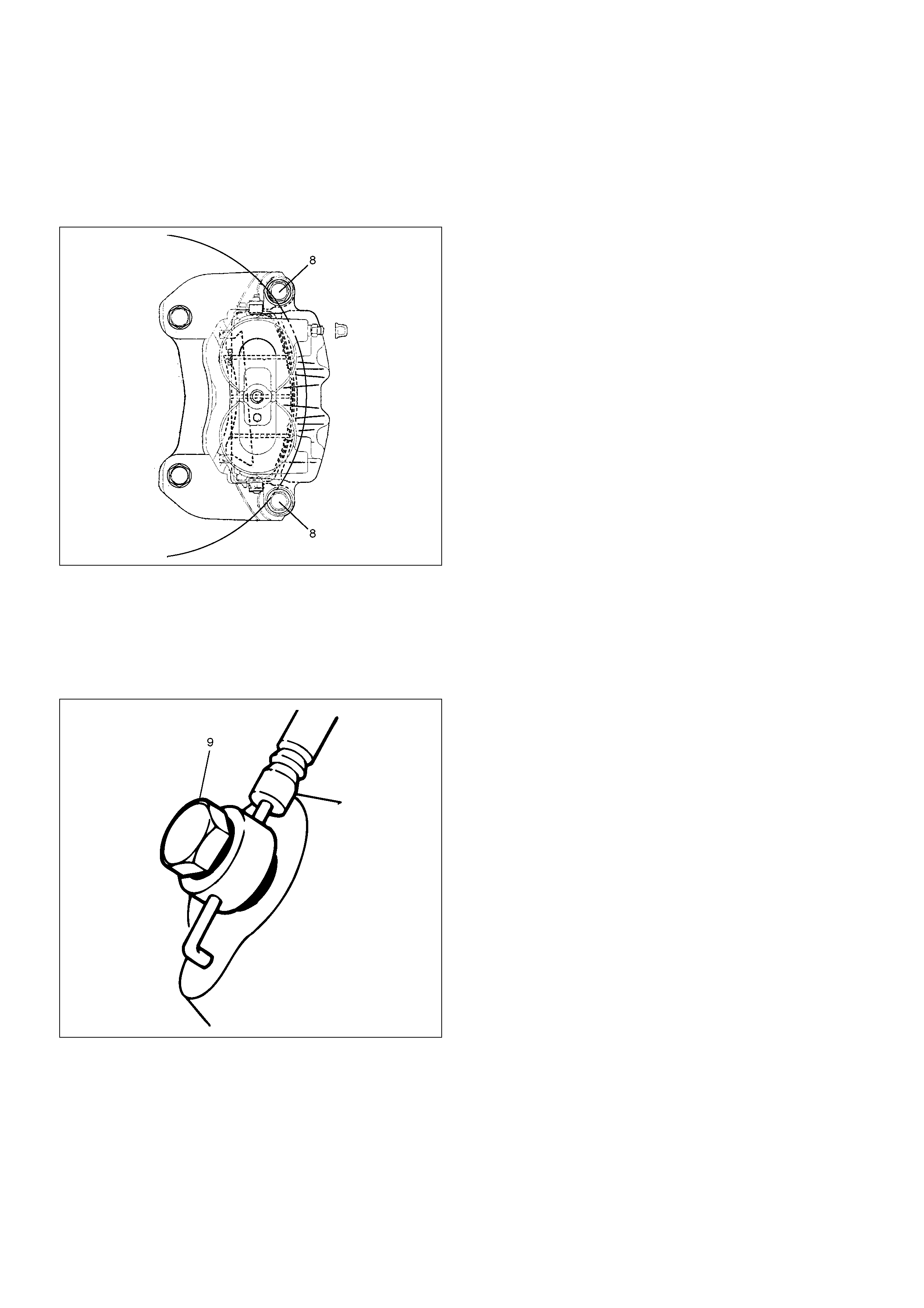
4.Install caliper assembly.
5.Install pin bolt (8) and tighten the bolt to the
specified torque.
Torque: 45 N·m (4.6 kg·m/33 lbft)
302R200010
6.Install brake flexible hose, always use new gaskets
and be sure to put the hooked edge of the flexible
hose end into the anti–rotation cavity then tighten
the I–bolt (9) to the specified torque.
Torque: 35 N·m (26 lbft)
302R200021
7.Install wheel and tyre assembly, referring to Wheels
and Tyres System in Section 10.
8.Bleed brakes. Refer to Hydraulic Brakes in this
section.
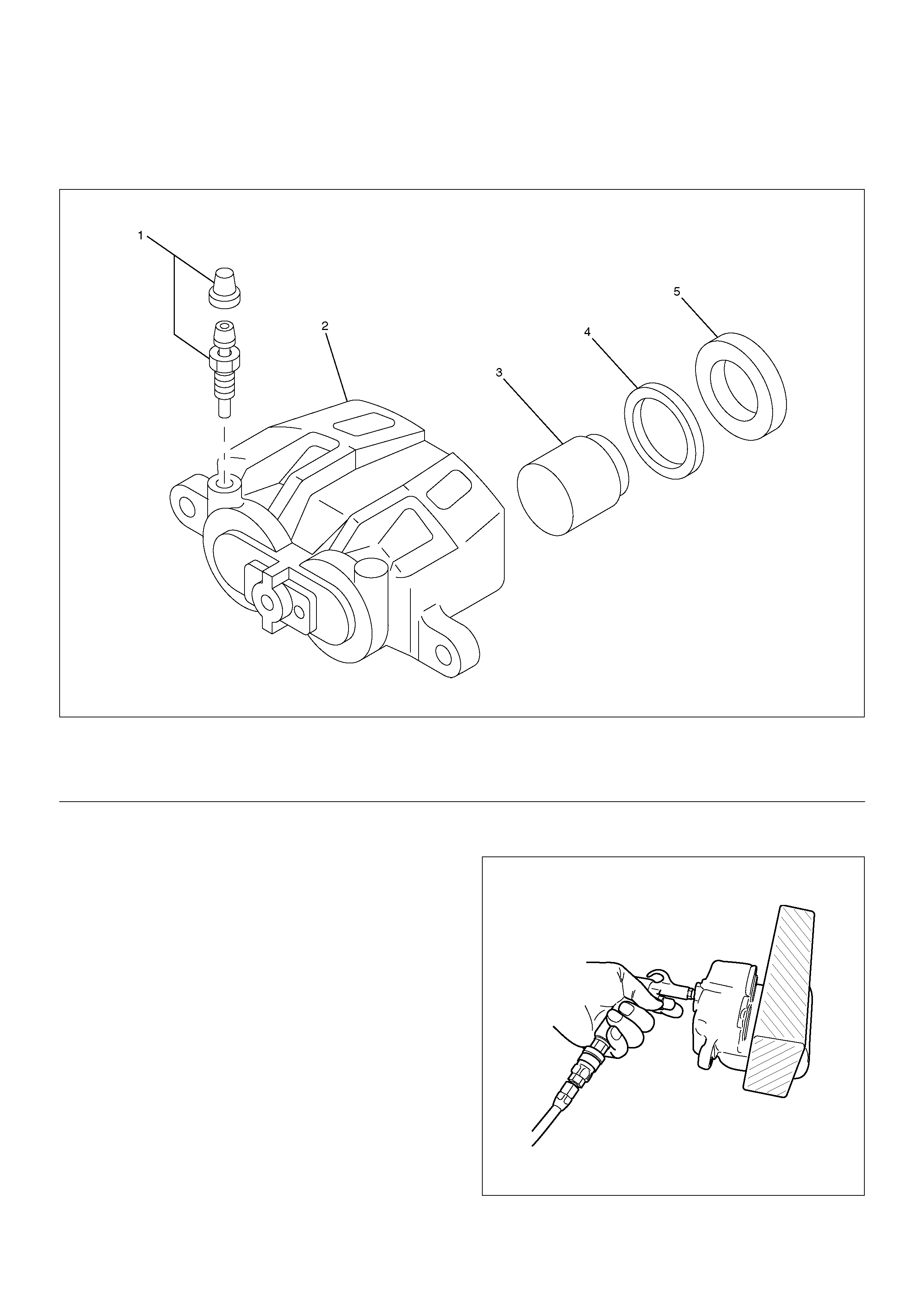
Front Disc Brake Caliper
Front Disc Brake Caliper Disassembled View
302R200018
EndOFCallout
Disassembly
1.Insert a block of wood into the caliper and force out
the piston by blowing compressed air into the
caliper at the flexible hose attachment. This
procedure must be done prior to removal of the dust
boot.
Remove piston.
WARNING: Do not place your fingers in front of the
piston in an attempt to catch or protect it when
applying compressed air. This could result in
personal injury.
CAUTION: Use just enough air to ease the piston
out of the bore. If the piston is blown out, it may be
damaged.
302R200012
Legend
(1) Bleeder with Cap
(2) Caliper Body
(3) Piston
(4) Piston Seal
(5) Dust Boot: Piston
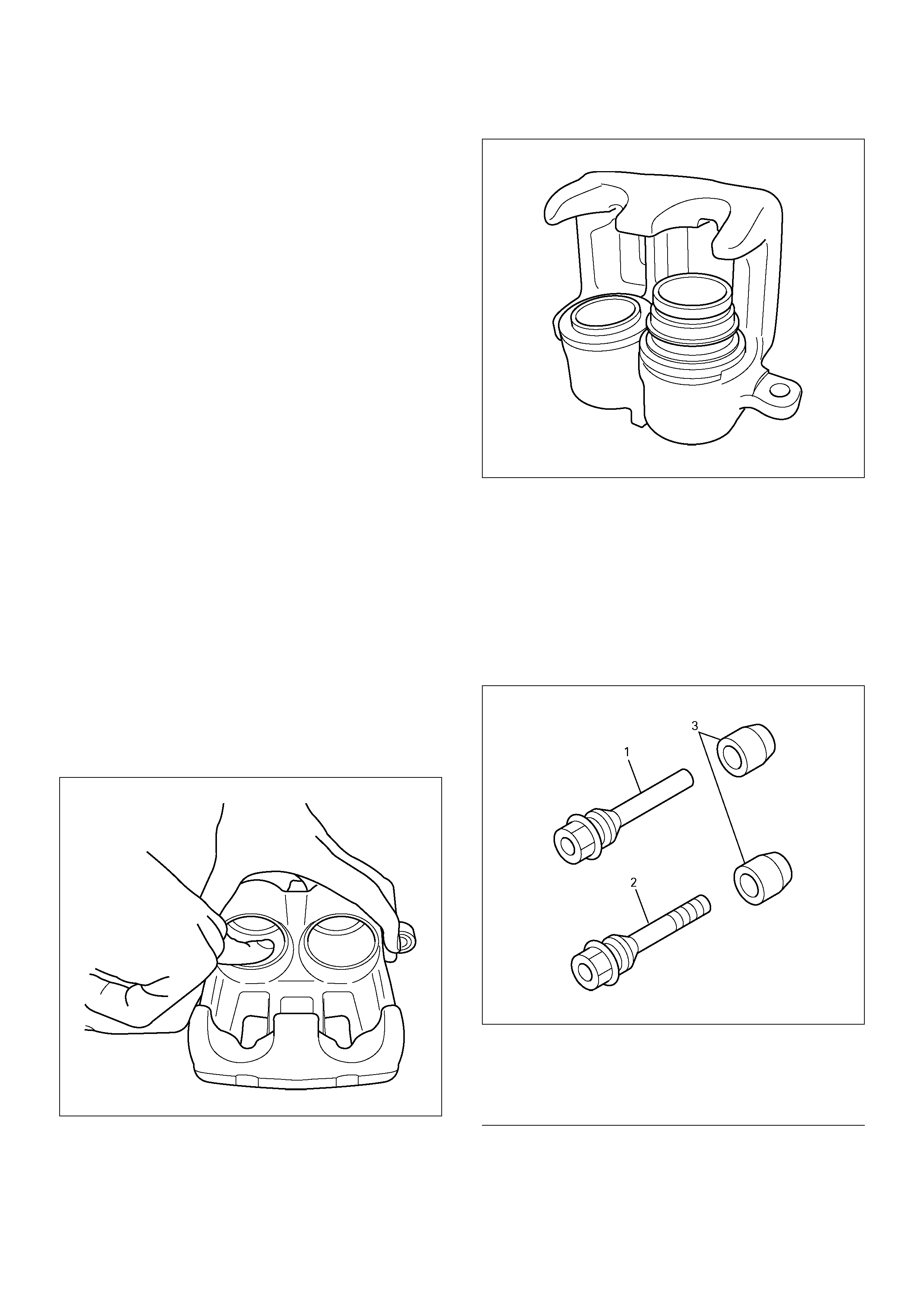
2. Remove dust boot: piston.
3. Remove piston seal.
4. Remove bleeder with cap.
5. Remove caliper body.
Inspection and Repair
Make necessary parts replacement, if wear, damage,
corrosion or any other abnormal conditions are found
through inspection.
Check the following parts:
• Rotor
• Cylinder body
• Cylinder bore
•Piston
• Guide pin, lock pin
• Support bracket
NOTE: The piston seal, boot ring and dust boot are to
be replaced each time the caliper is overhauled.
Discard these used rubber parts and replace them with
new ones.
Reassembly
1. Install caliper body.
2. Install bleeder with cap and tighten the cap to the
specified torque.
Torque: 8 N·m (0.8 kg·m/69 lbin)
3. Apply special rubber grease to the piston seal and
cylinder wall, then insert the piston seal into the
cylinder. The special rubber grease is included in
the repair kit.
302R20001 3
4. When inserting the piston into the cylinder, use
finger pressure only and do not use a mallet or other
impact tool, since damage to the cylinder wall or
piston seal can result.
Install piston.
302R200015
5. Apply special grease (approximately 1g) to the
piston and attach the dust boot to the piston and
caliper. Insert the dust boot ring into the dust boot.
6. Install guide bolt and lock bolt dust boot.
7. Install the dust boot on the support bracket after
applying special grease (approximately 1 g) onto
the dust boot inner surface. Apply special grease
onto the lock pin and guide pin setting hole of the
support bracket.
302R200022
EndOFCallout
8. Install pin bolt and tighten the bolt to the specified
torque.
Torque: 45 N·m (4.6 kg·m/33 lbft)
Legend
(1) Guide Pin
(2) Lock Pin
(3) Pin Boot
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Torque Specifications
E05R200012
Type Floating, pin slide
Pad dimension 48.7 cm (7.55 in )
Adjusting method Self–adjusting
Piston diameter 45.4 mm (1.79 in) ´2
Disc type Ventilated
Disc thickness 26 mm (1.02 in)
Disc effective diameter 242 mm (9.53 in)
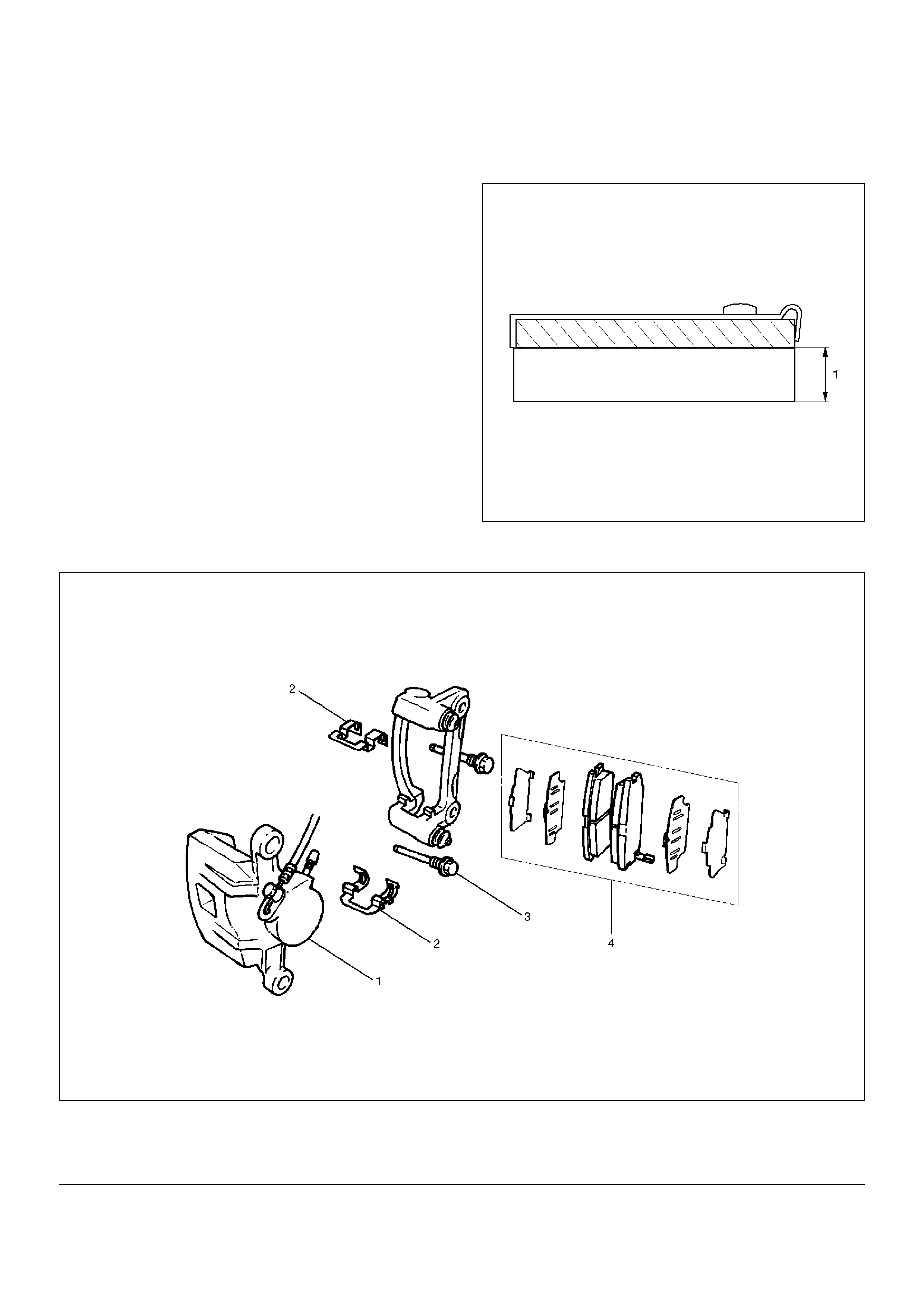
Rear Disc Brake Pads
Brake Pads Inspection
Check the outer pads by looking at each caliper from
above. Check the thickness on the inner pad by looking
down through the inspection hole in the top of the
caliper. Whenever the pad is worn to about the
thickness of the pad base, the pad should be removed
for further measurements. The pad should be replaced
anytime the pad thickness (1) is worn to within 1.0 mm
(0.039 in) of the pad itself.
The disc pads have a wear indicator that makes a noise
when the pad wears to where replacement is required.
Minimum limit (1): 1.0 mm (0.039 in)
302RW016
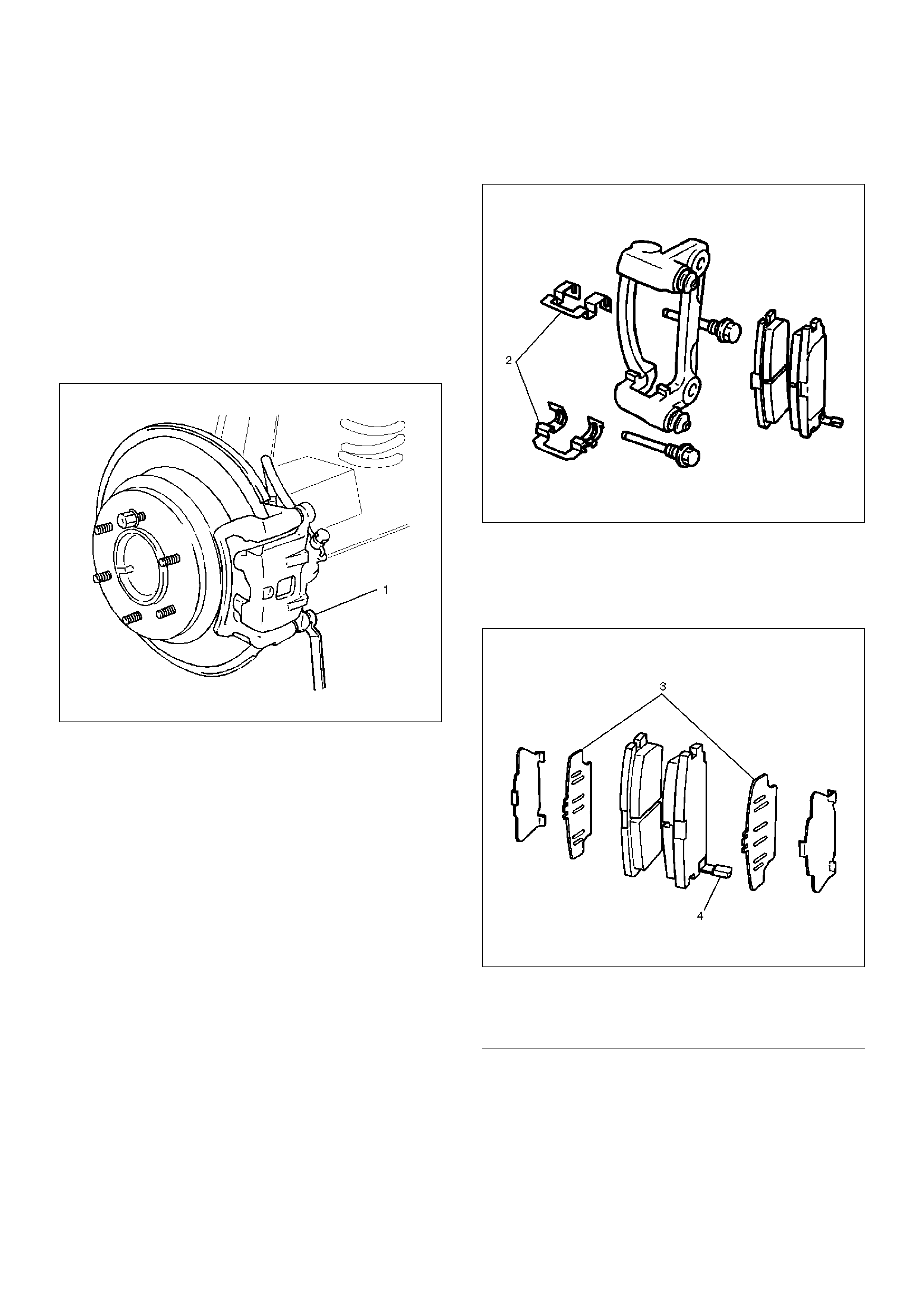
Brake Pads and Associated Parts
306RW001
EndOFCallout
Legend
(1) Caliper Assembly
(2) Clip
(3) Lock Bolt
(4) Pad Assembly
Removal
NOTE: If a squealing noise occurs from the rear brake
while driving, check the pad wear indicator plate. If the
indicator plate contacts the rotor, the disc pad assembly
should be replaced.
•Draw out two–thirds of the brake fluid from the
reservoir.
•Raise the vehicle and support it with suitable safety
stands.
1.Remove wheel and tyre assembly, referring to
“Wheels and Tyres System" in Section 10.
2. Remove lock bolt (1)
306RW002
3. Rotate caliper assembly and support the caliper
assembly so that the brake hose is not stretched or
damaged.
4. Remove pad assembly with shim.
5. Remove clip.
Installation
1. Install clip (2).
306RW003
2. Apply special grease (approximately 0.2g) to both
contacting surfaces of the inner shims. Wipe off
extruded grease after installing. Install pad
assembly with shim.
306RW004
EndOFCallout
Legend
(3) Inner Shim
(4) Wear Indicator
306RW005
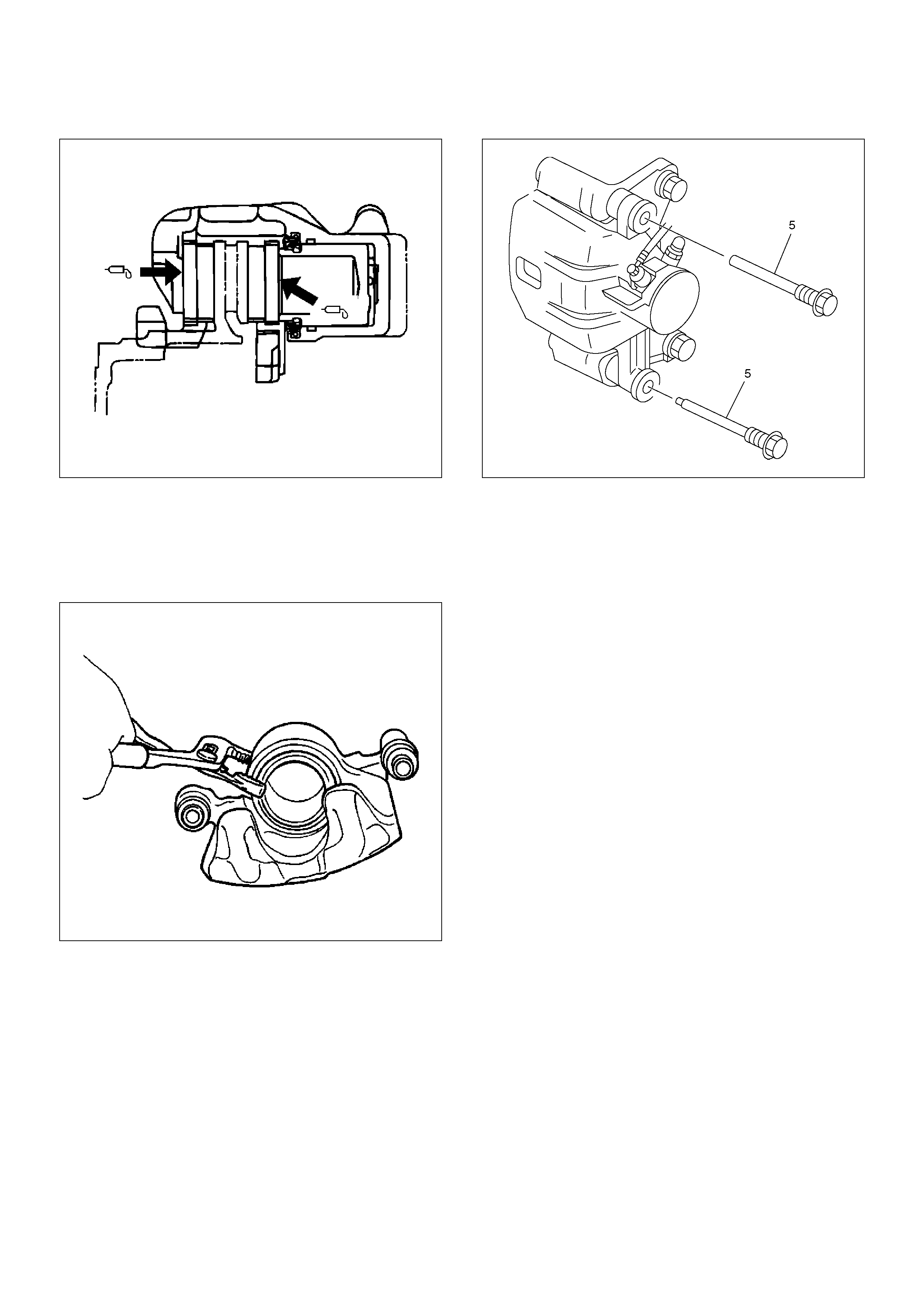
3.Use adjustable pliers to bottom the piston into the
caliper bore. Be careful not to damage the piston
dust boot and do not damage the flexible hose by
twisting or pulling it. Install caliper assembly.
Set caliper assembly in place.
302RS008
4.Install lock bolt (5) and tighten the bolt to the
specified torque.
Torque: 43 N·m (4.4 kg·m/32 lbft)
5.Install wheel and tyre assembly, referring to “Wheels
and Tyres System" in Section 10.
6. Pump the brake pedal several times to make sure
that the pedal is firm. Check the brake fluid level in
the reservoir after pumping the brakes.
306R200003
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Inspection
In the manufacturing of the brake rotor, all the
tolerances regarding surface finish, parallelism and
lateral runout are held very closely. Maintaining these
tolerances provides the surface necessary to assure
smooth brake operation.
Lateral Runout
Lateral runout is the movement of the rotor from side to
side as it rotates on the spindle. This could also be
referred to as “rotor wobble".
This movement causes the piston to be knocked back
into its bore. This results in additional pedal travel and a
vibration during braking.
Checking Lateral Runout
1.Adjust the wheel bearing correctly. Refer to Drive
Shaft System section.
2. Attach a dial indicator to some portion of the
suspension so that the stem contacts the rotor face
about 29 mm (1.14 in) from the rotor edge.
3. Move the rotor one complete rotation.
The lateral runout should not exceed 0.13 mm
(0.005 in)
Maximum runout: 0.13 mm (0.005 in)
306RY00013
Parallelism
Parallelism is the measurement of thickness of the rotor
at four or more points around the circumference of the
rotor. All measurement must be made at 22 mm (0.87
in) from the edge of the rotor.
The rotor thickness must not vary more than 0.010 mm
(0.0004 in) from point to point.
Maximum parallelism: 0.010 mm (0.0004 in)
420RS013
Replacing Brake Rotors
When installing new brake rotors, do not refinish the
surfaces. These parts are at the correct level of surface
finish.
Refinishing Brake Rotors
Accurate control of the rotor tolerances is necessary for
proper performance of the disc brakes. Machining of the
rotor should be done only with precision equipment. All
brake rotors have a minimum thickness dimension cast
into them. This dimension is the minimum wear
dimension and not a refinish dimension. The minimum
wear dimension is 16.6 mm (0.654 in). The minimum
refinish dimension is 16.97 mm (0.668 in).
When refinishing rotors, always use sharp cutting tools
or bits. Dull or worn tools leave a poor surface finish
which will affect initial braking performance. Vibration
dampening attachments should always be used when
refinishing braking surfaces. These attachments
eliminate tool chatter and will result in better surface
finish.
After refinishing, replace any rotor that does not meet
the minimum thickness of 16.97 mm (0.668 in). Do not
use a brake rotor that will not meet the specification.
Minimum wear dimension: 16.6 mm (0.654 in)
Refinish dimension: 16.97 mm (0.668 in)
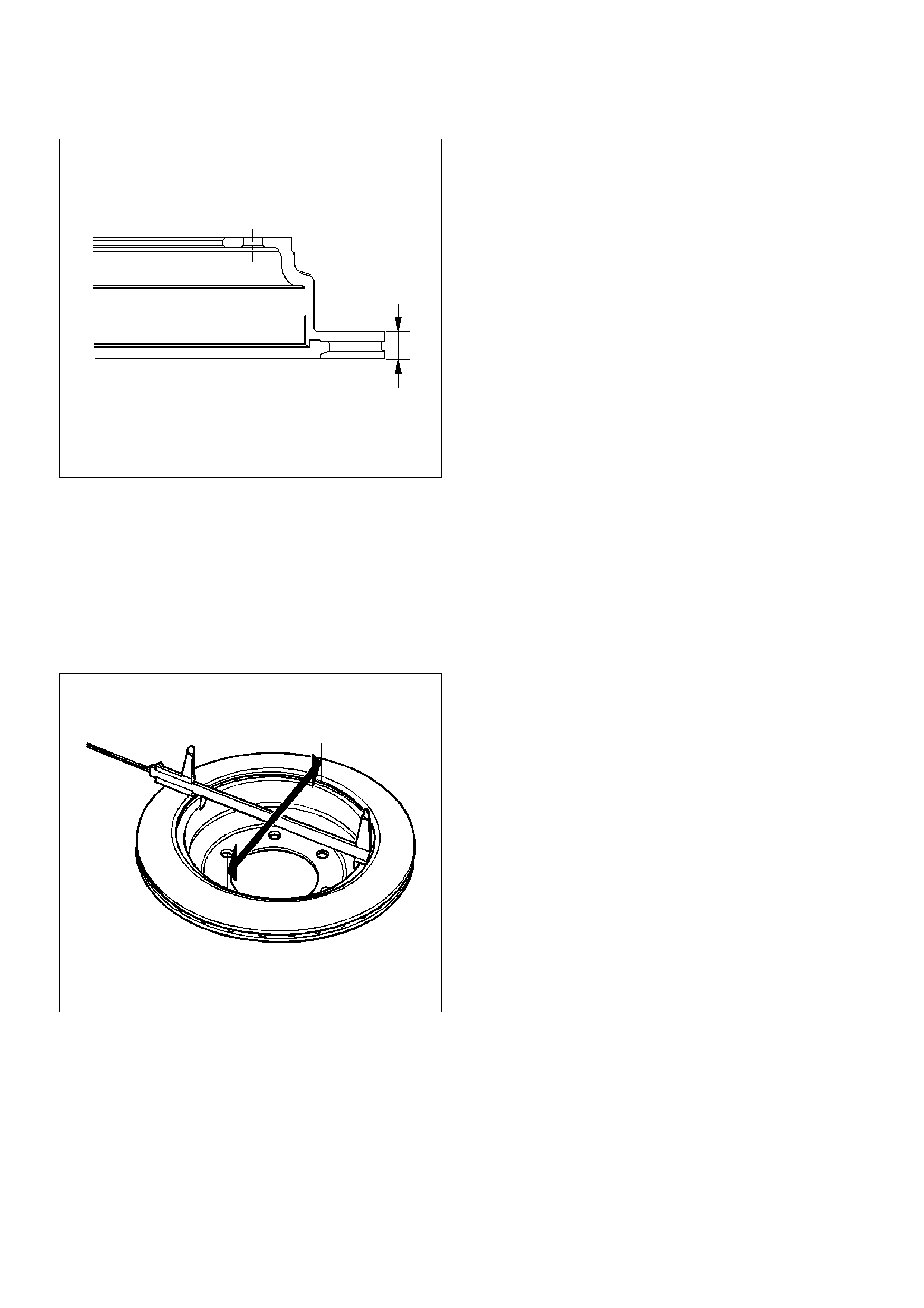
420RW002
Rear Drum (In Disc) Inside Diameter Check
Check the rear drum inside diameter by measuring at
more than two portions as shown in the illustration.
If the inside diameter is greater than the limit, replace
the rear rotor.
Standard: 210.0 mm (8.27 in)
Limit: 211.4 mm (8.32 in)
420RS035

Rear Disc Brake Caliper Assembly
Rear Disc Brake Caliper Assembly and Associated Parts
306RW007
EndOFCallout
Removal
1.Raise the vehicle and support with suitable safety
stands.
2.Remove wheel and tyre assembly, referring to
“Wheels and Tyres System".
3. Remove the bolt and gaskets, then disconnect the
flexible hose from the caliper and after
disconnecting the flexible hose (1), cap or tape the
openings to prevent entry of foreign material.
306RW008
4. Since the brake fluid flows out from the connecting
coupler, place a drain pan under the vehicle.
5. Remove lock bolt (3).
Legend
(1) Brake Flexible Hose
(2) Clip
(3) Lock Bolt
(4) Support Bracket
(5) Guide Bolt
(6) Pad Assembly with Shim
(7) Caliper Assembly
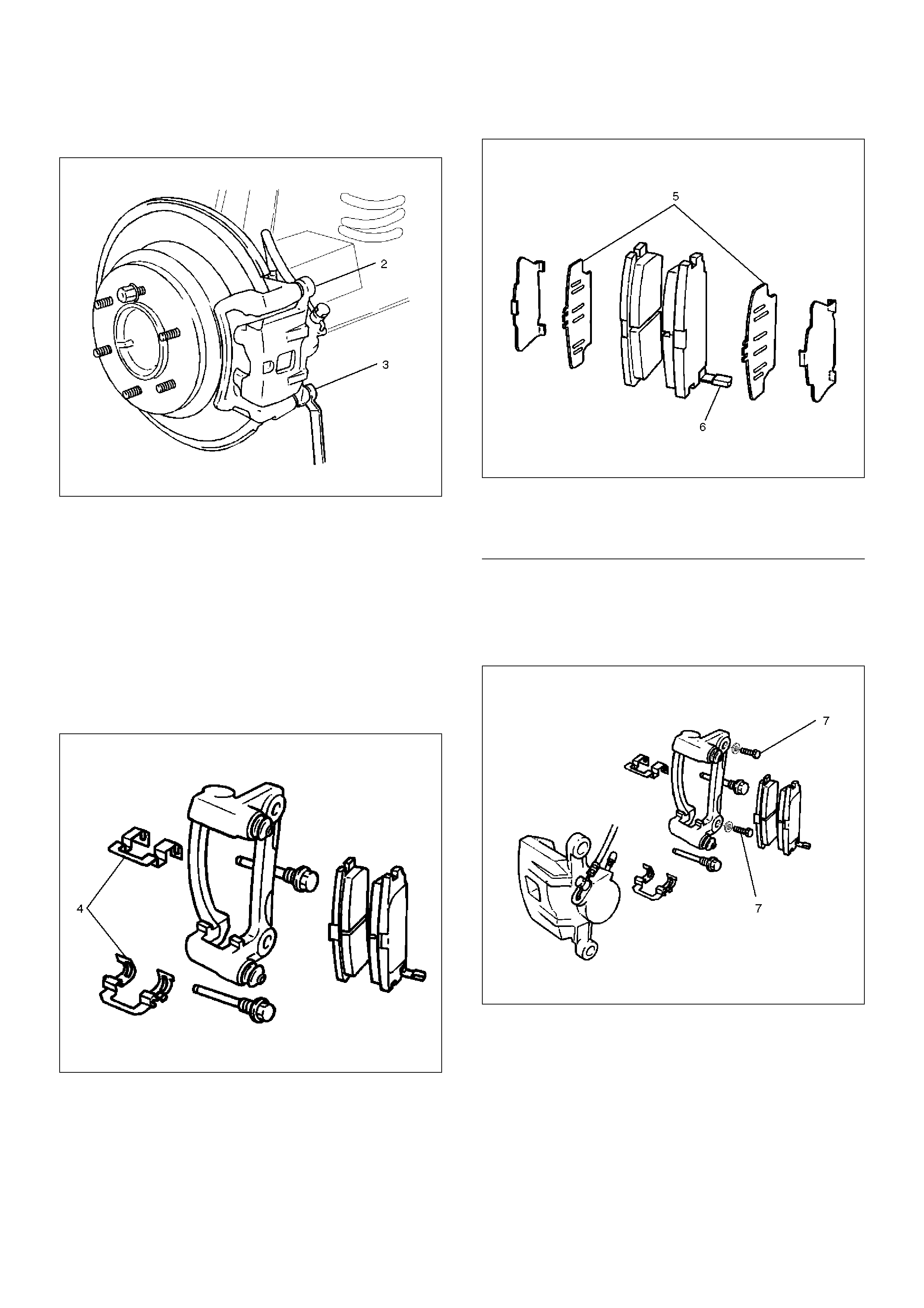
6. Remove guide bolt (2).
306RW009
7. Remove caliper assembly.
8. Remove support bracket with pad assembly and
take care not to damage the flexible brake hose
when removing the support bracket.
9. Remove pad assembly with shim and mark the
lining locations if they are to be reinstalled.
10. Remove clip.
Installation
1. Install clip (4).
306RW010
2. Apply special grease (approximately 0.2g) to both
contacting surfaces of the inner shims (5). Wipe off
extruded grease after installing. Install pad
assembly with shim.
306RW011
EndOFCallout
3. Install support bracket and tighten the bolt (7) to the
specified torque.
Torque: 103 N·m (10.5 kg·m/76 lbft)
306RW012
4. Install caliper assembly.
5. Install lock bolt and guide bolt (8) and tighten the
bolt to the specified torque.
Torque: 43 N·m (4.4 kg·m/33 lbft)
Legend
(5) Inner Shim
(6) Wear indicator
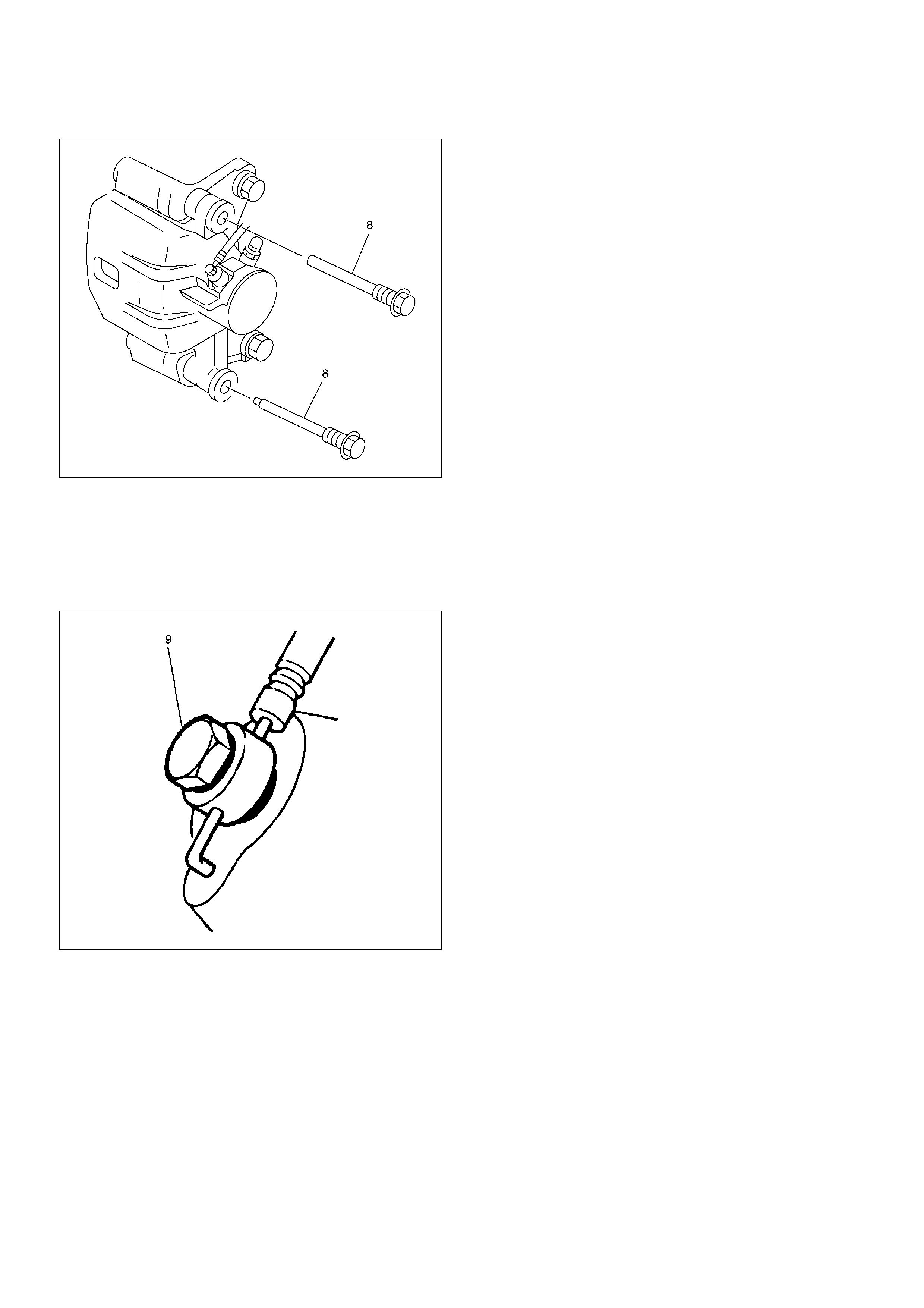
306R200004
6.Install brake flexible hose, always use new gaskets
and be sure to put the hooked edge of the flexible
hose end into the anti–rotation cavity then tighten
the eye–bolt (9) to the specified torque.
Torque: 34 N·m (3.5 kg·m/25 lbft)
302RW017
7.Install the wheel and tyre assembly, referring to
“Wheels and Tyres System" .
8.Bleed brakes. Refer to “Hydraulic Brakes" in this
section.
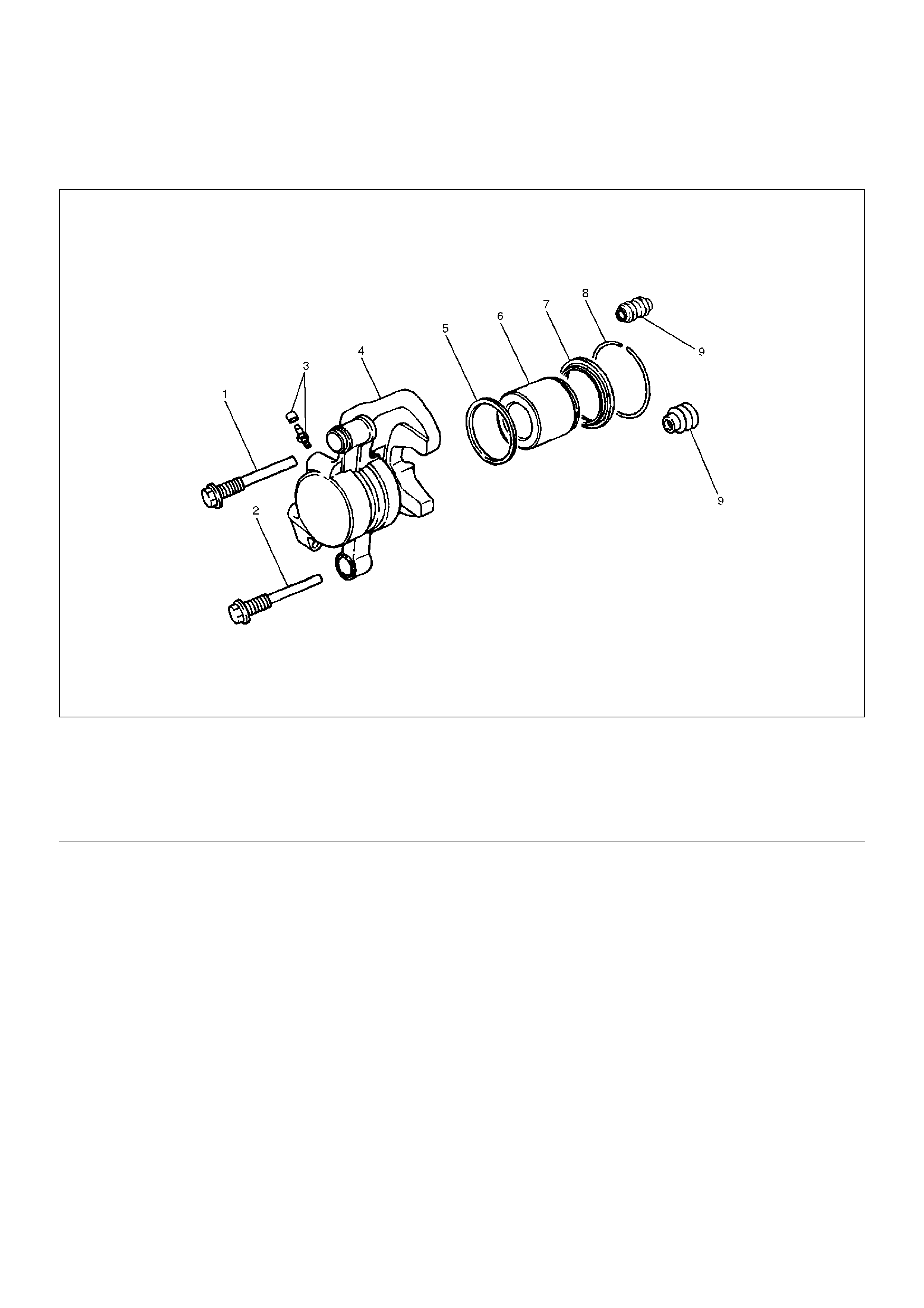
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
Rear Disc Brake Caliper Disassembled View
306RW014
EndOFCallout
Disassembly
1. Remove guide bolt.
2. Remove lock bolt.
3. Remove dust boot; guide bolt and lock bolt.
4. Remove dust boot ring, using a small screwdriver.
Legend
(1) Guide Bolt
(2) Lock Bolt
(3) Bleeder with Cap
(4) Caliper Body
(5) Piston Seal
(6) Piston
(7) Dust Boot: Piston
(8) Dust Boot Ring
(9) Dust Boot: Guide Bolt and Lock Bolt
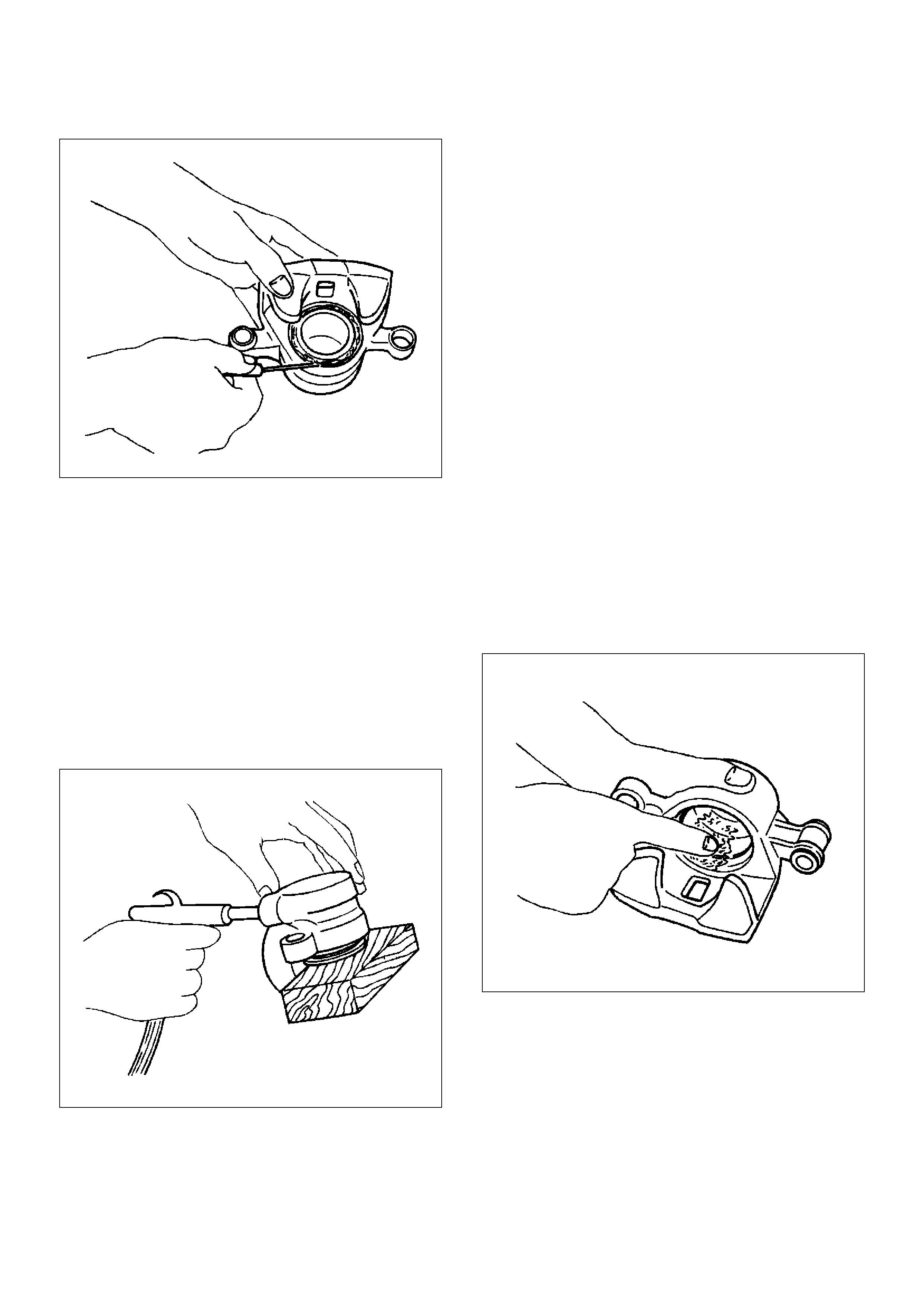
302RS016
5.Insert a block of wood into the caliper and force out
the piston by blowing compressed air into the
caliper at the flexible hose attachment. This
procedure must be done prior to removal of the dust
boot.
Remove piston.
WARNING: Do not place your fingers in front of the
piston in an attempt to catch or protect it when
applying compressed air. This could result in
personal injury.
CAUTION: Use just enough air to ease the piston
out of the bore. If the piston is blown out, it may be
damaged.
302RS017
6. Remove dust boot: piston.
7. Remove piston seal.
8. Remove bleeder with cap.
9.Remove caliper body.
Inspection and Repair
Make necessary parts replacement, if wear, damage,
corrosion or any other abnormal conditions are found
through inspection.
Check the following parts:
•Rotor
• Cylinder body
• Cylinder bore
•Piston
• Guide bolt, lock bolt
• Support bracket
NOTE: The piston dust seal and dust boot are to be
replaced each time the caliper is overhauled. Discard
these used rubber parts and replace with new ones.
Reassembly
1. Install caliper body.
2. Install bleeder with cap and tighten the cap to the
specified torque.
Torque: 8 N·m (0.8 kg·m/69 lbft)
3. Install piston seal and apply special rubber grease
to the piston seal and cylinder wall, then insert the
piston seal into the cylinder. The special rubber
grease is included in the repair kit.
302RS018
4. When inserting the piston into the cylinder, use
finger pressure only and do not use a mallet or other
impact tool, since damage to the cylinder wall or
piston seal can result.
Install piston.
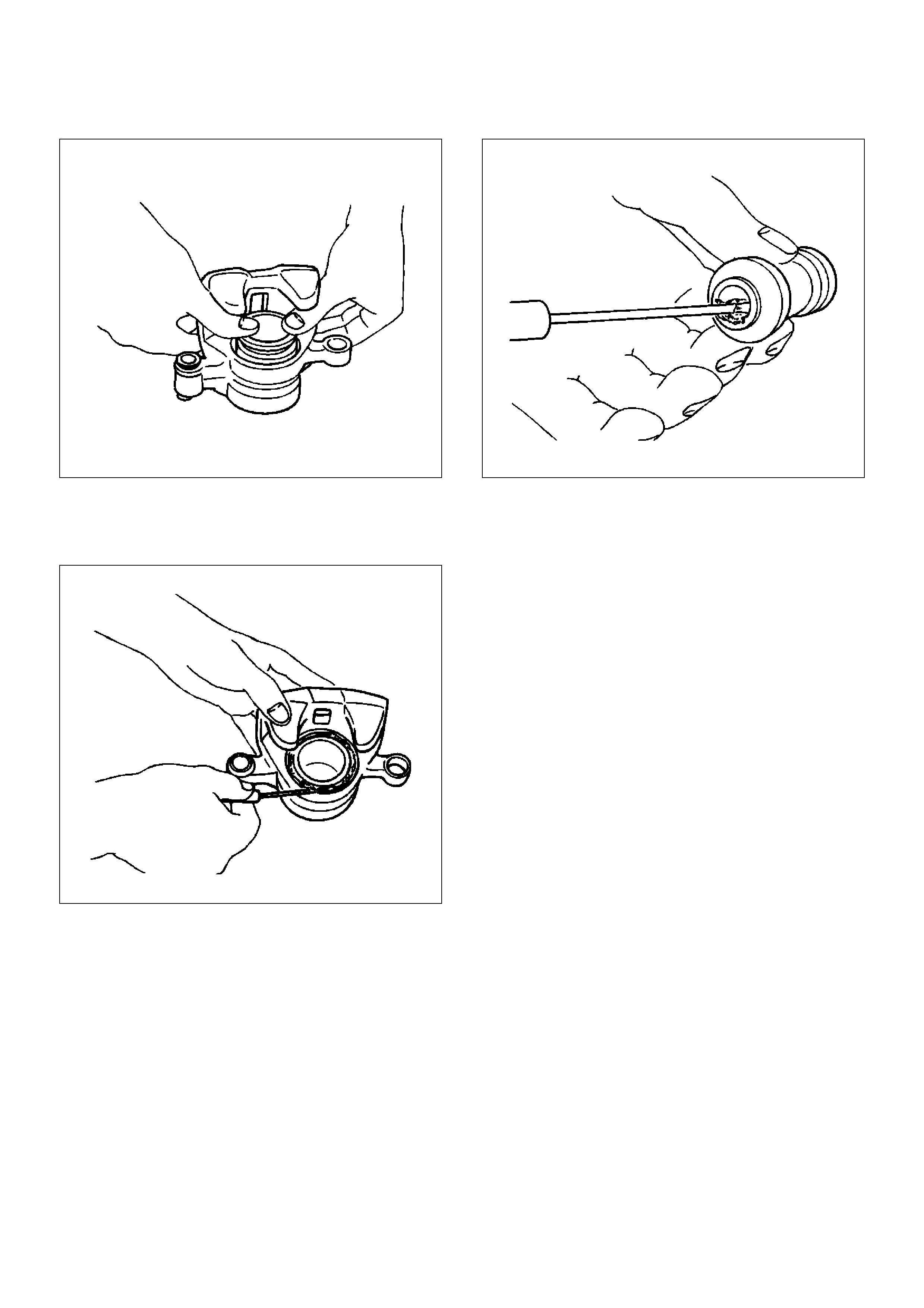
302RS019
5. Apply special grease (approximately 1g) to the
piston and attach the dust boot to the piston and
caliper. Insert the dust boot ring into the dust boot.
302RS020
6. Install guide bolt and lock bolt dust boot.
7. Install the dust boot on the support bracket after
applying special grease (Approx. 1g) onto the dust
boot inner surface. Also apply special grease onto
the lock bolt and guide bolt setting hole of the
support bracket.
302RS021
8. Install lock bolt and guide bolt and tighten the bolt to
the specified torque.
Torque: 43 N·m (4.4 kg·m/32 lbft)
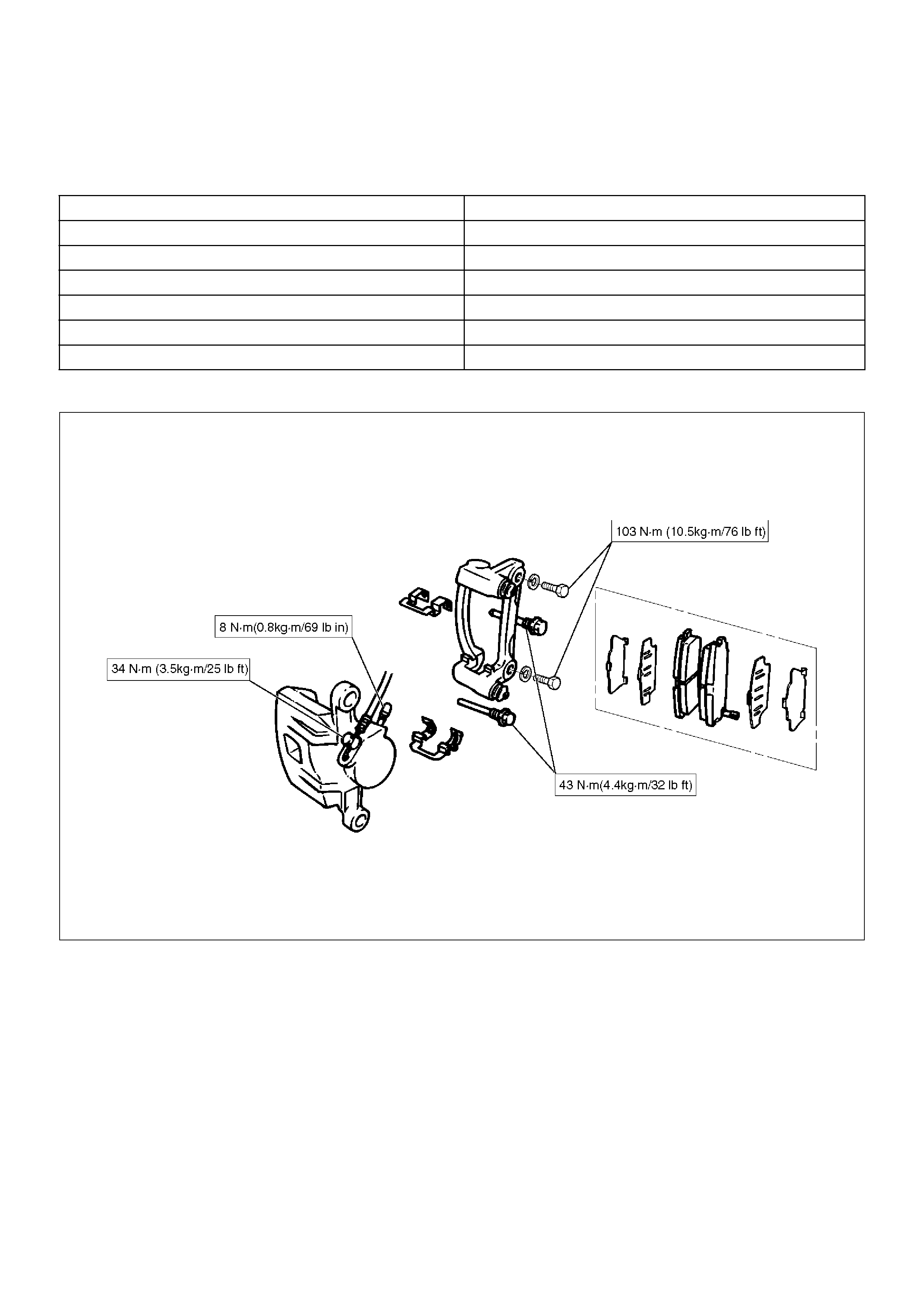
Main Data and Specifications
General Specifications
Torque Specifications
E05RX010
Type Floating, pin slide
Pad dimension 33 cm2 (5.11 in2)
Adjusting method Self–adjusting
Piston diameter 41.3 mm (1.63 in)
Disc type Ventilated
Disc thickness 18 mm (0.71 in)
Disc effective diameter 269.2 mm (10.60 in)