
SPECIFICATIONS
TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
DIAGRAMS AND SCHEMATICS
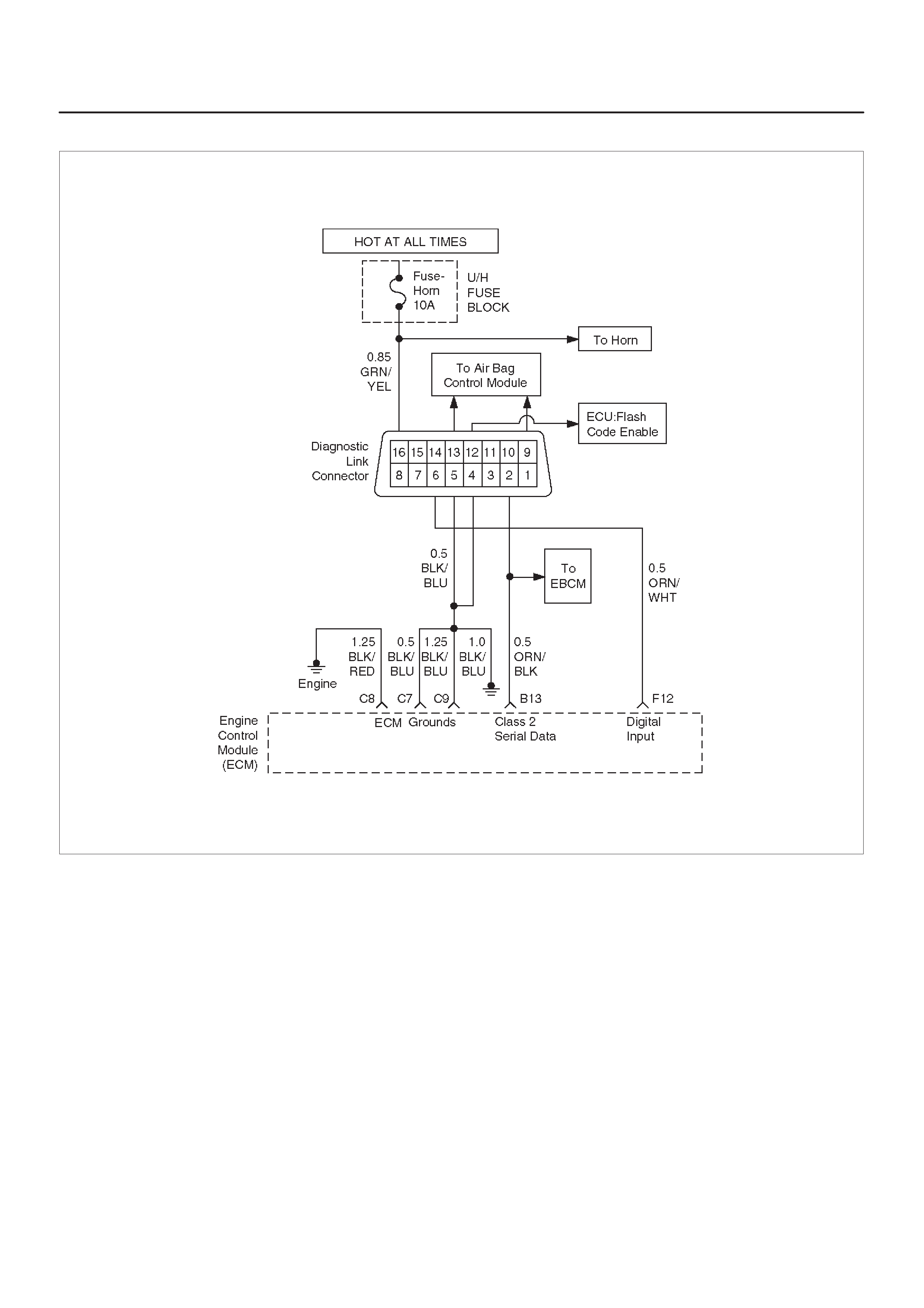
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (3 of 10)
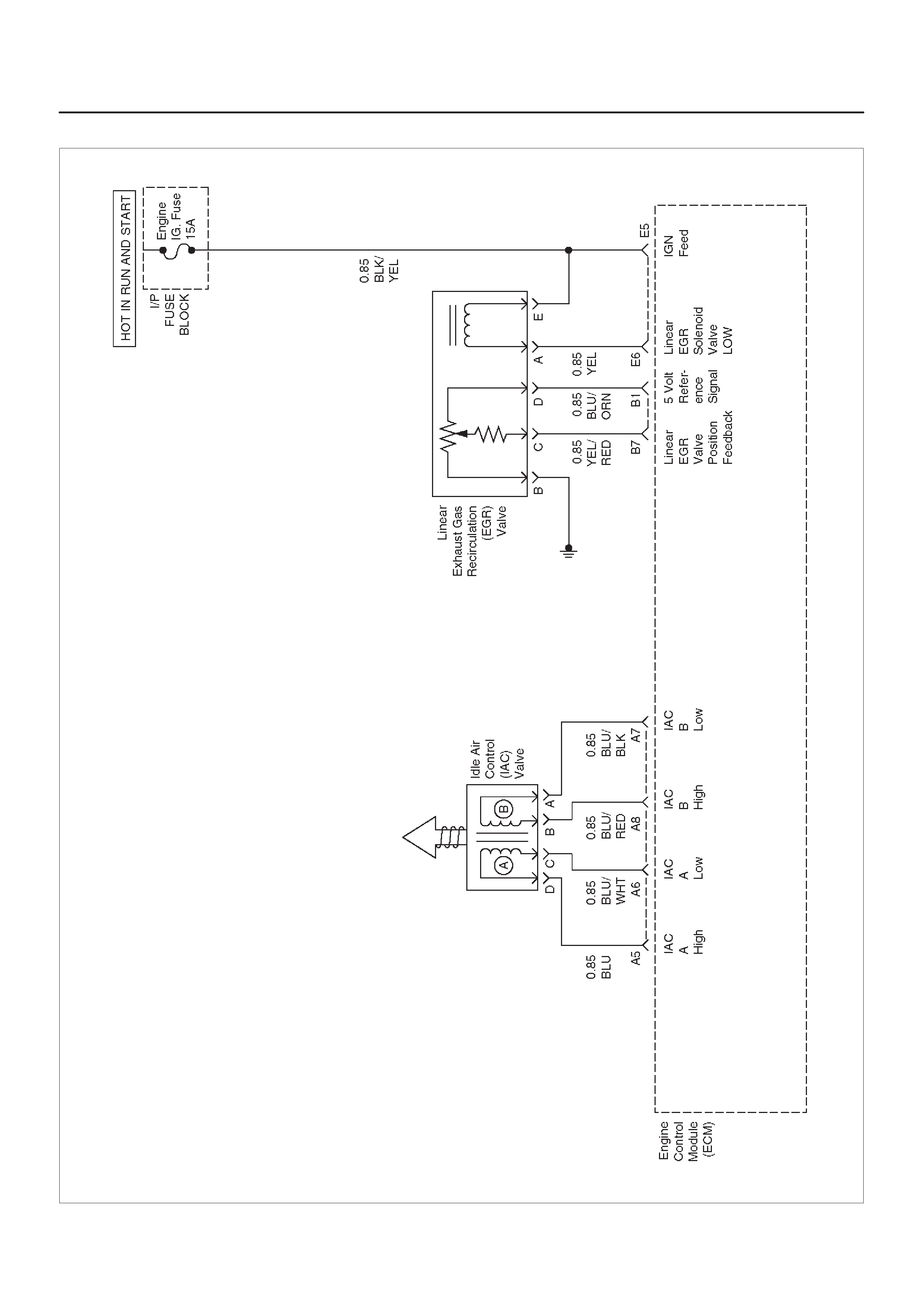
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (4 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (5 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (6 of 10)
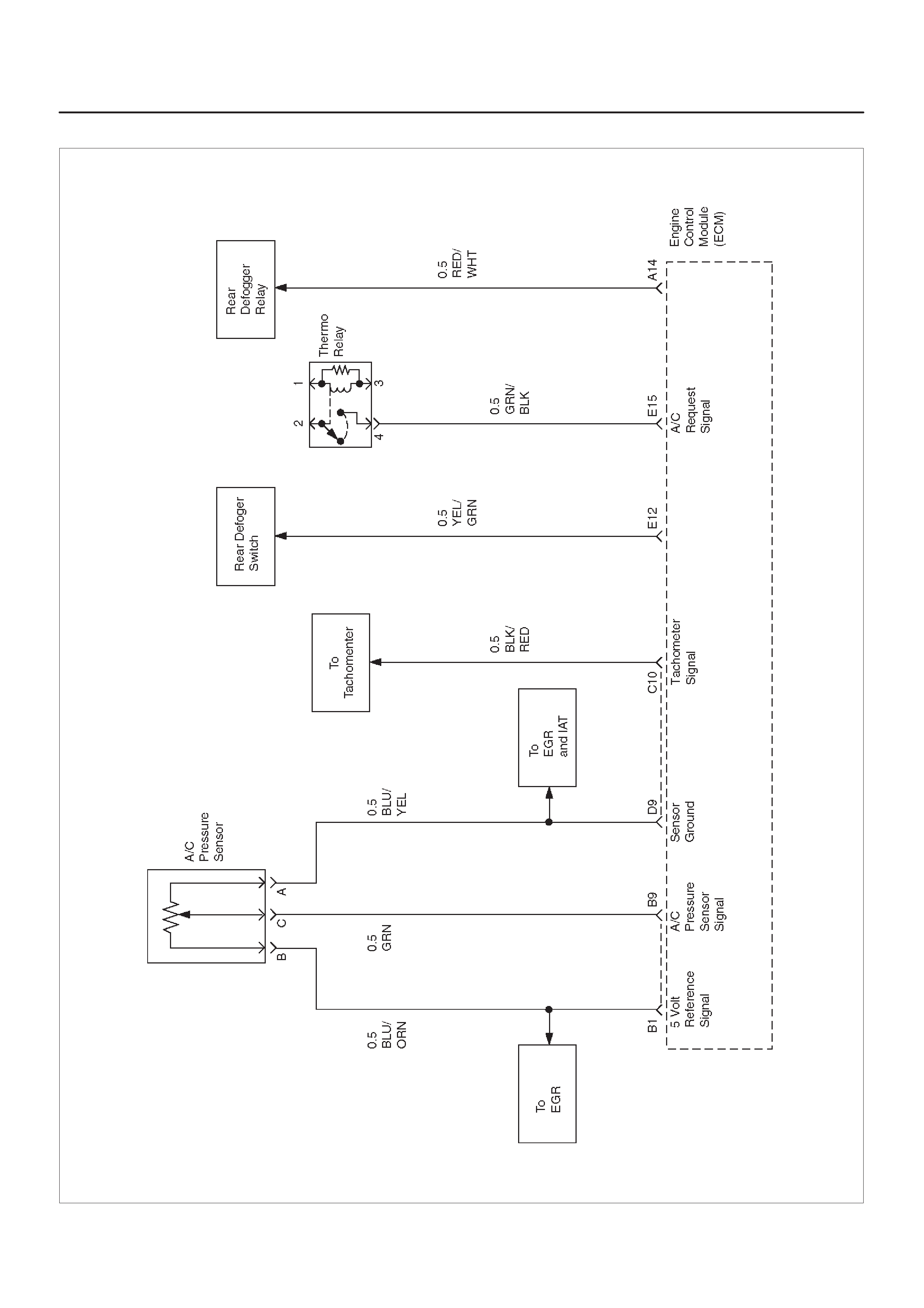
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (7 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (8 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (9 of 10)
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (10 of 10)
ECM PINOUTS
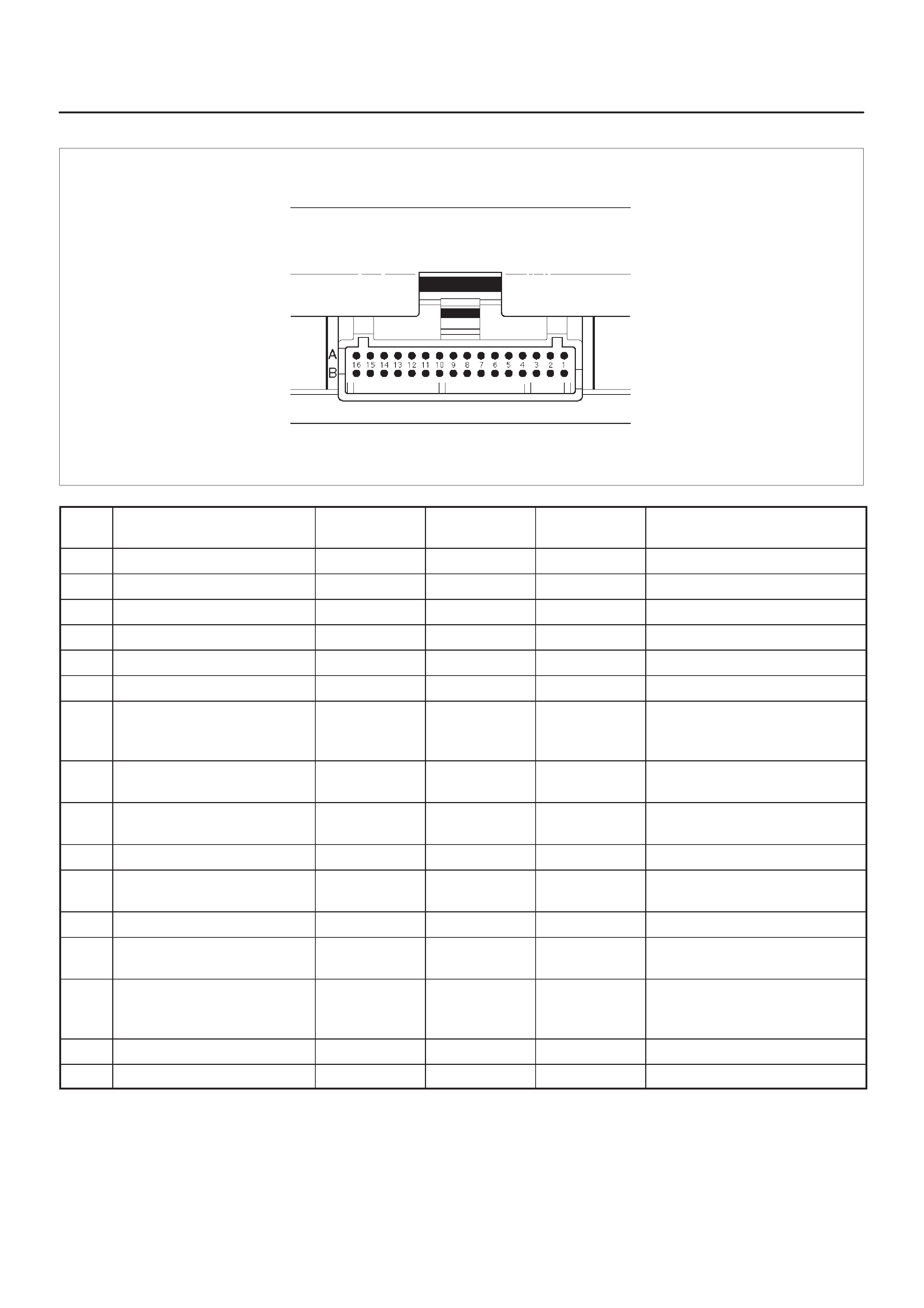
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin Red Connector
– Row ”A”
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin Red Connector
– Row ”B”
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector
– Row ”C”
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector
– Row ”D”
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector
– Row ”E”
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector
– Row ”F”
COMPONENT LOCATOR
Undercarriage Component Locator Table
Fuse And Relay Panel (Underhood
Electrical Center)
DIAGNOSIS Strategy–Based Diagnostics
Strategy–Based Diagnostics
DTC Stored
No DTC
No Matching Symptom
Intermittents
No Trouble Found
Verifying Vehicle Repair
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Non–OEM Parts
Environment
Emissions Control Information Label
Maintenance Schedule
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Basic Knowledge Of Tools Required
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Class II Serial Data Communications
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD)
On–Board Diagnostic Tests
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation
Common OBD Terms
The Diagnostic Executive
DTC Types
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
A Tech 2 Scan Tool
Tech 2 Features
Getting Started
Operating Procedure (Example)
DTC Modes
DTC Information Mode
Miscellaneous Test
Lamps Test
Relays Test
EVAP Test
Idle Air Control System Test
Fuel System Test
EGR Control Test
Injector Balance Test
Plotting Snapshot Graph
Plotting Graph Flow Chart (Plotting graph
after obtaining vehicle information)
Flow Chart for Snapshot Replay (Plotting
Graph)
PRIMARY SYSTEM–BASED DIAGNOSTICS
Primary System–Based Diagnostics
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensors
HO2S Heater
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM
CHECK
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
Test Description
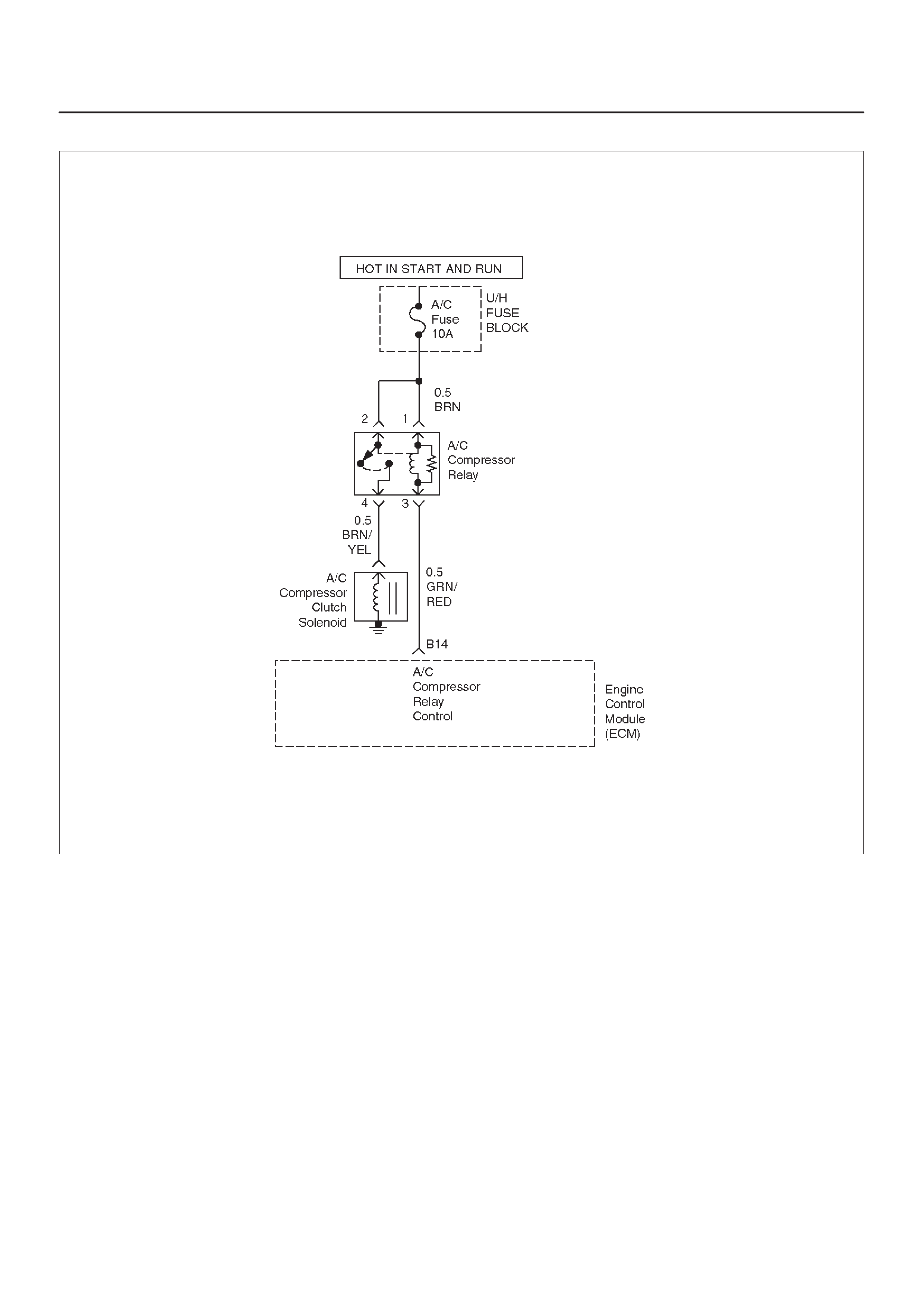
A/C CLUTCH CONTROL CIRCUIT
DIAGNOSIS
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
DIAGNOSIS
VISUAL CHECK OF THE EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION CANISTER
SECTION 6E1 - ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Techline
Techline

IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
DIAGNOSIS
MULTIPLE ECM INFORMATION SENSOR
DTCs SET
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
DIAGNOSIS
ENGINE Tech 2 DATA DEFINITIONS AND
RANGES
TYPICAL SCAN DATA VALUES
Test Conditions
2.2L L–4 Engine
NO MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
(MIL)
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
Test Description
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) ON
STEADY
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
Test Description
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
FUEL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL TEST
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
Test Description
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
Fuel Gauge Installation
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Circuit Description
Test Description
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
Fuel Gauge Installation
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) SYSTEM CHECK
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM CHECK
Circuit Description
Diagnostic Aids
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
OUTPUT CHECK
Circuit Description
Test Description
ECM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
ECM Diagnostic Trouble Codes
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0106
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
CIRCUIT/RANGE PERFORMANCE
PROBLEM
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0117
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0118
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0121
THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
PROBLEM
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0122
THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR
CIRCUITLOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0123
THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0131
O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW VOLTAGE
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0132
O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH VOLTAGE
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0134
O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT NO ACTIVITY
DETECTED (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135
O2 SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0171
SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0172
SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1)
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0201
INJECTOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION –
CYLINDER 1
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0202
INJECTOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION –
CYLINDER 2
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0203
INJECTOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION –
CYLINDER 3

DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0204
INJECTOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION –
CYLINDER 4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0325
KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327
KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT LOW
INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0336
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0337
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0341
CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0342
CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0351
IGNITION COIL ”A” PRIMARY/SECONDARY
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0352
IGNITION COIL ”B” PRIMARY/SECONDARY
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0401
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
FLOW INSUFFICIENT DETECTED
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0402
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
EXCESSIVE FLOW DETECTED
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0404
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0405
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0406
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0443
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP)
CONTROL SYSTEM PURGE CONTROL
VALVE CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0480
COOLING FAN 1 CONTROL CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0481
COOLING FAN 2 CONTROL CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0502
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS) CIRCUIT
LOW INPUT
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0506
IDLE CONTROL SYSTEM RPM LOWER
THAN EXPECTED
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0507
IDLE CONTROL SYSTEM RPM HIGHER
THAN EXPECTED
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0563
SYSTEM VOLTAGE HIGH
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0601
INTERNAL CONTROL MODULE MEMORY
CHECK SUM ERROR
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1106
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH
VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1107
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW
VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1111
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1112
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT) SENSOR
CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1114
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW
VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1115
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH
VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1121
THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH
VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1122
THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR
CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW
VOLTAGE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1171
FUEL SYSTEM LEAN DURING
ACCELERATION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 1404
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
CLOSED VALVE
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1625
ECM UNEXPECTED RESET
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1627
PCM A/D CONVERSION MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1635
5 VOLT REFERENCE VOLTAGE CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1640
ODM OUTPUT CIRCUIT FAULT
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
DEFAULT MATRIX TABLE
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor

EEPROM
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
Air Filter
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
Intake Air Duct
Knock Sensor
Oil Pressure Switch
FUEL METERING SYSTEM
Accelerator Cable Assembly
Accelerator Pedal Replacement
Fuel Filler Cap
Fuel Filter
Fuel Injectors
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Fuel Pump Assembly
Fuel Pump Relay
Fuel Rail Assembly
Fuel Tank
Throttle body (TB)
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
Ignition Control Module (ICM)
Ignition Coil
Spark Plugs
Spark Plug Cables
EMISSIONS Catalytic Converter
Air Conditioning Relay
Ignition Timing Adjustment
EVAP Canister Hoses
EVAP Canister
Linear Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) Valve
Wiring and Connectors
ECM Connectors And Terminals
Connectors And Terminals
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted Shielded
Cable
Twisted Leads
Weather–Pack Connector
Com–Pack III
Metri–Pack
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — ECM AND
SENSORS
58X Reference ECM Input
A/C Request Signal
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor And
Signal
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EEPROM)
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor
(Pre Catalyst)
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Control
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Engine Control Module (ECM)
ECM Function
ECM Components
ECM Voltage Description
ECM Inputs/Outputs
ECM Service Precautions
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
Transmission Range Switch
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
Use of Circuit Testing Tools
Aftermarket Electrical And Vacuum
Equipment
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — AIR
INDUCTION
Air Induction System
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — FUEL
METERING
Acceleration Mode
Accelerator Controls
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
CMP Signal
Clear Flood Mode
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode
Engine Speed/Vehicle Speed/ Fuel
Disable Mode
Fuel Cutoff Mode
Fuel Injector
Fuel Metering System Components
Fuel Metering System Purpose
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
Fuel Rail
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
Run Mode
Starting Mode
Throttle Body Unit
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — ELECTRONIC
IGNITION SYSTEM
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
Electronic Ignition
Ignition Coils

Ignition Control
Ignition Control Module (ICM)
Ignition Control ECM Output
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Spark Plug
A/C CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose
A/C Request Signal
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION (EVAP) SYSTEM
EVAP Emission Control System Purpose
EVAP Emission Control System Operation
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — EXHAUST
GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
EGR Purpose
Linear EGR Valve
Linear EGR Control
Linear EGR Valve Operation And Results
Of Incorrect Operation
EGR Pintle Position Sensor
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — POSITIVE
CRANKCASE VENTILATION (PCV)
SYSTEM
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose
SPECIAL TOOLS
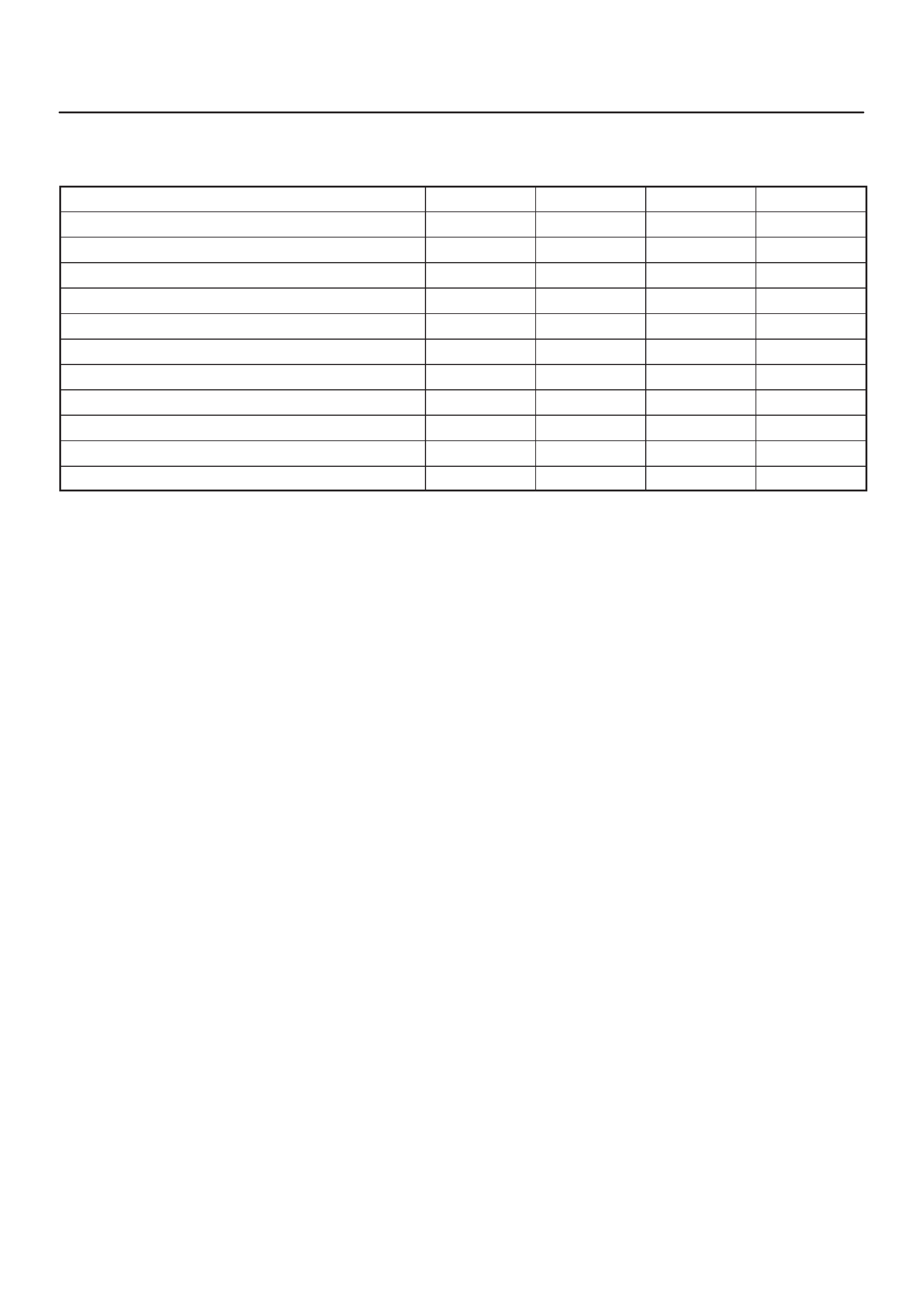
SPECIFICATIONS
TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
Application N–m Lb Ft kg·m Lb In
Crankshaft Position Sensor Mounting Bolt 9 0.9 — 78
EGR Nut 14 1.4 — 130
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor 30 3.1 22 —
Fuel Drain Plug 20 2.0 14 —
Fuel Pressure Regulator Attaching Screw 6.5 0.6 — 60
Fuel Rail Bolts 7 0.7 — 75
Fuel Tank Undercover Retaining Bolts 36 3.7 27 —
Heated Oxygen Sensor 42 4.3 32 —
Spark Plugs 25 2.5 18 —
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts 13 1.3 — 120
VSS Retaining Bolt 13 1.3 — 120
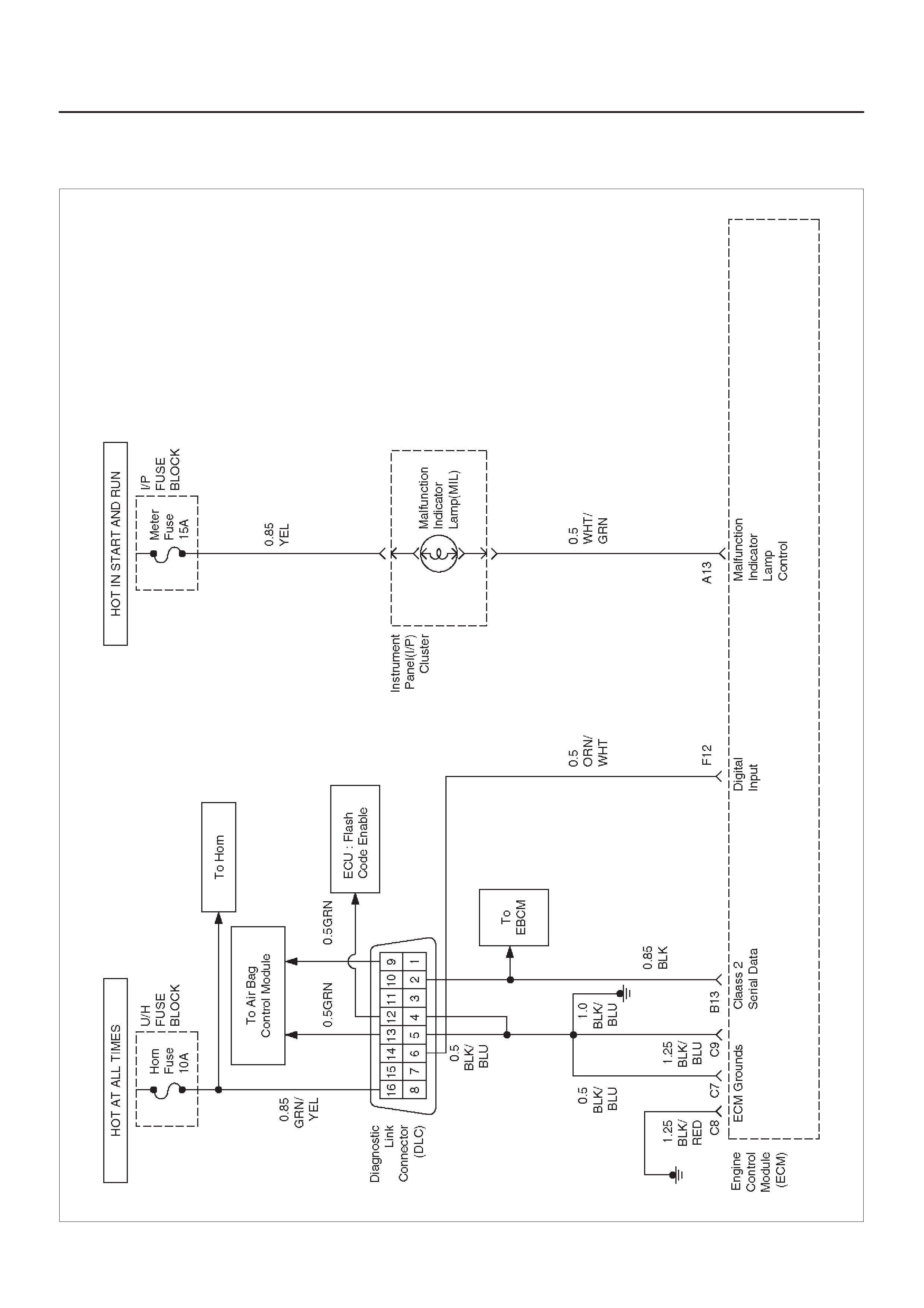
DIAGRAMS AND SCHEMATICS
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (1 of 10)
D06RX097
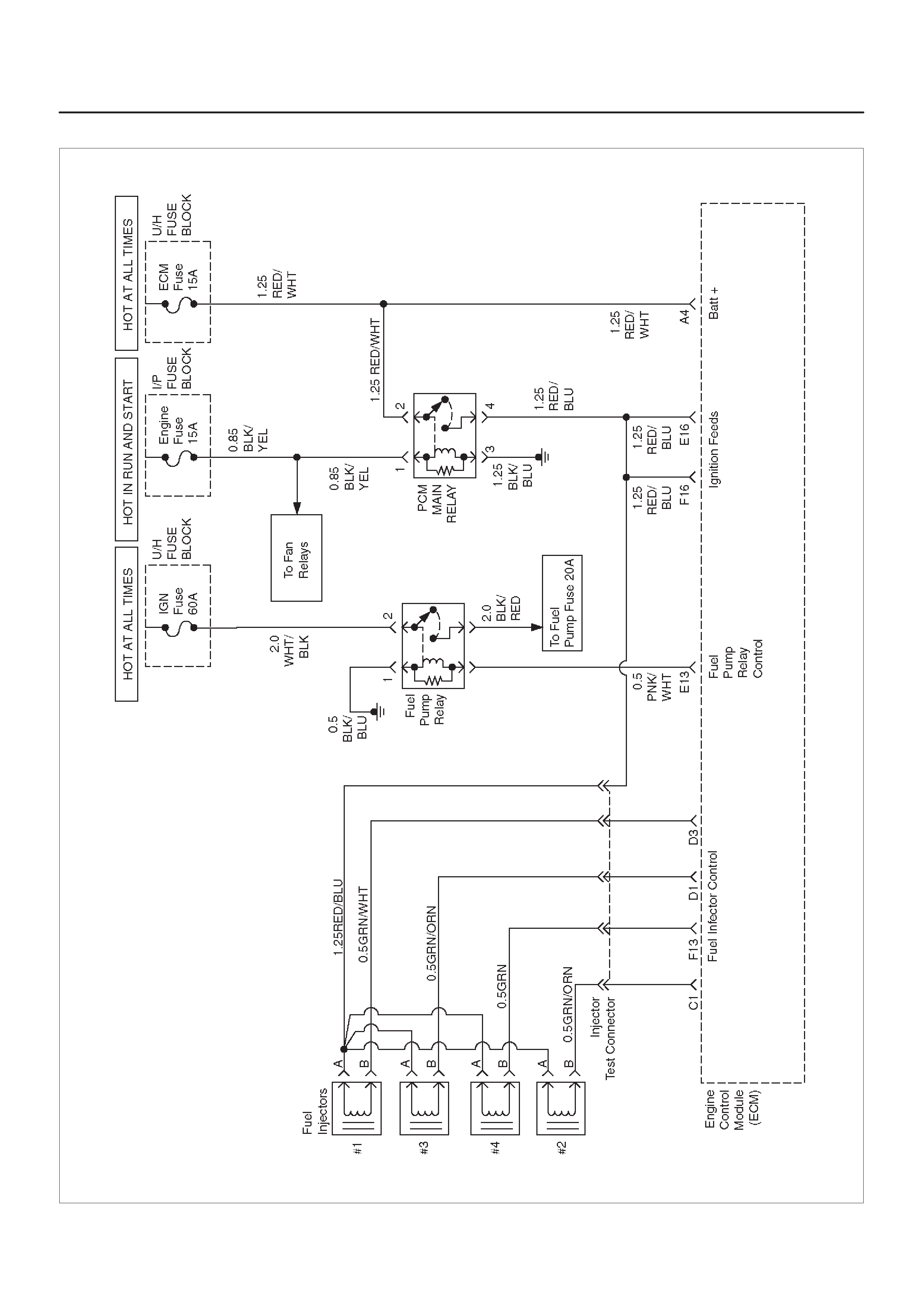
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (2 of 10)
060RX091
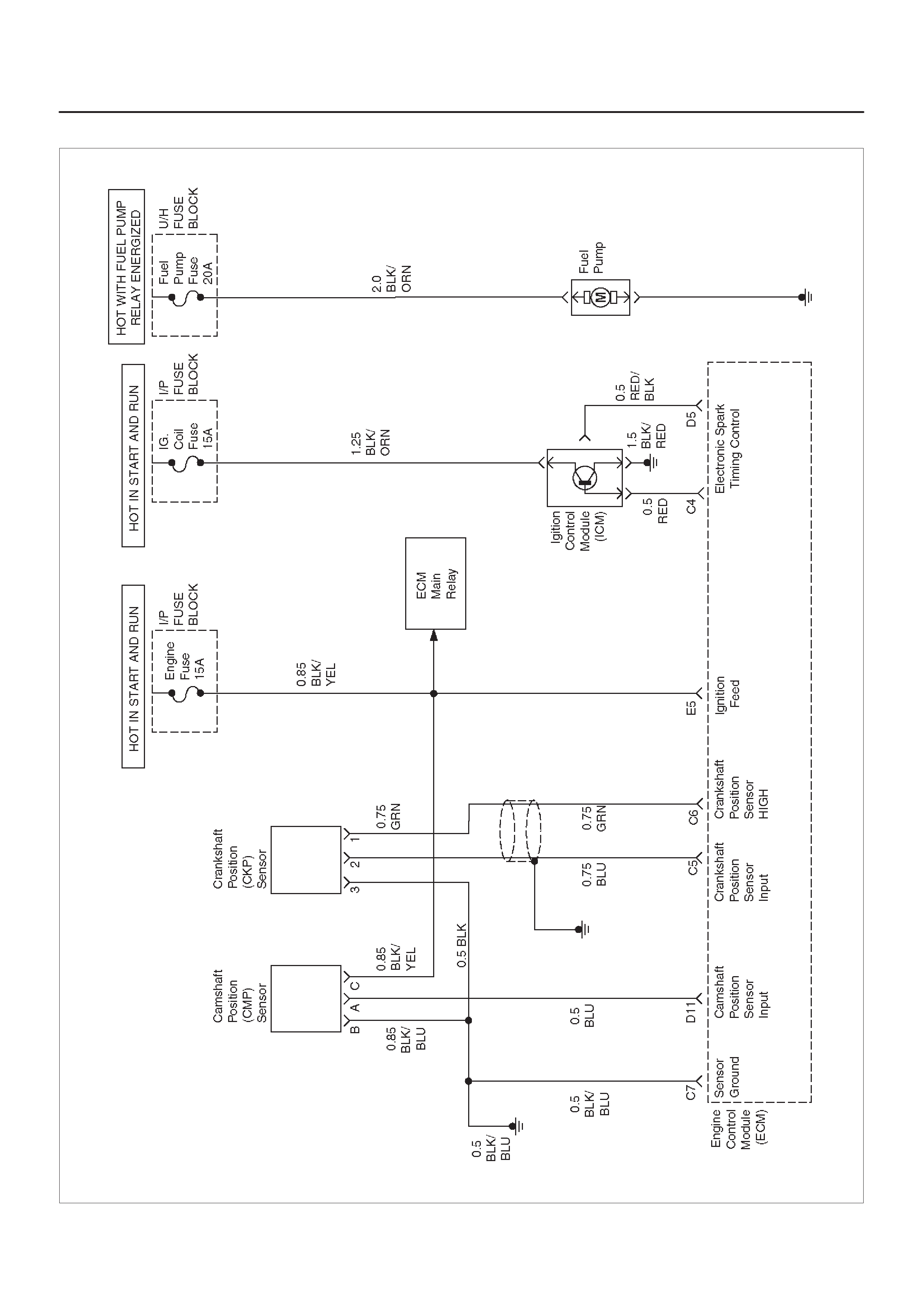
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (3 of 10)
D06RX099
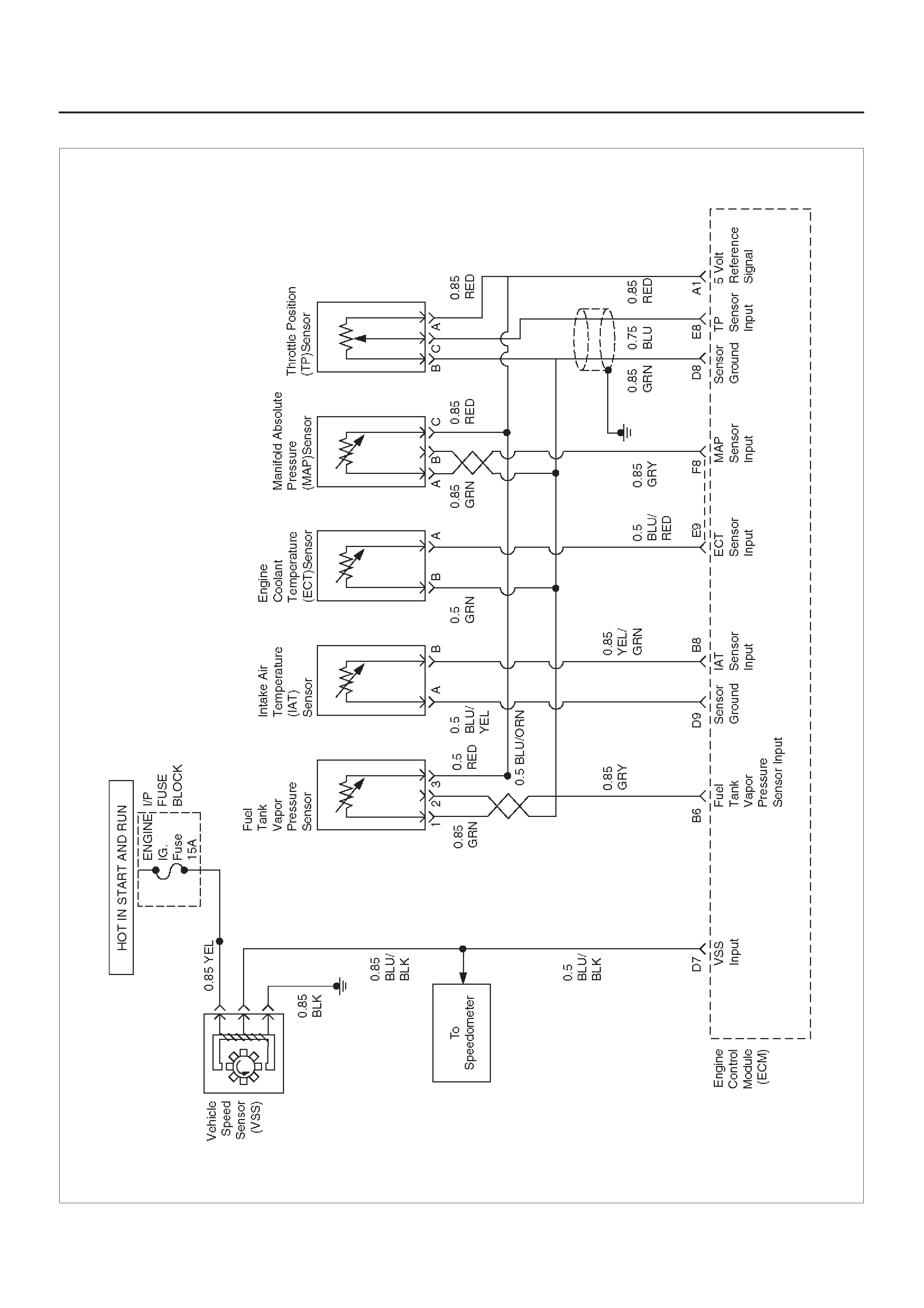
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (4 of 10)
060RX095
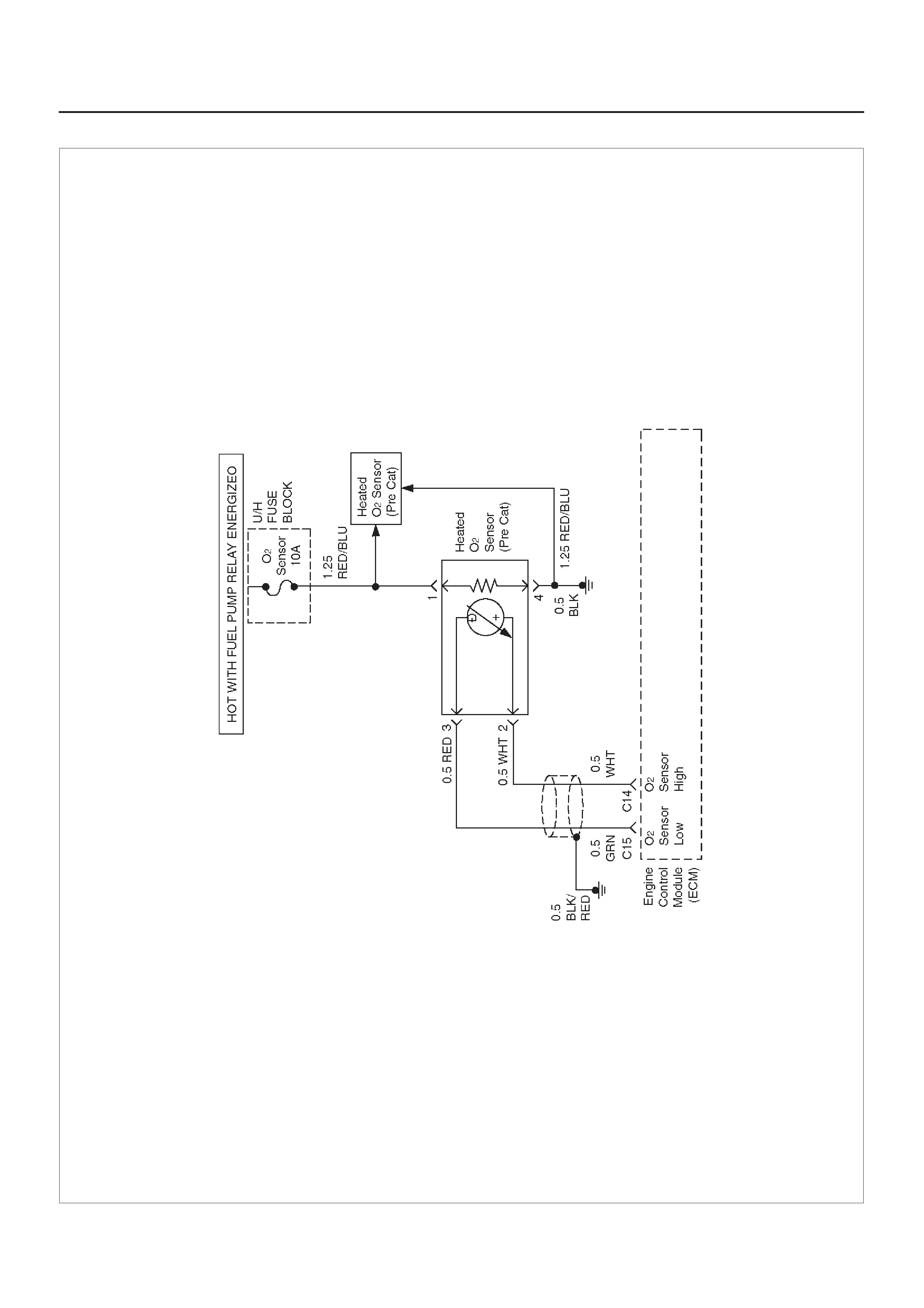
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (5 of 10)
D06RX119
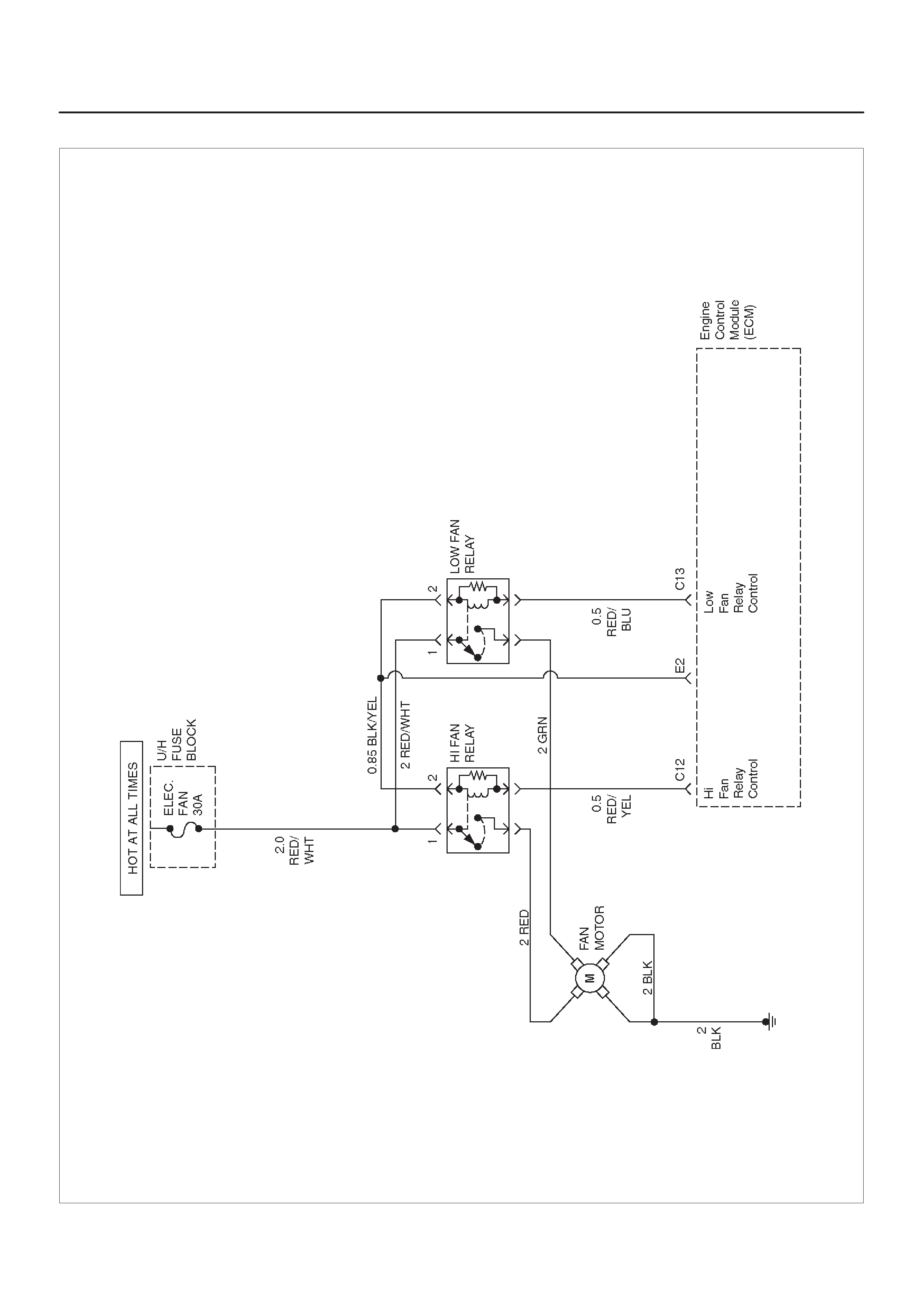
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (6 of 10)
D06RX102
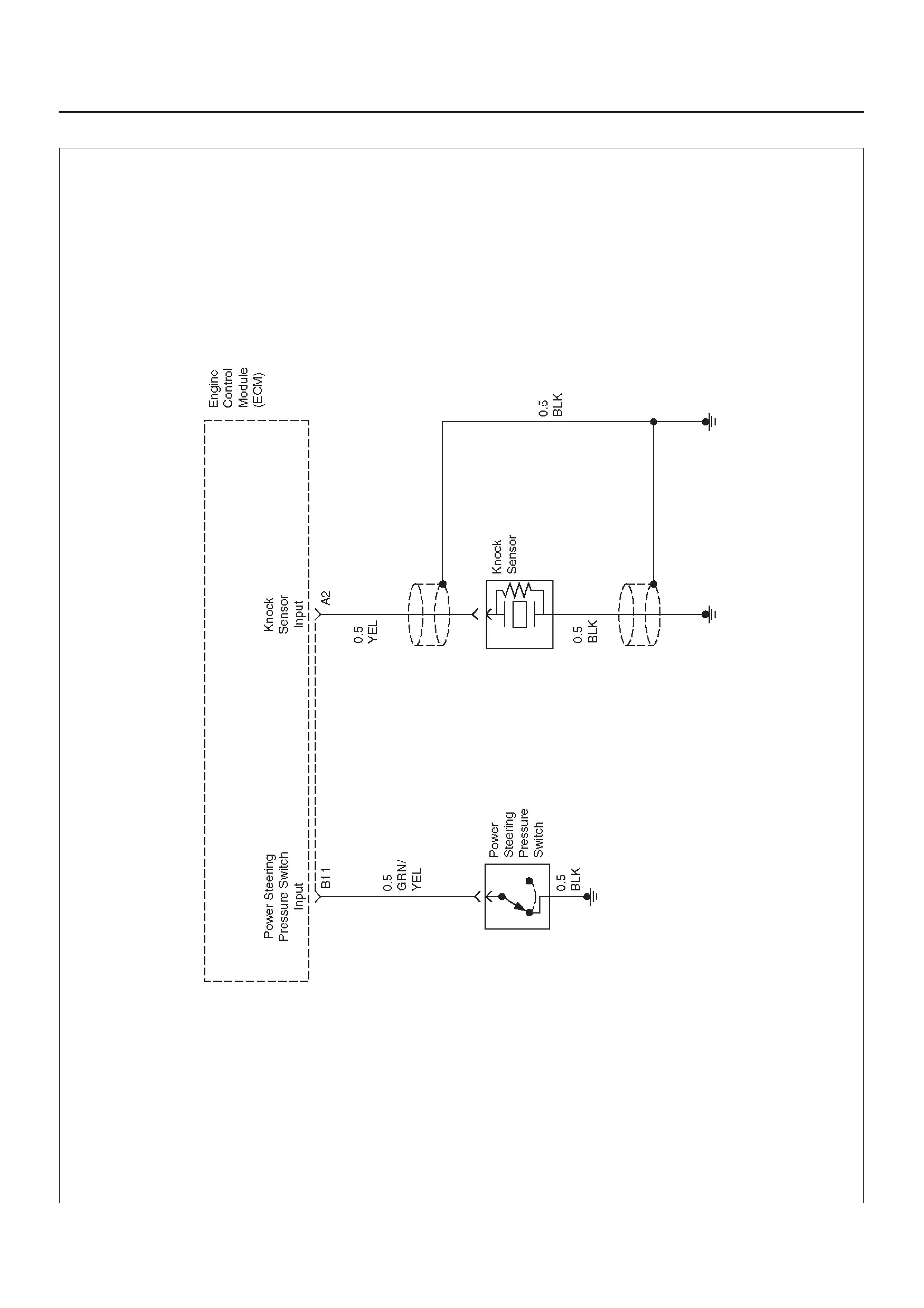
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (7 of 10)
D06RX103
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (8 of 10)
D06RX104

ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (9 of 10)
D06RX105
ECM WIRING DIAGRAM (10 of 10)
D06RX106

ECM PINOUTS
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin Red Connector – Row ”A”
TS23344
PIN PIN Function Wire Color IGN ON ENG RUN Refer To
A1 5 Volt Reference Signal RED 5.0 V 5.0 V Appropriate Sensor
A2 Knock Sensor Input YEL —3.0 V (MAX) General Description and
Operation, Knock Sensor
A3 Not Used —
A4 Battery Feed RED/WHT B+ B+ Chassis Electrical
A5 Idle Air Control (IAC) ”A”
High BLU B+/0.8 V B+/0.8 V General Description and
Operation, IAC
A6 IAC ”A” Low BLU/WHT B+/0.8 V B+/0.8 V General Description and
Operation, IAC
A7 IAC ”B” Low BLU/BLK B+/0.8 V B+/0.8 V General Description and
Operation, IAC
A8 IAC ”B” High BLU/RED B+/0.8 V B+/0.8 V General Description and
Operation, IAC
A9 Not Used — — — —
A10 Not Used — — — —
A11 Not Used — — — —
A12 Not Used — — — —
A13 Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) Control WHT/GRN 0.4–0.9 V B+ Chassis Electrical
A14 Rear Defogger Relay RED/WHT B+ B+ Classis Electrical
A15 EVAP Canister Vent
Solenoid Control RED/BLU B+ 0–5 V
(varies) General Description and
Operation, EVAP Emission
Control System
A16 Not Used — — — —
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin Red Connector – Row ”B”
TS23344
PIN
PIN Function Wire Color IGN ON ENG RUN Refer To
B1 5 Volt Reference Signal BLU/ORG 5.0 V 5.0 V Appropriate Sensor
B2 Not Used — — — —
B3 Not Used — — — —
B4 Not Used — — — —
B5 Not Used — — — —
B6 Not Used — — — —
B7 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Position Feedback YEL/RED 0.6 V 0.6 V General Description and
Operation, Linear EGR
Control
B8 Intake Air Temperature
(IAT) Sensor YEL/GRN ~3V
(0V = 151°C) ~3 V
(5V = –40°C) General Description and
Operation, IAT
B9 A/C Pressure Sensor
Signal GRN ~1 V ~1 V A/C System
B10 Not Used — — — —
B11 Power Steering Pressure
(PSP) Switch Input GRN/YEL B+ B+ General Description and
Operation, PSP
B12 Illumination Switch GRN/YEL B+ B+ Chassis Electrical
B13 Class 2 Data ORN/BLK 0.0 V 0.0 V Diagnosis, Class 2 Serial
Data
B14 A/C Compressor Clutch
Relay Control Compressor GRN/RED 0
(A/C OFF) B+
(A/C ON) General Description and
Operation, A/C Clutch Circuit
Operation
B15 Not Used — — — —
B16 Not Used — — — —
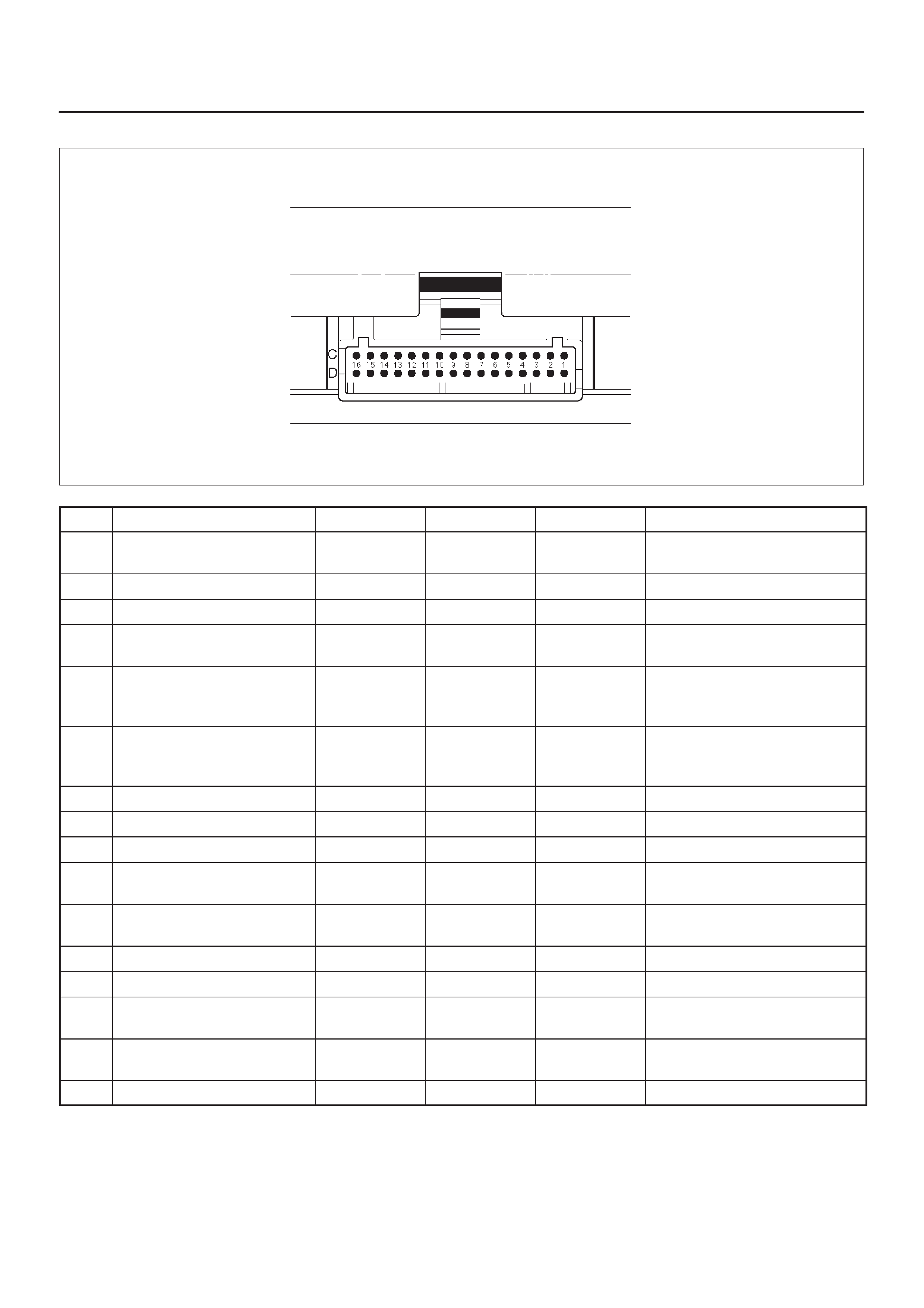
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector – Row ”C”
TS23345
PIN PIN Function Wire Color IGN ON ENG RUN Refer To
C1 Injector Cylinder #2 GRN/RED B+ Varies B+ Varies General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C2 Not Used — — — —
C3 Not Used — — — —
C4 Ignition Control Module
(ICM) Input RED 0.0 V 0.1 V General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
C5 Crankshaft Position (CKP)
Sensor Low BLUE 4.98 V 0.76 V
(at idle) General Description and
Operation, Crankshaft
Position Sensor
C6 Crankshaft Position
Sensor (CKP) High GRN 5V 5V General Description and
Operation, Crankshaft
Position Sensor
C7 ECM Ground BLK/BLU 0.0 V 0.0 V Chassis Electrical
C8 ECM Ground BLK/BLU 0.0 V 0.0 V Chassis Electrical
C9 ECM Ground BLK/BLU 0.0 V 0.0 V Chassis Electrical
C10 Tachometer Signal BLK/RED — — General Description and
Operation
C11 Fuel Gauge PWM Output YEL/RED Varies with
Fuel Level Varies with
Fuel Level General Description and
Operation
C12 High Fan Relay Control RED/YEL 10.5 V B+ Chassis Electrical
C13 Low Fan Relay Control RED/BLU — — Chassis Electrical
C14 Bank 1 HO2S 1 High WHT 0.3 V –0.1 to 1.1 V General Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
C15 Bank 1 HO2S 1 Low RED 0.0 V 0.1 V General Description and
Operation, Fuel HO2S 1
C16 Not Used — — — —
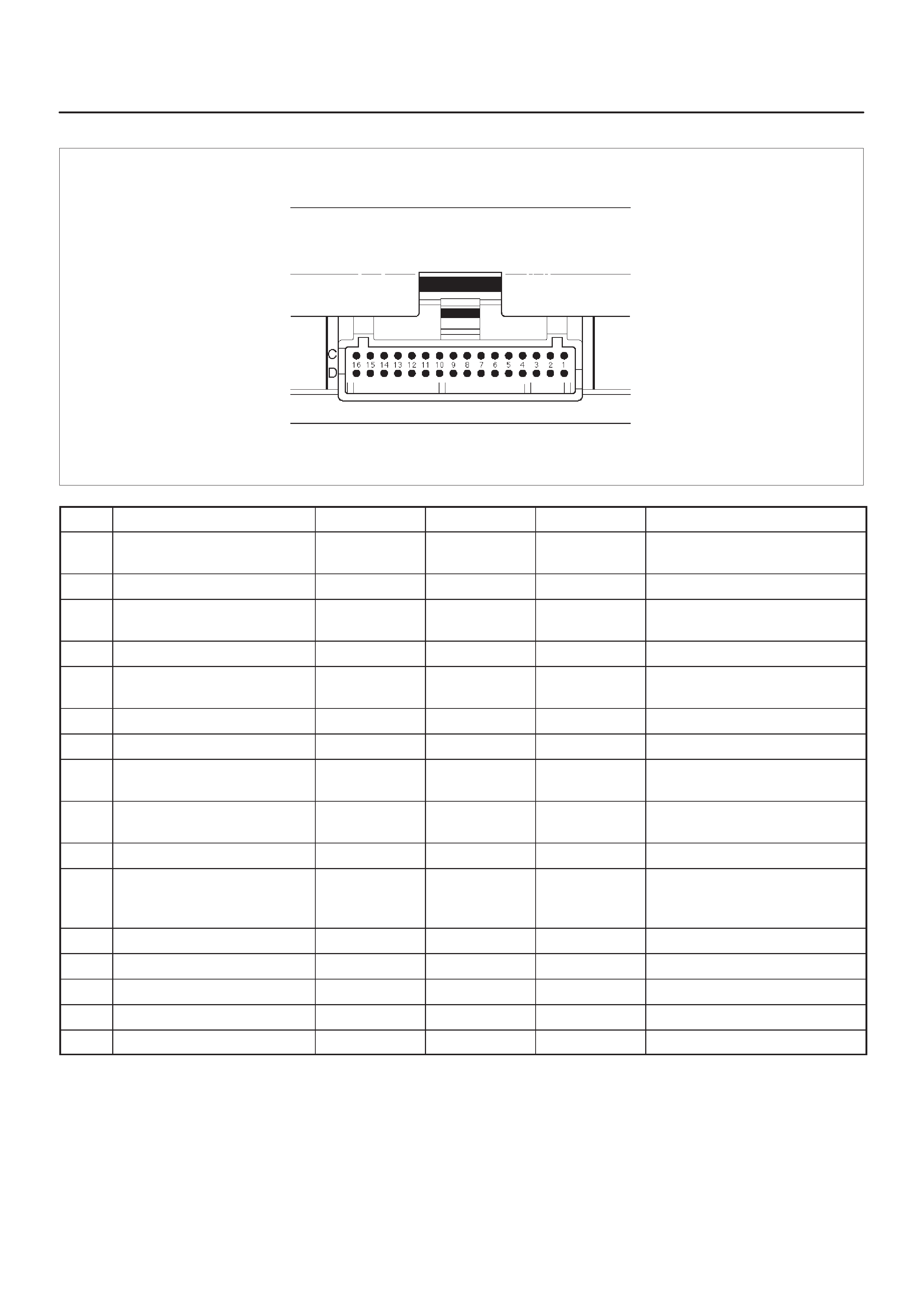
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector – Row ”D”
TS23345
PIN PIN Function Wire Color IGN ON ENG RUN Refer To
D1 Injector Cylinder #3 GRN/ORN B+ B+ General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D2 Not Used — — — —
D3 Injector Cylinder #1 GRN/WHT B+ B+ General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
D4 Not Used — — — —
D5 Ignition Control Module
(ICM) Input RED/BLK — — General Description and
Operation
D6 Not Used — — — —
D7 VSS Input BLU/BLK — — Chassis Electrical
D8 Sensor Ground 5 V
Reference A Return GRN 0.0 V 0.0 V Appropriate Sensor
D9 Sensor Ground 5 V
Reference B Return BLU/YEL 0.0 V 0.0 V Appropriate Sensor
D10 Not Used — — — —
D11 Camshaft Position Sensor
Input BLU 5.0 V 4.6 V General Description and
Operation, Camshaft
Position Sensor
D12 Not Used — — — —
D13 Not Used — — — —
D14 Not Used — — — —
D15 Not Used — — — —
D16 Not Used — — — —
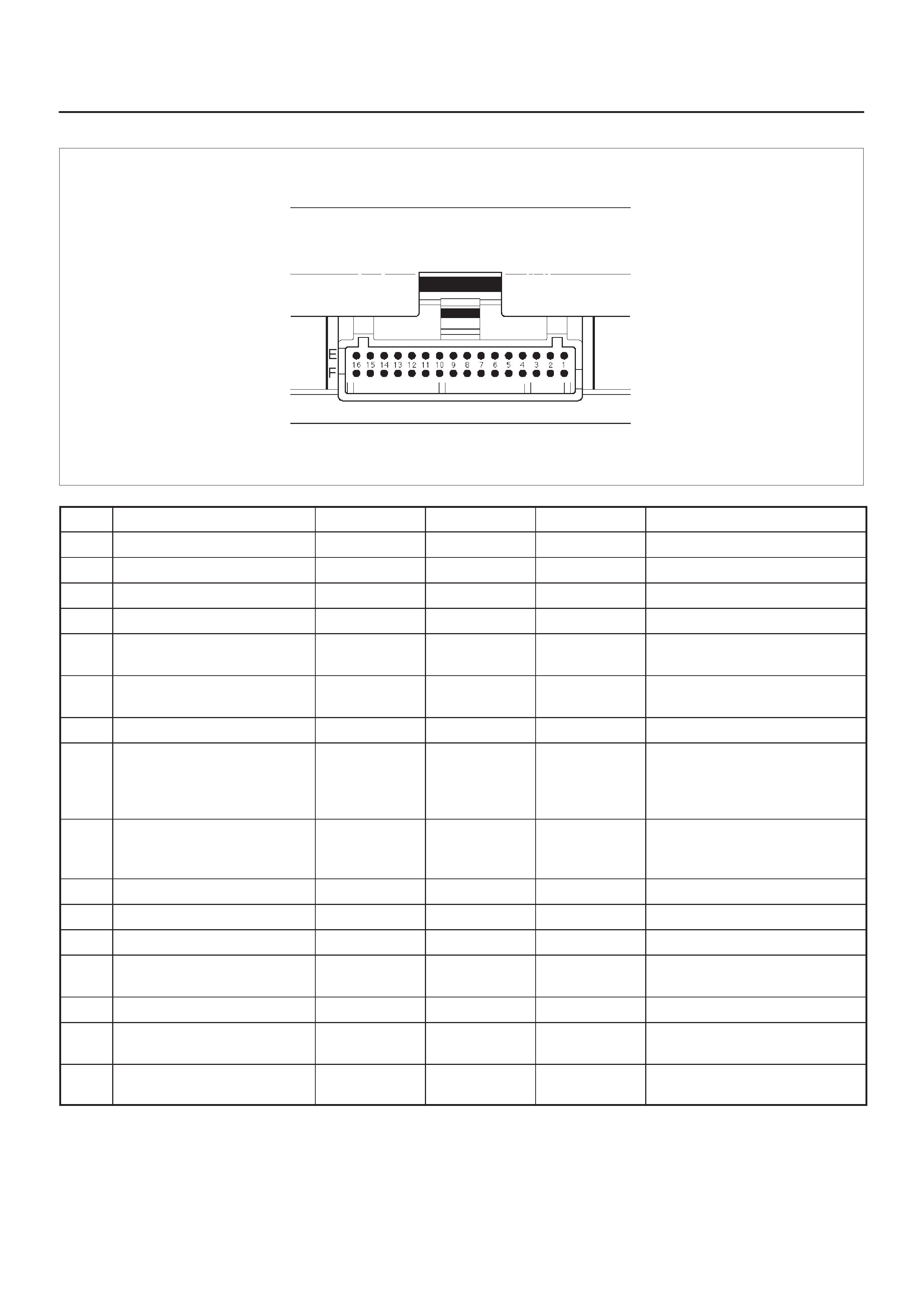
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector – Row ”E”
TS23346
PIN PIN Function Wire Color IGN ON ENG RUN Refer To
E1 Not Used — — — —
E2 Fan Control RED/GRN 0.0V B+ Chassis Electrical
E3 Not Used — — — —
E4 Not Used — — — —
E5 Ignition Feed BLK/YEL B+ B+ General Description and
Operation
E6 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve Low YEL B+ Varies B+ Varies General Description and
Operation, EGR Control
E7 Not Used — — — —
E8 Throttle Position (TP)
Sensor Input BLU 0.25 V
(0% = 0.25 V) 0.25 V
(at idle)
(100% =
4.75 V)
General Description and
Operation, Throttle Position
Sensor
E9 Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT)
Sensor Input
BLU/RED 2.3 V
(O V =
151°C)
2.1 V
(5 V = –40°C) General Description and
Operation, Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) Sensor
E10 Not Used — — — —
E11 Not Used — — — —
E12 Rear Defogger Switch YEL/GRN B+ B+ Chassis Electrical
E13 Fuel Pump (FP) Relay
Control PNK/WHT 0.0 V B+ On–Vehicle Service, Fuel
Pump Relay
E14 Not Used — — — —
E15 A/C Request (Thermo
Relay) GRN/BLK 0.0 V 0.0 V Electric Cooling Fans
E16 Ignition Feed RED/BLU B+ B+ General Description and
Operation
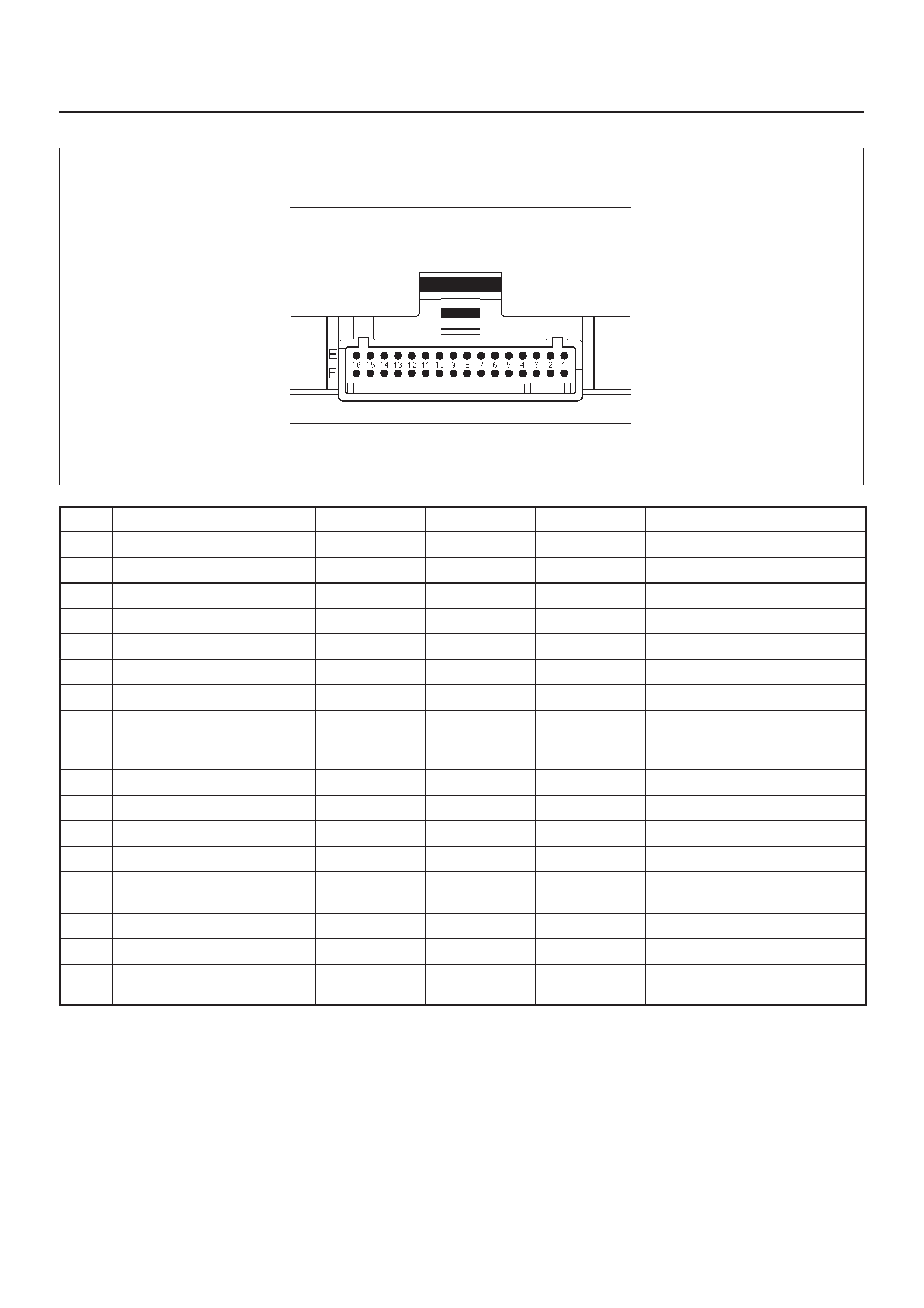
ECM Pinout Table, 32–Pin White Connector – Row ”F”
TS23346
PIN PIN Function Wire Color IGN ON ENG RUN Refer To
F1 Not Used — — — —
F2 Not Used — — — —
F3 Not Used — — — —
F4 Not Used — — — —
F5 Not Used — — — —
F6 Not Used — — — —
F7 Not Used — — — —
F8 Manifold Absolute
Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Input
GRY ~4.7 V
(0 V = 10kPa) ~1.1 V
(5 V =
104kPa)
General Description and
Operation, Manifold Absolute
Pressure
F9 Not Used — — — —
F10 Not Used — — — —
F11 Not Used — — — —
F12 DLC (Digital Input) — — — Class 2 Serial Data
F13 Injector ”C” Cylinder #4 GRN B+ B+ General Description and
Operation, Fuel Injector
F14 Not Used — — — —
F15 Not Used — — — —
F16 Ignition Feed RED/BLU B+ B+ General Description and
Operation
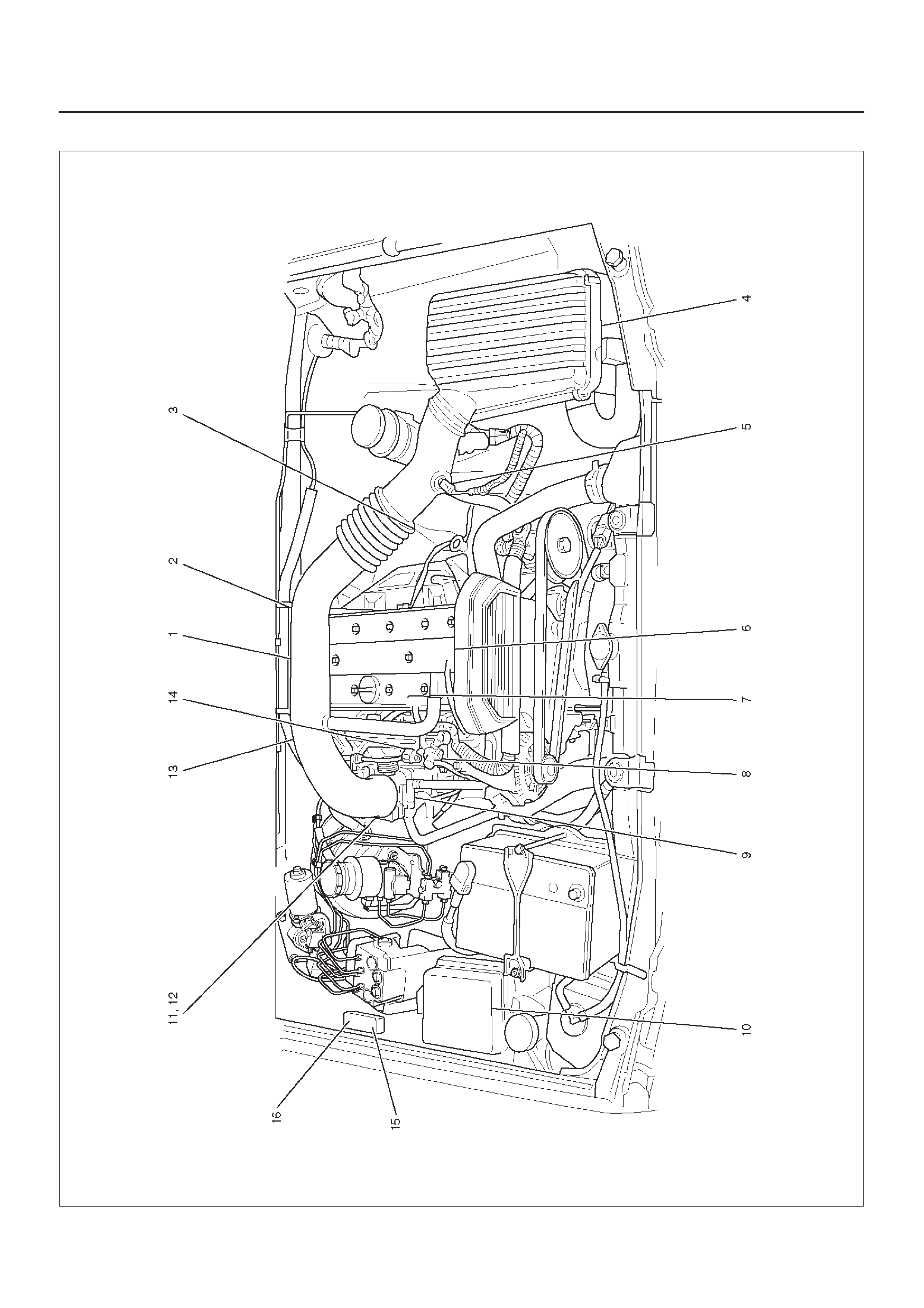
COMPONENT LOCATOR
755RX030
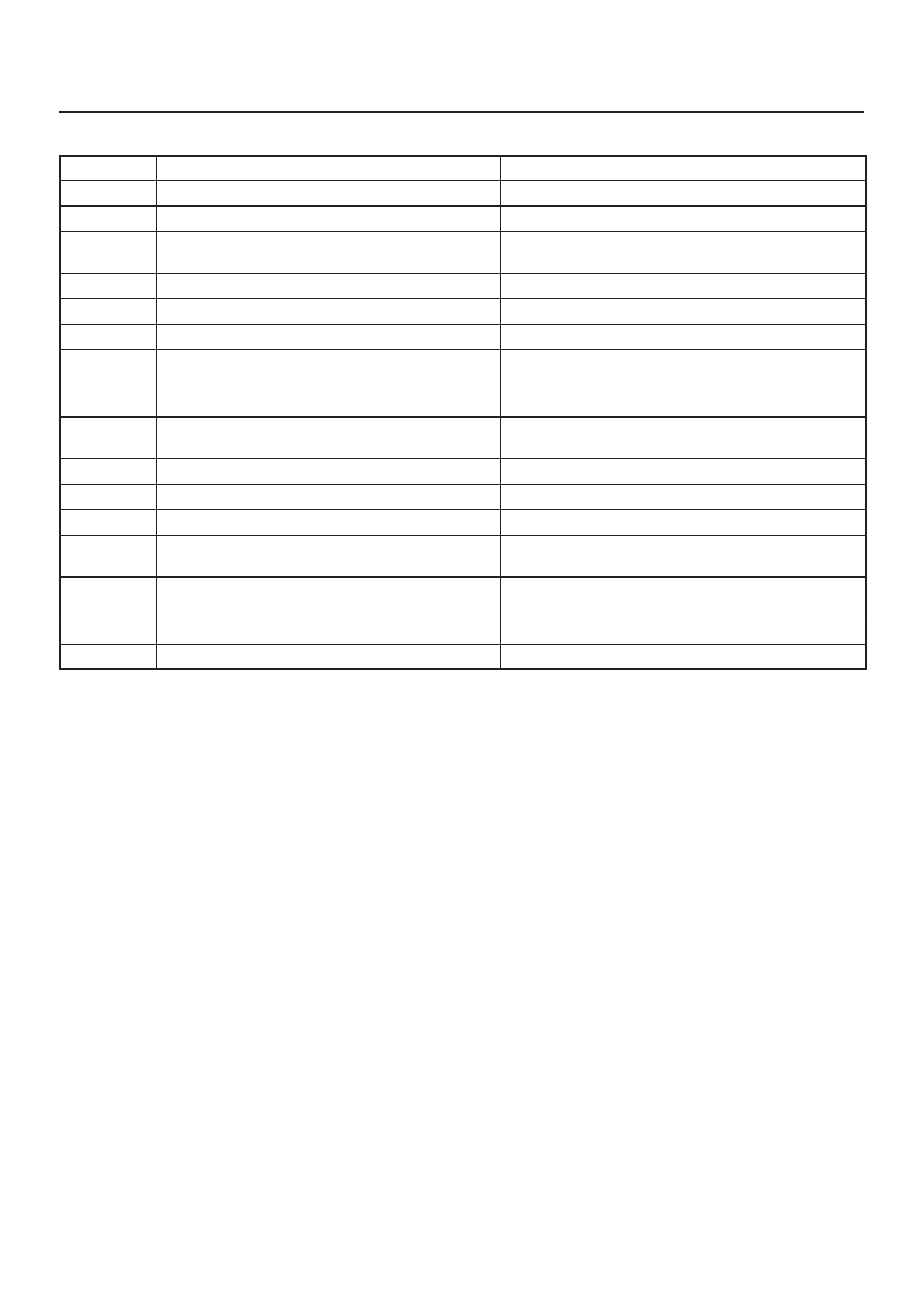
Engine Component Locator Table
Number Name Location
1Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Rear of engine, near ignition coils
2Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve On the left rear of the engine at the bulkhead
3Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S), Bank 1,
Sensor 1 On the exhaust pipe, left side of engine,
immediately behind the exhaust manifold
4Air Cleaner Left front of the engine bay
5Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor On the intake air duct near the air cleaner
6Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Inside the front cover assembly
7Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Port On the right front corner of the valve cover
8Fuel Pressure Regulator On the forward end of the fuel rail, to the right of
the PVC port
9Throttle Body Between the intake air duct and the intake
manifold
10 Fuse/Relay Box Along the inside of the right fender
11 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor On the front of the throttle body
12 Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve On the rear of the throttle body
13 Ignition Control Module (ICM) Mounted on a heat sink on the lower right side of
the engine block, above the starter motor
14 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor Bolted to the front edge of the intake manifold,
under the fuel rail
15 High Fan Relay In the relay box
16 Low Fan Relay In the relay box
010RX001
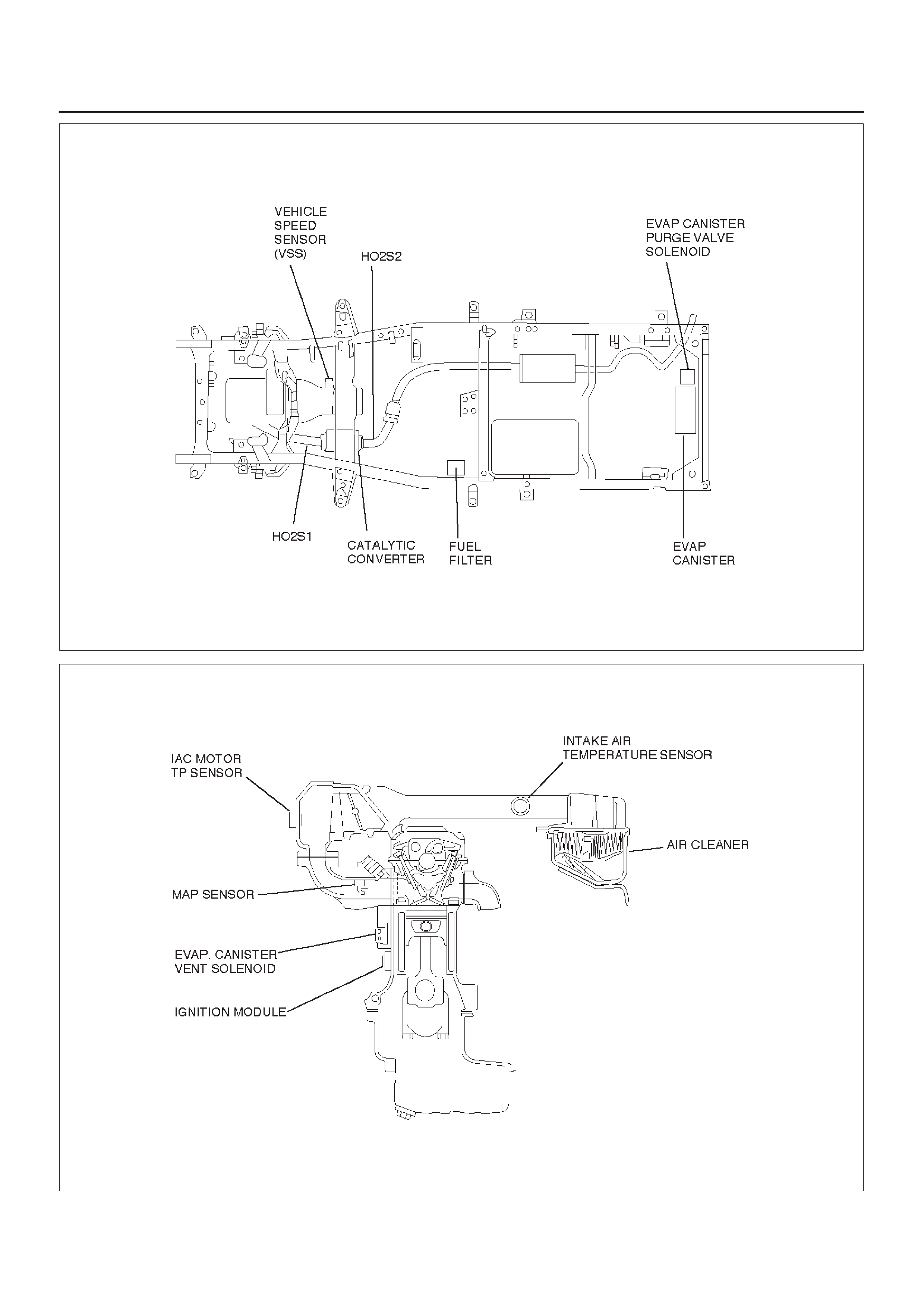
028RX001
Undercarriage Component Locator Table
Name Location
Fuel Pump Assembly Installed in the top of the fuel tank
EVAP Canister Behind rear axle, near fuel tank filler nozzle
EVAP Canister Purge Valve Solenoid Behind rear axle, near fuel tank filler nozzle
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Protrudes from the right side of the transmission housing, near the
output shaft
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Lower left hand front of engine, behind power steering pump bracket
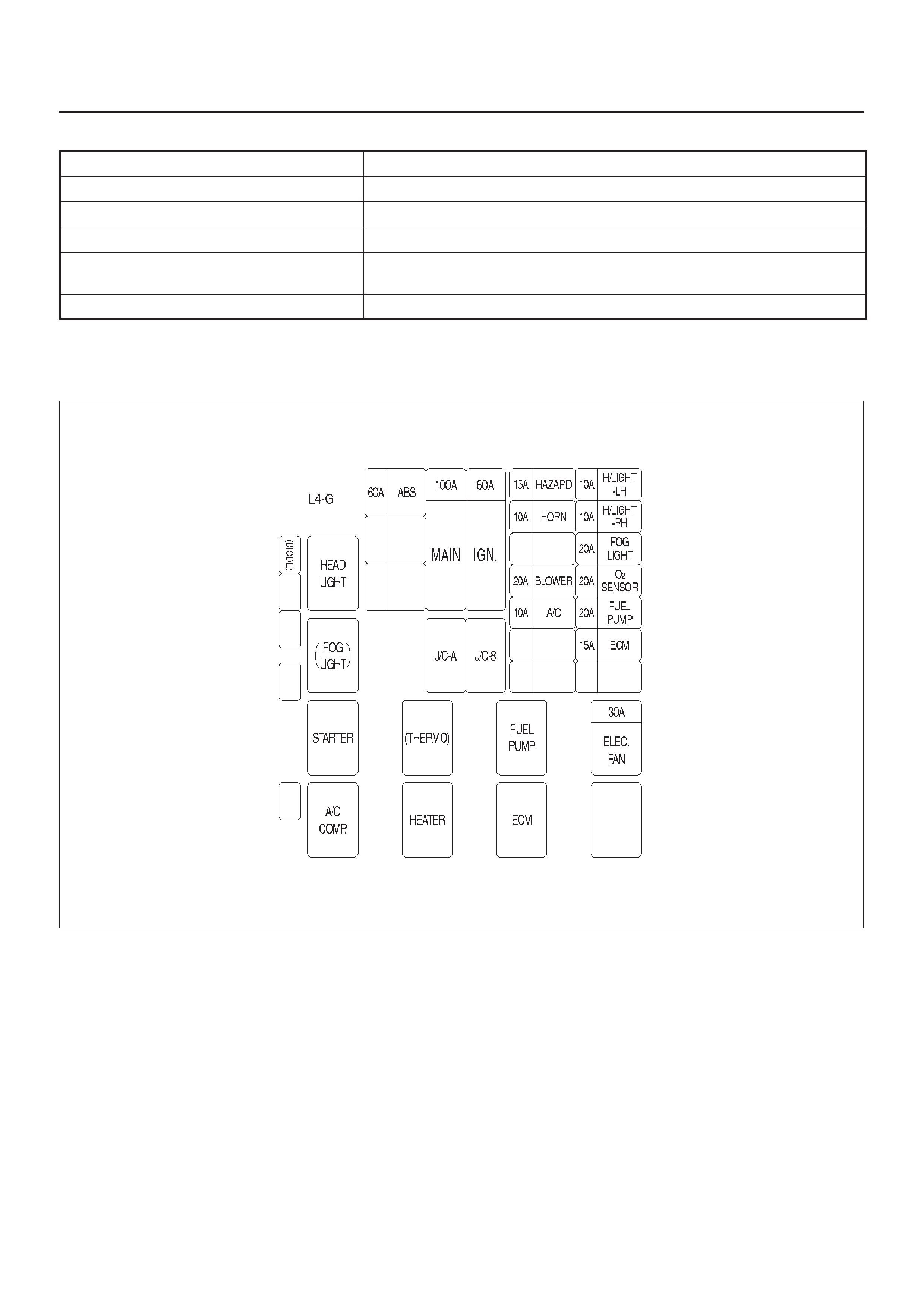
Fuse And Relay Panel (Underhood Electrical Center)
Underhood (U/H) Fuse and Relay Panel
060RX096

DIAGNOSIS Strategy–Based
Diagnostics
Strategy–Based Diagnostics
The strategy–based diagnostic is a uniform approach to
repair all Electrical/Electronic (E/E) systems. The
diagnostic flow can always be used to resolve an E/E
system problem and is a starting point when repairs are
necessary. The following steps will instruct the technician
how to proceed with a diagnosis:
1.Verify the customer complaint.
DTo verify the customer complaint, the technician
should know the normal operation of the system.
2.Perform preliminary checks.
DConduct a thorough visual inspection.
DReview the service history.
DDetect unusual sounds or odors.
DGather diagnostic trouble code information to
achieve an effective repair.
3.Check bulletins and other service information.
DThis includes videos, newsletters, etc.
4.Refer to service information (manual) system
check(s).
D”System checks” contain information on a system
that may not be supported by one or more DTCs.
System checks verify proper operation of the
system. This will lead the technician in an organized
approach to diagnostics.
5.Refer to service diagnostics.
DTC Stored
Follow the designated DTC chart exactly to make an
effective repair.
No DTC
Select the symptom from the symptom tables. Follow the
diagnostic paths or suggestions to complete the repair.
You may refer to the applicable component/system check
in the system checks.
No Matching Symptom
1.Analyze the complaint.
2.Develop a plan for diagnostics.
3.Utilize the wiring diagrams and the theory of
operation.
Combine technician knowledge with efficient use of the
available service information.
Intermittents
Conditions that are not always present are called
intermittents. To resolve intermittents, perform the
following steps:
1.Observe history DTCs, DTC modes, and
freeze–frame data.
2.Evaluate the symptoms and the conditions described
by the customer.
3.Use a check sheet or other method to identify the
circuit or electrical system component.
4.Follow the suggestions for intermittent diagnosis
found in the service documentation.
Most Scan Tools, such as the Tech 2, have
data–capturing capabilities that can assist in detecting
intermittents.
No Trouble Found
This condition exists when the vehicle is found to operate
normally. The condition described by the customer may
be normal. Verify the customer complaint against another
vehicle that is operating normally. The condition may be
intermittent. Verify the complaint under the conditions
described by the customer before releasing the vehicle.
1.Re–examine the complaint.
When the complaint cannot be successfully found or
isolated, a re–evaluation is necessary. The complaint
should be re–verified and could be intermittent as
defined in
Intermittents,
or could be normal.
2.Repair and verify.
After isolating the cause, the repairs should be made.
Validate for proper operation and verify that the
symptom has been corrected. This may involve road
testing or other methods to verify that the complaint
has been resolved under the following conditions:
DConditions noted by the customer.
DIf a DTC was diagnosed, verify a repair by
duplicating conditions present when the DTC was
set as noted in the Failure Records or Freeze
Frame data.
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of the vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD II system
diagnostics. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
IMPORTANT:Follow the steps below when you verify
repairs on OBD II systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
1.Review and record the Failure Records and the
Freeze Frame data for the DTC which has been
diagnosed (Freeze Fame data will only be stored for
an A or B type diagnostic and only if the MIL (”Check
Engine” lamp) has been requested).
2.Clear the DTC(s).
3.Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Failure Records and Freeze Frame data.
4.Monitor the DTC status information for the DTC which
has been diagnosed until the diagnostic test
associated with that DTC runs.
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Non–OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Something as simple as a
high–performance exhaust system that affects exhaust
system back pressure could potentially interfere with the

operation of the EGR valve and thereby turn on the MIL
(”Check Engine” lamp). Small leaks in the exhaust
system near the post catalyst oxygen sensor can also
cause the MIL (”Check Engine” lamp) to turn on.
Aftermarket electronics, such as transceiver, stereos,
and anti–theft devices, may radiate EMI into the control
system if they are improperly installed. This may cause a
false sensor reading and turn on the MIL (”Check Engine”
lamp).
Environment
Temporary environmental conditions, such as localized
flooding, will have an effect on the vehicle ignition system.
If the ignition system is rain–soaked, it can temporarily
cause engine misfire and turn on the MIL (”Check Engine”
lamp).
Emissions Control Information Label
The engine compartment ”Vehicle Emissions Control
Information Label” contains important emission
specifications and setting procedures. In the upper left
corner is exhaust emission information. There is also an
illustrated emission components and vacuum hose
schematic.
This label is located in the engine compartment of every
vehicle. If the label has been removed it should be
replaced, it can be ordered from Isuzu Dealer ship.
Maintenance Schedule
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any diagnostic
procedure or diagnosing the cause of an emission test
failure. This can often lead to repairing a problem without
further steps. Use the following guidelines when
performing a visual/physical inspection:
DInspect all vacuum hoses for pinches, cuts,
disconnection, and Droper routing.
DInspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other
components.
DInspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper
connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched wires,
contact with sharp edges or contact with hot exhaust
manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge Of Tools Required
NOTE:Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain when
performing diagnostic procedures could result in an
incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to
effectively use this section of the Service Manual.
SERIAL DATA COMMUNICATIONS
Class II Serial Data Communications
Government regulations require that all vehicle
manufacturers establish a common communication
system. This vehicle utilizes the ”Class II” communication
system. Each bit of information can have one of two
lengths: long or short. This allows vehicle wiring to be
reduced by transmitting and receiving multiple signals
over a single wire. The messages carried on Class II data
streams are also prioritized. If two messages attempt to
establish communications on the data line at the same
time, only the message with higher priority will continue.
The device with the lower priority message must wait. The
most significant result of this regulation is that it provides
Tech 2 manufacturers with the capability to access data
from any make or model vehicle that is sold.
The data displayed on the other Tech 2 will appear the
same, with some exceptions. Some Scan Tools will only
be able to display certain vehicle parameters as values
that are a coded representation of the true or actual value.
For more information on this system of coding, refer to
Decimal/Binary/Hexadecimal Conversions. On this
vehicle the Tech 2 displays the actual values for vehicle
parameters. It will not be necessary to perform any
conversions from coded values to actual values.
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD)
On–Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which is
a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic executive. When a
diagnostic test reports a pass result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
DThe diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
DThe diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
DThe fault identified by the diagnostic test is not
currently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the diagnostic
executive records the following data:
DThe diagnostic test has been completed since the last
ignition cycle.
DThe fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently
active.
DThe fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
DThe operating conditions at the time of the failure.
Remember, a fuel trim DTC may be triggered by a list of
vehicle faults. Make use of all information available (other

DTCs stored, rich or lean condition, etc.) when
diagnosing a fuel trim fault.
Comprehensive Component Monitor
Diagnostic Operation
Input Components:
Input components are monitored for circuit continuity and
out–of–range values. This includes rationality checking.
Rationality checking refers to indicating a fault when the
signal from a sensor does not seem reasonable, i.e.
Throttle Position (TP) sensor that indicates high throttle
position at low engine loads or MAP voltage). Input
components may include, but are not limited to the
following sensors:
DVehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
DCrankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
DThrottle Position (TP) sensor
DEngine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
DCamshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DManifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor
In addition to the circuit continuity and rationality check
the ECT sensor is monitored for its ability to achieve a
steady state temperature to enable ”Closed Loop” fuel
control.
Output Components:
Output components are diagnosed for proper response to
control module commands. Components where
functional monitoring is not feasible will be monitored for
circuit continuity and out–of–range values if applicable.
Output components to be monitored include, but are not
limited to the following circuit:
DIdle Air Control (IAC) Motor
DEVAP Canister Purge Valve Solenoid
DA/C relays
DCooling fan relay(s)
DVSS output
DMIL control
Refer to ECM and Sensors in General Descriptions.
Passive and Active Diagnostic Tests
A passive test is a diagnostic test which simply monitors a
vehicle system or component. Conversely, an active test,
actually takes some sort of action when performing
diagnostic functions, often in response to a failed passive
test. For example, the EGR diagnostic active test will
force the EGR valve open during closed throttle decel
and/or force the EGR valve closed during a steady state.
Either action should result in a change in manifold
pressure.
Intrusive Diagnostic Tests
This is any on–board test run by the Diagnostic
Management System which may have an effect on
vehicle performance or emission levels.
Warm–Up Cycle
A warm–up cycle means that engine at temperature must
reach a minimum of 70°C (160°F) and rise at least 22°C
(40°F) over the course of a trip.
Freeze Frame
Freeze Frame is an element of the Diagnostic
Management System which stores various vehicle
information at the moment an emissions–related fault is
stored in memory and when the MIL is commanded on.
These data can help to identify the cause of a fault. Refer
to Storing And Erasing Freeze Fame Data for more
detailed information.
Failure Records
Failure Records data is an enhancement of the OBD
Freeze Frame feature. Failure Records store the same
vehicle information as does Freeze Frame, but it will store
that information for any fault which is stored in on–board
memory, while Freeze Frame stores information only for
emission–related faults that command the MIL ON.
Common OBD Terms
Diagnostic
When used as a noun, the word diagnostic refers to any
on–board test run by the vehicle’s Diagnostic
Management System. A diagnostic is simply a test run on
a system or component to determine if the system or
component is operating according to specification. There
are many diagnostics, shown in the following list:
DOxygen sensors
DOxygen sensor heaters
DEGR
Enable Criteria
The term ”enable criteria” is engineering language for the
conditions necessary for a given diagnostic test to run.
Each diagnostic has a specific list of conditions which
must be met before the diagnostic will run. ”Enable
criteria” is another way of saying ”conditions required”.
The enable criteria for each diagnostic is listed on the first
page of the DTC description in Section 6E under the
heading ”Conditions for Setting the DTC”. Enable criteria
varies with each diagnostic, and typically includes, but is
not limited to the following items:
Dengine speed
Dvehicle speed
DECT
DMAP
Dbarometric pressure
DIAT
DTP
DA/C ON

Trip
T echnically , a trip is a key on–run–key off cycle in which all
the enable criteria for a given diagnostic are met, allowing
the diagnostic to run. Unfortunately, this concept is not
quite that simple. A trip is official when all the enable
criteria for a given diagnostic are met. But because the
enable criteria vary from one diagnostic to another, the
definition of trip varies as well. Some diagnostics are run
when the vehicle is at operating temperature, some when
the vehicle first starts up; some require that the vehicle be
cruising at a steady highway speed, some run only when
the vehicle is at idle; some diagnostics function with the
TCC disabled. Some run only immediately following a
cold engine start–up.
A trip then, is defined as a key on–run–key off cycle in
which the vehicle was operated in such a way as to satisfy
the enabling criteria for a given diagnostic, and this
diagnostic will consider this cycle to be one trip. However ,
another diagnostic with a different set of enable criteria
(which were not met) during this driving event, would not
consider it a trip. No trip will occur for that particular
diagnostic until the vehicle is driven in such a way as to
meet all the enable criteria.
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Executive are listed as
follows:
DCommanding the MIL (”Check Engine” lamp) ON and
OFF
DDTC logging and clearing
DFreeze Frame data for the first emission related DTC
recorded
DNon–emission related Service Lamp (future)
DOperating conditions Failure Records buffer, (the
number of records will vary)
DCurrent status information on each diagnostic
DSystem Status (I/M ready)
The Diagnostic Executive records DTCs and turns ON
the MIL when emission–related faults occur. It can also
turn OFF the MIL if the conditions cease which caused the
DTC to set.
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are designed
to locate a faulty circuit or component through a process
of logical decisions. The charts are prepared with the
requirement that the vehicle functioned correctly at the
time of assembly and that there are no multiple faults
present.
There is a continuous self–diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complimented by
the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual. The
language of communicating the source of the malfunction
is a system of diagnostic trouble codes. When a
malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) (”Check Engine” lamp) is
illuminated.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same as
the MIL you are already familiar with (”Check Engine”
lamp). However, OBD requires that it illuminate under a
strict set of guide lines.
Basically, the MIL is turned ON when the ECM detects a
DTC that will impact the vehicle emissions.
The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic Executive.
The MIL will be turned ON if an emissions–related
diagnostic test indicates a malfunction has occurred. It
will stay ON until the system or component passes the
same test, for three consecutive trips, with no
emissions–related faults.
Extinguishing the MIL
When the MIL is ON, the Diagnostic Executive will turn
OFF the MIL after
three (3) consecutive
trips that a ”test
passed” has been reported for the diagnostic test that
originally caused the MIL to illuminate.
Although the MIL has been turned OFF, the DTC will
remain in the ECM memory (both Freeze Frame and
Failure Records) until
forty(40) warm–up cycles after no
faults
have been completed.
If the MIL was set by either a fuel trim or misfire–related
DTC, additional requirements must be met. In addition to
the requirements stated in the previous paragraph, these
requirements are as follows:
DThe diagnostic tests that are passed must occur with
375 RPM of the RPM data stored at the time the last
test failed.
DPlus or minus ten (10) percent of the engine load that
was stored at the time the last test failed.
DSimilar engine temperature conditions (warmed up or
warming up) as those stored at the time the last test
failed.
Meeting these requirements ensures that the fault which
turned on the MIL has been corrected.
The MIL (”Check Engine” lamp) is on the instrument panel
and has the following functions:
DIt informs the driver that a fault that affects vehicle
emission levels has occurred and that the vehicle
should be taken for service as soon as possible.
DAs a bulb and system check, the MIL will come ON
with the key ON and the engine not running. When the
engine is started, the MIL will turn OFF.
DWhen the MIL remains ON while the engine is
running, or when a malfunction is suspected due to a
driveability or emissions problem, a Powertrain
On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check must be
performed. The procedures for these checks are
given in On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check.
These checks will expose faults which may not be
detected if other diagnostics are performed first.

DTC Types
Each DTC is directly related to a diagnostic test. The
Diagnostic Management System sets DTC based on the
failure of the tests during a trip or trips. Certain tests must
fail two (2) consecutive trips before the DTC is set. The
following are the four (4) types of DTCs and the
characteristics of those codes:
DType A
DEmissions related
DRequests illumination of the MIL of the first trip with a
fail
DStores a History DTC on the first trip with a fail
DStores a Freeze Frame (if empty)
DStores a Fail Record
DUpdates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
DType B
DEmissions related
D”Armed” after one (1) trip with a fail
D”Disarmed” after one (1) trip with a pass
DRequests illumination of the MIL on the
second
consecutive trip
with a fail
DStores a History DTC on the second consecutive trip
with a fail (The DTC will be armed after the first fail)
DStores a Freeze Frame on the second consecutive
trip with a fail (if empty)
DStores a Fail Record when the first test fails (not
dependent on
consecutive trip
fails)
DUpdates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
(Some special conditions apply to misfire and fuel trim
DTCs)
DType C (if the vehicle is so equipped)
DNon–Emissions related
DRequests illumination of the Service Lamp or the
service message on the Drive Information Center
(DIC) on the
first trip
with a fail
DStores a History DTC on the
first trip
with a fail
D
Does not
store a Freeze Frame
DStores Fail Record when test fails
DUpdates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
DType D. (
Type D
non–emissions related are not
utilized on certain vehicle applications).
DNon–Emissions related
DDoes not request illumination of any lamp
DStores a History DTC on the
first trip
with a fail
D
Does not
store a Freeze Frame
DStores Fail Record when test fails
DUpdates the Fail Record each time the diagnostic
test fails
IMPORTANT:Only four Fail Records can be stored.
Each Fail Record is for a different DTC. It is possible that
there will not be Fail Records for every DTC if multiple
DTCs are set.
Storing and Erasing Freeze Frame Data and Failure
Records
Government regulations require that engine operating
conditions be captured whenever the MIL is illuminated.
The data captured is called Freeze Frame data. The
Freeze Frame data is very similar to a single record of
operating conditions. Whenever the MIL is illuminated,
the corresponding record of operating conditions is
recorded to the Freeze Frame buffer.
Freeze Frame data can only be overwritten with data
associated with a misfire or fuel trim malfunction. Data
from these faults take precedence over data associated
with any other fault. The Freeze Frame data will not be
erased unless the associated history DTC is cleared.
Each time a diagnostic test reports a failure, the current
engine operating conditions are recorded in the
Failure
Records
buffer. A subsequent failure will update the
recorded operating conditions. The following operating
conditions for the diagnostic test which failed
typically
include the following parameters:
DEngine Speed
DEngine Load
DEngine Coolant Temperature
DVehicle Speed
DTP
DMAP/BARO
DInjector Base Pulse Width
DLoop Status
Intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp
In the case of an ”intermittent” fault, the MIL (”Check
Engine” lamp) may illuminate and then (after three trips)
go OFF. However, the corresponding diagnostic trouble
code will be stored in the memory. When unexpected
diagnostic trouble codes appear, check for an intermittent
malfunction.
A diagnostic trouble code may reset. Consult the
”Diagnostic Aids” associated with the diagnostic trouble
code. A physical inspection of the applicable sub–system
most often will resolve the problem.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communicating with the control module
is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located at the lower
left of the instrument panel. The DLC is used to connect to
the Tech 2 Scan tool. Some common uses of the Tech 2
are listed below:
DIdentifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
DClearing DTCs
DPerforming output control tests
DReading serial data

TS24064
Verifying Vehicle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more comprehensive
for vehicles with OBD II system diagnostics. Following a
repair, the technician should perform the following steps:
1.Review and record the Fail Records and/or Freeze
Frame data for the DTC which has been diagnosed
(Freeze Frame data will only be stored for an A or B
type diagnostic and only if the MIL has been
requested).
2.Clear DTC(s).
3.Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the Fail
Records and/or Freeze Frame data.
4.Monitor the DTC status information for the DTC which
has been diagnosed until the diagnostic test
associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps are very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using
A Tech 2 Scan Tool
The procedure for reading diagnostic trouble code(s) is to
use a diagnostic Scan tool. When reading DTC(s), follow
instructions supplied by tool manufacturer.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
IMPORTANT:Do not clear DTCs unless directed to do
so by the service information provided for each diagnostic
procedure. When DTCs are cleared, the Freeze Frame
and Failure Record data which may help diagnose an
intermittent fault will also be erased from memory.
If the fault that caused the DTC to be stored into memory
has been corrected, the Diagnostic Executive will begin to
count the ”warm–up” cycles with no further faults
detected, the DTC will automatically be cleared from the
ECM memory.
To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), use the
diagnostic Scan tool ”clear DTCs” or ”clear information”
function. When clearing DTCs follow instructions
supplied by the tool manufacturer.
When a Tech 2 is not available, DTCs can also be cleared
by disconnecting one of the following sources for at least
thirty (30) seconds.
NOTE: To prevent system damage, the ignition key must
be OFF when disconnecting or reconnecting battery
power.
DThe power source to the control module. Examples:
fuse, pigtail at battery ECM connectors etc.
DThe negative battery cable. (Disconnecting the
negative battery cable will result in the loss of other
on–board memory data, such as preset radio tuning).
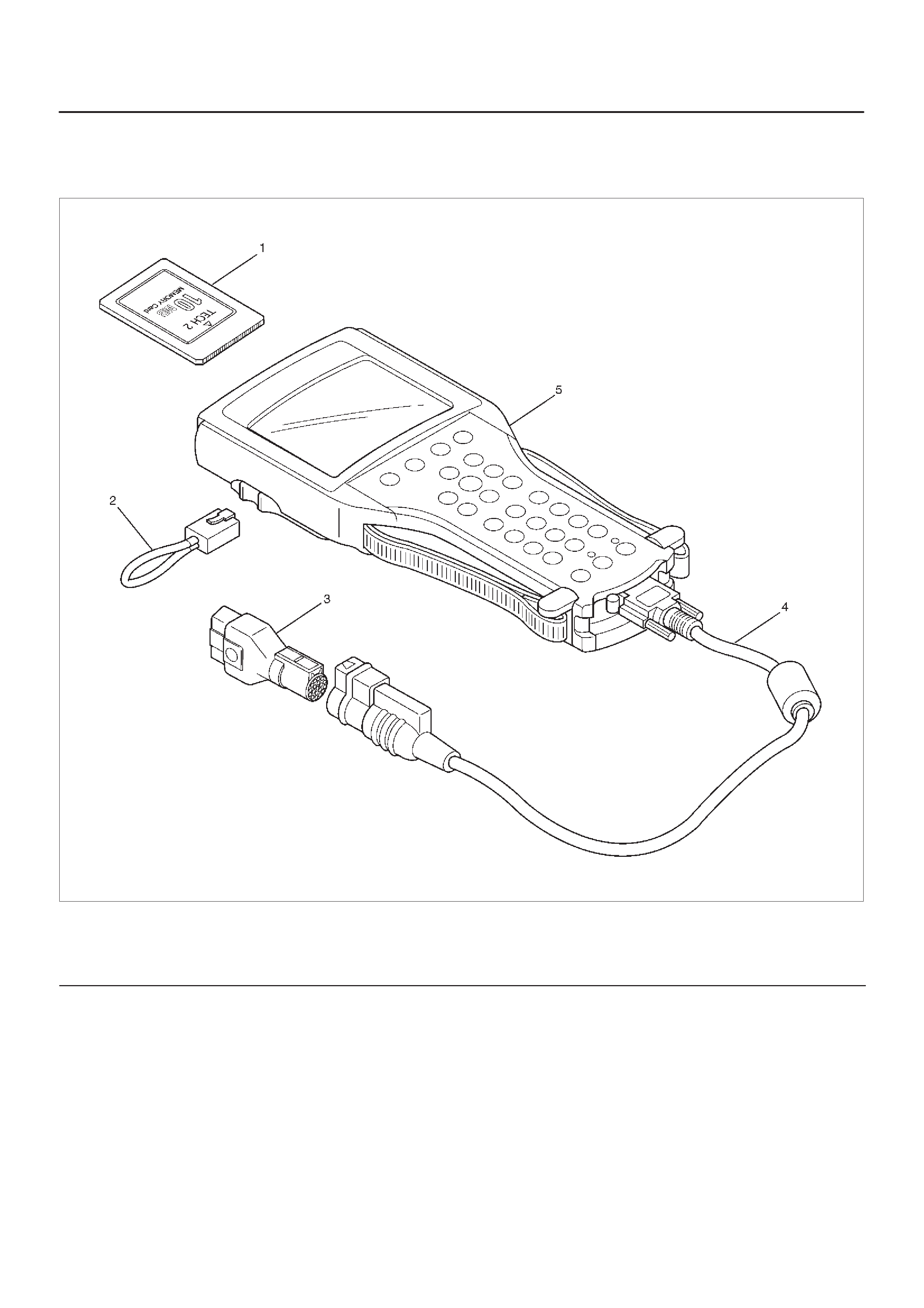
Tech 2
From 98 MY, Isuzu dealer service departments are
recommended to use the T ech 2 scan tool. Please refer to
the Tech 2 user guide.
901RW180
Legend
(1) PCMCIA Card
(2) R232 Loop Back Connector
(3) SAE 16/19 Adaptor
(4) DLC Cable
(5) Tech 2

Tech 2 Features
1.Tech 2 is a 12 volt system. Do not apply 24 volt.
2.After connecting and/or installing, the Vehicle
Communications Interface (VCI) module, PCMCIA
card and DLC connector to the Tech 2, connect the
tool to the vehicle DLC.
3.Make sure the Tech 2 is powered OFF when
removing or installing the PCMCIA card.
4.The PCMCIA card has a capacity of 10 Megabytes
which is 10 times greater than the memory of the T ech
1 Mass Storage Cartridge.
5.The Tech 2 has the capability of two snapshots.
6.The PCMCIA card is sensitive to magnetism and
static electricity, so care should be taken in the
handling of the card.
7.The Tech 2 can plot a graph when replaying a
snapshot.
8.Always return to the Main Menu by pressing the EXIT
key several times before shutting down.
9.To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), open
Application Menu and press “F1: Clear DTC Info”.
Getting Started
DBefore operating the Isuzu PCMCIA card with the
Tech 2, the following steps must be performed:
1.The Isuzu 99 System PCMCIA card (1) inserts into
the Tech 2 (5).
2.Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC cable
(4).
3.Connect the DLC cable to the Tech 2 (5)
4.Make sure the vehicle ignition is off.
5.Connect the Tech 2 SAE 16/19 adapter to the vehicle
DLC.
810RW317
6.Turn on the vehicle ignition.
7.Power the Tech 2 ON and V erify the Tech 2 power up
display.
060RW009
NOTE: The RS232 Loop back connector is only to use for
diagnosis of Tech 2 and refer to user guide of the Tech 2.
Operating Procedure (Example)
The power up screen is displayed when you power up the
tester with the Isuzu system PCMCIA card. Follow the
operating procedure below.
060RX060
060RX058

Menu
DThe following table shows which functions are used
for the available equipment versions.
060RW224
DTC Modes
060RW229
On OBD II vehicles there are five options available in T ech
2 DTC mode to display the enhanced information
available. After selecting DTC, the following menu
appears:
DDTC Info
DFreeze Frame
DFail Records (not all applications)
DClear Info
060RW223
The following is a brief description of each of the sub
menus in DTC Info and DTC. The order in which they
appear here is alphabetical and not necessarily the way
they will appear on the Tech 2.
DTC Information Mode
Use the DTC info mode to search for a specific type of
stored DTC information. There are six choices. The
service manual may instruct the technician to test for
DTCs in a certain manner. Always follow published
service procedures.
060RW221
DTC Status
This selection will display any DTCs that have not run
during the current ignition cycle or have reported a test
failure during this ignition up to a maximum of 33 DTCs.
DTC tests which run and pass will cause that DTC
number to be removed from Tech 2 screen.
Fail This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed during
the present ignition cycle.

History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in the
ECM’s history memory. It will display all type A and B
DTCs that have requested the MIL and have failed within
the last 40 warm-up cycles. In addition, it will display all
type C and type D DTCs that have failed within the last 40
warm-up cycles.
Last Test Failed
This selection will display only DTCs that have failed the
last time the test run. The last test may have run during a
previous ignition cycle if a type A or type B DTC is
displayed. For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure
must have occurred during the current ignition cycle to
appear as Last Test Fail.
MILSVC or Message Request
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option. This selection will report type B DTCs
only after the MIL has been requested.
Not Run Since Code Cleared
This option will display up to 33 DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Test Failed Since Code Cleared
This selection will display all active and history DTCs that
have reported a test failure since the last time DTCs were
cleared. DTCs that last failed more than 40 warm-up
cycles before this option is selected will not be displayed.
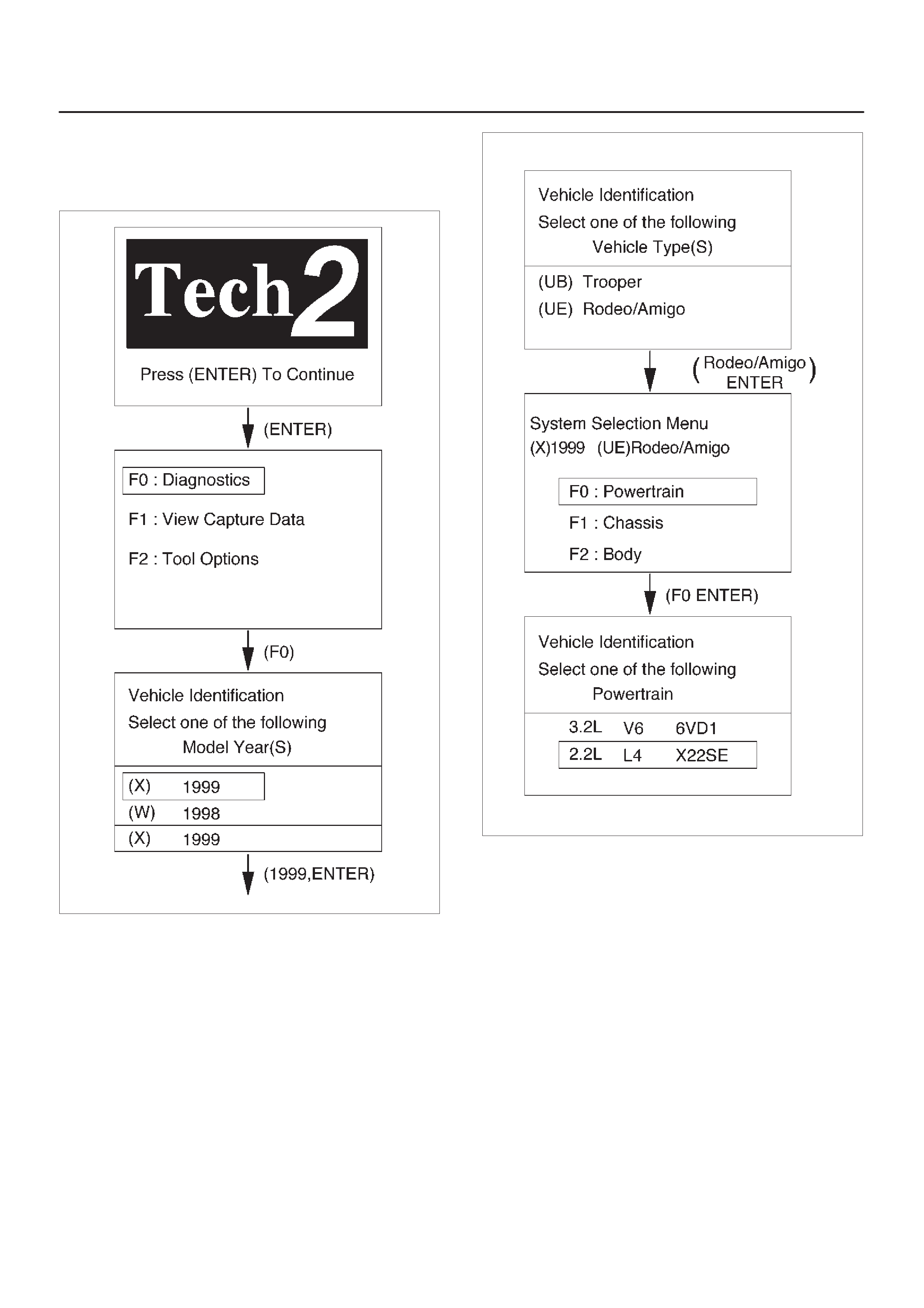
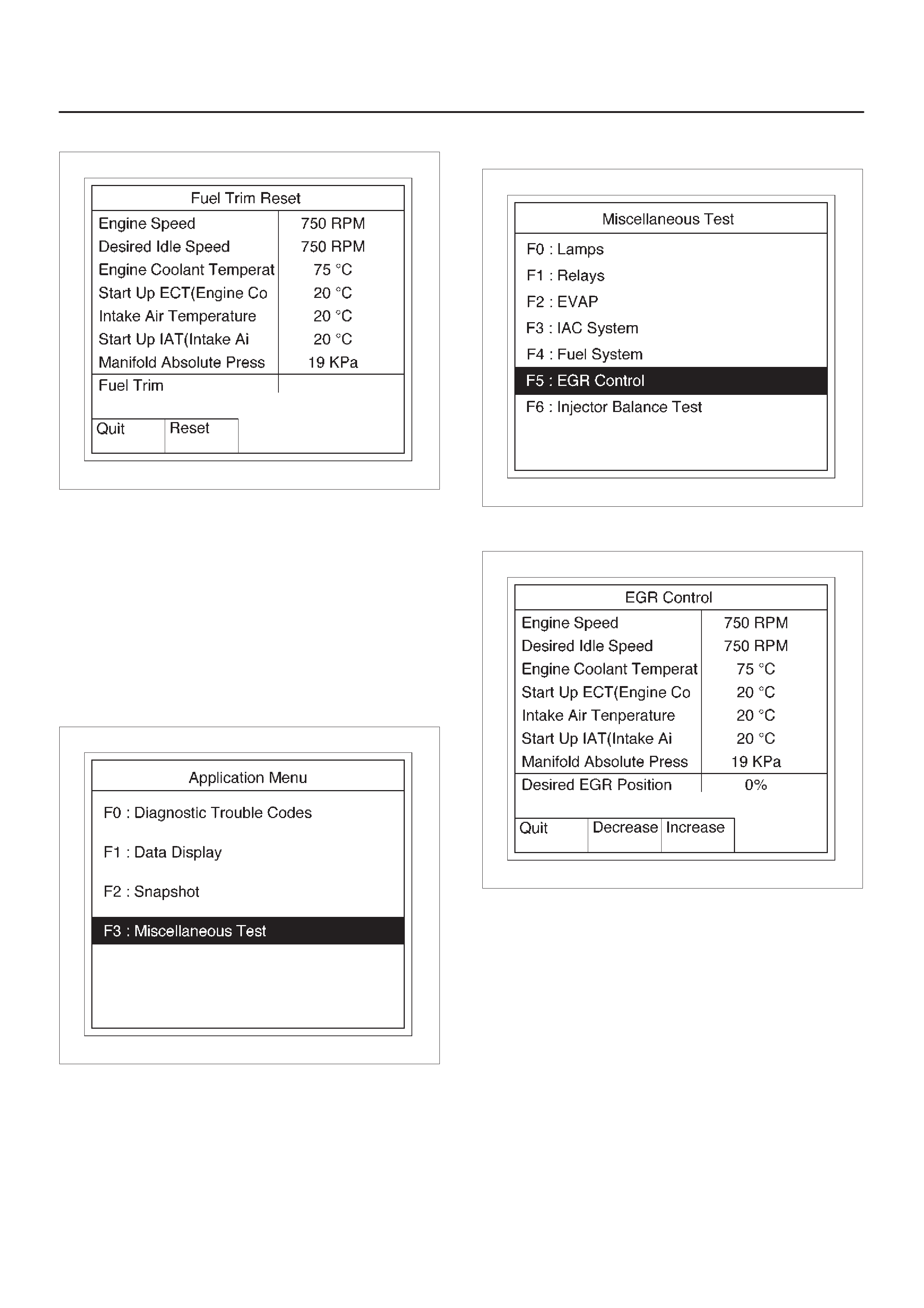
Miscellaneous Test
This test consists of eight menus-Lights, Relays, EVAP,
IAC System, Fuel System, EGR Control, Variable Intake
Manifold Solenoid, and Injector Balance Tests.
In these tests, Tech 2 sends operating signals to the
systems to confirm their operations thereby to judge the
normality of electric circuits.
To judge intermittent trouble,
1.Confirm DTC freeze frame data, and match the
freeze frame data as test conditions with the data list
displayed by Miscellaneous Test.
2.Confirm DTC setting conditions, and match the
setting conditions as test conditions with the data list
displayed by Miscellaneous Test.
Lamps Test
This test is conducted check MIL and Low Fuel Lamp for
its working.
Tech2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Run the Engine at idle.
3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4.Select F0:Lamps Test in the Miscellaneous Test.
060RX043
060RX044

5.Select F0:Malfunction Indicator Lamp.
060RX019
6.Push “On” soft key.
7.Make sure Lamp illuminates.
8.If lamp illuminates, the Lamp is operating correctly.
DF1; Up Shift Lamp = Not Used
DF2; Low Fuel Lamp = Not Used
Relays Test
This test is conducted to check Fuel Pump Relay, A/C
Clutch Low Fan and High Fan for prepor operation.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Ignition SW is “On”.
3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4.Select F1:Relay Test in the Miscellaneous Test.
060RX046
5.Select F0:Fuel Pump Relay.
060RX047
6.Push “On” soft key.
060RX022
7.Control Fuel Pump Relay and check a data list.
8.If the data list chenges, the Fuel Pump Relay is
normal.
9.Select F1:A/C Clutch Relay.
10.*Run the Engine at idle.
11.Turn on Air Condtioning.
060RX023
12.Push “On” and “Off” of soft key.
13.Control A/C Clutch Relay and check a data list.
14.If the data list changes, the A/C Clutch Relay is
normal.
15.Select F2: Low Fan Relay.
060RX048
16.Push “On” and “Off” of soft key.
17.Control Low Fan Relay and check a data list.
18.If the data list changes, the Low Fan Relay is normal.
19.Run the Fan Motor.
20.Select F3: High Fan Relay.
060RX049
21.Push “On” and “Off” of soft key.
22.Control High Fan Relay and check a data list.
If the data list changes, the High Fan Relay is normal.
23.Run the Fan Motor.

EVAP Test
This test is conducted check EV AP system for its working.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Run the Engine at idle.
3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4.Select F2:EVAP Test in the Miscellaneous Test.
060RX050
5.Select F0: Purge Solenoid.
060RX025
6.Push “Decrease” or “Increase” soft key.
060RX026
7.Control EVAP Purge Solenoid and check a data list.
8.If the data list changes, the purge Solenoid is normal.
Ignition SW is “On”.
DF1; Vent Solenoid = Not Used
Idle Air Control System Test
This test is conducted check to IAC system for proper
operation.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Run the Engine at idle.

3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4.Select F3: IAC System Test in the Miscellaneous
Test.
060RX051
5.Select F1: IAC Control Test.
060RX052
6.Push “Increase” or “Decrease” soft key.
7.Control IAC system and check a data list.
DF0: IAC Control
060RX015
8.Select F1: IAC Reset.
9.Push “Reset IAC” soft key.
10.Control IAC Reset and check data list.

11.If data list changes, the IAC has been Reset.
060RW231–1
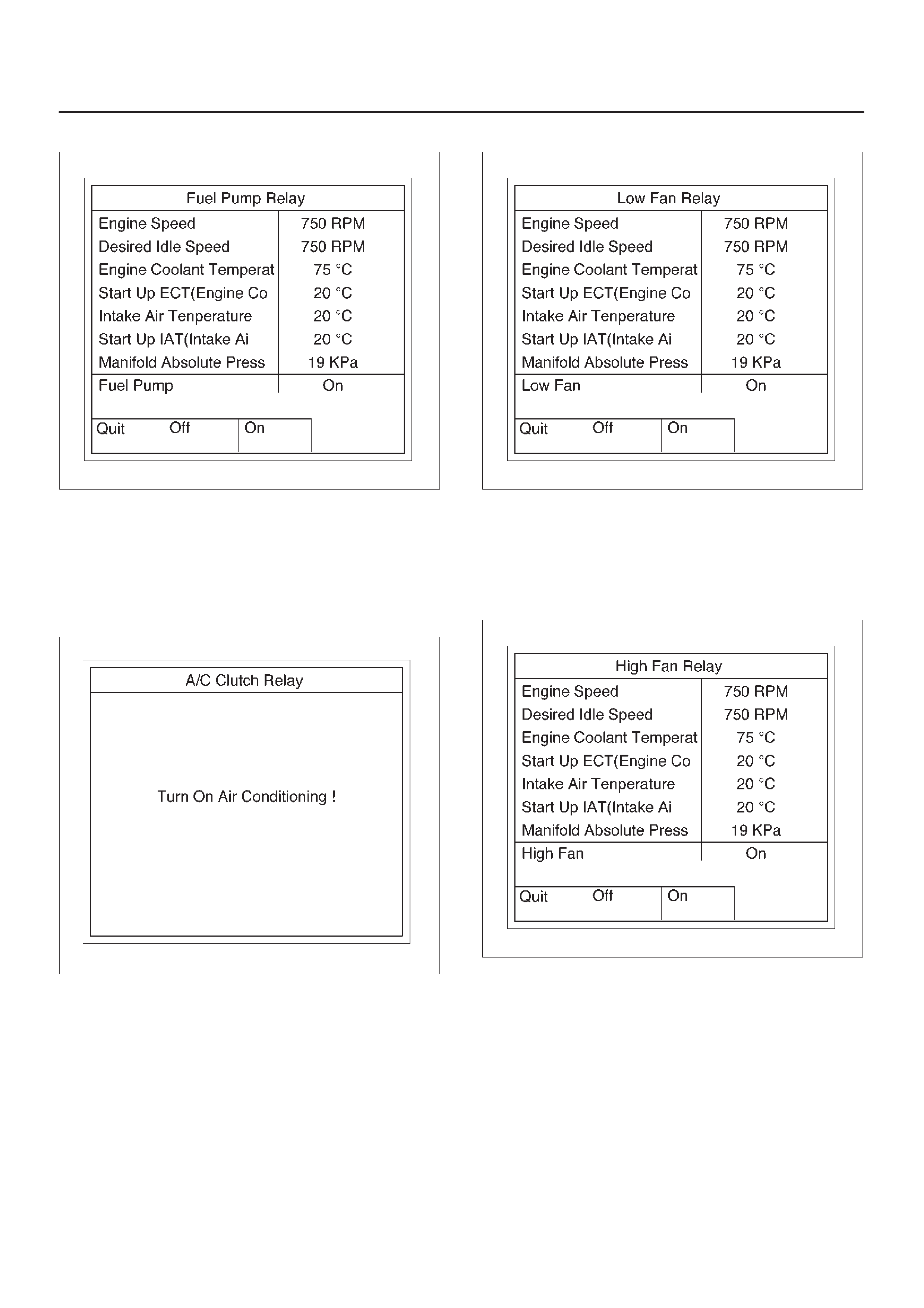
Fuel System Test
This test is conducted check Fuel Level Gauge for proper
operation.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Ignition SW is “On”.
3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4.Select F4: Fuel System in the Miscellaneous Menu.
060RX053
5.Select F0: Fuel Trim Reset.
060RX028
6.Push “Reset” of soft key.
060RX029
DF1; Fuel Gauge Level = Not Used
EGR Control Test
This test is conducted check EGR valve for proper
operation.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Run the Engine at idle.
3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4. Select F5: EGR Control Test in the Miscellaneous
Test.
060RX054
5.Control EGR Valve and check data list.
060RX017
6.If the change, the EGR Control is normal.
Injector Balance Test
This test is conducted to make sure the appropriate
electric signals are being sent to injectors Nos. 1–6.
Tech 2 must be used for this test.
Test Procedure:
1.Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC.
2.Run the Engine at idle.
3.Select F3: Miscellaneous Test in the Application
Menu.
060RW228
4.Select F6: Injector Balance Test in the Miscellaneous
Test.
060RX055
5.Select injector number and push “injector off” of soft
key.
060RW230–1
6.Make sure of engine speed change.
7.If engine speed changes, the injector electric circuit is
normal.
If engine speed does not change, the injector electric
circuit or the injector itself is not normal.
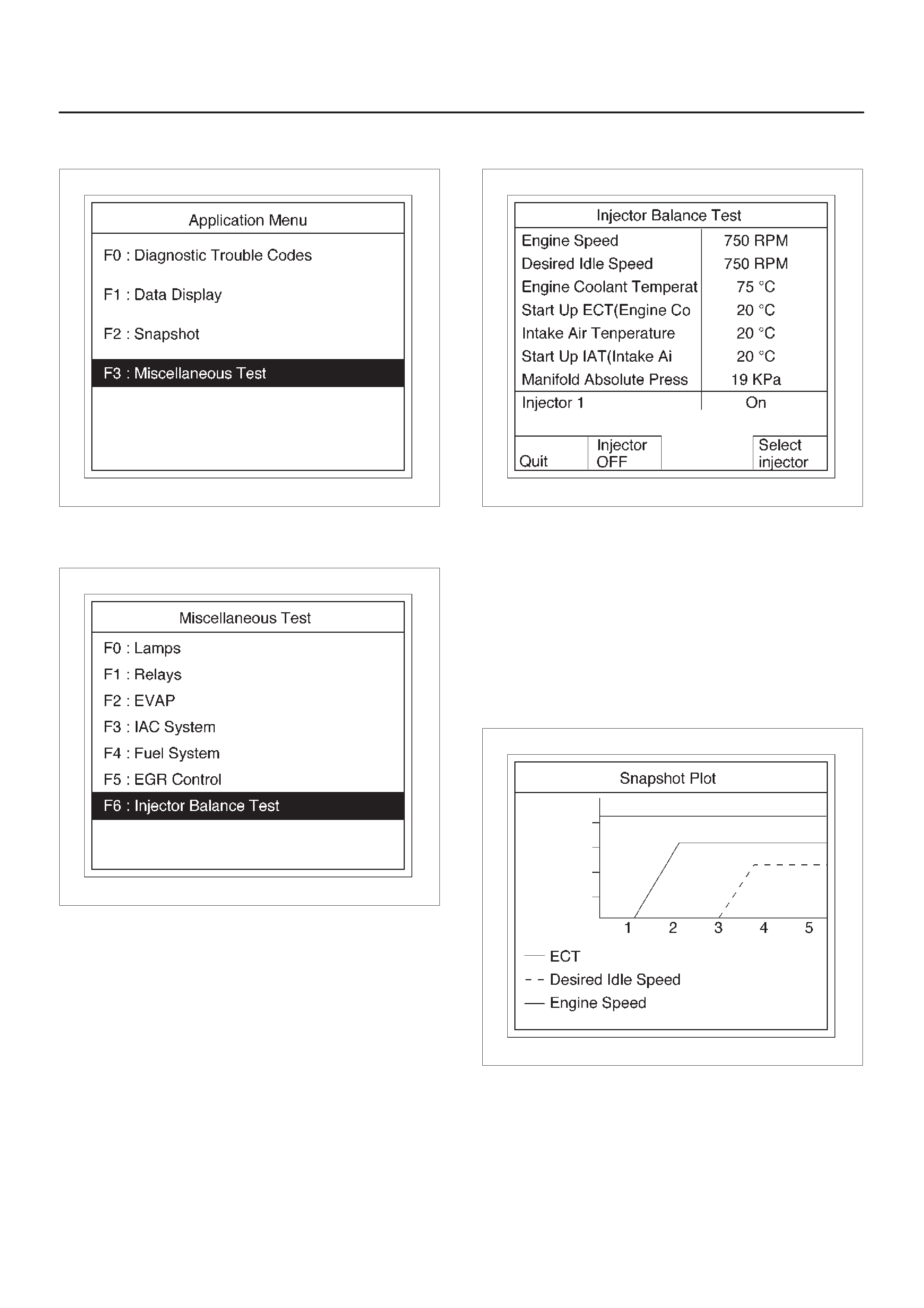
Plotting Snapshot Graph
This test selects several necessary items from the data
list to plot graphs and makes data comparison on a long
term basis. It is an effective test particularly in emission
related evaluations.
060RX037
For trouble diagnosis, you can collect graphic data (snap
shot) directly from the vehicle. You can replay the
snapshot data as needed. There fore, accurate diagnosis
is possible, even though the vehicle is not available.
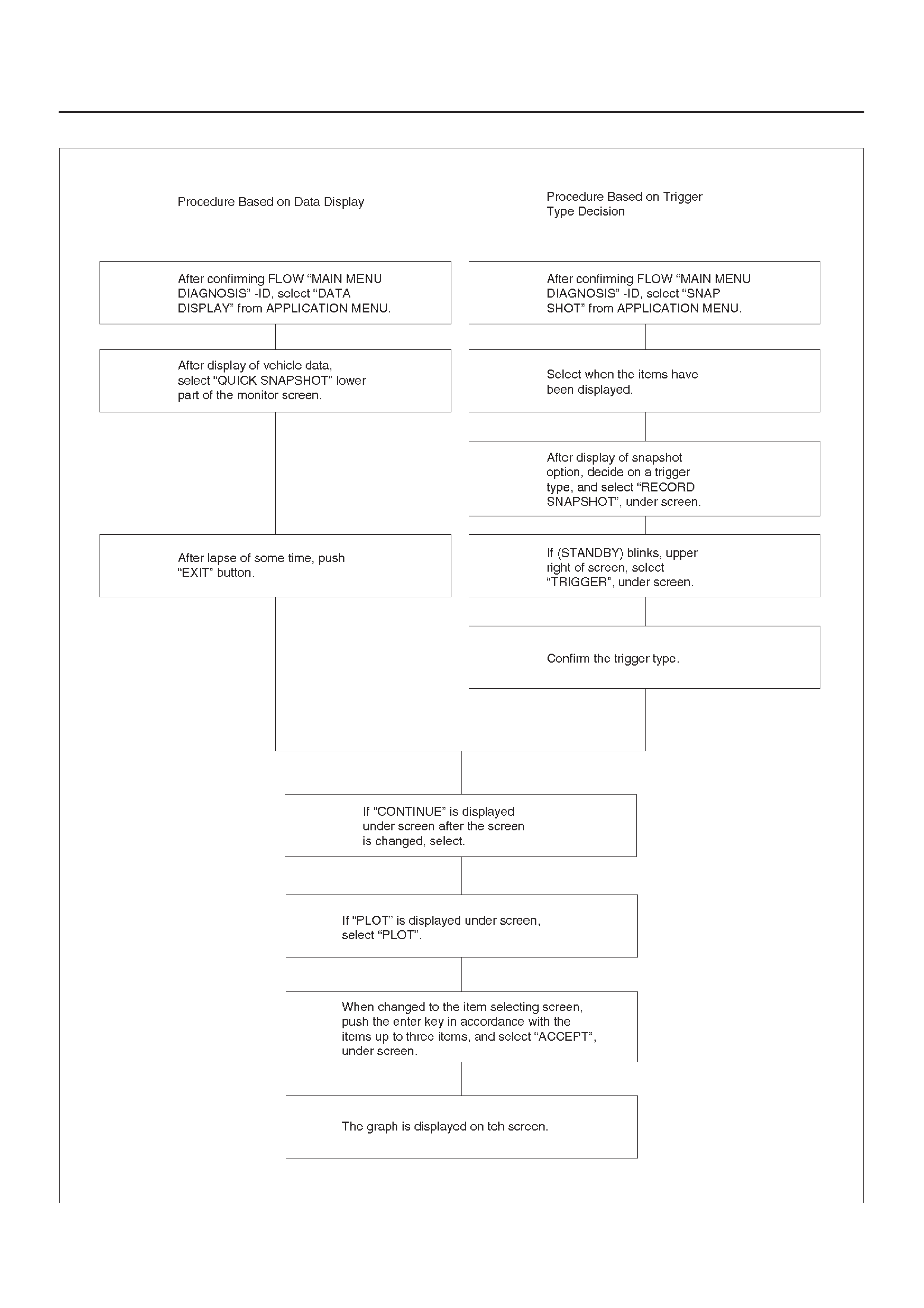
Plotting Graph Flow Chart (Plotting graph after obtaining vehicle information)
060RX085

Flow Chart for Snapshot Replay (Plotting Graph)
060RX040

PRIMARY SYSTEM–BASED
DIAGNOSTICS
Primary System–Based Diagnostics
There are primary system–based diagnostics which
evaluate system operation and its effect on vehicle
emissions. The primary system–based diagnostics are
listed below with a brief description of the diagnostic
function:
Oxygen Sensor Diagnosis
The fuel control heated oxygen sensor (HO2S 1) is
diagnosed for the following conditions:
DHeater performance (time to activity on cold start)
DSlow response
DResponse time (time to switch R/L or L/R)
DInactive signal (output steady at bias voltage –
approx. 450 mV)
DSignal fixed high
DSignal fixed low
The catalyst monitor heated oxygen sensor (HO2S 2) is
diagnosed for the following conditions:
DHeater performance (time to activity on cold start).
DSignal fixed low during steady state conditions or
power enrichment (hard acceleration when a rich
mixture should be indicated).
DSignal fixed high during steady state conditions or
deceleration mode (deceleration when a lean mixture
should be indicated).
DInactive sensor (output steady at approx. 438 mV).
If the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal
are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must
be replaced. DO NOT attempt to repair the wiring,
connector or terminals. In order for the sensor to function
properly, it must have clean reference air provided to it.
This clean air reference is obtained by way of the oxygen
sensor wire(s). Any attempt to repair the wires, connector
or terminals could result in the obstruction of the
reference air and degrade oxygen sensor performance.
Refer to On–Vehicle Service, Heated Oxygen Sensors.
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensors
The main function of the fuel control heated oxygen
sensors is to provide the control module with exhaust
stream oxygen content information to allow proper fueling
and maintain emissions within mandated levels. After it
reaches operating temperature, the sensor will generate
a voltage, inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen
present in the exhaust gases. The control module uses
the signal voltage from the fuel control heated oxygen
sensors while in ”Closed Loop” to adjust fuel injector
pulse width. While in ”Closed Loop”, the ECM can adjust
fuel delivery to maintain an air/fuel ratio which allows the
best combination of emission control and driveability . The
fuel control heated oxygen sensors are also used to
determine catalyst efficiency.
HO2S Heater
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the amount
of time required for ”Closed Loop” fuel control to begin
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The
oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of
time required for fuel control sensor (HO2S 1) to become
active. Oxygen sensor heaters are required by the
catalyst monitor sensor (HO2S 2) to maintain a
sufficiently high temperature which allows accurate
exhaust oxygen content readings further away from the
engine.
ON–BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM CHECK
D06RX108
Circuit Description
The on–board diagnostic system check is the starting
point for any driveability complaint diagnosis. Before
using this procedure, perform a careful visual/physical
check of the ECM and engine grounds for cleanliness and
tightness.
The on–board diagnostic system check is an organized
approach to identifying a problem created by an
electronic engine control system malfunction.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for poor connections or a damaged
harness. Inspect the ECM harness and connectors for
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal–to–wire connection,
and damaged harness.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The MIL (”Check Engine” lamp) should be ON
steady with the ignition ON/engine OFF. If not,
isolate the malfunction in the MIL circuit.
2. Checks the Class 2 data circuit and ensures that the
ECM is able to transmit serial data.
3. This test ensures that the ECM is capable of
controlling the MIL and the MIL driver circuit is not
shorted to ground.
4. If the engine will not start, the Cranks But Will Not
Run chart should be used to diagnose the condition.
7. A Tech 2 parameter which is not within the typical
range may help to isolate the area which is causing
the problem.
On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
11. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Observe the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL or
”Check Engine lamp”).
Is the MIL (”Check Engine lamp”) ON? —Go to Step 2 Go to No MIL
21. Ignition OFF.
2. Install a Tech 2.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Attempt to display ECM engine data with the T ech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display ECM data? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 8
31. Using the Tech 2 output tests function, select MIL
dash lamp control and command the MIL OFF.
2. Observe the MIL.
Did the MIL turn OFF? —Go to Step 4
Go to MIL
(”Check
Engine
Lamp”) On
Steady
4Attempt to start the engine.
Did the engine start and continue to run? —Go to Step 5
Go to Cranks
But Will Not
Run
5Select ”Display DTCs” with the Tech 2.
Are any DTCs stored? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6Are two or more of the following DTCs stored? P0107,
P0113, P0118, P0122, P0123.
—
Go to
“Multiple
ECM
Information
Sensor DTCs
Set”
Go to
applicable
DTC table
7Compare ECM data values displayed on the Tech 2 to
the typical engine scan data values.
Are the displayed values normal or close to the typical
values? —
Go to “Typial
Scan” Data
Value
Go to
indicated
Component
System
Checks
81. Ignition OFF, disconnect the ECM.
2. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
3. Check the Class 2 data circuit for an open, short to
ground, or short to voltage. Also, check the DLC
ignition feed circuit for an open or short to ground
and the DLC ground circuits for an open.
4. If a problem found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 2 Go to Step 9
91. Attempt to reprogram the ECM. Refer to Engine
Control Module (ECM) in On–Vehicle Service.
2. Attempt to display ECM data with the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display ECM engine data? —Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
A/C CLUTCH CONTROL CIRCUIT DIAGNOSIS
D06RX107
Circuit Description
When air conditioning and blower fan are selected, and if
the system has a sufficient refrigerent charge, a 12–volt
signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the engine
control module (ECM). The A/C request signal may be
temporarily cancelled during system operation by the
electronic thermostat in the evaporator case. The
electronic thermostat may intermittently remove the
control circuit ground for the A/C thermostat relay to
prevent the evaporator from forming ice. When the A/C
request signal is received by the ECM, the ECM supplies
a ground from the compressor clutch relay if the engine
operating conditions are within acceptable ranges. With
the A/C compressor relay energized, battery voltage is
supplied to the compressor clutch coil.
The ECM will enable the compressor clutch to engage
whenever A/C has been selected with the engine running,
unless any of the following conditions are present:
DThe throttle is greater than 90%.
DThe ignition voltage is below 10.5 volts.
DThe engine speed is greater than 4500 RPM for 5
seconds or 5400 RPM.
DThe engine coolant temperature (ECT) is greater
than 125°C (257°F)
DThe intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 5°C
(41°F).
DThe power steering pressure switch signals a high
pressure condition position.
Diagnostic Aids
To diagnose an intermittent fault, check for the following
conditions:
DPoor connection at the ECM – Inspect harness
connections for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery voltage,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the A/C clutch while moving connnectors and
wiring harnesses related to the A/C. A sudden clutch
malfunction will indicate the source of the intermittent.
A/C Clutch Diagnosis
This chart should be used for diagnosing the electrical
portion of the A/C compressor clutch circuit. A Tech 2 will
be used in diagnosing the system. The Tech 2 has the
ability to read the A/C request input to the ECM. The Tech
2 can display when the ECM has commended the A/C
clutch ON. The Tech 2 should have the ability to override
the A/C request signal and energize the A/C compressor
relay.
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diagnosis
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTCs.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P1546.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1546 ”Ran and
Passed”? —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the A/C Compressor Relay from the
Underhood Electrical Center.
3. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
4. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the Fused pins of the A/C Compressor Clutch
Relat connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4Check the suspect circuit(s) between the A/C
Compressor Clutch Relay connector and the Fuse for
the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Controlm Module (ECM)
connectors from the ECM.
3. Check the A/C Compressor Clutch Relay control
circuit between the ECM and Underhood Electrical
Center for the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
61. Reinstall the A/C Compressor Clutch Relay.
2. Using a fused jumper, ground the A/C Compressor
Clutch Relay control circuit at the ECM connector.
3. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
Does the A/C Compressor turn ON? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 7
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Check the A/C Compressor Clutch circuit between
the A/C Compressor Clutch Relay and A/C
Compressor Clutch for the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8Replace the A/C Compressor Clutch Relay.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———
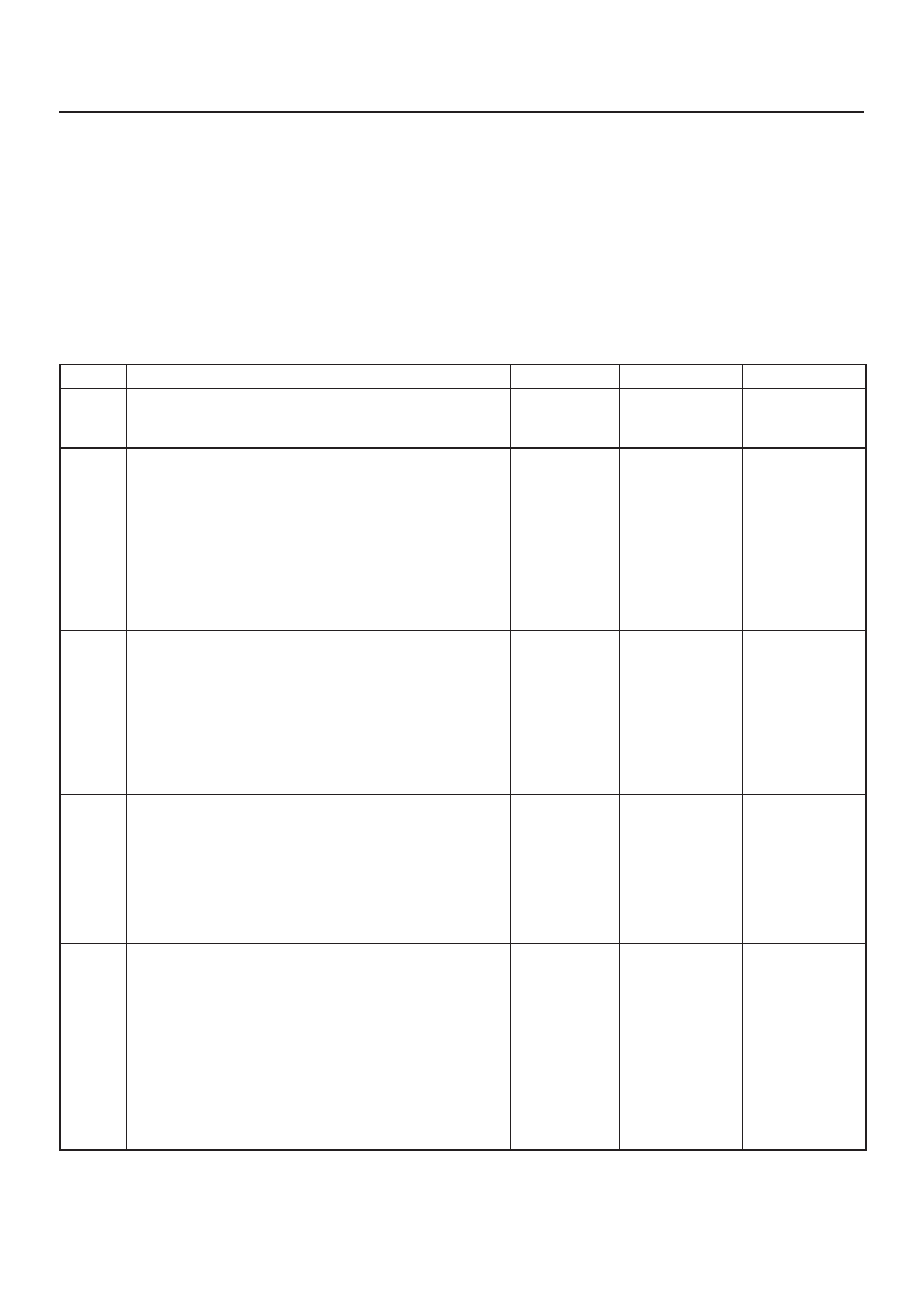
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
DIAGNOSIS
If the engine cranks but will not run or immediately stalls,
the Engine Cranks But Will Not Start chart must be used
to determine if the failure is in the ignition system or the
fuel system.
VISUAL CHECK OF THE
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CANISTER
014RX001
DIf the canister is cracked or damaged, replace the
canister.
DIf fuel is leaking from the canister, replace the canister
and check hoses and hose routing.
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE
0006
The Tech 2 displays the IAC pintle position in counts. A
count of ”0” indicates the ECM is commanding the IAC
pintle to be driven all the way into a fully–seated position.
This is usually caused by a vacuum leak.
The higher the number of counts, the more air is being
commanded to bypass the throttle blade. In order to
diagnose the IAC system, refer to IAC System Check.
For other possible causes of idle problems, refer to
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling in Symptoms.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
DIAGNOSIS
014RX002
To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes, use a Tech 2.
901RX031

IMPORTANT:Use of a Tech 2 is recommended to clear
diagnostic trouble codes from the ECM memory.Diagnostic trouble codes can also be cleared by turning
the ignition OFF and disconnecting the battery powerfrom the ECM for 30 seconds. Turning off the ignition and
disconnecting the battery power from the ECM will cause
all diagnostic information in the ECM memory to becleared. Therefore, all the diagnostic tests will have to bere–run.
Since the ECM can have a failure which may affect only
one circuit, following the diagnostic procedures in this
section will determine which circuit has a problem andwhere it is.If a diagnostic chart indicates that the ECM connectionsor the ECM is the cause of a problem, and the ECM isreplaced, but this does not correct the problem, one of the
following may be the reason:
DThere is a problem with the ECM terminalconnections. The terminals may have to be removedfrom the connector in order to check them properly.
DThe problem is intermittent. This means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is being
checked. In this case, make a careful physicalinspection of all components and wiring associated
with the affected system and refer to the Symptoms
portion of the manual.
DThere is a shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness.
Solenoids and relays are turned ON and OFF by the
ECM using internal electronic switches called drivers.
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness will not
damage the ECM but will cause the solenoid or relay
to be inoperative.
MULTIPLE ECM INFORMATION
SENSOR DTCs SET
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) monitors various
sensors to determine the engine operating conditions.
The ECM controls fuel delivery, spark advance, and
emission control device operation based on the sensor
inputs.
The ECM provides a sensor ground to all of the sensors.
The ECM applies 5 volts through a pull–up resistor, and
determines the status of the following sensors by
monitoring the voltage present between the 5–volt supply
and the resistor:
DThe Fuel Tank Vapor Pressure Sensor
DThe throttle position (TP) sensor
DThe manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
The ECM provides the following sensors with a 5–volt
reference and a sensor ground signal:
DThe Linear exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve
DThe A/C Pressure Sensor
The ECM monitors the separate feedback signals from
these sensors in order to determine their operating
status.
Diagnostic Aids
Be sure to inspect ECM and engine grounds for being se-
cure and clean.
A short to voltage in one of the sensor input circuits may
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
DP0108
DP0113
DP0118
DP0123
If a sensor input circuit has been shorted to voltage, en-
sure that the sensor is not damaged. A damaged sensor
will continue to indicate a high or low voltage after the af-
fected circuit has been repaired. If the sensor has been
damaged, replace it.
An open in the sensor ground circuit between the ECM
and the splice will cause one or more of the following
DTCs to be set:
DP0108
DP0113
DP0118
DP0123
A short to ground in the 5–volt reference A circuit will
cause one or more of the following DTCs to be set:
DP0107
DP0122
DP0112
DP0117
DP0454
DP0405
DP0532
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM. Inspect the harness
connectors for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, and a poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness is not damaged, observe an
affected sensor’s displayed value on the Tech 2 with
the ignition ON and the engine OFF while you move
the connectors and the wiring harnesses related to
the following sensors:
DIAT
DECT
DTP
DMAP
DEGR
DA/C Pressure Sensor
Multiple ECM Information Sensor DTCs Set
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Turn the ignition OFF, disconnect the ECM.
2. Turn the ignition ON, check the 5 volt reference
circuits for the following conditions:
DA poor connection at the ECM.
DAn open between the ECM connector and the
splice.
DA short to ground.
DA short to voltage.
Is there an open or short? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3Repair the open or short.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
4Check the sensor ground circuit for the following
conditions:
DA poor connection at the ECM or the affected
sensors.
DAn open between the ECM connector and the
affected sensors.
Is there an open or a poor connection? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair the open or the poor connection.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
6Measure the voltage between the EGR pintle position
sensor signal circuit at the ECM harness connector and
ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 7 Go to Step 13
7Measure the voltage between the MAP sensor signal
circuit at the ECM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 8 Go to Step 14
8Measure the voltage between the TP sensor signal
circuit at the ECM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 9 Go to Step 15
9Measure the voltage between the IAT sensor signal
circuit at the ECM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 10 Go to Step 16
10 Measure the voltage between the ECT sensor signal
circuit at the ECM harness connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 20 Go to Step 17
11 Measure the voltage between the A/C Pressure
Sensor circut at the ECM harness connector and
ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 13 Go to Step 19
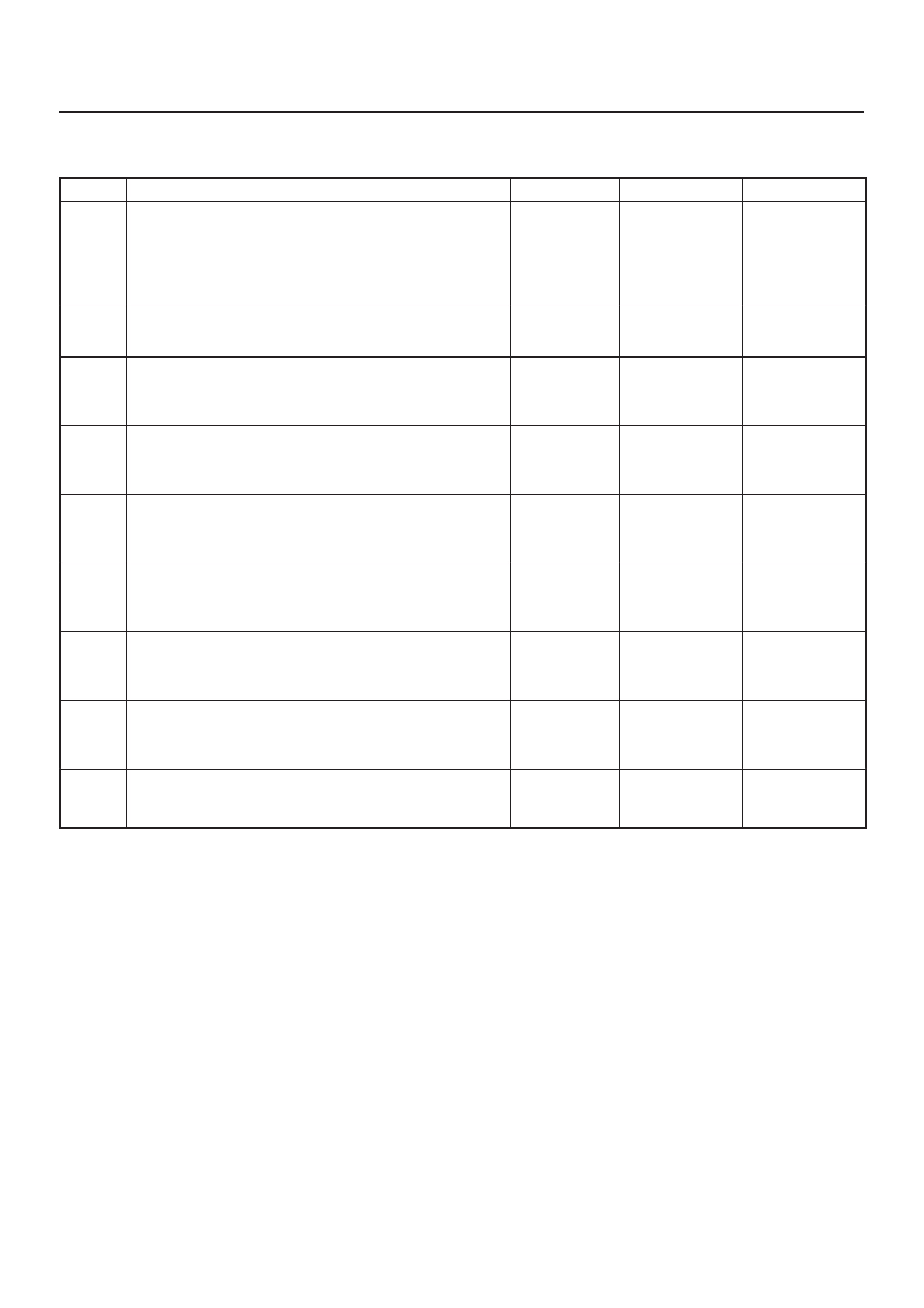
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 1. Disconnect the EGR valve.
2. Measure the voltage between the EGR pintle
position sensor signal circuit at the ECM harness
connector and ground.
Does the voltage measure near the specified value? 0 V Go to Step 12 Go to Step 17
13 Replace the EGR valve.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
14 Locate and repair the short to voltage in the MAP
sensor signal circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
15 Locate and repair the short to voltage in the TP sensor
signal circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
16 Locate and repair the short to voltage in the IA T sensor
signal circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
17 Locate and repair the short to voltage in the ECT
sensor signal circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
18 Locate and repair the short to voltage in the A/C
Pressure Sensor circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
19 Locate and repair the short to voltage in the EGR pintle
position sensor signal circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
20 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
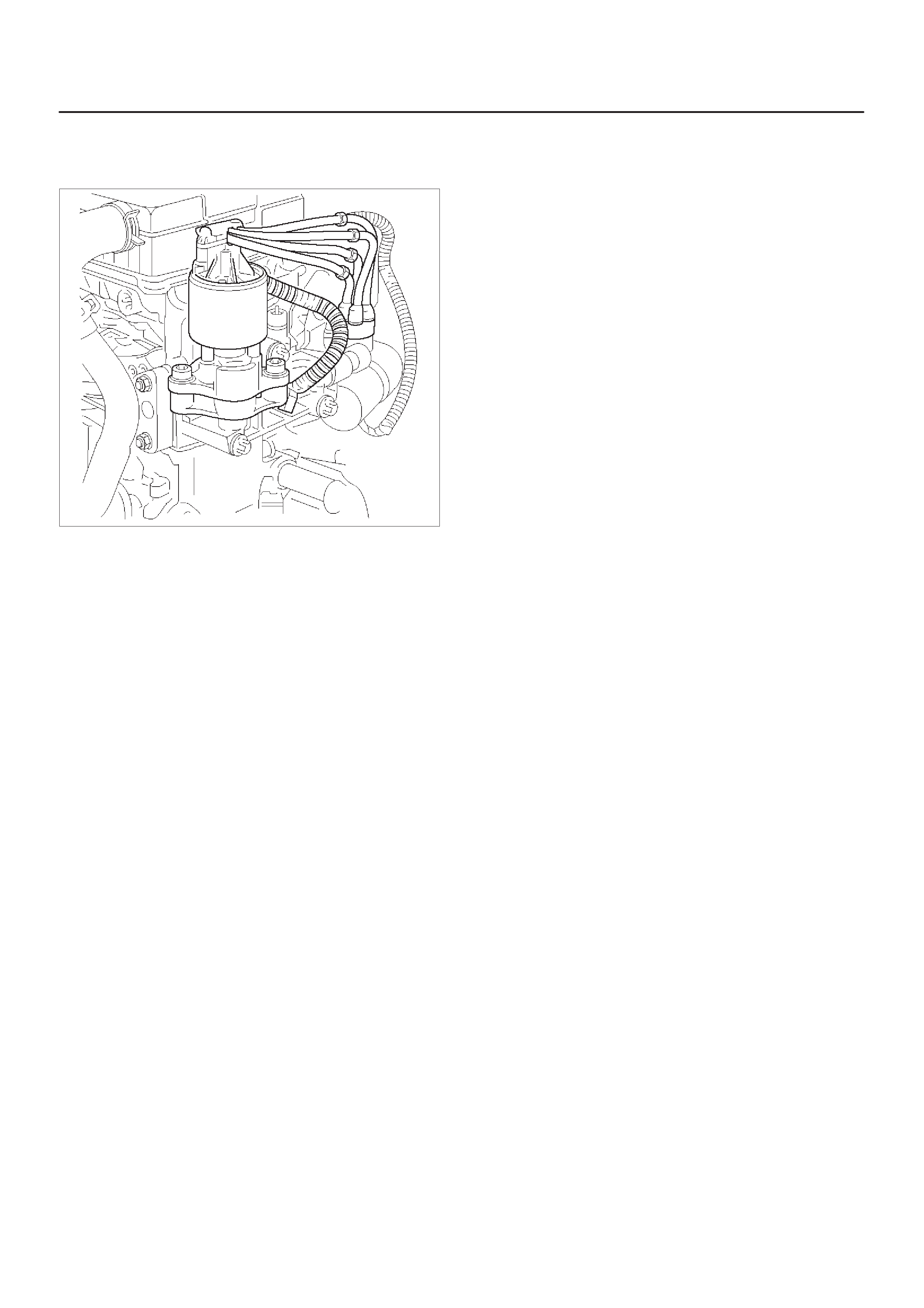

EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) DIAGNOSIS
057RX001
An EGR flow check diagnosis of the linear EGR system is
covered by DTC P0401, P0404, and P0405. If EGR
diagnostic trouble code P0401 is encountered, refer to
the DTC charts.
ENGINE Tech 2 DATA DEFINITIONS
AND RANGES
A/C CLUTCH – Tech 2 Displays ON or OFF
Indicates whether the ECM has commanded the A/C
clutch ON. Used in A/C system diagnostics.
A/C REQUEST – Tech 2 Displays YES or NO
Indicates the state of the A/C request input circuit from the
HVAC controls. The ECM uses the A/C request signal to
determine whether A/C compressor operation is being
requested.
AIR/FUEL RATIO – Tech 2 Range 0.0–25.5
Air/fuel ratio indicates the ECM commanded value. In
”Closed Loop”, the air/fuel ratio should normally be
displayed around ”14.2–14.7.” A lower air/fuel ratio
indicates a richer commanded mixture, which may be
seen during power enrichment or TWC protection modes.
A higher air/fuel ratio indicates a leaner commanded
mixture. This can be seen during deceleration fuel mode.
BARO kPa – Tech 2 Range 10–105 kPa/0.00–5.00
Volts
The barometric pressure reading is determined from the
MAP sensor signal monitored during key up and wide
open throttle (WOT) conditions. The barometric pressure
is used to compensate for altitude differences and is
normally displayed around ”61–104” depending on
altitude and barometric pressure.
CMP ACT. COUNTER – Cam Position Activity
DECEL FUEL MODE – Tech 2 Displays ACTIVE or
INACTIVE
”ACTIVE” displayed indicates that the ECM has detected
conditions appropriate to operate in deceleration fuel
mode. The ECM will command the deceleration fuel
mode when it detects a closed throttle position while the
vehicle is traveling over 20 mph. While in the deceleration
fuel mode, the ECM will decrease the amount of fuel
delivered by entering ”Open Loop” and decreasing the
injector pulse width.
DESIRED EGR POS. – Tech 2 Range 0%–100%
Represents the EGR pintle position that the ECM is
commanding.
DESIRED IDLE – Tech 2 Range 0–3187 RPM
The idle speed that the ECM is commanding. The ECM
will compensate for various engine loads based on engine
coolant temperature, to keep the engine at the desired
speed.
ECT – (Engine Coolant Temperature) Tech 2 Range
–40°C to 151°C (–40°F to 304°F)
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is mounted in the
coolant stream and sends engine temperature
information to the ECM. The ECM applies 5 volts to the
ECT sensor circuit. The sensor is a thermistor which
changes internal resistance as the temperature changes.
When the sensor is cold (high resistance), the ECM
monitors a high signal voltage and interprets that as a cold
engine. As the sensor warms (decreasing resistance),
the voltage signal will decrease and the ECM will interpret
the lower voltage as a warm engine.
EGR DUTY CYCLE – Tech 2 Range 0%–100%
Represents the EGR valve driver PWM signal from the
ECM. A duty cycle of 0% indicates that no EGR flow is
being commanded; a 100% duty cycle indicates
maximum EGR flow commanded.
EGR FEEDBACK – Tech 2 Range 0.00–5.00 Volts
Indicates the EGR pintle position sensor signal voltage
being monitored by the ECM. A low voltage indicates a
fully extended pintle (closed valve); a voltage near 5 volts
indicates a retracted pintle (open valve).
EGR TEST COUNT – Tech 2 Range 0–255
Indicates the number of EGR flow test samples collected
during the current ignition cycle. Under normal operation,
only one sample is allowed during an ignition cycle. If the
ECM battery feed has been disconnected or a DTC
P0401 has been cleared, 10 EGR flow test samples will
be allowed during the ignition cycle. This is to allow repair
verification during a single ignition cycle.
ENGINE LOAD – Tech 2 Range 0%–100%
Engine load is calculated by the ECM from engine speed
and MAP sensor readings. Engine load should increase
with an increase in RPM or air flow.
ENGINE RUN TIME – Tech 2 Range 00:00:00–
99:99:99 Hrs:Min:Sec
Indicates the time elapsed since the engine was started.
If the engine is stopped, engine run time will be reset to
00:00:00.
ENGINE SPEED – Range 0–9999 RPM
Engine speed is computed by the ECM from the 58X
reference input. It should remain close to desired idle
under various engine loads with engine idling.

FUEL PUMP – Tech 2 Displays ON or OFF
Indicates the ECM commanded state of the fuel pump
relay driver circuit.
FUEL TRIM CELL – Tech 2 Range 0–21
The fuel trim cell is dependent upon engine speed and
MAF sensor readings. A plot of RPM vs. MAF is divided
into 22 cells. Fuel trim cell indicates which cell is currently
active.
FUEL TRIM LEARN – Tech 2 Displays NO or YES
When conditions are appropriate for enabling long term
fuel trim corrections, fuel trim learn will display YES. This
indicates that the long term fuel trim is responding to the
short term fuel trim. If the fuel trim learn displays NO, then
long term fuel trim will not respond to changes in short
term fuel trim.
HO2S BANK 1, SEN. 1 – Tech 2 Range 0–1000 mV
Represents the fuel control exhaust oxygen sensor
output voltage. Should fluctuate constantly within a range
between 10 mV (lean exhaust) and 1000 mV (rich
exhaust) while operating in ”Closed Loop”.
HO2S BANK 1, SEN. 1 – Tech 2 Displays NOT
READY or READY
Indicates the status of the exhaust oxygen sensor. The
Tech 2 will indicate that the exhaust oxygen sensor is
ready when the ECM detects a fluctuating HO2S voltage
sufficient to allow ”Closed Loop” operation. This will not
occur unless the exhaust sensor is warmed up.
HO2S WARM UP TIME BANK 1, SEN. 1 – Tech 2
Range 00:00:00–99:99:99 HRS:MIN:SEC
Indicates warm–up time for each HO2S. The HO2S
warm–up time is used for the HO2S heater test. The ECM
will run the heater test only after a cold start (determined
by engine coolant and intake air temperature at the time
of start–up) and only once during an ignition cycle. When
the engine is started the ECM will monitor the HO2S
voltage. When the HO2S voltage indicates a sufficiently
active sensor, the ECM looks at how much time has
elapsed since start–up. If the ECM determines that too
much time was required for the HO2S to become active,
a DTC will set. If the engine was warm when started,
HO2S warm–up will display ”00:00:00.”
IAC POSITION – Tech 2 Range 0–255 Counts
Displays the commanded position of the idle air control
pintle in counts. A larger number of counts means that
more air is being commanded through the idle air
passage. Idle air control should respond fairly quickly to
changes in engine load to maintain desired idle RPM.
IAT (INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE) – Tech 2 Range
–40°C to 151°C (–40°F to 304°F)
The ECM converts the resistance of the intake air
temperature sensor to degrees. Intake air temperature
(IA T) is used by the ECM to adjust fuel delivery and spark
timing according to incoming air density.
IGNITION 1 – Tech 2 Range 0–25.5 Volts
This represents the system voltage measured by the
ECM at its ignition feed.
INJ. PULSE BANK 1 – Tech 2 Range 0–1000 msec.
Indicates the amount of time the ECM is commanding
each injector ON during each engine cycle. A longer
injector pulse width will cause more fuel to be delivered.
Injector pulse width should increase with increased
engine load.
MAP – Tech 2 Range 10–105 kPa (0.00–4.97 Volts)
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the change in the intake manifold pressure from engine
load, EGR flow, and speed changes. As intake manifold
pressure increases, intake vacuum decreases, resulting
in a higher MAP sensor voltage and kPa reading. The
MAP sensor signal is used to monitor intake manifold
pressure changes during the EGR flow test, to update the
BARO reading, and as an enabling factor for several of
the diagnostics.
MIL – Tech 2 Displays ON or OFF
Indicates the ECM commanded state of the malfunction
indicator lamp (”Check Engine Lamp”).
POWER ENRICHMENT – Tech 2 Displays ACTIVE
or INACTIVE
”ACTIVE” displayed indicates that the ECM has detected
conditions appropriate to operate in power enrichment
mode. The ECM will command power enrichment mode
when a large increase in throttle position and load is
detected. While in the power enrichment mode, the ECM
will increase the amount of fuel delivered by entering
”Open Loop” and increasing the injector pulse width. This
is done to prevent a possible sag or hesitation from
occurring during acceleration.
SPARK – Tech 2 Range –64° to 64°
Displays the amount of spark advance being commanded
by the ECM on the IC circuit.
START–UP ECT – Tech 2 Range –40°C to 151°C
(–40°F to 304°F)
Indicates the engine coolant temperature at the time that
the vehicle was started. Used by the HO2S diagnostic to
determine if the last start–up was a cold start.
START–UP ECT – Tech 2 Range –40°C to 151°C
(–40°F to 304°F)
Indicates the intake air temperature at the time that the
vehicle was started. Used by the HO2S diagnostic to
determine if the last start–up was a cold start.
TP ANGLE – Tech 2 Range 0%–100%
TP (throttle position) angle is computed by the ECM from
the TP sensor voltage. TP angle should display ”0%” at
idle and ”100%” at wide open throttle.
TP SENSOR – Tech 2 Range 0.00–5.00 Volts
The voltage being monitored by the ECM on the TP
sensor signal circuit.
VEHICLE SPEED – Tech 2 Range 0–255 km/h
(0–155 mph)
The vehicle speed sensor signal is converted into km/h
and mph for display.
WEAK CYLINDER – Tech 2 Displays Cylinder
Number
This indicates that the ECM has detected crankshaft
speed variations that indicate 2% or more cylinder firing
events are misfires.
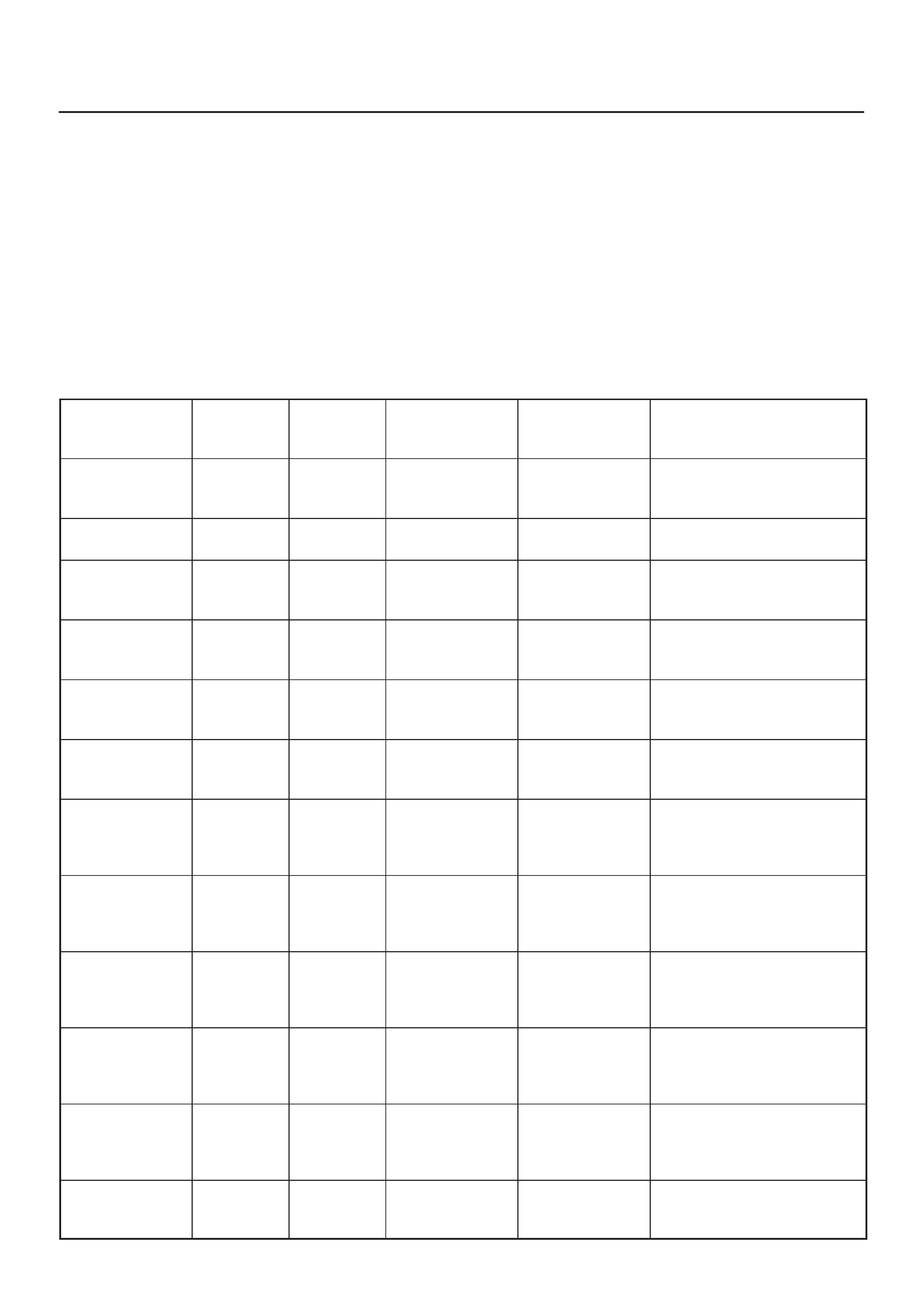
TYPICAL SCAN DATA VALUES
Use the Typical Scan Data Values Table only after the
On–Board Diagnostic System Check has been
completed, no DTC(s) were noted, and you have
determined that the on–board diagnostics are functioning
properly. Tech 2 values from a properly–running engine
may be used for comparison with the engine you are
diagnosing. The typical scan data values represent
values that would be seen on a normally–running engine.
NOTE:A Tech 2 that displays faulty data should not be
used, and the problem should be reported to the Tech 2
manufacturer. Use of a faulty Tech 2 can result in
misdiagnosis and unnecessary replacement of parts.
Only the parameters listed below are referred to in this
service manual for use in diagnosis. For further
information on using the Tech 2 to diagnose the ECM and
related sensors, refer to the applicable reference section
listed below. If all values are within the typical range
described below, for diagnosis, refer to the Symptoms
section.
Test Conditions
Engine running, lower radiator hose hot, transmission in
park or neutral, ”Closed Loop”, accessories OFF, brake
not applied and air conditioning OFF.
2.2L L–4 Engine
Tech 2
Parameter Data List Units
Displayed Typical Data
Values (IDLE) Typical Data
Values
(2500 RPM)
Refer To
Engine Speed Engine RPM Within -50 to
+100 of
“Desired Idle”
Actul engine
speed General Discription and
Operation
Desired Idle
Speed Engine RPM 750 800 General Discription and and
Operation, Idle Air Control
Engine Coolant
Tenpereture Engine °C80 – 100 (176 –
212 °F) 80 – 100 (176 –
212 °F) General Discription and and
Operation, Engin coolant
tempereture sensor
Start Up ECT Engine °C––General Discription and and
Operation, Engin coolant
tempereture sensor
Intake Air
Tenpereture Engine °C0 – 100,
depends on
underhood
0 – 80, depends
on underhood General Discription and and
Operation, Intake Air
tempereture sensor
Start Up IAT Engine °C––General Discription and and
Operation, Intake Air
tempereture sensor
Manifold
Absolute
Pressure
Engine kPa 23 – 40 19 – 32 General Discription and
Operation, Manifold
Absolute Pressure Sensor.
DTC P0106,P0107,P0108
Manifold
Absolute
Pressure
Engine V0.65 – 1.32 0.46 – 1.10 General Discription and
Operation, Manifold
Absolute Pressure Sensor.
DTC P0106,P0107,P0108
Barometric
Pressure Engine kPa 61 – 104
(depends pn
altitude and
barometric)
61 – 104
(depends pn
altitude and
barometric)
General Discription and
Opreration
Throttle Position Engine % 0 3 – 5 General Discription and
Opreration, Throttle Position
Sensor. DTC
P0121,P0122,P0123
Throttle Position
Sensor Engine V0.35 – 0.39 0.55 – 0.59 General Discription and
Opreration, Throttle Position
Sensor. DTC
P0121,P0122,P0123
Air Fuel Ratio Engine Ratio:_to1 14.6:1 14.6:1 General Discription and
Operation, Fuel System
Metering Purpose, Fuel Trim
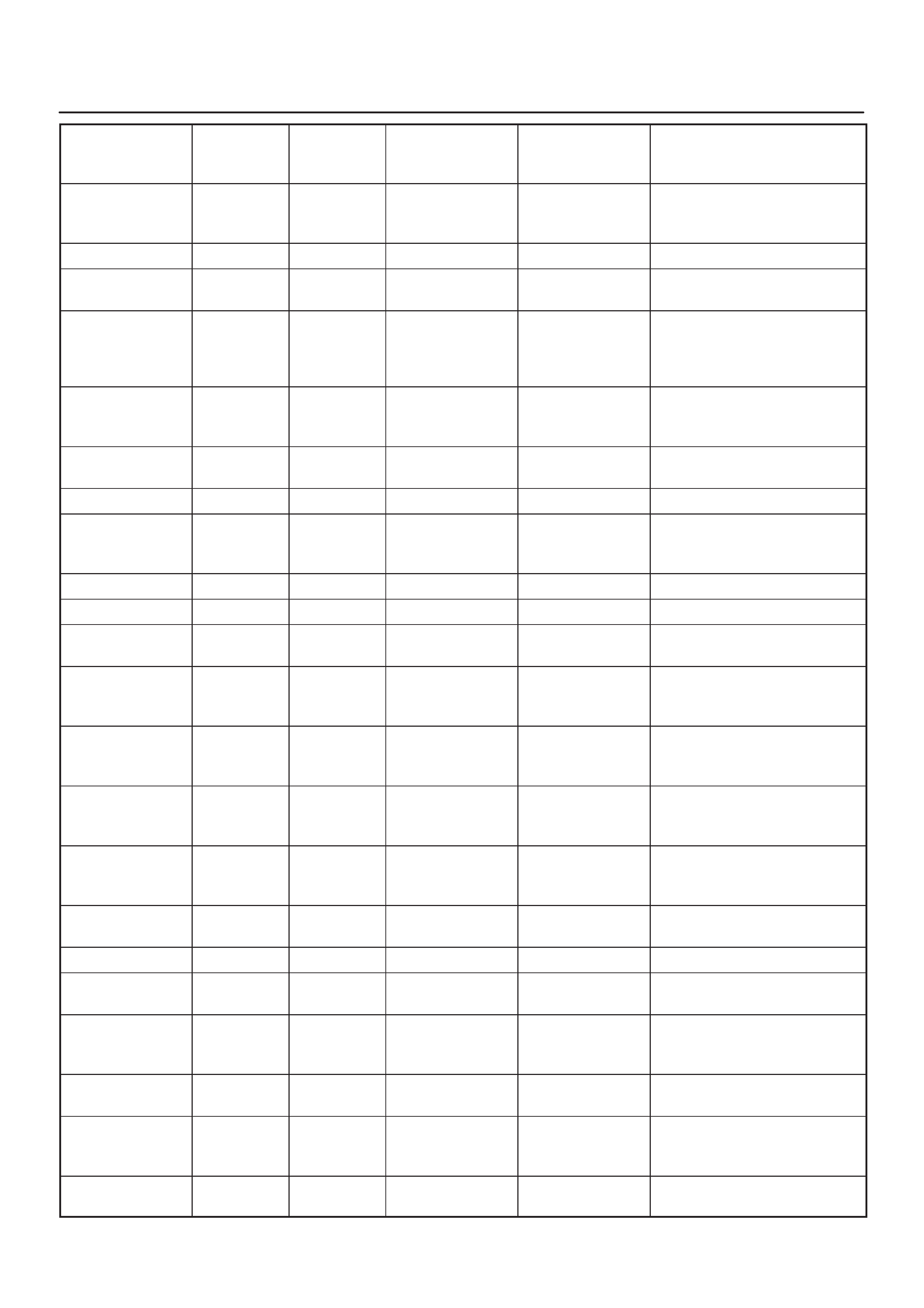
Tech 2
Parameter Refer ToTypical Data
Values
(2500 RPM)
Typical Data
Values (IDLE)
Units
Displayed
Data List
Spark Advance Engine °CA 10 – 12 27 – 29 General Discription and and
Operation, Electronic
Ignition System
Engine Load Engine % – – –
Fuel system
Status Engine Closed
Loop ––EVAP System
EGR Duty Cycle Engine %00General Discription and and
Operation, Liner EGR
Operation and Results of
Incorrect Operation
Desired EGR
Position Engine %00General Discription and and
Operation, EGR Pintle
Position Sensor
EGR
Normalized Engine % 0 0 –
EGR Feed Back Engine V0.6 – 0.8 0.6 – 0.8 –
EGR Closed
Pintle Position Engine Steps 20 – 40 20 – 40 General Discription and and
Operation, EGR Pintle
Position Sensor
Knock Counter Engine Yes/No Yes Yes DTC P0325,P0327
Knock Retard Engine °CA – – DTC P0325,P0327
A/C Pressure
Sensor Engine mV 0–DTC P0532,P0533
A/C Clutch
Relay Engine On/Off Off –General Discription and and
Operation, A/C Culutch
Circuit Operation
A/C Request Engine Yes/No No –General Discription and and
Operation, A/C Request
Signal
Low Fan
Comanded Engine Yes/No ––General Discription and and
Operation, Cooling Fan
Control. DTC P0480,P0481
High Fan
Comanded Engine Yes/No ––General Discription and and
Operation, Cooling Fan
Control. DTC P0480,P0481
Camshaft
Activity Engine Counts 0 – 255 0 – 255 DTC P0341,P0342
Fuel Pump Engine On/Off On On Engine Fuel System
Deceleration
Fuel Cutoff Engine Inactive/Ac
tive Inactive Inactive General Discription and and
Operation
Idle Air Control Engine Steps ––General Discription and and
Operation, Intake Air
tempereture sensor
Vehicle Speed Engine MPH or
km/h 00Manual Transmission
Ignition Voltage Engine V12.8 – 14.1 12.8 – 14.1 General Discription and and
Operation, Electronic
Ignition System
Malfunction
Indicator Lamp Engine On/Off Off Off On–Board Diagnostic
System Check
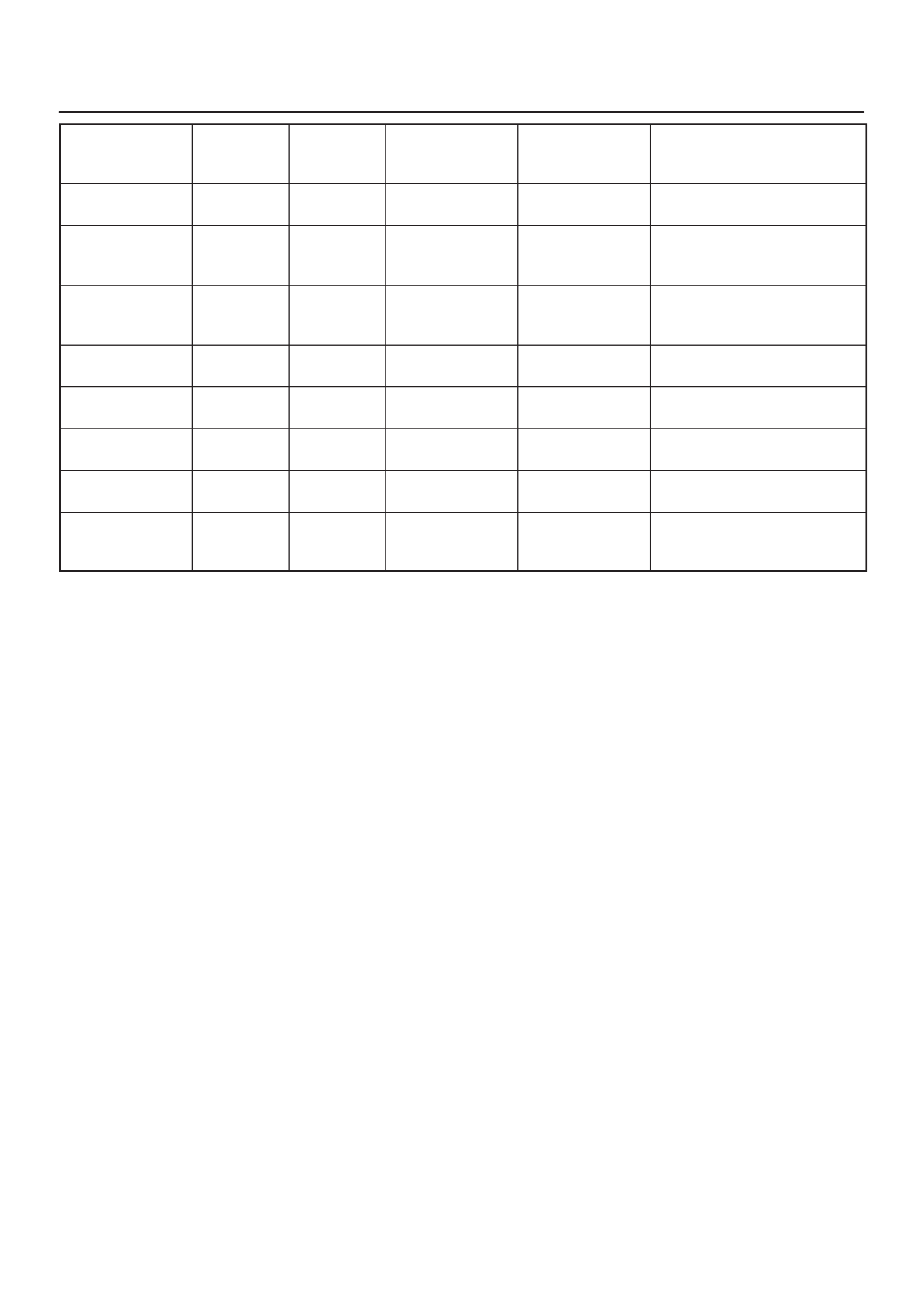
Tech 2
Parameter Refer ToTypical Data
Values
(2500 RPM)
Typical Data
Values (IDLE)
Units
Displayed
Data List
ABS Rough
Road Engine
Misfire Value Okey Okey DTC P1380,P1381
B1S1 Status
(Bank1,Sensor1) Engine
HO2S Rich/Lean ––General Discription and and
Operation, Fuel Control
HO2S
B1S1 O2 Sensor
(Bank1,Sensor1) Engine
HO2S mV 50 – 950
changing quickly 50 – 950
changing quickly General Discription and and
Operation, Fuel Control
HO2S
Fuel Trim
Learned Engine
HO2S Yes/No Yes Yes Diagnosis, Fuel Trim Monitor
Fuel Trim Cell Engine
HO2S Cell No. 18 2 or 6 Diagnosis, Fuel Trim Cell
Diagnostic Weights
B1 Long Fuel
Trim Engine
HO2S %––DTC P0171,P0172
B2 Short Fuel
Trim Engine
HO2S %––DTC P0171,P0172
Power
Enrichment Engine
HO2S Yes/No No No General Discription and and
Operation, Acceleration
Mode
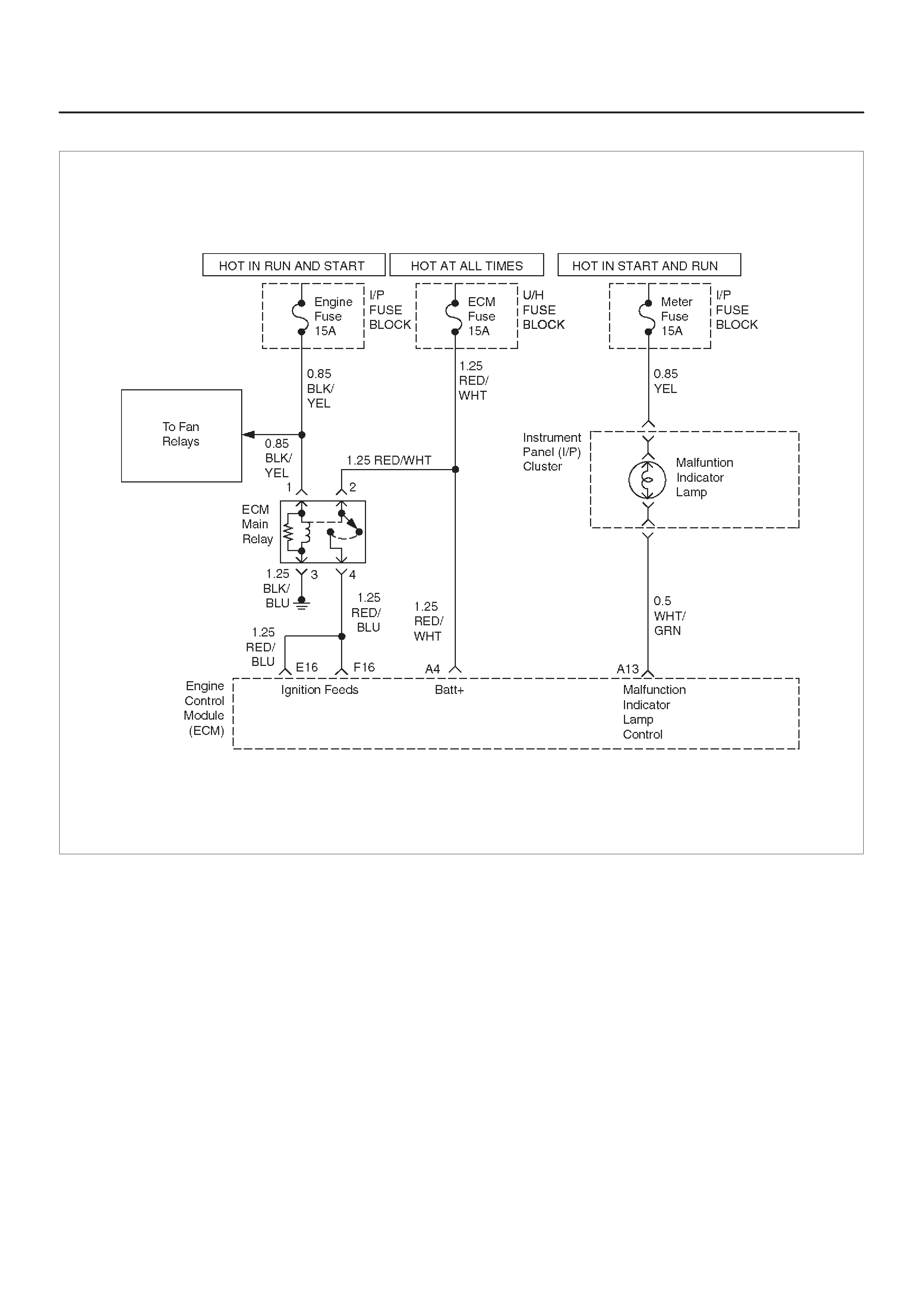
NO MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)
D06RX109
Circuit Description
The ”Check Engine” lamp (MIL) should always be
illuminated and steady with the ignition ON and the
engine stopped. Ignition feed voltage is supplied to the
MIL bulb through the meter fuse. The engine control
module (ECM) turns the MIL ON by grounding the MIL
driver circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent MIL may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
DInspect the ECM harness and connections for
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal–to–wire
connection, and damaged harness.
DIf the engine runs OK, check for a faulty light bulb, an
open in the MIL driver circuit, or an open in the
instrument cluster ignition feed.
DIf the engine cranks but will not run, check for an open
ECM ignition or battery feed, or a poor ECM to engine
ground.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. A ”No MIL” condition accompanied by a no–start
condition suggests a faulty ECM ignition feed or
battery feed circuit.
9. Using a test light connected to B+, probe each of
the ECM ground terminals to ensure that a good
ground is present. Refer to ECM Terminal End View
for terminal locations of the ECM ground circuits.
12. In this step, temporarily substitute a known good
relay for the ECM relay. The horn relay is nearby,
and it can be verified as ”good” simply by honking
the horn. Replace the horn relay after completing
this step.
No Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
3Check the meter fuse for the instrument cluster ignition
feed circuit.
Is the fuse OK? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 16
41. Ignition ON.
2. Engine OFF.
3. Probe the ignition feed circuit at the cluster
connector with a test light to ground.
Is the test light ON? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 13
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM.
3. Jumper the MIL driver circuit at the ECM connector
to ground.
4. Ignition ON.
Is the MIL ON? —Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
6Check the ECM ignition feed and battery feed fuses
(15A Engine fuse and 15A ECM fuse).
Are both fuses OK? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 15
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Probe the ignition feed circuit at the ECM harness
connector with a test light to ground.
Is the test light ON? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 12
8Probe the battery feed circuit at the ECM harness
connector with a test light to ground.
Is the test light ON? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 14
9Check for a faulty ECM ground connection.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 Check for damaged terminals at the ECM.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
11 Check for an open MIL driver circuit between the ECM
and the MIL.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
12 Substitute a known ”good” relay for the ECM main
relay.
Was the malfunction fixed? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
14 Locate and repair the open ECM battery feed circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
15 Locate and repair the short to ground in the ECM
ignition feed circuit or ECM battery feed circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
16 Locate and repair the short to ground in the ignition
feed circuit to the instrument cluster, and replace the
fuse.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
17 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
18 Check the MIL driver circuit for a poor connection at the
instrument panel connector.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Go to
Instrument
Panel in
Electrical
Diagnosis
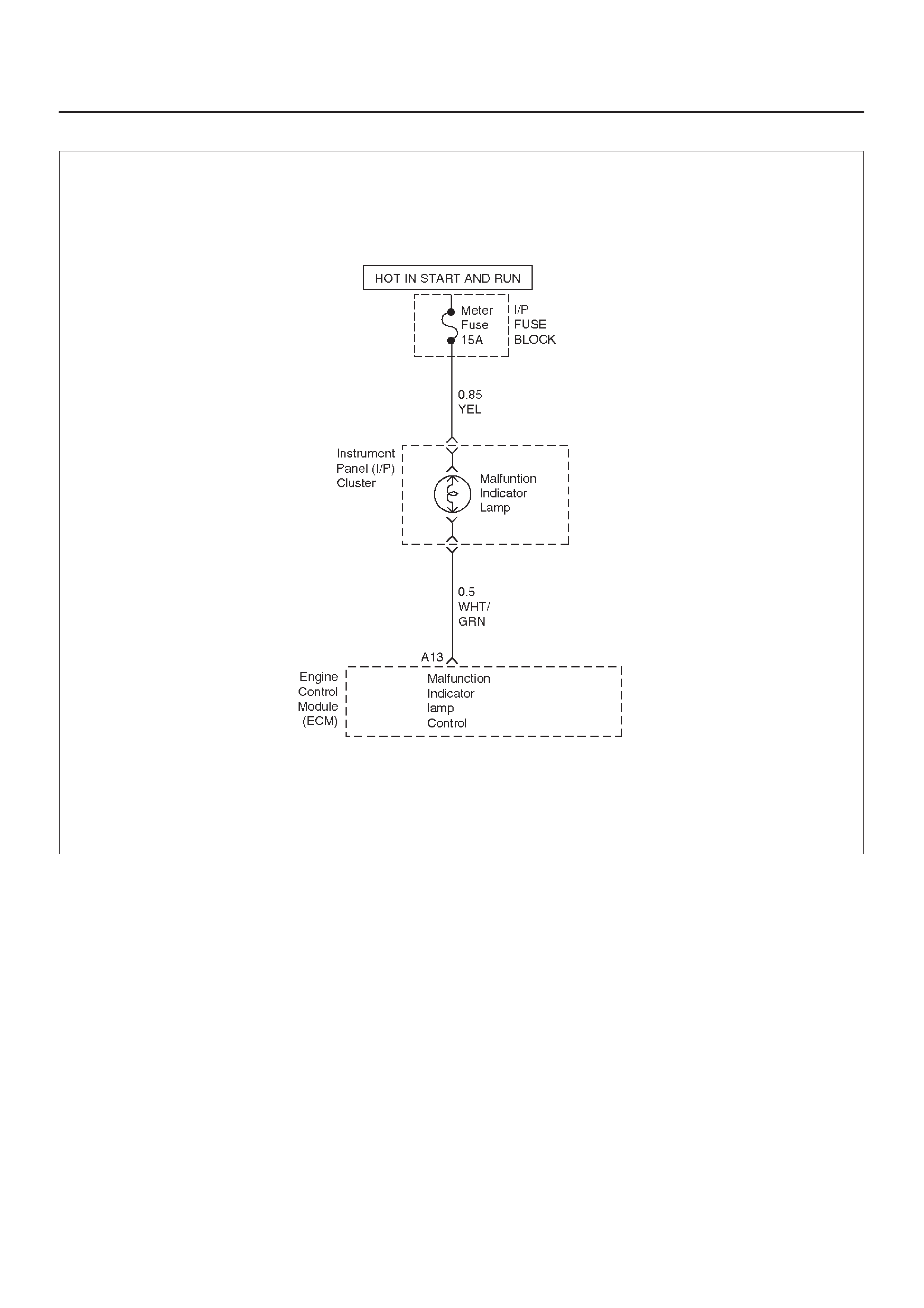
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL) ON STEADY
D06RX110
Circuit Description
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) should always be
illuminated and steady with the ignition ON and the
engine stopped. Ignition feed voltage is supplied directly
to the MIL indicator. The engine control module (ECM)
turns the MIL ON by grounding the MIL driver circuit.
The MIL should not remain ON with the engine running
and no DTC(s) set. A steady MIL with the engine running
and no DTC(s) suggests a short to ground in the MIL
driver circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
ECM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal–to–wire connection, and
damaged harness.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. If the MIL does not remain ON when the ECM is
disconnected, the MIL driver wiring is not faulty.
3. If the MIL driver circuit is OK, the instrument panel
cluster is faulty.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) ON Steady
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition OFF, disconnect the ECM.
2. Ignition ON, observe the MIL (Service Engine Soon
lamp).
Is the MIL ON? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 5
31. Ignition OFF, disconnect the instrument panel
cluster.
2. Check the MIL driver circuit between the ECM and
the instrument panel cluster for a short to ground.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the MIL driver circuit shorted to ground? —
Go to OBD
System
Check Go to Step 4
4Replace the instrument panel cluster.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
51. Ignition OFF, reconnect the ECM.
2. Ignition ON, reprogram the ECM. Refer to
On–Vehicle Service in Engine Control Module and
Sensors for procedures.
3. Using the Tech 2 output controls function, select
MIL dash lamp control and command the MIL OFF.
Did the MIL turn OFF? —
Go to OBD
System
Check Go to Step 6
6Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
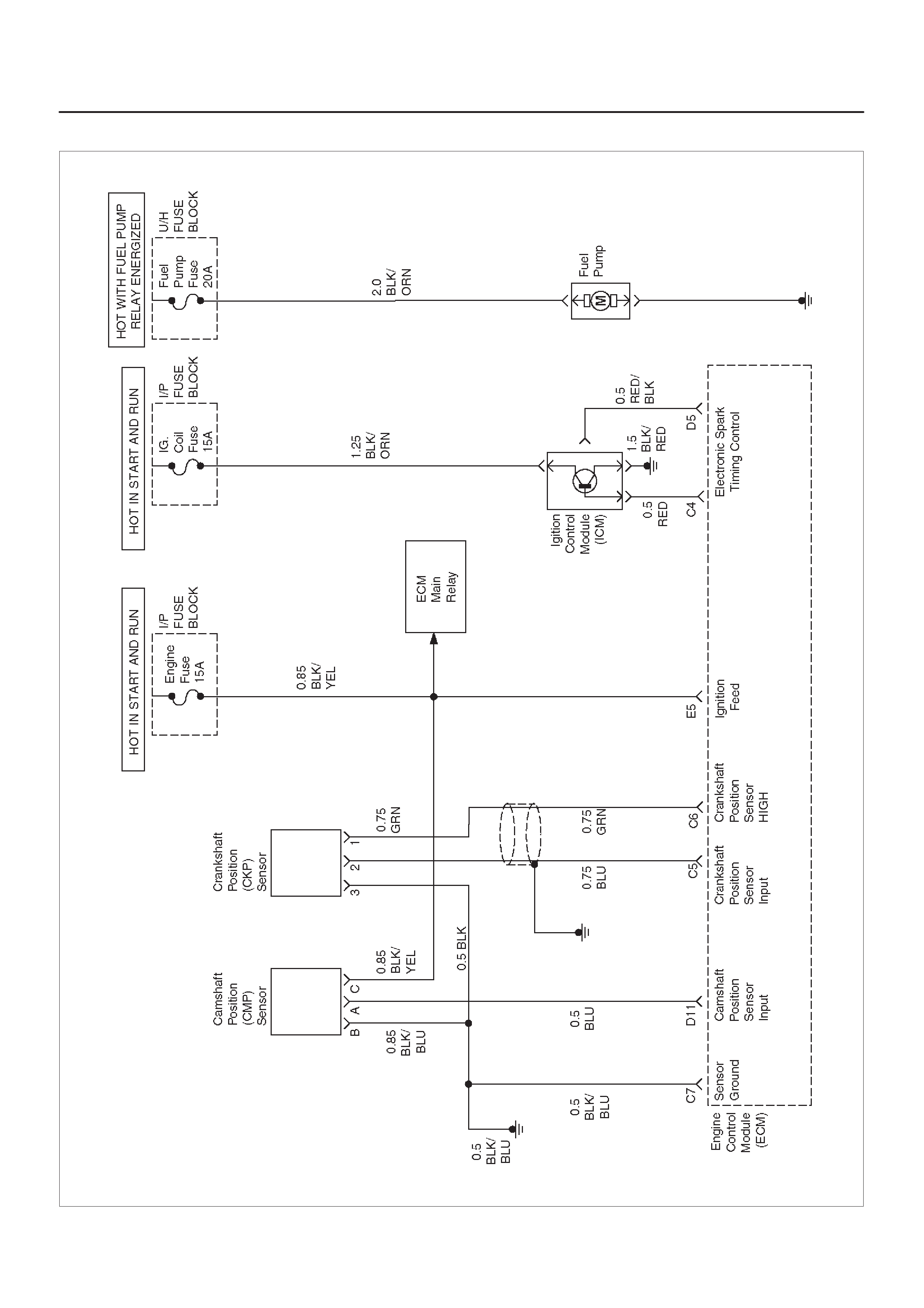
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN
D06RX099
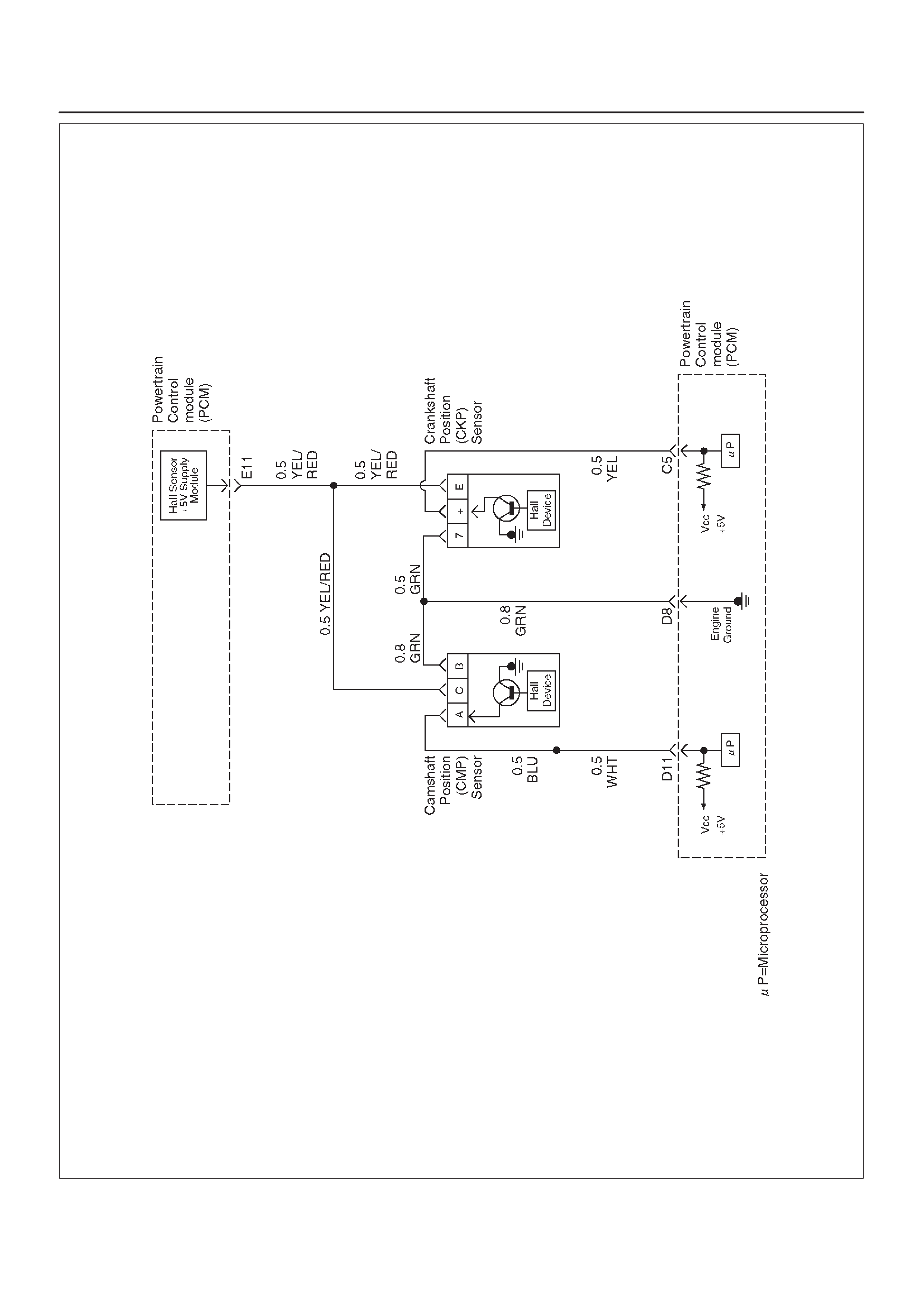
D06RX091

Circuit Description
The electronic ignition system uses a dual coil method of
spark distribution. In this type of ignition system, the
engine control module (ECM) triggers the correct driver
inside the ignition control module (ICM), which then
triggers the correct ignition coil based on the 58X signal
received from the crankshaft position sensor (CKP). The
spark plug connected to the coil fires when the ICM opens
the ground circuit for the coil’s primary circuit.
During crank, the ECM monitors the CKP 58X signal. The
CKP signal is used to determine which cylinder will fire
first. After the CKP 58X signal has been processed by the
ECM, it will command all four injectors to allow a priming
shot of fuel for all the cylinders. After the priming, the
injectors are left OFF during the next four 58X reference
pulses from the CKP. This allows each cylinder a chance
to use the fuel from the priming shot. During this waiting
period, a camshaft position (CMP) signal pulse will have
been received by the ECM. The CMP signal allows the
ECM to operate the injectors sequentially based on
camshaft position. If the camshaft position signal is not
present at start–up, the ECM will begin sequential fuel
delivery with a 1–in–4 chance that fuel delivery is correct.
The engine will run without a CMP signal, but will set a
DTC code.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor
connection, rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire
broken inside the insulation. Check for the following
items:
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
ECM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal–to–wire connection, and
damaged harness.
DFaulty engine coolant temperature sensor – Using a
Tech 2, compare engine coolant temperature with
intake air temperature on a completely cool engine.
Engine coolant temperature should be within 10°C of
intake air temperature. If not, replace the ECT sensor.
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Use the Tech 2 and check for any DTC’s.
Are any DTC’s stored? —
Go to
Applicable
DTC Table Go to Step 3
3Check the 15A ignition coil fuse, the 15A engine device
fuse, and the 15A ECM fuse.
Was a fuse blown? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4Check for a short to ground and replace the fuse.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
51. Ignition ON.
2. Use a grounded test lamp to verify that B+ is
available at the ignition coil fuse, the engine device
fuse, and the ECM fuse.
Was B+ available at the fuses? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6Repair the open ignition feed circuit.
—
Go to Fuel
System
Electrical Test Go to Fuel
System
Diagnosis
71. Disconnect the ignition secondary wire at the No.1.
2. Install a spark tester 5–8840–0279–0 at the end of
the disconnected ignition coil.
3. Clip the spark tester 5–8840–0279–0 to a good
ground (not near the battery).
4. Observe the spark tester while the engine is
cranking.
Was a crisp blue spark observed? (Only one or two
sparks followed by no result is considered the same as
”No Spark.”) —Go to Step 16 Go to Step 8
81. Disconnect the ignition module harness connector.
2. Check for an open or short circuit between the
ignition control module and the ECM?
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
9Repair the faulty circuit. — Verify repair —
10 1. Ignition ON.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) check the ignition
wire coil at the ignition module harness connector?
Was the voltage equal to the specified value? B+ Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Repair the open circuit. — Verify repair —
12 1. Ignition OFF.
2. With DVM, check for an open in the ground wire at
the ignition module harness connector.
Was the ground wire OK? —Go to Step 14 Go to Step 13
13 Repair the faulty wire. — Verify repair —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
14 Replace the ignition module, verify the repair.
Attempt to start the engine.
Is there still a problem? —Go to Step 15 Verify repair
15 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
16 Use an ohmmeter to check the ignition coil primary
winding resistance.
Was the primary winding resistance approximately
equal to the specified value? 0.8–18 WGo to Step 17 Go to Step 18
17 Use an ohmmeter to check the ignition coil secondary
winding resistance.
Was the secondary winding resistance equal to the
specified value? 9,000–12,000
WGo to Step 19 Go to Step 18
18 Replace the ignition coil. — Verify repair —
19 T est the resistance of the coil–to–spark plug secondary
ignition wire.
Was the resistance greater than the specified value? 10,000 W per
foot Go to Step 20 Go to Step 21
20 Replace the coil–to–spark plug secondary ignition wire
and any other secondary wires which exceed the
specified value.
Is there still a problem? 10,000 W per
foot Go to Step 21 Verify repair
21 1. Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders.
2. Visually inspect the spark plug electrodes.
3. Replace any spark plugs with loose or missing
electrodes or cracked insulators.
Did your inspection reveal any spark plugs exhibiting
excessing fouling? —
Correct the
fouling
condition Go to Step 30
22 Verfiy repair.
Attempt to start the engine.
Is there still a problem? —Go to Step 23 Go to Step 22
23 1. Ignition OFF , install a fuel pressure gauge at the test
fitting on the fuel supply line in the engine
compartment.
CAUTION:Use a shop cloth to absorb any fuel
leakage while making the connection.
2. Check the engine and observe the fuel pressure.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified values, and
does it hold steady for 2 seconds? 285–375 kPa
(43–55 psi) Go to Step 25 Go to Step 24
24 Is any fuel pressure indicated?
—
Go to Fuel
System
Electrical Test Go to Fuel
System
Diagnosis
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
25 1. Raise the vehicle and disconnect the CKP sensor
harness.
2. Ignition ON.
3. With a test light to ground, probe the CKP ignition
feed harness terminal.
Did the light illuminate? —Go to Step 26 Go to Step 27
26 1. Ignition ON.
2. At the CKP harness connector , connect a test lamp
between the ignition and ground terminals.
Did the lamp illuminate? —Go to Step 28 Go to Step 29
27 Check the CKP High circuit between the sensor and the
ECM for a short to ground or open circuit.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 30
28 Replace the CKP position sensor.
Is there still a problem? —Go to Step 31 —
29 Check the CKP Low circuit between the sensor and the
ECM for: an open circuit, a short to ground, or short to
voltage.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 30
30 Replace the ECM. — Verify repair —
31 1. Test the fuel for contamination.
2. If a problem is found, clean the fuel system and
correct the contaminated fuel condition as
necessary. Replace the fuel filter and replace any
injectors that are not delivering fuel (see Injector
Balance Test).
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 32
32 To diagnose the following conditions, refer to Engine
Mechanical:
DSlipped camshaft drive belt.
DLeaking or sticky valves or rings.
DExcessive valve deposits.
DLoose or worn rocker arms.
DWeak valve springs
DLeaking head gasket.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
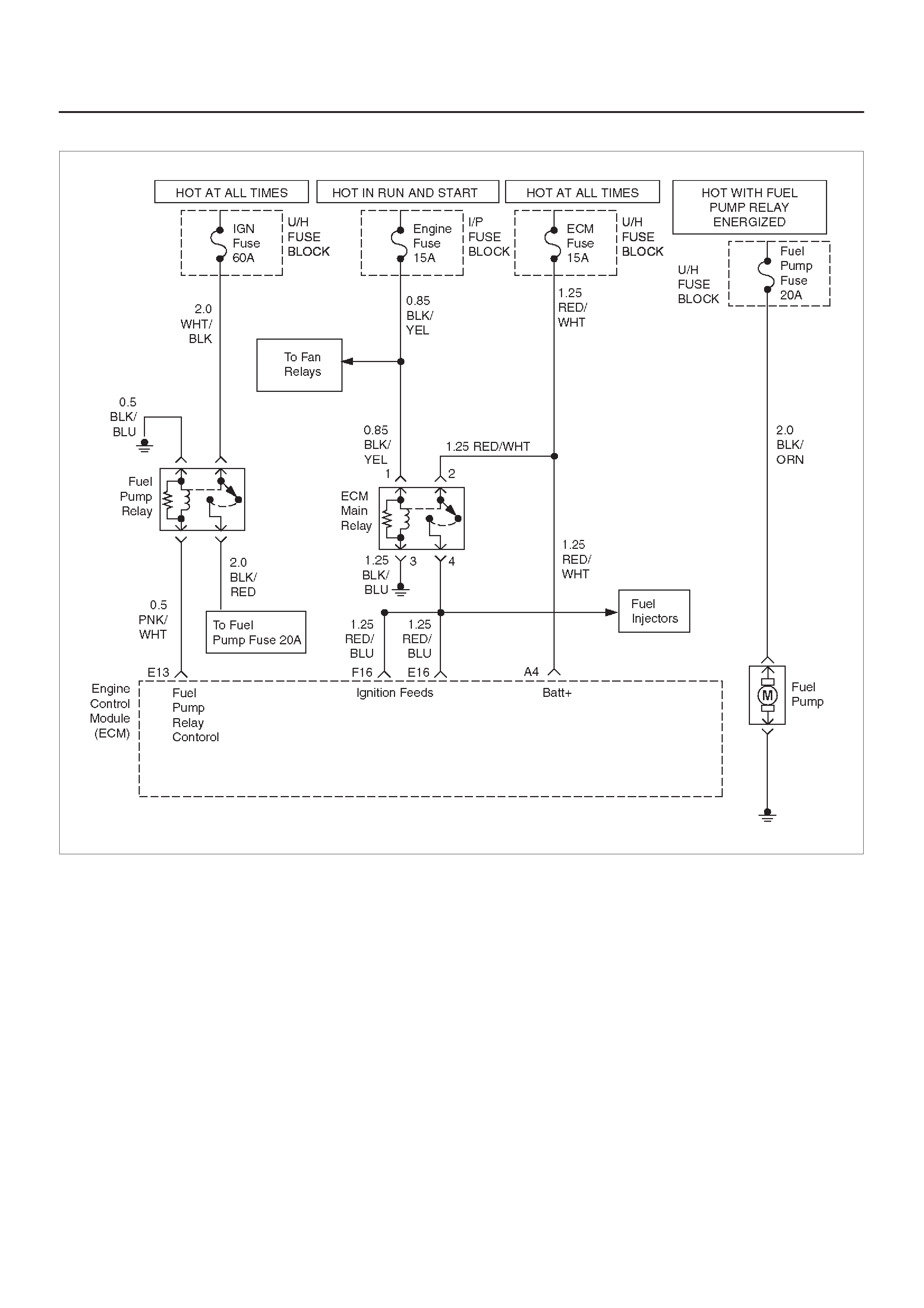
FUEL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL TEST
D06RX111
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is first turned ON, the powertrain
control module (ECM) energizes the fuel pump relay
which applies power to the in–tank fuel pump. The fuel
pump relay will remain ON as long as the engine is
running or cranking and the ECM is receiving 58X
crankshaft position pulses. If no 58X crankshaft position
pulses are present, the ECM de–energizes the fuel pump
relay within 2 seconds after the ignition is turned ON or the
engine is stopped.
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel rail and injectors,
then to the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator controls fuel pressure by allowing excess fuel to
be returned to the fuel tank. With the engine stopped and
ignition ON, the fuel pump can be turned ON by using a
command by the Tech 2.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside
the insulation. Check for the following items:
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
ECM harness and connectors for improper mating,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, poor terminal–to–wire connection, and
damaged harness.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. If the fuel pump is operating but incorrect pressure
is noted, the fuel pump wiring is OK and the ”Fuel
System Pressure Test” chart should be used for
diagnosis.
CAUTION:To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
DIt is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure, below.
DA small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before disconnecting, to
catch any fuel that may leak out. Place the towel in
an approved container when the procedure is
completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1.Remove the fuel cap.
2.Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood
relay center.
3.Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4.Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Gauge Installation
1.Remove the shoulder fitting cap.
2.Install fuel gauge 5–8840–0378–0 to the fuel feed line
located in front of and above the right side valve
cover.
3.Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
Fuel System Electrical Test
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Read the ”Caution” above.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure and install the fuel
pump pressure gauge to the test fitting.
3. Use a Tech 2 to command the fuel pump ON.
Is there an immediate pressure build–up which
indicates the pump is running? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. V erify that the pump is not running by removing the
fuel filler cap and listening.
2. Command the pump ON with the Tech 2.
Did the pump turn OFF after 2 seconds? —Test
completed Go to Step 12
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the fuel pump relay.
3. Ignition SW “On”, Engin Off.
4. Using a test light connected to ground, probe the
battery feed to the relay.
Did the light illuminate? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair short or open battery feed to fuel pump relay.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
61. Connect a test light between the two wires that
connect to the fuel pump relay pull–in coil.
2. Ignition ON.
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds and then turn
off? —Go to Step 12 Go to Step 7
71. With a test light connected to battery (–), probe the
fuel pump relay connector at the wire which runs
from the relay pull–in coil to the ECM.
2. Ignition ON.
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds and then turn
off? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Locate and repair open in the fuel pump relay ground
circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
9Check for short or open between the ECM and the fuel
pump relay.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 1. Check the fuel pump relay circuit for a poor terminal
connection at the ECM.
2. If a problem is found, replace terminal as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
12 1. Reconnect the fuel pump relay.
2. Disconnect the fuel pump electrical connector at the
fuel tank.
3. Using a test light connected to ground, probe the
fuel pump feed wire (harness side).
4. Command the fuel pump ON with a Tech 2.
Did the light illuminate for 2 seconds? —Go to Step 15 Go to Step 13
13 1. Honk the horn to verify that the horn relay is
functioning.
2. Substitute the horn relay for the fuel pump relay.
3. Leave the test light connected as in step 12.
4. Command the fuel pump ON with the Tech 2.
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds when the fuel
pump was commanded ON? —Go to Step 17 Go to Step 14
14 1. Re–connect the horn relay in its proper location.
2. Check for a short circuit, blown fuse or open circuit
between the relay and the fuel tank.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
15 1. With the fuel pump electrical connector at the fuel
tank disconnected, connect a test light between the
feed wire and the ground wire (harness side).
2. Command the fuel pump ON with a Tech 2.
Did the test light illuminate for 2 seconds? —Go to Step 18 Go to Step 16
16 Repair the open circuit in the fuel pump ground wire.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
17 1. Re–connect the horn relay in its proper location.
2. Replace the fuel pump relay.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
18 Replace the fuel pump.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
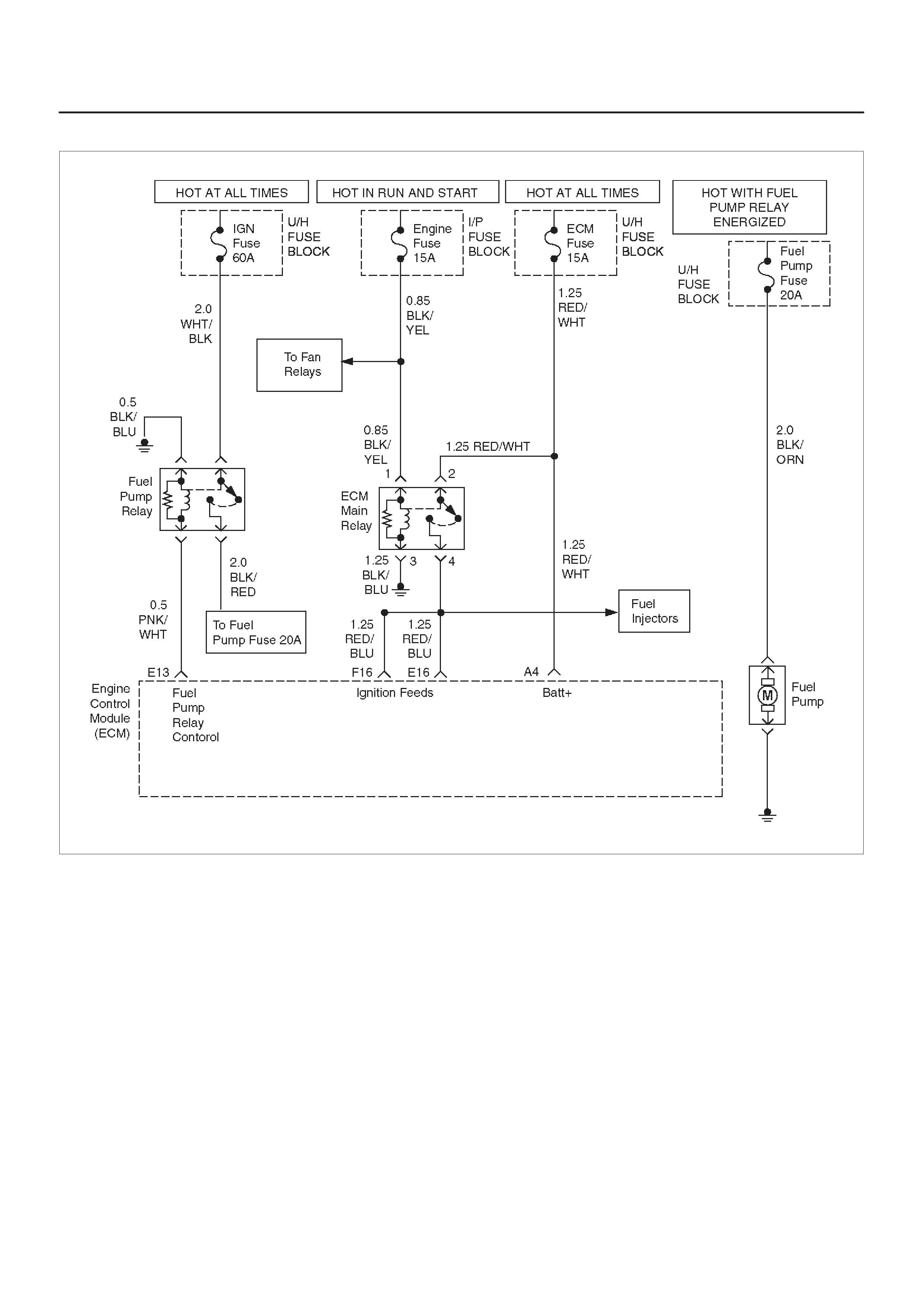
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
D06RX111
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the engine control
module (ECM) will turn ON the in–tank fuel pump. The
in–tank fuel pump will remain ON as long as the engine is
cranking or running and the ECM is receiving 58X
crankshaft position pulses. If there are no 58X crankshaft
position pulses, the ECM will turn the in–tank fuel pump
OFF 2 seconds after the ignition switch is turned ON or 2
seconds after the engine stops running.
The in–tank fuel pump is an electric pump within an
integral reservoir. The in–tank fuel pump supplies fuel
through an in–line fuel filter to the fuel rail assembly. The
fuel pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure above
the pressure needed by the fuel injectors. A fuel pressure
regulator, attached to the fuel rail, keeps the fuel available
to the fuel injectors at a regulated pressure. Unused fuel is
returned to the fuel tank by a separate fuel return line.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Connect the fuel pressure gauge to the fuel feed
line as shown in the fuel system illustration. Wrap a
shop towel around the fuel pressure connection in
order to absorb any fuel leakage that may occur
when installing the fuel pressure gauge. With the
ignition switch ON and the fuel pump running, the
fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge
should be 283–376 kPa (41–55 psi). This pressure
is controlled by the amount of pressure the spring
inside the fuel pressure regulator can provide.
3. A fuel system that cannot maintain a constant fuel
pressure has a leak in one or more of the following
areas:
DThe fuel pump check valve.
DThe fuel pump flex line.

DThe valve or valve seat within the fuel pressure
regulator.
DThe fuel injector(s)
4.Fuel pressure that drops off during acceleration,
cruise, or hard cornering may case a lean condition.
A lean condition can cause a loss of power, surging,
or misfire. A lean condition can be diagnosed using
a Tech 2. If an extremely lean condition occurs, the
oxygen sensor(s) will stop toggling. The oxygen
sensor output voltage(s) will drop below 500 mV.
Also, the fuel injector pulse width will increase.
IMPORTANT:Make sure the fuel system is not
operating in the ”Fuel Cut–Off Mode.”
When the engine is at idle, the manifold pressure is
low (high vacuum). This low pressure (high vacuum)
is applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm.
The low pressure (high vacuum) will offset the
pressure being applied to the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by the spring inside the fuel pressure
regulator. When this happens, the result is lower fuel
pressure. The fuel pressure at idle will vary slightly as
the barometric pressure changes, but the fuel
pressure at idle should always be less than the fuel
pressure noted in step 2 with the engine OFF.
16. Check the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation in order to
determine if that particular fuel injector is leaking. If
checking the spark plug associated with a particular
fuel injector for fouling or saturation does not
determine that a particular fuel injector is leaking,
use the following procedure:
DRemove the fuel rail, but leave the fuel lines and
injectors connected to the fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Rail
Assembly in On–Vehicle Service.
DLift the fuel rail just enough to leave the fuel injector
nozzles in the fuel injector ports.
CAUTION:In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury that may result from fuel spraying on
the engine, verify that the fuel rail is positioned over
the fuel injector ports and verify that the fuel injector
retaining clips are intact.
DPressurize the fuel system by connecting a 10 amp
fused jumper between B+ and the fuel pump relay
connector.
DVisually and physically inspect the fuel injector
nozzles for leaks.
17. A rich condition may result from the fuel pressure
being above 376 kPa (55 psi). A rich condition may
cause a DTC P0132 or a DTC P0172 to set.
Driveability conditions associated with rich
conditions can include hard starting (followed by
black smoke) and a strong sulfur smell in the
exhaust.
20. This test determines if the high fuel pressure is due
to a restricted fuel return line or if the high fuel
pressure is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
21. A lean condition may result from fuel pressure
below 333 kPa (48 psi). A lean condition may cause
a DTC P0131 or a DTC P0171 to set. Driveability
conditions associated with lean conditions can
include hard starting (when the engine is cold),
hesitation, poor driveability, lack of power, surging,
and misfiring.
22. Restricting the fuel return line causes the fuel
pressure to rise above the regulated fuel pressure.
Command the fuel pump ON with the Tech 2. The
fuel pressure should rise above 376 kPa (55 psi) as
the fuel return line becomes partially closed.
NOTE:Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 414 kPa
(60 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 414 kPa (60 psi) may
damage the fuel pressure regulator.
CAUTION:To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury:
DIt is necessary to relieve fuel system pressure
before connecting a fuel pressure gauge. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure, below.
DA small amount of fuel may be released when
disconnecting the fuel lines. Cover fuel line
fittings with a shop towel before disconnecting, to
catch any fuel that may leak out. Place the towel in
an approved container when the procedure is
completed.
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
1.Remove the fuel cap.
2.Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood
relay center.
3.Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4.Crank the engine for an additional 3 seconds.
Fuel Gauge Installation
1.Remove the shoulder fitting cap.
2.Install fuel gauge 5–8840–0378–0 to the fuel feed line
located on the upper right side of the engine near the
EGR valve.
3.Reinstall the fuel pump relay.
Fuel System Diagnosis
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Turn the air conditioning system OFF.
3. Relieve fuel system pressure and install the fuel
pressure gauge.
4. Turn the ignition ON.
NOTE: The fuel pump will run for approximately 2
seconds. Use the Tech 2 to command the fuel pump
ON.
5. Observe the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel
pressure gauge with the fuel pump running.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits? 283–376 kPa
(41–55 psi) Go to Step 3 Go to Step 17
3NOTE: The fuel pressure will drop when the fuel pump
stops running, then it should stabilize and remain
constant.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge remain constant? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 12
41. When the vehicle is at normal operating
temperature, turn the ignition ON to build fuel
pressure and observe the measurement on the
gauge.
2. Start the engine and observe the fuel pressure
gauge.
Did the reading drop by the amount specified after the
engine was started? 21–105 kPa
(3–15 psi) Go to Step 5 Go to Step 9
5Is fuel pressure dropping off during acceleration,
cruise, or hard cornering? —Go to Step 6 Check for
improper fuel
6Visually and physically inspect the following items for a
restriction:
DThe in–pipe fuel filter.
DThe fuel feed line.
Was a restrication found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Remove the fuel tank and visually and physically
inspect the following items:
DThe fuel pump strainer for a restriction.
DThe fuel line for a leak.
DVerify that the correct fuel pump is in the vehicle.
Was a problem found in any of these areas? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8Replace the fuel pump.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
91. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure
regulator.
2. With the engine idling, apply 12–14 inches of
vacuum to the fuel pressure regulator.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge drop by the amount specified? 21–105 kPa
(3–15 psi) Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Locate and repair the loss of vacuum to the fuel
pressure regulator.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
11 Replace the fuel pressure regulator.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
12 1. Run the fuel pump with the Tech 2.
2. After pressure has built up, turn off the pump and
clamp the supply hose shut with suitable locking
pliers which will not damage the hose.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge remain constant? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 15
13 Visually inspect the fuel supply line and repair any
leaks.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Remove the fuel tank and inspect for leaky hose or
in–tank fuel line.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
15 1. If the pliers are still clamped to the fuel supply hose,
remove the locking pliers.
2. With suitable locking pliers which will not damage
the hose, clamp the fuel return line to prevent fuel
from returning to the fuel tank.
3. Run the fuel pump with the Tech 2.
4. After pressure has built up, remove power to the
pump.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge remain constant? —Go to Step 11 Go to Step 16
16 Locate and replace any leaking fuel injector(s).
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
17 Is the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge above the specified limit? 376 kPa (55
psi) Go to Step 18 Go to Step 21
18 1. Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to the Fuel
Pressure Relief.
2. Disconnect the fuel return line from the fuel rail.
3. Attach a length of flexible hose to the fuel rail return
outlet passage.
4. Place the open end of the flexible hose into an
approved gasoline container.
5. Run the fuel pump with the Tech 2.
6. Observe the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel
pressure gauge with the fuel pump running.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits? 290–376 kPa
(42–55 psi) Go to Step 19 Go to Step 20
19 Locate and correct the restriction in the fuel return line.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
20 Visually and physically inspect the fuel rail outlet
passages for a restriction.
Was a restriction found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
StepNoYesValue(s)Action
21 Is the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge above the specified value? 0 kPa (0 psi) Go to Step 22 Go to Step 23
22 1.Command the fuel pump ON with the Tech 2.
2.Using suitable pliers which will not damage the fuel
hose, gradually apply pressure with the pliers to
pinch the flexible fuel return hose closed.
CAUTION:Do not let the fuel pressure exceed
the second specified value.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge rise above the first specified value? 414 kPa (60
psi) Go to Step 11 Go to Step 7
23 1. Command the fuel pump ON with the Tech 2.
2. Remove the fuel filler cap and listen for the sound of
the fuel pump running.
3. Turn the pump off.
Was the fuel pump running? —Go to Step 7
Go to Fuel
System
Electrical Test
Chart
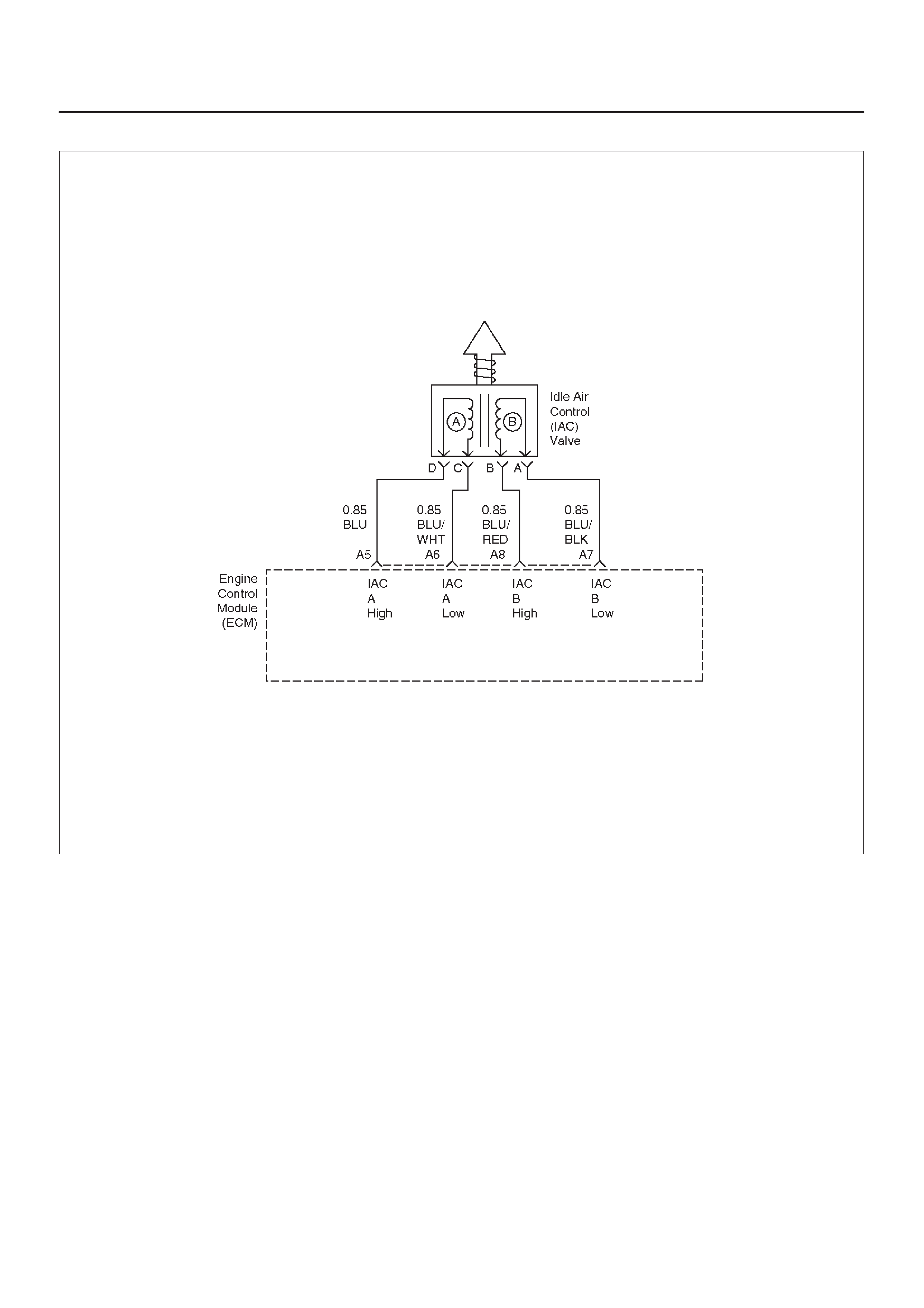
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) SYSTEM CHECK
D06RX112
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls engine idle
speed with the idle air control (IAC) valve. T o increase idle
speed, the ECM retracts the IAC valve pintle away from
its seat, allowing more air to bypass the throttle bore. To
decrease idle speed, it extends the IAC valve pintle
towards its seat, reducing bypass air flow. A Tech 2 will
read the ECM commands to the IAC valve in counts.
Higher counts indicate more air bypass (higher idle).
Lower counts indicate less air is allowed to bypass (lower
idle).
Diagnostic Aids
A slow , unstable, or fast idle may be caused by a non-IAC
system problem that cannot be overcome by the IAC
valve. Out of control range IAC Tech 2 counts will be
above 60 if idle is too low, and zero counts if idle is too
high. The following checks should be made to repair a
non-IAC system problem:
DVacuum leak (high idle) – If idle is too high, stop the
engine. Fully extend (low) IAC with the Tech 2. Start
the engine. If idle speed is above 800 RPM, locate
and correct the vacuum leak, including the PCV
system. Check for binding of the throttle blade or
linkage.
DLean heated oxygen sensor signal (high air/fuel ratio)
– The idle speed may be too high or too low. Engine
speed may vary up and down, and disconnecting the
IAC valve does not help. Diagnostic trouble codes
P0131, P0151, P0171, may be set. Tech 2 oxygen
(O2) voltage will be less than 100 mV (0.1 V). Check
for low regulated fuel pressure, water in fuel, or a
restricted injector.
DRich heated oxygen sensor signal (low air/fuel ratio) –
The idle speed will be too low. Tech 2 IAC counts will
usually be above 80. The system is obviously rich
and may exhibit black smoke in the exhaust.
Tech 2 O2 voltage will be fixed at about 750 mV (0.75
V). Check for high fuel pressure, or a leaking or
sticking injector. A silicon-contaminated heated
oxygen sensor will show an O2 voltage slow to
respond on Tech 2.
DThrottle body – Remove the IAC valve and inspect the
bore for foreign material.
DIAC valve electrical connections – IAC valve
connections should be carefully checked for proper
contact.
DPCV valve – An incorrect or faulty PCV valve may
result in an incorrect idle speed. Refer to
Diagnosis,
Rough Idle, Stalling.
If intermittent poor driveability or
idle symptoms are resolved by disconnecting the
IAC, carefully recheck the connections and valve
terminal resistance, or replace the IAC.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
1. The Tech 2 is used to extend and retract the IAC
valve. Valve movement is verified by an engine
speed change. If no change in engine speed
occurs, the valve can be resettled when removed
from the throttle body.
2. This step checks the quality of the IAC movement in
step 1. Between 700 revolutions per minute (RPM)
and about 1500 RPM, the engine speed should
change smoothly with each flash of the tester light
in both extend and retract. If the IAC valve is
retracted beyond the control range (about 1500
RPM), it may take many flashes to extend the IAC
valve before engine speed will begin to drop. This
is normal on certain engines. Fully extending the
IAC may cause engine stall. This may be normal.
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
11. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Connect the Tech 2.
3. Set the parking brake.
4. Block the wheels.
5. Turn the air conditioning “OFF.”
6. Idle the engine in Park (A/T) or Neutral (M/T).
7. Operate the IAC test.
8. The engine speed should decrease and increase as
the IAC is cycled.
Does the RPM change? —Go to
Step 2
Go to
Step 3
2RPM should change smoothly.
Does the RPM change within the range specified? 700-1500
RPM —Go to
Step 3
3Check the IAC passages.
Are the IAC passages OK? —Go to
Step 4
Go to
Step 5
4Clear any obstruction from the IAC passages.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
5Replace the IAC. Refer to
On-V ehicle Service, Idle Air
Control Valve.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
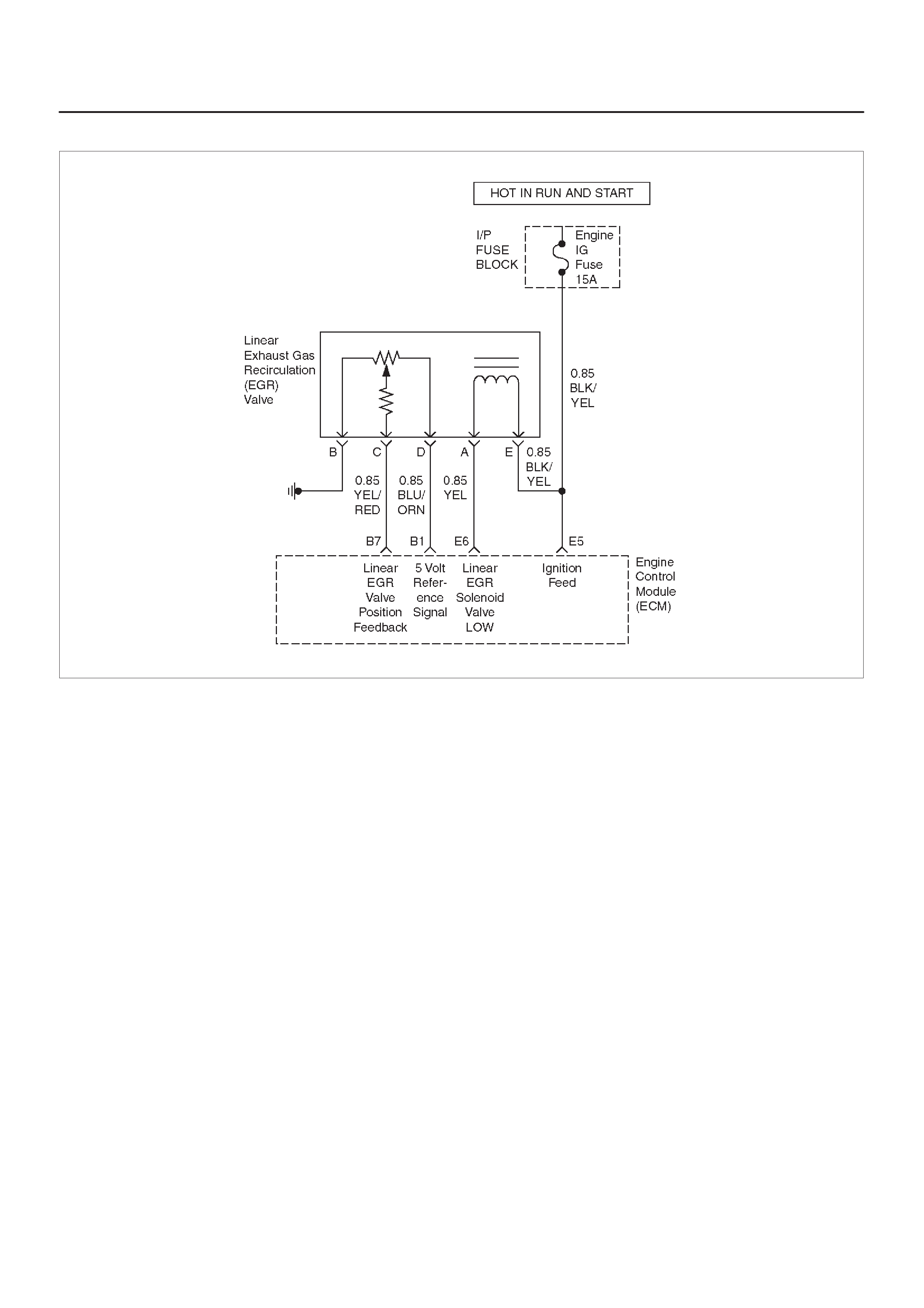
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM CHECK
D06RX113
Circuit Description
A properly operating exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
system will directly affect the air/fuel requirements of the
engine. Since the exhaust gas introduced into the air/fuel
mixture is an inert gas (contains very little or no oxygen),
less fuel is required to maintain a correct air/fuel ratio.
Introducing exhaust gas into the combustion chamber
lowers combustion temperatures and reduces the
formation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the exhaust gas.
Lower combustion temperatures also prevent detonation.
If the EGR pintle were to stay closed, the inert exhaust
gas would be replaced with air and the air/fuel mixture
would be leaner. The powertrain control module (ECM)
would compensate for the lean condition by adding fuel,
resulting in higher long term fuel trim values.
Diagnostic Aids
The EGR valve chart is a check of the EGR system. An
EGR pintle constantly in the closed position could cause
detonation and high emissions of NOx. It could also result
in high long term fuel trim values in the open throttle cell,
but not in the closed throttle cell. An EGR pintle constantly
in the open position would cause rough idle. Also, an EGR
valve mounted incorrectly (rotated 180°) could cause a
rough idle without setting an EGR DTC. Check for the
following items:
DEGR passages – Check for restricted or blocked EGR
passages.
DManifold absolute pressure sensor – A manifold
absolute pressure sensor may shift in calibration
enough to affect fuel delivery. Refer to Manifold
Absolute Pressure Output Check.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Check
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1Check the EGR valve for looseness.
Is the EGR valve loose? —Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2Tighten the EGR valve.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
31. Place the transmission selector in Park or Neutral.
2. Start the engine and idle until warm (”Closed Loop”).
3. Using a Tech 2, command EGR ”50% ON.”
Does the engine idle rough and lose RPMs? —
EGR system
working
properly. No
problem
found. Go to Step 4
41. Engine OFF.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Using a test light to ground, check the EGR harness
between the ignition feed and ground.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the EGR harness ignition feed.
Was the problem corrected? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Remove the EGR valve.
2. Visually and physically inspect the EGR valve
pintle, valve passages and adapter for excessive
deposits, obstructions or any restrictions.
Does the EGR valve have excessive deposits,
obstructions or any restrictions? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Clean or replace EGR system components as
necessary.
Was the problem corrected? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Ground the EGR valve metal case to battery (–).
2. Using a T ech 2, command EGR ON and observe the
EGR valve pintle for movement.
Does the EGR valve pintle move according to
command? —Go to Step 9 Go to DTC
P0404 chart
91. Remove the EGR inlet and outlet pipes from the
intake and exhaust manifolds.
2. Visually and physically inspect manifold EGR ports
and EGR inlet and outlet pipes for blockage or
restriction caused by excessive deposits or other
damage.
Do the manifold EGR ports or inlet and outlet pipes
have excessive deposits, obstructions, or any
restrictions? —Go to Step 10
EGR system
working
properly. No
problem
found.
10 Clean or replace EGR system components as
necessary.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
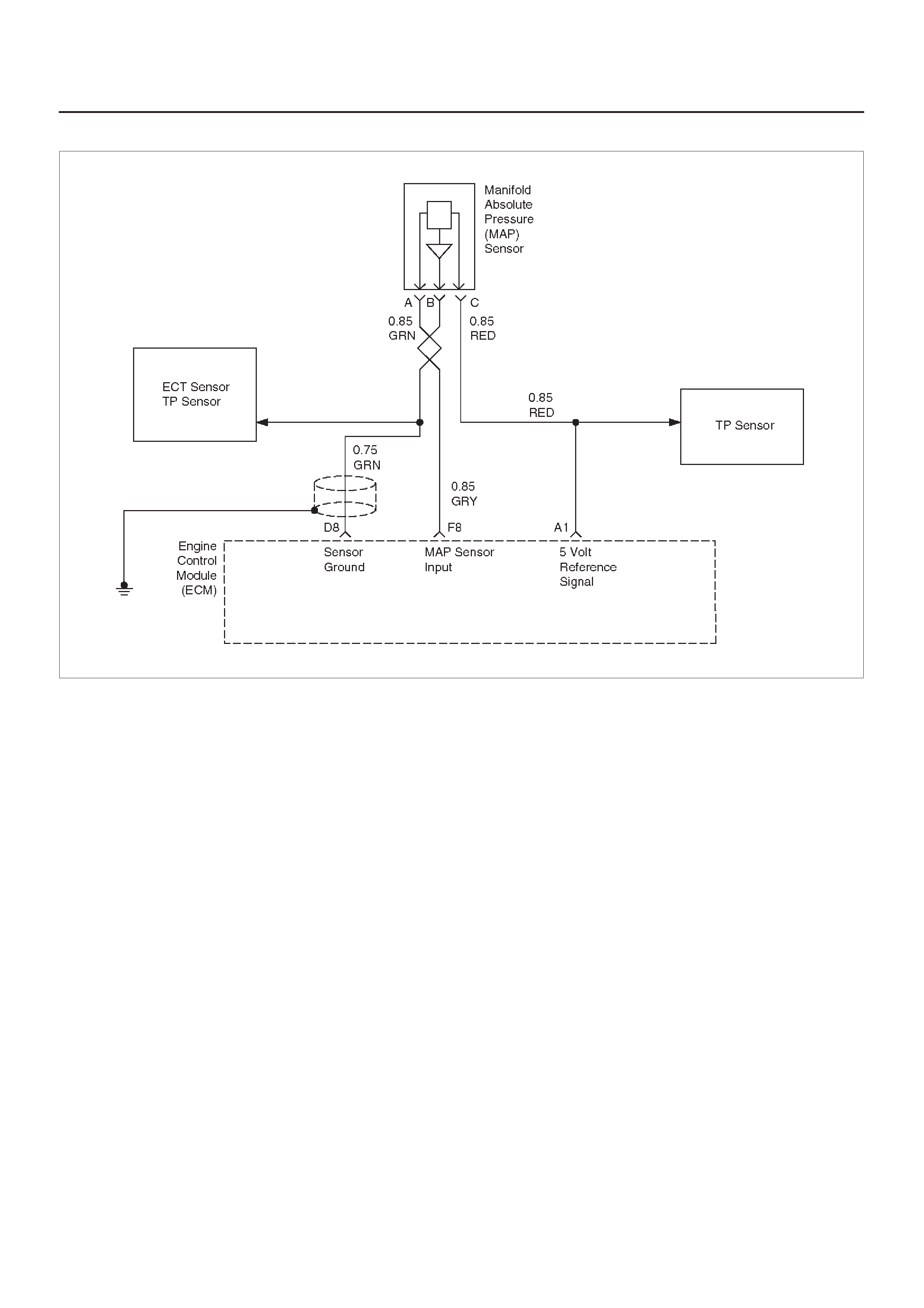
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) OUTPUT CHECK
D06RX114
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake MAP which result from engine
load (intake manifold vacuum) and engine speed
changes; and converts these into a voltage output. The
powertrain control module (ECM) sends a 5–volt
reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the MAP
changes, the output voltage of the sensor also changes.
By monitoring the sensor output voltage, the ECM knows
the MAP. A lower pressure (low voltage) output voltage
will be about 1–2 volts at idle. Higher pressure (high
voltage) output voltage will be about 4–4.8 volts at wide
open throttle. The MAP sensor is also used, under certain
conditions, to measure barometric pressure, allowing the
ECM to make adjustments for different altitudes. The
ECM uses the MAP sensor to diagnose proper operation
of the EGR system, in addition to other functions.
Test Description
IMPORTANT:Be sure to use the same diagnostic test
equipment for all measurements.
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1.When you compare the Tech 2 readings to a known
good vehicle, it is important to compare vehicles
that use MAP sensors that have the same part
number.
2.Applying 34 kPa (10 Hg) vacuum to the MAP sensor
should cause the voltage to be 1.5–2.1 volts less
than the voltage at step 1. Upon applying vacuum to
the sensor, the change in voltage should be
instantaneous. A slow voltage change indicates a
faulty sensor.
3.Check the vacuum hose to the sensor for leaking or
restriction. Be sure that no other vacuum devices
are connected to the MAP hose.
IMPORTANT:Make sure the electrical connector
remains securely fastened.
4. Disconnect the sensor from the bracket. Twist the
sensor with your hand to check for an intermittent
connection. Output changes greater than 0.10 volt
indicate a bad sensor.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Output Check
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
11. Turn the ignition OFF and leave it OFF for 15
seconds.
2. Ignition ON. Do not crank engine.
3. The Tech 2 should indicate a manifold absolute
pressure (MAP) sensor voltage.
4. Compare this scan reading to the scan reading of a
known good vehicle obtained using the exact same
procedure as in Steps 1–4.
Is the voltage reading the same +/– 0.40 volt? —Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
21. Disconnect the vacuum hose at the MAP sensor
and plug the hose.
2. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the MAP sensor.
3. Start the engine.
4. Apply 34 kPa (10 Hg) of vacuum and note the
voltage change.
Is the voltage change 1.5–2.1 volts less than step 1? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3Check the sensor hose for leakage or restriction.
Does the hose supply vacuum to the MAP sensor only? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4Repair the hose to ensure the hose supplies vacuum to
the MAP sensor only.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
5Check the sensor connection.
Is the sensor connection good? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6Refer to On–Vehicle Service, MAP Sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
7Repair the poor connection.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
ECM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
The following table lists the diagnostic trouble codes
supported by this vehicle application. If any DTCs not
listed here are displayed by a Scan Tool, the Tech 2 data
may be faulty; notify the Tech 2 manufacturer of any
DTCs displayed that are not included in the following
table.
ECM Diagnostic Trouble Codes
DTC Description Type Illuminate MIL
P0106 MAP Circuit/Range Performance Problem BYes
P0107 MAP Sensor Circuit Low Input AYes
P0108 MAP Sensor Circuit High Input AYes
P0112 IAT Sensor Circuit Low Input AYes
P0113 IAT Sensor Circuit High Input AYes
P0117 ECT Sensor Circuit Low Input AYes
P0118 ECT Sensor Circuit High Input AYes
P0121 TP Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem D No
P0122 TP Sensor Circuit Low Input AYes
P0123 TP Sensor Circuit High Input AYes
P0131 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1) AYes
P0132 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1) AYes
P0134 O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank Sensor 1) AYes
P0135 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1) BYes
P0171 Fuel Trim System Too Lean (Bank 1) BYes
P0172 Fuel Trim System Too Rich (Bank 1) BYes
P0201 Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 1 AYes
P0202 Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 2 AYes
P0203 Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 3 AYes
P0204 Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 4 AYes
P0325 Knock Sensor Circuit Malfunction BYes
P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Low Input BYes
P0336 CKP Sensor Circuit Range/Performance BYes
P0337 CKP Sensor Circuit Low Input BYes
P0341 CMP Sensor Circuit Range/Performance BYes
P0342 CMP Sensor Circuit Low Input BYes
P0351 Ignition Coil ”A” Primary/Secondary AYes
P0352 Ignition Coil ”B” Primary/Secondary AYes
P0401 EGR Flow Insufficient Detected AYes
P0402 EGR Excessive Flow Detected BYes
P0404 EGR Circuit Range/Performance BYes
P0405 EGR Sensor Circuit Low AYes
P0406 EGR Sensor Circuit High AYes
P0443 EVAP Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit Malfunction AYes
P0480 Cooling Fan 1 Control Circuit Malfunction D No
P0481 Cooling Fan 2 Control Circuit Malfunction D No
P0502 VSS Circuit Low Input BYes
P0506 Idle Control System RPM Lower than expected BYes
DTC Illuminate MILTypeDescription
P0507 Idle Control System RPM Higher than expected BYes
P0563 System Voltage High AYes
P0601 Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error AYes
P1106 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage D No
P1107 MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage D No
P1111 IAT Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage D No
P1112 IAT Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage D No
P1114 ECT Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage D No
P1115 ECT Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage D No
P1121 TP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage D No
P1122 TP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage D No
P1171 Fuel System Lean During Acceleration AYes
P1404 EGR Closed Valve BYes
P1625 PCM Unexpected Reset DYes
P1627 PCM A/D Conversion Malfunction AYes
P1635 5 Volt Reference Voltage Circuit Malfunction AYes
P1640 ODM Output Circuit Fault D No
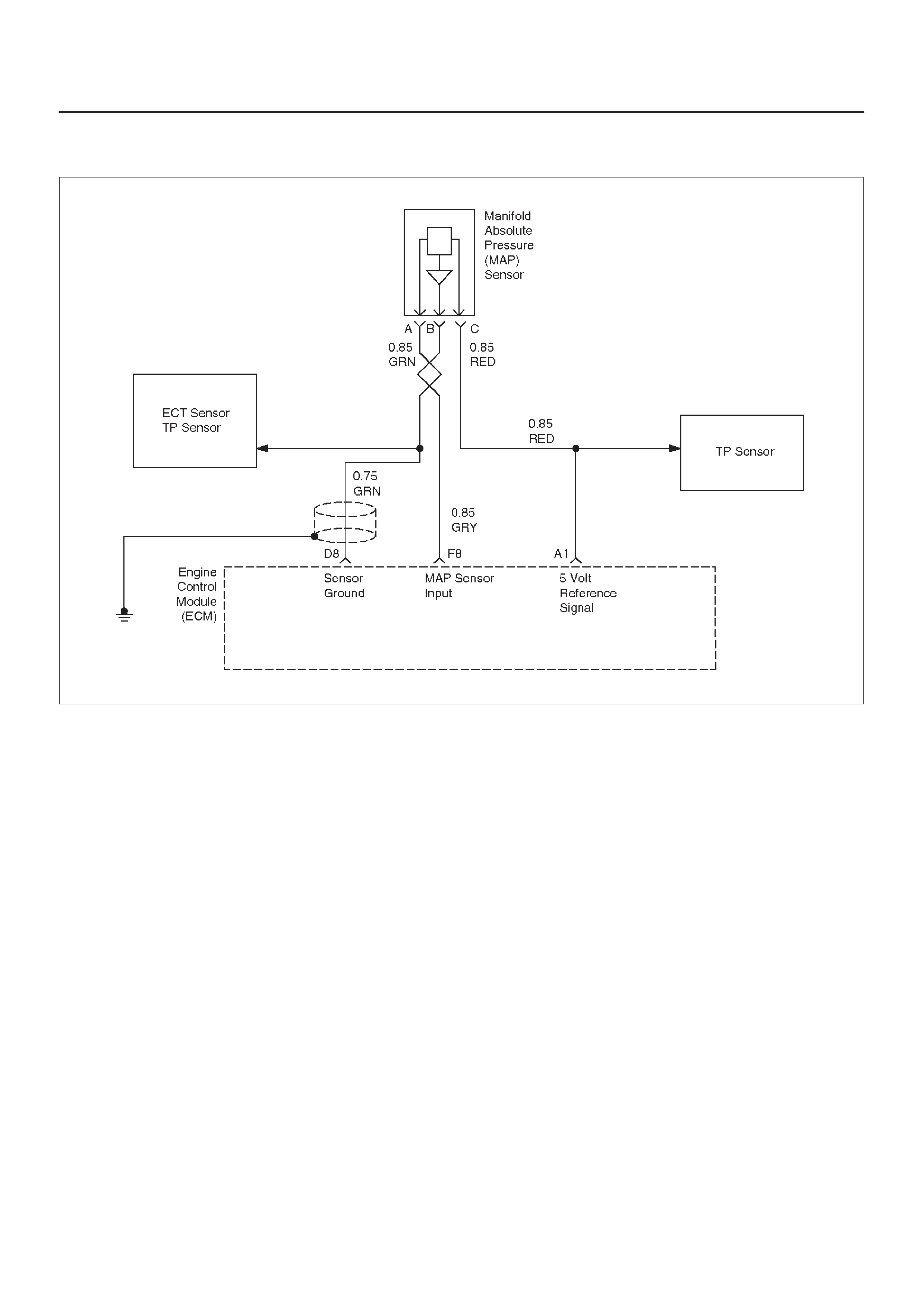
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0106 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE (MAP) CIRCUIT/RANGE PERFORMANCE PROBLEM
D06RX114
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the engine control module (ECM) varies
from below 2 volts at idle (low manifold pressure) to above
4 volts with the ignition ON engine not running or at
wide–open throttle (high manifold pressure).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used on the 2.2L engine. This is calculated using inputs
from the MAP sensor, RPM, CKP Sensor, and the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) sensor. The MAP sensor is the
main sensor used in this calculation, and measuring
engine load is its main function. The MAP sensor is also
used to determine manifold pressure changes while the
exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow test diagnostic is
being run, to determine engine vacuum level for some
other diagnostics and to determine barometric pressure
(BARO). Refer to DTC P0401.
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range (10–104 kpa) of the MAP sensor. If the
ECM detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively
low, Diagnostic Trouble Code P0106 will be set.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0106 is a Type B Code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo ECT, CKP, EGR, EVAP, MAP orTP sensor DTC’s
present.
DEngine speed is steady, changing less than 20 RPM.
DThrottle position is steady, throttle angle changes less
than 5%.
DEGR flow rate is steady, changing less than 2%.
DIAC valve counts are steady, changing less than 3
counts.
DEngine speed is between 1000 RPM and 4000 RPM.
DECT is above –10°C (14°F).
DNo change in brake switch, A/C clutch, 3 or power
steering pressure switch status.
The above conditions are met for longer than 1.5 seconds
and the following condition is met in two consecutive trips:
DActual MAP value varies more than 10 kPa.
DThe MAP value must vary for a total of 10 seconds over
a 20–second period of time that the samples were
monitored.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0106 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0106 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt Reference with the TP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit.
DThe MAP sensor shares a ground with the TP sensor
and Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; an open circuit, a short to ground, or a short
to voltage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor.
A change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0106 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set. If it is determined
that the Diagnostic Trouble Code occurs intermittently,
performing the Diagnostic Trouble Code P1106 or P1107
Diagnostic Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
DTC P0106 MAP Circuit/Range Performance Problem
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, engine OFF
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTC’s.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for Diagnostic
Trouble Code P0106.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that DTC P0106 ran and
passed? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Check for the following condition:
DVacuum hoses disconnected, damaged, or
incorrectly routed?
DIntake manifold vacuum leaks;
DVacuum leaks at throttle body;
DVacuum leaks at EGR valve flange and pipes;
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
sensor electrical connector.
2. Observe the MAP value displayed on the Tech 2.
Is the MAP value near the specified value? 0 V 10.3 kPa Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Check the MAP sensor signal circuit; between the MAP
sensor and the Engine Control Module (ECM), for a
short to voltage? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
6Check the MAP sensor circuit, between the MAP
sensor and the ECM, the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
7Check the 5 volt signal circuit, between the MAP
sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a fused jumper between the MAP sensor
circuit and the 5 volt signal circuit, both at the wiring
harness’ MAP sensor connector.
3. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
4. Observe the MAP value displayed on the Tech 2?
Does the Tech 2 read the following value? (if no, start
with the diagnosis chart for other sensors in the circuit
and see if 5V returns.) 5 volts 104
kPa Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
9Check the MAP sensor ground circuit, between the
MAP sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a Digital Multimeter (DVM), set to measure
voltage, between the ground circuit and the 5 volt
signal circuit, both at the wiring harness’ MAP
sensor connector.
3. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
5 volts
Does the DVM read the following value? —Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Replace the MAP sensor.
Verify repair. ———
12 Replace the ECM. ———
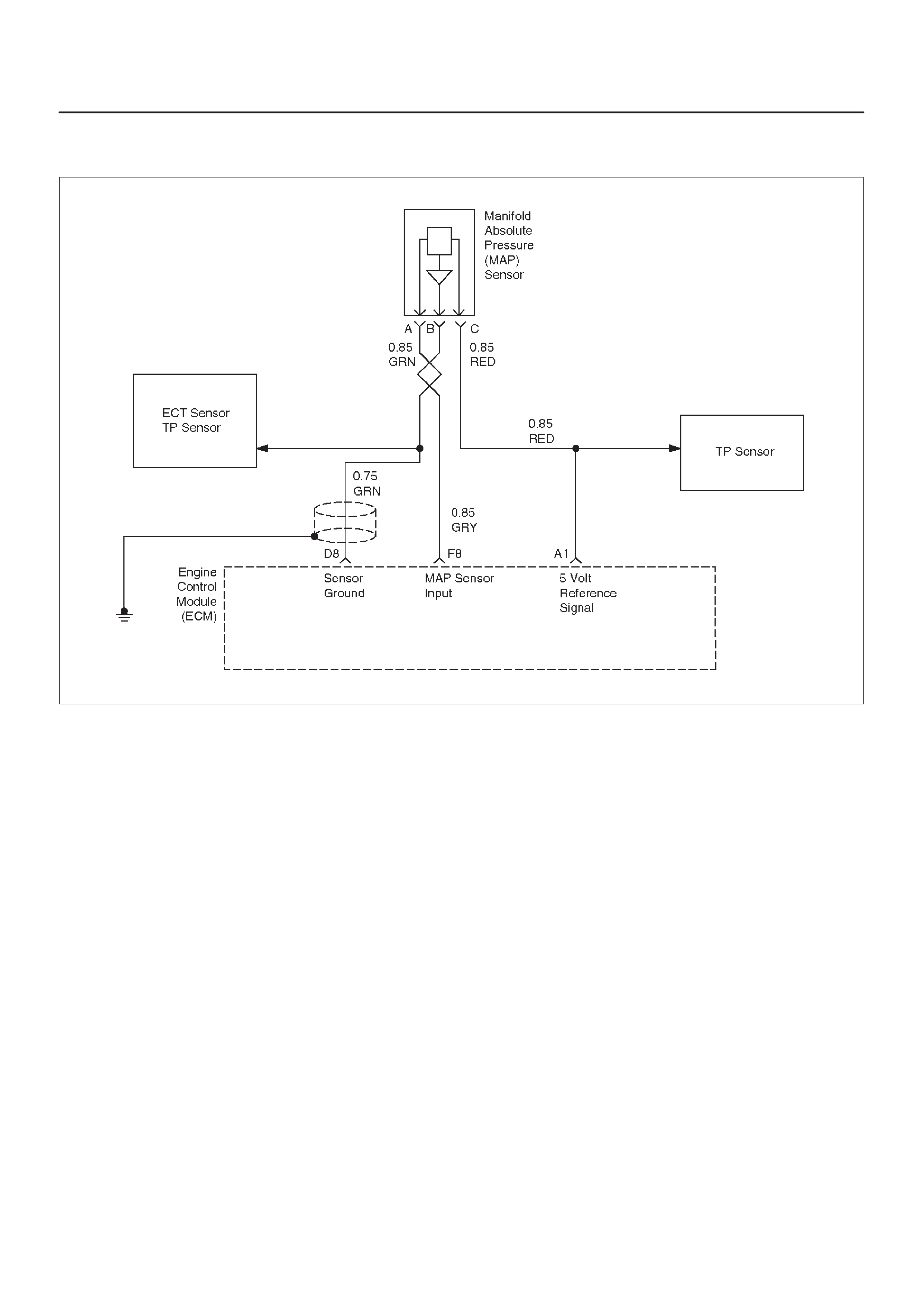
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0107 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
D06RX114
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the powertrain control module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (low manifold pressure) to
above 4 volts with the ignition ON, engine not running or at
wide–open throttle (high manifold pressure).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used on the 2.2L engine. This is calculated using inputs
from the MAP sensor, the CKP Sensor, and the Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) sensor. The MAP sensor is the main
sensor used in this calculation, and measuring engine
load is its main function. The MAP sensor is also used to
determine manifold pressure changes while the exhaust
gas recirculation (EGR) flow test diagnostic is being run,
to determine engine vacuum level for some other
diagnostics and to determine barometric pressure
(BARO). Refer to DTC P0401.
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range (10–104 kpa) of the MAP sensor. If the
ECM detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively
low, Diagnostic Trouble Code P0107 will be set. DTC
P0107 is a Type A Code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo TP sensor Diagnostic Trouble Codes present.
DEngine is running.
DSystem voltage greater than 11 volts.
DThrottle angle is above 0% if engine speed is less than
or equal to 1300 RPM.
DThrottle angle is above 5% if engine speed is above
1300 RPM.
DThe MAP sensor indicates manifold absolute pressure
below 11 kPa for a total of approximately 10 seconds
over a 16–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
DThe ECM will use a MAP value based on speed density
calculation.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history DTC P0107 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm–up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0107 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt Reference with the TP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit.
DThe MAP sensor shares a ground with the TP sensor
and Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor.
A change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
DA faulty 5 volt reference circuit could also set a TP
Sensor Diagnostic Trouble Code because the two
sensors share the same 5 volt reference pin at the
ECM.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0107 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set. If it is determined
that the Diagnostic Trouble Code occurs intermittently,
performing the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0107
Diagnostic Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
DTC P0107 – MAP Sensor Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. With the throttle closed, observe the MAP value
displayed on the Tech 2.
Is the MAP value near the specified value? 0V 10.3 kPa
at sea level Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor «Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0107.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0107 failed? —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
3. Jumper the 5 volt reference circuit and the MAP
signal together at the MAP sensor harness
connector.
4. Ignition ON.
5. Observe the MAP value displayed on the Tech 2.
Is the MAP value near the specified value? (if no, start
with the diagnosis chart for other sensors in the circuit
and see if 5V returns.) 5 V 104 kPa Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect the jumper.
2. Connect a fused jumper between the 5 Volt signal
circuit and the MAP sensor signal circuit at the MAP
sensor harness connector.
3. Observe the MAP value displayed on the Tech 2.
Is the MAP value near the specified value? 5 V 104 kPa Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and check the 5 volt reference
circuit for an open or short to ground.
3. If the 5 volt reference circuit is open or shorted to
ground, repair it as necessary.
Was the 5 volt reference circuit open or shorted to
ground? —Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Check the 5 volt reference circuit for a poor connection
at the ECM and replace the terminal if necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check the MAP signal
circuit for an open, short to ground, or short to the
sensor ground circuit.
3. If the MAP sensor signal circuit is open or shorted to
ground, repair it as necessary.
W as the MAP signal circuit open or shorted to ground? —Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check the MAP sensor signal circuit for a poor
connection at the ECM and the MAP sensor; replace
the terminal if necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
10 Replace the MAP sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
11 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
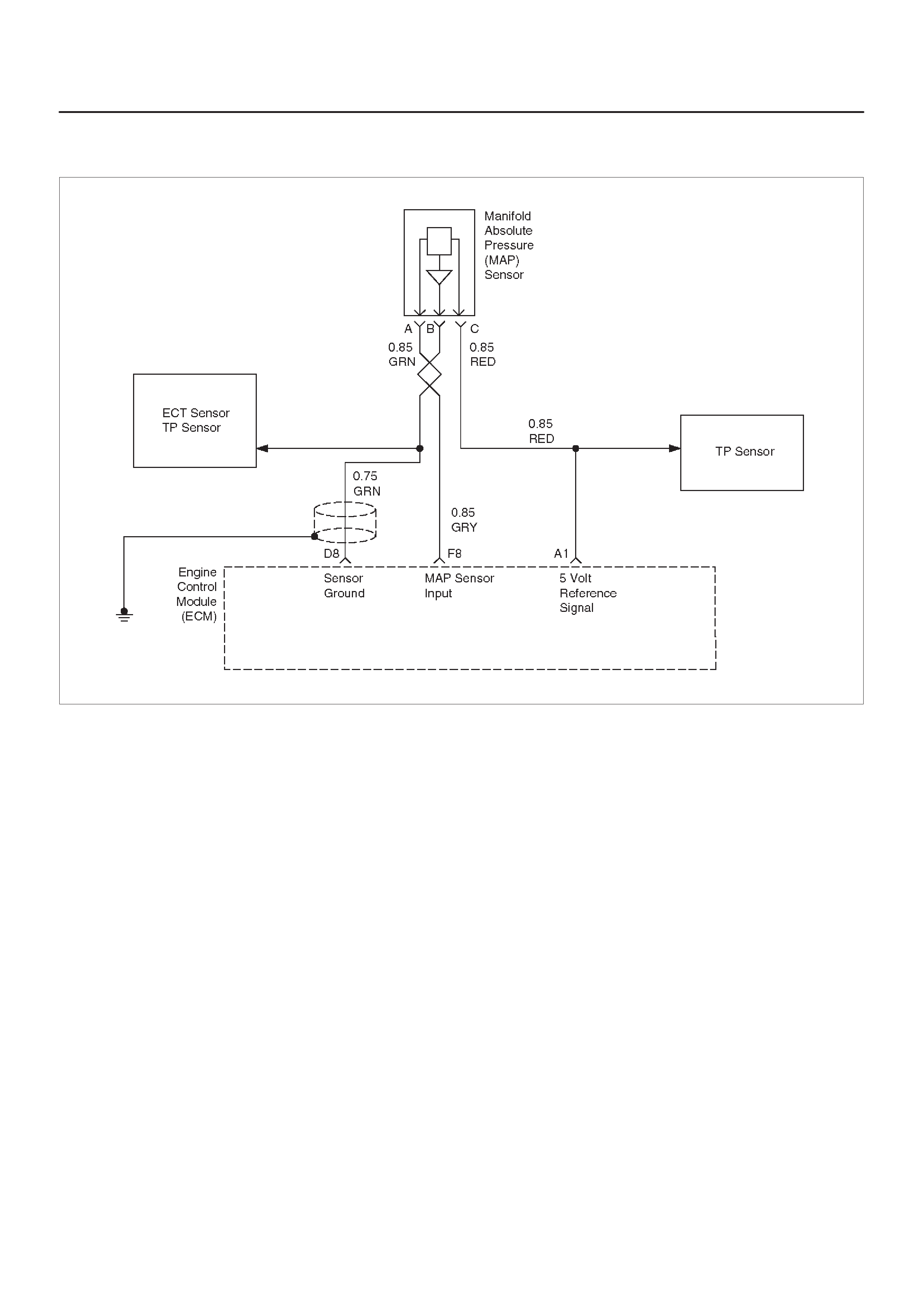
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0108 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE (MAP) CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
D06RX114
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the powertrain control module (ECM)
varies from below 2 volts at idle (low manifold pressure) to
above 4 volts with the ignition ON, engine not running or at
wide–open throttle (high manifold pressure).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used on the 2.2L engine. This is calculated using inputs
from the MAP sensor, RPM, CKP Sensor, and the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) sensor. The MAP sensor is the
main sensor used in this calculation, and measuring
engine load is its main function. The MAP sensor is also
used to determine manifold pressure changes while the
exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) flow test diagnostic is
being run, to determine engine vacuum level for some
other diagnostics and to determine barometric pressure
(BARO). Refer to DTC P0401.
The ECM monitors the MAP signals for voltages outside
the normal range (10–104 kpa) of the MAP sensor. If the
ECM detects a MAP signal voltage that is excessively
low, Diagnostic Trouble Code P0108 will be set. DTC
P0108 is a Type A Code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo TP sensor Diagnostic Trouble Codes present.
DEngine is running.
DThrottle position is below 2.7% if engine speed is below
1000 RPM.
DThrottle position is below 10% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
DThe MAP sensor indicates manifold absolute pressure
above 90 kPa for a total of approximately 10 seconds
over a 16–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will default to a BARO value of 79.3 kPa.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0108 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0108 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt Reference with the TP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit.
DThe MAP sensor share a ground with the TP sensor
and Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; an open circuit, a short to ground, or a short
to voltage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor.
A change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0108 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set.
DTC P0108 MAP Sensor Circuit High Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. If the engine idle is rough, unstable or incorrect,
repair the idle problem before using this chart. Refer
to Symptoms section.
2. With the engine idling, note the MAP value on the
Tech 2.
Is the MAP reading above the specified value? About 4V 90
kPa Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON engine OFF
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTC’s.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for Diagnostic
Trouble Code P0108.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that DTC P0108 failed this
ignition? —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the MAP sensor electrical connector.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Observe the MAP value displayed on the Tech 2.
Is the MAP value near the specified value? (if no, start
with the diagnosis chart for other sensors in the circuit
and see if 5V returns.) 0 V 10.3 kPa Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Check the MAP sensor signal circuit; between the MAP
sensor and the Engine Control Module (ECM), for a
short to voltage.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
6Check the MAP sensor circuit, between the MAP
sensor and the ECM, the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Check the 5 volt signal circuit, between the MAP
sensor and the ECM for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a fused jumper between the MAP sensor
circuit and the 5 volt signal circuit, both at the wiring
harness’ MAP sensor connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Observe the MAP value displayed on the Tech 2?
Does the Tech 2 read the following value? 5 volts 104
kPa Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
9Check the MAP sensor ground circuit, between the
MAP sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a Digital Multimeter (DVM), set to measure
voltage, between the ground circuit and the 5 volt
signal circuit, both at the wiring harness’ MAP
sensor connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
Does the DVM read the following value? 5 Volts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Replace the MAP sensor.
Verify repair. ———
12 Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———
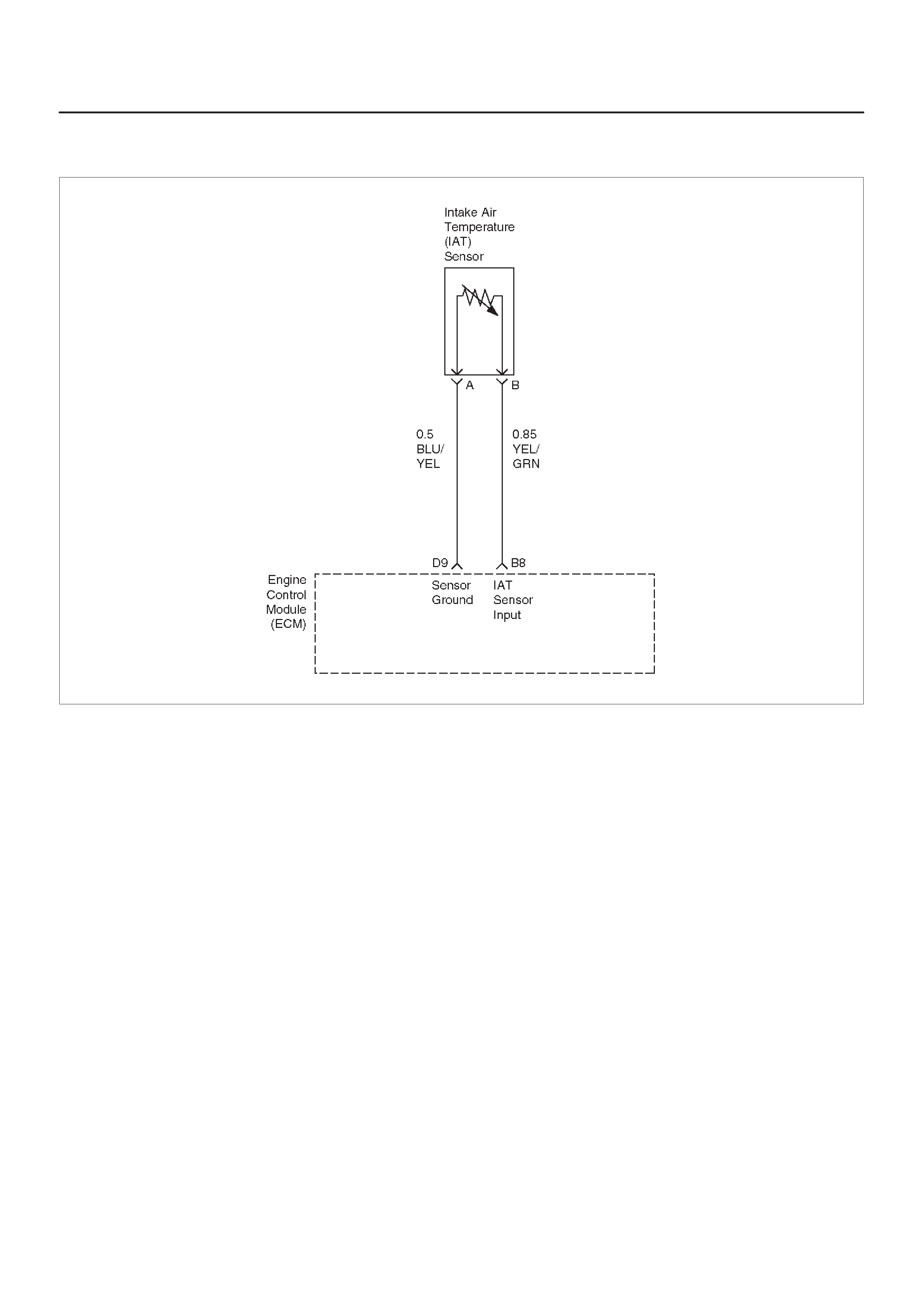
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0112 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
D06RX116
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The engine control module (ECM) applies 5 volts
through a pull–up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower, causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0112 will set when the ECM
detects an excessively low signal voltage (short to
ground) on the intake air temperature sensor signal
circuit. DTC P0112 is a Type A Code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe engine has been running for over 2 minutes.
DVehicle speed is greater than 48 km/h (30 mph).
DIA T signal voltage less than 0.10 volts for a total of 12.5
seconds over a 25–second period of time.
The above conditions are met for at least 2 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will use a default IAT valve based on ECM
inputs and engine run time.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history DTC P0112 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm–up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DDTC P0112 can be cleared by using the Scan Tool’s
”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery and open
circuits. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
IA T display on the T ech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the IAT sensor. A change
in the IAT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0112 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Verifies that the fault is present.
3.If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0112 can be repeated
only by duplicating the Failure Records condition,
refer to the Temperature vs. Resistance Value table.
The table may be used to test the IAT sensor at
various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of
a ”shifted” sensor that may be stored above or
below a certain temperature. If this is the case,
replace the IAT sensor. If the IAT sensor appears
to be OK, the fault is intermittent; refer to
Diagnostic Aids.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
°C°F OHMS
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 113 1188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P0112 Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Using a Tech 2, monitor the intake air temperature
(IAT).
Is the intake air temperature greater than the specified
value? 148°C
(283°F) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, engine OFF. Review and record Tech 2
Failure Records data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor the ”DTC” info for
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0112.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0112 failed this
ignition? —Refer to Test
Description
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the IAT sensor electrical connector.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Observe the intake air temperature on the Tech 2.
Is the intake air temperature below the specified value? –38°C
(–36°F) Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM electrical connectors.
3. Check the IAT sensor signal circuit for a short to
ground.
Is the IAT sensor signal circuit shorted to ground? —Verify Repair Go to Step 7
6Replace the IAT sensor.
Is the action complete? —Verify Repair —
7Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —Verify Repair —
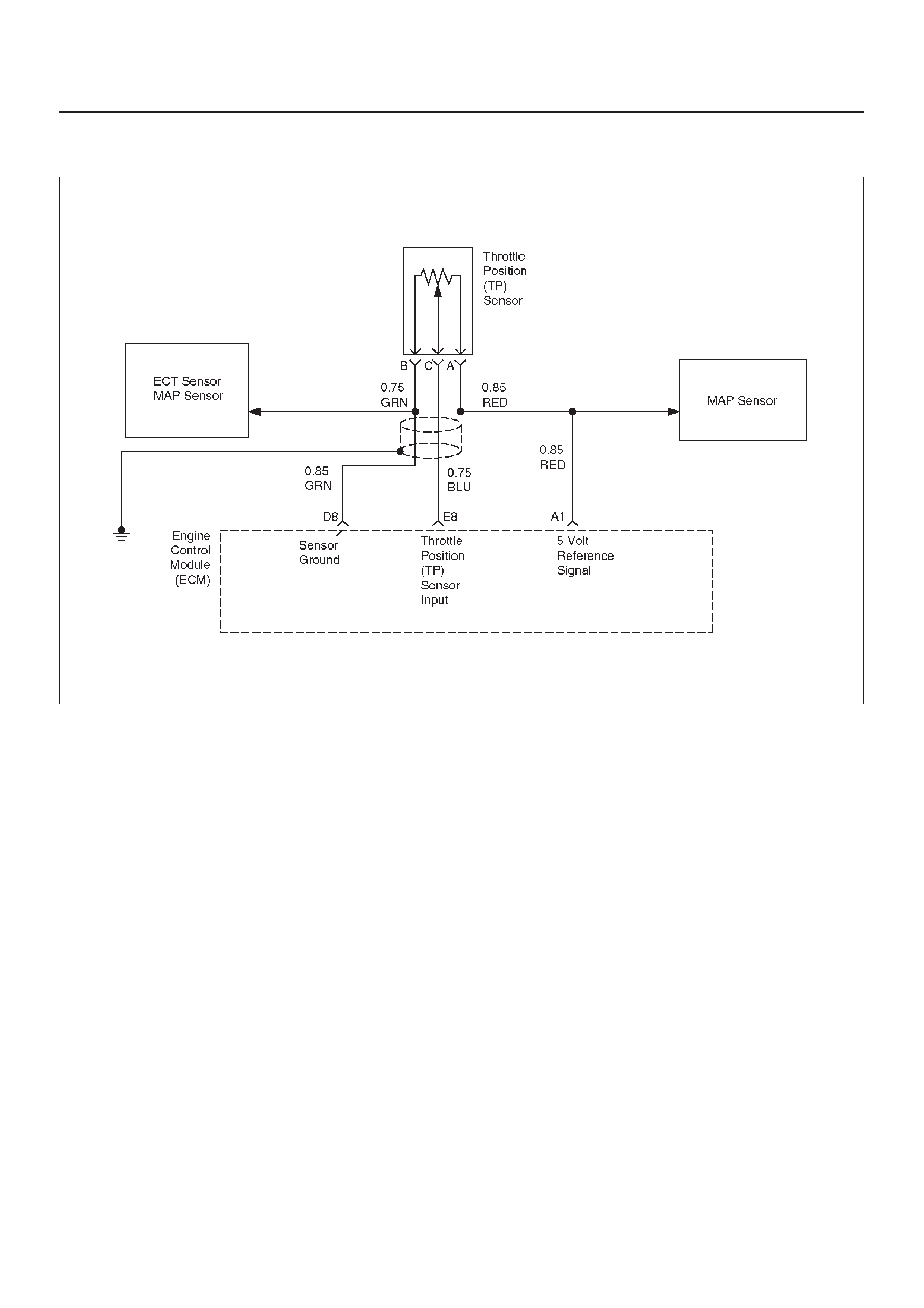
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0113 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
D06RX118
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The engine control module (ECM) applies 5 volts
through a pull–up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0113 will set when the ECM
detects an excessively high signal voltage on the intake
air temperature sensor signal circuit. DTC P0113 is a
Type A Code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe engine has been running for over 4 minutes.
DVehicle speed is less than 32 km/h (20 mph).
DECT signal temperature is above 60°C (140°F).
DMass air flow is less than 20g/second.
DIAT signal voltage almost 5 volts which indicates an
intake air temperature less than –39°C (–38°F) for a
total of 12.5 seconds over a 25–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will use a default IAT valve based on ECM
inputs and engine run time.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0113 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0113 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the IAT
sensor. A change in the IAT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0113 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.Verifies that the fault is present.
3.If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0113 can be repeated
only by duplicating the Failure Records conditions,
refer to the ”Temperature vs. Resistance Values”
table.
The table may be used to test the IAT sensor at
various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of
a ”shifted” sensor that may be open above or
below a certain temperature. If this is the case,
replace the IAT sensor. If the IAT sensor appears
to be OK, the fault is intermittent; refer to
Diagnostic Aids.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
°C°F OHMS
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 1131188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P0113 Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit High Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Ignition ON, engine OFF. Observe the ”Intake Air
Temp” display on the Tech 2.
Is the ”Intake Air Temp” below the specified value? 5V –38°C
(–36°F) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor «Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0113.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0113 failed? —Refer to Test
Description
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the IAT sensor electrical connector.
3. Jumper the IA T signal circuit and the sensor ground
circuit together at the IAT sensor harness
connector.
4. Ignition ON.
5. Observe the ”Intake Air Temp” display on the Tech
2.
Is the ”Intake Air Temp” at the specified value? 0V 140°C
(284°F) Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
51. Jumper the IAT signal circuit at the IAT sensor
harness connector to chassis ground.
2. Observe the ”Intake Air Temp” display on the Tech
2.
Is the ”Intake Air Temp” at the specified value? 0V 140°C
(284°F) Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
6Check for poor connections at the IAT sensor and
replace terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? —Verify Repair Go to Step 10
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check the IAT sensor
ground circuit for an open.
3. If the IAT sensor ground circuit is open, repair it as
necessary.
Was the IAT sensor ground circuit open? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check the IAT signal
circuit for an open.
3. If the IAT sensor signal circuit is open, repair it as
necessary.
Was the IAT signal circuit open? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check for a poor sensor ground or IAT signal circuit
terminal connection at the ECM and replace
terminal(s) if necessary.
Did any of the terminals need to be replaced? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
10 Replace the IAT sensor
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
11 Replace the ECM
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
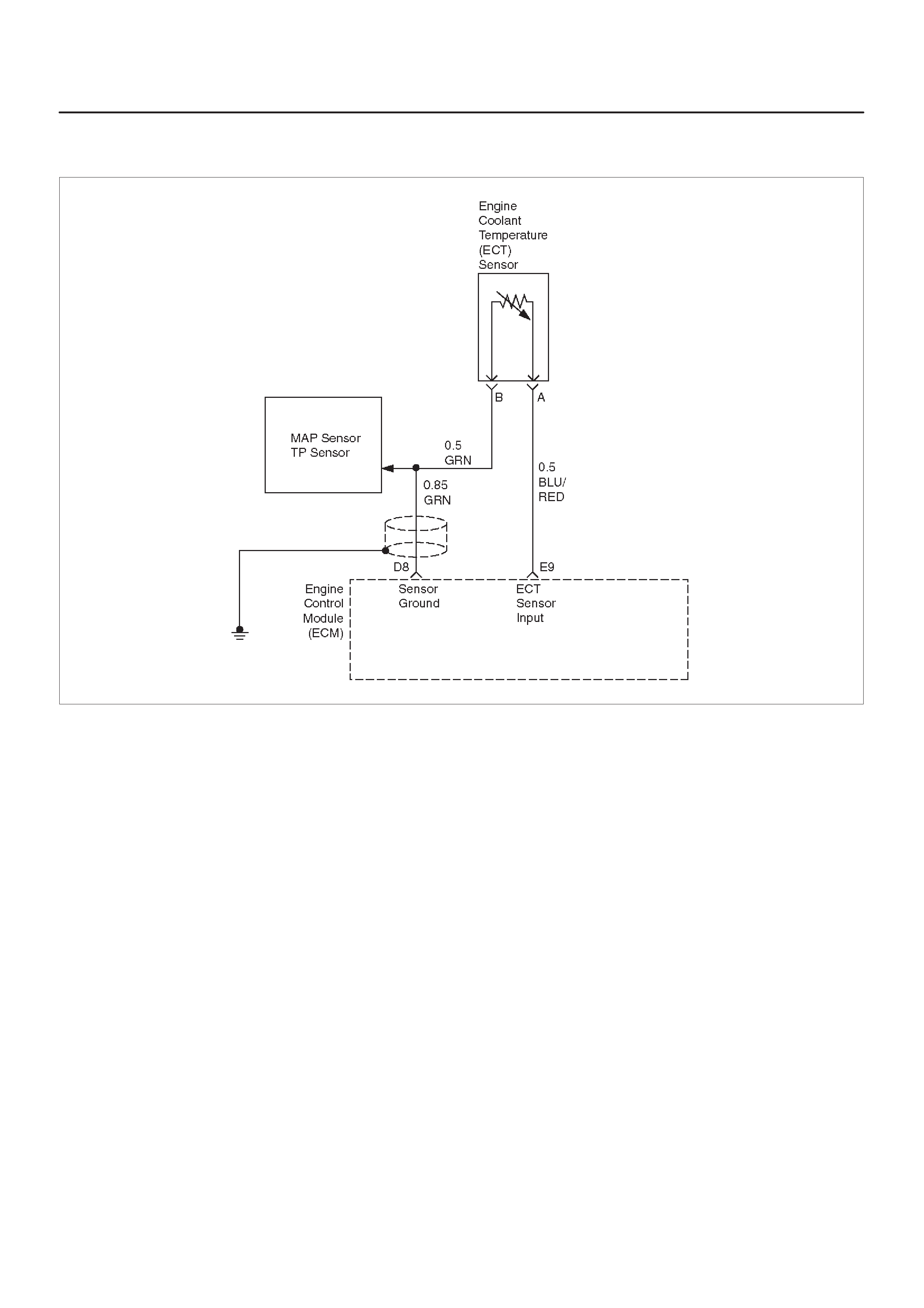
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0117 ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
D06RX117
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted in the engine coolant stream. The
engine control module (ECM) applies a voltage (about 5
volts) through a pull–up resistor to the ECT signal circuit.
When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor (thermistor)
resistance is high, therefore the ECM will measure a high
signal voltage. As the engine coolant warms, the sensor
resistance becomes lower, and the ECT signal voltage
measured at the ECM drops. With a fully warmed–up
engine, the ECT signal voltage should measure about 1.5
to 2.0 volts. DTC P0117 is a Type A Code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine running time is longer than two minutes.
DThe ECT sensor signal indicates an engine coolant
temperature greaterthan 150°C (302°F) (about 0.14
V) for a total of 12.5 seconds overa 25–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will substitute the ECT reading with a default
engine coolant temperature value. The default value is
based on start–up intake air temperature and running
time.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0117 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0117 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the ECT
sensor. A change in the ECT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0117 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set. If it is determined
that the Diagnostic Trouble Code occurs intermittently,
performing the Diagnostic Trouble Code P1114
Diagnostic Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.Verifies that the fault is present.
3.If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0117 can be repeated
only by duplicating the Failure Records conditions,
refer to the ”Temperature vs. Resistance Values”
table.
The table may be used to test the ECT sensor at
various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of
a ”shifted” sensor that may be shorted above or
below a certain temperature. If this is the case,
replace the ECT sensor. If the ECT sensor
appears to be OK, the fault is intermittent; refer to
Diagnostic Aids.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
°C°F OHMS
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 1131188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P0117 – Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON engine OFF.
2. Observe the ”Eng Cool T emp” display on the T ech 2.
Is the ”Eng Cool Temp” below the specified value? 139°C
(282°F) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC P0117.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0117 failed this
ignition? —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the ECT sensor electrical connector.
2. Observe the ”Eng Cool T emp” display on the T ech 2.
Is the ”Eng Cool Temp” at or below the specified value? –39°C
(–38°F) Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and check the ECT signal
circuit for a short to ground or a short to the sensor
ground circuit.
3. If the ECT signal circuit is shorted, repair it as
necessary.
Was the ECT signal circuit shorted to ground? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
6Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
7Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
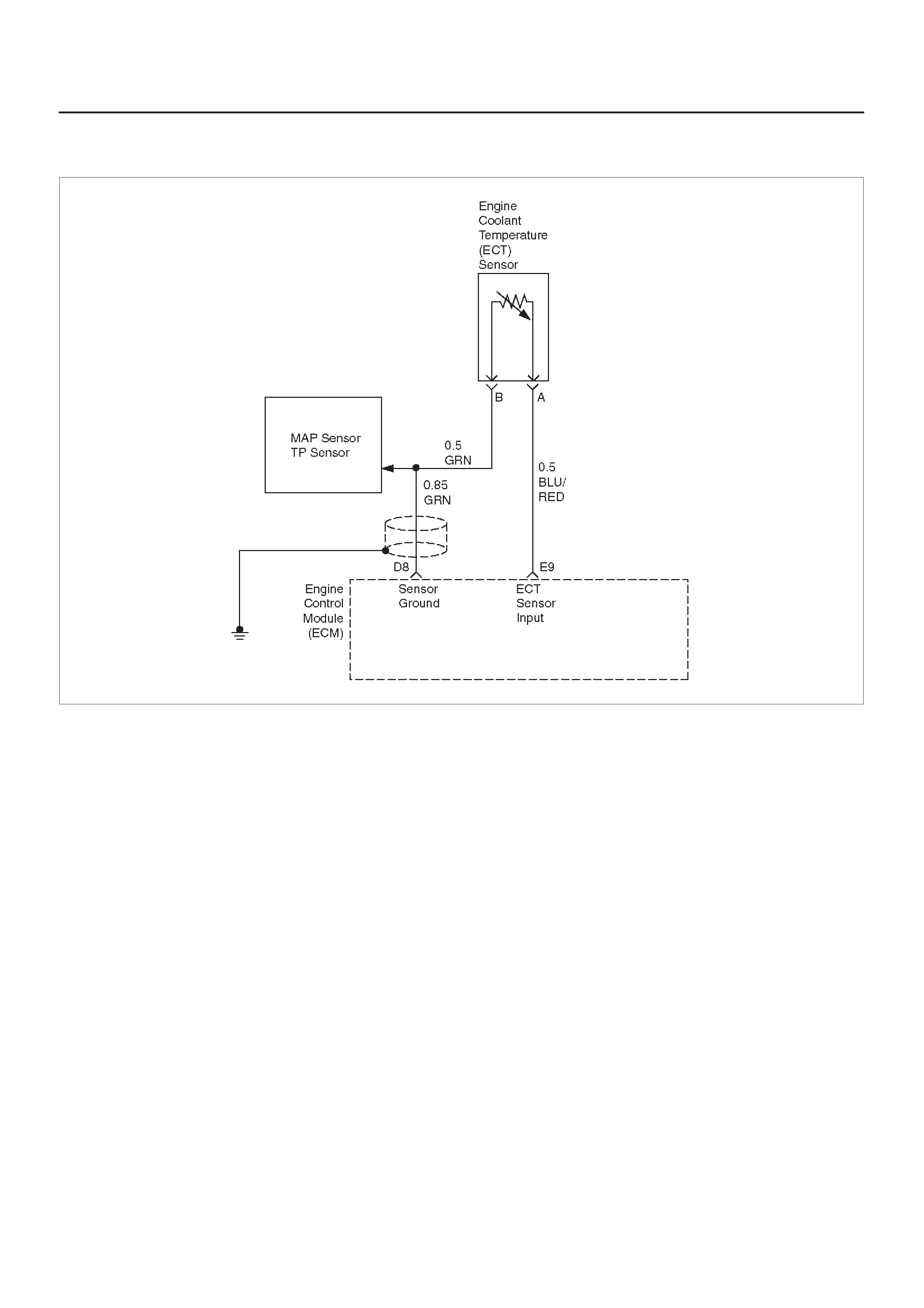
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0118 ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
D06RX117
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted in the engine coolant stream. The
engine control module (ECM) applies a voltage (about 5
volts) through a pull–up resistor to the ECT signal circuit.
When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor (thermistor)
resistance is high, therefore the ECM will measure a high
signal voltage. As the engine coolant warms, the sensor
resistance becomes less, and the ECT signal voltage
measured at the ECM drops. With a fully warmed up
engine, the ECT signal voltage should measure about 1.5
to 2.0 volts. If the ECM detect a continuous open in the
ECT sensor or circuit, then a code P0118 will set. DTC
P0118 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine running time is longer than 2.5 minutes.
DThe ECT sensor signal indicates an engine coolant
temperature of –39°C (–38°F) or less (about 5 volts)
for a total of 12.5 seconds over a 25–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will substitute the ECT reading with a default
engine coolant temperature value. The default value is
based on start–up intake air temperature and running
time.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0118 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0118 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuit. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the ECT
sensor. A change in the ECT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0118 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set. If it is determined
that the Diagnostic Trouble Code occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1115 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.Verifies that the fault is present.
3.If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0118 can be repeated
only by duplicating the Failure Records condition,
refer to the ”Temperature vs. Resistance Value”
table.
The table may be used to test the ECT sensor at
various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of
a ”shifted” sensor that may be shorted above or
below a certain temperature. If this is the case,
replace the ECT sensor. If the ECT sensor
appears to be OK, the fault is intermittent; refer to
Diagnostic Aids.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
°C°F OHMS
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 113 1188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P118 – ECT Sensor Circuit High Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON engine OFF.
2. Observe the ”Eng Cool T emp” display on the T ech 2.
Is the ”Eng Cool Temp” below the specified value? –39°C
(–38°F) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor the ”DTC” info for
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0118.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0118 failed? —Refer to Test
Description
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the ECT sensor electrical connector.
2. Jumper the ECT signal circuit and the sensor
ground circuit together at the ECT sensor harness
connector.
3. Observe the ”Eng Cool T emp” display on the T ech 2.
Is the ”Eng Cool T emp” at or above the specified value? 140°C
(284°F) Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
51. Jumper the ECT signal circuit at the ECT sensor
harness connector to chassis ground.
2. Observe the ”Eng Cool T emp” display on the T ech 2.
Is the ”Eng Cool T emp” at or above the specified value? 140°C
(284°F) Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
6Check for poor connections at the ECT sensor and
replace terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
10
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check the ECT sensor
ground circuit for an open.
3. If the ECT sensor ground circuit is open, repair it as
necessary.
Was the ECT sensor ground circuit open? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check the ECT signal
circuit for an open.
3. If the ECT sensor signal circuit is open, repair it as
necessary.
Was the ECT signal circuit open? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check for a poor sensor ground or ECT signal circuit
terminal connection at the ECM and replace
terminal(s) if necessary.
Did any of the terminals need to be replaced? — Verify repair Go to Step
11
10 Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
11 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
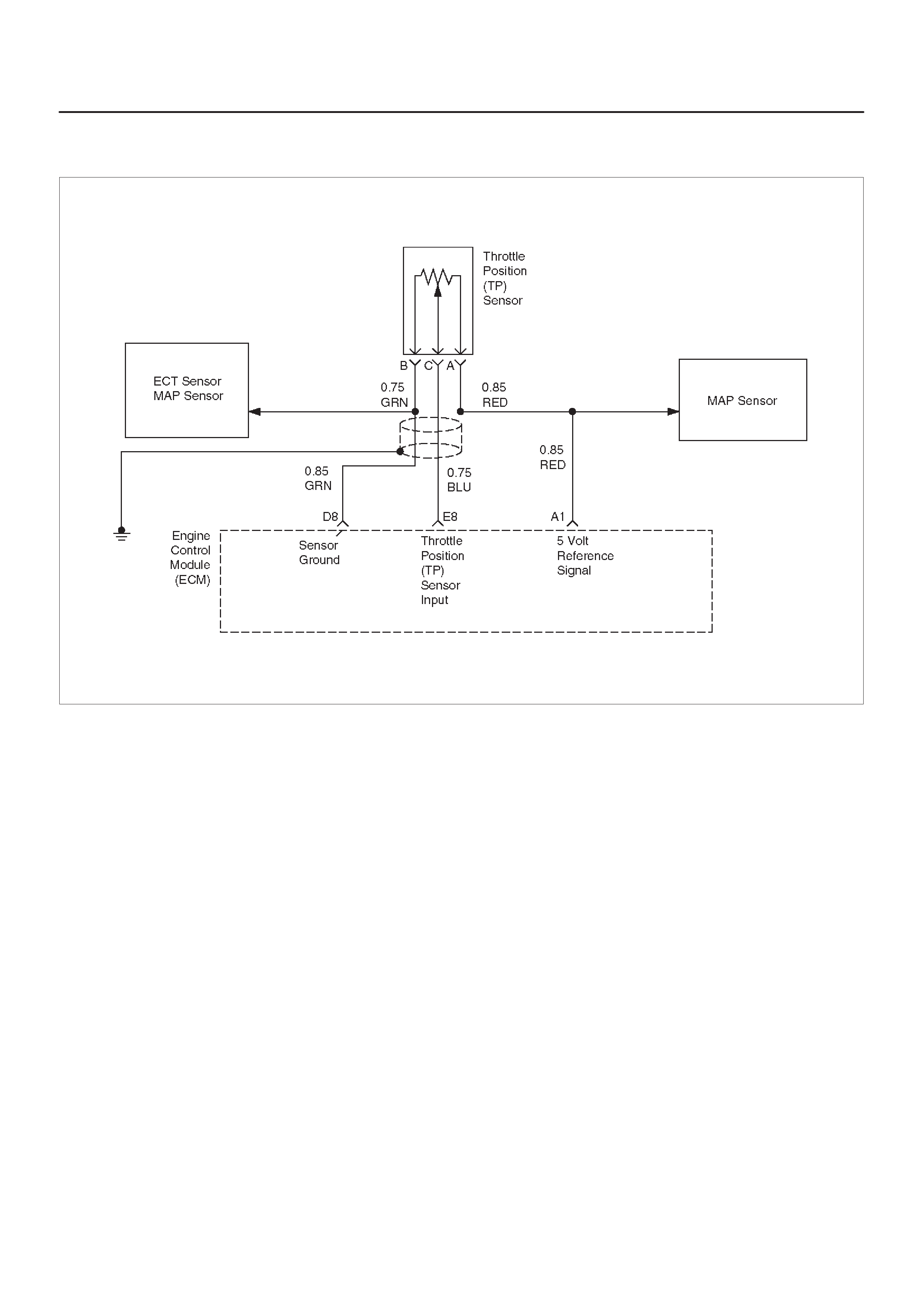
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0121 THROTTLE POSITION (TP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE PROBLEM
D06RX118
Circuit Description
The throttle position (Throttle Position) sensor circuit
provides a voltage signal that changes relative to throttle
blade angle. The signal voltage will vary from about 0.25
volts at closed throttle to about 4.75 volts at wide open
throttle (WOT).
The Throttle Position (TP) signal is used by the
powertrain control module (ECM) for fuel control and
most of the ECM–controlled outputs. The ECM monitors
throttle position and compares actual throttle positions
from the TP sensor to a predicted TP value calculated
from engine speed. If the ECM detects an out–of–range
condition, then a DTC code P0121 will set. DTC P0121 is
type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe Engine is running.
DNo MAP, ECT, TP, CKP, EGR, EVAP or DTC’s are set.
DIAC is between 10 and 160 counts.
DECT is above –10°C (14°F).
DThe MAP value changes by less than 2 kPa.
All the above mentioned conditions are met, and one of
the following conditions occurs for a total of 12.5 seconds
over a 25–second period of time.
Stuck High–
DMAP value is below 55 kPa.
DActual TP value is greater than the ECM’s estimated
TP value (Estimated TP value is based on MAP and
RPM).
Stuck Low–
DMAP value is below 50 kPa.
DActual TP value is less than the ECM’s estimated TP
value (Estimated TP value is based on MAP and
RPM).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
DThe ECM will use a default throttle position based on
MAP and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0121 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDTC P0121 can be cleared by using the Scan Tool’s
”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DSkewed MAP signal or faulty MAP sensor – An
incorrect MAP signal may cause the ECM to incorrectly
calculate the predicted TP sensor value during high
engine load situations. Check for an unusually low
MAP reading. This condition can cause DTC P0121 to
be set.
DThe TP sensor shares a 5 Volt reference with the MAP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit.
DThe TP sensor shares a ground with the MAP sensor
and the Fuel Pressure sensor.
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; an open circuit, a short to ground, or a short
to voltage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe
the MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor.
A change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
If DTC P0121 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set. If
it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1122 or P1121 Diagnostic Chart
may isolate the cause of the fault.
DTC P0121 TP Sensor/Range Performance Problem
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON engine OFF
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTC’s.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC P0121.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that DTC P0121 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Monitor the TP value on the T ech 2 while moving the
throttle between 0% and 100%.
Does the TP value on the Tech 2 move smoothly from
0% (0.25 volts) to 100% (4.75 volts)? (if no, start with
the diagnosis chart for other sensors in the circuit and
see if 5V returns.) —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 11
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
electrical connector, located on the RH side of the
Throttle body.
3. Start the vehicle, and monitor the TP value with the
Tech 2.
Does the TP value on the T ech 2 hold steadily within the
given range? 0–0.25 volts
0% Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Check the TP sensor signal circuit; between the TP
sensor and the Engine Control Module (ECM), for a
short to voltage.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
6Check the TP sensor circuit, between the TP sensor
and the ECM, the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
7Check the 5 volt signal circuit, between the TP sensor
and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a fused jumper between the TP sensor circuit
and the 5 volt signal circuit both at the wiring
harness’ TP sensor connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Observe the TP value displayed on the Tech 2?
Does the Tech 2 read the following value? about 5 volts
100% Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
9Check the TP sensor ground circuit, between the TP
sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a Digital Multimeter (DVM), set to measure
voltage, between the ground circuit and the 5 volt
signal circuit, both at the wiring harness’ TP sensor
connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
Does the DVM read the following value? about 5 volts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Replace the TP sensor.
Verify repair. ———
12 Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———
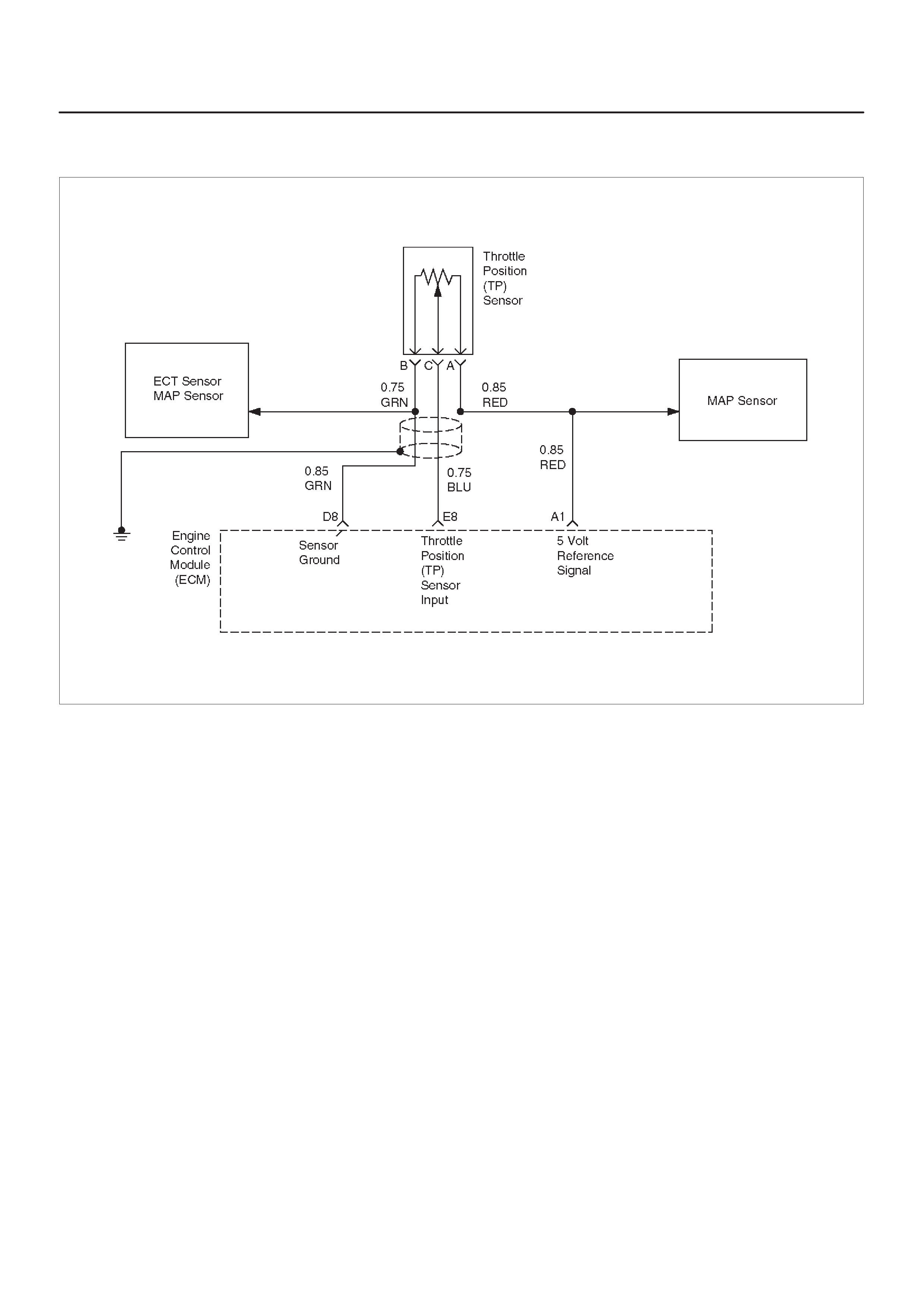
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0122 THROTTLE POSITION (TP)
SENSOR CIRCUITLOW INPUT
D06RX118
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from below 1 volt at closed throttle
to about 4 volts at wide open throttle(WOT).
The TP signal is used by the engine control module
(ECM) for fuel control and most of the ECM–controlled
outputs. If the ECM detect a continuous short to ground
in the TP sensor or circuit, then a code P0122 will set.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0122 is type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe ignition is ON.
DThrottle Position sensor signal voltage is less than 0.22
volt for a total of 0.78 second over a 1.5–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
DThe ECM will use a default throttle position based on
MAP and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0122 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0122 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe TP sensor shares a 5 V olt reference with the MAP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit or
components itself.
DThe TP sensor share a ground with the MAP and the
Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the throttle position display on the T ech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
TP sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0122 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set. If it is determined
that the Diagnostic Trouble Code occurs intermittently,
performing the Diagnostic Trouble Code P1122
Diagnostic Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
DTC P0122 – TP Sensor Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON engine OFF.
2. With the throttle closed, observe the ”Throttle
Position Sensor” display on the Tech 2.
Is the ”Throttle Position Sensor” below the specified
value? 0.22 V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor the “Diagnostic Trouble
Code” info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0122.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0122 failed? —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the TP sensor electrical connector.
3. Jumper the 5 volt reference circuit and the Throttle
Position signal together at the Throttle Position
sensor harness connector.
4. Ignition ON.
Observe the ”Throtle Position Sensor” display on the
Tech 2.
Is the ”Throttle Position Sensor” at the specified value? 5 V Go to Step
10 Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect jumper.
2. Connect a test light between B+ and the Throttle
Position sensor signal circuit at the Throttle Position
sensor harness connector.
Observe the ”Throttle Position Sensor” display on the
Tech 2.
Is the ”Throttle Position Sensor” at the specified value?
(if no, start with the diagnosis chart for other sensors in
the circuit and see if 5V returns.) 5 V Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and check the 5 volt reference
circuit for an open or short to ground.
3. If the 5 volt reference circuit is open or shorted to
ground, repair it as necessary.
Was the 5 volt reference circuit open or shorted to
ground? —Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Check the 5 volt reference circuit for a poor connection
at the ECM and replace the terminal if necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
12
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check the TP signal
circuit for an open, short to ground, or short to the
sensor ground circuit.
3. If the TP sensor signal circuit is open or shorted to
ground, repair it as necessary.
Was the TP signal circuit open or shorted to ground? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check the TP sensor signal circuit for a poor
connection at the ECM and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
12
10 Check the TP sensor signal circuit for a poor
connection at the TP sensor and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
11
11 Replace the TP sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
12 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
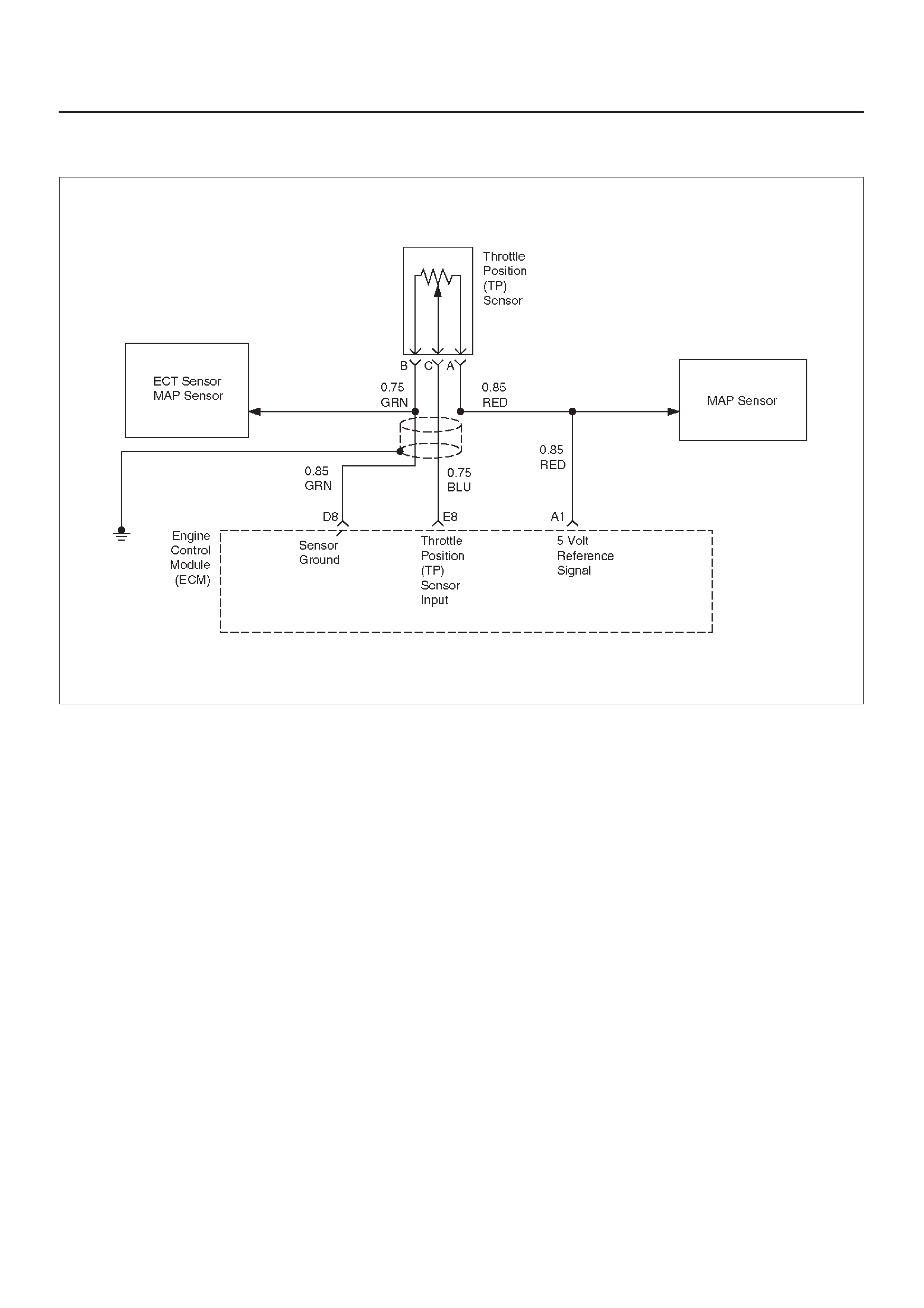
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0123 THROTTLE POSITION (TP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH INPUT
D06RX118
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to throttle blade angle. The
signal voltage will vary from below 1 volt at closed throttle
to about 4 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is used by the engine control module
(ECM) for fuel control and most of the ECM–controlled
outputs. If the ECM detect a continuous open in the TP
sensor or circuit, then a code P0123 will set. DTC P0123
is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe ignition is ON.
DThrottle Position sensor signal voltage is greater than
4.78 volts for a total of 0.78 second over a 1.5–second
period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
DThe ECM will use a default throttle position based on
MAP and RPM.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0123 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0123 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe TP sensor shares a 5 V olt reference with the MAP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit or
components itself.
DThe TP sensor share a ground with the MAP and the
Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage, shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the Throttle Position sensor display on the
Tech 2 while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
related to the TP sensor. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
DFaulty Throttle Position sensor – With the ignition key
ON engine OFF observe the TP sensor display on the
Tech 2 while slowly depressing the accelerator to wide
open throttle. If a voltage over 4.88 volts is seen at any
point in normal accelerator travel, replace the TP
sensor.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0123 cannot be duplicated,
the information included in the Failure Records data can
be useful in determining vehicle mileage since the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was last set. If it is determined
that the Diagnostic Trouble Code occurs intermittently,
performing theDiagnostic Trouble Code P1121
Diagnostic Chart may isolate the cause of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
7.Components that share the TP sensor 5 volt
reference circuit include the following devices:
DEGR valve
DMAP sensor
Disconnect the component while observing the
Throttle Position sensor display on the Tech 2. If
the reading changes drastically when this
component is disconnected, replace the
component that affected the reading.
DTC P0123 – TP Sensor Circuit High Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. With the throttle closed, observe the ”Throttle
Position Sensor” display on the Tech 2.
Is the ”Throttle Position Sensor” above the specified
value? 4.78 V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0123.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0123 failed. —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the Throttle Position sensor electrical
connector.
2. Observe the ”Throttle Position Sensor” display on
the Tech 2.
Is the ”Throttle Position Sensor” near the specified
value? (if no, start with the diagnosis chart for other
sensors in the circuit and see if 5V returns.) 0 V Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Probe the sensor ground circuit at the Throttle Position
sensor harness connector with a test light connected to
B+.
Is the test light ON? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step
10
61. Ignition OFF disconnect the ECM.
2. Ignition ON engine OFF.
3. Check for a short to voltage on the TP sensor signal
circuit.
4. If the TP sensor signal circuit is shorted, repair it as
necessary.
Was the TP sensor signal circuit shorted? — Verify repair Go to Step
12
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
71. Ignition ON.
2. Monitor the ”Throttle Position Sensor” Tech 2
display while disconnecting each of the
components that share the 5 volt reference circuit
(one at a time).
3. If the ”Throttle Position Sensor” Tech 2 display
changes, service the component(s) that caused the
display to change when disconnected.
Does disconnecting any of these components cause
the ”Throttle Position Sensor” display to change? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Ignition OFF disconnect the ECM.
2. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
3. Check for a short to B+ on the 5 volt reference
circuit.
4. If the 5 volt reference circuit is shorted, repair it as
necessary.
Was the 5 volt reference circuit shorted? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check for poor electrical connections at the Throttle
Position sensor and replace terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
11
10 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM, and check for an open sensor
ground circuit to the Throttle Position sensor.
3. If a problem is found, repair it as necessary.
Was the sensor ground circuit to the Throttle Position
sensor open? — Verify repair Go to Step
12
11 Replace the Throttle Position sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
12 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
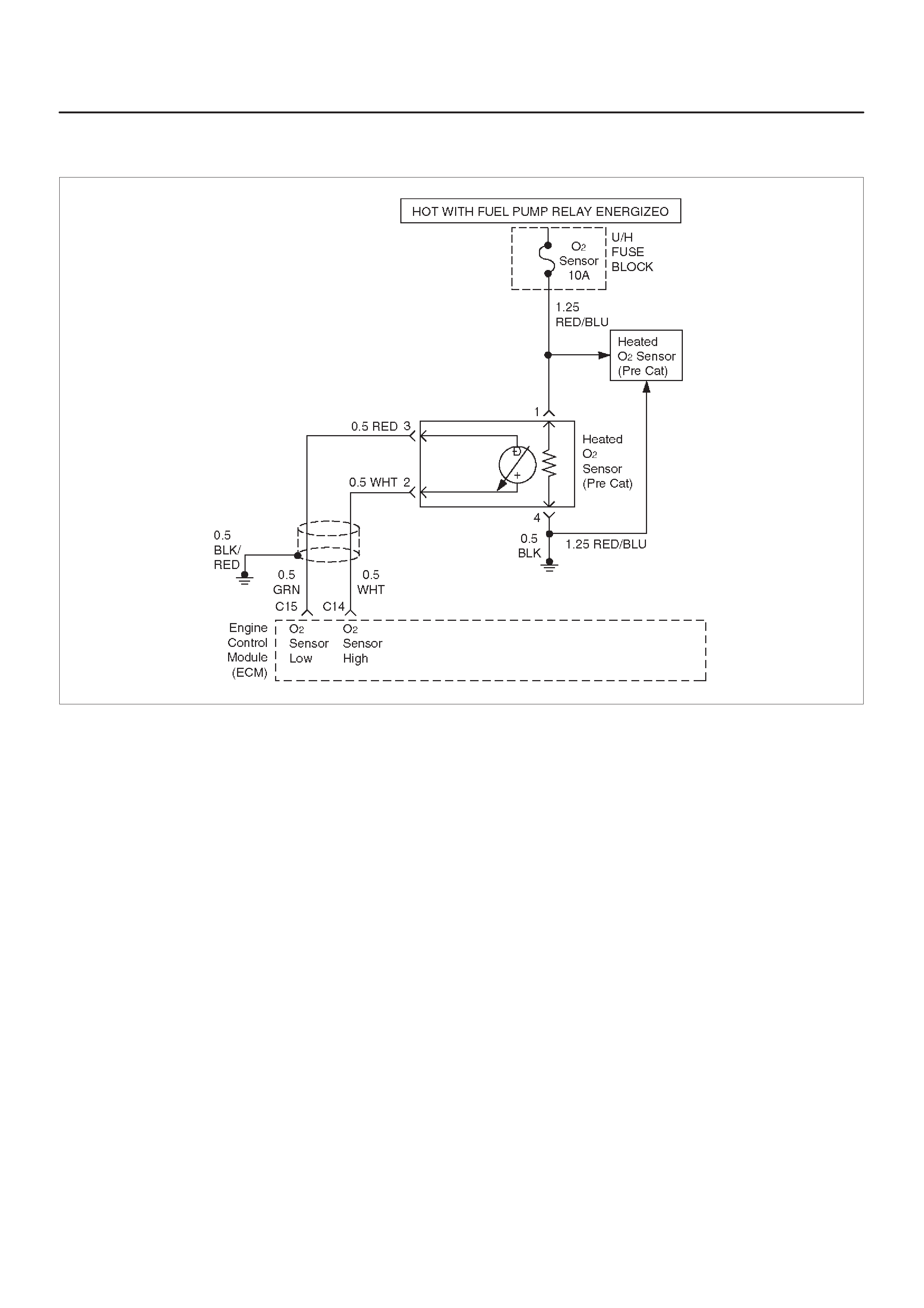
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0131 O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW
VOLTAGE (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
D06RX119
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) supplies a bias voltage
of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S) signal and low circuits. When measured with a 10
megaW digital voltmeter, this may display as low as 350
mV. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage within a range
of about 1000 mV when the exhaust is rich, down through
about 10 mV when exhaust is lean. The ECM constantly
monitors the HO2S signal during ”Closed Loop” operation
and compensates for a rich or lean condition by
decreasing or increasing injector pulse width as
necessary. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remains
excessively low for an extended period of time,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 will be set. DTC P0131 is
a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo related Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DVehicle is operating in ”Closed Loop”.
DEngine coolant temperature is above 60°C (140°F)
D”Closed Loop” commanded air/fuel ratio is between
14.5 and 14.8.
DThrottle angle is between 3% and 19%.
All above conditions met for 0.3 seconds and the following
condition is met:
DBank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains below 22 mV
during normal ”Closed Loop” operation for a total of
76.5 seconds over a 90–second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0131 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DHeated oxygen sensor wiring – The sensor pigtail may
be routed incorrectly and/or contacting the exhaust
system. Also, check for shorts to ground, shorts to
battery positive and open circuits.
DPoor ECM to engine block grounds.
DFuel pressure – The system will go lean if pressure is
too low. The ECM can compensate for some decrease.
However, if fuel pressure is too low, a Diagnostic

Trouble Code P0131 may be set. Refer to Fuel System
Diagnosis.
DLean injector(s) – Perform ”Injector Balance Test.”
DVacuum leaks – Check for disconnected or damaged
vacuum hoses and for vacuum leaks at the intake
manifold, throttle body, EGR system, and PCV system.
DExhaust leaks – An exhaust leak may cause outside air
to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the
HO2S, causing the system to appear lean. Check for
exhaust leaks that may cause a false lean condition to
be indicated.
DFuel contamination – Water, even in small amounts,
can be delivered to the fuel injectors. The water can
cause a lean exhaust to be indicated. Excessive
alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. For the
procedure to check for fuel contamination, Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
If none of the above conditions are present, replace the
affected HO2S.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
3. Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 failing during
operation may indicate a condition described in the
”Diagnostic Aids” above. If the Diagnostic Trouble
Code P0131 test passes while the Failure Records
conditions are being duplicated, an intermittent
condition is indicated.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0131 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? — Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install the Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the parameters specified
under ”Conditions for Setting the Diagnostic
Trouble Code” criteria included in Diagnostic
Support.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage.
Does the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remain below the
specified value? 300 mV Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON engine OFF review and record Tech 2
Failure Records data and note parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 until the
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0131 test runs.
Note test result.
Does Tech 2 indicate DTC P0131 failed this ignition? — Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM.
3. Check the Bank 1 HO2S 1 high and low circuits for a
short to ground or a short to the heater ground
circuit.
Are the Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal circuits shorted to
ground? — Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair the Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
61. Turn the ignition OFF HO2S 1 and ECM
disconnected.
2. Check for continuity between the high and low
signal circuits.
Was there continuity between the high and low circuits? — Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Repair the short between the high and low circuits.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Reconnect the ECM, leave the sensor
disconnected.
3. Ignition ON.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage near
the specified value? 430–450 mV
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 9
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —

DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0132 O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH
VOLTAGE (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
D06RX119
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) supplies a bias voltage
of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S) signal and low circuits. When measured with a 10
megaW digital voltmeter, this may display as low as 320
mV. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage within a range
of about 1000 mV when the exhaust is rich, down through
about 10 mV when exhaust is lean. The ECM constantly
monitors the HO2S signal during ”Closed Loop” operation
and compensates for a rich or lean condition by
decreasing or increasing injector pulse width as
necessary. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remains
excessively high for an extended period of time,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132 will be set. DTC P0132 is
a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo related Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DEngine coolant temperature is above 60°C (140°F).
D”Closed Loop” commanded air/fuel ratio is between
14.5 and 14.8.
DThrottle angle is between 3% and 19%.
All above conditions met for 0.3 seconds or vehicle in
Decelleration Fuel Cut–Off (DFCO) mode for 3 seconds,
and one of the following two conditions met:
DBank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains above 952 mV
during normal ”Closed Loop” operation for a total of
76.5 seconds over a 90–second period.
OR
DBank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains above 500 mV
during ”deceleration fuel cutoff mode” (DFCO)
operation for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0132 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function or by
disconnecting the ECM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the following items:
DFuel pressure – The system will go rich if pressure is
too high. The ECM can compensate for some
increase. However, if fuel pressure is too high, a

Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis.
DPerform ”Injector Balance Test” – Refer to Fuel System
Diagnosis.
DCheck the EVAP canister for fuel saturation – If full of
fuel, check canister control and hoses. Refer to
Evaporative (EVAP) Emission Control System.
DCheck for a leak in the fuel pressure regulator
diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to the
regulator for the presence of fuel.
DAn intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system
to go rich due to a false indication of the engine
accelerating.
DSilicon contamination of the HO2S can also cause a
high HO2S voltage to be indicated. This condition is
indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion of
the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. If
contamination is noticed, replace the affected HO2S.
DOperate the vehicle while monitoring the HO2S voltage
with a Tech 2. If the HO2S voltage is limited within a
range between 300 mV to 600 mV, check the HO2S
high and low circuit wiring and associated terminal
connections. If the wiring and connections are OK,
replace the HO2S.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
3. Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132 failing during
”deceleration fuel cutoff mode” operation may
indicate a condition described in the ”Diagnostic
Aids” above. If the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132
test passes while the Failure Records conditions are
being duplicated, an intermittent condition is
indicated. Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle
mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may
help determine how often the condition that caused
the Diagnostic Trouble Code to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0132 – O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install the Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within parameters specified
under ”Conditions for Setting the DTC” included in
Diagnostic Support.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage.
Does the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remain above the
specified value?
952 mV (500
mV in
deceleration
fuel cutoff
mode) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON review and record Tech 2 Failure
Records data.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132 until the
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0132 test runs.
4. Note the test result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0132 failed this ignition? —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect Bank 1 HO2S 1.
3. Ignition ON.
4. At HO2S 1 connector (ECM side) use a Digital
Voltmeter (DVM) to measure voltages at the high
and low signal terminals.
Are the voltages in the specified range? 5–14 V Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair short to voltage in signal circuit. — Verify repair —
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM connector.
3. Check for damage to the ECM pins and terminals.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Disconnect Bank 1 HO2S 1 and jumper the HO2S
high and low circuits (ECM side) to ground.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage.
Is Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage below the specified value? 10 mV Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Replace Bank 1 HO2S 1.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
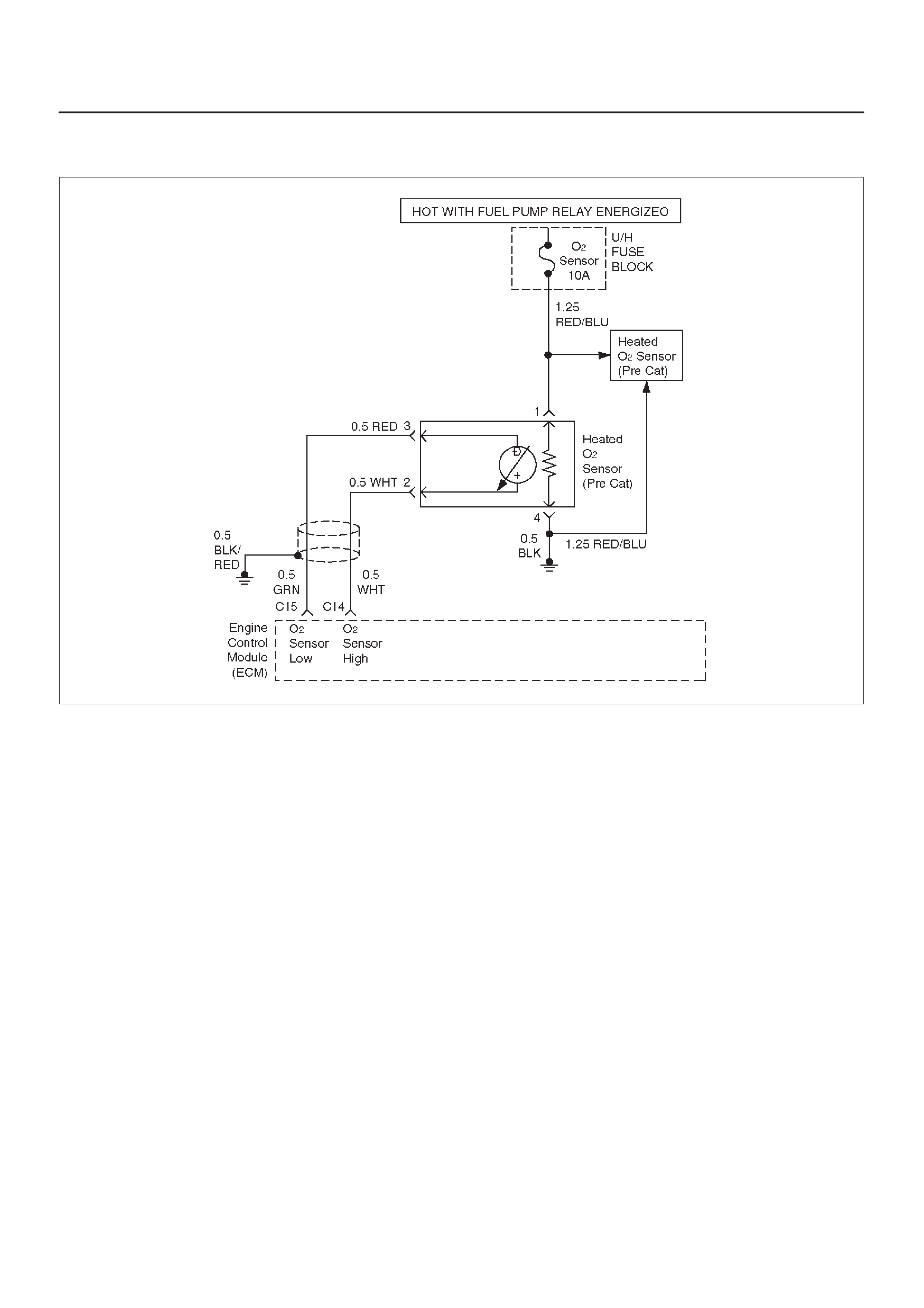
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0134 O2 SENSOR CIRCUIT NO
ACTIVITY DETECTED (BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
D06RX119
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) supplies a bias voltage
of about 450 mV between the heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S) high and low circuits. When measured with a 10
MW digital voltmeter, this may display as low as 320 mV.
The oxygen sensor varies the voltage within a range of
about 1000 mV when the exhaust is rich, down through
about 10 mV when exhaust is lean. The ECM constantly
monitors the HO2S signal during ”Closed Loop” operation
and compensates for a rich or lean condition by
decreasing or increasing injector pulse width as
necessary. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage remains at or
near the 450 mV bias for an extended period of time,
Diagnostic T rouble Code P0134 will be set, indicating an
open sensor signal or sensor low circuit. DTC P0134 is a
type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo related Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DEngine run time is longer than 120 seconds.
DOxygen sensor heater has been determined to be
functioning properly, and the oxygen sensor has
warmed to operating temperature.
All the above conditions are met and the following
condition is met:
DBank 1 HO2S 1 signal voltage remains between 400
mV and 500 mV for a total of 76.5 seconds over a
90–second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the second time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0134 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0134 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for backed–out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, poor terminal–to–wire
connection, and damaged harness.
DFaulty HO2S heater or heater circuit – With the ignition
ON engine OFF after a cooldown period, the HO2S 1
voltage displayed on the Tech 2 is normally 455–460
mV. A reading over 1000 mV indicates a signal line
shorted to voltage. A reading under 5 mV indicates a
signal line shorted to ground or signal lines shorted
together. Disconnect the HO2S and connect a test light
between the HO2S ignition feed and heater ground
circuits. If the test light does not light for 2 seconds
when the ignition is turned on, repair the open ignition
feed or sensor ground circuit as necessary. If the test
light lights and the HO2S signal and low circuits are
OK, replace the HO2S.
DIntermittent test – With the ignition ON monitor the
HO2S signal voltage while moving the wiring harness
and related connectors. If the fault is induced, the
HO2S signal voltage will change. This may help isolate
the location of the malfunction.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0134 – O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Install the Tech 2.
2. Run the engine at operating temperature.
3. Operate the engine above 1200 RPM for three
minutes.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage
varying outside the specified values? 400–500 mV Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Ignition ON, engine OFF review and record Tech 2
Failure Records data and note parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0134 until the
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0134 test runs.
4. Note the test result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0134 failed this ignition? —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
4Check for a damaged harness.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5Check for poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 high and low circuit
terminal connections at the Bank 1 HO2S 1 harness
connector and replace terminal(s) if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6Check for poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 high and low circuit
terminal connections at the ECM and replace terminals
if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Ignition OFF.
2. With the ECM disconnected, check continuity of the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit.
3. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit measures over 0.5
W, repair open or poor connection as necessary.
Was a Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit problem found and
corrected? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
81. Ignition OFF.
2. With the ECM disconnected, check continuity of the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 low circuit.
3. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 low circuit measures over 5 W,
repair open or poor connection as necessary.
Was a Bank 1 HO2S 1 low circuit problem found and
corrected? —Verify repair Go to Step 9
91. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Disconnect Bank 1 HO2S 1 and jumper the HO2S
high and low circuits (ECM side) to ground.
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage.
Is Bank 1 HO2S 1 voltage approximately equal to the
specified value? 10 mV Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
10 Replace Bank 1 HO2S 1.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
11 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
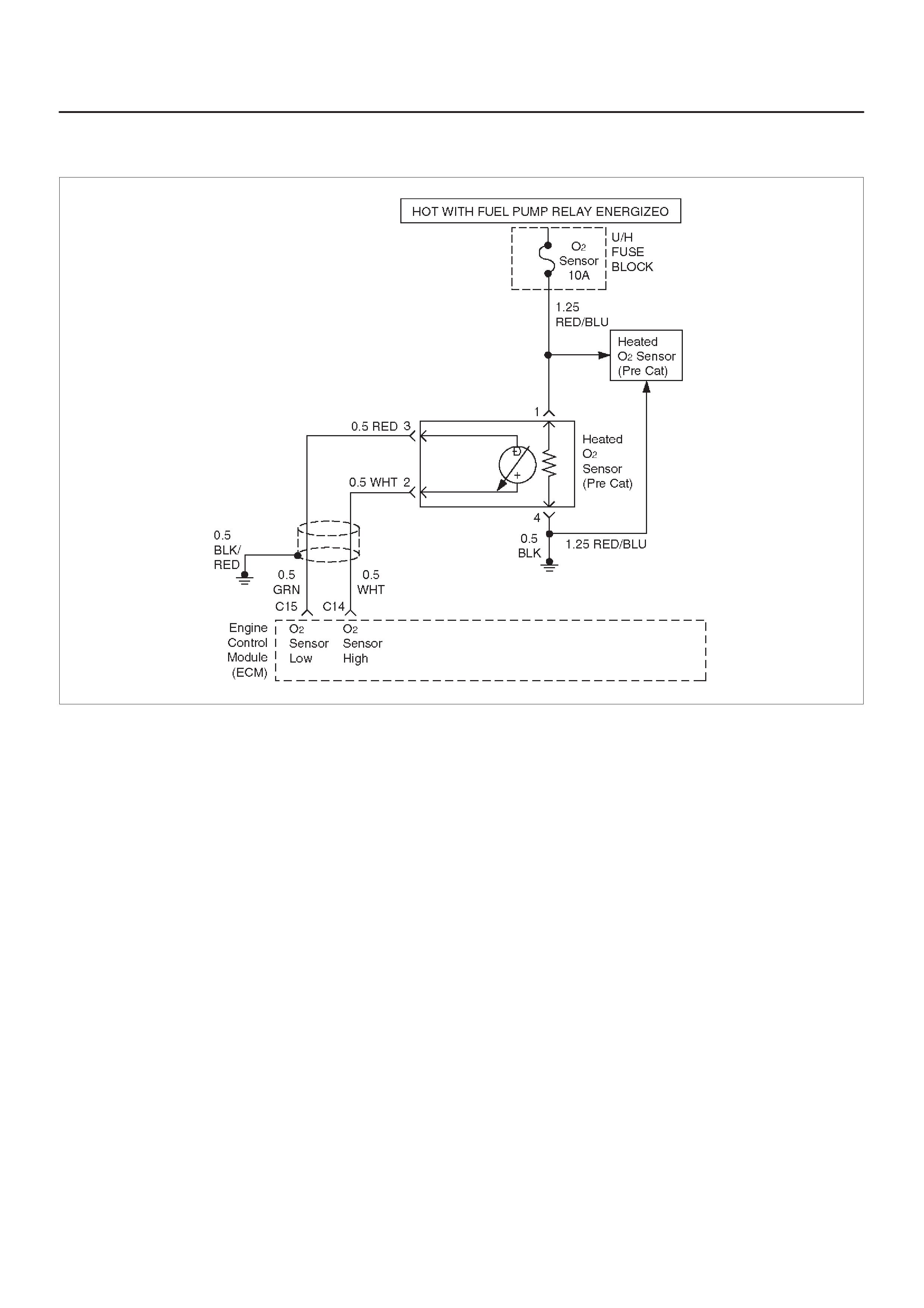
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135 O2 SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
D06RX119
Circuit Description
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the amount
of time required for “Closed Loop” fuel control operation
and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The oxygen
sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of time
required for fuel control sensors Bank 1 HO2S 1.
The engine control module (ECM) will run the heater test
only after a cold start (determined by engine coolant and
intake air temperature at the time of start–up) and only
once during an ignition cycle. When the engine is started
the ECM will monitor the HO2S voltage. When the HO2S
voltage indicates a sufficiently active sensor, the ECM
looks at how much time has elapsed since start–up. If the
ECM determines that too much time was required for the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 to become active, a Diagnostic Trouble
Code P0135 will set. DTC P0135 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo related Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DIntake air temperature (IAT) is less than 32°C (90°F)
at start–up.
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) is less than 32°C
(90°F) at start–up.
DIAT and ECT are within 5°C (9°F) of each other at
start–up.
DIgnition voltage is between 11 and 16.6 V.
DAverage calculated air flow is less than 18 g/second
during sample period.
DThrottle angle is less than 40%.
DBank 1 HO2S 1 voltage does not change more than
148 mV from the bias voltage (between 400 mV and
500 mV) for a longer amount of time than it should. The
maximum amount of time to come up to operating
range is 240 seconds. This warm–up time depends on
the engine coolant temperature at start–up and intake
air temperature at start–up.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0135 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0135 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor.
A change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.The HO2S should be allowed to cool before
performing this test. If the HO2S heater is
functioning, the signal voltage will gradually increase
or decrease as the sensor element warms. If the
heater is not functioning, the HO2S signal will
remain near the 450 mV bias voltage.
4.Ensures that the ignition feed circuit to the HO2S is
not open or shorted. The test light should be
connected to a good chassis ground, in case the
HO2S low or HO2s heater ground circuit is faulty.
5.Checks the HO2S heater ground circuit.
6.Checks for an open or shorted HO2S heater
element.
10.An open HO2S signal or low circuit can cause the
HO2S heater to appear faulty. Check these circuits
before replacing the sensor.
DTC P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2NOTE: If the engine has just been operating, allow
engine to cool for about one half hour before
proceeding.
1. Ignition OFF, engine OFF.
2. Install a Tech 2.
3. Ignition ON engine OFF monitor the Bank 1 HO2S 1
voltage.
Does the HO2S voltage go from bias voltage to above
and below the specified values?
Above 650
mV or below
250 mV
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
3Inspect the fuse for the Bank 1 HO2S 1 ignition feed.
Is the fuse open? —Go to Step 15 Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Raise the vehicle.
3. Disconnect the Bank 1 HO2S 1 electrical connector.
4. Using a test light connected to a good ground (do
not use Bank 1 HO2S 1 heater ground or Bank 1
HO2S 1 low), probe the ignition feed circuit at the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 electrical connector (ECM harness
side).
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5Connect the test light between the Bank 1 HO2S 1
ignition feed and the Bank 1 HO2S 1 heater ground.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
61. Allow the HO2S to cool for at least 10 minutes.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), measure the
resistance between the Bank 1 HO2S 1 ignition
feed and the Bank 1 HO2S 1 heater ground at the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 pigtail.
Is the HO2S heater resistance within the specified
values? 3–6 ohms Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
7Repair the open Bank 1 HO2S 1 ignition feed circuit to
Bank 1 HO2S 1.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
8Repair the open Bank 1 HO2S 1 heater ground circuit
to Bank 1 HO2S 1.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
91. Check for a poor connection at the Bank 1 HO2S 1
harness terminals.
2. If a poor connection is found, replace terminals.
Was a poor connection found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 Check for a poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 high or low circuit
terminal connection at the Bank 1 HO2S 1 harness
connector and replace terminal(s) if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and check the continuity of the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal circuit and the Bank 1 HO2S
1 low circuit.
3. If the Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit or HO2S low circuit
measures over 5 W, repair open or poor connection
as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Check for a poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 low circuit terminal
connection at the ECM and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check for a poor Bank 1 HO2S 1 high circuit terminal
connection at the ECM and replace the terminal if
necessary.
Did the terminal require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Replace the Bank 1 HO2S 1.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
15 Locate and repair the short to ground in Bank 1 HO2S 1
ignition feed circuit and replace the fault fuse.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
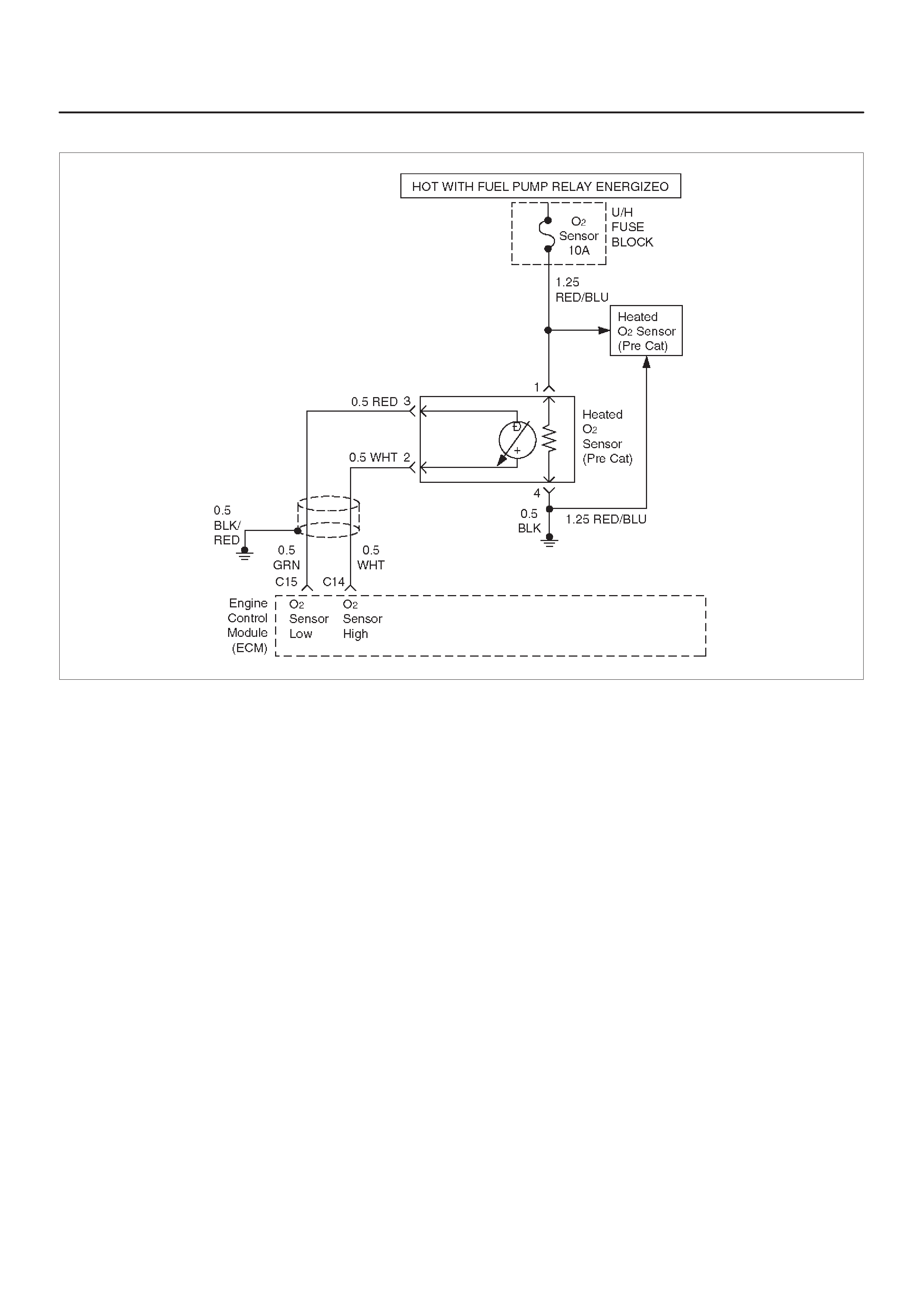
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0171 SYSTEM TOO LEAN (BANK 1)
D06RX119
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a ”Closed Loop”
air/fuel metering system is used. While in ”Closed Loop”,
the engine control module (ECM) monitors the Bank 1
HO2S 1 signal and adjusts fuel delivery based upon the
HO2S signal voltage. A change made to fuel delivery will
be indicated by the long and short term fuel trim values
which can be monitored with a Tech 2. Ideal fuel trim
values are around 0%; if the HO2S signal indicates a lean
condition the ECM will add fuel, resulting in fuel trim
values above 0%. If a rich condition is detected, the fuel
trim values will be below 0%, indicating that the ECM is
reducing the amount of fuel delivered. If an excessively
lean condition is detected on Bank 1, the ECM will set
Diagnostic T rouble Code P0171. DTC P0171 is a type B
code.
The ECM’s maximum authority to control long term fuel
trim allows a range between –14% and +20%. The ECM
monitors fuel trim under various engine speed/load fuel
trim cells before determining the status of the fuel trim
diagnostic.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo Tech 2 test is being run.
DNone of the following: EGR Diagnostic Trouble Codes,
HO2S Diagnostic Trouble Codes, (response,
transition, open, low volts, no activity), TP sensor
Diagnostic Trouble Codes, MAP Diagnostic Trouble
Codes, IAT Diagnostic Trouble Codes, canister purge
Diagnostic Trouble Codes, EVAP Diagnostic Trouble
Codes, injector circuit Diagnostic Trouble Codes, or
misfire Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DEngine coolant temperature is between 65°C (149°F)
and 104°C (219°F).
DIntake air temperature is between –40°C (–40°F) and
120°C (248°F).
DManifold absolute pressure is between 23.75 kPa and
99 kPa.
DEngine speed is between 400 and 6000 RPM.
DBarometric pressure is greater than 72.3 kPa.
DSystem voltage is greater than 9.5v.
DEngine is operating in ”Closed Loop”.
DThe average of the short term fuel trim samples is
greater than 0.97 and the average of adaptive index
multiplier samples is greater than 1.21.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.

Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0171 will clear
after 40 consecutivewarm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0171 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the Bank 1 HO2S 1 display on the Tech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
engine harness. A change in the display will indicate
the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.Diagnostic Trouble Codes other than P0171 may
indicate a condition present which may cause a lean
condition. If this is the case, repairing the condition
which caused the other Diagnostic Trouble Code will
most likely correct the Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0171.
4.If the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0171 test passes
while the Failure Records conditions are being
duplicated, the lean condition is intermittent. Refer
to Diagnostic Aids or Symptoms for additional
information on diagnosing intermittent problems.
DTC P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any DTCs set other than P0171?
—
Go to the
applicable
DTC charts
and repair the
other DTCs
before
proceeding
with this
chart. Go to Step 3
31. Start the engine and operate the vehicle in ”Closed
Loop”.
2. Observe the ”BANK 1 L.T. FUEL TRIM” and display
on the Tech 2.
Are the displayed values greater than the specified
values? L.T. Fuel
Trim: 20% Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Review and record the T ech 2 Failure Records data.
2. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0171 and
operate the vehicle to duplicate the Failure Records
conditions.
3. Monitor the Tech 2 “Diagnostic Trouble Code” info
for Diagnostic T rouble Code P0171 while operating
the vehicle to duplicate the Failure Records
conditions.
4. Continue operating the vehicle until the Diagnostic
Trouble Code P0171 test runs and note the test
result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0171 failed this ignition? —Go to Step 5
The lean
condition is
not present. If
a driveability
symptom still
exists, refer
to Symptoms
section.
5Visually and physically inspect the vacuum hoses for
disconnects, splits, kinks, improper routing and
improper connections and repair any problem found.
Did your inspection reveal a problem requiring repair? —Verify repair Go to Step 6
6Visually and physically inspect the crankcase
ventilation valve for proper installation and repair any
problem found (refer to Crankcase Ventilation
System).
Did your inspection reveal a problem requiring repair? —Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Start the engine and note the idle quality.
Is a high or unsteady idle being experienced? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step
10
8With the engine idling, observe the ”IDLE AIR
CONTROL” display on the Tech 2.
Is the displayed value above the specified value? Above 5
counts Go to Step
10 Go to Step 9
91. Visually and physically inspect the throttle body,
intake manifold, EGR valve and the EGR feed pipe
for vacuum leaks.
2. Repair any vacuum leaks as necessary.
Did your inspection reveal a vacuum leak? — Verify repair Go to Step
10
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Perform the ”Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Check” and
correct any IAC problem as necessary.
Did this test isolate a problem requiring repair? — Verify repair Go to Step
11
11 Check the fuel for excessive water, alcohol, or other
contaminants (see Diagnosis in Engine Fuel for the
procedure) and correct the contaminated fuel condition
if present (see Engine Fuel).
Was the fuel contaminated? — Verify repair Go to Step
12
12 1. Visually and physically inspect the ECM injector
grounds, power grounds and sensor grounds to
ensure that they are clean, tight, and in their proper
locations.
2. If a faulty ground condition is present, correct it as
necessary.
Did your inspection reveal a condition requiring repair? —Verify repair Go to Step
13
13 Perform the procedure in ”Fuel System Pressure Test”
and repair fuel system problem if necessary.
Did the test isolate a condition requiring repair? — Verify repair Go to Step
14
14 Perform the ”Evaporative Emissions Control (EVAP)
Canister Purge Valve Check” and repair EVAP system
problem if necessary.
Did the test isolate a problem? — Verify repair Go to Step
15
15 1. Visually and physically inspect the intake manifold,
injector O–rings, EGR adapter, EGR valve and the
EGR feed pipes for vacuum leaks.
2. Repair any problem that is found.
Did your inspection reveal a problem? — Verify repair Go to Step
16
16 Visually and physically inspect the Bank 1 exhaust
manifold for leaks and loose or missing hardware and
correct any problem found.
Did your inspection reveal a problem? — Verify repair Go to Step
17
17 Perform the ”Injector Balance Test,” and correct any
problem found (refer to Fuel Metering System).
Did the test isolate a problem? — Verify repair Go to Step
18
18 1. Visually and physically inspect the Bank 1 HO2S 1
to ensure that it is installed securely and that the
Bank 1 HO2S 1 pigtail and wiring harness are not
contacting the exhaust or otherwise damaged.
2. If a problem is found, correct it as necessary.
Did your inspection reveal a problem? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
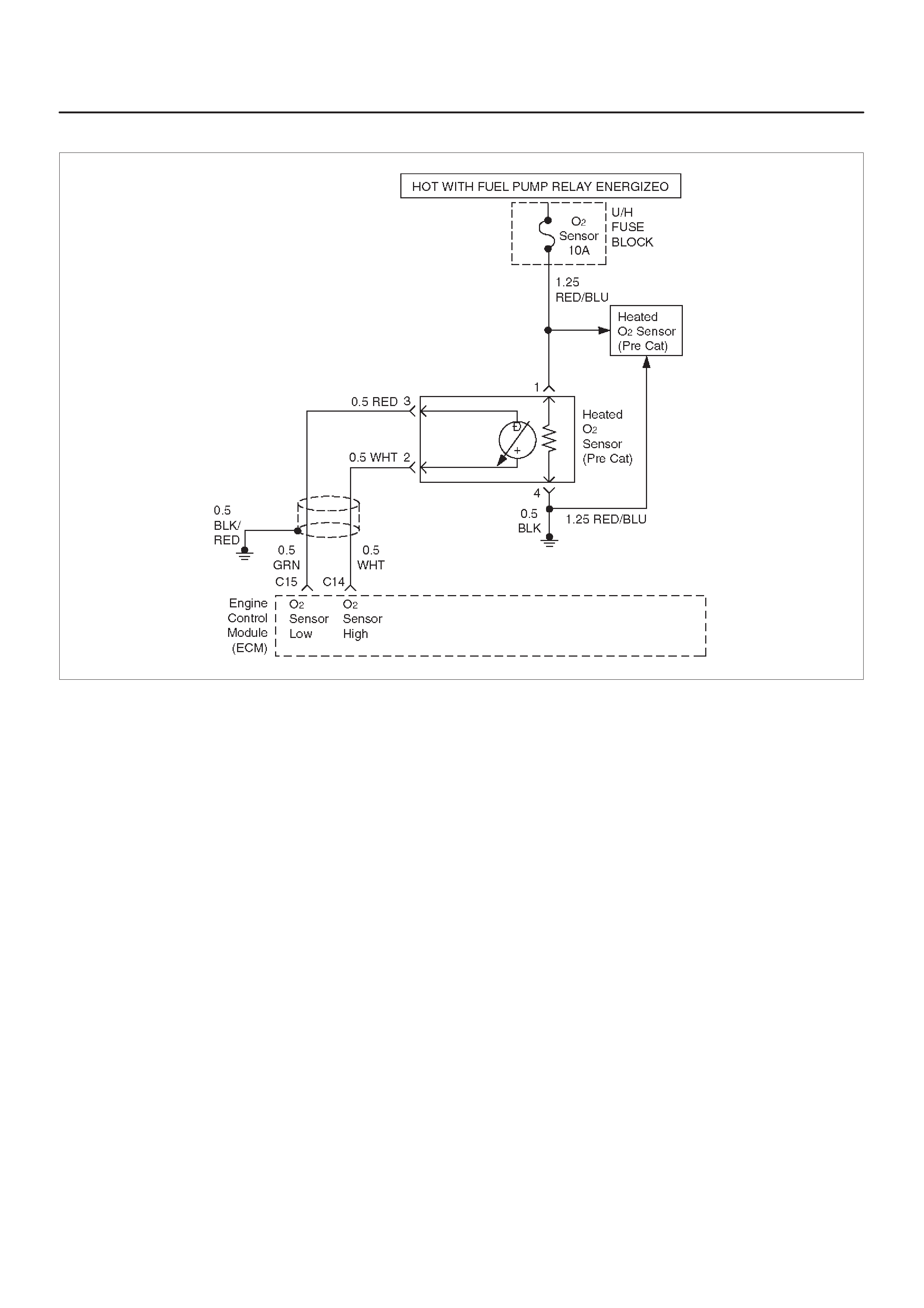
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0172 SYSTEM TOO RICH (BANK 1)
D06RX119
Circuit Description
To provide the best possible combination of driveability,
fuel economy, and emission control, a ”Closed Loop”
air/fuel metering system is used. While in ”Closed Loop”,
the engine control module (ECM) monitors the Bank 1
heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1 and adjusts fuel delivery
based upon the HO2S signal voltages. A change made to
fuel delivery will be indicated by the long and short term
fuel trim values which can be monitored with a Tech 2.
Ideal fuel trim values are around 0%; if the HO2S signals
are indicating a lean condition the ECM will add fuel,
resulting in fuel trim values above 0%. If a rich condition is
detected, the fuel trim values will be below 0%, indicating
that the ECM is reducing the amount of fuel delivered. If
an excessively rich condition is detected on Bank 1, the
ECM will set Diagnostic Trouble Code P0172. DTC
P0172 is a type B code.
The ECM’s maximum authority to control long term fuel
trim allows a range between –14% and +20%. The ECM’s
maximum authority to control short term fuel trim allows a
range between –11% and +20%. The ECM monitors fuel
trim under various engine speed/load fuel trim cells
before determining the status of the fuel trim diagnostic.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo Tech 2 test is being run.
DNone of the following was set: EGR Diagnostic Trouble
Codes, HO2S Diagnostic Trouble Codes, (response,
transition, open, low volts, no activity), TPS Diagnostic
Trouble Codes, MAP Diagnostic Trouble Codes, IAT
Diagnostic Trouble Codes, canister purge Diagnostic
Trouble Codes, EVAP Diagnostic Trouble Codes,
injector circuit Diagnostic Trouble Codes, or misfire
Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DEngine coolant temperature is between 65°C (149°F)
and 104°C (219°F).
DIntake air temperature is between –40°C (–40°F) and
120°C(248°F).
DManifold absolute pressure is between 23.75 kPa and
99 kPa.
DSystem voltage is greater than 9.5 volts.
DEngine speed is between 400 and 6000 RPM.
DBarometric pressure is greater than 72.3 kPa.
DEngine is operating in ”Closed Loop”.
DThe average of the long term full trim samples is less
than 1.03 and the average of the adaptive index
multiplier samples is less than or equal to 0.82.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.

DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0172 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0172 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the Bank 1 HO2S 1 display on the Tech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
engine harness. A change in the display will indicate
the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.Diagnostic Trouble Codes other than P0172 may
indicate a condition present which may cause a lean
condition. If this is the case, repairing the condition
which caused the other DTC will most likely correct
the DTC P0172.
4.If the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0172 test passes
while the Failure Records conditions are being
duplicated, the rich condition is intermittent. Refer to
Diagnostic Aids or Symptoms for additional
information on diagnosing intermittent problems.
DTC P0172 – System Too Rich (Bank 1)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes set other than
P0172?
—
Go to the
applicable
DTC charts
and repair the
other DTCs
before
proceeding
with this
chart. Go to Step 3
31. Start the engine and operate the vehicle in ”Closed
Loop”.
2. Observe ”BANK 1 L.T. FUEL TRIM” display on the
Tech 2.
Are the displayed values more negative than the
specified values? L.T. Fuel
Trim: –14% Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Review and record the T ech 2 Failure Records data.
2. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0172 and
operate the vehicle to duplicate the Failure Records
conditions.
3. Monitor the Tech 2 “Diagnostic Trouble Code” info
for Diagnostic T rouble Code P0172 while operating
the vehicle to duplicate the Failure Records
conditions.
4. Continue operating the vehicle until the Diagnostic
T rouble Code P0172 test runs and note test result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0172 failed this ignition? —Go to Step 5
The rich
condition is
not present. If
a driveability
symptom still
exists, refer
to Symptoms.
5Visually and physically inspect the air filter element and
replace it if necessary.
Did the air filter require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6Visually and physically inspect the air intake duct for
collapse or restriction and repair if necessary.
Did your inspection reveal a condition requiring repair? —Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Start the engine and note the idle quality.
Is a low or unsteady idle being experienced? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step
10
8With the engine idling, observe the ”IDLE AIR
CONTROL” display on the Tech 2.
Is the ”IDLE AIR CONTROL” value below the specified
value? Below 100
counts Go to Step
10 Go to Step 9
91. Ignition OFF.
2. Physically inspect the throttle body bore, throttle
plate, and IAC passages for coking and foreign
objects.
3. If a problem was found, repair as necessary.
Did your inspection reveal a condition requiring repair? —Verify repair Go to Step
10
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 1. Perform the ”Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Check.”
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Did the test isolate a problem requiring repair? — Verify repair Go to Step
11
11 1. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure
regulator and inspect the hose for the presence of
fuel.
2. If fuel is present in the vacuum hose, replace the
fuel pressure regulator (refer to Fuel Metering
System).
Did the fuel pressure regulator require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
12
12 Ignition ON engine OFF monitor the TP Angle display
on the Tech 2 while slowly depressing the accelerator
pedal.
Does the TP Angle display increase steadily and
evenly from minimum value at closed throttle to
maximum value at wide–open throttle?
Minimum 0%
Maximum
100% Go to Step
13 Go to Step
17
13 1. Perform the ”Fuel System Pressure Test.”
2. If the test isolates a problem, repair as necessary
(refer to Engine Fuel or Fuel Metering System).
Did the test isolate a problem requiring repair? — Verify repair Go to Step
14
14 1. Perform the ”Evaporative Emissions Control
(EVAP) Canister Purge Valve Check.”
2. If the test isolates a problem, repair as necessary.
Did the test isolate a problem requiring repair? — Verify repair Go to Step
15
15 1. Perform the ”Injector Balance Test.”
2. If the test isolates a problem, repair as necessary
(refer to Fuel Metering System).
Did the test isolate a problem requiring repair? — Verify repair Go to Step
16
16 1. Remove and visually/physically inspect the Bank 1
HO2S 1 for silicon contamination. This will be
indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion
of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream.
2. If contamination is evident on the Bank 1 HO2S 1,
replace the contaminated sensors.
Did the sensor require replacement? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
17 1. Check the TP sensor mounting screws and tighten
or replace them as necessary if they are loose or
missing.
2. If the screws are OK, replace the TP sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
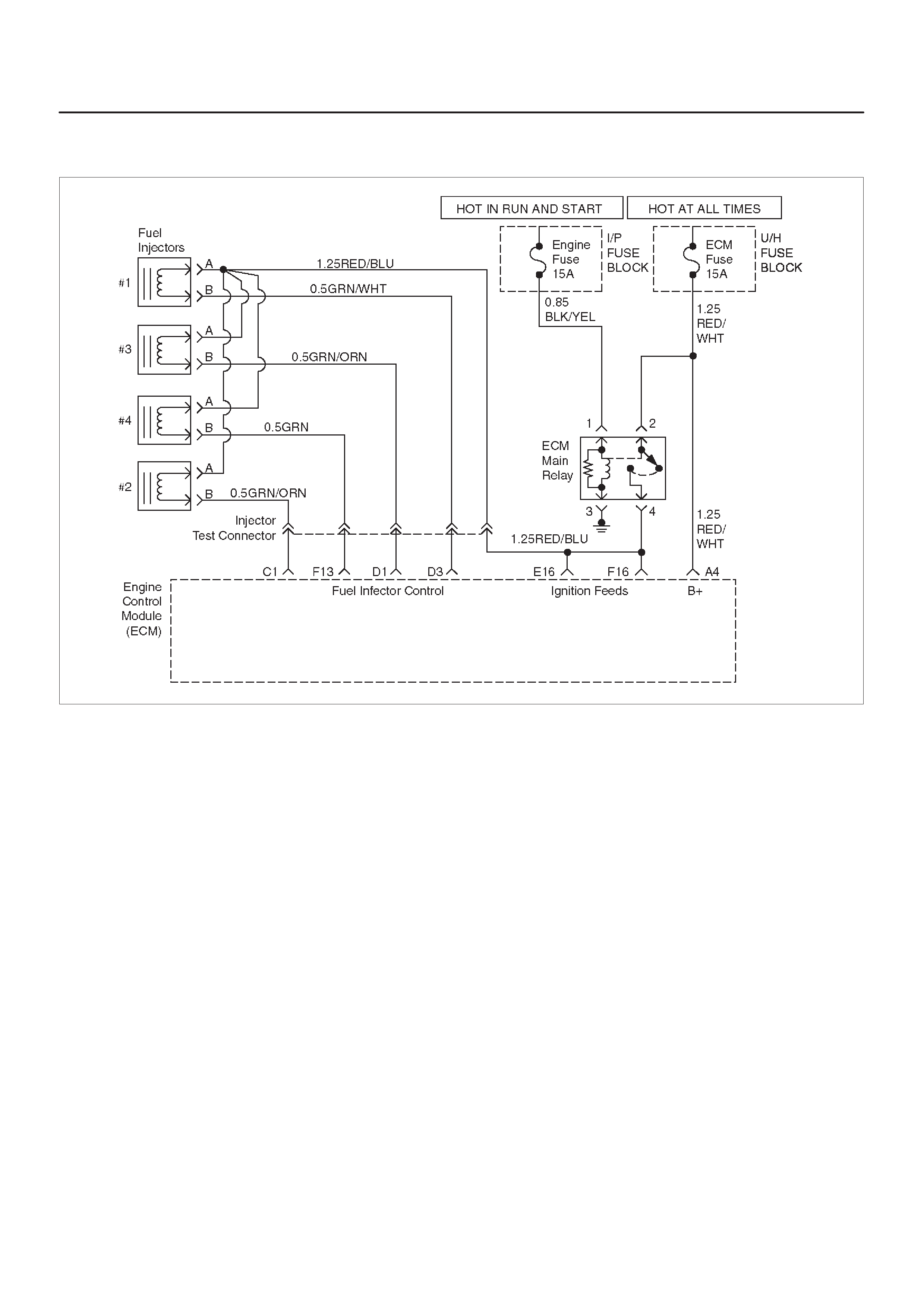
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0201 INJECTOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION – CYLINDER 1
D06RX120
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) has four individual
injector driver circuits. Each controls an injector. When a
driver circuit is grounded by the ECM, the injector is
activated. The ECM monitors the current in each driver
circuit. The ECM measures a voltage drop through a fixed
resistor and controls it. The voltage on each driver is
monitored to detect a fault. If the voltage is not what the
ECM expects to monitor on the circuit, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code is set. This Diagnostic Trouble Code is also
set if an injector driver is shorted to voltage. DTC P0201
is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe battery voltage is more than 9 volts.
DEngine is running.
DFuel pump is ON.
DThe injector voltage does not equal the ignition voltage
when the injector is commanded OFF or the injector
voltage does not equal 0 volts when the injector is
commanded ON.
DThe above conditions are met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL on the third consecutive
trip cycle in which the diagnostic has been run and the
fault is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0201 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles occur without a
fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0201 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
An injector driver circuit that is open or shorted to voltage
will cause a Diagnostic T rouble Code P0201 to set. It will
also cause a misfire due to an inoperative injector. A
misfire Diagnostic Trouble Code will also be set indicating
which cylinder is inoperative.
Long term and short term fuel trims that are excessively
high or low are a good indication that an injector is faulty.
Use Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure to check for faulty
injectors.

Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
3.This step determines if Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0201 is the result of a hard failure or an
intermittent condition.
5. This step tests the harness wiring and ECM control
of the injectors using a test light.
The fuel injector test connector is a gray 5 pin
connector at the right rear of the valve cover. It
can be identified by a blue connector lock which is
tethered to the harness.
5–8840–2606–0 is a test light with one light for
each cylinder. The test light fits on the injector test
connector.
If the test light is ON steady before cranking the
engine as well as while cranking the engine, then
the injector driver circuit is shorted to voltage.
If the test light blinks, the ECM and the wiring to
the injectors are OK. Fuel Injector Coil Test
Procedure will check if the injectors are faulty.
7. Because the test light was ON steady, voltage to the
injector is OK, but the driver circuit is grounded at all
times. This step determines if the circuit is shorted
to ground or the ECM is faulty.
901RX032
13. Normal injector resistance is slightly more than if
tested directly at the injector because it includes
resistance of the harness wires. The normal value is
about 13.5 W.
DTC P0201 – Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 1
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Will the engine start?
—Go to Step 3
Go to Engine
Cranks But
Will Not Run
Chart
31. Install the Tech 2. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble
Code.
2. Idle the engine for one minute.
Does Diagnostic Trouble Code P0201 reset? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Review the Freeze Frame data with the ignition ON
and the engine OFF and note the parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions as noted.
Does P0201 reset? —Go to Step 5
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the injector test connector.
3. Install the injector test light 5–8840–2606–0 on the
injector test connector.
4. Crank the engine while observing the light for
cylinder 1.
Does the injector test light blink? —
Go to Fuel
Injector Coil
Test
Procedure Go to Step 6
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
6Note whether the injector test light was OFF or ON
steady in step 5.
Was the test light ON steady while cranking the
engine? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step
10
71. Disconnect the ECM connector for the affected
injectors.
2. With a test light connected to B+, probe the affected
injector driver circuit.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Repair short to ground in the injector driver circuit.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
10 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
terminal on the ECM side of the injector test
connector. Only the Ign+ terminal should illuminate
the test light.
Besides the Ign+, did any other terminal illuminate the
test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
12
11 Repair the short to voltage in the injector driver circuit. —Verify repair —
12 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
pin on the injector side of the connector.
Did any terminal illuminate the test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
13
13 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition OFF.
3. Clip one lead of an ohmmeter to the ignition pin on
the injector side of the test connector.
4. T ouch the other lead to each of the other four pins in
the test connector, one pin at a time.
Instead of normal injector resistance, did the ohmmeter
indicate an open in one of the injector circuits? —Go to Step
14 Go to Step
15
14 Repair the open circuit or open injector. — Verify repair —
15 Check for an open circuit between the injector test
connector and the ECM connector for the Injector 1
control circuit.
Was there an open circuit? —Go to Step
16 Go to Step 9
16 Repair the open circuit. — Verify repair —

DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0202 INJECTOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION – CYLINDER 2
D06RX120
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) has four individual
injector driver circuits. Each controls an injector. When a
driver circuit is grounded by the ECM, the injector is
activated. The ECM monitors the current in each driver
circuit. The ECM measures a voltage drop through a fixed
resistor and controls it. The voltage on each driver is
monitored to detect a fault. If the voltage is not what the
ECM expects to monitor on the circuit, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code is set. This Diagnostic Trouble Code is also
set if an injector driver is shorted to voltage. DTC P0202
is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe battery voltage is greater than 9 volts.
DEngine is running.
DFuel pump is ON.
DThe injector voltage does not equal the ignition voltage
when the injector is commanded OFF or the injector
voltage does not equal 0 volts when the injector is
commanded ON.
DThe above conditions are met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL on the third consecutive
trip cycle in which the diagnostic has been run and the
fault is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0202 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles occur without a
fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0202 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
An injector driver circuit that is open or shorted to voltage
will cause a Diagnostic T rouble Code P0202 to set. It will
also cause a misfire due to an inoperative injector. A
misfire Diagnostic Trouble Code will also be set indicating
which cylinder is inoperative.
Long term and short term fuel trims that are excessively
high or low are a good indication that an injector is faulty.
Use Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure to check for faulty
injectors.
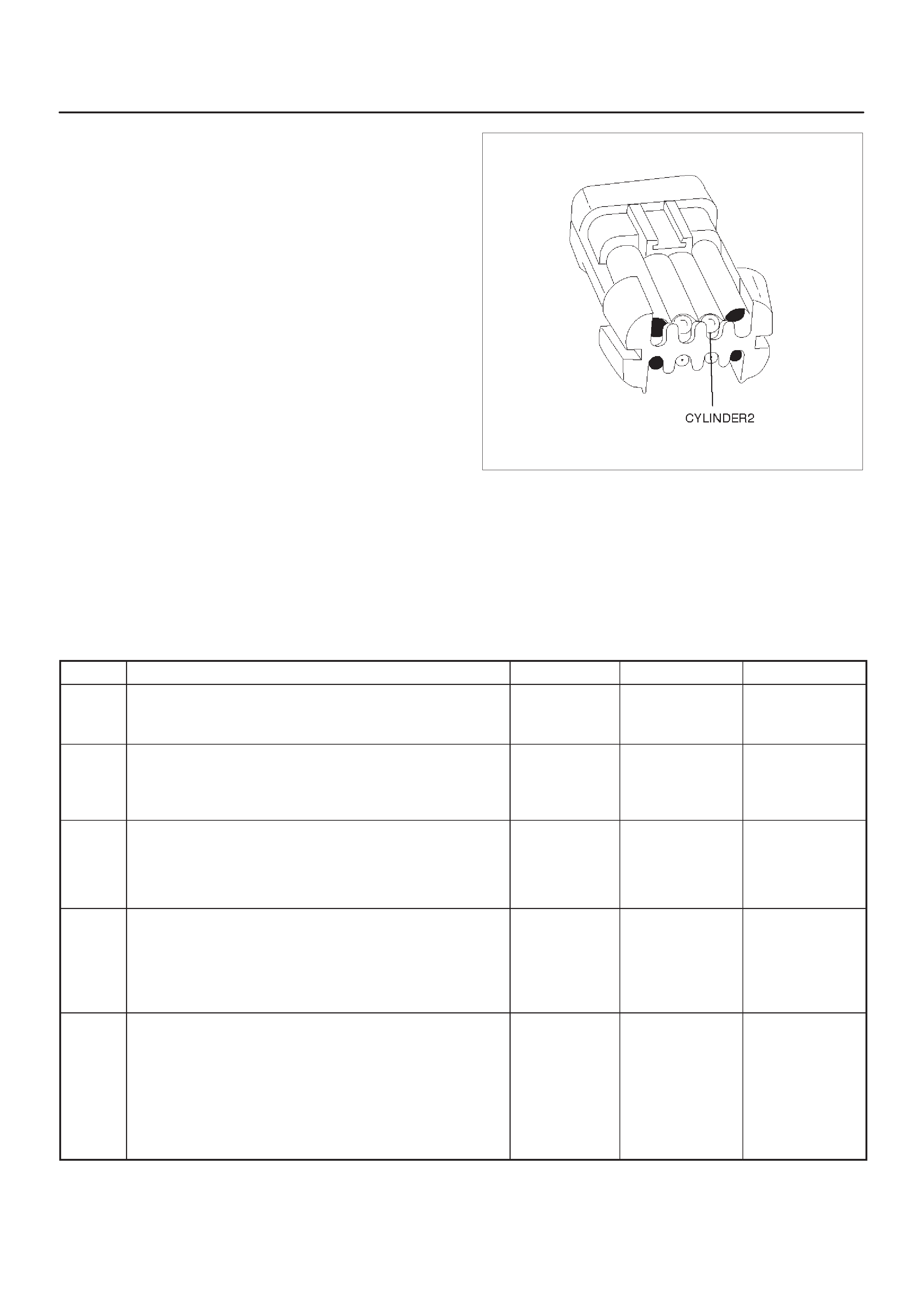
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
3.This step determines if Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0202 is the result of a hard failure or an
intermittent condition.
5.This step tests the harness wiring and ECM control
of the injectors using a test light.
The fuel injector test connector is a gray 5 pin
connector at the right rear of the valve cover. It
can be identified by a blue connector lock which is
tethered to the harness.
5–8840–2606–0 is a test light with one light for
each cylinder. The test light fits on the injector test
connector.
If the test light is ON steady before cranking the
engine as well as while cranking the engine, then
the injector driver circuit is shorted to voltage.
If the test light blinks, the ECM and the wiring to
the injectors are OK. Fuel Injector Coil Test
Procedure will check if the injectors are faulty.
7.Because the test light was ON steady, voltage to the
injector is OK, but the driver circuit is grounded at all
times. This step determines if the circuit is shorted
to ground or the ECM is faulty.
901RX033
13. Normal injector resistance is slightly more than if
tested directly at the injector because it includes
resistance of the harness wires. The normal value is
about 13.5 W.
DTC P0202 – Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 2
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Will the engine start?
—Go to Step 3
Go to Engine
Cranks But
Will Not Run
Chart
31. Install the Tech 2. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble
Code.
2. Idle the engine for one minute.
Does Diagnostic Trouble Code P0202 reset? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Review the Freeze Frame data with the ignition ON
and the engine OFF and note the parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions as noted.
Does P0202 reset? —Go to Step 5
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the injector test connector.
3. Install the injector test light 5–8840–2606–0 on the
injector connector.
4. Crank the engine while observing the light for
cylinder 2.
Does the injector test light blink? —
Go to Fuel
Injector Coil
Test
Procedure Go to Step 6
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
6Note whether the injector test light was OFF or ON
steady in step 5.
Was the test light ON steady while cranking the
engine? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step
10
71. Disconnect the ECM connector for the affected
injectors.
2. With a test light connected to B+, probe the affected
injector driver circuit.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Repair short to ground in the injector driver circuit.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
10 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
terminal on the ECM side of the injector test
connector. Only the Ign+ terminal should illuminate
the test light.
Besides the Ign+, did any other terminal illuminate the
test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
12
11 Repair the short to voltage in the injector driver circuit. —Verify repair —
12 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
pin on the injector side of the connector.
Did any terminal illuminate the test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
13
13 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition OFF.
3. Clip one lead of an ohmmeter to the ignition pin on
the injector side of the test connector.
4. T ouch the other lead to each of the other four pins in
the test connector, one pin at a time.
Instead of normal injector resistance, did the ohmmeter
indicate an open in one of the injector circuits? —Go to Step
14 Go to Step
15
14 Repair the open circuit or open injector. — Verify repair —
15 Check for an open circuit between the injector test
connector and the ECM connector for the Injector 2
control circuit.
Was there an open circuit? —Go to Step
16 Go to Step 9
16 Repair the open circuit. — Verify repair —
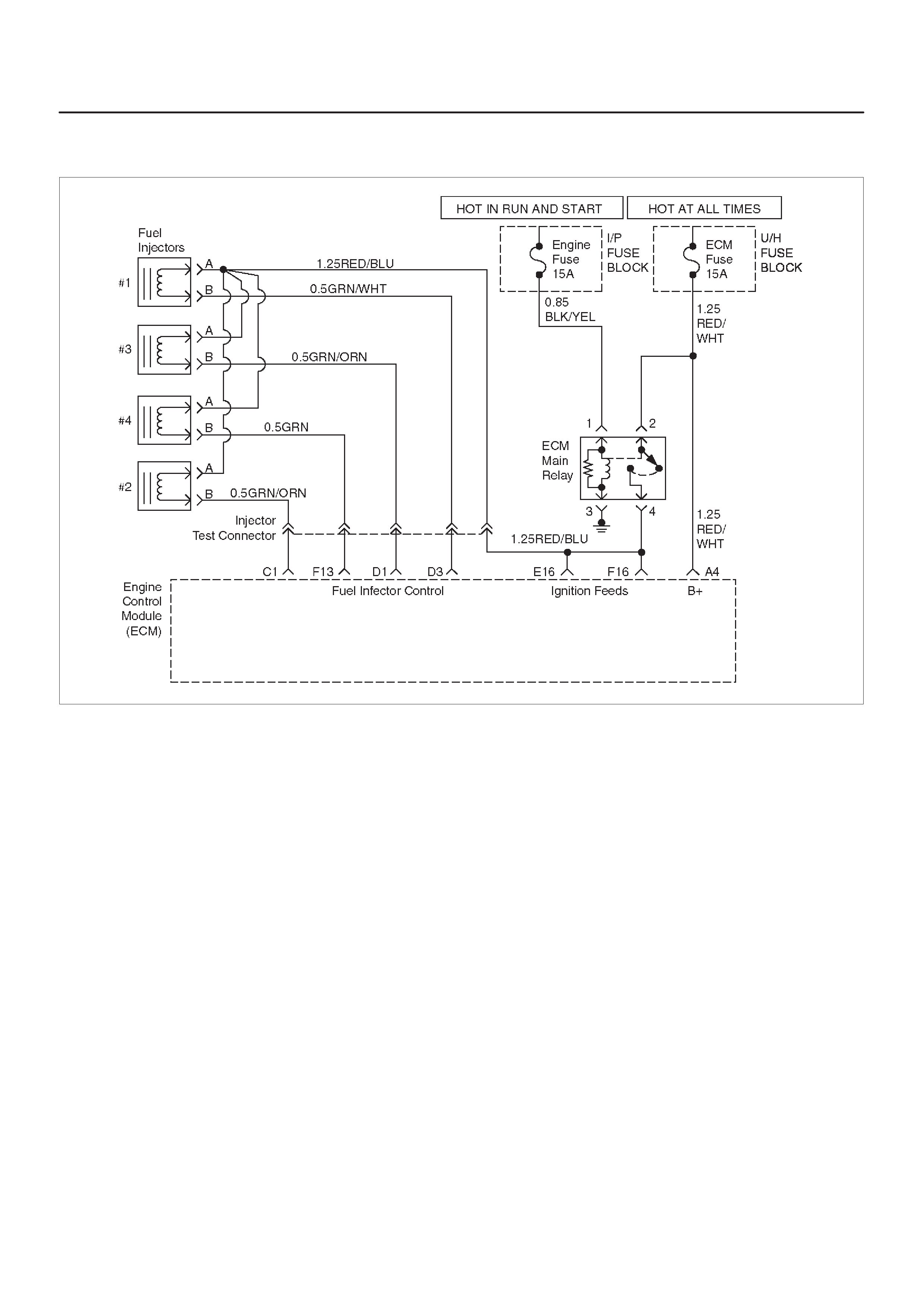
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0203 INJECTOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION – CYLINDER 3
D06RX120
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) has four individual
injector driver circuits. Each controls an injector. When
the driver circuit is grounded by the ECM, the injector is
activated. The ECM monitors the current in each driver
circuit. The ECM measures a voltage drop through a fixed
resistor and controls it. The voltage on each driver is
monitored to detect a fault. If the voltage is not what the
ECM expects to monitor on the circuit, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code is set. This Diagnostic Trouble Code is also
set if an injector driver is shorted to voltage. DTC P0203
is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe battery voltage is greater than 9 volts.
DEngine is running.
DFuel pump is ON.
DThe injector voltage does not equal the ignition voltage
when the injector is commanded OFF or the injector
voltage does not equal 0 volts when the injector is
commanded ON.
DThe above conditions are met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was setas Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL on the third consecutive
trip cycle in which the diagnostic has been run and the
fault is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0203 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles occur without a
fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0203 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
An injector driver circuit that is open or shorted to voltage
will cause a Diagnostic T rouble Code P0203 to set. It will
also cause a misfire due to an inoperative injector. A
misfire Diagnostic Trouble Code will also be set indicating
which cylinder is inoperative.
Long term and short term fuel trims that are excessively
high or low are a good indication that an injector is faulty.
Use Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure to check for faulty
injectors.
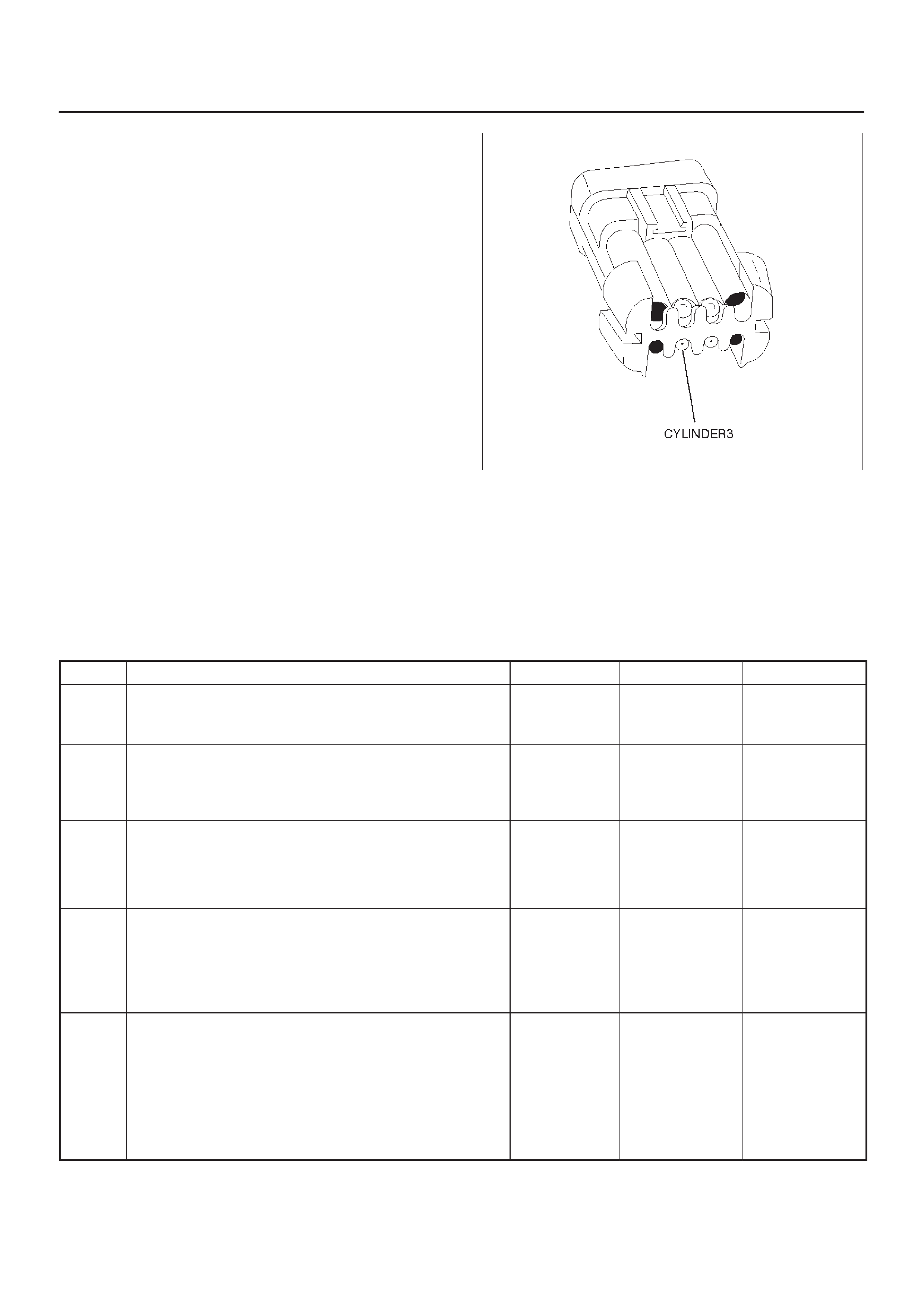
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
3.This step determines if Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0203 is the result of a hard failure or an
intermittent condition.
5.This step tests the harness wiring and ECM control
of the injectors using a test light.
The fuel injector test connector is a gray 5 pin
connector at the right rear of the valve cover. It
can be identified by a blue connector lock which is
tethered to the harness.
5–8840–2606–0 is a test light with one light for
each cylinder. The test light fits on the injector test
connector.
If the test light is ON steady before cranking the
engine as well as while cranking the engine, then
the injector driver circuit is shorted to voltage.
If the test light blinks, the ECM and the wiring to
the injectors are OK. Fuel Injector Coil Test
Procedure will check if the injectors are faulty.
7.Because the test light was ON steady, voltage to the
injector is OK, but the driver circuit is grounded at all
times. This step determines if the circuit is shorted
to ground or the ECM is faulty.
901RX034
13. Normal injector resistance is slightly more than if
tested directly at the injector because it includes
resistance of the harness wires. The normal value is
about 13.5 W.
DTC P0203 – Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 3
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Will the engine start?
—Go to Step 3
Go to Engine
Cranks But
Will Not Run
Chart
31. Install the Tech 2. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble
Code.
2. Idle the engine for one minute.
Does Diagnostic Trouble Code P0203 reset? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Review the Freeze Frame data with the ignition ON
and the engine OFF and note the parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions as noted.
Does P0203 reset? —Go to Step 5
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the injector test connector.
3. Install the injector test light 5–8840–2606–0 on the
injector connector.
4. Crank the engine while observing the light for
cylinder 3.
Does the injector test light blink? —
Go to Fuel
Injector Coil
Test
Procedure Go to Step 6
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
6Note whether the injector test light was OFF or ON
steady in step 5.
Was the test light ON steady while cranking the
engine? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step
10
71. Disconnect the ECM connector for the affected
injectors.
2. With a test light connected to B+, probe the affected
injector driver circuit.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Repair short to ground in the injector driver circuit.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
10 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
terminal on the ECM side of the injector test
connector. Only the Ign+ terminal should illuminate
the test light.
Besides the Ign+, did any other terminal illuminate the
test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
12
11 Repair the short to voltage in the injector driver circuit. —Verify repair —
12 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
pin on the injector side of the connector.
Did any terminal illuminate the test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
13
13 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition OFF.
3. Clip one lead of an ohmmeter to the ignition pin on
the injector side of the test connector.
4. T ouch the other lead to each of the other four pins in
the test connector, one pin at a time.
Instead of normal injector resistance, did the ohmmeter
indicate an open in one of the injector circuits? —Go to Step
14 Go to Step
15
14 Repair the open circuit or open injector. — Verify repair —
15 Check for an open circuit between the injector test
connector and the ECM connector for the Injector 3
control circuit.
Was there an open circuit? —Go to Step
16 Go to Step 9
16 Repair the open circuit. — Verify repair —
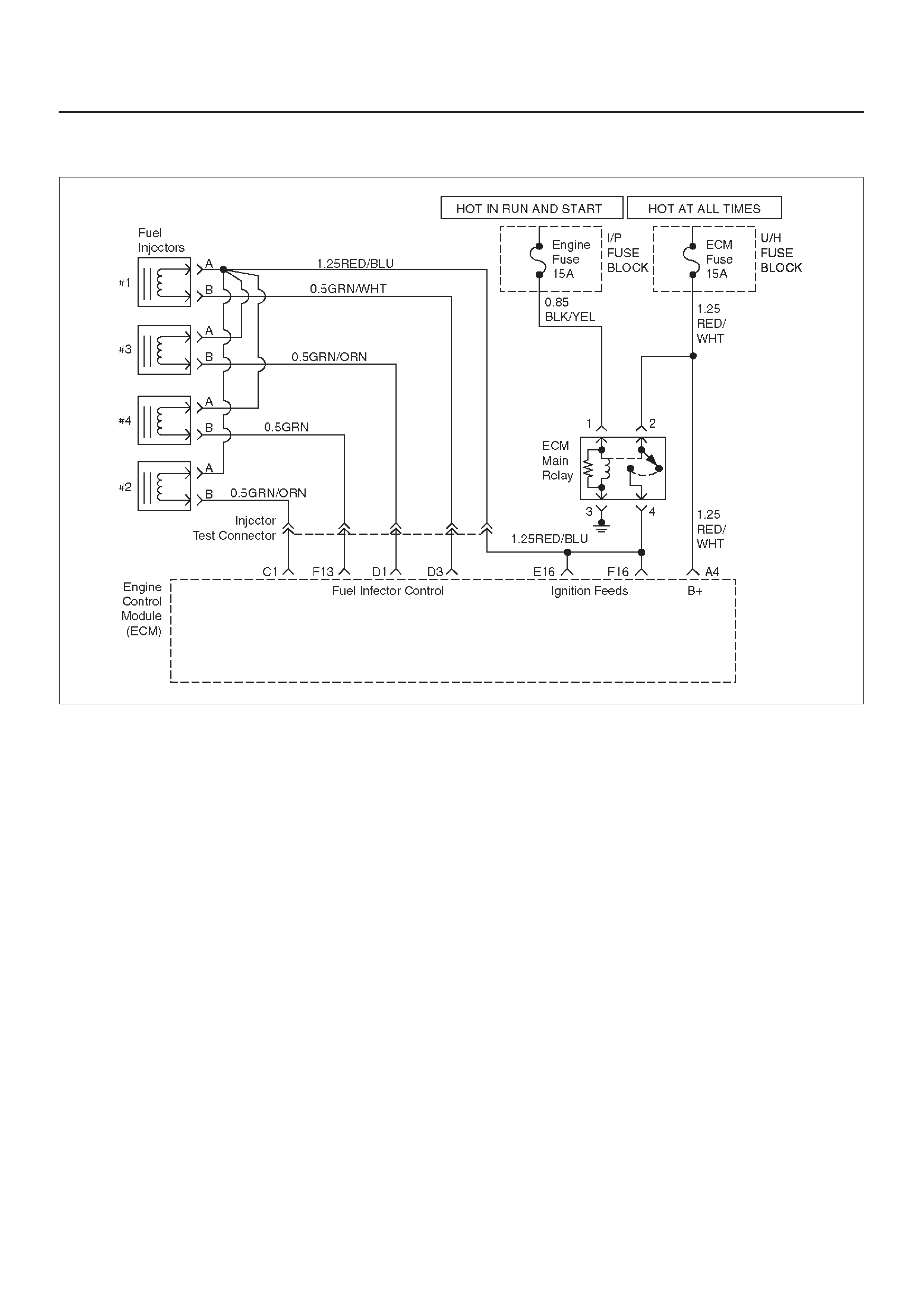
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0204 INJECTOR CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION – CYLINDER 4
D06RX120
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) has four individual
injector driver circuits. Each controls an injector. When
the driver circuit is grounded by the ECM, the injector is
activated. The ECM monitors the current in each driver
circuit. The ECM measures a voltage drop through a fixed
resistor and controls it. The voltage on each driver is
monitored to detect a fault. If the voltage is not what the
ECM expects to monitor on the circuit, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code is set. This Diagnostic Trouble Code is also
set if an injector driver is shorted to voltage. DTC P0204 is
a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe battery voltage is greater than 9 volts.
DEngine is running.
DFuel pump is ON.
DThe injector voltage does not equal the ignition voltage
when the injector is commanded OFF or the injector
voltage does not equal 0 volts when the injector is
commanded ON.
DThe above conditions are met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
D”Open Loop” fuel control will be in effect.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL on the third consecutive
trip cycle in which the diagnostic has been run and the
fault is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0204 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles occur without a
fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0204 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
An injector driver circuit that is open or shorted to voltage
will cause a Diagnostic T rouble Code P0204 to set. It will
also cause a misfire due to an inoperative injector. A
misfire Diagnostic Trouble Code will also be set indicating
which cylinder is inoperative.
Long term and short term fuel trims that are excessively
high or low are a good indication that an injector is faulty.
Use Fuel Injector Coil Test Procedure to check for faulty
injectors.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
3.This step determines if Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0204 is the result of a hard failure or an
intermittent condition.
5.This step tests the harness wiring and ECM control
of the injectors using a test light.
The fuel injector test connector is a gray 5 pin
connector at the right rear of the valve cover. It
can be identified by a blue connector lock which is
tethered to the harness.
5–8840–2606–0 is a test light with one light for
each cylinder. The test light fits on the injector test
connector.
If the test light is ON steady before cranking the
engine as well as while cranking the engine, then
the injector driver circuit is shorted to voltage.
If the test light blinks, the ECM and the wiring to
the injectors are OK. Fuel Injector Coil Test
Procedure will check if the injectors are faulty.
7. Because the test light was ON steady, voltage to the
injector is OK, but the driver circuit is grounded at all
times. This step determines if the circuit is shorted
to ground or the ECM is faulty.
901RX035
13. Normal injector resistance is slightly more than if
tested directly at the injector because it includes
resistance of the harness wires. The normal value is
about 13.5 W.
DTC P0204 – Injector Circuit Malfunction – Cylinder 4
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Will the engine start?
—Go to Step 3
Go to Engine
Cranks But
Will Not Run
Chart
31. Install the Tech 2. Clear the DTC.
2. Idle the engine for one minute.
Does DTC P0204 reset? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Review the Freeze Frame data with the ignition ON
and the engine OFF and note the parameters.
2. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions as noted.
Does P0204 reset? —Go to Step 5
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the injector test connector.
3. Install the injector test light 5–8840–2606–0 on the
injector connector.
4. Crank the engine while observing the light for
cylinder 4.
Does the injector test light blink? —
Go to Fuel
Injector Coil
Test
Procedure Go to Step 6
6Note whether the injector test light was OFF or ON
steady in step 5.
Was the test light ON steady while cranking the
engine? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step
10
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
71. Disconnect the ECM connector for the affected
injectors.
2. With a test light connected to B+, probe the affected
injector driver circuit.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Repair short to ground in the injector driver circuit.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —
Go to OBD
System
Check —
10 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
terminal on the ECM side of the injector test
connector. Only the Ign+ terminal should illuminate
the test light.
Besides the Ign+, did any other terminal illuminate the
test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
12
11 Repair the short to voltage in the injector driver circuit. —Verify repair —
12 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use a test light connected to ground to probe each
pin on the injector side of the connector.
Did any terminal illuminate the test light? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
13
13 1. Disconnect the injector test connector.
2. Ignition OFF.
3. Clip one lead of an ohmmeter to the ignition pin on
the injector side of the test connector.
4. T ouch the other lead to each of the other four pins in
the test connector, one pin at a time.
Instead of normal injector resistance, did the ohmmeter
indicate an open in one of the injector circuits? —Go to Step
14 Go to Step
15
14 Repair the open circuit or open injector. — Verify repair —
15 Check for an open circuit between the injector test
connector and the ECM connector for the Injector 3
control circuit.
Was there an open circuit? —Go to Step
16 Go to Step 9
16 Repair the open circuit. — — Verify repair
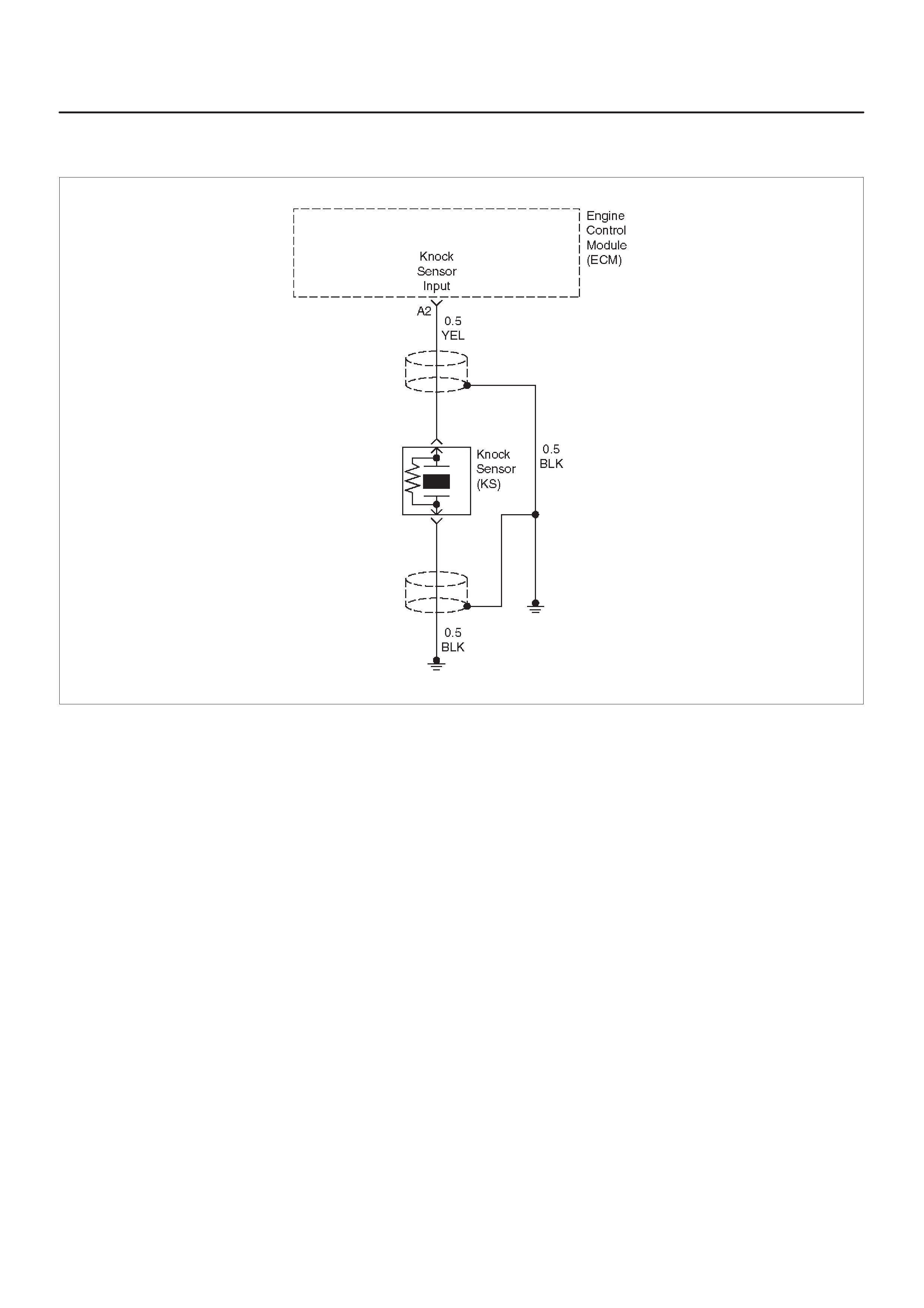
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0325 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION
D06RX121
Circuit Description
The knock sensor (KS) system is used to detect engine
detonation. The knock sensor produced an AC voltage
signal. The knock sensor sends this signal to the ECM.
The amplitude and the frequency of the AC voltage signal
depends upon the knock level being detected. The ECM
will then retard the spark timing based on the signals from
the Knock Sensor. DTC P0325 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
DNo P0327 Diagnostic Trouble Code set.
DEngine speed is above 2500 rpm.
All the above mentioned conditions are met, and the
following conditions are met for 8.75 seconds within a 10
second monitoring period:
DAny of the four A/D voltages exceeds 1.5625 Volts.
DInstantaneous A/D delta Voltage falls below 0.019531
Volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
the second time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will record operating conditions at the time
the diagnostic fails.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code is stored.
DThe ECM will use a calculated spark retard value in
order to minimize the knock during the conditions when
the knock is likely to occur. The calculated value will
vary based on the engine speed and load.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe MIL will turn off after 3 consecutive ignition cycles
in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code will clear after 40
consecutive warm up cycles without a fault.
DA Tech 2 can clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
Diagnostic Aids
Correct any abnormal engine noise before using the
diagnostic table.
Check for an open ignition feed circuit.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the
technician to complete some basic checks and store
the freeze frame data and failure records data on
the Tech 2 if applicable. This creates an electronic
copy of the data taken when the malfunction
occurred. The information is then stored on the
Tech 2 for later reference.
2. If the conditions for the test as described above are
met, a Diagnostic Trouble Code P0325 will set and
MIL will illuminate.
4. If the engine has an internal knock or audible noise
that causes a knocking type noise on the engine
block, the knock sensor may be responding to the
noise.
6. The Tech 2 displays knock sensor activity in counts,
approximately 20–50 at idle. The counts should
increase when engine speed is increased and the
counts should decrease when engine speed is
decreased.
7. Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the
complaint, should be thoroughly checked for backed
out terminals, improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, poor
terminal to wiring connections or physical damage
to the wiring harness.
8. If the KS module was previously replaced and the
Diagnostic Trouble Code resets, a malfunctioning
ECM is indicated.
9. Checking the internal resistance of the knock sensor
verifies if the knock sensor or the wiring to the
knock sensor is OK.
DTC P0325 KS Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the Powertrain ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check” performed?
——Go to Step 2
Go to
Powertrain
OBD System
Check
21. Start the engine.
2. Install a Tech 2.
3. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
4. Run the engine at slightly more than 10% throttle
angle.
Does the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminate? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch ON, with engine OFF.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions and
Conditions for Setting the DTC as noted.
Does the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminate? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step
13
4Listen to the engine while raising and lowering the
engine speed.
Is a knock or audible noise present? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair the mechanical engine problem or a loose
bracket or component.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
13 —
6Slowly increase the engine speed to the specified
value.
Does the KS Activity increase with the engine speed? 2500 RPM Go to Step 7 Go to Step
11
7Check for a poor connection at the ECM connector,
Knock sensor signal circuit and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
13 Go to Step 8
8Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
13 —
91. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM connectors at the ECM.
3. With a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) connected to
ground, measure the resistance of the knock
sensor through the knock sensor signal circuit.
Is the measured value within the specified value? 90K – 110K WGo to Step 7 Go to Step
10
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Check the knock sensor electrical connector for a poor
connection and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
13 Go to Step
11
11 Check the knock sensor signal circuit for an open or a
short to ground or to voltage and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
13 Go to Step
12
12 Replace the Knock Sensor (KS).
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
13 —
13 1. Using the Tech 2, clear the Diagnostic Trouble
Codes.
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting
this Diagnostic Trouble Code as specified in the
supporting text.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that this diagnostic has ran
and passed? —Go to Step
14 Go to Step 2
14 Check is any additional Diagnostic T rouble Codes are
set.
Are any Diagnostic T rouble Codes displayed that have
not been diagnosed? —
Go to
applicable
DTC table System OK
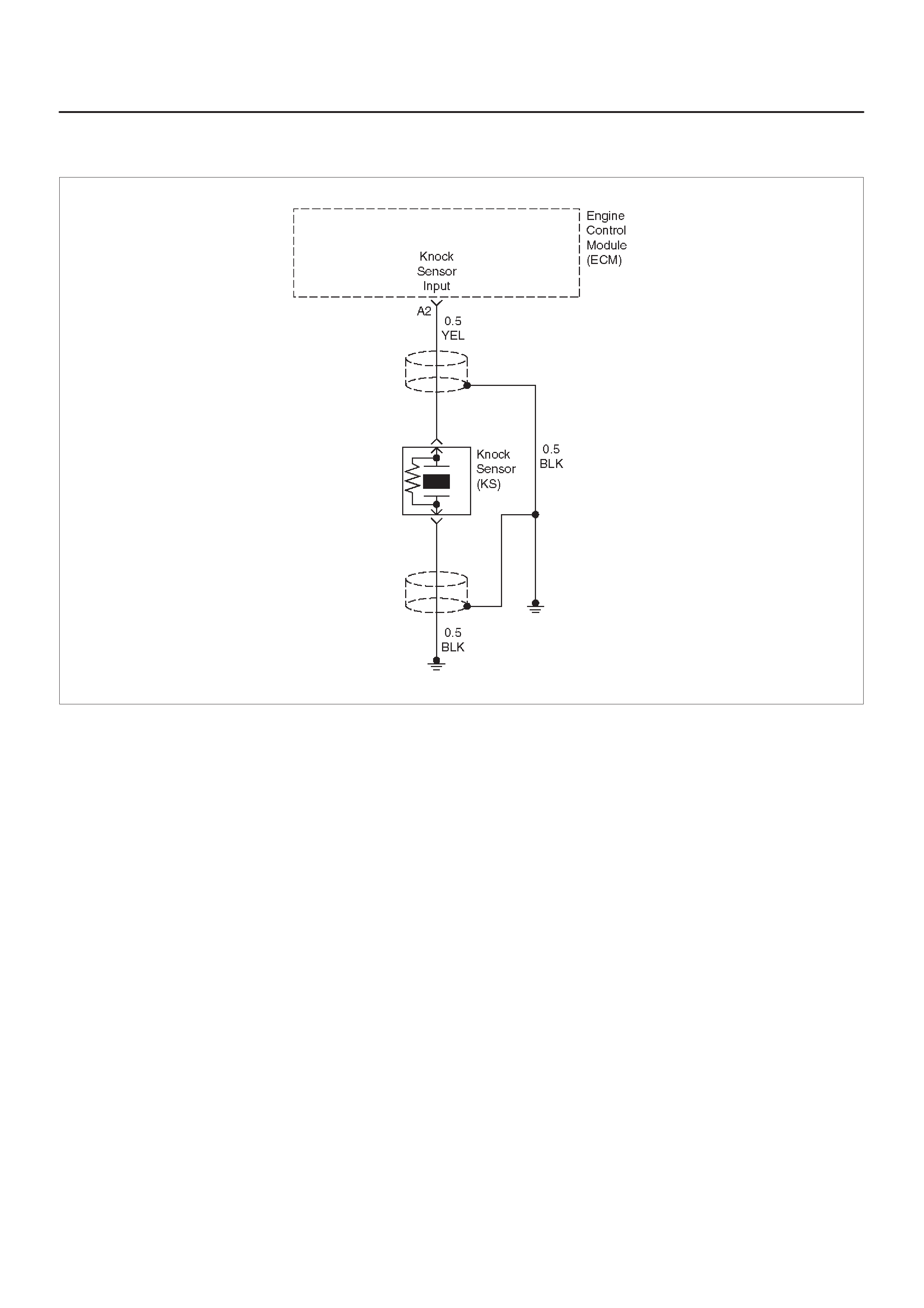
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327 KNOCK SENSOR (KS) CIRCUIT
LOW INPUT
D06RX121
Circuit Description
The ECM uses the Knock Sensor (KS) in order to detect
engine detonation. This allows the ECM to retard the
Ignition Control (IC) spark timing based on the KS signal
the ECM receives. The circuitry within the knock sensor
pulls down the ECM–supplied 5 volt signal, so that under
a no knock condition the signal on the KS circuit
measures about 1.3 volts. The knock sensors produce an
AC signal that rides on the 1.3 volts DC. The signal’s
amplitude and frequency are dependent upon the amount
of the knock being experienced.
The ECM determines whether the knock is occurring by
comparing the signal level on the KS circuit with a voltage
level on the noise channel. The noise channel allows the
CM to reject any false knock signal by indicating the
amount of normal engine mechanical noise present. The
normal engine noise varies depending on the engine
speed and load. Then the ECM determines that an
abnormally high noise channel voltage level is being
experienced, a Diagnostic Trouble Code P0327 sets.
This DTC is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
A/D Test
The following conditions are met for 7.5 seconds within a
10 second monitoring period:
DEngine speed is equal to or greater than 2000 RPM.
DA/D Voltage is less than or equal to 0.0977 Volts.
Gain Test
The following conditions are met for 7.5 seconds within a
10 second monitoring period:
DEngine speed is greater than 2500 RPM.
DGain is equal to or greater than 23.875 dB.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the MIL the second time the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store the conditions which were present
then the Diagnostic Trouble Code set.
DThe ECM will use a calculated spark retard value in
order to minimize the knock during the conditions when
the knock is likely to occur. The calculated value will
vary based on the engine speed and load.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code will clear after 40
consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred without a
fault.
DThe T ech 2 ”Clear Info” will clear the Diagnostic Trouble
Code.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
A poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the knock sensor
and the ECM connectors for: , broken locks, improperly
formed or damaged terminals.
DBacked out terminals
DBroken locks
DImproperly formed or damaged terminals
Also, check the wiring harness for: shorts to ground,
shorts to battery positive, and open circuits.
DA misrouted harness. Inspect the knock sensor
harness in order to ensure that it is not routed too close
to high voltage wires such as spark plug leads.
DImproper Knock Sensor torque specification. Torque
the Knock Sensor to 19N·m (1.9kg·m/14 lbs·ft). Refer
to Fastener Notice.
Review the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed in order to help determine how
often the conditions that caused the DTC to set occur.
This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Ensures that the fault is present.
6. Ensures that the knock sensor is capable of
detecting detonation.
DTC P0327 KS Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the Powertrain ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to
Powertrain
OBD System
Check
21.Operate the engine within the conditions specified
in the diagnostic support Conditions for Setting the
DTC.
2.Using a Tech 2, monitor theDiagnostic Trouble
Code information for Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0327 until the Diagnostic Trouble Code P0327 test
runs.
3.Observe the test results.
Does the Tech 2 indicate the DTC P0327 failed this
ignition? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
31.Turn ON the Ignition leaving the engine OFF.
2.Review the Tech 2 Fail Records data.
3.
IMPORTANT:Before clearing the DTCs, use the Tech
2 to record the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records
for reference. This data will be lost when the Clear Info
function is used.
4. Record the Tech 2 Fail Records data.
5. Operate the vehicle within the Fail Records
conditions.
6. Using a Tech 2, monitor the DTC info for the DTC
P0327 until the DTC P0327 test runs.
7. Observe the test results.
Does the Tech 2 indicate the DTC P0327 Failed This
Ignition? —Go to Step 4
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the KS Sensor electrical connector.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), measure the
voltage between the KS signal circuit at the knock
sensor harness connectors and ground.
Is the voltage at the specified value? Approx. 5.0 V Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
5Measure the resistance of the KS sensor by connecting
the between the KS sensor terminal and the engine
block.
Is the resistance of the KS sensor near the specified
value? 100K WGo to Step 6 Go to Step 9
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
61. Check the KS signal circuit for a poor terminal
connection at the knock sensor.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary. Refer to
Wiring Repairs in Engine Electrical.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 9
71. Re–Connect the KS Sensor in order to monitor the
voltage between the KS sensor terminal and the
engine ground.
2. Tap on the engine lift bracket, near the KS Sensor,
while observing the signal indicated on the Tech 2.
Is any signal indicated on the while tapping on the
engine lift bracket? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step 8
81. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the ECM.
3. Turn ON the ignition.
4. Check the KS signal circuit between the ECM and
the KS sensor connector for an open, a short to
voltage, or a short to ground.
5. If a wiring problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
10
9Replace the KS Sensor. Refer to Knock Sensor.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
11 —
10 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
11 —
11 1. Using the T ech 2, select the DTC and the Clear Info.
2. Start the engine.
3. Idle at the normal operating temperature.
4. Select the DTC and the Specific.
5. Enter the DTC number which was set.
6. Operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting
this DTC as specified in the supporting text.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that this diagnostic ran and
passed? —Go to Step
12 Go to Step 2
12 Using the Tech 2, select the Capture Info and the
Review Info.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been
diagnosed? —
Go to
applicable
DTC table System OK
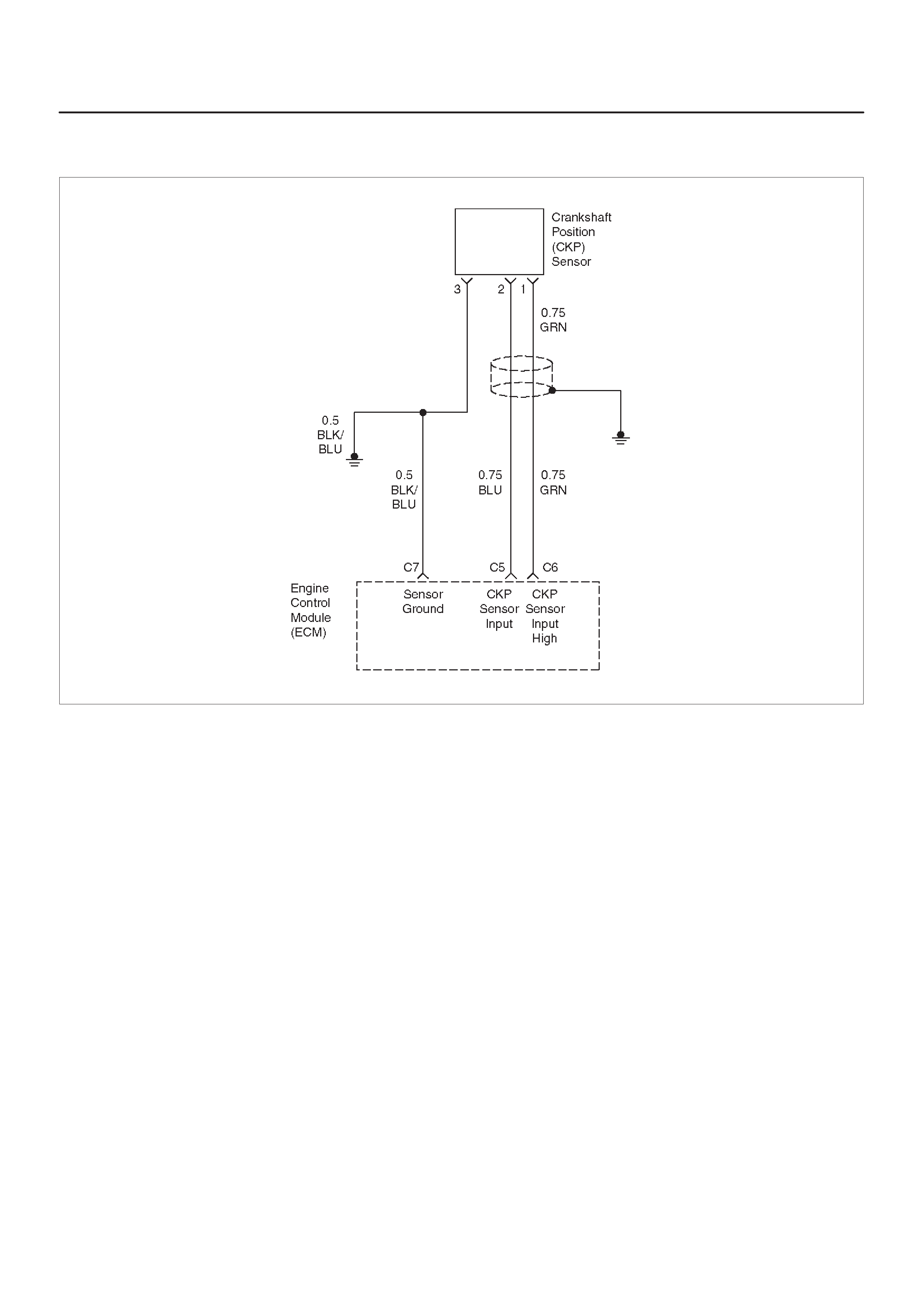
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0336 CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
D06RX122
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor . During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft pulses will be produced. The engine control
module (ECM) uses the 58X reference signal to calculate
engine RPM and crankshaft position. The ECM
constantly monitors the number of pulses on the 58X
reference circuit and compares them to the number of
camshaft position (CMP) signal pulses being received. If
the ECM receives an incorrect number of pulses on the
58X reference circuit, Diagnostic Trouble Code P0336 will
set. Diagnostic Trouble Code P0336 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine is running.
DExtra or missing pulse is detected between
consecutive 58X reference pulses.
DAbove condition is detected in 10 of 100 crankshaft
rotations.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0336 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0336 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
DPoor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
disconnect the ECM, turn the ignition on and observe
a voltmeter connected to the 58X reference circuit at
the ECM harness connector while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the ECM. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0336 – CKP Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start?
—Go to Step 3
Refer to
Engine
Cranks But
Will Not Run
chart
31. Review and record Failure Records information.
2. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Code P0336.
3. Start the engine and idle for 1 minute.
4. Observe Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
Is Diagnostic Trouble Code P0336 set? —Go to Step 4
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Disconnect the ECM and CKP sensor.
2. Check for an open or a short to ground in the 58X
reference circuit between the CKP sensor
connector and the ECM harness connector.
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Reconnect the ECM and CKP sensor.
2. Connect a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) to measure
voltage on the 58X reference circuit at the ECM
connector.
3. Observe the voltage while cranking the engine.
Is the voltage near the specified value? 2.5 V Go to Step 8 Go to Step 6
6Check the connections at the CKP sensor and replace
the terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Replace the CKP sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
8Check connections at the ECM and replace the
terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
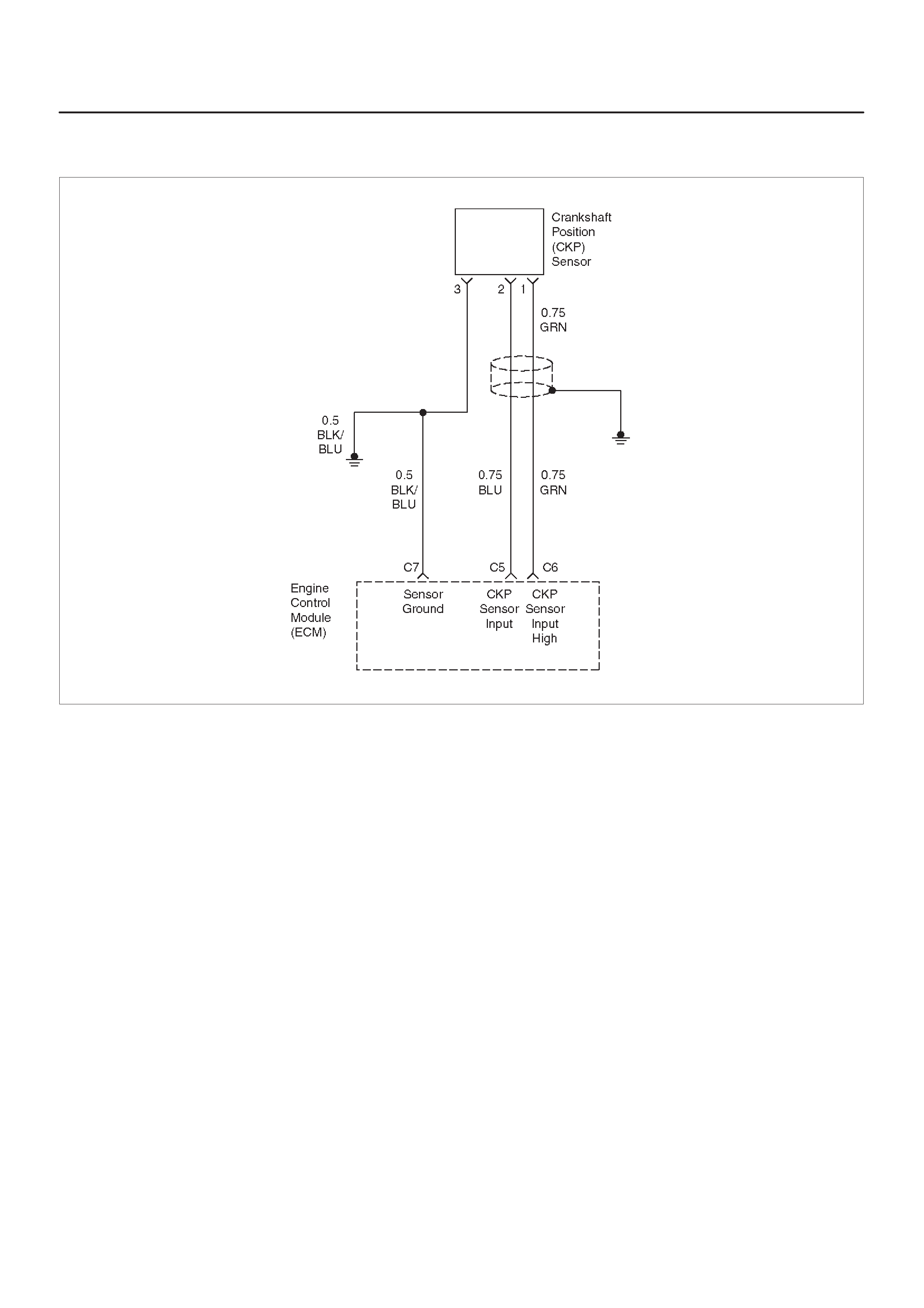
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0337 CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
D06RX122
Circuit Description
The 58X reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor . During one crankshaft revolution,
58 crankshaft reference pulses will be produced. The
engine control module (ECM) uses the 58X reference
signal to calculate engine RPM and crankshaft position.
The ECM constantly monitors the number of pulses on
the 58X reference circuit and compares them to the
number of camshaft position (CMP) signal pulses being
received. If the ECM does not receive pulses on the 58X
reference circuit, Diagnostic Trouble Code P0337 will set.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0337 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo camshaft position (CMP) sensor DTCs are set.
DEngine cranking.
DCrankshaft position (CKP) sensor signal is not present
between two cam pulses.
DCKP reference pulse is not detected within 24 CMP
pulses.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0337 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0337 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
DPoor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
disconnect the ECM, turn the ignition on and observe
a voltmeter connected to the 58X reference circuit at
the ECM harness connector while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the ECM. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0337 – CKP Sensor Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Disconnect the CKP sensor.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), verify that 5 V
reference and ground are being supplied at the
sensor connector (ECM side).
Are 5 V and ground being supplied to the sensor? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON.
2. With a DVM, backprobe the ECM connector 5 V
reference and ground connections.
Are 5 V reference and ground available at the ECM? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 9
4Check 5 V reference or ground between the CKP
sensor and ECM and repair the open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and CKP sensor.
3. Check for an open or a short to ground in the 58X
reference circuit between the CKP sensor
connector and the ECM harness connector.
4. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Reconnect the ECM and CKP sensor.
2. Connect a DVM to measure voltage on the 58X
reference circuit at the ECM connector.
3. Observe the voltage while cranking the engine.
Is the voltage near the specified value? 2.5 V Go to Step 9 Go to Step 7
7Check the connections at the CKP sensor and replace
the terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8Replace the CKP sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Check the connections at the ECM and replace the
terminals if necessary.
Did any terminals require replacement? — Verify repair Go to Step
10
10 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
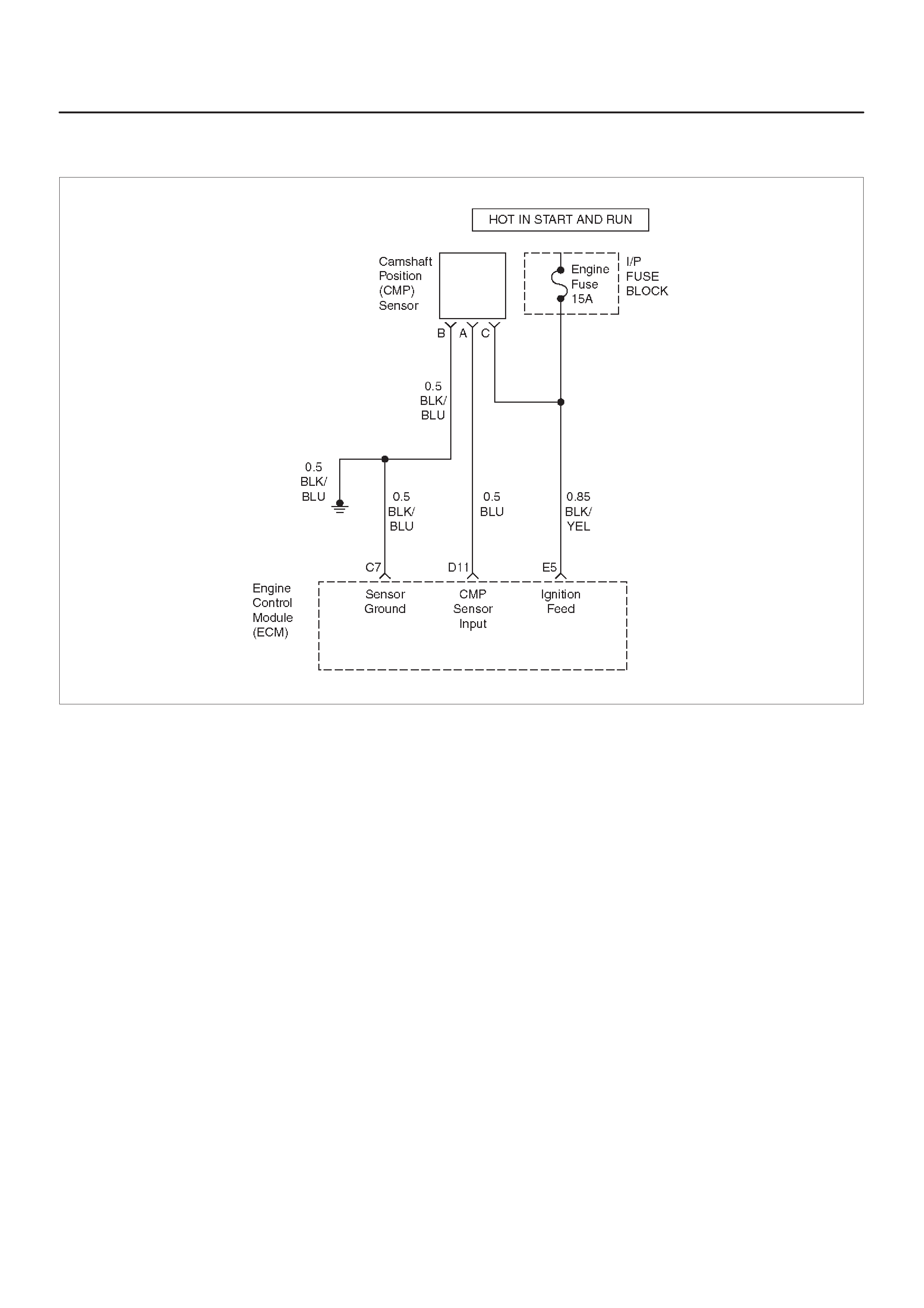
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0341 CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
D06RX123
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal is produced
by the CMP sensor pulses when the engine is running and
crankshaft position (CKP) sync pulses are also being
received. The engine control module (ECM) uses the
CMP signal pulses to initiate sequential fuel injection. The
ECM constantly monitors the number of pulses on the
CMP signal circuit and compares the number of CMP
pulses to the number of 58X reference pulses received. If
the ECM receives an incorrect number of pulses on the
CMP reference circuit, Diagnostic Trouble Code P0341
will set and the ECM will initiate injector sequence without
the CMP signal with a one in four chance that injector
sequence is correct. The engine will continue to start and
run normally, although the misfire diagnostic will be
affected if a misfiring condition occurs. DTC P0341 is a
type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe engine is running (CMP reference pulses are
being received).
DAbove condition fails for 10 occurrences within 100 test
samples (15.6 m/s).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will initiate injector sequence without the
CMP signal with a one in four chance that injector
sequence is correct.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) was set as
Freeze Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0341 will
clear after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have
occurred without a fault.
DDiagnostic T rouble Code (DTC) P0341 can be cleared
by using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DIf a CKP Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is also
indicated, there may be a problem with the ground
circuit because the CMP ground is spliced to the CKP
ground wire.
DIf a fuel injector Diagnostic T rouble Code (DTC) is also
indicated, there may be a problem with the power
supply to the CMP. The wire supplying CMP power is
spliced to the wire supplying power to the fuel injectors.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
disconnect the ECM, turn the ignition ON and observe
a voltmeter connected to the CMP signal circuit at the
ECM harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the CMP sensor. A change
in voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0341 – CMP Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” information for DTC
P0341 until the DTC P0341 test runs.
Does the T ech 2 indicate DTC P0341 failed this ignition
cycle? —Go to Step 3
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
31. Monitor voltage on the CMP signal circuit while
cranking the engine.
Does the voltage toggle between the specified values? 0–4 V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4Check for a poor connection of the CMP signal wire at
the ECM terminal.
Was a poor connection found? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair the damaged pin or terminal at the ECM. — Verify repair —
6Replace the ECM
Is the repair complete? — — Verify repair
71. Disconnect the CMP connector from the CMP
Sensor.
2. Ignition ON.
3. At the CMP connector, use a Digital Voltmeter
(DVM) to check the voltage between the voltage
signal wire and sensor ground.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value? B+ Go to Step
12 Go to Step 8
81. Ignition ON.
2. Use a DVM to measure between the ground and the
CMP positive connector.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value? B+ Go to Step
10 Go to Step 9
9Repair the open circuit.
Is the repair complete? — Verify repair —
10 1. Ignition ON.
2. Use a DVM to measure at the CMP connector
between the battery + and the CMP ground wire.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value? B+ Go to Step
12 Go to Step
11
11 Repair the open ground wire.
Is the repair complete? — Verify repair —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 Use an ohmmeter to check continuity of the signal wire
between the CMP and the ECM.
Was there an open circuit? —Go to Step
13 Go to Step
14
13 Repair the open signal wire.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
14 1. Ignition ON.
2. Check the signal wire for a short to ground or a short
to voltage.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
16
15 Repair the signal circuit problem.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
16 Replace the CMP Sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
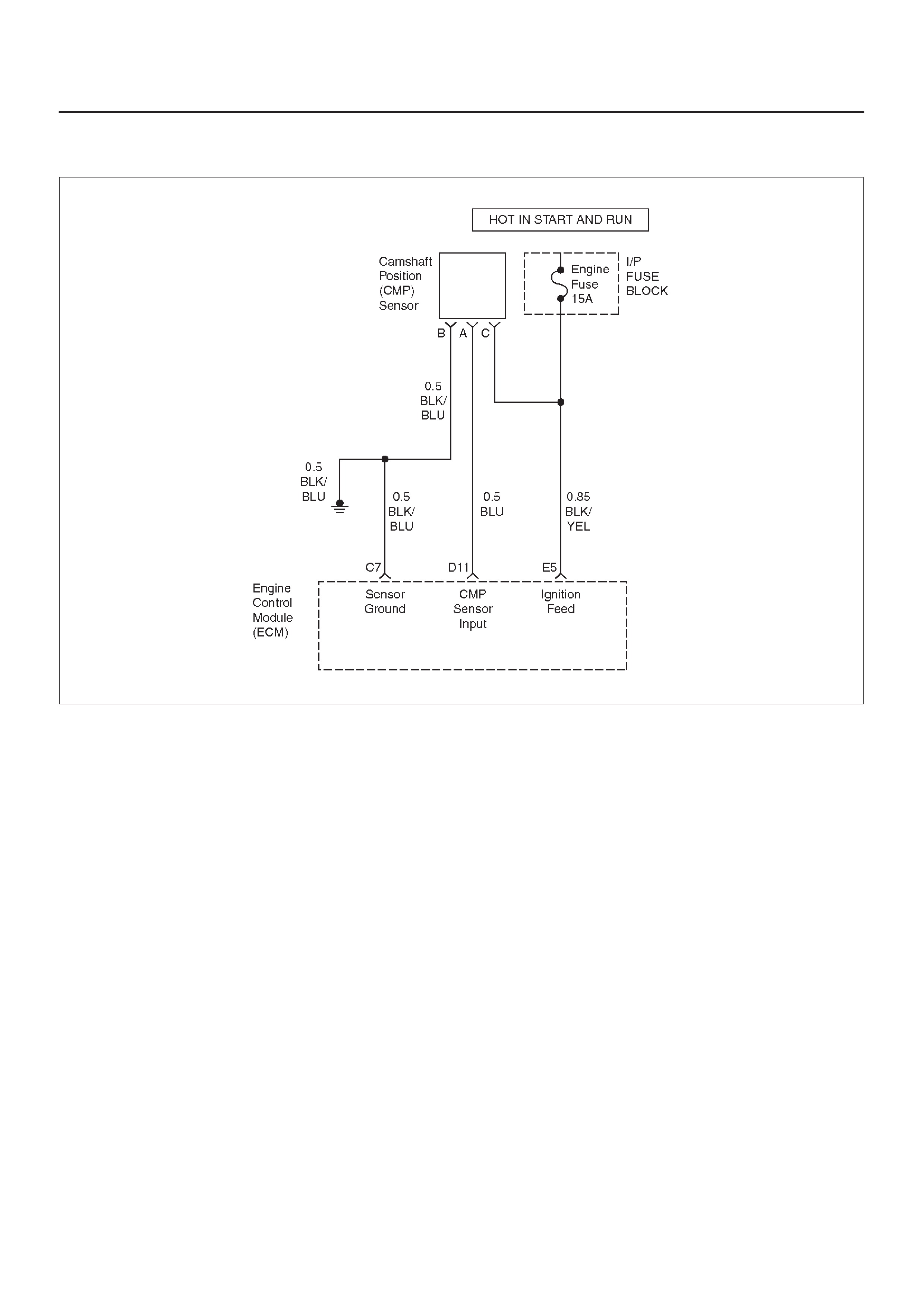
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0342 CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
D06RX123
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal is produced
by the CMP sensor pulses when the engine is running and
crankshaft position (CKP) sync pulses are also being
received. The ECM uses the CMP signal pulses to initiate
sequential fuel injection. The ECM constantly monitors
the number of pulses on the CMP signal circuit and
compares the number of CMP pulses to the number of
58X reference pulses received. If the ECM does not
receive pulses on the CMP reference circuit, Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) P0342 will set and the ECM will
initiate injector sequence without the CMP signal with a
one in four chance that injector sequence is correct. The
engine will continue to start and run normally, although
the misfire diagnostic will be affected if a misfiring
condition occurs. Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0342
is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe engine is running.
DThe CMP sensor signal is not received by the ECM
once every 4 cylinders.
DThe above condition occurs for 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will initiate injector sequence without the
CMP signal with a one in four chance that injector
sequence is correct.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) was set as
Freeze Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0342 will
clear after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have
occurred without a fault.
DDiagnostic T rouble Code (DTC) P0342 can be cleared
by using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DIf a CKP Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is also
indicated, there may be a problem with the ground
circuit because the CMP ground is spliced to the CKP
ground wire.
DIf a fuel injector Diagnostic T rouble Code (DTC) is also
indicated, there may be a problem with the power
supply to the CMP. The wire supplying CMP power is
spliced to the wire supplying power to the fuel injectors.
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for the following:
DPoor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
disconnect the ECM, turn the ignition ON and observe
a voltmeter connected to the CMP signal circuit at the
ECM harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the CMP sensor. A change
in voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2.Ensures that the fault is present.
DTC P0342 – Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” information for DTC
P0342 until the DTC P0342 test runs.
Did the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0342 failed this ignition
cycle? —Go to Step 3
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
31. Use a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) to monitor voltage on
the CMP signal circuit while cranking the engine.
Does the voltage toggle between the specified values? 0–4 V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4Check for a poor connection of the CMP signal wire at
the ECM terminal.
Was a poor connection found? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair the damaged pin or terminal at the ECM. — Verify repair —
6Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete? — Verify repair —
71. Disconnect the CMP connector from the CMP
Sensor.
2. Ignition ON.
3. At the CMP connector, check the voltage between
the voltage signal wire and sensor ground.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value? B+ Go to Step
12 Go to Step 8
81. Ignition ON.
2. Use a DVM to measure between the ground and the
CMP positive connector.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value? B+ Go to Step
10 Go to Step 9
9Repair the open circuit.
Is the repair complete? — Verify repair —
10 1. Ignition ON.
2. Use a DVM to measure at the CMP connector
between the battery + and the CMP ground wire.
Does the DVM indicate the specified value? B+ Go to Step
12 Go to Step
11
11 Repair the open ground wire.
Is the repair complete? — Verify repair —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 Use an ohmmeter to check continuity of the signal wire
between the CMP and the ECM.
Was there an open circuit? —Go to Step
13 Go to Step
14
13 Repair the open signal wire.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
14 1. Ignition ON.
2. Check the signal wire for a short to ground or a short
to voltage.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
16
15 Repair the signal circuit problem.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
16 Replace the CMP Sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
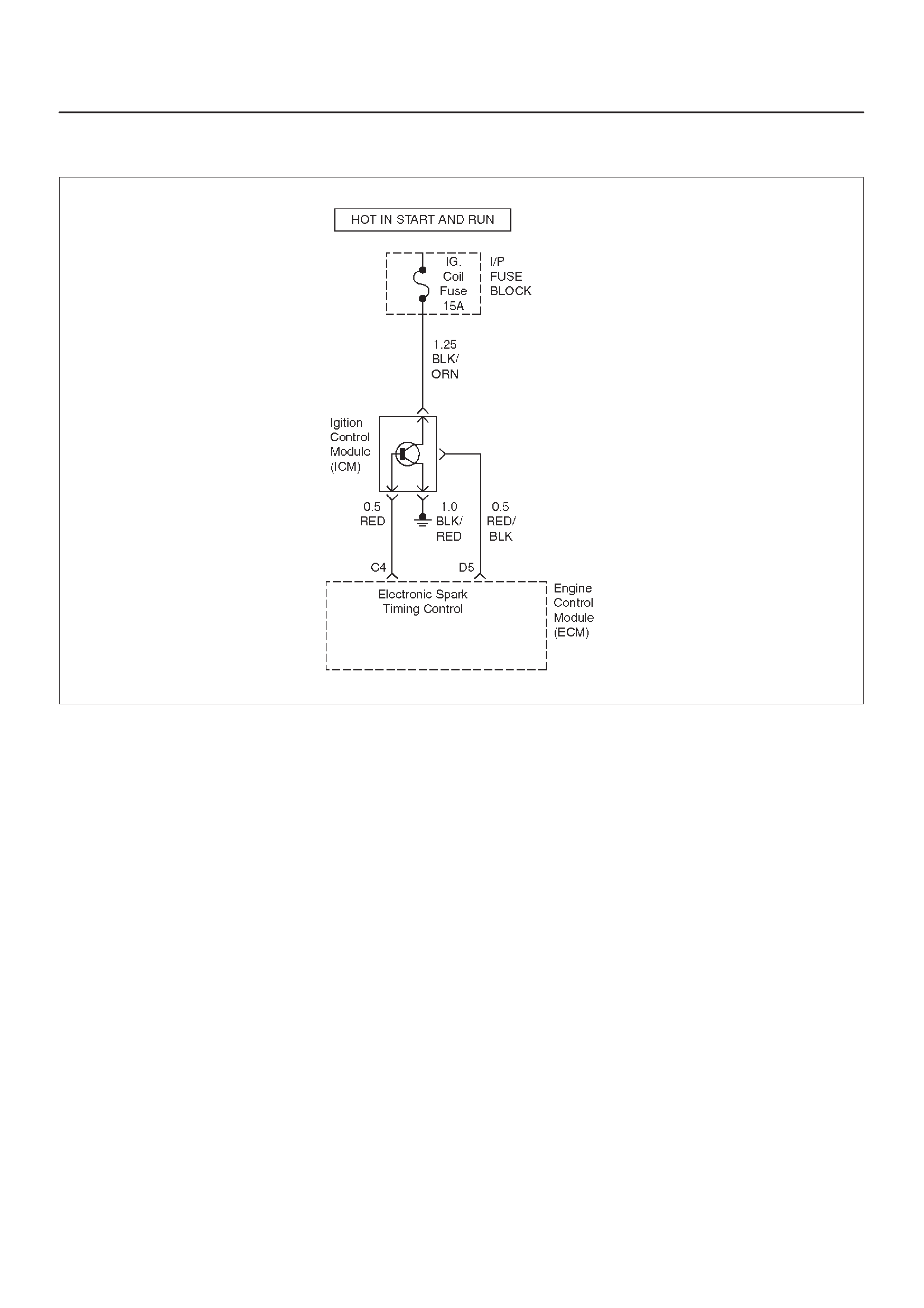
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0351 IGNITION COIL ”A”
PRIMARY/SECONDARY CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
D06RX124
Circuit Description
The ignition control circuit provides a zero volt or a 5 volt
signal to the ignition control module. The normal circuit
voltage is zero volts. When the module receives the 5 volt
signal from the engine control module (ECM), it provides
a ground path for the B+ voltage supplied to the ignition
primary coil. When the ECM turns off the 5 volts to the
module, the module will remove the ground path of the
ignition primary coils; causing the magnetic field
produces a voltage in the secondary coils which fires the
spark plug.
The circuit between the ECM and the ignition control
module is monitored for an open circuit, short to voltage,
and short to ground. When the ECM detects a problem in
the ignition control circuit, it will set DTC P0351. DTC
P0351 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition ON.
DOutput voltage is not equal to 5 volts when output is
ON.
DOutput voltage is not equal to 0 volt when output is
OFF.
DTwenty test failures within 40 samples of continuous
circuit monitoring.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history DTC P0351 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm–up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DDTC P0351 can be cleared by using the Scan Tool’s
”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at the ECM – Inspect the harness
connectors for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connections.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; Open circuits, shorts to ground, or shorts to
V oltage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
Tech 2 display related to DTC P0351 while moving the
connector and wiring related to the ignition system. A
change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0351 Ignition Coil ”A” Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminals at
the ignition control module.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 3
3Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminals at
the ECM connector.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and the ignition control
module.
3. Check the ignition control circuit for a short to
voltage.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 5
5Check the ignition control circuit for a short to voltage.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 6
6Check for an open in the ignition control circuit.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 7
7Replace the ignition control module.
Verify repair.
Is there still a problem? —Go to Step 8 —
8Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete? —Verify Repair —
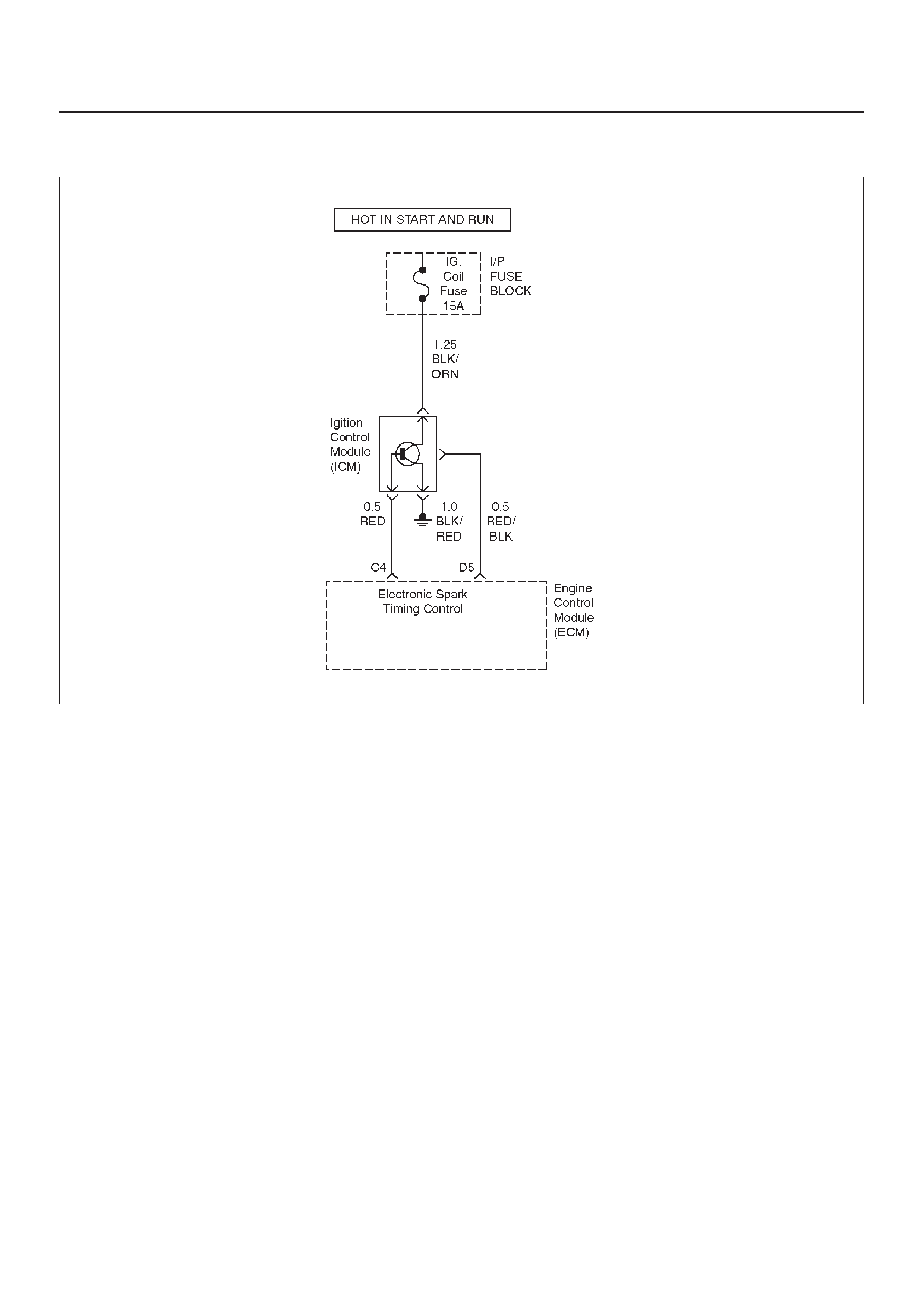
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0352 IGNITION COIL ”B”
PRIMARY/SECONDARY CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
D06RX124
Circuit Description
The ignition control circuit provides a zero volt or a 5 volt
signal to the ignition control module. The normal circuit
voltage is zero volts. When the module receives the 5 volt
signal from the engine control module (ECM), it provides
a ground path for the B+ voltage supplied to the ignition
primary coil. When the ECM turns off the 5 volts to the
module, the module will remove the ground path of the
ignition primary coils; causing the magnetic field
produces a voltage in the secondary coils which fires the
spark plug.
The circuit between the ECM and the ignition control
module is monitored for an open circuit, short to voltage,
and short to ground. When the ECM detects a problem in
the ignition control circuit, it will set DTC P0352. DTC
P0352 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition ON.
DOutput voltage is not equal to 5 volts when output is
ON.
DOutput voltage is not equal to 0 volt when output is
OFF.
DTwenty test failures within 40 samples of continuous
circuit monitoring.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history DTC P0352 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm–up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DDTC P0352 can be cleared by using the Scan Tool’s
”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at the ECM – Inspect the harness
connectors for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connections.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; Open circuits, shorts to ground, or shorts to
V oltage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
Tech 2 display related to DTC P0351 while moving the
connector and wiring related to the ignition system. A
change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
DTC P0352 Ignition Coil ”B” Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminals at
the ignition control module.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 3
3Check for a faulty connection or damaged terminals at
the ECM connector.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECM and the ignition control
module.
3. Check the ignition control circuit for a short to
voltage.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 5
5Check the ignition control circuit for a short to voltage.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 6
6Check for an open in the ignition control circuit.
Was a problem found? —Verify Repair Go to Step 7
7Replace the ignition control module.
Verify repair.
Is there still a problem? —Go to Step 8 —
8Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete? —Verify Repair —
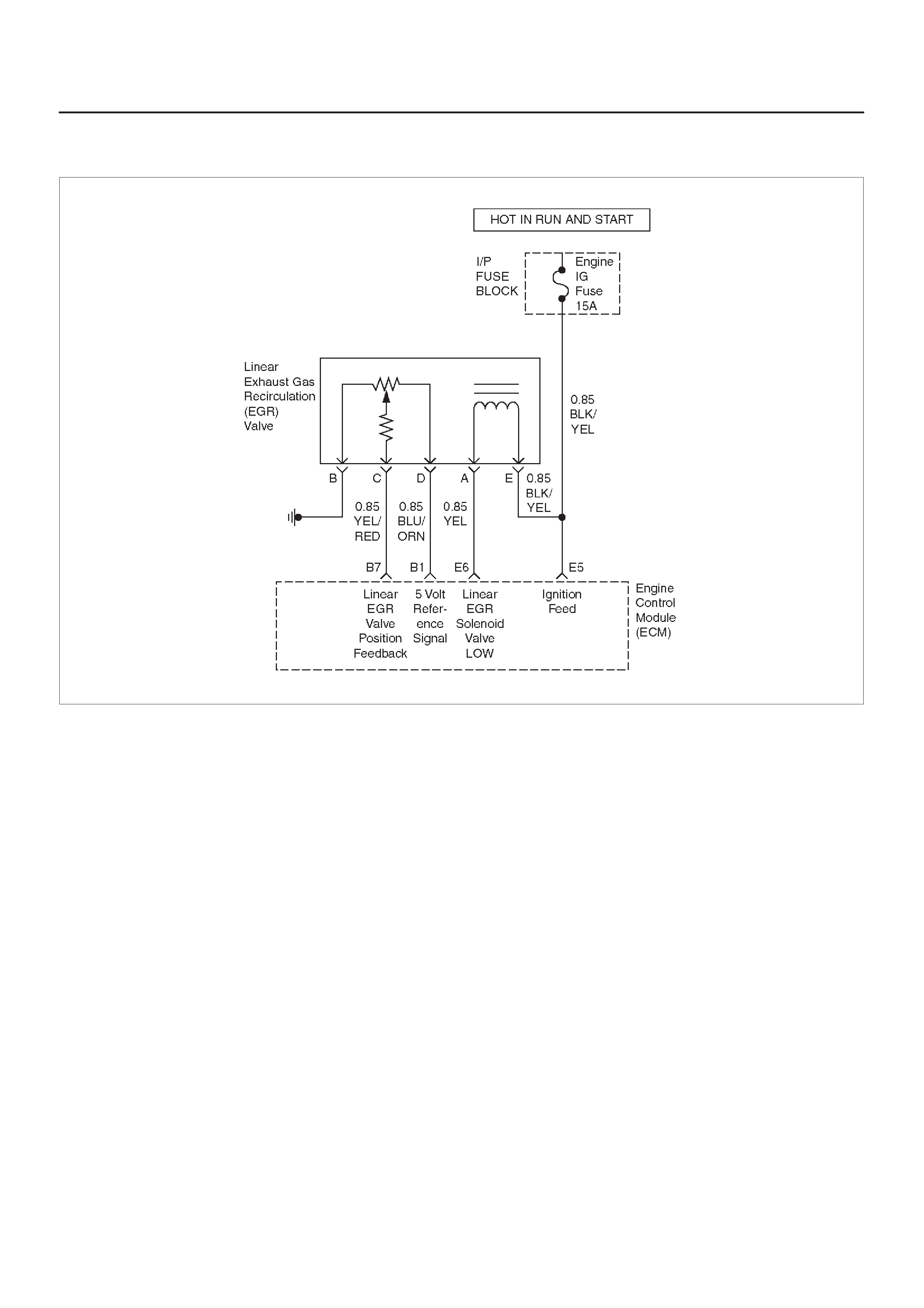
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0401 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) FLOW INSUFFICIENT DETECTED
D06RX113
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) tests the exhaust gas
recirculation (EGR) system during deceleration by
momentarily commanding the EGR valve to open while
monitoring the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
signal. When the EGR valve is opened, the ECM monitors
the change in MAP input signal. The ECM compares the
MAP change to a RPM vs. BARO table. When the ECM
interprets the change in MAP to be out of limits, the ECM
will set DTC P0401. The number of test samples required
to accomplish this may vary according to the severity of
the detected flow error.
Normally, the ECM will only allow one EGR flow test
sample to be taken during an ignition cycle. To aid in
verifying a repair, the ECM allows twelve test samples
during the first ignition cycle following a T ech 2 ”Clear Info”
or a battery disconnect. Between nine and twelve
samples should be sufficient for the ECM to determine
adequate EGR flow and pass the EGR test. DTC P0401
is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo TP sensor, VSS, EVAP Purge, IAC, IAT sensor,
MAP sensor , EGR Pintle Position sensor , ECT sensor ,
misfire DTCs set.
DBarometric pressure is above 72 kPa.
DEngine coolant temperature is greater than 60°C
(140°F).
DSystem voltage is between 11.5 and 16 volts.
DVehicle speed is greater than 23 km/h (14 mph).
DIAC position is steady, changing less than 5 counts.
DA/C clutch status is unchanged.
Start Test
DTP angle is less than 0.8%.
DEGR duty cycle is less than 1%.
DMAP is steady, changing less than 1 kPa.
DEngine speed is between 1200 RPM and 2000 RPM.
DCompensated MAP between 10.3 kPa and 49.8 kPa.
Run Test
DDelta MAP is recorded during valve open conditions.
DEGR valve is ramped over a time interval.
Run Test will be aborted if any of the following are true:
DVehicle speed changes by greater than 16 km/h
(10mph).
DEngine RPM changes by greater than 100 rpm.
DEGR is opened less than 95% of the commanded
amount.
During the Start Test and the Run Test, the EGR is closed
then opened. The associated change in MAP is
compared with the ECM’s expected change value. If the

difference between the two values exceeds the ECM’s
internal limit, a Diagnostic Trouble Code P0401 will set.
DTC P0401 is a type A code.
NOTE: Several deceleration cycles will be necessary to
run a sufficient number of EGR flow tests to determine a
”pass” or ”fail” condition.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
the first time the fault is detected.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code is stored.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code will clear after 40
consecutive warm up cycles without a fault.
DThe MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DThe MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code will clear after 40
consecutive warm up cycles without a fault.
DDiagnostic T rouble Codes can be cleared by using the
Tech 2.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to
be OK, observe the Actual EGR Position display on the
Tech 2 while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
related to the EGR valve. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
DEnsure EGR valve is correctly mounted. See
On–Vehicle Service.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
NOTE: If the EGR valve shows signs of excessive heat,
check the exhaust system for blockage (possibly a
plugged catalytic converter) using the ”Restricted
Exhaust System Check.”
DTC P0401 – Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Start the engine.
2. Monitor the MAP signal with a Tech 2 while idling.
3. While idling, depress the accelerator pedal about
halfway down and immediately let the engine return
to idle.
Did the MAP value on the Tech 2 show an immediate
large change? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3Replace the MAP sensor. — Verify repair —
41. Inspect the exhaust system for modification of
original installed parts or leaks.
2. If a problem was found, repair exhaust system as
necessary.
Was a condition present that required repair? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
51. Remove the EGR valve.
2. Visually and physically inspect the pintle, valve
passages and the adapter for excessive deposits or
any kind of a restriction.
3. If a problem if found, clean or replace EGR system
components as necessary.
Was a condition present that required repair? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
61. Remove the EGR inlet and outlet pipes from the
exhaust manifold and the intake manifold.
2. Inspect the manifold EGR ports and the EGR inlet
and outlet pipes for a blockage caused by excessive
deposits or other damage.
3. If a problem is found, correct the condition as
necessary.
Was a condition present that required repair? —Go to Step 7
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
71. Review and record the T ech 2 Failure Records data.
2. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Code and monitor the
Tech 2 System Info Screen while operating the
vehicle as specified in ”Diagnostic Aids.”
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0401 until the
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0401 test runs.
4. Note the test result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0401 failed this ignition? — — Repair
complete
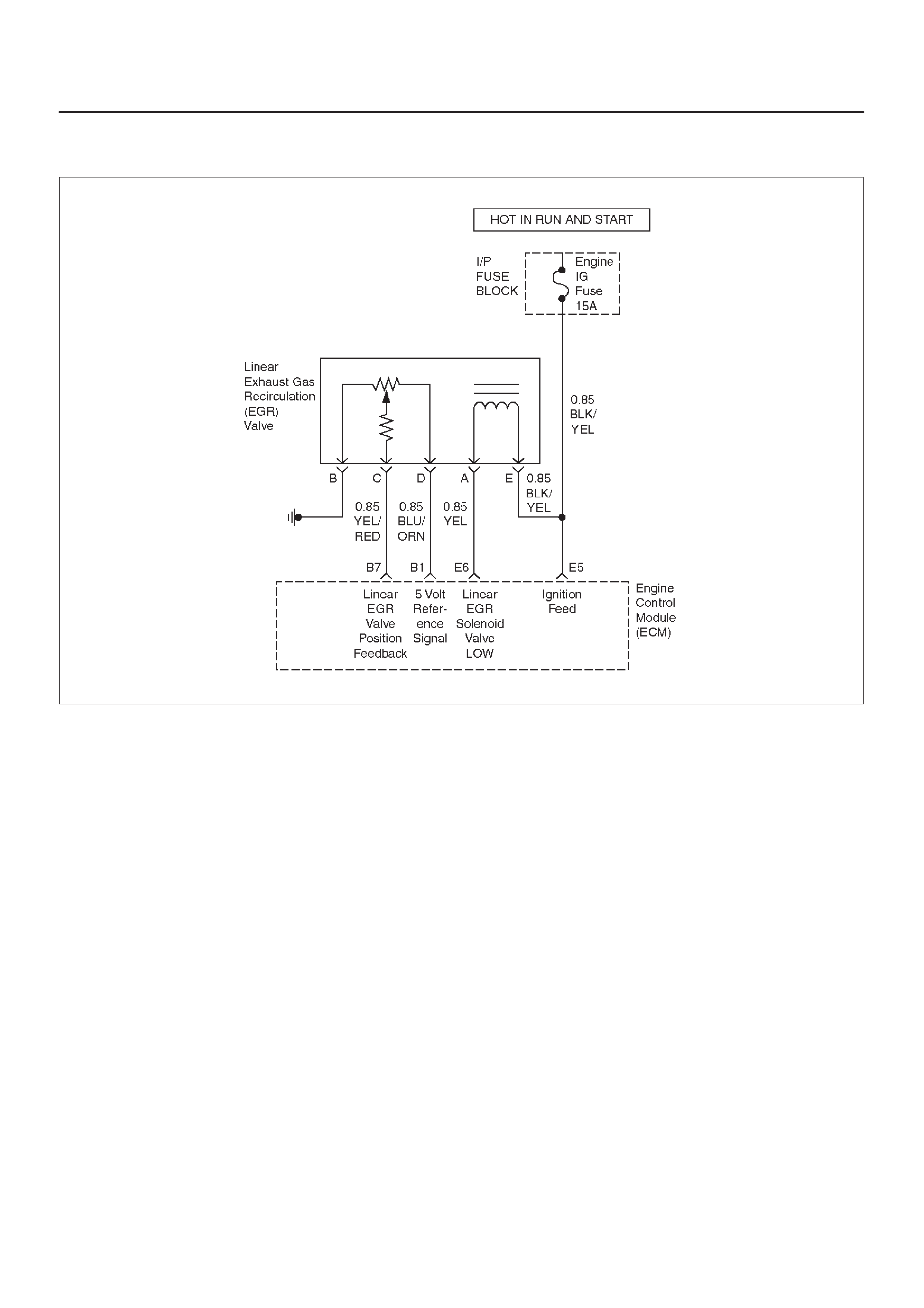
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0402 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) EXCESSIVE FLOW DETECTED
D06RX113
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) closes the Exhaust
Gas Recirculation (EGR) system on engine start–up to
test for excessive (any) flow. If the ECM determines that
EGR flow occurred on start–up, in two consecutive trips,
then DTC P0402 will set. DTC P0402 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIntake Air Temperature (IAT) is above 5°C (41°F).
DEngine RPM is less than 500 RPM.
DEGR Pintle Position if greater than 55 counts.
The above mentioned conditions must be met for 0.6
seconds during engine start–up on two consecutive trips.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to
be OK, observe the Actual EGR Position display on the
Tech 2 while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
related to the EGR valve. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
DEnsure EGR valve is correctly mounted. See
On–Vehicle Service.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
NOTE: If the EGR valve shows signs of excessive heat,
check the exhaust system for blockage (possible a
plugged catalytic converter) using the ”Restricted
Exhaust System Check.”
DTC P0402 EGR Excessive Flow Detected
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Review and record the T ech 2 Failure Records data.
2. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Code and monitor the
Tech 2 System Info Screen while operating the
vehicle as specified in ”Diagnostic Aids.”
3. Using a Tech 2, monitor “Diagnostic T rouble Code”
info for Diagnostic Trouble Code P0401 until the
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0401 test runs.
4. Note the test result.
Does the Tech 2 indicate Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0401 failed this ignition? —
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Inspect the exhaust system for modification of
original installed parts or leaks.
2. If a problem was found, repair exhaust system as
necessary.
Was a condition present that required repair? — Verify repair Go to Step 4
41. Remove the EGR valve.
2. Visually and physically inspect the pintle, valve
passages and the adapter for excessive deposits or
any kind of a restriction.
3. If a problem if found, clean or replace EGR system
components as necessary.
Was a condition present that required repair? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Remove the EGR inlet and outlet pipes from the
exhaust manifold and the intake manifold.
2. Inspect the manifold EGR ports and the EGR inlet
and outlet pipes for a blockage caused by excessive
deposits or other damage.
3. If a problem is found, correct the condition as
necessary.
Was a condition present that required repair? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
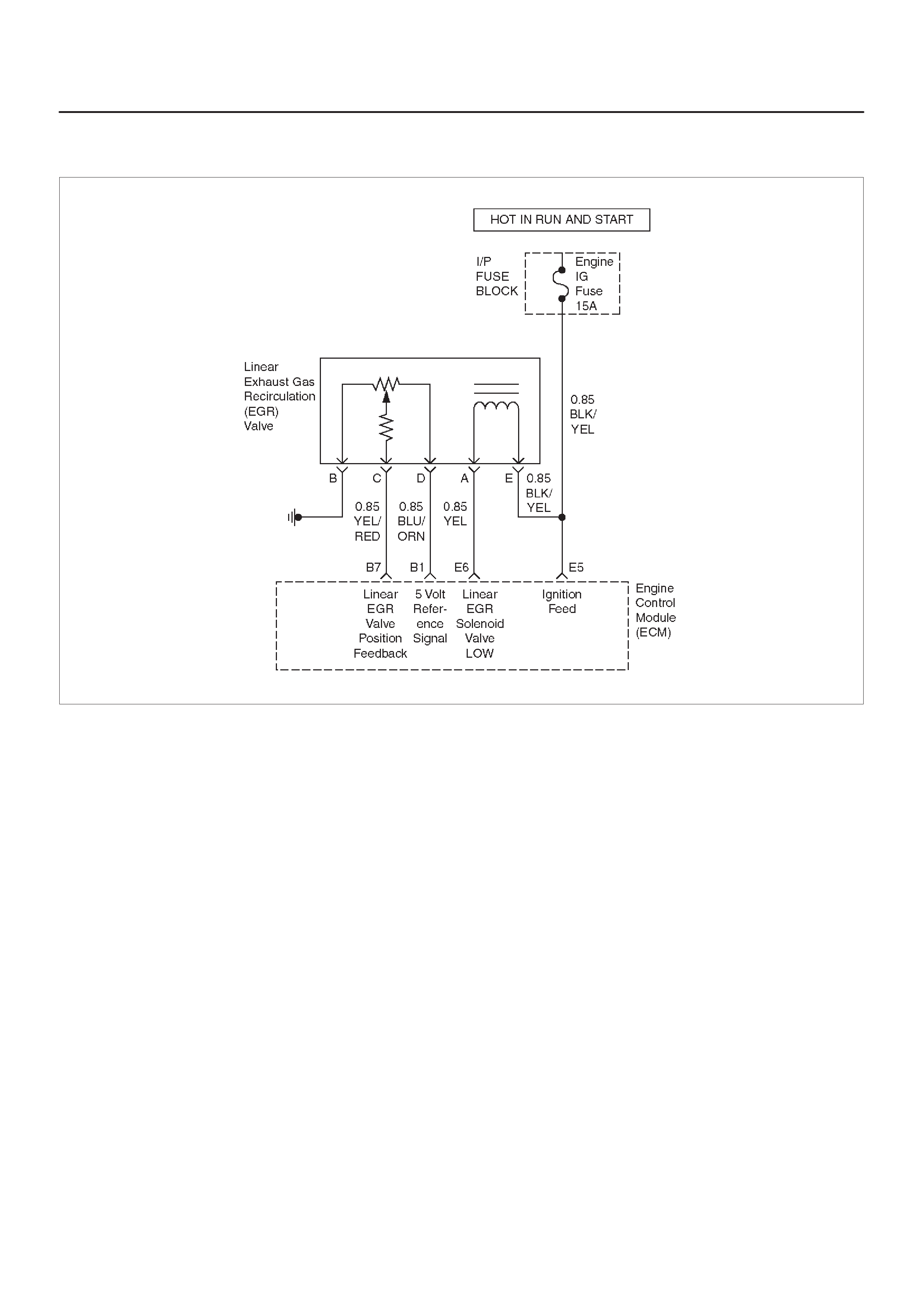
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0404 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE
D06RX113
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused
by high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this
by feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber. When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are
reduced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear
EGR valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust
gases to the engine without the use of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls exhaust flow going into the
intake manifold from the exhaust manifold through an
orifice with a ECM controlled pintle. The ECM controls
the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position
(TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors.
The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a Tech 2 as the
Desired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing
the EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This
feedback signal can also be monitored on a Tech 2 and is
the actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR
position should always be near the commanded or
Desired EGR Position.
If the ECM detects a large difference between the
desired EGR position and actual EGR position, then
Diagnostic T rouble Code P0404 will set. DTC P0404 is a
type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIAT is greater than 5°C (41°F).
DEGR commanded ON (Desired EGR Position is
greater than 0%).
DActual EGR Position differs from Desired EGR
Position by more than 15% for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DMalfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate the
second time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will record operating conditions at the time
the diagnostic fails.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code is stored.
DThe EGR Valve is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
DDiagnostic T rouble Code(s) can be cleared by using a
Tech 2.

Diagnostic Aids
Due to the moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in colder weather at
times. After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for
repairs, the valve warms and the problem disappears. By
watching the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on
a cold vehicle with a Tech 2, the fault can be verified
easily. Check the freeze frame data to determine if the
Diagnostic Trouble Code was set when the vehicle was
cold by viewing the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the
technician to complete some basic checks and store
the freeze frame and failure records data on the
Tech 2 if applicable. This created an electronic copy
of the data taken when the fault occurred. The
information is then stored on the Tech 2 for later
reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR valve
accurately and if the fault if present.
3. When the EGR valve electrical connector is
disconnected, the Tech 2 should display the Actual
EGR Position as 0%. If is does not, the fault lies
either in the EGR signal circuit or the ECM.
4. A test light, when connected to ground, will glow
dimly when the EGR valve is commanded to 25%,
and brighter as the EGR valve is commanded to
100%. If the test light flashes, check the sensor
ground for an open.
5. An open or poor connection condition may have
caused this Diagnostic Trouble Code to set. Be
sure to check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor
tension.
7. The test light will have glowed brightly in the
previous step if the EGR control circuit was shorted
to B+ and the Actual EGR Position on the Tech 2
will display 100%. A test light that did not illuminate,
indicates that the circuit may be open or shorted to
ground.
9. If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to
voltage, the DVM will read battery voltage and
additional Diagnostic Trouble Codes may be set and
engine performance will be poor.
13. Although the circuitry acted correctly when
checked, a problem may still lie within the terminals
which would not show up in probe type testing. Be
sure to check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor
tension.
17. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and
therefore must be replaced. Be sure all gasket
material is removed from the EGR mounting
surface. Even a small amount of material may
cause a Diagnostic Trouble Code P0401 to set. For
on vehicle service of the EGR Valve, refer to EGR
Valve.
18. Check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor
tension.
19. Clearing the Diagnostic Trouble Codes is a very
important step for this diagnostic. The clearing
function allows the EGR valve to relearn a new
pintle position as the old position was inaccurate
due to the malfunction that caused the Diagnostic
Trouble Code. The Diagnostic Trouble Code must
be cleared with the ignition switch ON, with the
engine OFF or when the engine is idling. If the
ECM sees a EGR command, the new pintle position
will not be learned.
DTC P0404 EGR Circuit Range/Performance
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to
Powertrain
OBD System
Check
21. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Install a Tech 2.
3. Command the EGR valve to the specified values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired EGR
Position? 25%, 50%,
75%, 100% Go to Step
19 Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve electrical connector.
3. With a test light connected to B+, probe the ground
circuit to the EGR valve.
Does the light illuminate? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
41. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Probe the EGR control circuit to the EGR valve.
3. Command the EGR valve to the specified values
using a Tech 2.
As the command is raised, does the test light glow
brighter, flash or maintain a steady glow? 25%, 50%,
75%, 100% Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
5Repair the open or poor connection in the EGR ground
circuit.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
19 —
6With the test light still connected to ground, probe the
signal circuit.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
7With the test light still connected to ground, again probe
the control circuit without commanding the EGR valve
with the Tech 2.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step
11
8Check the signal circuit for a short to voltage and repair
as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
12
9With a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) connected to ground,
probe the 5 V reference circuit.
Is the voltage measured near the specified value? 5 V Go to Step
13 Go to Step
14
10 Check the control circuit for a short to voltage and
repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
12
11 Connect the test light to B+ and again probe the control
circuit.
Does the light illuminate? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
16
12 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
19 —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
13 Check the EGR ground circuit for a poor connection or
proper terminal tension at the ECM and repair as
necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
17
14 Check the 5 V reference circuit for a short to voltage
and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
12
15 Check the control circuit for a short to ground and repair
as necessary?
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
12
16 Check the control circuit for an open or poor connection
at the EGR valve electrical connector and repair as
necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
18
17 Replace the EGR valve.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
19 —
18 Check the ECM electrical connector for a poor
connection and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
19 Go to Step
12
19 1. Using the Tech 2, clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
2. Start engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate vehicle within the conditions for setting this
Diagnostic Trouble Code as specified in the
supporting text.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that this diagnostic ”Ran and
Passed?” —Verify repair Go to Step 2
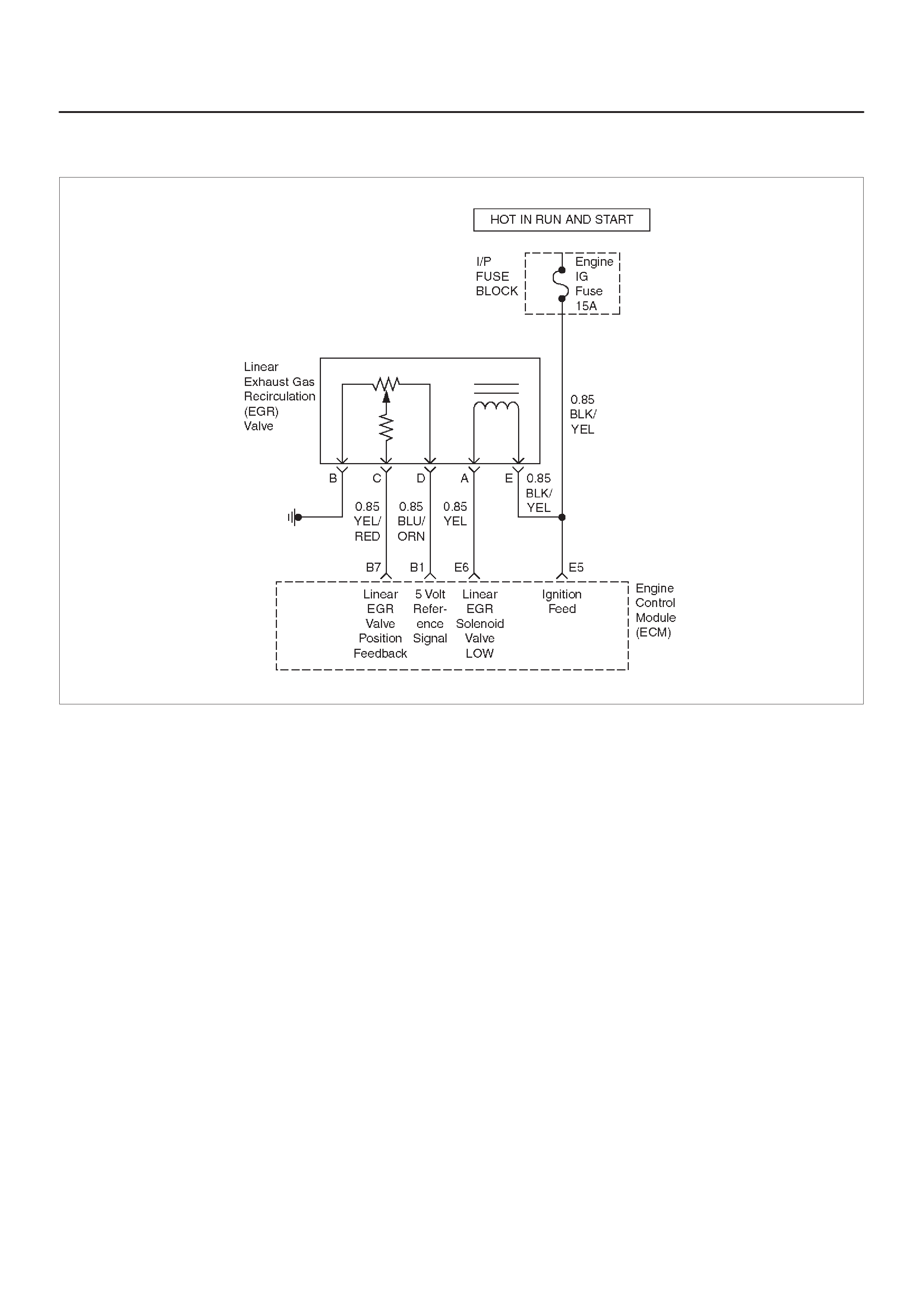
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0405 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) SENSOR CIRCUIT LOW
D06RX113
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused
by high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this
by feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber . When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are
reduced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear
EGR valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust
gases to the engine without the use of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls exhaust flow going into the
intake manifold form the exhaust manifold through an
orifice with a ECM controlled pintle. The ECM controls
the pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position
(TP) and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors.
The ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate
when necessary by controlling an ignition signal through
the ECM. This can be monitored on a Tech 2 as the
Desired EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing
the EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This
feedback signal can also be monitored on a Tech 2 and is
the actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR
Position should always be near the commanded or
Desired EGR Position.
If the ECM detects a continuous short to ground in the
signal circuit or the sensor , then Diagnostic Trouble Code
P0405 will set. DTC P0405 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIAT is greater than 5°C (41°F).
DThe ECM sees less than 0.10 voltage from the EGR
valve sensor.
DA malfunction is present for 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
the first time the malfunction is detected.
DThe ECM will record operating conditions at the time
the diagnostic fails.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code is stored.
DThe EGR Valve is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code will clear after 40
consecutive warm up cycles without a fault.
DDiagnostic T rouble Codes can be cleared by using the
Tech 2.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to the moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in colder weather at
times. After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for
repairs, the valve warms and the problem disappears. By
watching the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on
a cold vehicle with a Tech 2, the fault can be verified
easily. Check the freeze frame data to determine if the
Diagnostic Trouble Code set when the vehicle was cold
by viewing the Engine Coolant Temperature (EGR).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
1. The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the
technician to complete some basic checks and store
the freeze frame and failure records data on the
Tech 2 if applicable. This creates an electronic copy
of the data taken when the fault occurred. The
information is then stored on the Tech 2 for later
reference.
2. Commanding the EGR valve open determines
whether the EGR system can control the EGR valve
accurately and if the fault is present.
3. If the EGR valve 5 volt reference is shorted to
ground, the DVM will read no voltage and an
additional Diagnostic Trouble Code will be set and
engine performance will be poor. When this circuit
is open, only a Diagnostic Trouble Code P0405 will
be set.
4. Jumping the 5 volt reference circuit to the signal
circuit checks the signal circuit and ECM. The Tech
2 should display the Actual EGR Position as 100% if
the signal circuit and ECM are OK.
6. Although the ECM and circuitry acted correctly in the
previous step, a problem may still lie within the
terminals which would not show up in probe type
testing. Check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor
tension.
10. All circuits to the EGR valve are OK at this point.
The fault lies internally in the EGR valve and
therefore must be replaced. Be sure all gasket
material is removed from the EGR mounting
surface. Even a small amount of material may
cause a Diagnostic Trouble Code P0405 to set.
Refer the EGR Valve for on vehicle service of the
EGR valve.
14. Check the terminals for being backed out,
improperly formed or damaged, and for poor
tension.
DTC P0405 – EGR Sensor Circuit Low
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1Was the Powertrain On–Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to
Powertrain
OBD System
Check
21. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Install a Tech 2.
3. Command the EGR valve to the specified values.
Does the Actual EGR Position follow the Desired EGR
Position? 25%, 50%,
75%, 100% Go to Step
15 Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Disconnect the EGR valve electrical connector.
3. With a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) connected to
ground, probe the 5 V reference circuit to the EGR
valve.
Does the DVM read near the specified value? 5 V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4Jumper the EGR valve 5 volt reference circuit to the
signal circuit.
Does the Actual EGR Position display the specified
value? 100% Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
51. Connect the test light to B+.
2. Probe the 5 V reference circuit to the EGR valve.
Does the test light illuminate? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
6Check the 5 V reference and signal circuit’s for a poor
connection or proper terminal tension and repair as
necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
10
71. Connect the test light to B+.
2. Probe the signal circuit to the EGR valve.
Does the light illuminate? —Go to Step
11 Go to Step
12
8Check for a short to ground in the EGR valve 5 V
reference circuit and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
13
9Check for an open in the EGR valve 5 V reference
circuit and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
14
10 Replace the EGR valve.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
15 —
11 Check for a short to ground in the EGR valve signal
circuit and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
13
12 Check for an open in the EGR valve signal circuit and
repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
14
13 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? —Go to Step
15 —
14 Check the affected circuit for a poor connection or
proper terminal at the ECM and repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary? —Go to Step
15 Go to Step
13
15 1. Using the Tech 2, clear the Diagnostic Trouble
Codes.
2. Start engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate vehicle within the conditions for setting this
Diagnostic Trouble Code as specified in the
supporting text.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that this diagnostic ran and
passed? —Verify repair Go to Step 2
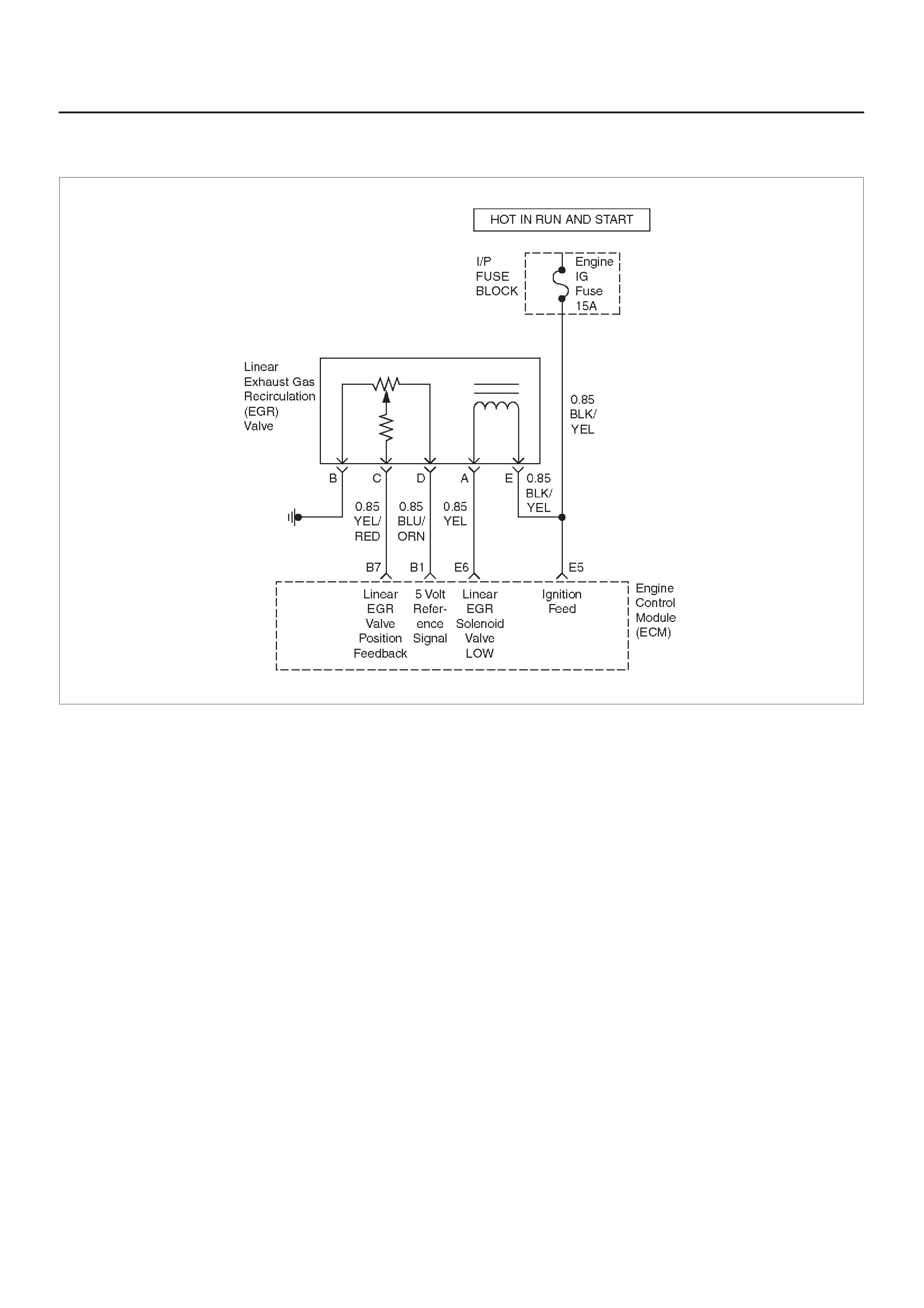
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0406 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) SENSOR CIRCUIT HIGH
D06RX113
Circuit Description
An Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system is used to
lower Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused
by high combustion temperatures. It accomplishes this by
feeding small amounts of exhaust gases back into the
combustion chamber . When the air/fuel mixture is diluted
with the exhaust gases, combustion temperatures are
reduced.
A linear EGR valve is used on this system. The linear
EGR valve is designed to accurately supply exhaust
gases to the engine without the use of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls exhaust flow going into the
intake manifold form the exhaust manifold through an
orifice with a ECM controlled pintle. The ECM controls the
pintle position using inputs from the Throttle Position (TP)
and Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensors. The
ECM then commands the EGR valve to operate when
necessary by controlling an ignition signal through the
ECM. This can be monitored on a Tech 2 as the Desired
EGR Position.
The ECM monitors the results of its command through a
feedback signal. By sending a 5 volt reference and a
ground to the EGR valve, a voltage signal representing
the EGR valve pintle position is sent to the ECM. This
feedback signal can also be monitored on a Tech 2 and is
the actual position of the EGR pintle. The Actual EGR
Position should always be near the commanded or
Desired EGR Position.
If the ECM detects a continuous short to ground in the
signal circuit or the sensor, then DTC P0406 will set.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0406 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIAT is greater than 5°C (41°F).
DThe ECM sees less than 0.10 voltage from the EGR
valve sensor.
DA malfunction is present for 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate.
DThe ECM will record operating conditions at the time
the diagnostic fails.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code is stored.
DThe EGR Valve is disabled.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code will clear after 40
consecutive warm–up cycles without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code(s) can be cleared by using
the Tech 2.
Diagnostic Aids
Due to the moisture associated with exhaust systems, the
EGR valve may freeze and stick in colder weather at

times. After the vehicle is brought into a warm shop for
repairs, the valve warms and the problem disappears. By
watching the Actual EGR and Desired EGR Positions on
a cold vehicle with a Tech 2, the fault can be verified
easily. Check the freeze frame data to determine if the
Diagnostic Trouble Code set when the vehicle was cold
by viewing the Engine Coolant Temperature (EGR).
DTC P0406 EGR Sensor Circuit High
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the Powertrain ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check” performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to
Powertrain
OBD System
Check
21. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTC’s.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P0406.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0406 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve from the wiring harness.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the ignition feed circuit at the Linear Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) Valve wiring harness
connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4Check the ignition feed circuit, between the EGR
sensor and the ”Engine IG.” fuse, for the following
conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
5Using a DVM, check the resistance of the EGR
solenoid.
Does the DVM read the following value? less then 5 WGo to Step 6 Go to Step 14
6Check the EGR solenoid valve Low circuit, between the
EGR sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Linear Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Valve from the wiring harness.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Observe the EGR value on the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display the following value(s)? 0 Volts 0% Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
8Check the EGR position feedback circuit, between the
EGR sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
91. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the 5 volt Reference signal circuit at the Linear
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve wiring
harness connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? about 5 volts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
10 Check the 5 volt Reference signal circuit, between the
EGR and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a DVM between the 5 volt Reference signal
circuit and the 5 volt signal return (ground) circuit at
the EGR wiring harness connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
Does the DVM read the following value? about 5 volts Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
12 Check the 5 volt signal return (ground) circuit, between
the EGR and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
13 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a fused jumper wire between the 5 volt
Reference signal circuit and the EGR valve position
feedback circuit at the EGR wiring harness
connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Observe the EGR value on the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display the following value(s)? 5 volts 100% Go to Step 14 Go to Step 15
14 Replace the Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Valve.
Verify Repair. ———
15 Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———
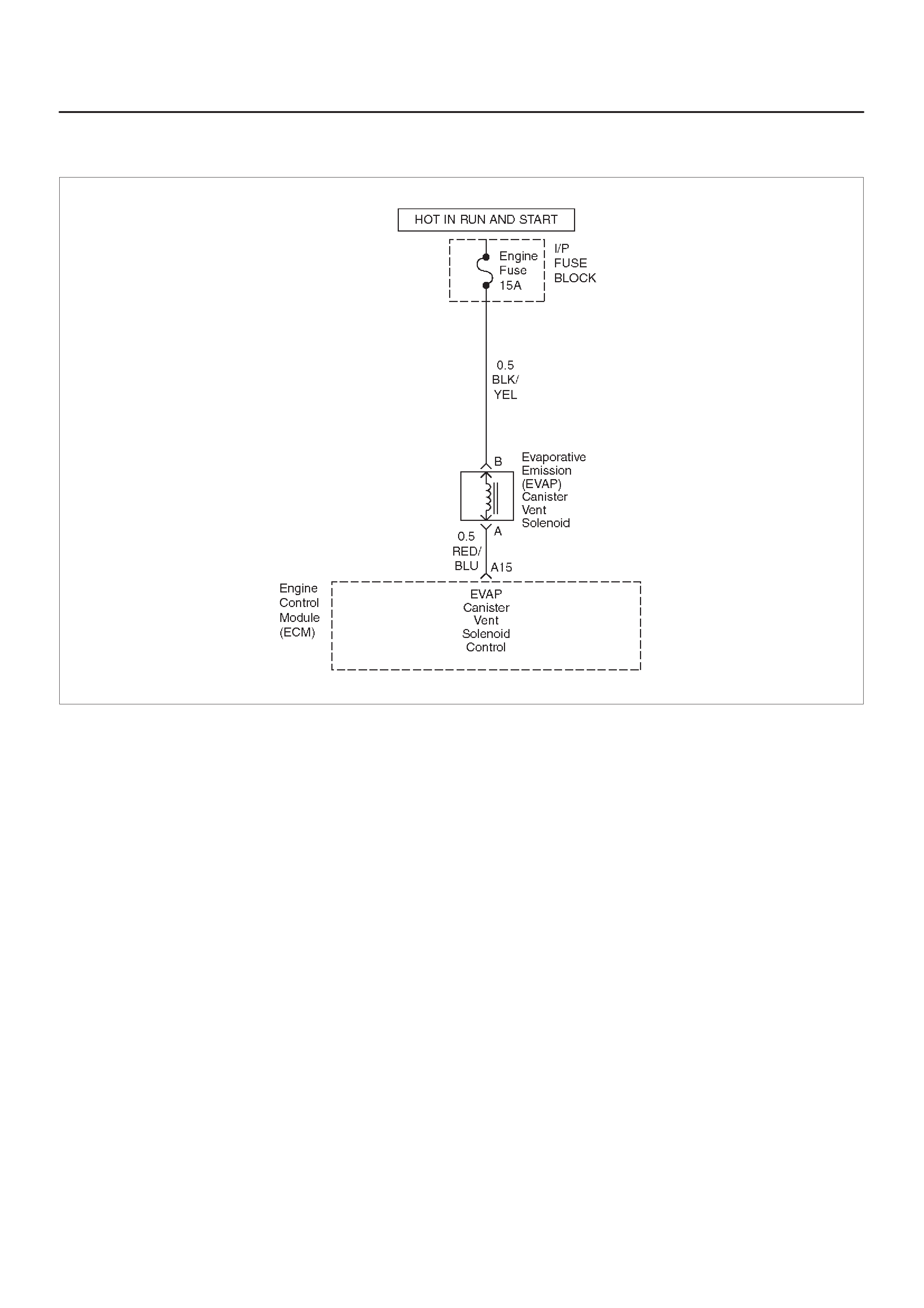
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0443 EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP)
CONTROL SYSTEM PURGE CONTROL VALVE CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
D06RX115
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Canister Purge Solenoid
Valve through the use of a control (ground) circuit. If the
ECM commands the Purge solenoid to maximum duty
cycle (100%) but the voltage remains High (12 Volts); or, if
the ECM commands the Purge solenoid to minimum duty
cycle (0%) but the voltage remains Low (0 volts), then
DTC P0443 will set. DTC P0443 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition voltage is greater than 10 volts
DEngine run time is greater than 32 seconds
The above mentioned conditions are met and one of the
following two conditions are met for 25 seconds within a
50 seconds test sample:
DECM senses voltage is High with the EVAP Canister
Purge Solenoid commanded ON.
DECM senses voltage is Low with the EVAP Canister
Purge Solenoid commanded OFF.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store the conditions that were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL after three consecutive
trips without a reported failure.
DA History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive trips
without a reported failure.
DThe DTC can be cleared using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear
Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DPoor connections , or a damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for: backed–out terminals,
improper mating or damaged terminals. Also check for
open circuits, shorts to ground, and shorts to voltage.
DTC P0443 EVAP Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTC’s.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P0443.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P0443 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid from
the wiring harness connector from the EVAP
Canister Purge Solenoid.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the ”Engine IG.” Fuse pin of the EVAP Canister
Purge Solenoid wiring harness connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4Check the suspect circuit between the EVAP Canister
Purge Solenoid connector and the ”Engine IG.” Fuse
for the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
5Using a DVM, check the resistance of the EVAP
Canister Purge Solenoid.
Does the DVM read the following value? less than 5 WGo to Step 6 Go to Step 7
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connectors from the ECM.
3. Check the EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid control
circuit between the ECM and EV AP Canister Purge
Solenoid for the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
7Replace the EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid.
Verify Repair. ———
8Replace the ECM. ———
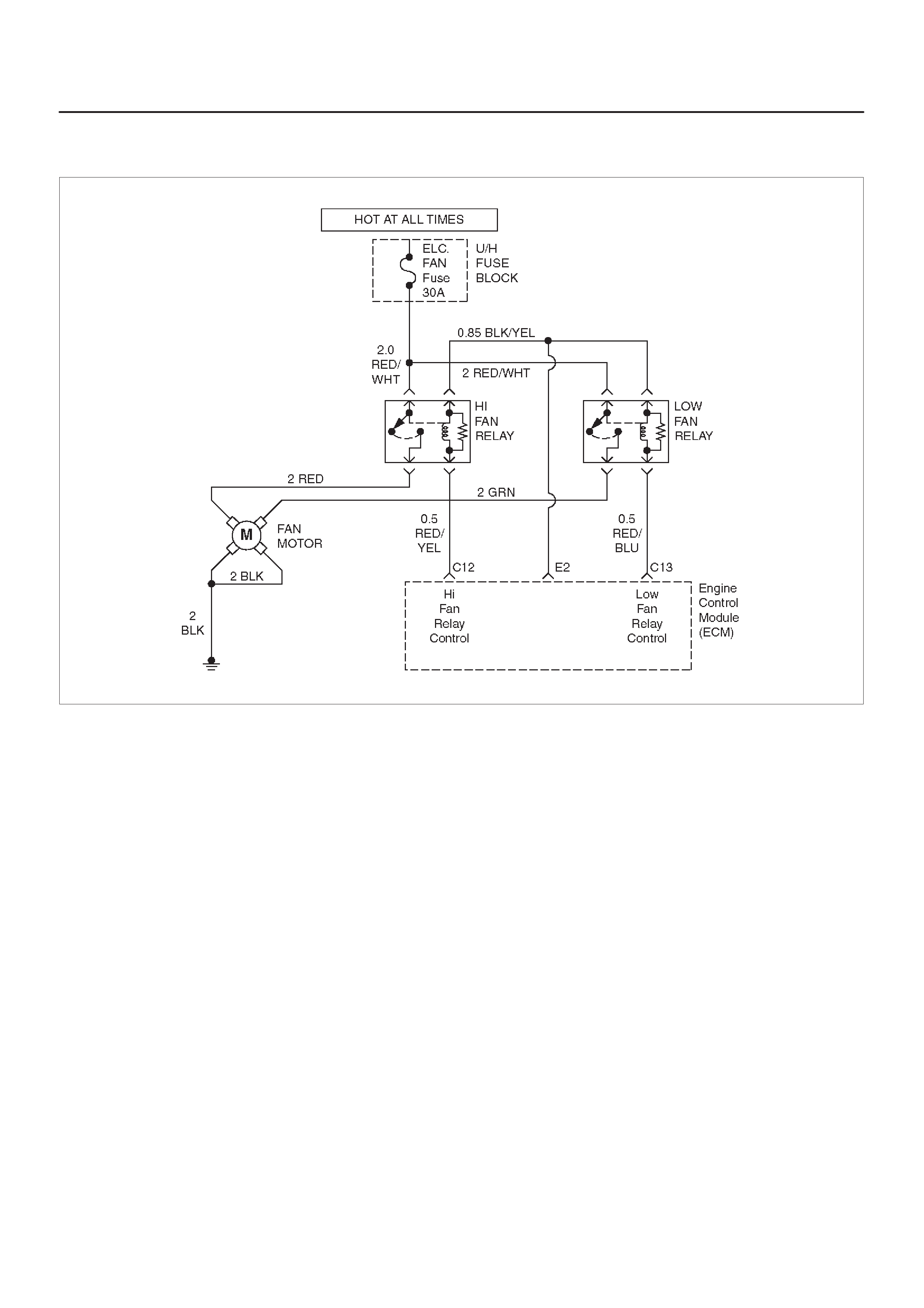
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0480 COOLING FAN 1 CONTROL
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
060RX090
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the
engagement of the cooling fan Low speed through the
use of a relay and a control circuit. If the ECM commands
the fan to Low speed and then senses that the fan did not
turn ON, or if the ECM commands the fan OFF from Low
speed and then senses that the fan did not turn OFF, the
ECM will set a DTC P0480. DTC P0480 is a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition voltage is greater than 10 volts.
DEngine run time is greater than 32 seconds.
The above conditions are met and one of the following
conditions are met for 25 seconds within a 50 second test
sample:
DECM sensed voltage is High with the Low Speed Fan
OFF.
OR
DECM sensed voltage is Low with the Low Speed Fan
ON.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not turn on the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp.
DThe ECM will store the conditions that were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive trips
without a reported failure.
DThe DTC can be cleared using the Scan Tool’s Clear
Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DPoor connections or a damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for: backed out terminals,
improper mating or damaged terminals. Also check for
open circuits, shorts to ground, and shorts to voltage.
DTC P0480 Cooling Fan 1 Control Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTCs.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P0480.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that DTC P0480 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the Low Fan Relay from the Underhood
Electrical Center.
3. Ignition OFF.
4. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the ”ELEC. FAN” Fuse pin of the Low fan Relay
connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
41. Ignition ON.
2. Using a DVM, check for voltage on the ”ENGINE
FAN” Fuse pin of the Low Fan Relay connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Check the suspect circuit between the Low Fan Relay
connector and Fuse for the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connectors from the ECM.
3. Check the Low Fan Relay control circuit between
the ECM and Underhood Electrical Center for the
following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Reinstall the Low Fan Relay.
2. Using a fused jumper, ground the Low Fan Relay
control circuit at the ECM connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
Does the fan run at low speed? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
8Replace the Low Fan Relay.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———

DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0481 COOLING FAN 2 CONTROL
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
060RX090
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) controls the
engagement of the cooling fan Low speed through the
use of a relay and a control circuit. If the ECM commands
the fan to Low speed and then senses that the fan did not
turn ON, or if the ECM commands the fan OFF from Low
speed and then senses that the fan did not turn OFF, the
ECM will set a DTC P0481. DTC P0481 is a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition voltage is greater than 10 volts.
DEngine run time is greater than 32 seconds.
The above conditions are met and one of the following
conditions are met for 25 seconds within a 50 second test
sample:
DECM sensed voltage is High with the High Speed Fan
OFF.
OR
DECM sensed voltage is High with the High Speed Fan
ON.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not turn on the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp.
DThe ECM will store the conditions that were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive trips
without a reported failure.
DThe DTC can be cleared using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear
Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DPoor connections or a damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for: backed out terminals,
improper mating or damaged terminals. Also check for
open circuits, shorts to ground, and shorts to voltage.

DTC P0481 Cooling Fan 2 Control Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTCs.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P0480.
Does the Tech 2 indicate that DTC P0480 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the Low Fan Relay from the Underhood
Electrical Center.
3. Ignition OFF.
4. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the ”ELEC. FAN” Fuse pin of the Low fan Relay
connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
41. Ignition ON.
2. Using a DVM, check for voltage on the ”ENGINE
FAN” Fuse pin of the Low Fan Relay connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 Volts Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Check the suspect circuit between the Low Fan Relay
connector and Fuse for the following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connectors from the ECM.
3. Check the Low Fan Relay control circuit between
the ECM and Underhood Electrical Center for the
following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Reinstall the High Fan Relay.
2. Using a fused jumper, ground the High Fan Relay
control circuit at the ECM connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
Does the fan run at High speed? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8

Step NoYesValue(s)Action
8Replace the High Fan Relay.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———
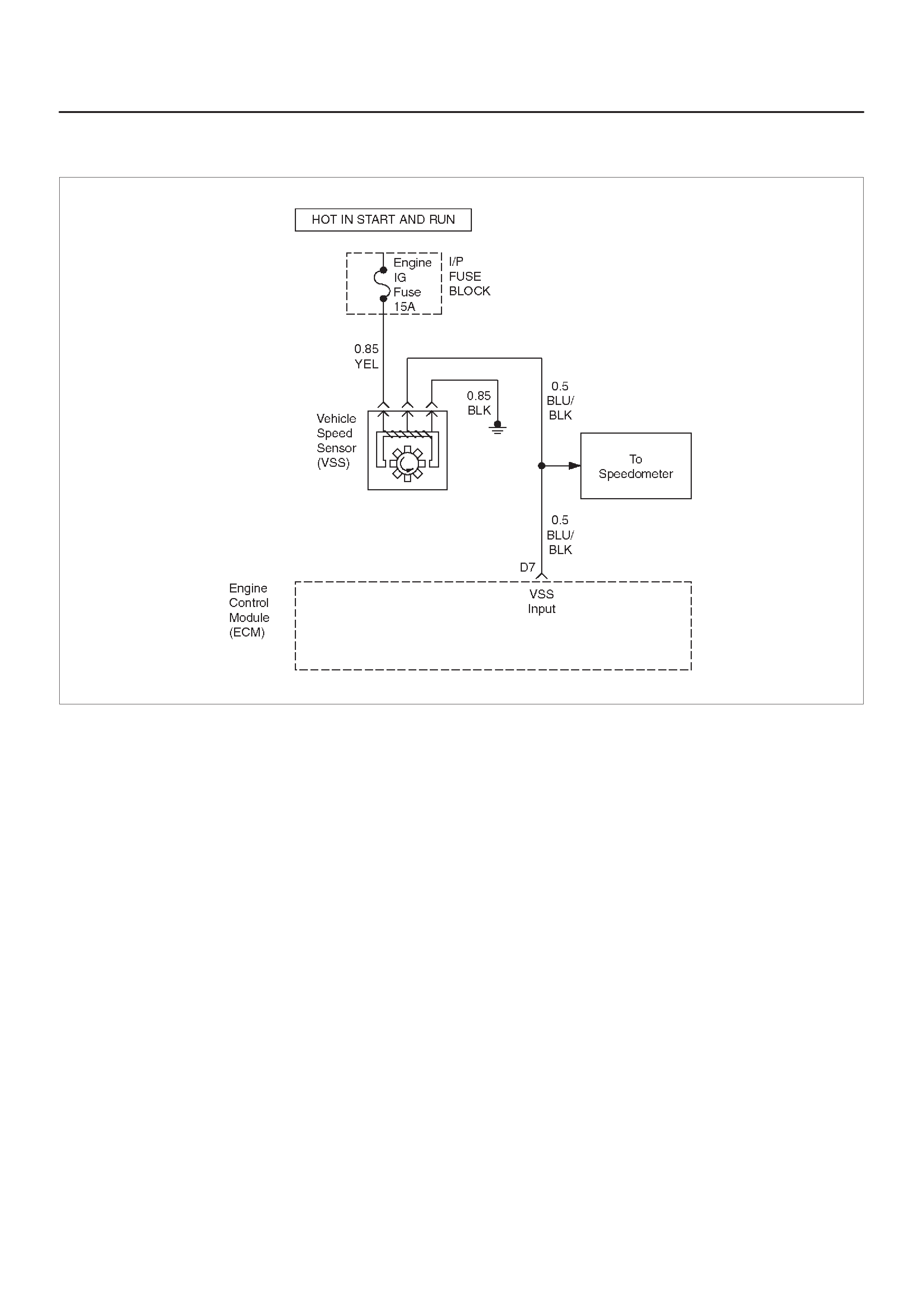
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0502 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS)
CIRCUIT LOW INPUT
D06RX125
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor has a magnet rotated by the
transmission output shaft. Attached to the sensor is a hall
effect circuit that interacts with the magnetic field created
by the rotating magnet. A 12–volt operating supply for the
speed sensor hall circuit is supplied from the meter fuse.
The VSS pulses to ground the 5–volt signal sent from the
engine control module (ECM) on the reference circuit.
The ECM interprets vehicle speed by the number of
pulses to ground per second on the reference circuit.
DTC P0502 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine is running.
DEngine coolant temperature is above 60°C (140°F).
DSystem voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
When the above conditions are met, one of the following
tests will run:
Decel Test
DMAP is less than 35 kPa.
DThrottle Position is less than 0.8%.
DEngine Speed is between 1500 RPM and 3500 RPM.
The Decel Test will fail if vehicle speed is less than 8 km/h
(5mph).
The Decel T est will pass if vehicle speed is greater than 24
km/h (15mph).
Power Test
DMAP is greater than 50 kPa.
DThrottle Position is between 25% and 70%.
DEngine Speed is between 2700 RPM and 4400 RPM.
The Power T est will fail if vehicle speed is less than 8 km/h
(5 mph).
The Power Test will pass if vehicle speed is greater than
8km/h (5mph) without any VSS DTC’s present, or if
vehicle speed is greater than 49 km/h (30mph) with VSS
Diagnostic Trouble Codes present.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the second time the fault is detected.
DBase shift logic on RPM only.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0502 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0502 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DPoor connection at ECM: Inspect harness connectors
for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal to wire connection.
DDamaged harness: Inspect the wiring harness to the
EVAP vent solenoid, the EVAP purge solenoid, and the
fuel tank pressure sensor for an intermittent open or
intermittent short circuit.
DTC P0502 – VSS Circuit Low Input
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the VSS connector.
3. Using a test light to battery +, probe the connector
ground wire.
Did the light illuminate? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3Repair the open in the sensor ground circuit. — Verify repair —
41. Ignition ON, sensor disconnected.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), measure at the
VSS connector between ground and voltage
supply.
Was the measurement near the specified value? Battery
voltage Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the open or short to ground in the VSS sensor
circuit. —Verify repair —
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Check the BLU/BLK wire between the VSS sensor
connector and the ECM for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the faulty condition located? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
7Using a DVM, measure the resistance between the
VSS sensor body and transmission case (ground).
Is the resistance above the specified value? 10 K WVerify repair Go to Step 9
81. Remove the VSS from the transmission case.
2. Visually inspect the VSS for damage.
Does the VSS appear to be OK? — Verify repair —
9Replace the VSS. — Verify repair —
10 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
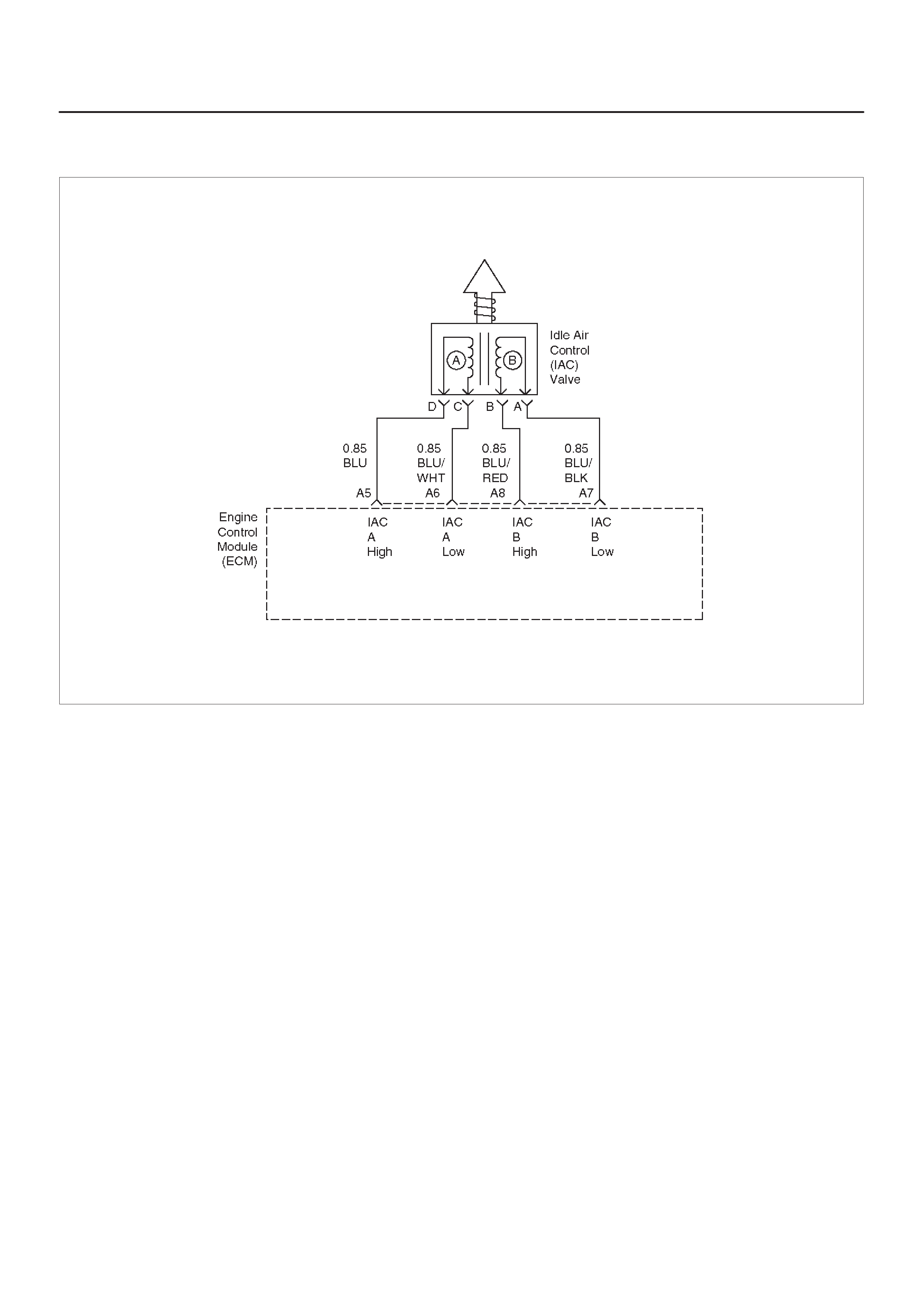
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0506 IDLE CONTROL SYSTEM RPM
LOWER THAN EXPECTED
D06RX112
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls engine idle
speed by adjusting the position of the idle air control (IAC)
motor pintle. The IAC is a bi–directional stepper motor
driven by two coils. The ECM applies current to the IAC
coils in steps (counts) to extend the IAC pintle into a
passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The
ECM reverses the current to retract the pintle, increasing
air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle
speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If
the ECM detects a condition where too low of an idle
speed is present and the ECM is unable to adjust idle
speed by increasing the IAC counts, DTC P0506 will set,
indicating a problem with the idle control system. DTC
P0506 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo intrusive tests being run.
DEngine run time is more than 125 seconds.
DNo TPS, VSS, ECT, EGR, MAP, IAT, low voltage, fuel
system or canister purge Diagnostic Trouble Codes
are set.
DBarometric pressure is greater than 72.7 kPa.
DCanister purge duty cycle is above 0%.
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) is above 50°C
(122°F).
DIntake air temperature above –40°C (–40°F).
DMAP is less than 60 kPa.
DIgnition voltage is between 9.5 volts and 16 volts.
DThe throttle is closed.
DAll conditions are met for 10 seconds.
DEngine speed is at least 100 RPM lower than desired
idle, based upon ECM expectations.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0506 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM or IAC motor – Inspect
harness connectors for backed–out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire
connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits.
DRestricted air intake system – Check for a possible
collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter element, or
foreign objects blocking the air intake system.
DThrottle body – Check for objects blocking the IAC
passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC
passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive deposits
in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate.
DLarge vacuum leak – Check for a condition that causes
a large vacuum leak, such as an incorrectly installed or
faulty PCV valve or brake booster hose disconnected.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0506 – Idle Control System RPM Lower Than Expected
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any other Diagnostic Trouble Codes set?
—
Go to other
Diagnostic
Trouble Code
first Go to Step 3
31. Start the engine.
2. T urn all accessories OFF (A/C, rear defroster, etc.)
3. Using a T ech 2, command RPM up to 1500, down to
500, and then up to 1500 while monitoring ”Engine
Speed” on the Tech 2.
Does the ”Engine Speed” remain within the specified
value of ”Desired Idle” for each RPM command? +/–50 RPM
No trouble
found. Go to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 4
41. Check the following circuits for an open, short to
voltage, short to ground, or poor connection at the
PCM:
DIAC ”A” low
DIAC ”A” high
DIAC ”B” low
DIAC ”B” high
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5Visually/physically inspect for the following conditions:
DThrottle body tampering (adjustment screw plug
removed).
DRestricted air intake system. Check for a possible
collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter
element, or foreign objects blocking the air intake
system.
DThrottle body. Check for objects blocking the IAC
passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in
the IAC passage and on the IAC pintle, and
excessive deposits in the throttle bore and on the
throttle plate.
Do any of the above require a repair? —
Refer to
appropriate
section for
on–vehicle
service Go to Step 6
61. Check for a poor connection at the IAC harness
connector.
2. If a problem is found, replace faulty terminals as
necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
7Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check the IAC valve
solenoids (A and B) for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground (the IAC body)
DA short together
Was the problem found? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Replace the IAC valve.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
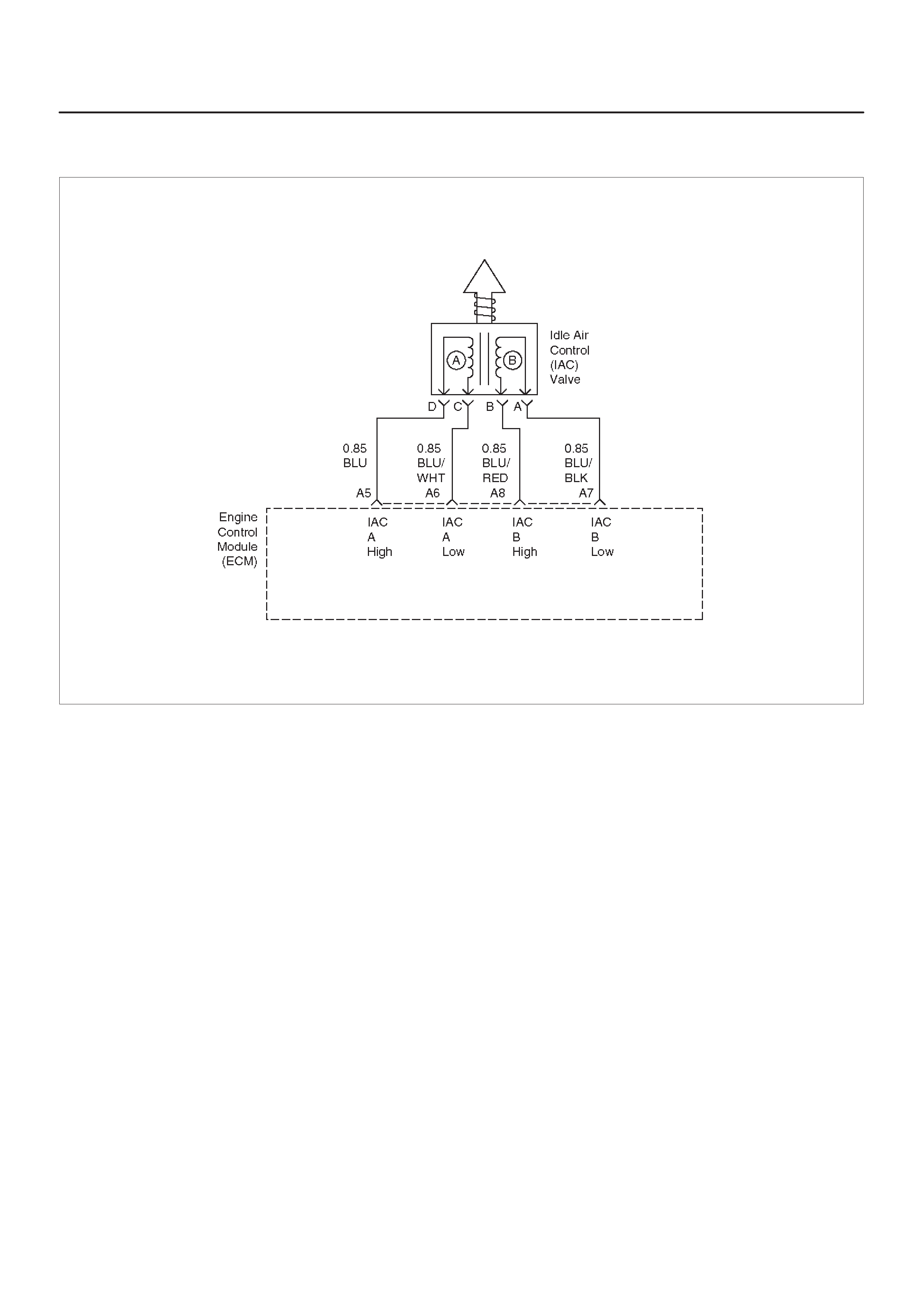
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0507 IDLE CONTROL SYSTEM RPM
HIGHER THAN EXPECTED
D06RX112
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls engine idle
speed by adjusting the position of the idle air control (IAC)
motor pintle. The IAC is a bi–directional stepper motor
driven by two coils. The ECM applies current to the IAC
coils in steps (counts) to extend the IAC pintle into a
passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The
ECM reverses the current to retract the pintle, increasing
air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle
speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If
the ECM detects a condition where too high of an idle
speed is present and the ECM is unable to adjust idle
speed by increasing the IAC counts, Diagnostic Trouble
Code P0507 will set, indicating a problem with the idle
control system. DTC P0507 is a type B code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo intrusive tests being run.
DEngine run time is more than 125 seconds.
DNo TPS, VSS, ECT, EGR, MAP, IAT, low voltage, fuel
system or canister purge DTCs are set.
DBarometric pressure is greater than 72.7 kPa.
DCanister purge duty cycle is above 0%.
DIntake air temperature above –40°C (–40°F).
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) is above 50°C
(122°F).
DIgnition voltage is between 9.5 volts and 16 volts.
DThe throttle is closed.
DAll conditions are met for 10 seconds.
DMAP is less than 60 kPa.
DEngine speed is at least 200 RPM lower than desired
idle, based upon PCM’s expectations.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe PCM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe PCM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0507 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0507 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at PCM or IAC motor – Inspect
harness connectors for backed–out terminals,
improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or
damaged terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire
connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits.
DVacuum leak – Check for a condition that causes a
vacuum leak, such as disconnected or damaged
hoses, leaks at EGR valve and EGR pipe to intake
manifold, leak at the throttle body, a faulty or incorrectly
installed PCV valve, leaks at the intake manifold, etc.
DThrottle body – Check for sticking throttle plate. Also
inspect the IAC passage for deposits or objects which
will not allow the IAC pintle to fully extend or properly
seat.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P0507 cannot be duplicated,
reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P0507 – Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any other Diagnostic Trouble Codes set?
—
Go to other
Diagnostic
Trouble Code
first Go to Step 3
31. Start the engine.
2. T urn all accessories OFF (A/C, rear defroster, etc.)
3. Using a T ech 2, command RPM up to 1500, down to
500, and then up to 1500 while monitoring ”Engine
Speed” on the Tech 2.
Does the ”Engine Speed” remain within the specified
value of ”Desired Idle” for each RPM command? +/–50 RPM
No trouble
found. Go to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 4
41. Check the following circuits for an open, short to
voltage, short to ground, or poor connection at the
PCM:
DIAC ”A” low
DIAC ”A” high
DIAC ”B” low
DIAC ”B” high
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5Visually/physically inspect for the following conditions:
DVacuum leaks
DThrottle body tampering (adjustment screw plug
removed).
DThrottle plate or throttle shaft for binding.
DAccelerator and cruise control cables for being
mis–adjusted or for binding.
DFaulty, missing, or incorrectly installed PCV
valve.
Do any of the above require a repair? —
Refer to
appropriate
section for
on–vehicle
service Go to Step 6
61. Check for a poor connection at the IAC harness
connector.
2. If a problem is found, replace faulty terminals as
necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
7Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check the IAC valve
solenoids (A and B) for the following conditions:
DAn open circuit
DA short to ground (the IAC body)
DA short together
Was the problem found? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Replace the IAC valve.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
9Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
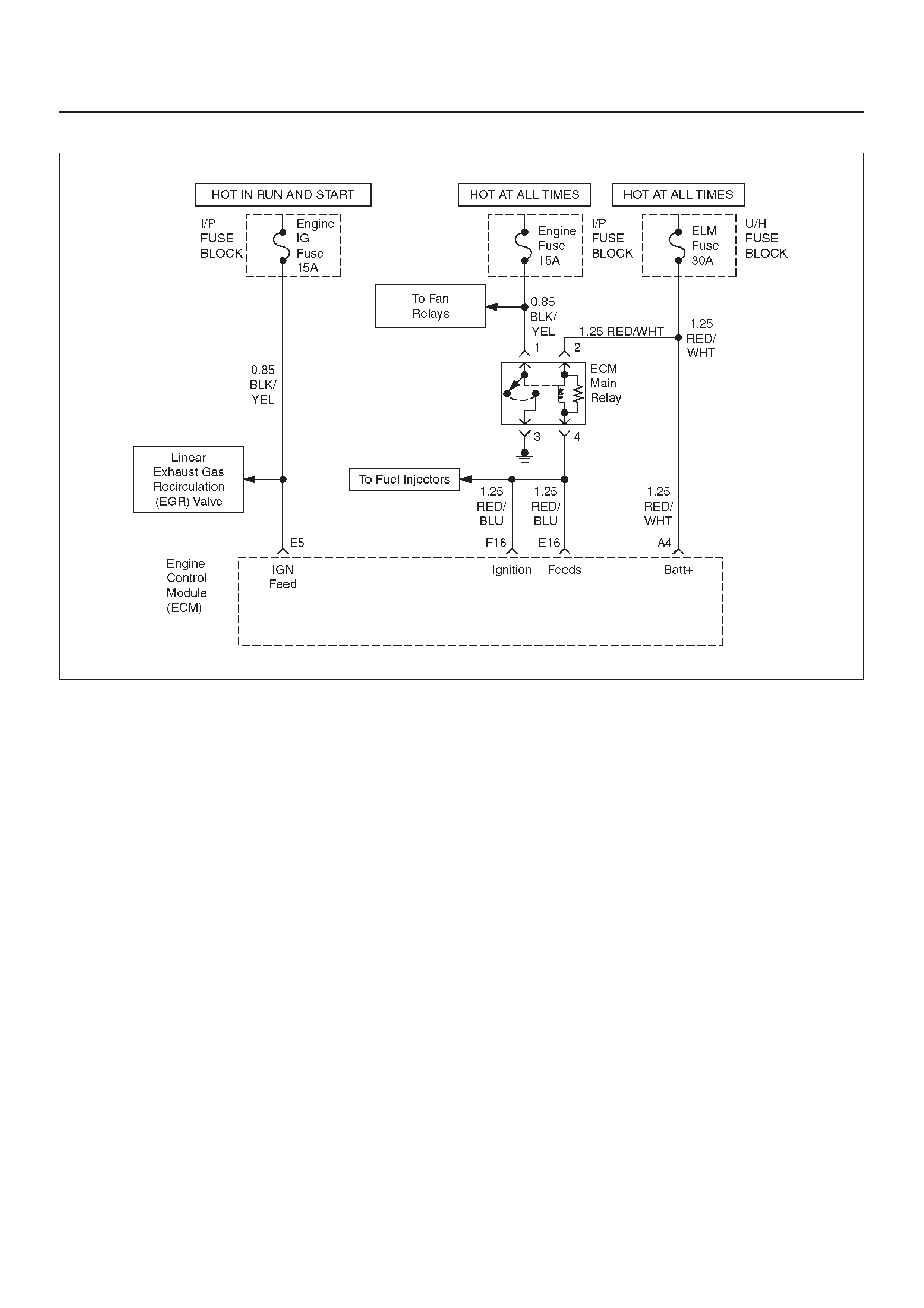
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0563 SYSTEM VOLTAGE HIGH
D06RX127
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the system
voltage on the ignition feed terminals to the ECM. A
system voltage Diagnostic Trouble Code will set
whenever the voltage is above a calibrated value. DTC
P0563 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition ON.
DSystem voltage is above 16.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL) for the first time the malfunction is detected.
DThe ECM will store as Failure Records conditions
which were present when the Diagnostic Trouble Code
was set. This information will not be stored as Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0563 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0563 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for a faulty charging system components.
DTC P0563 System Voltage High
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition OFF, engine OFF.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), measure the
battery voltage at the battery.
Is the battery voltage greater than the specified value? 16 V Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Charge the battery and clean the battery terminals.
2. Clean the battery ground cable connection if
corrosion is indicated.
Is the battery voltage greater than the specified value? 16 V Replace
battery Go to Step 4
41. Turn OFF all the accessories.
2. Install the Tech 2.
3. Select the ignition voltage parameter on the data
list.
4. Start the engine and raise the engine speed to 2000
RPM.
Is the voltage above the specified value? 16 V Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Replace or repair the generator (see Charging
System).
Is a malfunction present? — Verify repair —
6Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0601 INTERNAL CONTROL MODULE
MEMORY CHECK SUM ERROR
014RX002
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) used in this vehicle
utilizes an electrically erasable programmable read–only
memory (EEPROM). The EEPROM contains program
information and the calibrations required for engine,
transmission, and powertrain diagnostics operation.
Unlike the PROM used in past applications, the EEPROM
is not replaceable.
If the ECM detects a check sum error then DTC P0601 will
set. DTC P0601 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe ECM detects an internal program fault (check sum
error).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the malfunction is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code was set in the
Failure Records data only.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P0601 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P0601 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
DTC P0601 Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
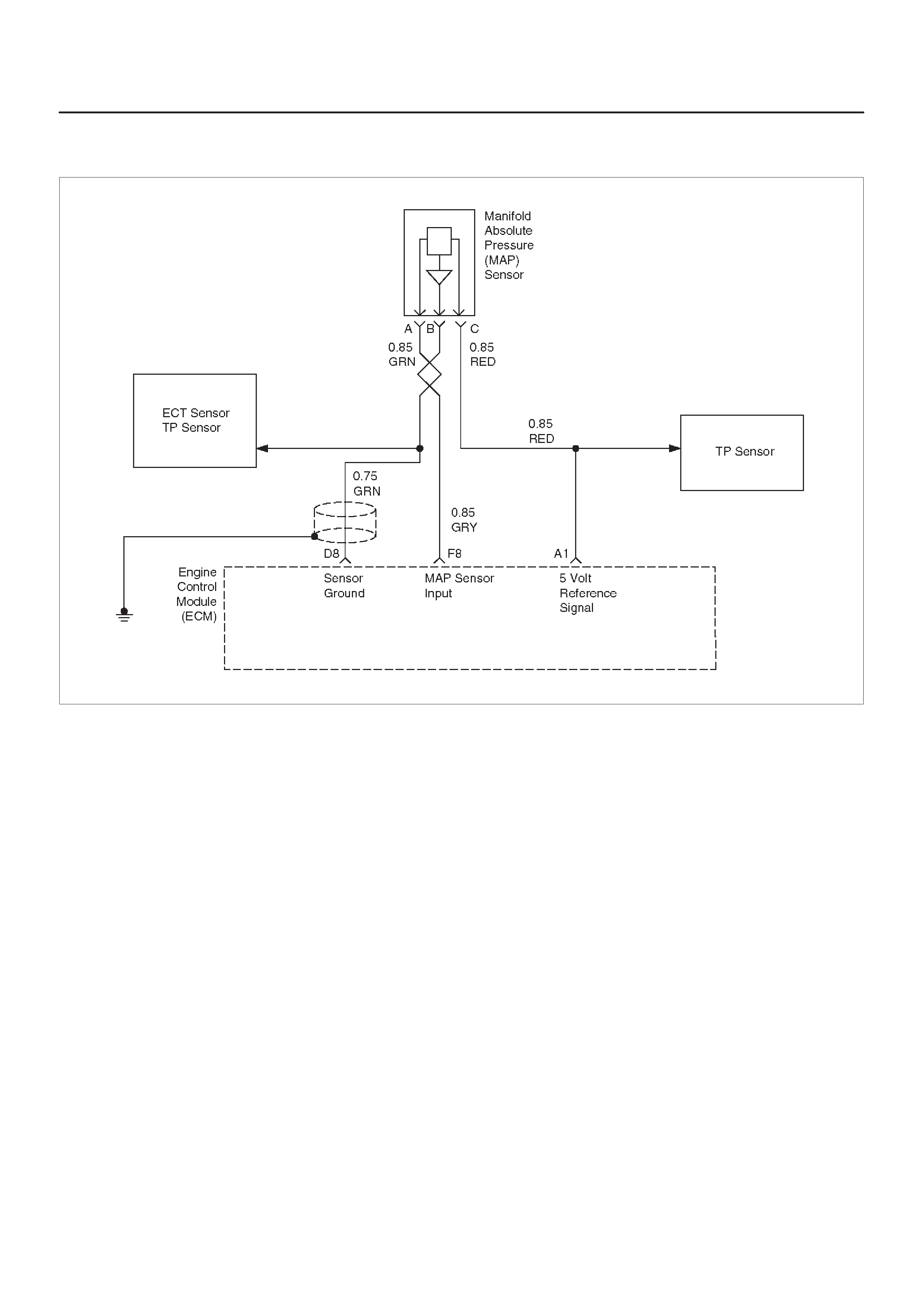
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1106 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH VOLTAGE
D06RX114
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the ECM varies from below 2 volts at idle
(low manifold pressure) to above 4 volts with the ignition
ON, engine not running or at wide–open throttle (high
manifold pressure).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used on the 2.2L engine. This is calculated using inputs
from the MAP sensor, RPM, the CKP sensor, and the
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor. The MAP sensor is
the main sensor used in this calculation, and measuring
engine load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold
pressure changes while the linear EGR flow test
diagnostic is being run, to determine engine vacuum level
for some other diagnostics and to determine barometric
pressure (BARO). Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code 401.
The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal to a
calculated MAP based on throttle position and various
other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a MAP
signal that is intermittently above the calculated value,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1106 will set. DTC P1106 is a
type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo TP sensor Diagnostic Trouble Codes are present.
DEngine is running.
DThrottle angle is below 2.7% if engine speed is below
1000 RPM.
DThrottle angle is below 10% if engine speed is above
1000 RPM.
DThe MAP sensor indicates an intermittent manifold
absolute pressure above 90 kPa for a total of
approximately 5 seconds over a 16–second period of
time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code was set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1106 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1106 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DLeaking or plugged vacuum supply line to the MAP
sensor.
DInspect ECM harness connectors for backed–out
terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly
formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt Reference with the TP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit.
DThe MAP sensor shares a ground with the TP sensor
and Fuel Pressure sensor.
DInspect the wiring harness for damage; shorts to
ground, shorts to battery positive, and open circuits. If
the harness appears to be OK, observe the MAP
display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the
display will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P1106 – MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0108 also set?
—
Go to DTC
P0108 chart
first Go to Step 3
3Are Diagnostic Trouble Code P0463, and/or P1121
also set? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the MAP sensor.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5Check the MAP signal circuit between the MAP sensor
connector and the ECM for an intermittent short to
voltage.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 8
6Check for an intermittent short to voltage on the 5 volt
reference circuit between the ECM and the following
components:
DFuel Tank Vapor Pressure Sensor
DTP sensor
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 7
7Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the ECM.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8Check for an intermittent open or a faulty splice in the
sensor ground circuit.
Was a problem found? (if no, start with the diagnosis
chart for other sensors in the circuit and see if 5V
returns.) —Go to Step
10
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
9Replace the faulty harness connector terminal for the
sensor ground circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
10 Locate and repair the intermittent open/short circuit in
the wiring harness as necessary.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
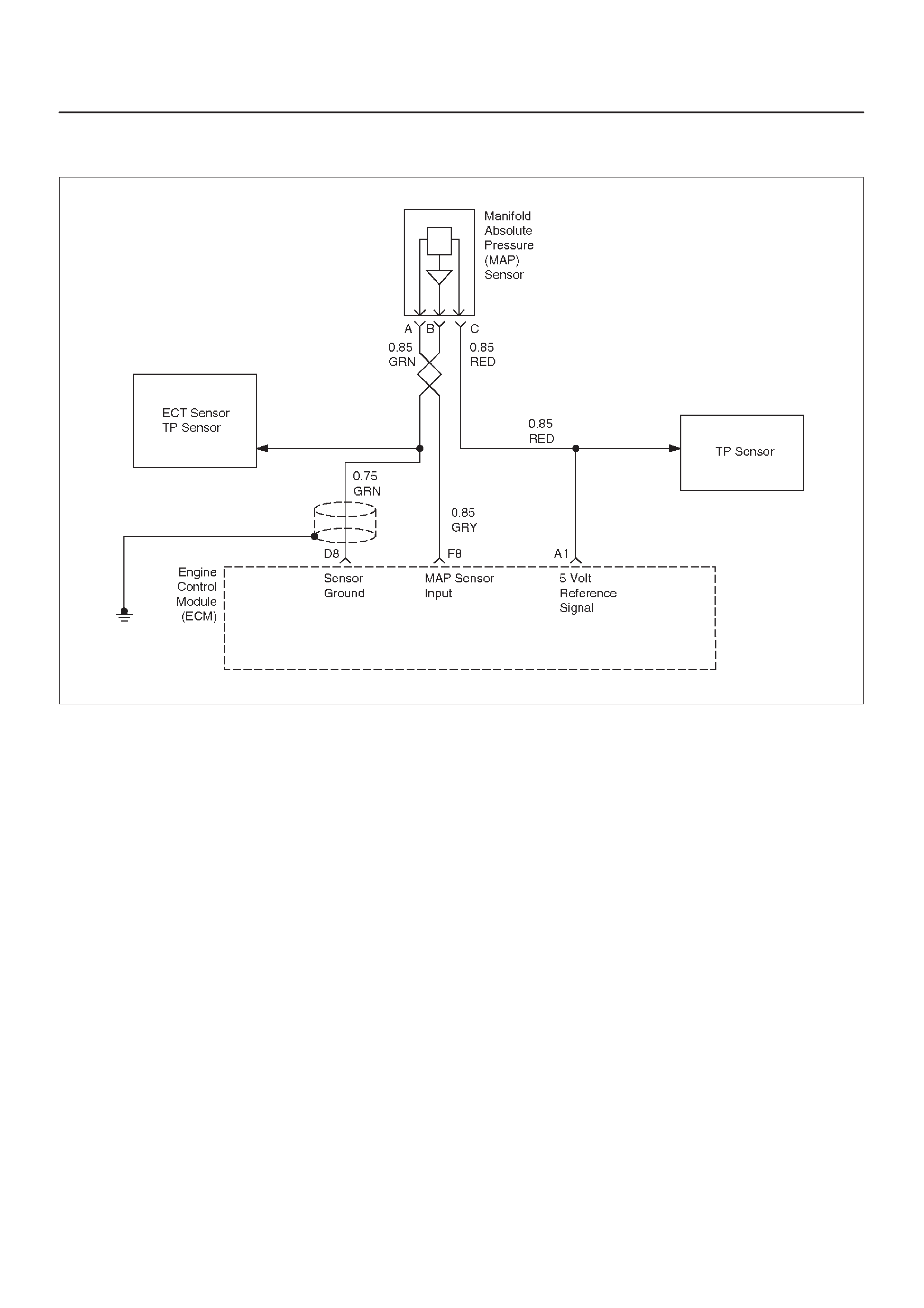
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1107 MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW VOLTAGE
D06RX114
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure. The MAP sensor
signal voltage to the engine control module (ECM) varies
from below 2 volts at idle (low manifold pressure) to above
4 volts with the ignition ON, engine not running or at
wide–open throttle (high manifold pressure).
A ”speed density” method of determining engine load is
used on the 2.2l engine. This is calculated using inputs
from the MAP sensor, the CKP sensor, and the Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) sensor. The MAP sensor is the main
sensor used in this calculation, and measuring engine
load is its main function.
The MAP sensor is also used to determine manifold
pressure changes while the linear EGR flow test
diagnostic is being run, to determine engine vacuum level
for some other diagnostics and to determine barometric
pressure (BARO). Refer to DTC P0401.
The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal to a
calculated MAP based on throttle position and various
other engine load factors. If the ECM detects a MAP
signal that is intermittently below the calculated value,
DTC P1107 will set. DTC P1107 is a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo TP sensor Diagnostic Trouble Codes are present.
DEngine is running.
DThrottle angle is below 0% if engine speed is less than
1300 RPM.
DThrottle angle is below 5% if engine speed is above
1300 RPM.
DThe MAP sensor indicates an intermittent manifold
absolute pressure above 11 kPa for a total of
approximately 5 seconds over a 16–second period of
time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code was set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1107 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1107 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe MAP sensor shares a 5 Volt Reference with the TP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit.
DThe MAP sensor shares a ground with the TP sensor
and Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor.
A change in the display will indicate the location of the
fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P1107 – MAP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0107 also set?
—
Go to DTC
P0107 chart
first Go to Step 3
3Is DTC P1122 and/or P0462 also set? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4Check for a poor 5 volt reference circuit terminal
connection at the MAP sensor.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5Check the MAP signal circuit between the MAP sensor
connector and the PCM for an intermittent open or
short to ground.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 8
6Check for an intermittent short to ground on the 5 volt
reference circuit between the ECM and the following
components:
DFuel Tank Vapor Pressure Sensor
DTP sensor
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 7
7Check for a poor 5 volt reference terminal connection at
the ECM.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8Check for an intermittent open or a faulty splice in the 5
volt reference circuit.
Was a problem found? (if no, start with the diagnosis
chart for other sensors in the circuit and see if 5V
returns.) —Go to Step
10
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
9Replace the faulty harness connector terminal for the 5
volt reference circuit and/or the MAP signal circuit as
necessary.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
10 Repair the intermittent open/short circuit in the wiring
harness as necessary.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
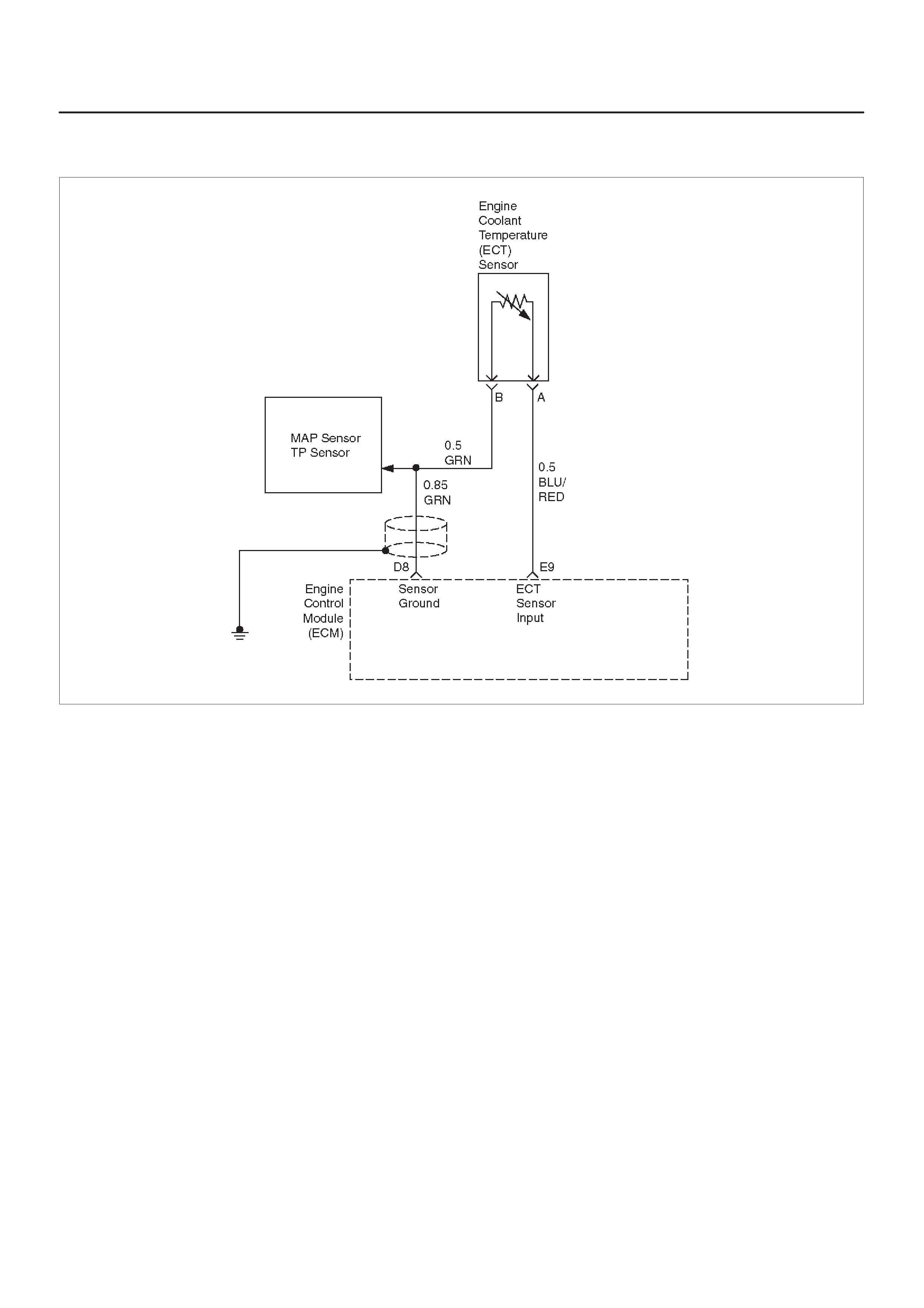
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1111 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH VOLTAGE
D06RX117
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The engine control module (ECM) applies 5 volts
through a pull–up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is
lower causing the ECM to monitor a lower voltage.
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1111 will set when the ECM
intermittently detects an excessively high signal voltage
on the intake air temperature sensor signal circuit. DTC
P1111 is a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe engine has been running for over 4 minutes.
DVehicle speed is less than 32 km/h (20 mph).
DEngine coolant temperature is above 60°C (140°F).
DCalculated air flow is less than 20g/second.
DIAT signal voltage indicates an intake air temperature
intermittently less than –39°C (–38°F) (4.94 volts) for
approximately 2.5 seconds over a 25–second period of
time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will substitute a default value for intake air
temperature.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1111 does not illuminate the
MIL.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history DTC P1111 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm–up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1111 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the IAT
sensor. A change in the IAT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
°C°FW
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 113 1188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P1111 – IAT Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0113 also set?
—
Go to DTC
P0113 chart
first Go to Step 3
31. Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the IAT sensor.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 4
41. Check for a poor IAT signal circuit terminal
connection at the IAT sensor.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Check the IA T signal circuit between the IA T sensor
connector and the ECM for an intermittent open.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Check the IA T signal circuit between the IA T sensor
connector and the ECM for an intermittent short to
voltage.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the ECM.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Check for an intermittent open or a faulty splice in
the sensor ground circuit.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
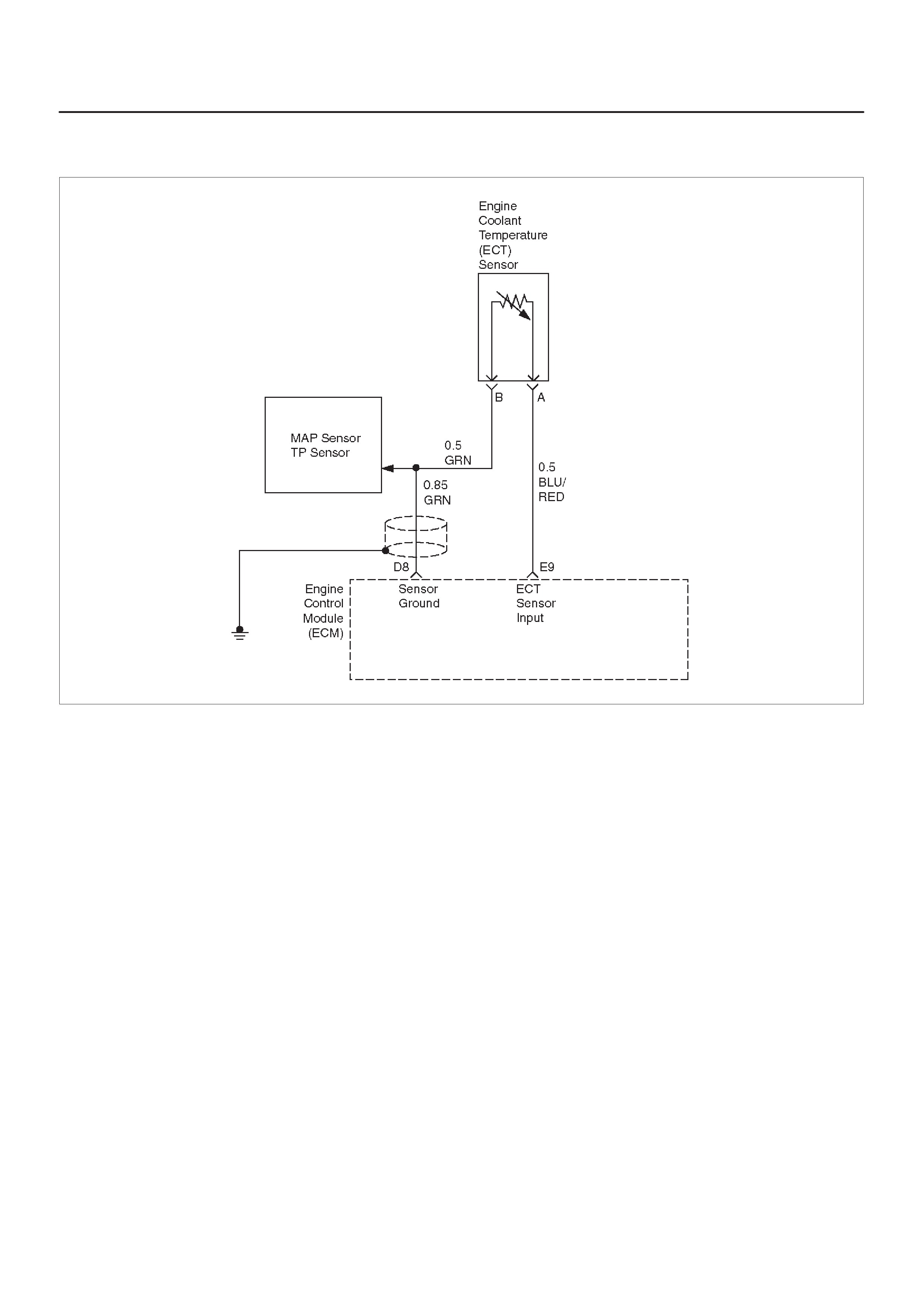
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1112 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW VOLTAGE
D06RX117
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which measures the temperature of the air entering the
engine. The engine control module (ECM) applies 5 volts
through a pull–up resistor to the IAT sensor. When the
intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the
ECM will monitor a high signal voltage on the IAT signal
circuit. If the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance
becomes lower, causing the ECM to monitor a lower
voltage. Diagnostic Trouble Code P1 1 12 will set when the
ECM intermittently detects an excessively low signal
voltage on the intake air temperature sensor signal
circuit. DTC P1112 is a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe engine has been running for over 2 minutes.
DVehicle speed is greater than 48 km/h (30 mph).
DIAT signal voltage is greater than 148°C (298°F)
(about 0.10 volt) for a total of 2.5 seconds over a
25–second period of time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
DThe ECM will substitute a default value for intake air
temperature.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1112 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1112 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the IAT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the IAT
sensor. A change in the IAT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2.Verifies that the fault is present.
3.If DTC P1112 can be repeated only by duplicating
the Failure Records conditions, refer to the
”Temperature vs. Resistance Value Chart.”
The chart may be used to test the IAT sensor at
various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of
a ”shifted” sensor that may be shorted above or
below a certain temperature. If this is the case,
replace the IAT sensor.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
°C°FW
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 1131188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P1112 – IAT Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0112 also set?
—
Go to DTC
P0112 chart
first Go to Step 3
31. Check the IA T signal circuit between the IA T sensor
connector and the PCM for an intermittent short to
ground.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
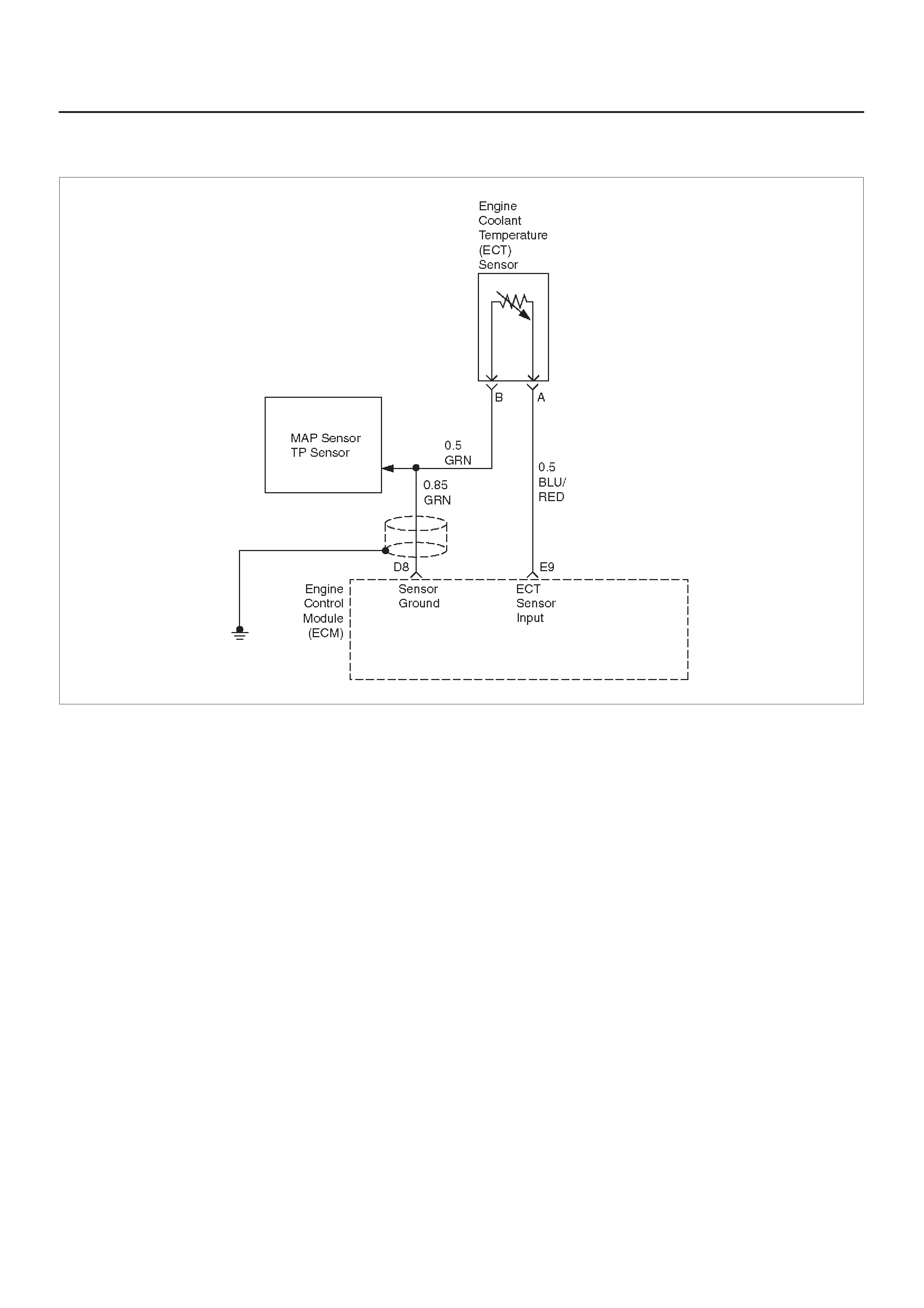
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1114 ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW VOLTAGE
D06RX117
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted in the engine coolant stream. The
engine control module (ECM) applies a voltage (about 5.0
volts) through a pull–up resistor to the ECT signal circuit.
When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor (thermistor)
resistance is high, therefore the ECM will measure a high
signal voltage. As the engine coolant warms, the sensor
resistance becomes less, and the ECT signal voltage
measured at the ECM drops. With a fully warmed up
engine, the ECT signal voltage should measure about 1.5
to 2.0 volts. If the ECM detects an ECT signal that is
intermittently below the range of the ECT sensor,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1114 will set. DTC P1114 is a
type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine run time longer than 2 minutes.
DThe ECT sensor signal is intermittently greater than
150°C (302°F) (about 0.10 volt) for a total of 10
seconds over a 100–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1114 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1114 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the ECT
sensor. A change in the ECT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
°C°FW
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 1131188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P1114 – ECT Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0117 also set? —Go to DTC
P0117 first Go to Step 3
31. Check the ECT signal circuit between the ECT
sensor connector and the ECM for an intermittent
short to ground.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
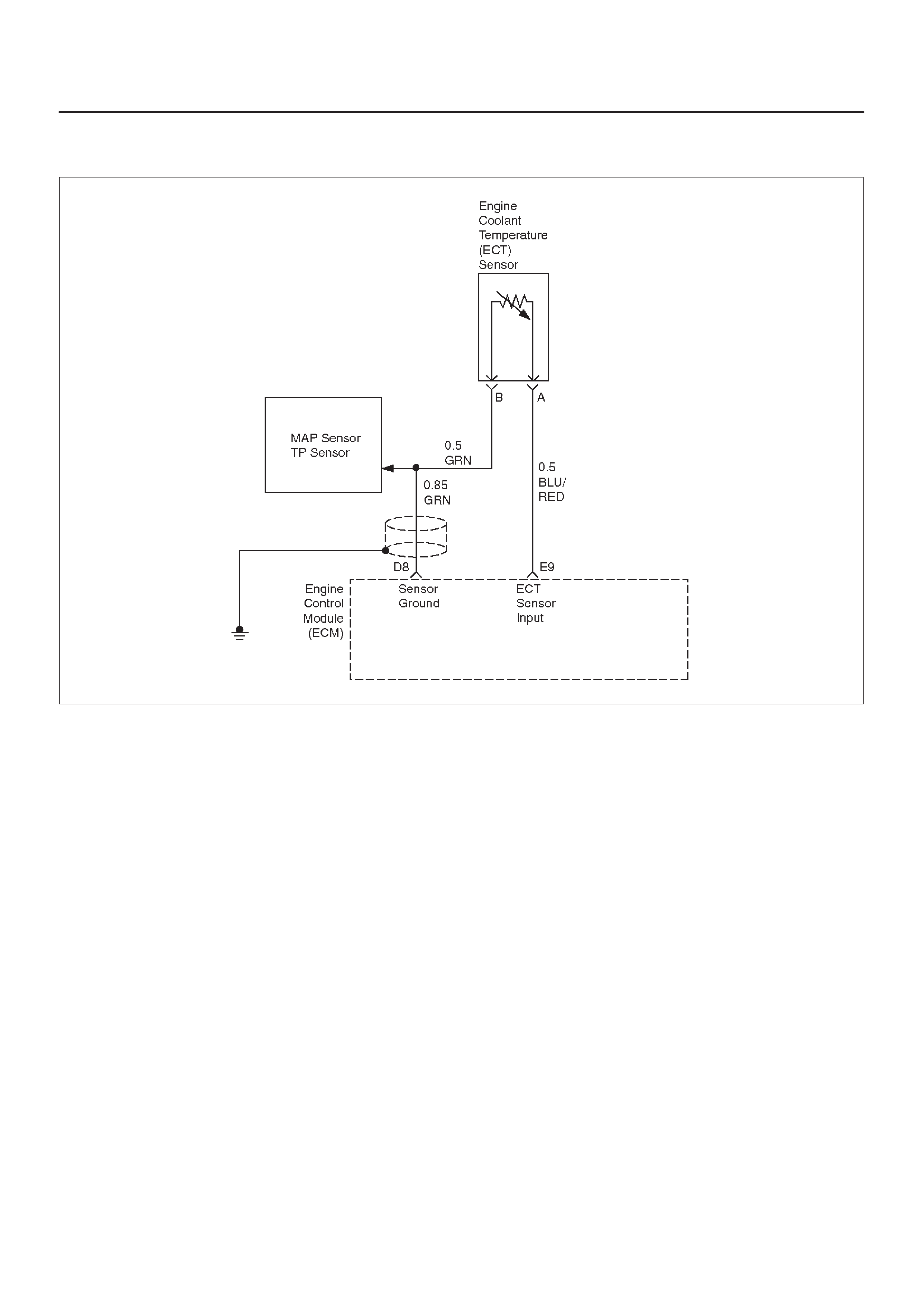
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1115 ENGINE COOLANT
TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH VOLTAGE
D06RX117
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted in the engine coolant stream. The
engine control module (ECM) applies a voltage (about 5.0
volts) through a pull–up resistor to the ECT signal circuit.
When the engine coolant is cold, the sensor (thermistor)
resistance is high, therefore the ECM will measure a high
signal voltage. As the engine coolant warms, the sensor
resistance becomes less, and the ECT signal voltage
measured at the ECM drops. With a fully warmed up
engine, the ECT signal voltage should measure about 1.5
to 2.0 volts. If the PCM detects an ECT signal that is
intermittently above the range of the ECT sensor,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1115 will set. Diagnostic
Trouble Code P1115 is a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine run time longer than 180 seconds.
DThe ECT sensor signal is intermittently greater than
–39°C (–38°F) (4.94 volts) for a total of 10 seconds
over a 100–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1115 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1115 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving
connectors and wiring harnesses related to the ECT
sensor. A change in the ECT display will indicate the
location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic T rouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
°C°FW
Temperature vs. Resistance Values (approximate)
100 212 177
80 176 332
60 140 667
45 113 1188
35 95 1802
25 77 2796
15 59 4450
5 41 7280
–5 23 12300
–15 5 21450
–30 –22 52700
–40 –40 100700
DTC P1115 ECT Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0118 also set? —Go to DTC
P0118 first Go to Step 3
31. Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the ECT sensor.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 4
41. Check for a poor ECT signal circuit terminal
connection at the ECT sensor.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Check the ECT signal circuit between the ECT
sensor connector and the ECM for an intermittent
open.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Check the ECT signal circuit between the ECT
sensor connector and the ECM for an intermittent
short to voltage.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the ECM.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Check for an intermittent open or a faulty splice in
the sensor ground circuit.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
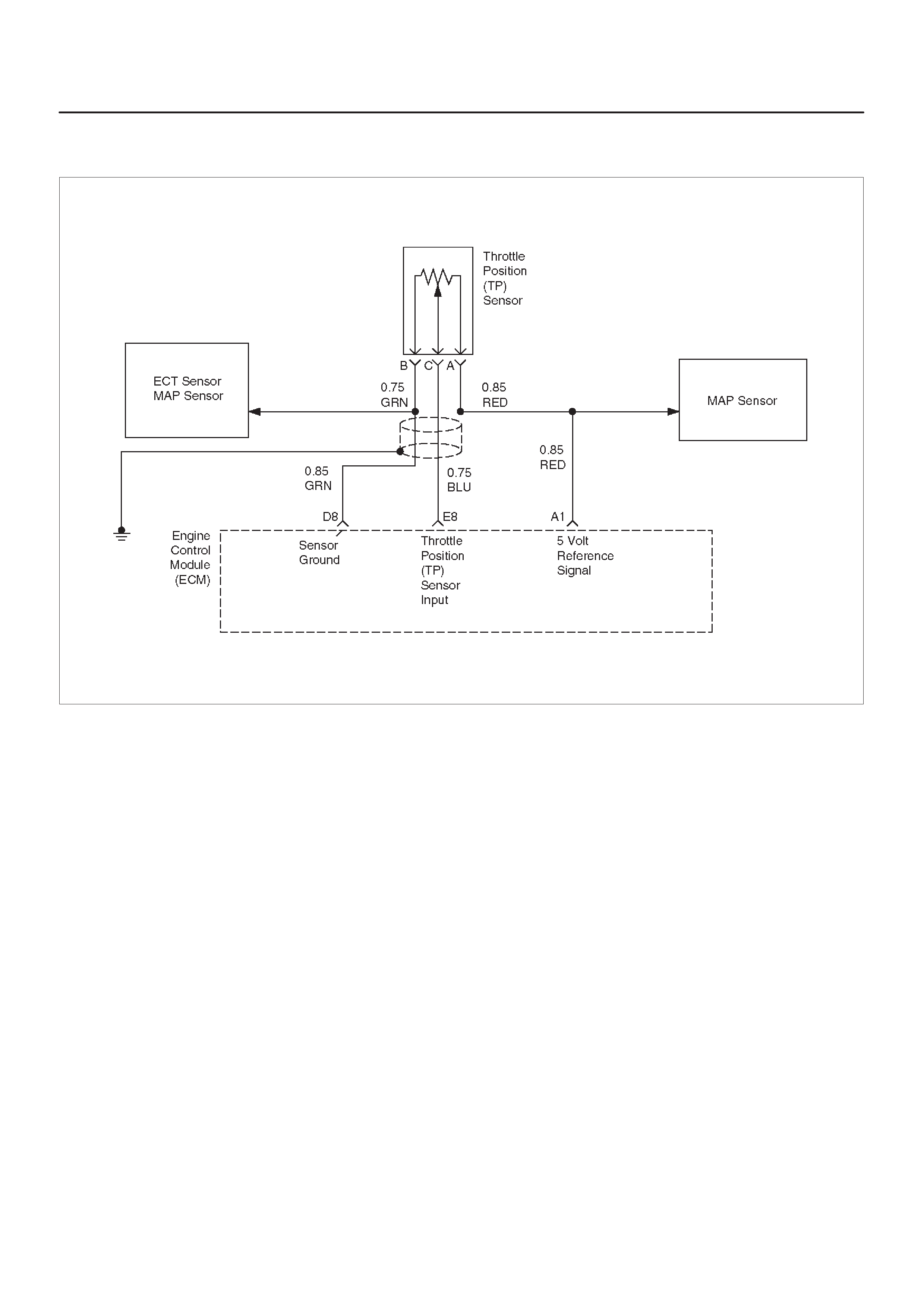
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1121 THROTTLE POSITION (TP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT HIGH VOLTAGE
D06RX118
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to the throttle blade angle.
The signal voltage will vary from less than 1 volt at closed
throttle to more than 4 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is used by the engine control module
(ECM) for fuel control and for most of the ECM controlled
outputs. If the ECM detects a TP signal that is
intermittently above the range of the TP sensor,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1 121 will be set. DTC P1121 is
a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe ignition is ON.
DTP sensor indicates a throttle position voltage
intermittently greater than 4.88 volts for a total of 0.15
seconds over a 1.5–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1121 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1121 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function or by
disconnecting the ECM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect the harness
connectors for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DThe TP sensor shares a 5 V olt reference with the MAP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit or
components itself.
DThe TP sensor share a ground with the MAP and the
Fuel Pressure sensor.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the throttle position display on the T ech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
TP sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
If Diagnostic Trouble Code P1121 cannot be duplicated,
reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help to determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P1121 – TP Sensor Circuit Intermittent High Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is Diagnostic Trouble Code P0123 also set? —Go to DTC
P0123 first Go to Step 3
3Is Diagnostic Trouble Code P1106 also set? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4Check for a poor sensor ground circuit terminal
connection at the TP sensor.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5Check the TP signal circuit between the TP sensor
connector and the ECM for an intermittent short to
voltage.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 8
6Check for an intermittent short to voltage on the 5 volt
reference circuit between the ECM and the following
components:
DMAP Sensor
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 7
7Check for a poor sensor ground terminal connection at
the ECM.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8Check for an intermittent open or a faulty splice in the
sensor ground circuit.
Was a problem found? (if no, start with the diagnosis
chart for other sensors in the circuit and see if 5V
returns.) —Go to Step
10
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
9Replace the faulty harness connector terminal for the
sensor ground circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
10 Repair intermittent open/short circuit in wiring harness
as necessary.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
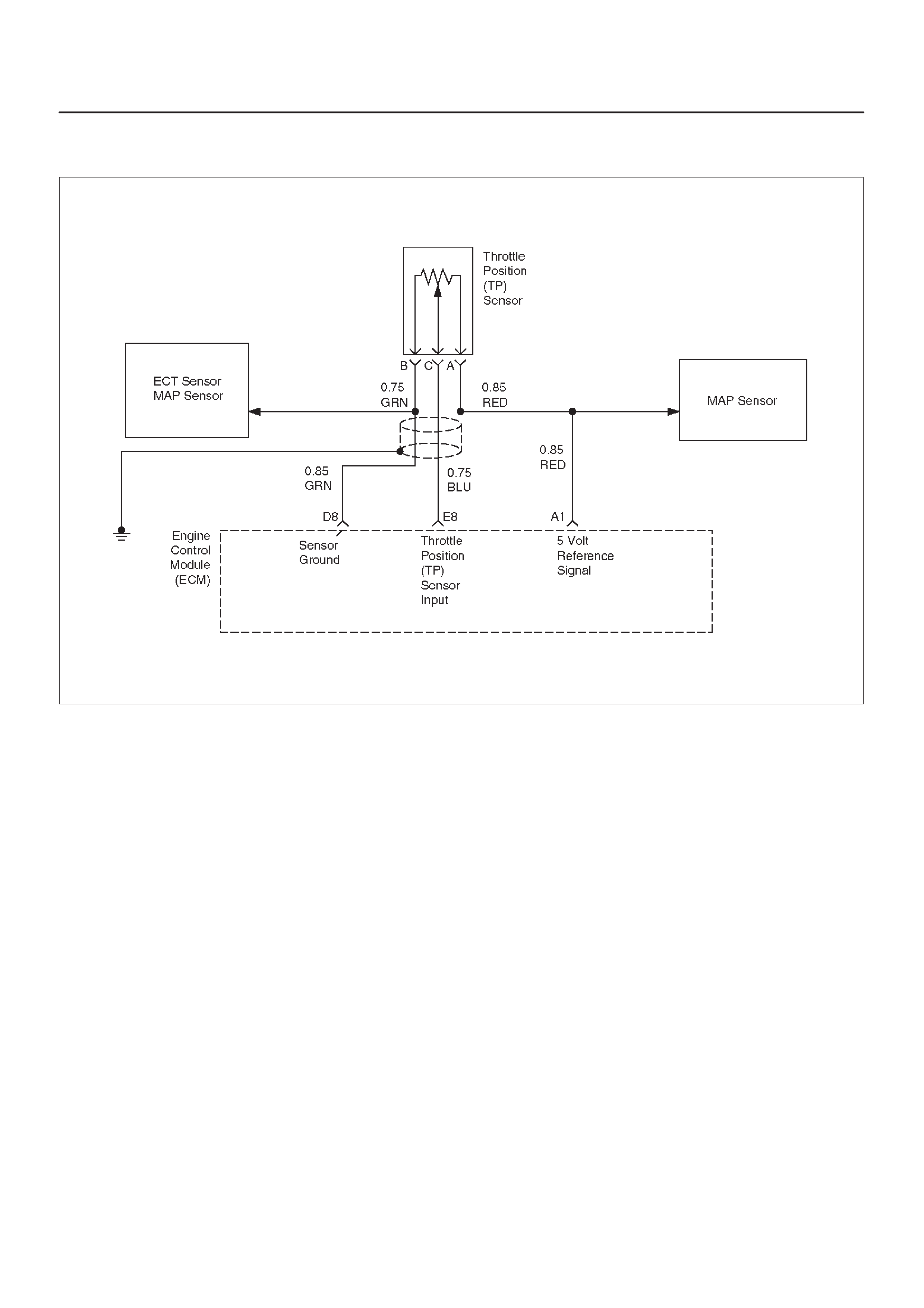
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1122 THROTTLE POSITION (TP)
SENSOR CIRCUIT INTERMITTENT LOW VOLTAGE
D06RX118
Circuit Description
The throttle position (TP) sensor circuit provides a voltage
signal that changes relative to the throttle blade angle.
The signal voltage will vary from less than 1 volt at closed
throttle to more than 4 volts at wide open throttle (WOT).
The TP signal is used by the engine control module
(ECM) for fuel control and for most of the ECM controlled
outputs. If the ECM detects a TP signal that is
intermittently above the range of the TP sensor,
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1 122 will be set. DTC P1122 is
a type D code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DThe ignition is ON.
DTP sensor indicates a throttle position signal
intermittently less than 0.10 volt for a total of 0.15
seconds over a 1.5–second period.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic Trouble Code set as Failure
Records data only. This information will not be stored
as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1122 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1122 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function or by
disconnecting the ECM battery feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect the harness
connectors for backed–out terminals, improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged
terminals, and poor terminal–to–wire connection.
DDamaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage; shorts to ground, shorts to battery positive,
and open circuits. If the harness appears to be OK,
observe the throttle position display on the T ech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
TP sensor. A change in the display will indicate the
location of the fault.
DThe TP sensor shares a 5 V olt reference with the MAP
sensor and Fuel Pressure sensor.
If these codes are also set, it could indicate a
problem with the 5 Volt reference circuit or
components itself.
DThe TP sensor share a ground with the MAP and the
Fuel Pressure sensor.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help to determine how often
the condition that caused the Diagnostic Trouble Code to
be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the
condition.
DTC P1122 – TP Sensor Circuit Intermittent Low Voltage
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Is DTC P0122 also set? —Go to DTC
P0122 first Go to Step 3
3Is DTC P1107 also set? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4Check for a poor 5 volt reference circuit or TP signal
circuit terminal connection at the TP sensor.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5Check the TP signal circuit between the TP sensor
connector and the ECM for an intermittent short to
ground.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step
10 Go to Step 8
6Check for an intermittent short to ground on the 5 volt
reference circuit between the ECM and the following
components:
DMAP Sensor
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7Check for a poor 5 volt reference circuit terminal
connection at the ECM.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8Check for an intermittent open or a faulty splice in the 5
volt reference circuit.
Was a problem found? (if no, start with the diagnosis
chart for other sensors in the circuit and see if 5V
returns.) —Go to Step
10
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids
9Replace the faulty harness connector terminal(s) for
the 5 volt reference circuit and/or the TP signal circuit
as necessary.
Is the action complete?
—
Repair
complete. If a
driveability
symptom still
exists, refer
to Symptoms. —
10 Repair intermittent open/short circuit in wiring harness
as necessary.
Is the action complete?
—
Repair
complete. If a
driveability
symptom still
exists, refer
to Symptoms. —
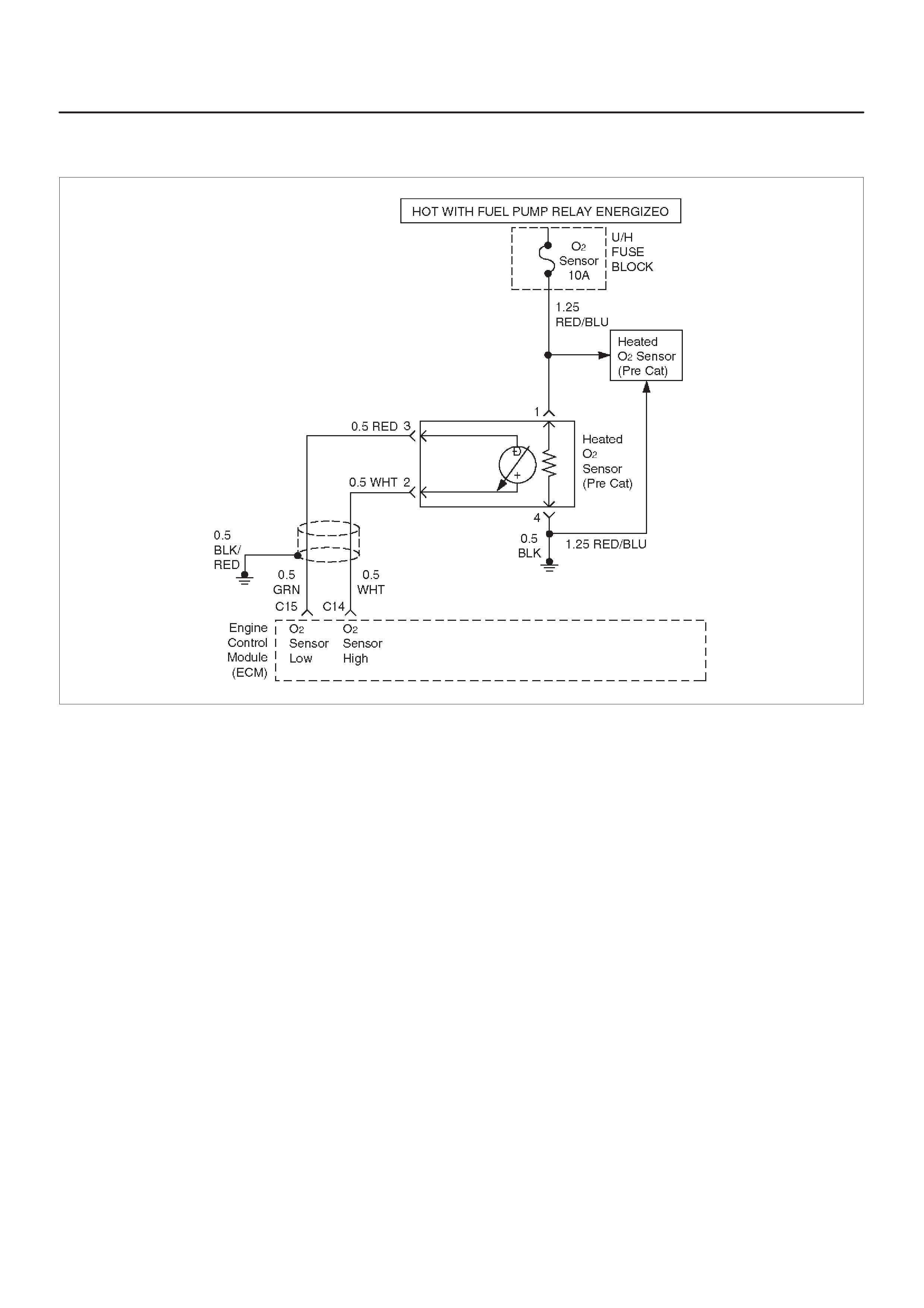
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1171 FUEL SYSTEM LEAN DURING
ACCELERATION
D06RX119
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) internal circuitry can
identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of supplying
adequate amounts of fuel during heavy acceleration
(power enrichment). The ECM monitors the voltage of the
oxygen sensor during power enrichment. When a power
enrichment mode of operation is requested during
”Closed Loop” operation (by heavy acceleration), the
ECM will provide more fuel to the engine. Under these
conditions the ECM should detect a ”rich” condition (high
oxygen sensor voltage). If this ”rich” exhaust is not
detected at this time, a Diagnostic Trouble Code P1171
will set. A plugged fuel filter or restricted fuel line can
prevent adequate amounts of fuel from being supplied
during power enrichment mode. DTC P1171 is a type A
code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DNo related Diagnostic Trouble Codes.
DEngine is operating in ”Closed Loop”.
DEngine coolant temperature is above 60°C (140°F).
DWhile in ”power enrichment” mode the oxygen sensor
voltage remains below 400 mV for 3 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the Diagnostic T rouble Code was set as Freeze
Frame and in the Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history Diagnostic Trouble Code P1171 will clear
after 40 consecutive warm–up cycles have occurred
without a fault.
DDiagnostic Trouble Code P1171 can be cleared by
using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DA restricted fuel filter or fuel line can supply adequate
amounts of fuel at idle, but may not be able to supply
enough fuel during heavy acceleration.
DWater or alcohol in the fuel may cause low HO2S
voltage during acceleration.
DCheck for faulty or plugged fuel injector(s).
DCheck for low fuel.

Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
4. When the engine is idling or at steady cruise, the
HO2S voltage should vary from between
approximately 100 mV to 900 mV. During ”power
enrichment” mode, more fuel is needed and the
HO2S voltage should rise above 447 mV. This step
checks to see if the HO2S is operating properly.
5. Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure
connector to absorb any small amount of fuel
leakage that may occur when installing the gauge.
Ignition ON, pump pressure should be 235–320
kPa.
7. Add Caution: Use correct pliers so damage to fuel
lines will not occur.
DTC P1171 – Fuel System Lean During Acceleration
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Are any component–related Diagnostic Trouble Codes
set? —
Go to
component
DTC charts Go to Step 3
31. Check the vehicle’s fuel tank for an adequate
amount of fuel.
2. Add fuel to the vehicle’s fuel tank if the tank is almost
empty.
Was fuel added to the vehicle’s fuel tank? —Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
41. Using a Tech 2, observe HO2S 1 voltage while
running warm engine(75°C–95°C [167°F–203°F])
at 1200 RPM.
2. HO2S 1 voltage should vary within the specified
range.
Does the voltage toggle back and forth within the
specified range? 100– 900 mV
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 5
51. Disconnect the fuel pump relay and crank the
engine to relieve the fuel pressure.
2. Install the fuel pressure gauge.
3. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
4. Disconnect the vacuum line going to the fuel
pressure regulator.
With the engine running, is the fuel pressure within the
specified range? 284– 325 kPa
Go to OBD
System
Check Go to Step 6
6Check for restricted fuel lines or restricted in–line filter .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
3. Using a Tech 2, enable the fuel pump to operate.
4. Using pliers, slowly close the return line (do not
exceed the first specified value).
Using the pliers, can the fuel pressure be manipulated
to exceed the second specified value? 414 kPa 325
kPa
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 8
8Check for:
DFaulty fuel pump
DRestricted fuel pump strainer (sock)
DIncorrect fuel pump
DIncorrect fuel being used
DHot fuel — Verify repair —

DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) 1404 EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) CLOSED VALVE
D06RX113
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the exhaust
gas recirculation(EGR) valve pintle position input to
ensure that the valve responds properly to commands
from the ECM to detect a fault if the pintle position sensor
and control circuits are open or shorted. If the ECM
detects a pintle position signal voltage below the normal
range of the pintle position sensor, or a signal voltage that
is not within a tolerance considered acceptable for proper
EGR control system operation, the ECM will set a DTC
P1404.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIAT is above 5°C (41°)
DEGR actual position is 16 counts below the EGR low
threshold for at least 6.3 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) after the second consecutive trip in which the
fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL OFF on the third consecutive
trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and
the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history DTC P1404 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm up cylcles without a fault.
DDTC P1404 can be cleared by using the Scan Tool’s
”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DExcessive deposits on EGR valve pintle or seat –
Check for deposits that may interfere with the EGR
valve pintle extending completely or cause the pintle to
stick.
DPoor connection or damaged harness – Inspect the
wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to
be OK, observe the EGR actual position display on the
Tech 2 while moving connectors and wiring harnesses
related to the EGR valve. A change in the display will
indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
NOTE: If the EGR valve show signs of excessive heat,
check the exhaust system for blockage (possible a
plugged catalytic converter) using the ”Restricted
Exhaust System Check”.
DTC P1404 EGR Closed Valve
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine OFF.
2. Review and record the T ech 2 Failure Records data,
the clear the DTCs.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P1404.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1404 ”Ran and
Passed” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve from the wiring harness.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the Ignition feed circuit at the Linear Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) Valve wiring harness
connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? 12 volts Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4Check the Ignition feed circuit, between the EGR
sensor and the ”Engine IG.” fuse, for the following
conditions:
DAn Open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
5Using a DVM, check the resistance of the EGR
solenoid.
Does the DVM read the following value? less than 5 WGo to Step 6 Go to Step 14
6Check the EGR solenoid valve Low circuit, between the
EGR sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn Open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve from the wiring harness.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Observe the EGR value on the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display the following value(s)? 0 volts 0% Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8Check the EGR position feedback circuit, between the
EGR sensor and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn Open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
91. Ignition ON, engine OFF.
2. Using a Digital Voltmeter (DVM), check for voltage
on the 5 volt Reference signal circuit at the Linear
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve wiring
harness connector.
Does the DVM read the following value? about 5 volts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
10 Check the 5 volt reference signal circuit, between the
EGR and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn Open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a DVM between the 5 volt reference signal
circuit and the 5 volt signal return (ground) circuit at
the EGR wiring harness connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
Does the DVM read the following value? about 5 volts Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
12 Check the 5 volt signal return (ground) circuit, between
the EGR and the ECM, for the following conditions:
DAn Open circuit
DA short to ground
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
13 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Place a fused jumper wire between the 5 volt
reference signal circuit and the EGR valve position
feedback circuit at the EGR wiring harness
connector.
3. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
4. Observe the EGR value on the Tech 2.
Does the Tech 2 display the following value? 5 volts 100% Go to Step 14 Go to Step 15
14 Replace the Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Value.
Verify repair. ———
15 Replace the ECM.
Verify repair. ———
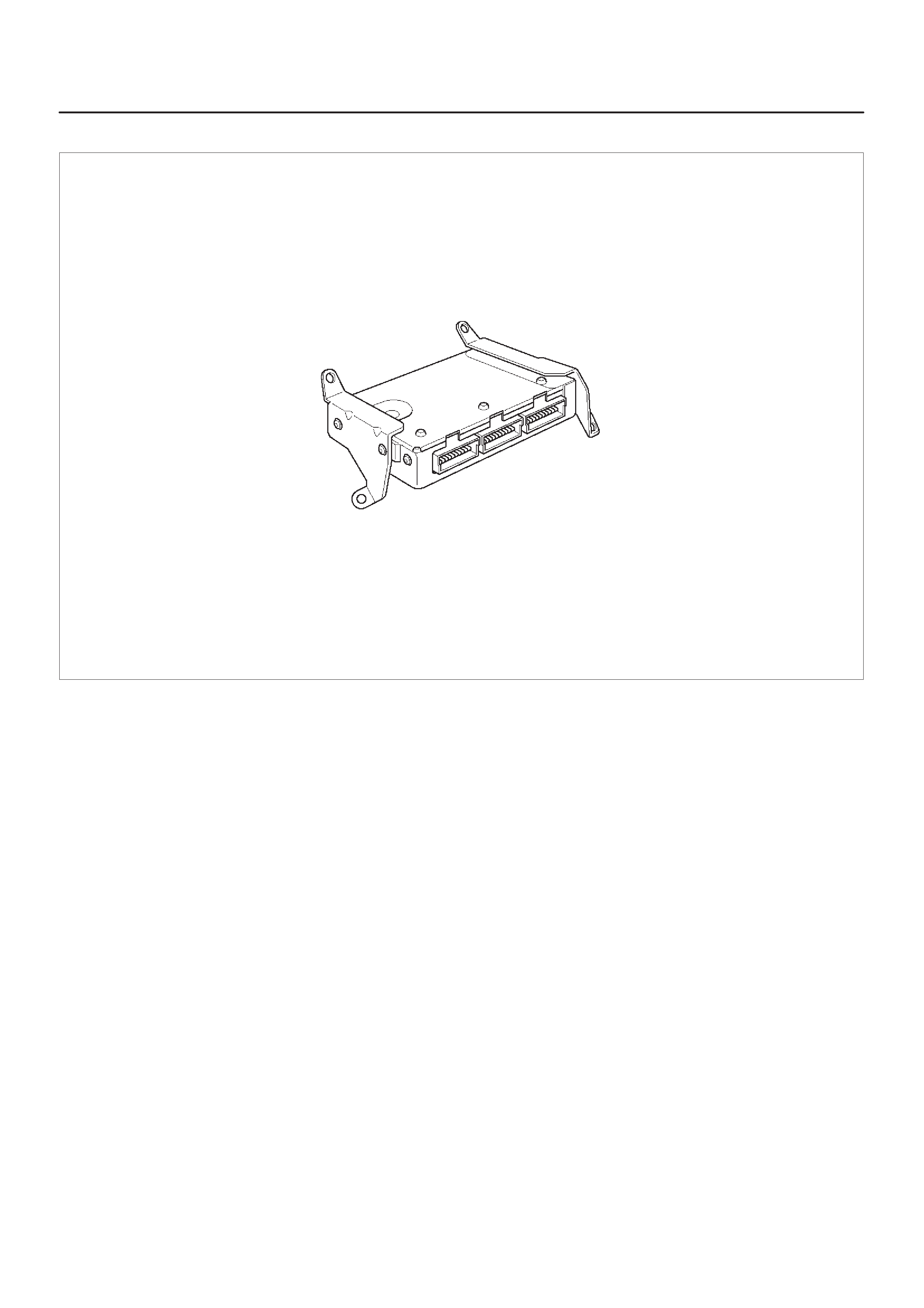
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1625 ECM UNEXPECTED RESET
014RX002
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) monitors unexpected
ECM reset. This will not turn on MIL light on, only records
code DTC P1625.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DClock or COP (Computer Operating Properly) reset.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records only. This
information will not be stored as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DThe ECM will turn the MIL “OFF” on the third
consecutive trip cycle during which the diagnostic has
been run and the fault condition is no longer present.
DA history DTC P1625 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm-up cycles have occurred without a fault.
DDTC P1625 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DP1625 alone stored does not need diagnosis. Clear
DTC code.
NOTE: DTC P1625 is a DTC to record a ECM reset
history. If DTC P1625 is not reset and no engine
abnormality is found after clearance of DTC, it is not
necessary to do any farther processing.
DTC P1625–ECM Unexpected Reset
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition is “On”.
2. Install the Tech 2.
3. Start the engine at let it Idle.
4. On the Tech 2, select “DTC info”.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1625 failed? —Go to Step 3
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
31. Ignition is “On”.
2. Clear DTC P1625 by using the Tech 2 “Clear Info”.
3. Start the engine at let it Idle.
4. On the Tech 2, select “DTC info”.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1625 failed? —Go to Step 4
Go to
Diagnostic
Aids
41. Check for aftermarket electronics, such as
transceiver stereos, and anti theft devices, they
may radiate EMI into the control system if they are
improperly installed. (This may cause a false
sensor reading and turn on the MIL.)
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair —
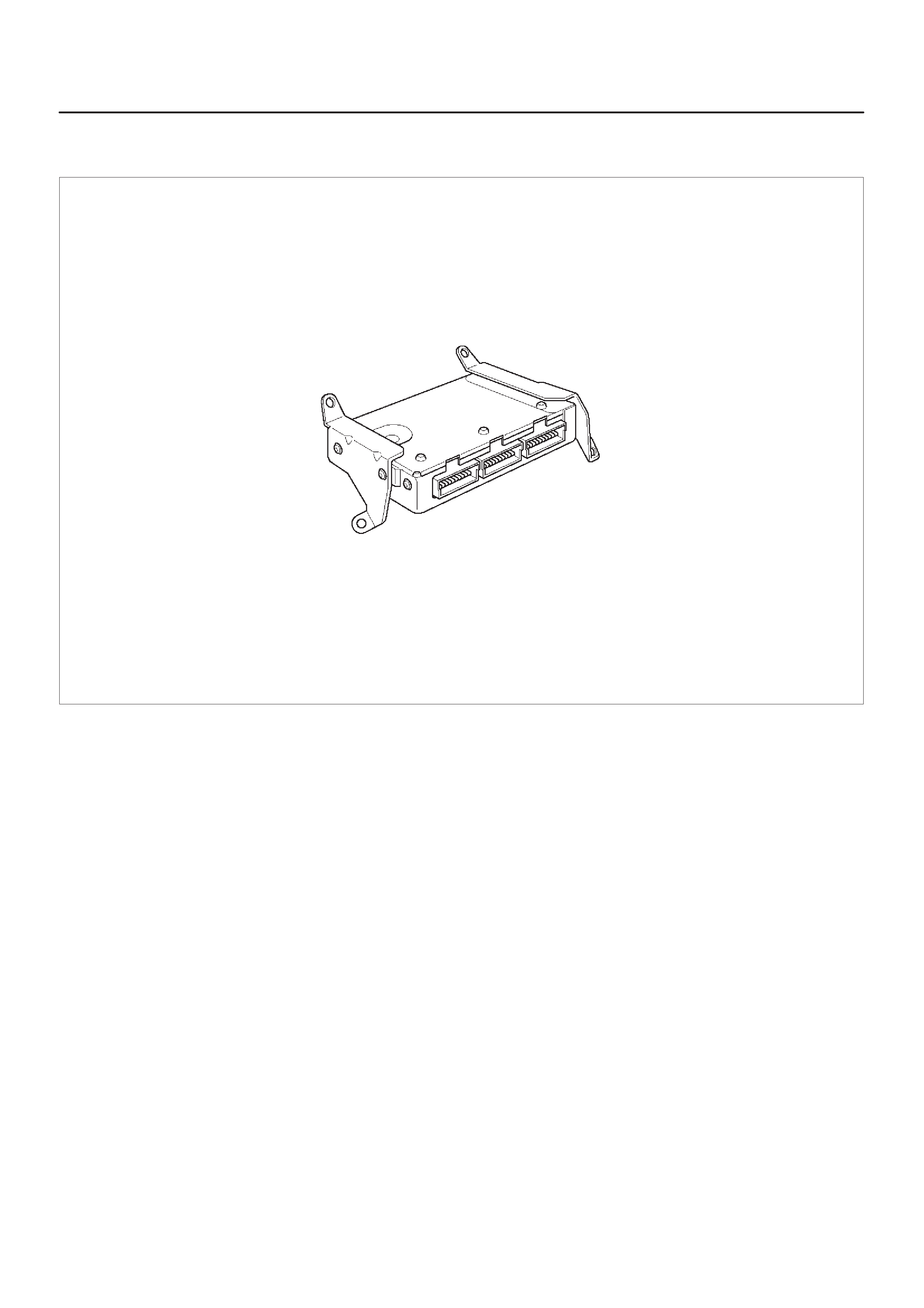
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1627 PCM A/D CONVERSION
MALFUNCTION
014RX002
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the 5 volt
reference signal when the Ignition is ON. If the ECM
senses an Analog to Digital (A/D) conversion error within
the ECM, then DTC P1627 will set. DTC P1627 is a type A
code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DEngine is running.
DAny A/D DTC’s set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store the conditions that were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL on the third consecutive
trip without a reported failure.
DA History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive trips
without a reported failure.
DThe DTC can be cleared using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear
Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
DPoor connections, or a damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for: backed–out terminals,
improper mating or damaged terminals. Also, check for
open circuits, shorts to ground, and shorts to voltage.
DTC P1627 PCM A/D Conversion Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTCs.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P1627.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1627 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
3Check the suspect 5 volt reference circuit(s) for the
following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 4
4Replace the ECM. ———
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1635 5 VOLT REFERENCE VOLTAGE
CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
014RX002
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the 5 volt
reference signal when the Ignition is ON. If the ECM
senses the 5 volt reference signal circuit is above 5.12
volts or below 4.88 volts, then DTC P1635 will set. DTC
P1635 is a type A code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition voltage is greater than 6.3 volts.
DEngine is running.
The above mentioned conditions are met and one of the
following two conditions are met for 5 seconds within a 10
second test sample:
DECM senses the 5 volt reference signal circuit is above
5.12 volts.
OR
DECM senses the 5 volt reference signal circuit is below
4.88 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) the first time the fault is detected.
DThe ECM will store the conditions that were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in Failure
Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DThe ECM will turn OFF the MIL on the third consecutive
trip without a reported failure.
DA History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive trips
without a reported failure.
DThe DTC can be cleared using the Scan Tool’s ”Clear
Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Poor connections, or a damaged harness – Inspect the
harness connectors for: backed–out terminals, improper
mating or damaged terminals. Also, check for open
circuits, shorts to ground, and shorts to voltage.
DTC P1635 5 Volt Reference Voltage Circuit Malfunction
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Ignition ON, Engine OFF.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data,
then clear the DTCs.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using the Tech 2, monitor ”DTC” info for DTC
P1635.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1635 ”Ran and
Passed?” —
Refer to
Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
3Check the suspect 5 volt reference circuit(s) for the
following conditions:
DA short to ground
DAn open circuit
DA short to voltage
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 4
4Replace the ECM. ———
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1640 ODM OUTPUT CIRCUIT FAULT
014RX002
Circuit Description
Output driver modules (ODMs) are used by the engine
control module(ECM) to turn ON many of the current
driven devices that are needed to control various engine
and transmission functions. Each ODM is capable of
controlling up to 11 separate outputs by applying ground
to the device which the ECM is commanding ON.
ODMs have the capability of diagnosing each output
circuit individually. DTC P1640 set indicates an improper
voltage level has been detected on an ODM output.
If the ECM detects an open circuit condition and a shorted
to voltage circuit condition on the same circuit at the same
time, then DTC P1640 will set. DTC P1640 is a type D
code.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DIgnition ON.
DAbove conditions occur for at least 2.5 seconds.
DThe ECM detects an open circuit condition and a
shorted to voltage circuit condition on the same circuit
at the same time.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DThe ECM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator
lamp (MIL).
DThe ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records only. This
information will not be stored as Freeze Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DA history DTC P1640 will clear after 40 consecutive
warm up cycles occur without a fault.
DDTC P1640 can be cleared by using the Scan Tool’s
”Clear Info” function.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
DPoor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed–out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal to wire connection.
DDamaged harness Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the ECM, turn the ignition ON and observe a voltmeter
connected to the MIL driver circuit at the ECM harness
connector while moving connectors and wiring
harnesses relates to the MIL. A change in voltage will
indicate the location of the fault.
DReviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since
the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how
often the condition that caused the DTC to be set
occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
The following ECM pins are controlled by
output driver modules (ODMs):
DA13 MIL LAMP
DA14 Rear Defogger
DB14 A/C Clutch
DB16 EVAP Canister Parge Solenoid
DA1 2 Low Fuel
DC10 Tacho Meter
DC11 Fuel Gauge
DC13 Fan Low
DC12 Fan High
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. The Tech 2 Driver Module Status indicates the ECM
pin that is affected.
9. The Tech 2 may indicate “short circuit” even when
the problem is an open circuit. The cause of an
open circuit may be in the component itself.
11. A short to ground on the ignition side of the
component will blow the fuse. Since the fuse was
checked in Step 2, a short to ground would be
between the affected component and the ECM.
DTC P1640 –Output Driver Module (ODM) “A” Fault
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
2Check the fuse for the driver circuit that was shown as
faulty.
Was the fuse blown? —Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Check for a short to ground between the fuse and
the affected component.
2. Replace the fuse after making any necessary
repairs.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
41. Disconnect the ECM connector for the affected
driver circuit.
Is there any damage to the ECM pin or connector? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Repair the damaged pin or terminal.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
6Was the Lamp of circuit for “Check Engine”? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 13
71. Leave the ECM connector for the lamp driver circuit
disconnected.
2. Ignition “ON.”
3. Using a DVM, check the voltage at the ECM
connector for the affected lamp driver circuit.
Was the voltage equal to the specified value? B+ Go to Step 15 Go to Step 8
81. Ignition “ON.”
2. Check for battery voltage at the fuse for the affected
lamp circuit.
Was battery voltage available at the fuse? —Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9Repair the open circuit between the ignition switch and
the fuse.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
10 1. Ignition “OFF.”
2. Disconnect the ECM connector for the affected
driver terminal.
3. Connect an ohmmeter between a good ground and
the ECM connector for the affected driver.
Did the ohmmeter indicate continuity? —Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Repair the short to ground between the affected
component and its ECM driver terminal.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 Repair the open circuit between the fuse and the ECM
driver terminal for the affected circuit.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
13 1. Connect the ECM.
2. Start the engine and let it idle.
3. Backprobe the affected terminal at the ECM with a
DVM.
Was the voltage equal to the specified value? B+ Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
14 1. Run the engine at idle.
2. Check for battery voltage at the fuse for the affected
circuit.
Was battery voltage available at the fuse? —Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
15 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —

SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Before using this section, perform the ”On–Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” and verify all of the
following items:
DThe engine control module (ECM) and malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL)(Check Engine lamp) are
operating correctly.
DThere are no DTC(s) stored.
DTech 2 data is within normal operating range. Refer to
Typical Scan Data Values.
DVerify the customer complaint and locate the correct
symptom in the table of contents. Perform the
procedure included in the symptom chart.
VISUAL/PHYSICAL CHECK
Several of the symptom procedures call for a careful
visual/physical check. This can lead to correcting a
problem without further checks and can save valuable
time. This check should include the following items:
DECM grounds for cleanliness, tightness and proper
location.
DVacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections, as shown on the ”Vehicle Emission
Control Information” label. Check thoroughly for any
type of leak or restriction.
DAir intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas.
DAir leaks at throttle body mounting area, manifold
absolute pressure (MAP) sensor and intake manifold
sealing surfaces.
DIgnition component for cracking, hardness, and
carbon tracking.
DWiring for proper connections, pinches and cuts.
INTERMITTENTS
An intermittent problem may or may not turn on the mal-
function indicator lamp (MIL) or store a Diagnostic
Trouble Code. DO NOT use the Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) charts for intermittent problems. The fault must be
present to locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical
check for the following conditions:
DPoor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not
fully seated in the connector (backed out).
DImproperly formed or damaged terminal.
DAll connector terminals in the problem circuit should
be carefully checked for proper contact tension.
DPoor terminal–to–wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to
check.
Road test the vehicle with a J 39200 Digital Multimeter
connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a fault in the circuit being monitored.
Use a Tech 2 to help detect intermittent conditions.
The Scan Tools have several features that can be used to
locate an intermittent condition. Use the following feature
to find intermittent faults:
DUsing a Scan Tool’s ”Freeze Frame” buffer or ”Failure
Records” buffer can aid in locating an intermittent
condition. Review and record the information in the
freeze frame or failure record associated with the
intermittent DTC being diagnosed. The vehicle can
be driven within the conditions that were present
when the DTC originally set.
To check for loss of diagnostic code memory, disconnect
the MAP sensor and idle the engine until the MIL (Check
Engine lamp) comes on. Diagnostic Trouble Code P0107
should be stored and kept in memory when the ignition is
turned OFF. If not, the ECM is faulty. When this test is
completed, make sure that you clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Code P0107 from memory.
An intermittent MIL (Check Engine lamp) with no stored
Diagnostic Trouble Code may be caused by the following:
DIgnition coil shorted to ground and arcing at ignition
wires or plugs.
DMIL (Check Engine lamp) wire to ECM shorted to
ground.
DPoor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams.
Check for improper installation of electrical options such
as lights, cellular phones, etc. Check all wires from the
ECM to the ignition coils for poor connections.
Check for an open diode across the A/C compressor
clutch and check for other open diodes (refer to wiring
diagrams in Electrical Diagnosis).
If problem has not been found, refer to ECM Connector
Symptom tables.
HARD START SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Engine cranks, but does not start for a long time. Does
eventually run, or may start but immediately stalls.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the ”On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Check engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for
shift in value.
1. After 8 hours with the hood up and the engine not
running, connect the Tech 2.
2. Ignition ON, engine not running.
3. Using the Tech 2, compare Engine Coolant
Temperature to Intake Air Temperature.
Are ECT and IAT within the specified value of each
other? ± 5°C (± 9°F) Go to Step 8 Go to Step 5
51. Using a Tech 2, display the engine coolant
temperature and note the value.
2. Check the resistance of the engine coolant
temperature sensor.
3. For resistance specifications, refer to Temperature
vs. Resistance chart in DTC P0118.
Is the actual resistance near the resistance value in the
chart for the temperature that was noted? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete? — Verify repair —
7Locate and repair high resistance or connection in the
ECT signal circuit or the ECT signal circuit or the ECM
sensor ground. — Verify repair —
8Check for a faulty , plugged, or incorrectly installed PCV
valve.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Visually/Physically inspect the secondary ignition
wires. Check for the following conditions:
DVerify that all ignition wire resistance are less than
the specified value.
DVerify that ignition wires are correctly routed to
eliminate cross–firing.
DV erify that ignition wires are not arcing to ground.
Spraying the secondary ignition wires with a light
mist of water may help locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? 22.4 k WVerify repair Go to Step 10
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Check for proper ignition voltage output with a spark
tester5-8840-0383-0.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil
fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Check for a loose ignition control module ground.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 1. Check the ignition coil secondary resistance.
2. Replace the coil if it is not within the specified range
of resistance.
Did the coil require replacement? 9 kW–12 kWVerify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check IAC operation. Perform the procedure in the
diagnostic chart DTC P0506, Step 6.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Check for water or alcohol contaminated fuel.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Perform the procedure in Fuel System Pressure T est to
determine if there is a problem with fuel delivery.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Check for the following engine mechanical problems
(refer to Engine Mechanical):
DLow compression
DLeaking cylinder head gaskets
DWorn camshaft
DCamshaft drive belt slipped or stripped
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
SURGES AND/or CHUGGLES SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Engine power variation under steady throttle or cruise.
Feels like the vehicle speeds up and slows down with no
change in the accelerator pedal.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Be sure that the driver understands A/C compressor
operation as explained in the owner ’s manual. Inform
the customer how the A/C clutch operate.
Is the customer experiencing a normal condition? —System OK Go to Step 5
5Check the fuel control Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1). When monitored on the Tech 2, the H02S1
should respond quickly to different throttle positions. If
it doesn’t check for silicon or other contaminants from
fuel or use of improper RTV sealant. The sensors may
have a white powdery coating. Silicone contamination
sends a rich exhaust signal which causes the ECM to
command an excessively lean air/fuel mixture.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6Check the fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System
Pressure Test.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Monitor ”Long Term Fuel Trim” on the Tech 2.
Is ”Long Term Fuel Trim” in the negative range (rich
condition)? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Check items that can cause the engine to run rich.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0172.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
9Check items that can cause the engine to run lean.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0171.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 Check for proper ignition voltage output with the spark
tester 5-8840-0383-0.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Check for a loose ignition control module ground.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 Visually/Physically inspect the secondary ignition
wires. Check for the following conditions.
DVerify that all ignition wire resistance are less than
the specified value.
DVerify that ignition wires are correctly routed to
eliminated cross–firing.
DV erify that ignition wires are not arcing to ground.
Spraying the secondary ignition wires with a light
mist of water may help to locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? 22.4 WVerify repair Go to Step 13
13 1. Check ignition coil secondary resistance.
2. Replace the coil if it is not within the specified range
of resistance.
Did the coil require replacement? 9 kW– 12 kWVerify repair Go to Step 14
14 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil
fouling, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits or improper heat range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 1. Check the injector connectors.
2. If any of the connectors are connected at an
improper cylinder, correct as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Check the ECM grounds to verify that they are clean
and tight. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Visually/physically check the vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks and proper connections and routing as shown on
the ”Vehicle Emission Control Information” label.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 Check the exhaust system for a possible restriction:
Ddamaged or collapsed pipes
Dinternal muffler failure
DRefer to Restricted Exhaust System Check to
measure back pressure and determine if the
catalytic converter is plugged. — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 1. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection.
DTech 2 data.
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer.
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
LACK OF POWER, SLUGGISH OR SPONGY SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Engine delivers less than expected power. Little or no
increase in speed when accelerator pedal is pushed down
part–way.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
41. Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or
restrictions. Refer to Air Intake System in
On–Vehicle Service.
2. Replace the air filter element if necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5Check for proper ignition voltage output with the spark
tester 5-8840-0385-0.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Remove the spark plugs and check gas or oil
fouling, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits or improper heat range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Check the fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System Test.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8Check for water or alcohol contaminated fuel.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check the ECM grounds to verify that they are clean
and tight. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 Check the exhaust system for a possible restriction:
DDamaged or collapsed pipes
DInternal muffler failure
DRefer to Restricted Exhaust System Check to
measure backpressure and determine if the
catalytic converter is plugged.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11

Step NoYesValue(s)Action
11 Check for the following engine mechanical problems:
DLow compression
DLeaking cylinder head gasket
DWorn or incorrect camshaft
DLoose timing belt
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 1. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection.
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer.
DAll electrical connections within suspected
circuit and/or system.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
DETONATION/SPARK KNOCK SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration.
The engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change
with throttle opening.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
41. If Tech 2 readings are normal and there are no
engine mechanical faults, fill the fuel tank with a
known quality gasoline that has a minimum octane
rating of 87. Refer to Typical Scan Values.
2. Re–evaluate the vehicle performance.
Is detonation present? —Go to Step 5 Verify repair
51. Check for obvious overheating problems:
DLow engine coolant.
DRestricted air flow to radiator, or restricted
water flow through radiator.
DIncorrect coolant solution. It should be a 50/50
mix of approved antifreeze/water.
DIncorrect EGR operation. Refer to DTC
P0401.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6Check fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System Pressure
Test.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Check items that can cause an engine to run lean.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0171.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8Check spark plugs for proper heat range. Refer to
General Information.
Were incorrect spark plugs installed? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
91. Remove excessive carbon buildup with a top engine
cleaner. Refer to instructions on the top engine
cleaner can.
2. Re–evaluate vehicle performance.
Is detonation still present? —Go to Step 10 Verify repair
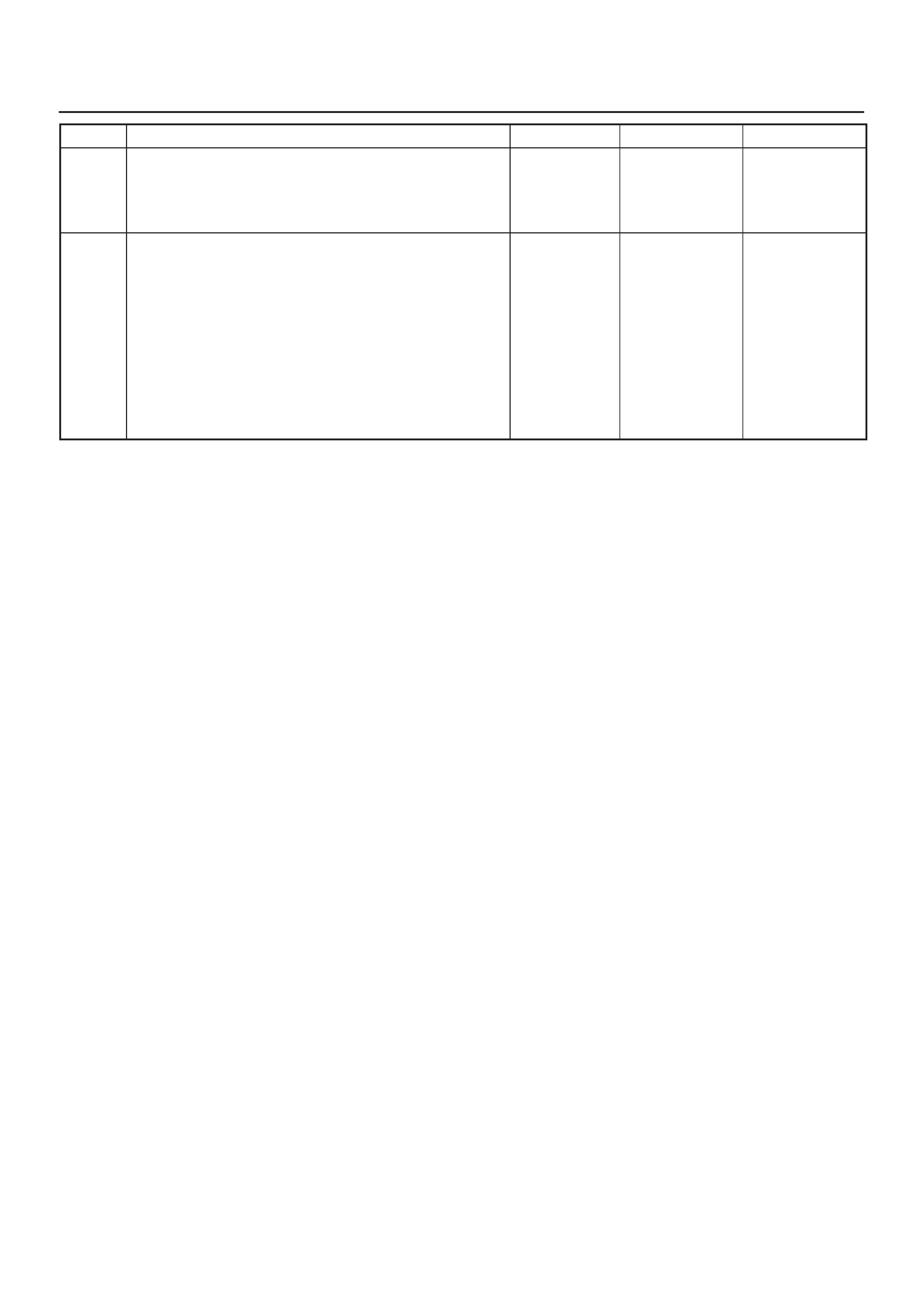
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Check for an engine mechanical problem. Perform a
cylinder compression check. Refer to Engine
Mechanical.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
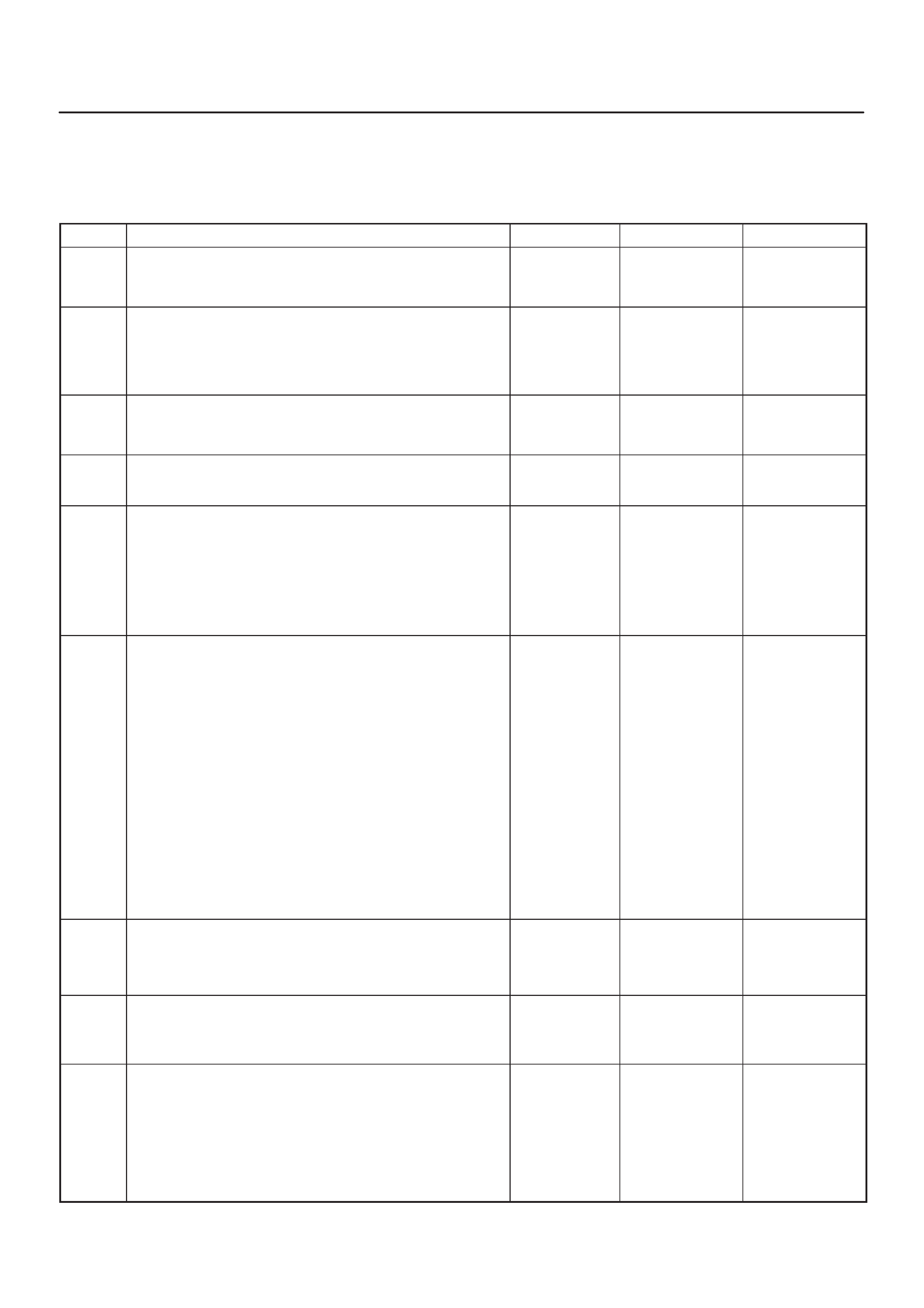
ROUGH, UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT IDLE, STALLING SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Engine runs unevenly at idle. If severe, the engine or
vehicle may shake. Engine idle speed may vary in RPM.
Either condition may be severe enough to stall the engine.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed, including the
rotor, ignition coil and secondary ignition wires? —Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Verify that the EGR valve is not mounted backwards.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Check for incorrect idle speed. Ensure that the
following conditions are present:
DEngine fully warm.
DAccessories are OFF.
2. Using a Tech 2, monitor IAC position.
Is the IAC position within the specified values?
Between 10
and 50
counts Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
61. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
DRestricted air intake system. Check for a
restricted air filter element, or foreign objects
blocking the air intake system.
DCheck for objects blocking the IAC passage or
throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC
passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive
deposits in the throttle bore and on the throttle
plate.
DCheck for a condition that causes a large
vacuum leak, such as an incorrectly installed
or faulty crankcase ventilation valve brake
booster hose.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Using a T ech 2, monitor TP angle with the engine idling.
Is the TP angle at the specified value and steady? 0% Go to Step 8
For further
diagnosis,
refer to DTC
P0123
8Check for proper ignition voltage output with the spark
tester 5-8840-0383-0.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
91. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil
fouling, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits or improper heat range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of the fouling
must be determined before replacing the spark
plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
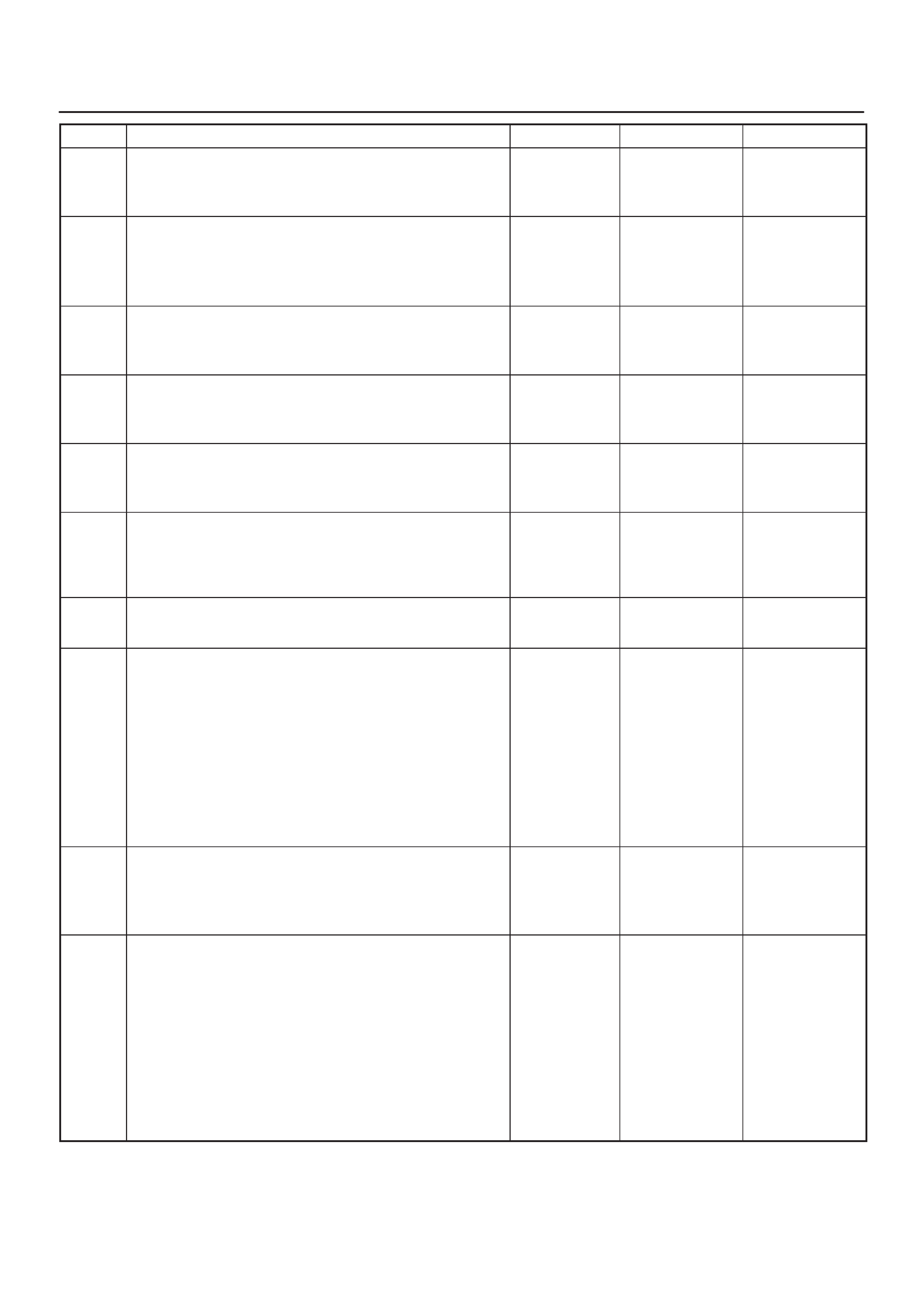
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Check for a loose ignition control module ground. Refer
to Electrical Ignition System.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Monitor ”Long Term Fuel Trim” on the Tech 2.
Is ”Long Term Fuel Trim” in the negative range (rich
condition)? —Go to Step 12 Go to Step 13
12 Check the items that can cause the engine to run rich.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0172.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Is ”Long Term Fuel Trim” significantly in the positive
range (lean condition)?
——Go to Step 14 Go to Step 15
14 Check items that can cause the engine to run leading.
Refer to ”Diagnostic Aids” in DTC P0171.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
15 Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Perform the Injector Coil/Balance Test.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 1. Check the following engine mechanical problems:
DLow compression
DLeaking cylinder head gasket
DWorn or incorrect camshaft
DSticking or leaking valves
DValve timing
DBroken valve springs
DCamshaft drive belt slipped or stripped.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 1. Check for faulty motor mounts. Refer to Engine
Mechanical for inspection of mounts.
2. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
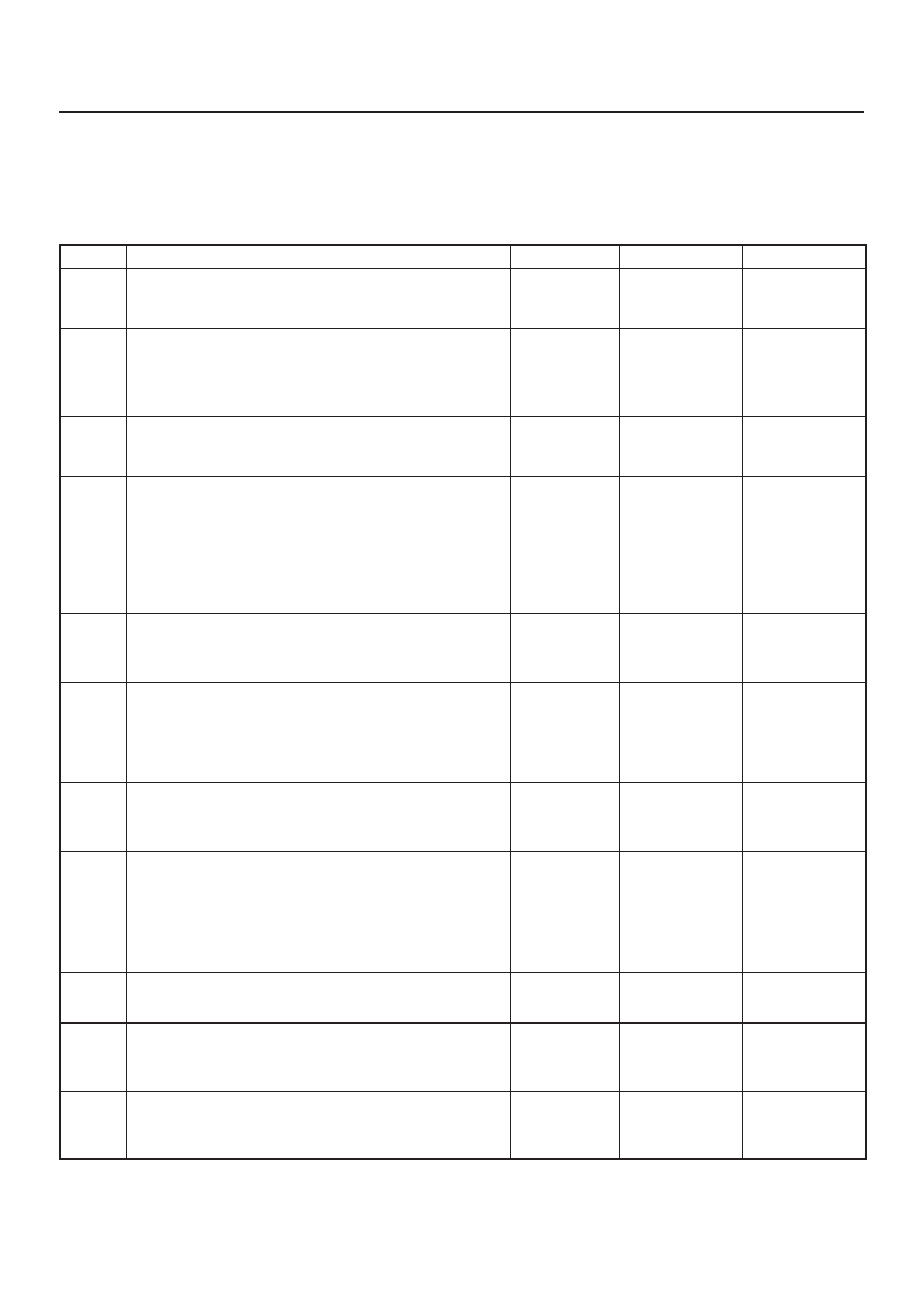
POOR FUEL ECONOMY SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road test, is
noticeably lower than expected. Also, economy is
noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time,
as previously shown by an actual road test.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Check owner’s driving habits.
DIs the A/C ON full time (defroster mode ON)?
DAre tires at the correct pressure?
DAre excessively heavy loads being carried?
DIs acceleration too much, too often? —Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Review the items in Step 4 with the customer and
advise as necessary.
Is the action complete? —System OK —
61. Visually/physically check: Vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and improper connections and routing as
shown on the ”Vehicle Emission Control
Information” label.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Remove and check the air filter element for dirt or for
restrictions.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
81. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil
fouling, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes of heavy deposits.
2. Is spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9Check for low engine coolant level.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 Check for an incorrect or faulty engine thermostat.
Refer to Engine Cooling.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Check for low engine compression. Refer to Engine
Mechanical.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
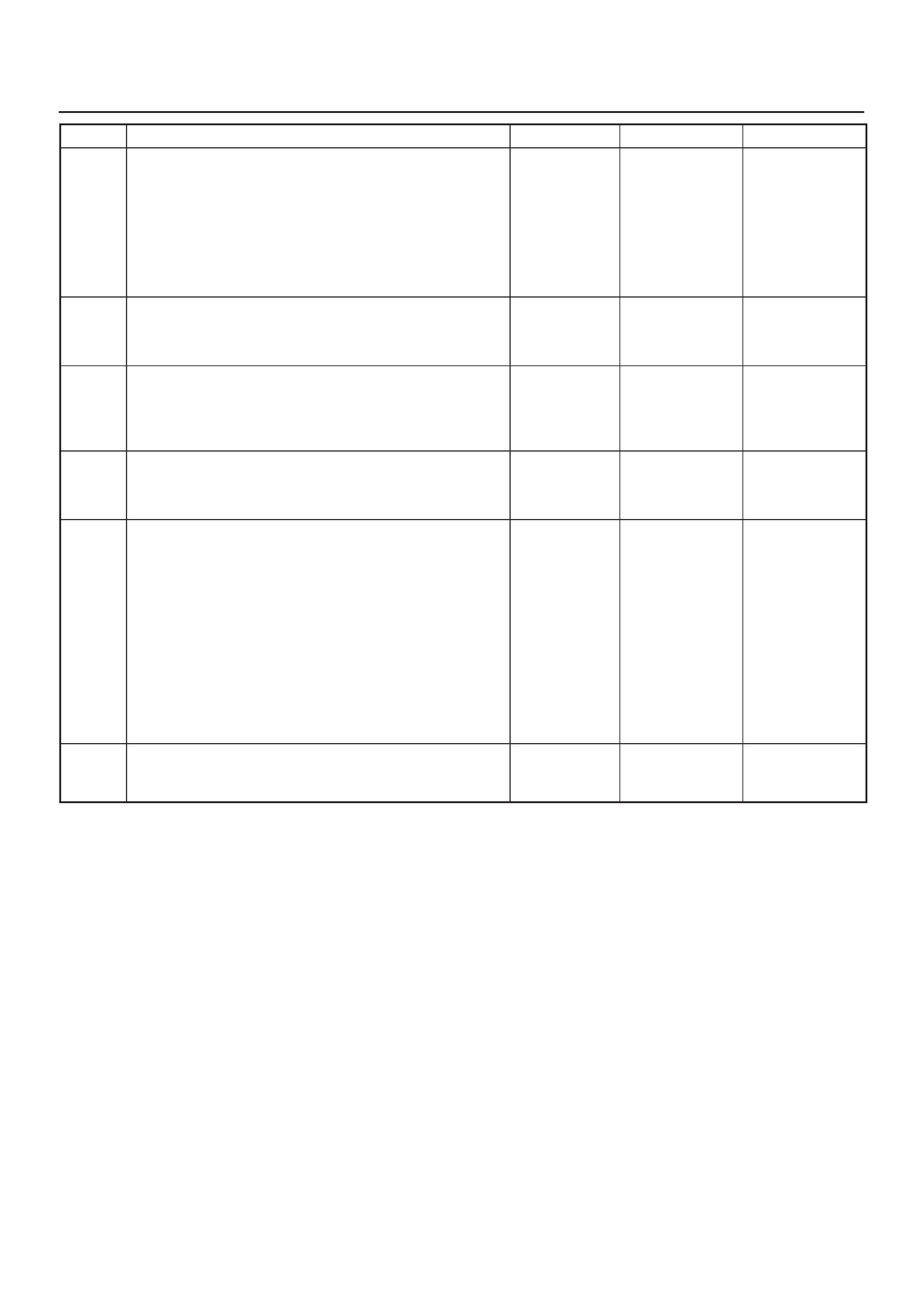
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 Check for excessive exhaust system back–pressure.
Refer to Restricted Exhaust System Check. Possible
problems could be:
DDamaged or collapsed pipes.
DInternal muffler failure.
DPlugged catalytic converter.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check for proper calibration of the speedometer.
Does the speed indicated on the speedometer closely
match the vehicle speed displayed on the Tech 2? —Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
14 Diagnose and repair the inaccurate speedometer
condition as necessary . Refer to Vehicle Speed Sensor
in Electrical Diagnosis. — Verify repair —
15 Check the air intake system and the crankcase for air
leaks.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll connections within a suspected circuit
and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Perform the procedure in Fuel System Pressure Test.
Was the fuel pressure normal? —
Contact
Technical
Assistance Verify repair
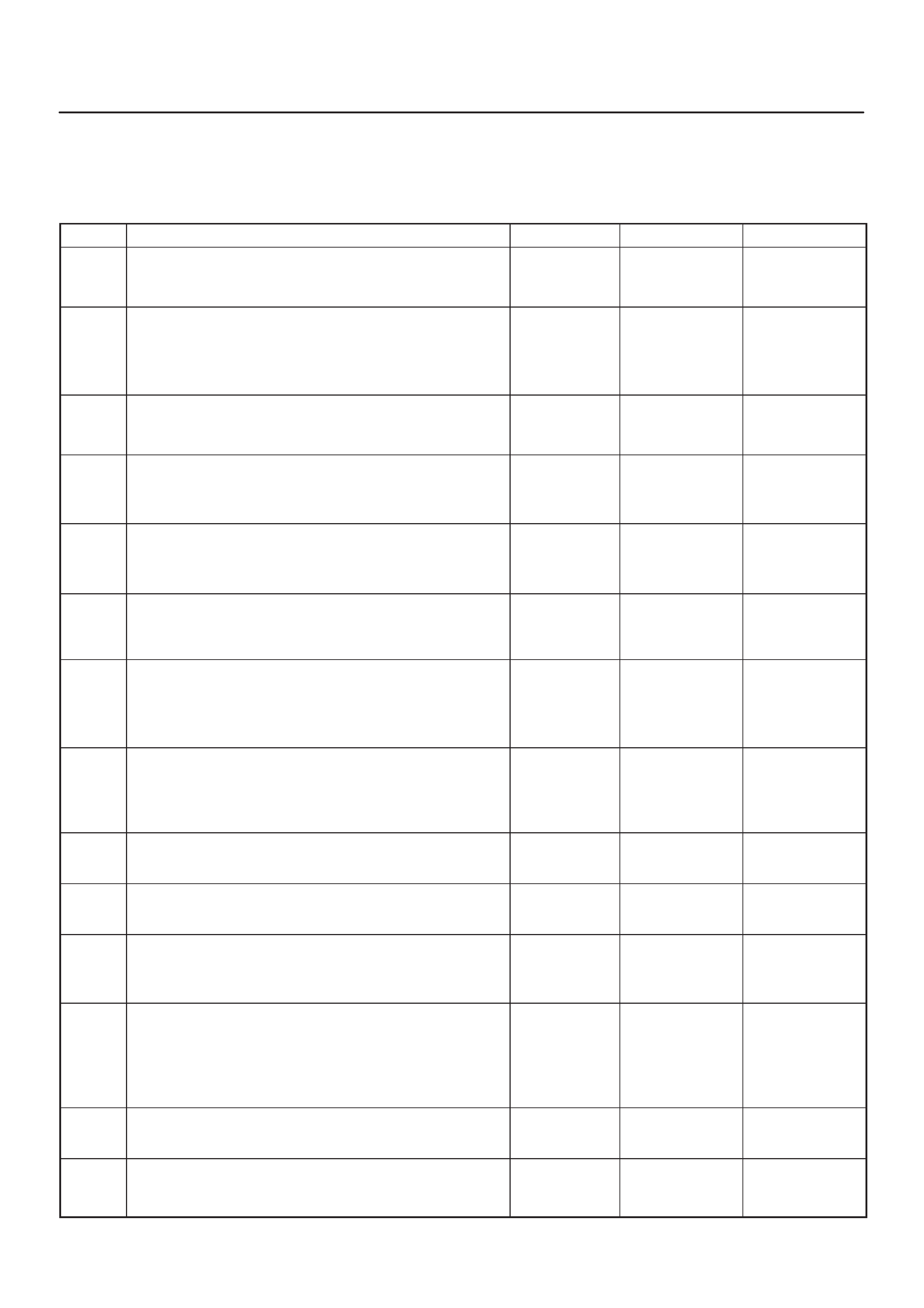
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS OR ODORS SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Vehicle fails an emission test. There is excessive ”rotten
egg” smell. (Excessive odors do not necessarily indicate
excessive emissions.)
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 3
3Was visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Check for vacuum leaks (vacuum lines, intake
manifold, throttle body, etc.)
Were any vacuum leaks found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 5
51. Check fuel cap for proper installation.
2. Secure the fuel cap if necessary.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 6
61. Check the fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System
Pressure Test.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 7
71. Check for faulty, plugged or incorrectly installed
PCV valve.
2. Verify that the PCV system is not plugged.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 8
8Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 9
9Perform the Injector Balance Test by Tech 2.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 10
10 Check for a problem with the engine cooling system.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 11
11 Check the EVAP canister for fuel loading. Refer to
Evaporative Emission Control System.
Was a problem found? —Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
12 1. Remove excessive carbon build-up with a top
engine cleaner. Refer to the instructions on the top
engine cleaner can.
2. Perform the exhaust emission test.
Does the vehicle pass the test? —System OK Go to Step 14
13 Perform the exhaust emission test.
Does the vehicle pass the test? —System OK Go to Step 14
14 Does the exhaust emission test indicate excessive HC
levels, or is ”Long Term Fuel Trim” significantly in the
negative range (rich condition)? —Go to Step 15 Go to Step 16
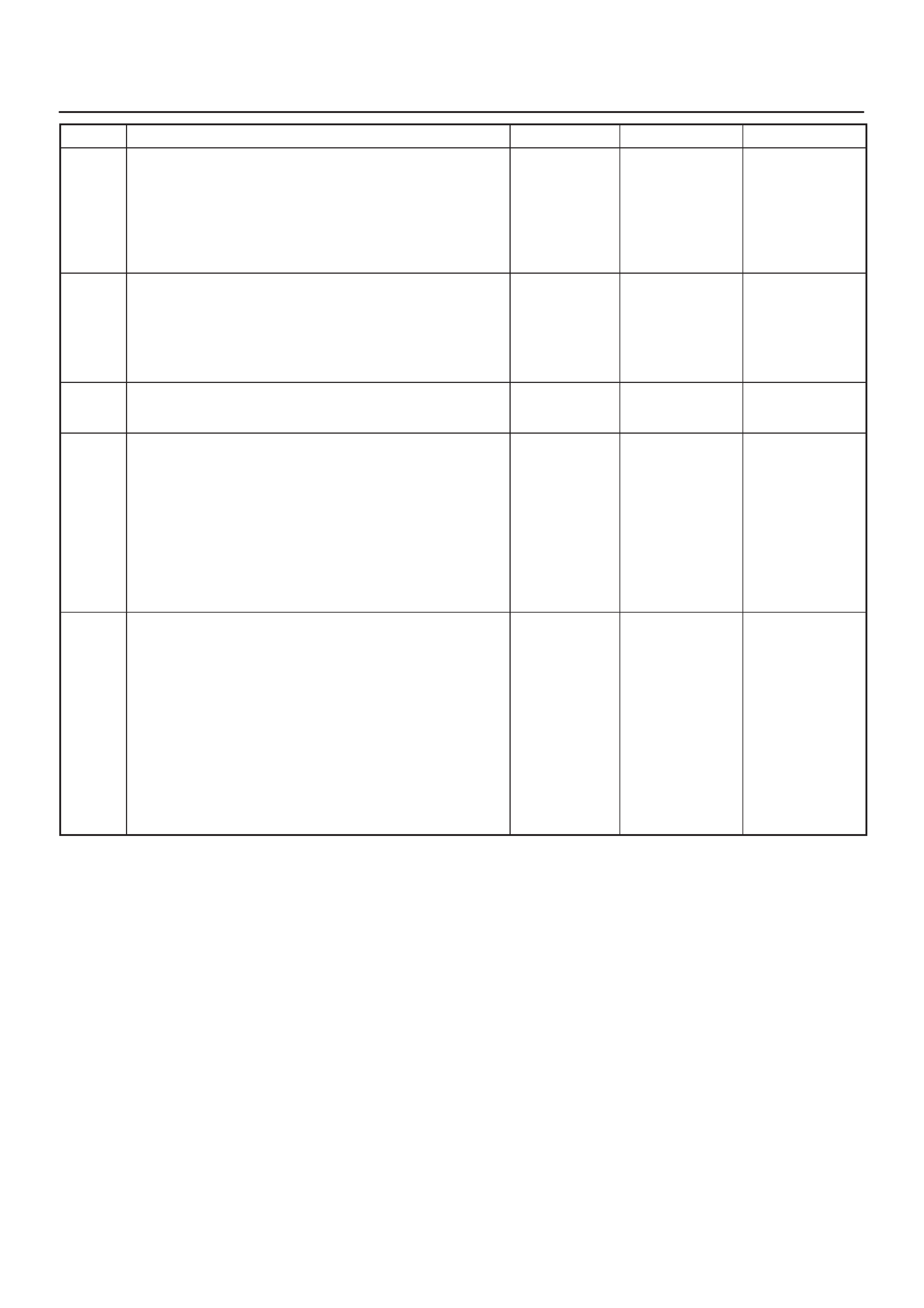
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
15 1. Check items that can cause the engine to run rich.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0172 Diagnostic
Support.
Make any necessary repairs.
2. Perform the exhaust emission test.
Does the vehicle pass the test? —System OK Go to Step 17
16 1. Check items that can cause the engine to run lean.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0171.
Make any necessary repairs.
2. Perform the exhaust emission test.
Does the vehicle pass the test? —System OK Go to Step 17
17 Check the EGR system (refer to DTC P0401).
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 Check for the following engine mechanical problems.
DLow compression
DLeaking cylinder head gasket
DWorn or incorrect camshaft
DSticking or leaking valves
DValve timing
DBroken Valve springs
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 1. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
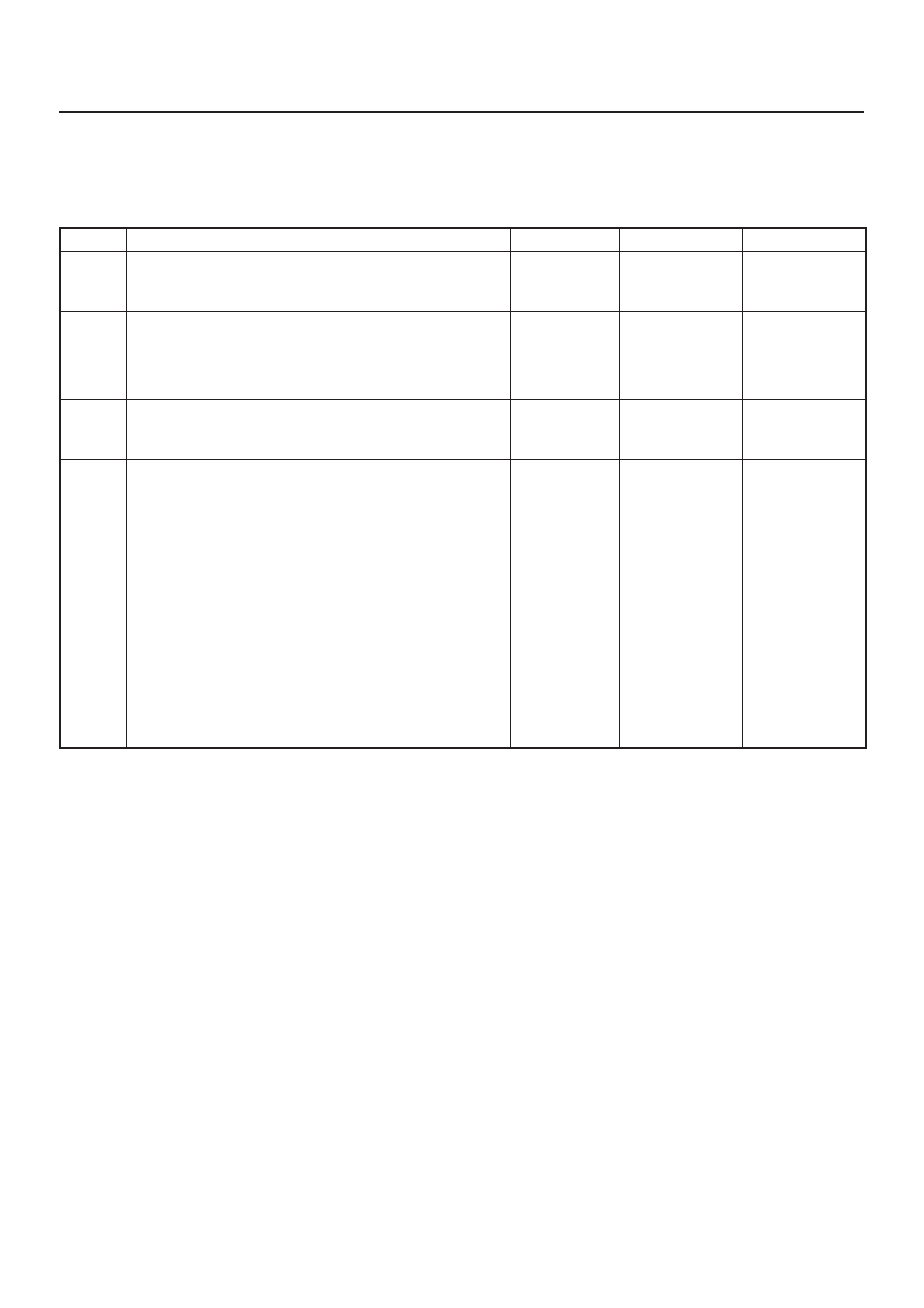
DIESELING, RUN–ON SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Engine continues to run after key is turned OFF, but runs
very rough. If engine runs smoothly, check the ignition
switch and adjustment.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
41. Check for a short between B+ and the ignition feed
circuit.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll connections within a suspected circuit
and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
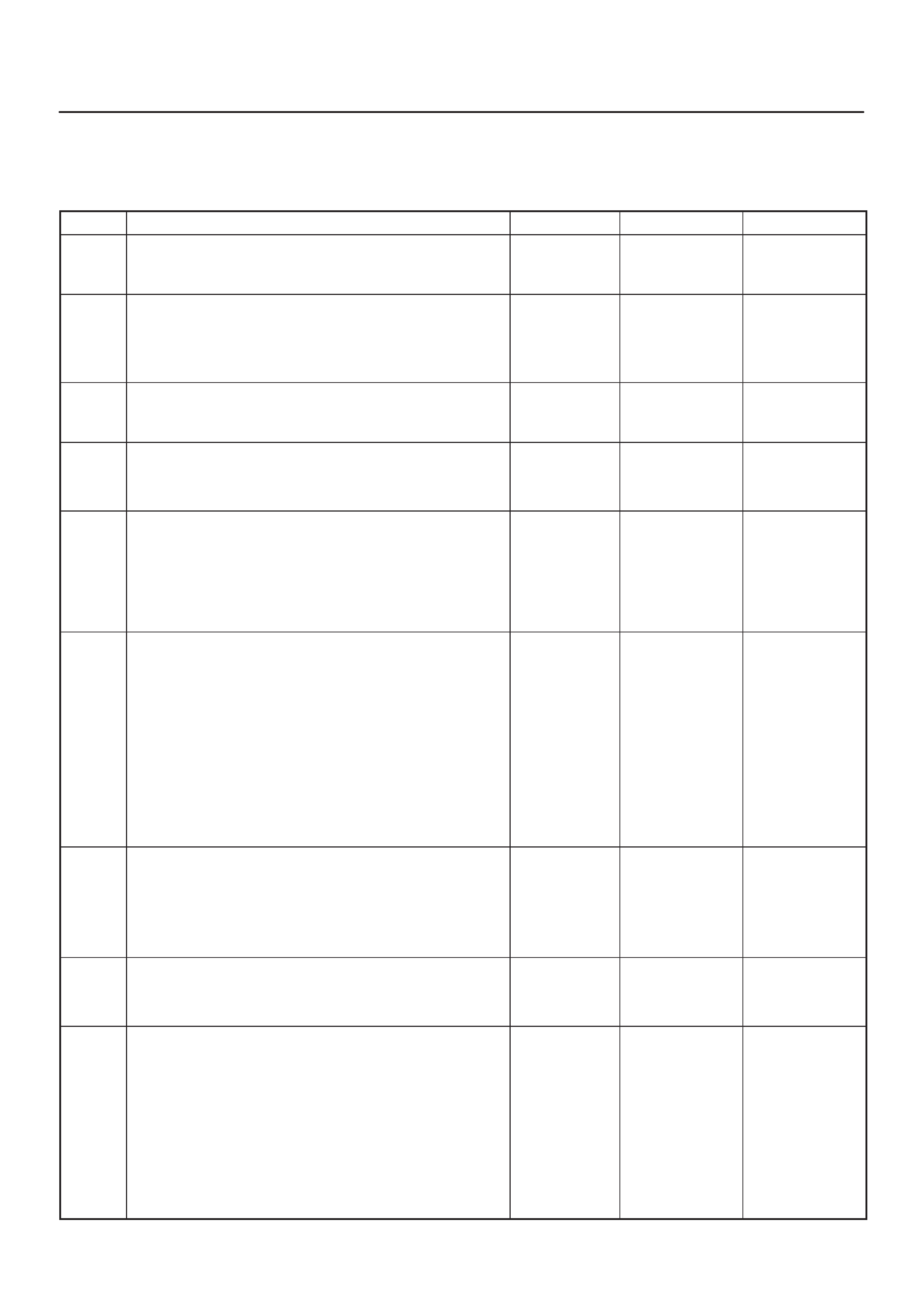
BACKFIRE SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Fuel ignites in the intake manifold, or in the exhaust
system, making a loud popping noise.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester 5-8840-0383-0.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
51. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil
fouling, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes of heavy deposits.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
61. Visually/physically inspect the secondary ignition
wires. Check for the following conditions:
DV erify that all ignition wire resistances are less
than the specified value.
DV erify that ignition wires are correctly routed to
eliminate cross–firing.
DVerify that ignition wires are not arcing to
ground. Spraying the secondary ignition wires
with a light mist of water may help locate an
intermittent problem.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7Check for an intermittent ignition system malfunction:
DIntermittent CKP 58X signal.
DIntermittent ignition feed circuit or sensor ground
circuit to the crankshaft position sensor.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8To determine if there is a problem with fuel delivery,
refer to Fuel System Diagnosis.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
91. Check for the following engine mechanical
problems:
DLow compression
DLeaking cylinder head gasket
DWorn or incorrect camshaft
DIncorrect valve timing
DSticking or leaking valves
DCamshaft drive belt slipped or stripped.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
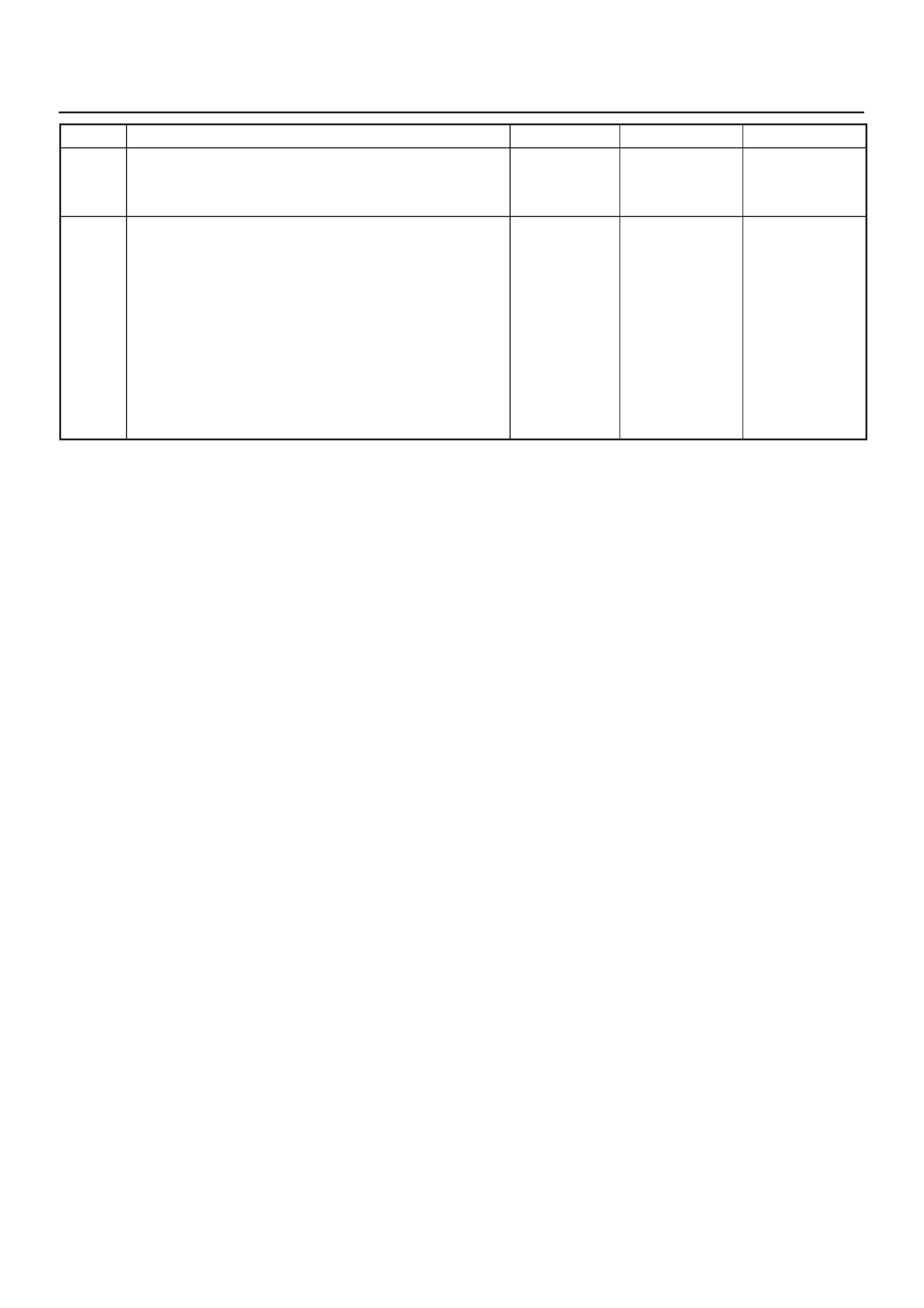
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
10 Check the intake and exhaust manifold(s) for casting
flash. Refer to Engine Mechanical.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance

CUTS OUT, MISSES SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine speed;
usually more pronounced as engine load increases.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
4Check the ECM grounds to verify that they are clean
and tight. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Monitor ”Long Term Fuel Trim” on the Tech 2.
Is the ”Long Term Fuel Trim” in the negative range (rich
condition)? —Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6Check items that can cause the engine to run rich.
Refer to ”Diagnostic Aids” in DTC P0172.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
7Is the long term fuel trim significantly in the positive
range (lean condition)? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Check items that can cause the engine to run lean.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0171.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
91. Check for incorrect idle speed. Ensure that the
following conditions are present:
DEngine fully warm.
DAccessories are OFF.
2. Using a Tech 2, monitor the IAC position.
Is the IAC position within the specified values?
Between 5
and 50
counts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
10 1. Visually/physically inspect for the following
conditions:
DRestricted air intake system. Check for a
restricted air filter element, or foreign objects
blocking the air intake system.
DCheck for objects blocking the IAC passage or
throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC
passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive
deposits in the throttle bore and on the throttle
plate.
DCheck for a condition that causes a large
vacuum leak, such as an incorrectly installed
or faulty crankcase ventilation valve or brake
booster hose disconnected.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
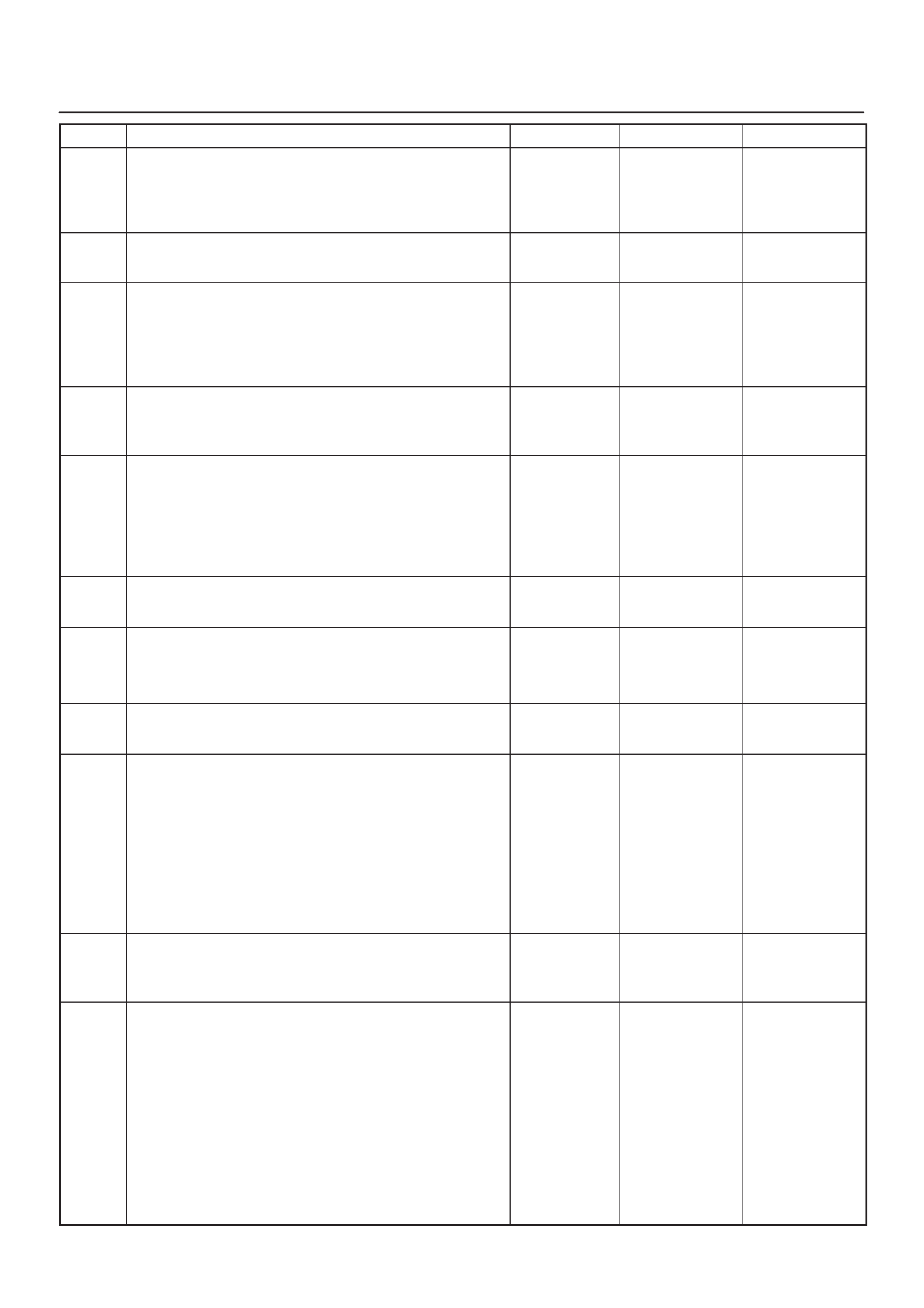
Step NoYesValue(s)Action
11 Check the injector connections. If any of the injectors
are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 1. Perform the Injector Coil/Balance Test.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 1. Check for fuel in the pressure regulator vacuum
hose.
2. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator
assembly.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester J 26792.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 1. Remove spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling,
cracks, wear, improper gap, burned electrodes of
heavy deposits.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Check for a loose ignition control module ground.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Using a Tech 2, monitor the TP angle with the engine
idling.
Is the TP angle at the specified value and steady? 0% Go to Step 18
For further
diagnosis,
refer to DTC
P0123
18 Check the PCV valve for proper operation.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 Check for the following engine mechanical problems:
DLow compression
DLeaking cylinder head gasket
DWorn or incorrect camshaft
DIncorrect valve timing
DSticking or leaking valves
DCamshaft drive belt slipped or stripped.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
20 Check for faulty motor mounts. Refer to Engine
Mechanical for inspection of the mounts.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 21
21 1. Review all the diagnostic procedures within this
table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
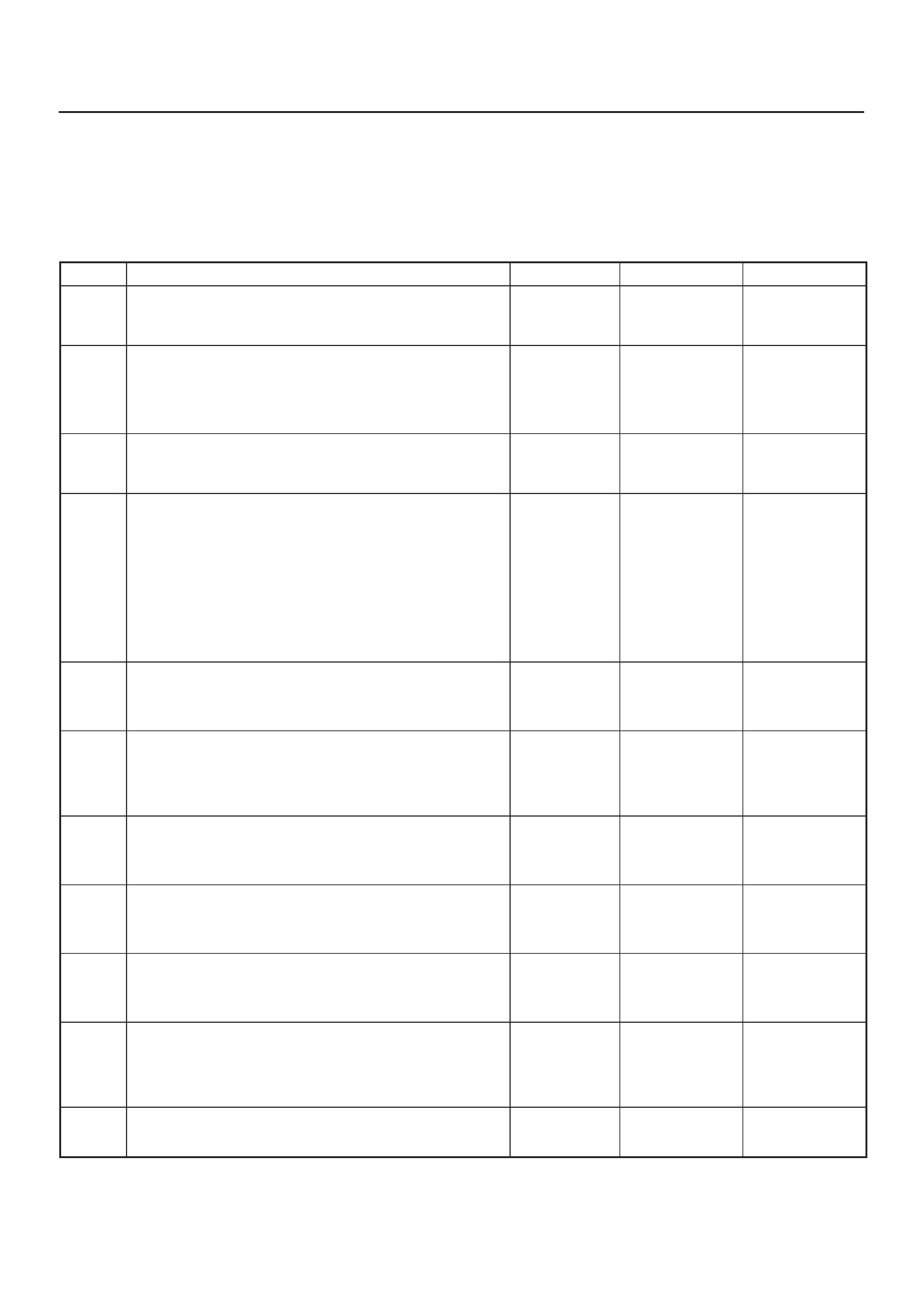
HESITATION, SAG, STUMBLE SYMPTOM
DEFINITION:
Momentary lack of response as the accelerator is pushed
down. Can occur at any vehicle speed. Usually most
pronounced when first trying to make the vehicle move,
as from a stop sign. May cause the engine to stall if severe
enough.
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Perform a bulletin search.
2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,
correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3Was a visual/physical check performed?
—Go to Step 4
Go to Visual /
Physical
Check
41. Check the fuel control heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S1). The HO2S1 should respond quickly to
different to throttle positions. If it doesn’t, check for
silicon or other contaminants from fuel or use of
improper RTV sealant. The sensors may have a
white powdery coating. Silicon contamination
sends a rich exhaust signal which causes the ECM
to command an excessively lean air/fuel mixture.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5Check the fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System
Pressure Test.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6Observe the ”TP angle” display on the Tech 2 while
slowly increasing throttle pedal.
Does the TP angle display steadily increase from 0% at
closed throttle to 100% at WOT? —Go to Step 7 Go to Step 13
7 Monitor ”Long Term Fuel Trim” on the Tech 2.
Is the ”Long Term Fuel Trim” in the negative range (rich
condition)? —Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Check items that can cause the engine to run rich.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0172.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
9Check items that can cause the engine to run lean.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in DTC P0171.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
10 Check for proper ignition voltage output with spark
tester 5-8840-0383-0. For the procedure, refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 11
11 Check for a loose ignition control module ground.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12

Step NoYesValue(s)Action
12 Visually/physically inspect the secondary ignition
wires. Check for the following conditions:
DVerify that all ignition wire resistances are less
than the specified value.
DValue that ignition wires are correctly routed to
eliminate cross–firing.
DV erify that ignition wires are not arcing to ground.
Spraying the secondary ignition wires with a light
mist of water may help locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? 30,000 WVerify repair Go to Step 14
13 Replace the TP sensor. — Verify repair —
14 1. Check the ignition coil secondary resistance.
2. Replace the coil if it is not within the specified value.
Was a problem found? 9 kW– 12kWVerify repair Go to Step 15
15 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil
fouling, cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes of heavy deposits.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must
be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 16
16 Check the ECM grounds to verify that they are clean
and tight. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 Visually/physically check vacuum hoses for splits,
kinks, and proper connections and routing as shown on
the Vehicle Emission Control Information label.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 1. Review all diagnostic procedures within this table.
2. If all procedures have been completed and no
malfunctions have been found, review/inspect the
following:
DVisual/physical inspection
DTech 2 data
DFreeze Frame data/Failure Records buffer
DAll electrical connections within a suspected
circuit and/or system
3. If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair
Contact
Technical
Assistance
RESTRICTED EXHAUST SYSTEM CHECK
Step Action Value(s) YesNo
1Was the On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
performed? —Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Remove the HO2S2.
DFor removal procedures, refer to Heated
Oxygen Sensors in On–Vehicle Service.
2. Install the Exhaust Backpressure Tester in place of
the Bank 1 HO2S.
3. Idle the engine at normal operating temperature.
Does the reading on the gauge exceed the specified
value? 8.62 kPa
(1.25 psi) Go to Step 5 Go to Step 3
3With the exhaust back–pressure tester in place of
HO2S, and the engine at normal operating
temperature:
Increase the engine speed to 2000 RPM while
observing the gauge.
Does the reading exceed the amount of the value
column? 8.62 kPa
(1.25 psi) Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
41. Re–install the HO2S2. (Refer to Heated Oxygen
Sensors in On–Vehicle Service for installation
procedure.)
2. Remove the HO2S1.
3. Install the Exhaust Back–Pressure T ester BT8515V
or equivalent in place of the HO2S1.
4. Bring the engine to normal operating temperature
while observing the gauge.
5. Increase the engine speed to 2000 RPM (allow 10
seconds for pressure build) and observe the gauge.
Did the reading exceed the specified value? 8.62 kPa
(1.25 psi) Go to Step 6 System OK
5Repair a restiction in the exhaust system after the
catalytic converter.
Possible faults include:
DCollapsed pipe
DInternal muffler failure — Verify repair —
6Replace the restricted catalytic converter. — Verify repair —
NOTE: Diagnostic Trouble Codes will be set by running
the vehicle to normal operating temperature after a cold
start with the O2 sensor disconnected. After performing
these tests, use the Tech 2 to erase the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes that were set by the lack of O2 sensor
activity.
DEFAULT MATRIX TABLE
SERVICE PROCEDURE DEFAULT
STRATEGY
A referral strategy has been established to assist the
technician with additional information when the cause of
the failure cannot be determined. If no problem is found
after performing diagnostics, then for further diagnostic
information, refer to the default matrix table.
DEFAULT MATRIX TABLE
Strategy Based Diagnostic Charts Initial Diagnosis Default Section(s)
On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check Vehicle does not enter diagnostics. Chassis Electrical
On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check Vehicle enters diagnostics and
communicates with the Tech 2. MIL is
ON in diagnostics. Engine does not
start and run.
Ignition System Check
On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check Engine starts and runs, no ECM codes
set. Customer complains of vibration. —
ECM Power and Ground Check On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check. Chassis Electrical
ECM Power and Ground Check On–Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check. ECM power and ground circuits
OK. Data link voltage incorrect.
Chassis Electrical
Symptoms Initial Diagnosis Default Section(s)
Intermittents 1. On–board diagnostic (OBD)
system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspections.
Chassis Electrical
Hard Starts 1. OBD system check.
2. Sensors (ECT, MAP, TP); MAP
output chart.
3. Fuel system electrical test, fuel
system diagnosis.
4. Ignition system.
5. IAC system check.
Engine Mechanical
Ignition System Check
Exhaust System Diagnosis
Surges and/or Chuggles 1. OBD system check.
2. Heated oxygen sensors.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
4. Ignition system.
Calibration ID ”Broadcast
Code”/Service Bulletins
Ignition System Check
Generator Output
Exhaust System Diagnosis
Lack of Power, Sluggish or Spongy 1. OBD system check.
2. Fuel system diagnosis.
3. Ignition system.
4. EGR operation.
5. EGR system check.
Refer to Exhaust System in
Engine Exhaust
TCC Operation
Calibration ID/Service Bulletins
Detonation / Spark Knock 1. OBD system check.
2. EGR operation.
3. EGR system check.
4. Fuel system diagnosis.
5. Ignition system.
Cooling System
Ignition System Check
Calibration ID/Service Bulletins
Symptoms Initial Diagnosis Default Section(s)
Hesitation, Sag, Stumble 1. OBD system check.
2. TP.
3. MAP output check.
4. Fuel system diagnosis.
5. Fuel injector and fuel injector
balance test.
6. EVAP emission canister purge
valve.
7. Ignition system.
EGR Operation
EGR System Check
Generator Output Voltage (refer
to Chassis Electrical)
Calibration ID/Service Bulletins
Ignition System Check
Cuts Out, Misses 1. OBD system check.
2. Cylinder balance test. Ignition System Check
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle,
Stalling 1. OBD system check.
2. Fuel injector and fuel injector
balance test.
3. EVAP emission canister purge
valve check.
4. Ignition system.
5. IAC operation.
6. EGR operation.
MAP Output Check
Throttle Linkage
IAC System Check
EGR System Check
A/C Clutch Control Circuit Diag-
nosis
Crankcase Ventilation System
Calibration ID/Service Bulletins
Generator Output Voltage (refer
to Chassis Electrical)
Exhaust Diagnosis
Poor Fuel Economy 1. OBD system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspection.
3. Ignition system.
4. Cooling system.
TCC Operation
Exhaust System (refer to Engine
Exhaust)
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run 1. OBD system check. Fuel System Electrical
Diagnosis
Fuel System Diagnosis
Fuel Injector
Fuel Injector Balance Test
Excessive Exhaust Emissions or
Odors 1. OBD system check.
2. Emission test.
3. Cooling system.
4. Fuel system diagnosis.
5. Fuel injector and fuel injector
balance test.
6. EVAP emission canister purge
valve.
7. Crankcase ventilation system.
8. Ignition system.
9. MAP output check.
EGR System Check
Exhaust Diagnosis
Calibration ID/Service Bulletins
Dieseling, Run–On 1. OBD system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspection.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
—
Backfire 1. OBD system check.
2. Ignition system.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
4. Fuel injector and fuel injector
balance test.
5. EGR operation, EGR system
check.
Exhaust System Diagnosis,
Intake Casting Flash, Ignition
System Check
Symptoms Initial Diagnosis Default Section(s)
Misfire 1. OBD system check.
2. Ignition system.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
4. Fuel injector and fuel injector
balance test.
Vibrations, Transmission,
Driveshaft and Axle
Catalyst Monitor 1. OBD system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspection.
3. Heated oxygen sensors.
Exhaust System
Fuel Trim 1. OBD system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspection.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
4. Heated oxygen sensors.
Exhaust System Intake Air
System
Evaporative Emissions 1. OBD system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspection.
3. Fuel system diagnosis.
—
Heated Oxygen Sensors 1. OBD system check.
2. Careful visual/physical inspection. Exhaust System
Camshaft Position (CMP)
Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Remove spark plug cover on top of valve cover by
removing four retaining bolts.
3.Disconnect electrical connector from the sensor.
014RX003
4.Remove drive belt. Refer to Engine Mechanical
Section.
5.Remove top harness cover installed on timing belt
cover by removing a retaining screw.
6.Remove the retaining bolts holding crankshaft pulley,
and pull crankshaft pulley while wiggling. Refer to
Engine Mechanical Section.
7.Remove the retaining screws for timing belt cover and
timing belt cover.
014RX004
8.Remove the retaining bolt for the sensor and pull up
camshaft position sensor.
014RX005
Installation Procedure
1.Insert camshaft position sensor in position.
2.Install retaining bolt.
014RX007
3.Install the timing belt cover and the retaining screws.
4.Install the crank shaft pulley and the mounting bolts.
Holes for mounting bolts are off the pitch. The pulley
can be mounted only one way to install all mounting
bolts. Tighten the bolts. Refer to Engine Mechanical
section.
5.Install the drive belt. Refer to Engine Mechanical
Section.
014RX005
6.Install the top harness cover onto timing belt cover.
7.Connect electrical connector to the sensor and
securely lock it.
8.Install the spark plug cover.
9.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX004
Crankshaft Position (CKP)
Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Remove the drive belt. Refer to Engine Mechanical
Section.
014RX003
3.Remove the pwer steering pump and
mounting–bracket from engine.
4.Disconnect electrical connector from the sensor.
014RX006
5.Remove the retaining bolt and sensor from the engine
block.
NOTE:Use caution to avoid any hot oil that might drip
out.
0013
Installation Procedure
1.Install the crank shaft position sensor to its position.
2.Install and tighten the mounting bolt. Refer to Engine
Mechanical Section.
0013
3.Reinstall the power steering pump and bracket to the
engine.
014RX006
4.Reinstall the accessory drive belt.
5.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX003
EEPROM
EEPROM
The Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM) is a permanent memory that is
physically soldered within the ECM. The EEPROM
contains program and calibration information that the
ECM needs to control Powertrain operation.
014RX002
901RX031
Functional Check
1.Perform the On–Board Diagnostic System Check.
2.Start the engine and run for least one minute.
3.Check for DTCs using Tech 2.
4.If the ECM fails to program, proceed as follow:
DEnsure that all ECM connections are OK.
DCheck the ITCS for latest version software.
DAttempt to program ECM again. If ECM still cannot
be programmed properly, replace ECM. The
replacement ECM must be programmed.
Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Drain enough engine coolant so that the coolant level
will be below the ECT sensor.
3.Remove electrical connector from the sensor located
on the intake manifold above the ignition coil.
4.Unscrew the sensor from the manifold.
014RX008
Installation Procedure
1.Install the sensor into the intake manifold. Do not over
tighten.
2.Connect electrical connector.
3.Add engine coolant to required level. Refer to Engine
Cooling System Section.
4.Connect the negative battery cable.
0016
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S)
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Locate the two oxygen sensors.
DBank 1 sensor 1 is mounted on the exhaust pipe
ahead of the catalytic converter.
DBank 1 sensor 2 is mounted on the exhaust pipe
behind the catalytic converter.
3.Disconnect pig tail electrical connector.
IMPORTANT:The pigtail is permanently attached to
the sensor. Be careful not to pull the wires out.
014RX010
4.Unscrew sensors form the exhaust pipe. Because of
the expansion and contraction of the metal in the
exhaust system over time, this may be difficult if the
engine temperature is below 48 degree C.
Inspection Procedure
NOTE: Both sensors are identical. Inspect each inthe
same way.
1.Inspect the pigtail and the electrical connector for
grease, dirt, corrosion and bare wire or worn
insulation.
2.Inspect the louvered end of the sensor for grease,
dirt, excessive carbon build up or other contaminants.
TS23739
Installation Procedure
NOTE: If HO2S is reinstalled after removal, special
anti–seize compound or the equivalent should be applied
to the threads. Special anti–seize compound, (P/N
5613695), is used on the HO2S threads. This compound
consists of glass beads suspended in a liquid graphite
solution. The graphite burns away with exhaust heat, but
the glass beads will remain, making the sensor easier to
remove.
1.Apply anti–seize compound or the equivalent to the
thread.
TS23739
2.Install HO2S on the exhaust pipe.
3.Tighten the sensor to 55 Nm (5.6 kg·m/40 lb ft)
4.Connect the pig tail to the wiring harness.
5.Connect the negative battery cable.
(Pre–Catalytic Converter Heater Oxygen Sensor Loca-
tion)
014RX010
(Post–Catalytic Converter Heater Oxygen Sensor
Location)
014RX009
Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.The IAT sensor is located in the intake air duct
between the air filter and the throttle body.
014RX011
3.Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
4.Remove the sensor from intake air duct by using a
rocking motion while pulling the sensor.
0018
Installation Procedure
1.Install the IAT sensor into intake air duct. Make sure
the sensoris pushed all the way into the intake air
duct.
2.Connect electrical connector.
3.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX011
Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
(The MAP sensoris located on the intake manifold
behind throttle body.)
3.Remove a mounting bolt securing the sensor to the
manifold.
4.Remove the sensor from the intake manifold using
rocking motion while pulling the sensor.
014RX012
Installation Procedure
1.Push MAP sensor into the manifold. Make sure the
sensor is pushed always into its position.
2.Install a mounting bolts and tighten.
3.Connect electrical connector.
4.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX013
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL)
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
Refer to Instrument Panel Removal Procedure.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Damage
Electronic components used in the control system are
often designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to same electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to even feel the zap of a static
discharge. There are several way for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and by induction. An example of
charging by friction is a person sliding across a car seat.
Charging by induction occurs when a person with well
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object and
momentarily touches ground. Charge of the same polarity
are drained off leaving the person highly charged with
opposite polarity. Static charge can cause damage,
therefore, it is important to use care when handling and
testing electronic components.
NOTE:To prevent possible Electrostatic Discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
DDo not touch the control module connector pins or
soldered components on the control module circuit
board.
DDo not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
DBefore removing the parts from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
DIf the parts been handled while sliding across the
seat, or while sitting from standing position, or walking
a distance, touch a known good ground before
installing the parts.
014RX002
NOTE:To prevent internal ECM damage, the ignition
must be OFF position in order to disconnect or reconnect
power to the ECM (for example: battery cable. pig tail,
ECM fuse, jumper cable, etc.).
IMPORTANT:When replacing the production ECM
with a service ECM, it is important to transfer the
broadcast code and production ECM number to the
service ECM label. This will allow positive identification of
ECM parts throughout the service life of the vehicle. Do
not record this information on ECM metal cover.
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Block the wheels.
3.Remove ashtray inner.
4.Remove a screw located behind ashtray.
014RX014
5.Pull out Face trim of console.
6.Remove two screws located inside of center console
storage box and pull up rear part of center console.
014RX015
7.Unscrew the shift knob.
8.Remove four screw holding front part of the console
and pull the console up.
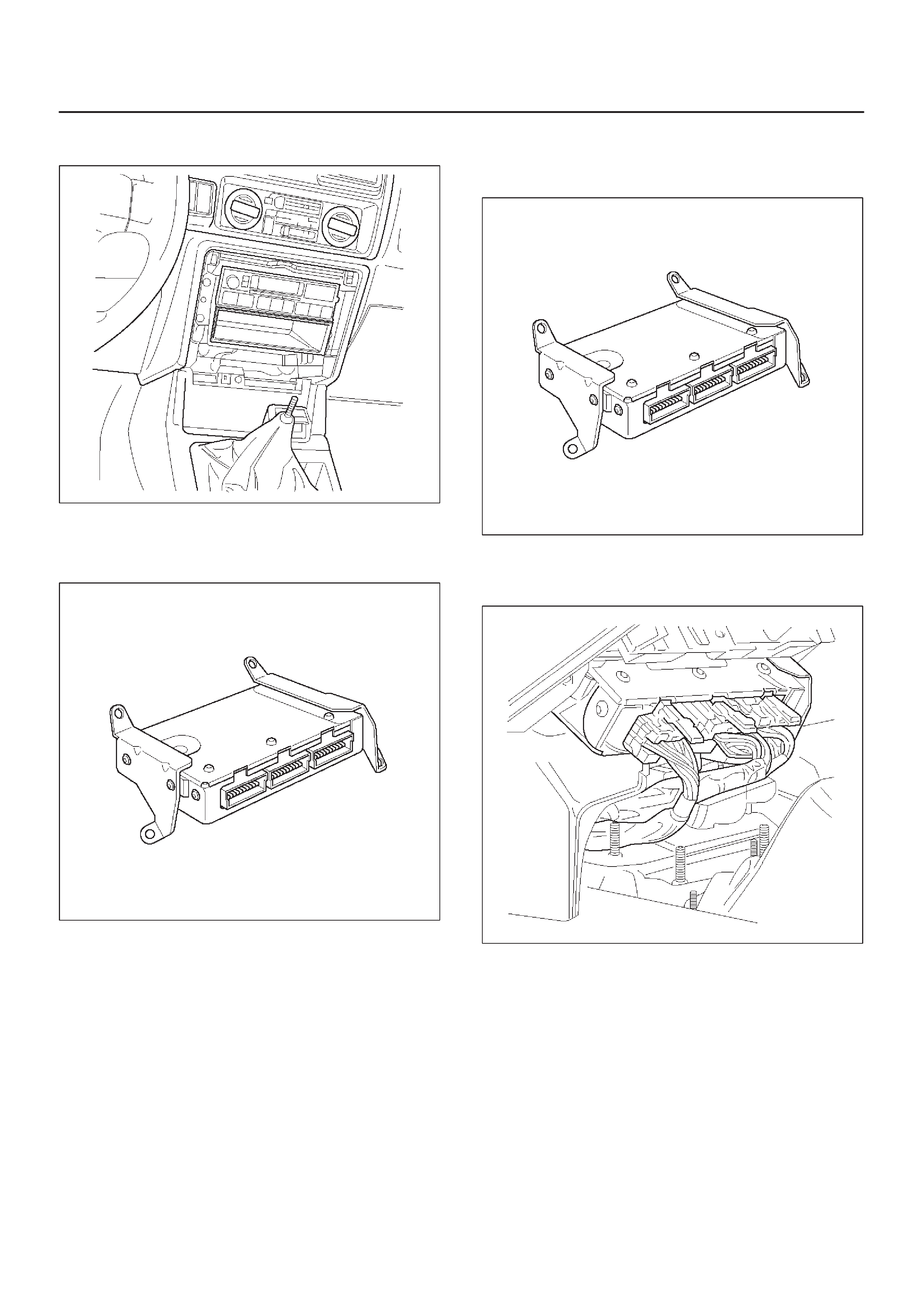
9.Disconnect the red, white and blue electrical
connector at the ECM.
014RX016
10.Remove two nuts in the front of ECM.
11.Remove two nuts in the rear of ECM.
12.Pull the ECM out from dashboard.
014RX002
Installation Procedure
1.Place ECM into its position and secure by four
mounting screws.
014RX002
2.Connect all three connectors to ECM. All connectors
are color keyed. Same color male and female
connectors join together.
014RX017
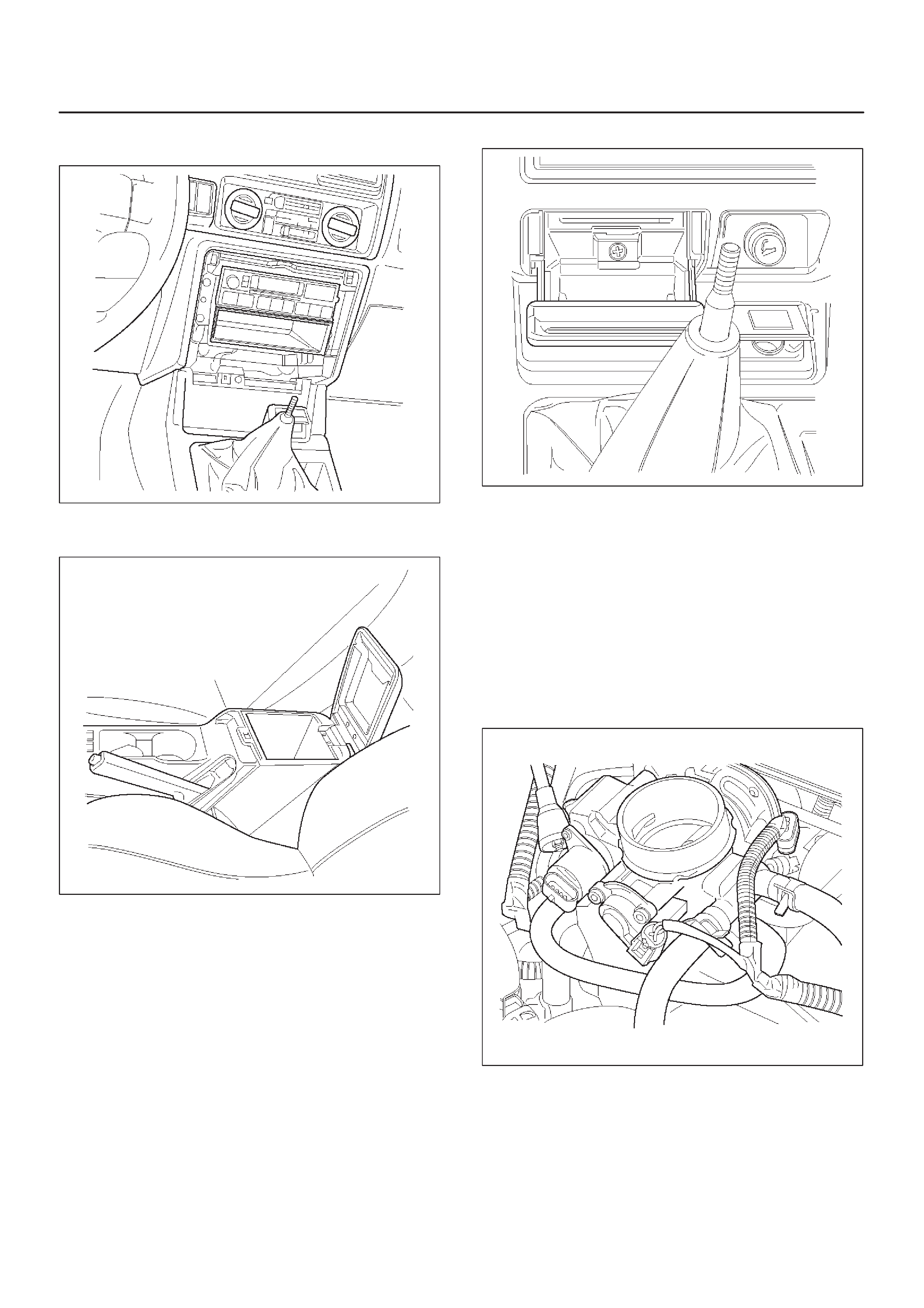
3. Install the front center console and secure by four
retaining screws.
014RX016
4.Install the rear center console and secure it by two
retaining screw into storage box.
014RX015
5.Snap face plate into its position and secure it by a
screw.
6.Insert ashtray inner.
7.Insert the shift knob.
8.Connect the negative battery cable.
9.Remove wheel blocks.
014RX014
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Disconnect the TPS electrical connector.
3.Remove the two screws and TP sensor from the
throttle body.
NOTE: Do not clean the TP sensor by soaking it in
solvent. The sensor will be damaged as a result.
101RX002
Function Check
Use a Tech 2 to check the TP sensor output voltage at
closed throttle.
DThe voltage should be under 0.25 volts.
DIf the reading is greater than 0.25 volts, check the
throttle shaft to see if it is binding. Check that the
throttle cable is properly adjusted, also. Refer to
Throttle Cable Adjustment.
DIf the throttle shaft is not binding and the throttle cable
is properly adjusted, install a new TP sensor.
101RX003
Installation Procedure
1.Install the TP sensor on the throttle body with two
screws.
101RX003
2.Connect the electrical connector.
3.Connect the negative battery cable.
101RX002
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.VSS is located on the right side of the transmission
case just ahead of the rear propeller shaft.
Disconnect the VSS electrical connector.
3.Remove the bolt and the VSS from the transmission
case by wiggling it slightly and pulling it straight out.
IMPORTANT:Have a container ready to catch any fluid
that leaks out when the VSS is removed from the transfer
case.
014RX020
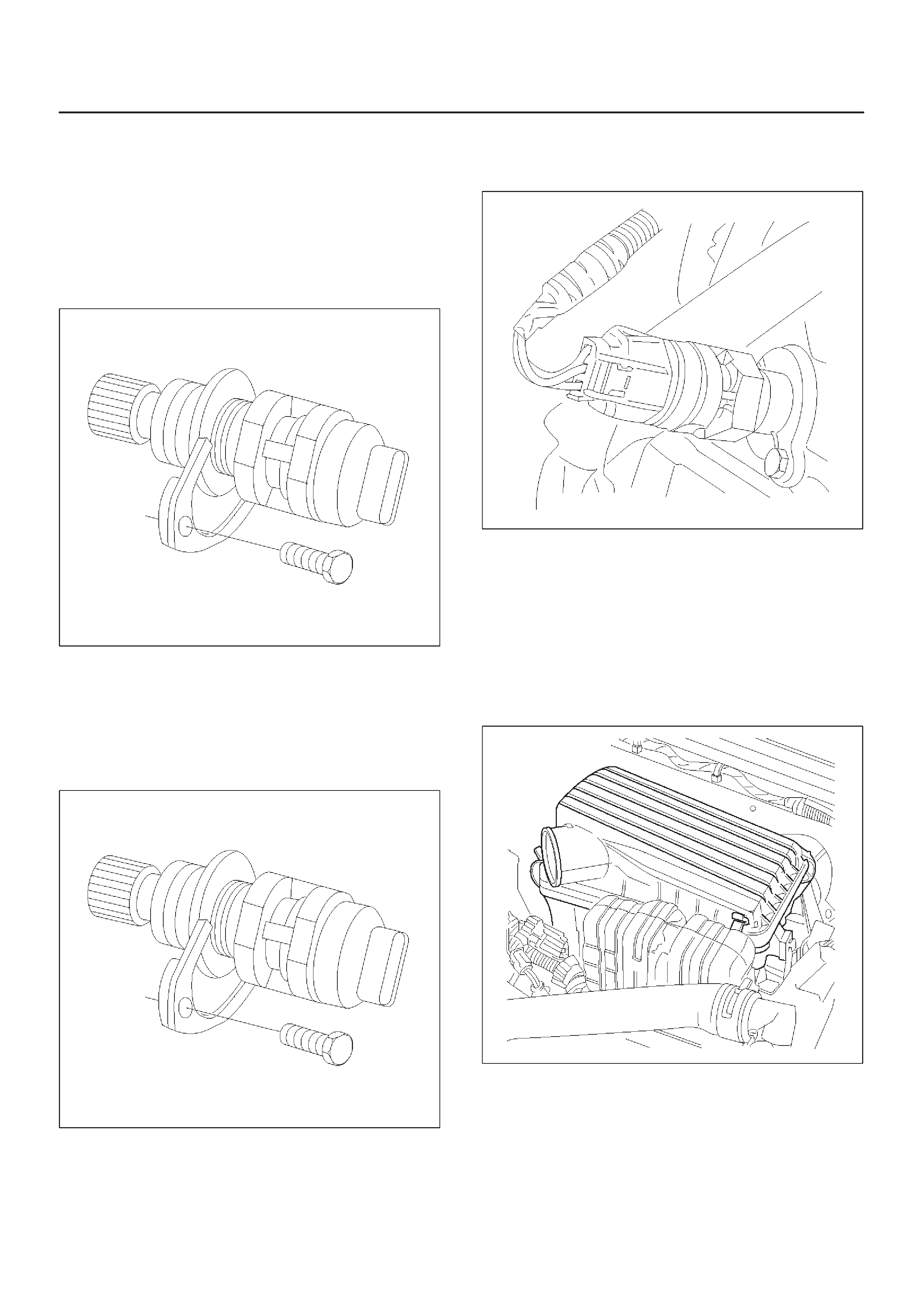
Inspection Procedure
1.Inspect the electrical connector for signs of corrosion
or warping. Replace the VSS if the electrical
connector is corroded or warped.
2.Inspect the VSS driven gear for chips, breaks, or worn
condition. Replace the VSS if the driven gear is
chipped, broken or worn.
3.Inspect the O–ring for wear, nicks, tears, or
looseness. Replace the O–ring if necessary.
014RX021
Installation Procedure
1.Install the VSS in the transmission case with the
notch for the connector facing the rear.
2.Secure the VSS with mounting bolt. Tighten the bolt to
16 Nm (12 lb ft).
014RX021
3.Connect electrical connector to the VSS.
4.Check the transmission oil level. Add oil if necessary .
5.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX020
Air Filter
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect electrical connector at the IAT sensor.
2.Release the four latches securing the lid to the air
cleaner housing.
3.Remove the air cleaner lid.
014RX019
4.Remove the air filter element.
014RX023
Installation Procedure
1.Install the air filter element in the air cleaner housing.
014RX023
2.Install the air cleaner lids.
3.Secure the three latches, holding the lid on the air
cleaner housing.
4.Connect the electrical connector to the IAT sensor.
014RX019
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
101RX002
2.Disconnect the IAC electrical connector.
3.Remove the two screws and IAC valve from the
throttle body.
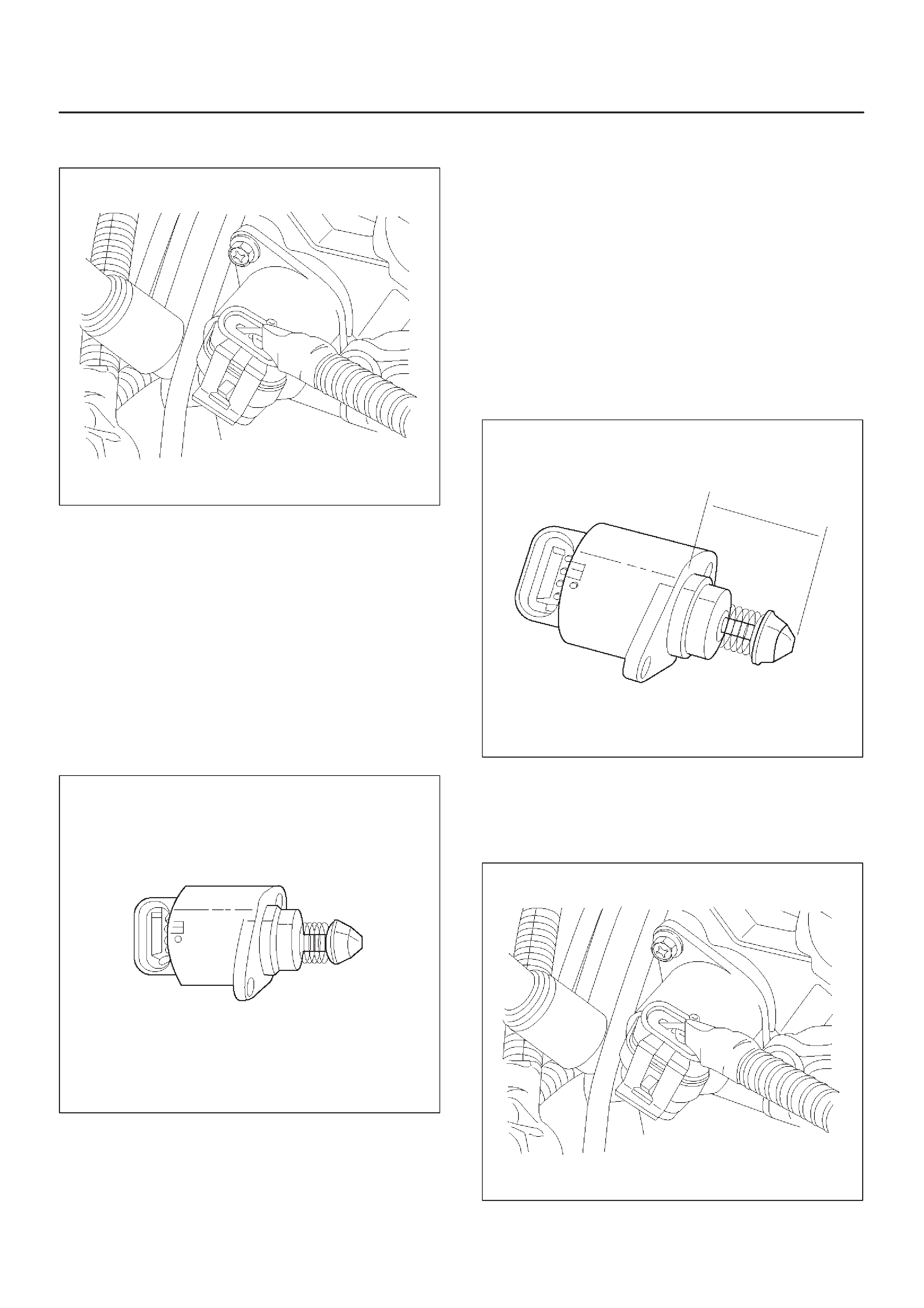
NOTE:Do not clean the IAC valve by soaking it in
solvent. The valve will be damaged as a result.
014RX022
Cleaning and Inspection Procedure
DClean the IAC valve O–ring sealing surface, pintle
valve seat and air passage.
DUse carburetor cleaner and a parts cleaning brush to
remove carbon deposit. Do not use a cleaner that
contain methyl ethyl ketone. This is an extremely
strong solvent and not necessary for this type of
deposit.
DShiny spots on the pintle are normal and do not
indicate misalignment or a bent pintle shaft.
DInspect the IAC valve O–ring for cuts, cracks or
distortion. Replace the O–ring if damaged.
0006
Measurement Procedure
DIn order to install a new IAC valve, measure the
distance between the tip of the pintle and the
mounting flange. If that measurement is 28 mm or
less, the valve need no adjustment. If the
measurement is greater than 28 mm, apply finger
pressure and retract the valve. The force required to
retract the pintle on a new valve will not damage the
valve, shaft or pintle.
NOTE:Do not push or pull on the IAC valve pintle on IAC
valve that have been in service. The force required to
move the pintle may damage it.
IMPORTANT:Use an identical replacement part in
order to replace a valve. IAC valve pintle shape and
diameter are designed for the specific application.
TS23746
Installation Procedure
1.Install IAC valve on the throttle valve body with the
two screws. Tighten the screw to 1 Nm ( 9 lb in).
014RX022
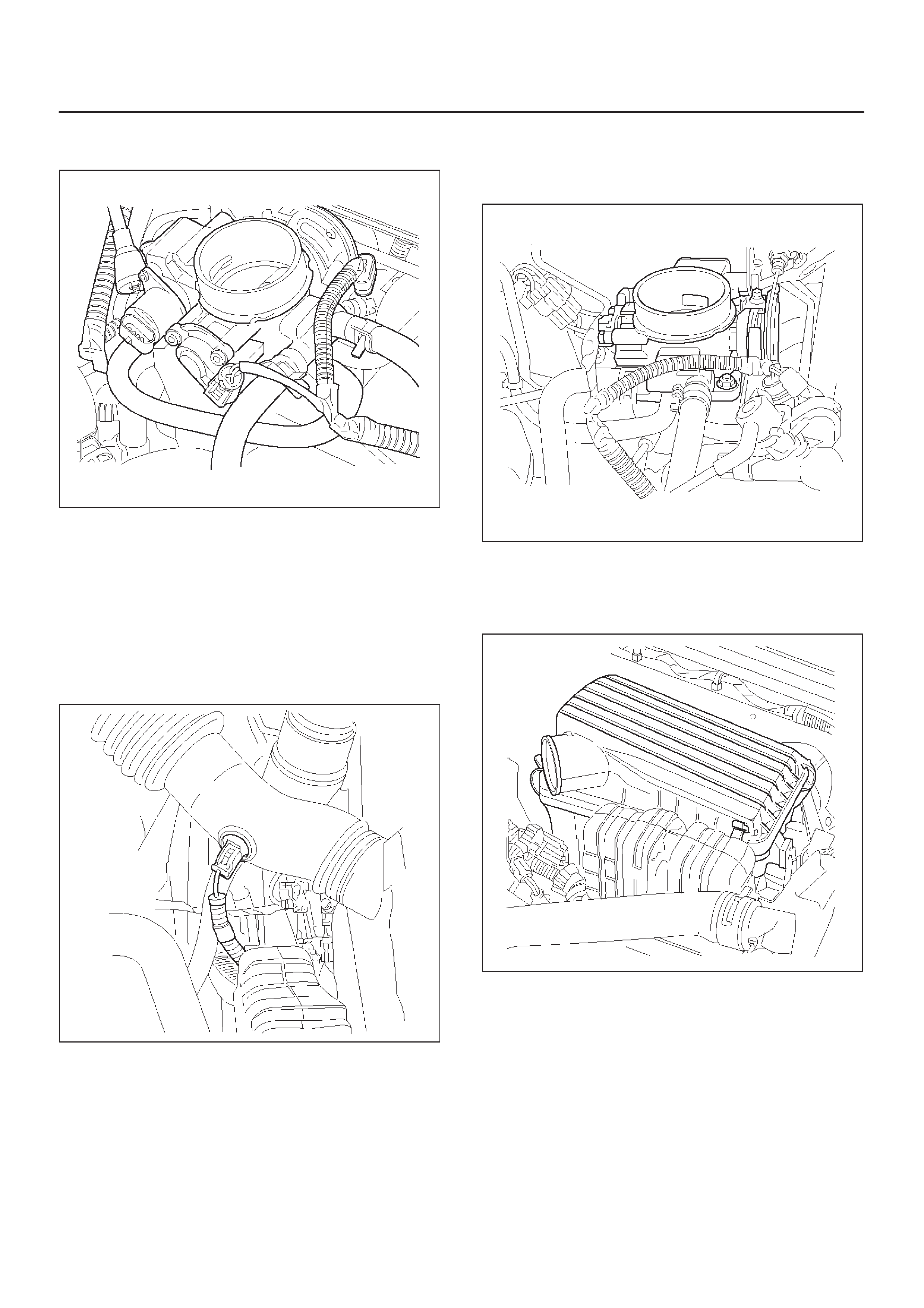
2.Connect electrical connector to IAC valve.
3.Connect the negative battery cable.
101RX002
Intake Air Duct
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Disconnect electrical connector at IAT sensor.
3.Remove the IAT sensor if necessary. Refer to Intake
Air Temperature Sensor Removal.
014RX011
4.Loosen retaining clamps at the throttle body and at
the air filter box.
5.Disconnect brake booster vacuum hose at intake
manifold and at brake booster.
014RX025
6.Remove retaining nut at the intake air duct bracket at
top of valve cover.
7.Disconnect the intake air duct from the throttle body
and at the air filter box.
014RX019
Installation Procedure
1.Connect the intake air duct at the throttle body and at
the air filter box. Make sure retaining hole is inserted
to the intake air duct bracket.
014RX019
2.Tighten retaining clamp at the throttle body and at the
air filter box.
3.Install a nut to the intake air duct bracket and tighten.
4.Connect brake booster vacuum hose to intake
manifold and to brake booster and secure them with
clamps.
014RX026
5.Install IAT sensor if necessary. Refer to Intake Air
Temperature Sensor Installation.
6.Connect electrical connector at IAT sensor.
7.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX011
IMPORTANT:Use an identical replacement part in
order to replace a valve. IAC valve pintle shape and
diameter are designed for the specific application.
Knock Sensor
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect negative battery cable.
2.Disconnect pig tail electrical connector at near the top
of generator.
014RX027
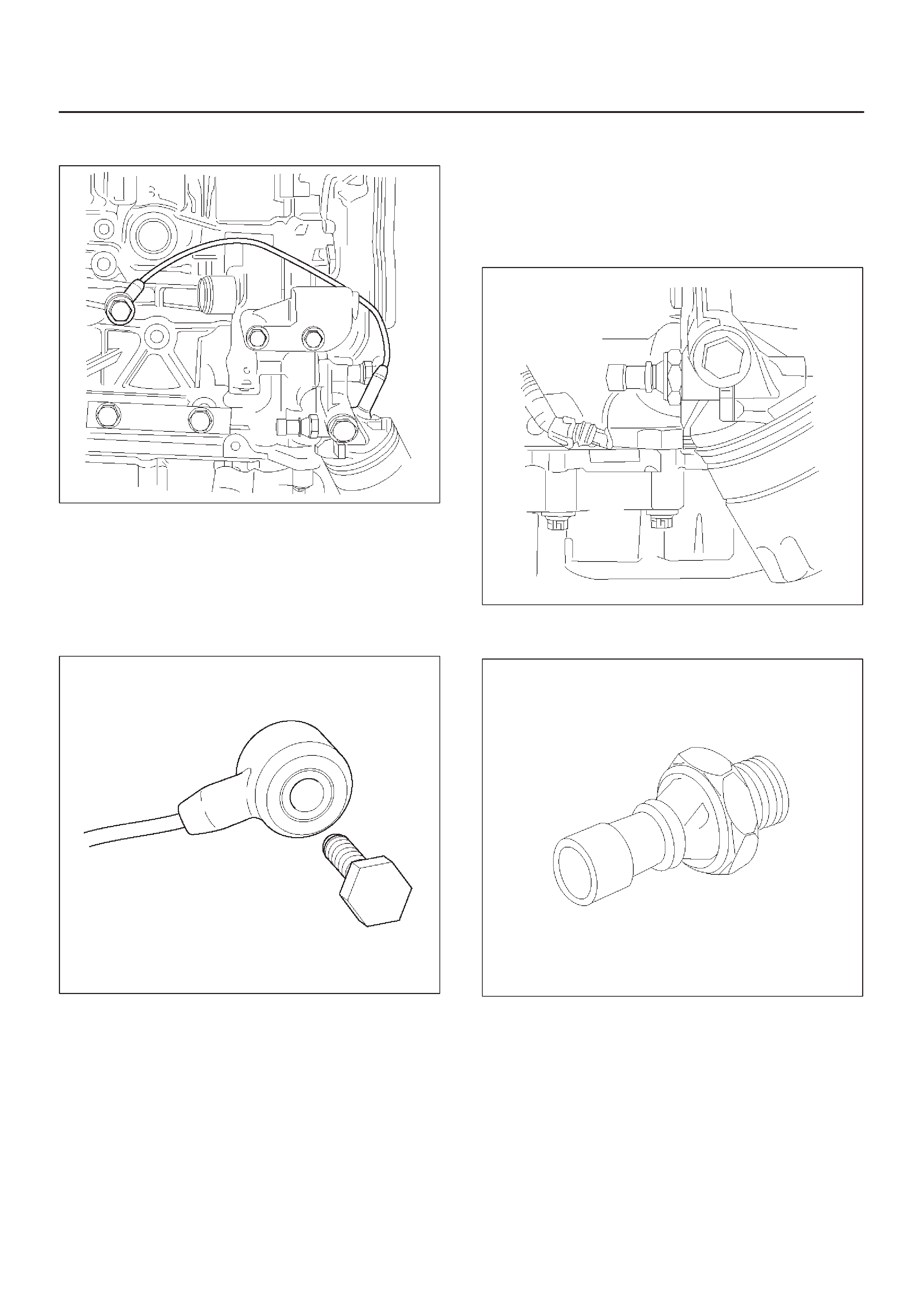
3. Unscrew retaining bolt from Knock Sensor located
passenger side of engine block just front of starter.
014RX028
4.Remove Knock Sensor with retaining bolt.
Installation Procedure
1.Install Knock Sensor with retaining bolt.
2.Connect pig tail electrical connector.
3.Connect battery negative cable.
014RX029
Oil Pressure Switch
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect battery negative cable.
2.Disconnect electrical connector at Oil Pressure
Switch.
014RX030
3.Unscrew Oil Pressure Switch from Oil Filter Mounting
Housing.
014RX031
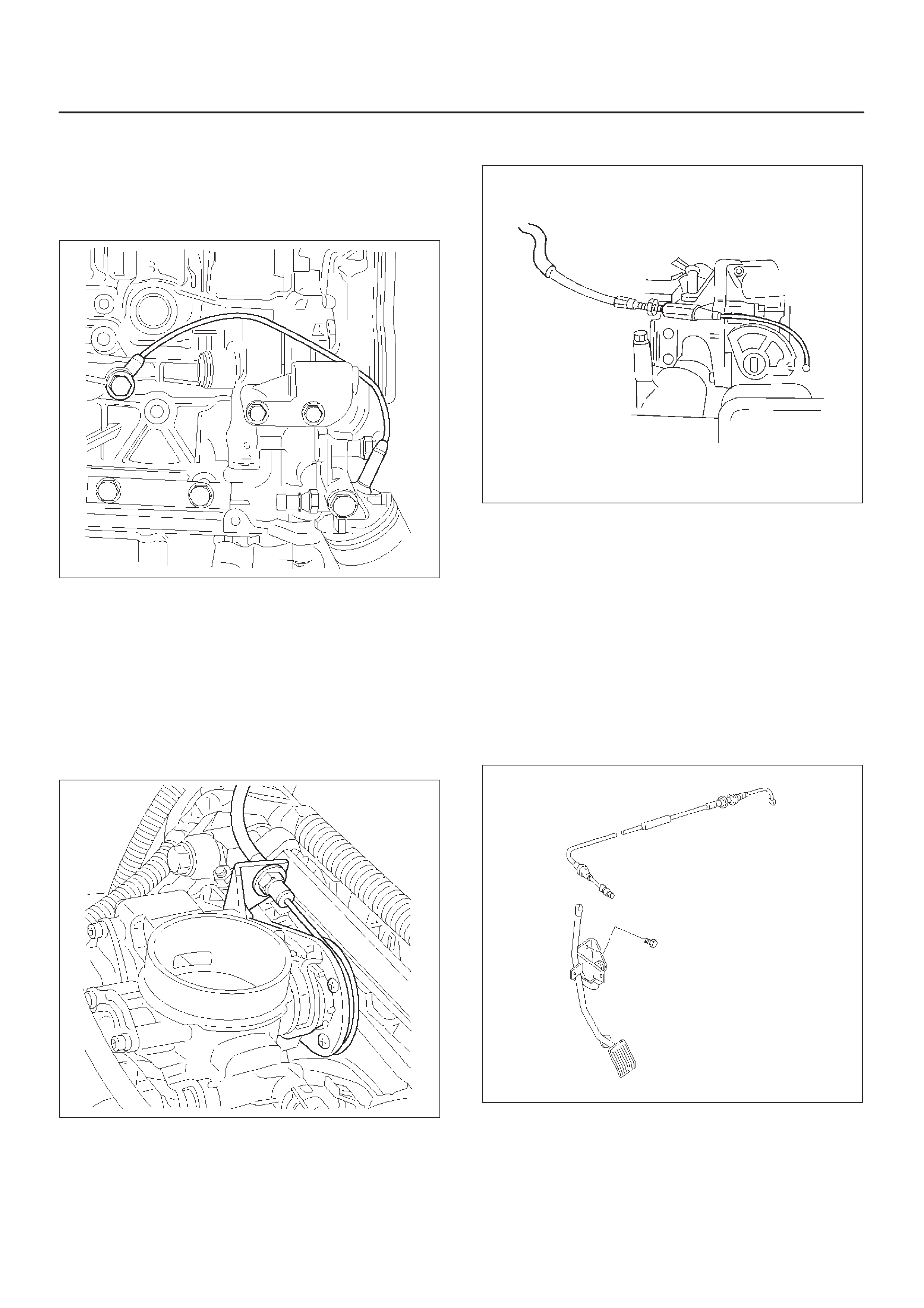
Installation Procedure
1. Install Oil Pressure Switch into Oil Filter Mounting
Housing and tighten.
2.Connect electrical connector.
3.Connect battery negative cable.
014RX028
FUEL METERING SYSTEM
Accelerator Cable Assembly
Removal Procedure
1.Loosen the adjusting nut on the cable bracket
mounting on the throttle body.
2.Remove the cable clip from holding bracket.
014RX026
3.Remove accelerator control cable (on the throttle
valve end).
101RW006
4.Remove the accelerator control cable (on the
accelerator pedal end).
5.Remove the grommet.
6.Remove the accelerator control cable.
Inspection Procedure
Check the following items, and replace the control cable if
any abnormality is found:
DThe control cable should move smoothly.
DThe control cable should not be bent or kinked.
DThe control cable should be free of damage and
corrosion.
014RX032
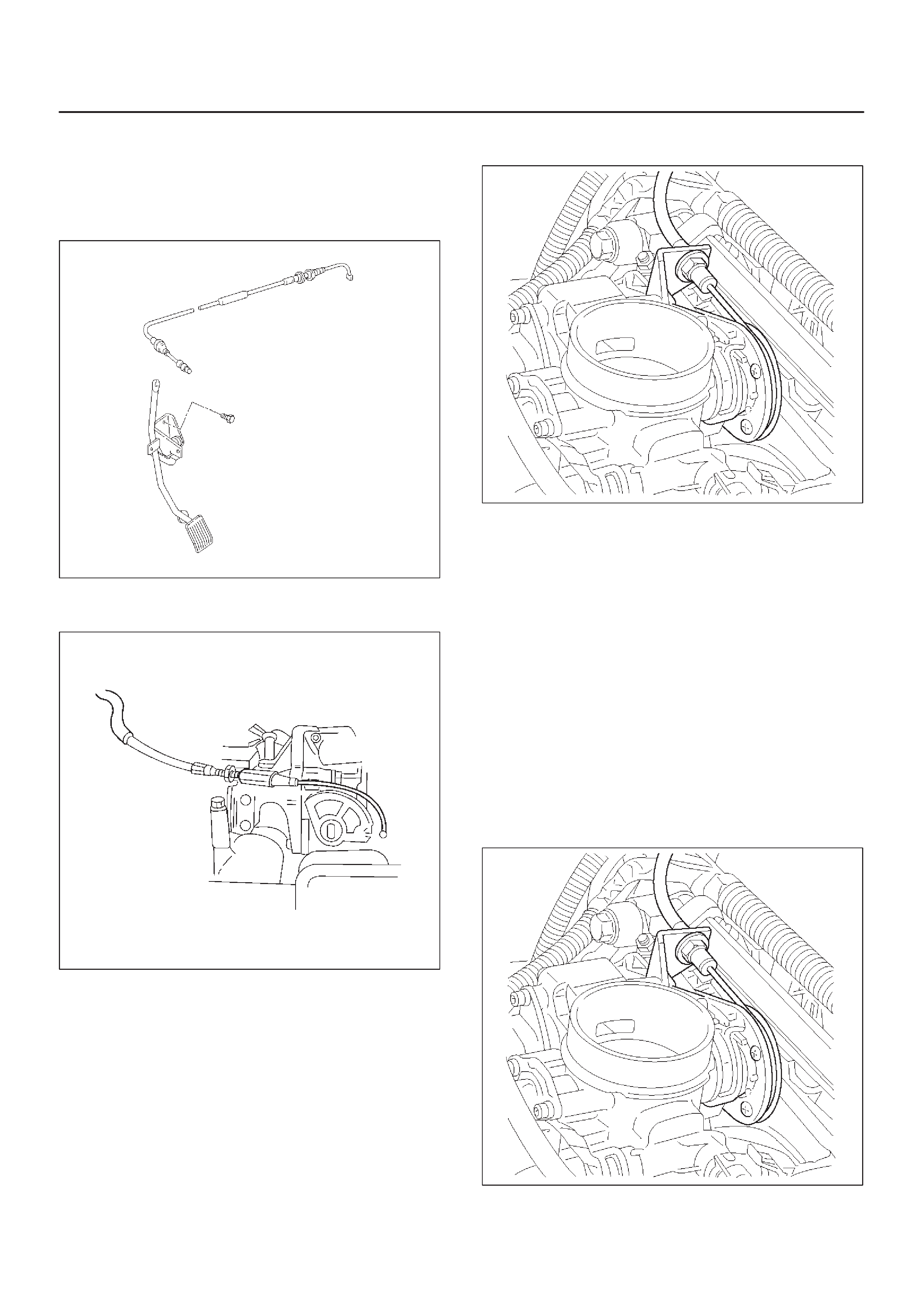
Installation Procedure
1.Install the accelerator control cable.
2.Install the grommet.
3.Install the accelerator control cable on the accelerator
pedal.
014RX032
4.Install the accelerator control cable on the throttle
valve.
101RW006
5.Install the cable clip to the holding bracket.
6.Adjust the accelerator cable. Refer to Accelerator
Cable Adjustment Section.
014RX026
Accelerator Cable Adjustment
Adjustment Procedure
1.Loosen the adjusting nut.
2.Loosen the jam nut.
3.Pull the outer cable while fully closing the throttle
valve.
4.Tighten the adjusting nut.
5.Tighten the jam nut.
6.Loosen the adjusting nut by three turns.
7.Tighten the jam nut again.
8.Manually operate valve.
IMPORTANT: The valve lever must return up to the
stopper screw. If the valve lever does not reach the
stopper screw, repeat the procedure again from Step 1.
014RX026
Accelerator Pedal Replacement
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the accelerator pedal control cable from
the acceleratorpedal assembly.
2.Remove the two screws retaining the accelerator
pedal to the bulkhead.
3.Remove the accelerator pedal from the bulkhead.
014RX033
Installation Procedure
1.Install the accelerator pedal assembly to the
bulkhead with two screws.
2.Connect the accelerator control cable to the
accelerator pedal assembly.
3.Adjust accelerator cable if necessary. Refer to
Accelerator Cable Adjustment Section.
014RX034
Fuel Filler Cap
Fuel Filler Cap
The Fuel filter cap includes a vacuum valve and a
pressure valve. If high vacuum or pressure occurs in the
fuel tank, each valve works to adjust the pressure in order
to prevent damage to the tank at the EGR valve.
Inspection Procedure
NOTE: Replace the fuel filler cap with the same typeof
filler cap that was originally installed on the vehicle.
DCheck the seal ring in the filler cap for any abnormality
and for seal condition.
DReplace the filler cap if any abnormality is found.
TS23767
Fuel Filter
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
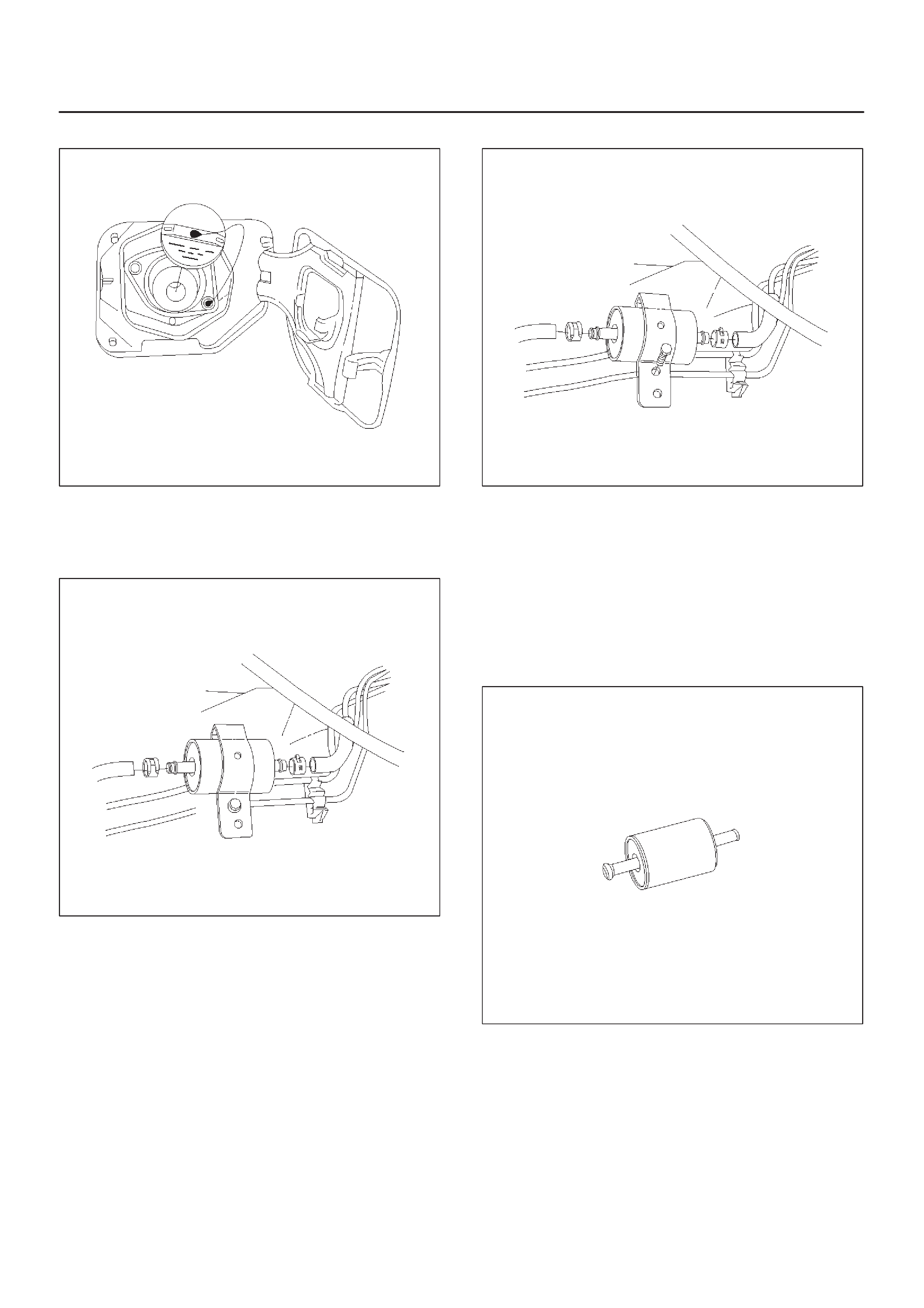
2.Remove the fuel filler cap.
041RW005
3. Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel filter on the
engine side.
4.Disconnect the fuel line from the fuel filter on the fuel
tank side.
041RW006
5.Remove the bolt on the fuel filter holder.
6.Remove the fuel filter.
041RW007
Inspection Procedure
1.Replace the fuel filter when the following occur:
DFuel leaks from the fuel filter body
DThe fuel filter body is damaged
DThe fuel filter is clogged with dust or sediment
2.If the drain hole is clogged at filler neck is clogged with
dust, clean the drain hole with air.
041RW008

Installation Procedure
1.Install the fuel filter in the correct direction.
2.Install the bolt on the fuel filter holder.
3.Connect the fuel line on the engine side.
4.Connect the fuel line on the fuel tank side.
5.Install the fuel filler cap.
6.Connect the negative battery cable.
041RW006
Fuel Injectors
Removal Procedure
NOTE:If the fuel injectors are leaking, the engine oil may
be contaminated with fuel. Check the oil for signs of
contamination and change the oil and filter if necessary.
NOTE:Use care in removing the fuel injector in order to
prevent damage to the fuel injector electrical connector
pins or fuel injector nozzles. The fuel injector is an
electrical component and should not be immersed in any
type of cleaner as this may damage the fuel injector.
IMPORTANT:Fuel injectors are serviced as complete
assembly only.
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
014RX035
2.Disconnect electrical connector from fuel injector.
3.Remove the fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Rail Removal
Procedure.
014RX036
4.Remove the fuel injector retainer clip.
5.Remove fuel injector assembly from fuel rail.
6.Remove O–ring from the fuel injector.
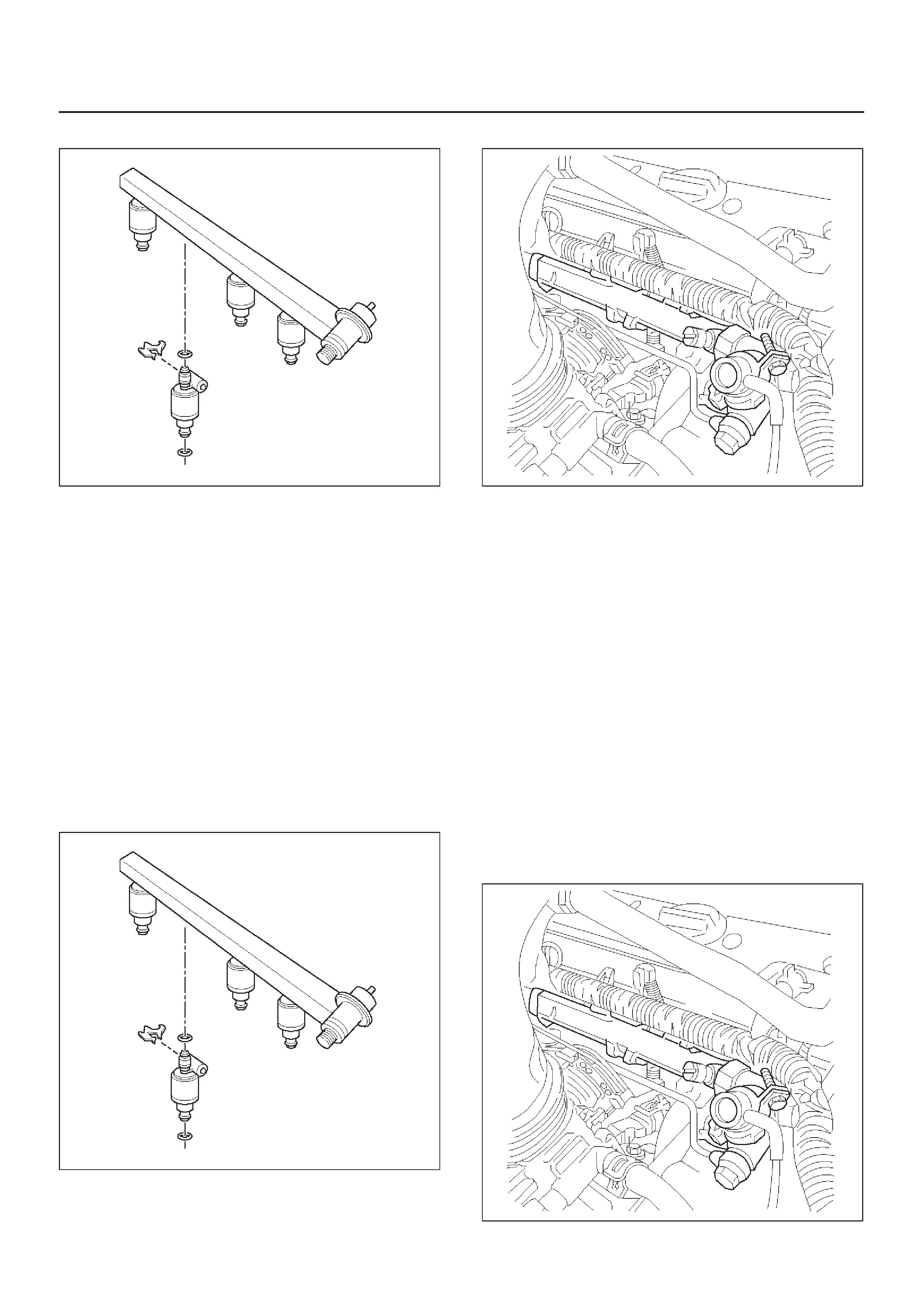
7.Remove O–ring backup from fuel injector.
014RX037
Inspection Procedure
1.Inspect O–ring for crack, damage or leaks.
2.Replace worn or damaged O–ring.
3.Lubricate the new O–rings with engine oil before
installation.
Installation Procedure
1.Lubricate the new O–ring with engine oil.
2.Install the O–ring backup on the fuel injector.
3.Install new O–ring on the fuel injector.
4.Install all four injector on the fuel rail.
5.Use new injector retainer clip to retain the injector to
the fuel rail.
6.Coat the end of the fuel injector with engine oil.
014RX037
7.Install fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Rail
Installation Procedure.
8.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX035
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Removal Procedure
CAUTION:To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
CAUTION:After relieving the fuel system pressure,
a small amount of fuel may be released when
servicing fuel lines or connections. Reduce the
chance of personal injury by covering the fuel line
fitting with a shop towel before disconnecting the
fittings. The towel will absorb any fuel that may leak
out. When the disconnect is completed, place the
towel in an approved container.
NOTE: Compressed air must never used to test or clean
a fuel pressure regulator , as damage to the fuel pressure
regulator may occur.
014RX035
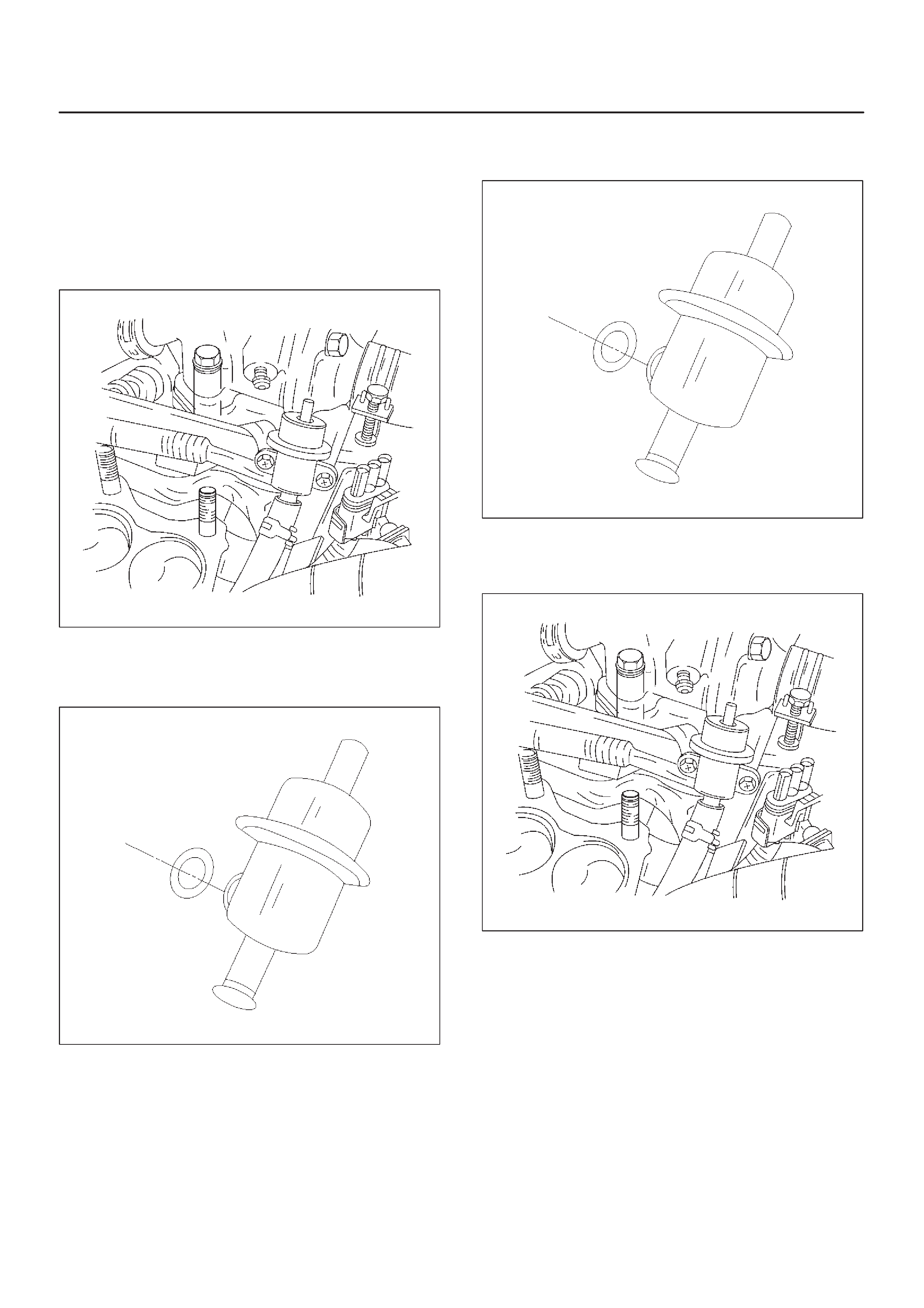
NOTE:To prevent damage to the fuel pressure regulator,
do not immerse the pressure regulator in solvent.
1.Depressurize the fuel system. Referto Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure.
2.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3.Remove the fuel pump relay.
4.Disconnect the vacuum line form fuel pressure
regulator.
014RX038
5.Remove the fuel pressure regulator retaining screw.
6.Remove the fuel pressure regulator retaining bracket.
7.Remove the fuel pressure regulator from fuel rail.
014RX039
Installation Procedure
1.Insert the fuel pressure regulator into the fuel rail.
014RX039
2. Install the fuel pressure regulator retaining bracket
ant tighten with a screw.
3.Connect vacuum line onto the fuel pressure regulator.
014RX038
4.Install the fuel pump relay.
5.Connect the negative battery cable.

6.Crank the engine until it starts. Cranking the engine
may take longer than usual due to trapped air in the
fuel line.
014RX035
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
CAUTION:To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
CAUTION:After relieving the fuel system pressure,
a small amount of fuel may be released when
servicing fuel lines or connections. Reduce the
chance of personal injury by covering the fuel line
fitting with a shop towel before disconnecting the
fittings. The towel will absorb any fuel that may leak
out. When the disconnect is completed, place the
towel in an approved container.
1.Remove the fuel filler cap.
041RW005
2.Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood
relay box.
3.Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4.Crank the engine for about 30 seconds.
5.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
014RW089
Fuel Pump Assembly
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Drain all fuel from fuel tank from filler neck.
3.Remove the fuel pump relay from the fuse and relay
box at right side of engine room.
014RW089
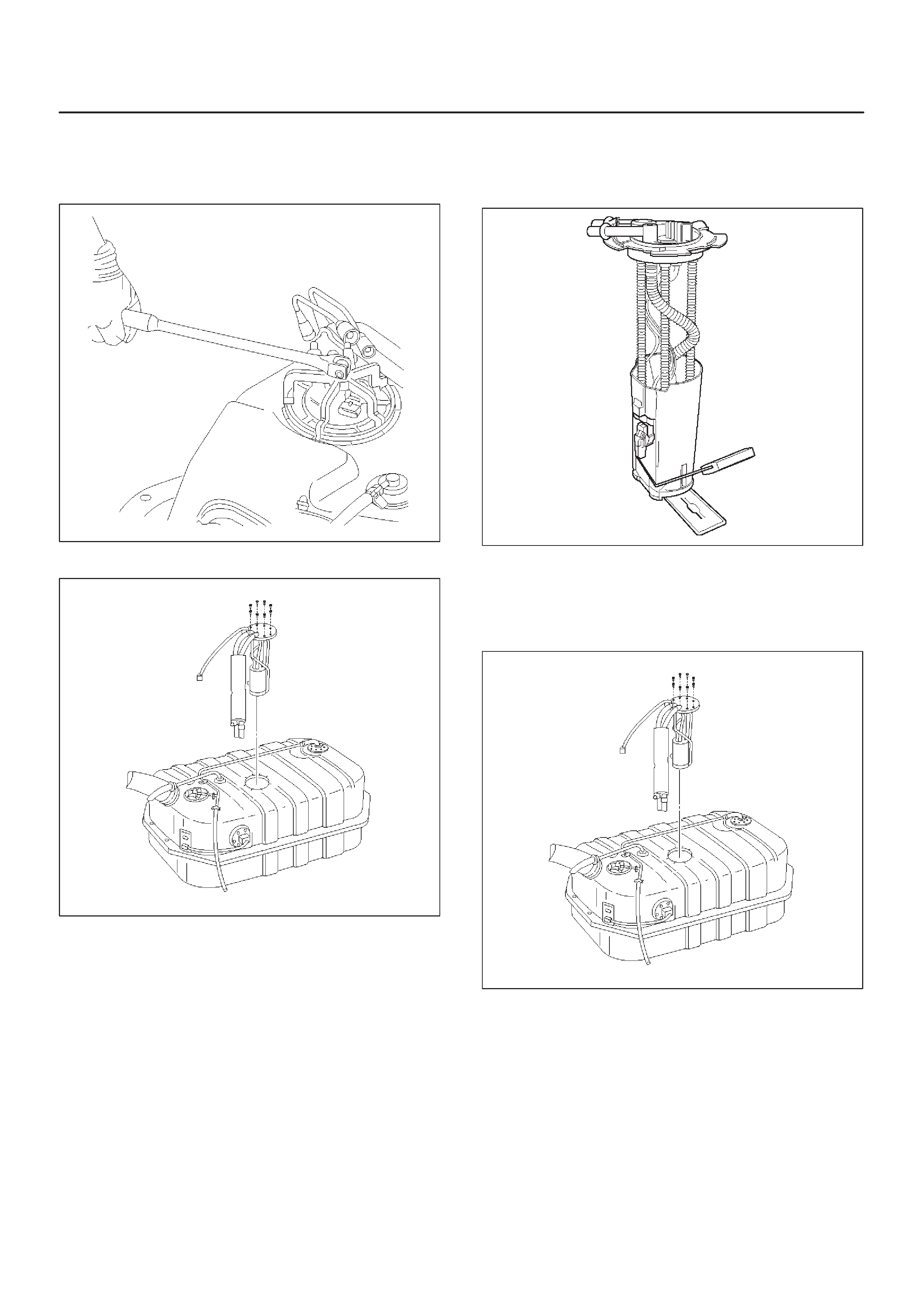
4.Remove fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Removal
Procedure.
5. Using J–39763, twist the fuel pump counter–clock
wise to release from fuel tank.
041RX001
6.Lift fuel pump to remove from fuel tank.
041RX002
Inspection Procedure
Inspect in–tank fuel filter for tears, damage or evidence of
dirt derbies or water in the fuel. If any of these condition
exist, replace the in–tank fuel filter.
041RX003
Installation Procedure
1.Insert the fuel pump assembly into fuel tank and place
them at its position.
041RX002

2.Using J–39763, twist fuel pump assembly clock wise
into the lock.
901RX036
3.Install the fuel tank. Refer to Fuel Tank Installation
Procedure.
4.Install the fuel pump relay.
5.Connect the negative battery cable.
041RX004
Fuel Pump Relay
Removal Procedure
1.Remove the fuse and relay box cover located right
side of engine room.
2.Determine correct relay by consulting to the diagram
on the cover.
3.Insert a small screwdriver or use thumb pressure to
release the retainer of the relay.
4.Pull the relay straight up and out of the fuse and relay
box.
Installation Procedure
1.Inserts the relay into the correct place in the fuse and
relay box with the catch slot aligned to retainer.
2.Press down until the catch of retainer engages.
3.Install fuse and relay box cover.
014RW089
Fuel Rail Assembly
Removal Procedure
NOTE:
DUse care when removing the fuel rail assembly in
order to prevent damage to the injector electrical
connector terminal and the injector spray tips.
DFitting should be capped and holes plugged during
servicing to prevent dirt and other contaminants from
entering open lines and passage.
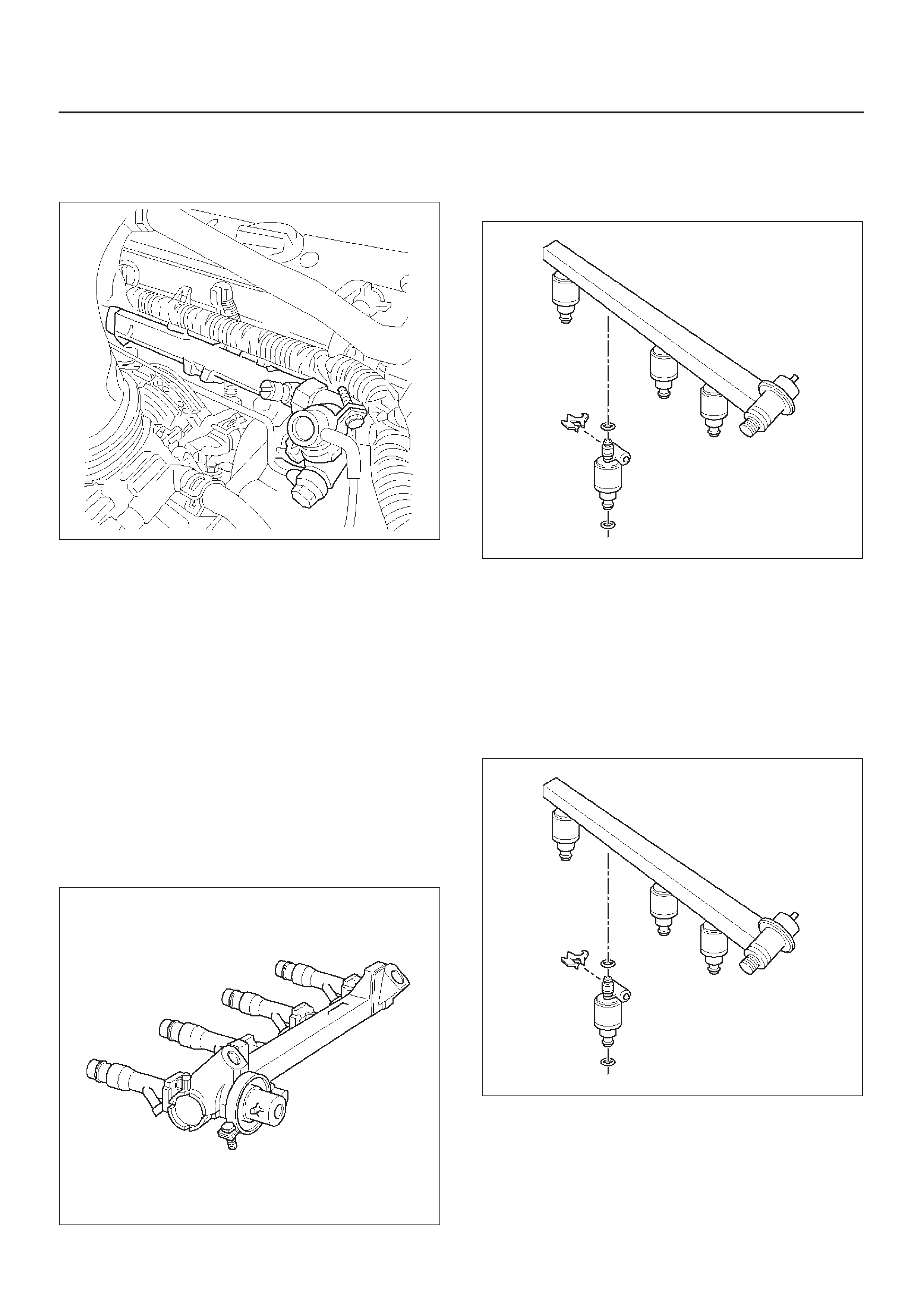
IMPORTANT:An eight–digit identification number is
stamped on side of the fuel rail. Refer to this number when
you service the fuel rail or when a replacement part is
required.
014RX035
1.Depressurize the fuel system. Refer to Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure.
2.Disconnect the fuel inlet at the rear of the engine.
3.Disconnect the fuel return line at front of the engine.
4.Disconnect the injector electrical connectors.
5.Remove the nuts holding wiring harness onto fuel rail.
6.Remove the bolts retaining fuel rail to the intake
manifold.
Lift up the injectors carefully to separate them from intake
manifold.
Lift up the fuel rail with injectors as assembly. Do not sep-
arate the fuel injectors from fuel rail.
If an injector become separated from fuel rail, injector
backup O–ring and injector retainer clip must be replaced.
Drain residual fuel from fuel rail into an approved contain-
er.
014RX036
7.If removal of fuel pressure regulator is necessary.
Refer to Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal
Procedure.
8.If removal of fuel injector is necessary. Refer to Fuel
Injectors Removal Procedure.
014RX037
Installation Procedure
1.Install the fuel injectors if necessary. Refer to Fuel
Injector Installation Procedure.
2.Install the fuel pressure regulator if necessary. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Regulator Installation Procedure.
3.Place the fuel injector rail assembly on the manifold
and insert the injectors into each port by pushing fuel
rail.
014RX037
4. Install two fuel rail retaining bolts. Tighten fuel rail
retaining bolts to 19 Nm (14 lb ft)
5.Place wiring harness in its place and secure it with two
nuts.
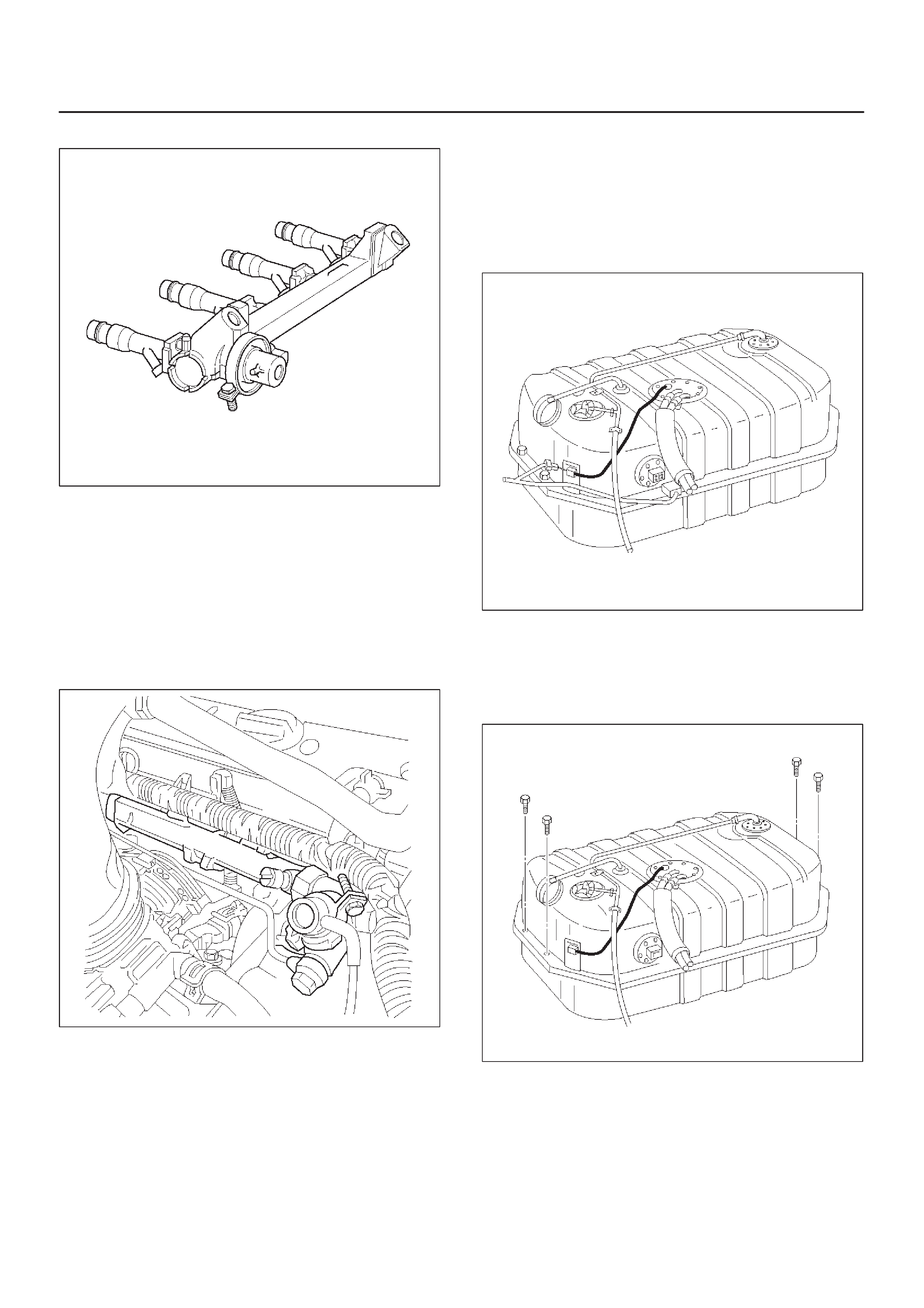
6.Connect electrical connector to each fuel injector.
014RX036
7. Connect the fuel supply line securely. Do not over
tighten.
8. Connect the fuel return line securely. Do not over
tighten.
9.Connect the negative battery cable.
10.Crank the engine until it start. Cranking the engine
may take longer than usual due to trapped air in the
fuel system. Check for leak. If fuel leak is observed,
stop engine immediately. Before correct fuel leak, be
sure to depressurize system again.
014RX035
Fuel Tank
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Remove fuel filer cap.
3.Drain the fuel from fuel filler neck.
4.Disconnect the fuel filler hose at fuel tank.
5.Disconnect the air breather hose at the fuel tank.
6.Disconnect the evaporator hose at the fuel tank.
7.Hold entire fuel tank at the bottom with stands.
8. Disconnect fuel supply lines and fuel return line at
near the fuel filter inside of body frame.
041RX005
9.Remove four bolts (two in front and two in rear)
holding fuel tank to the frame.
10.Lower tank assembly from the vehicle a little to make
access space on top.
11.Disconnect two electrical connectors at fuel pump.
041RX006
12.Remove fuel tank assembly from the vehicle.
13.Remove four nuts retaining tank under guard to the
tank.
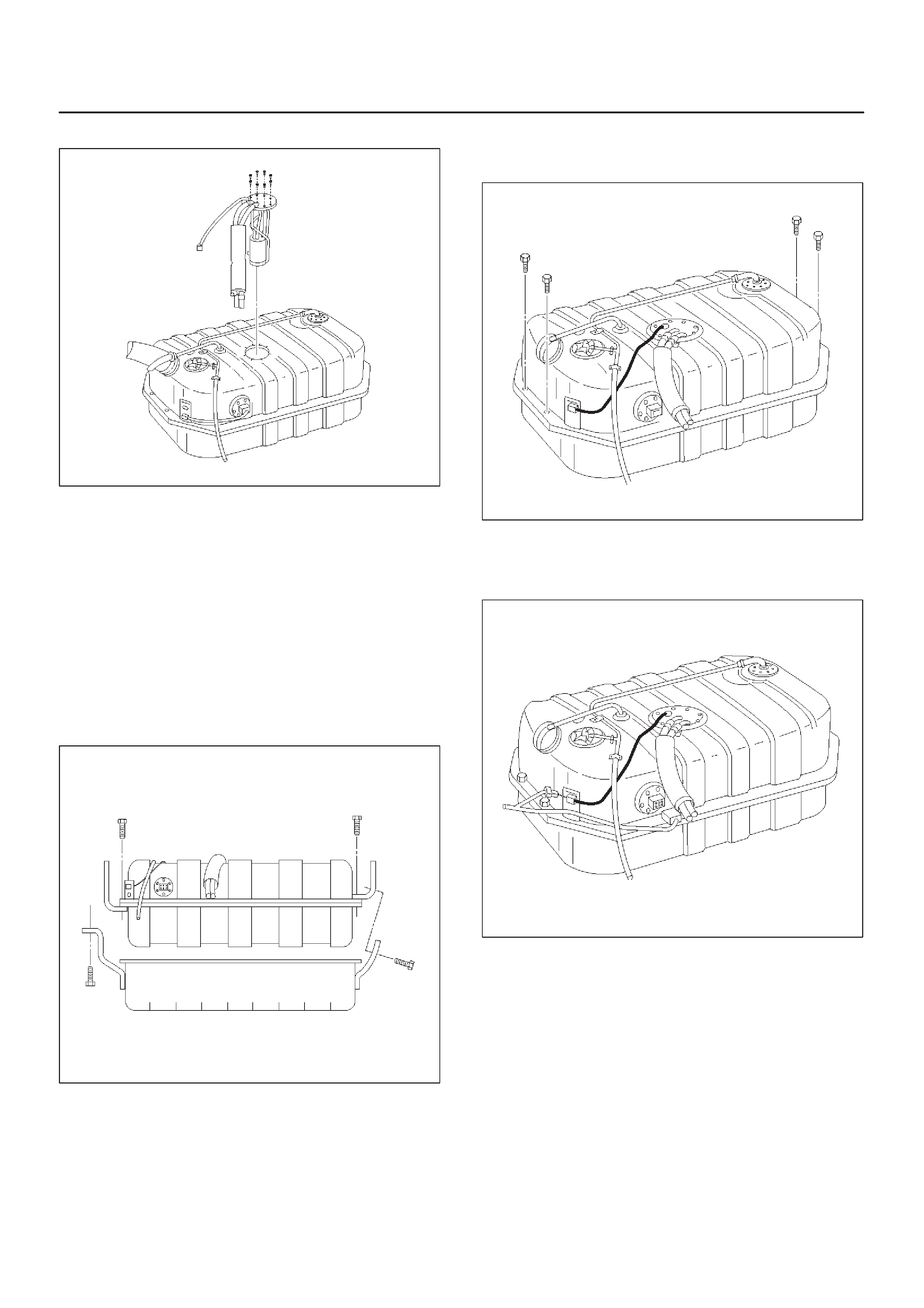
14.Remove the tank from the guard.
041RX002
Installation Procedure
1.Secure fuel tank into under guard with four retaining
bolts, if necessary.
2.Place the fuel tank assembly onto stands.
3.Lift the fuel tank assembly near the position.
4.Connect two electrical connectors at fuel pump.
5.Lift the fuel pump to its position and secure it with four
mounting bolts. Make sure that all hoses and fuel
lines are out of way between the fuel tank and the fuel
tank bracket. Tighten the fuel tank retaining bolts to
36 Nm (27 lb ft).
041RX007
6.Connect fuel supply and return lines.
7.Connect the fuel filler hose, the air breather hose and
EVAP hose onto fuel tank and secure them with
clamps.
041RX006
8.Pour fuel into fuel tank.
9.Install fuel filler cap securely.
10.Connect the battery negative cable.
041RX005
Throttle body (TB)
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Drain the cooling system. Refer to Cooling System.
3.Remove the air intake duct. Refer to Air Intake Duct
Removal Procedure.
4.Remove the accelerator cable from throttle. Refer to
Accelerator Cable Assembly Removal Procedure.
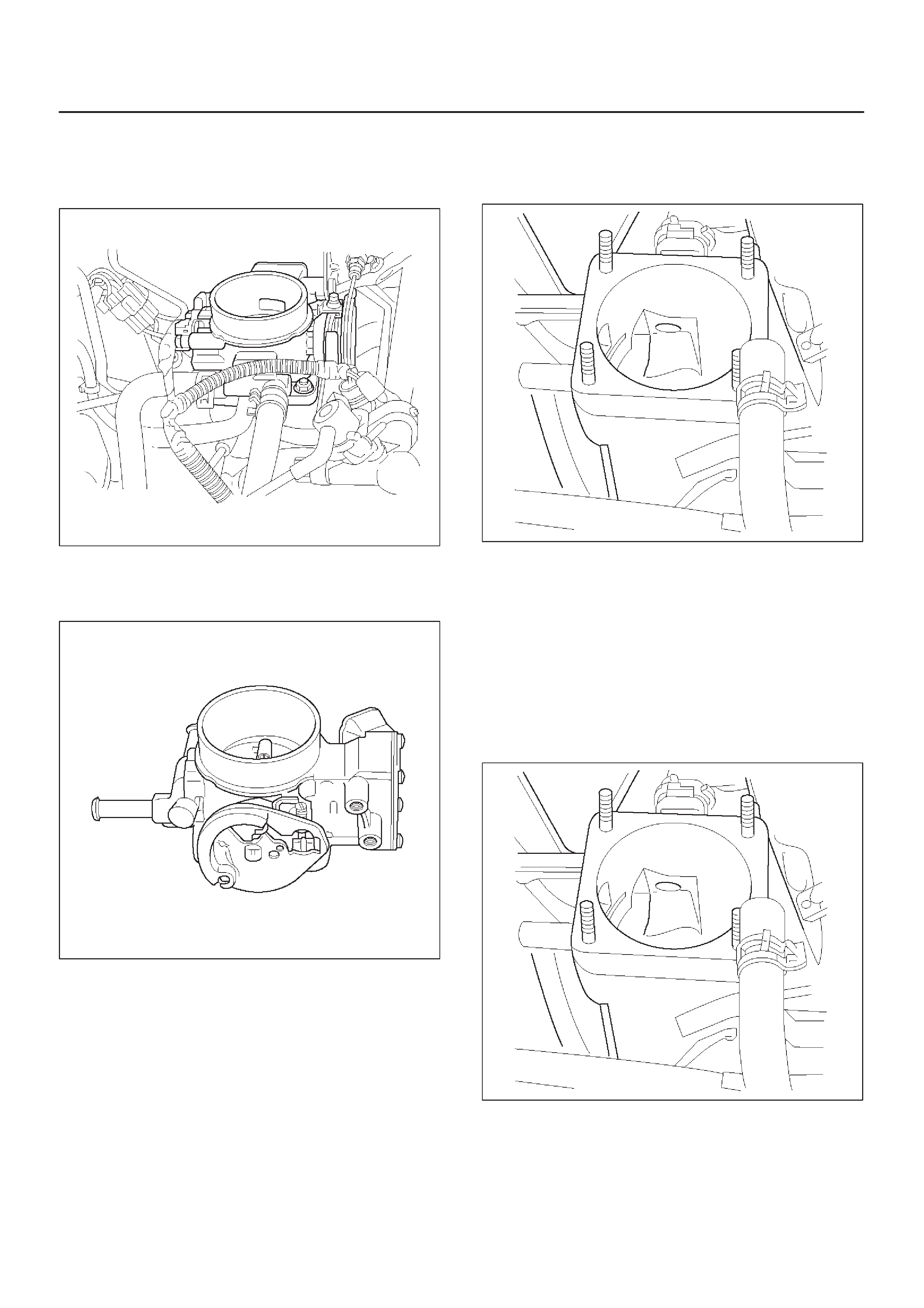

5.Disconnect the electrical connectors from the throttle
position sensor and the idle air control valve solenoid.
6.Disconnect all vacuum hoses below air horn.
7.Disconnect coolant lines.
014RX025
8.Remove the mounting bolts retaining the throttle body
the intake manifold.
9.Lift up the throttle body from the intake manifolds.
014RX040
10.Remove the gaskets from the intake manifolds.
11.Remove the IAC. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve
Solenoid Removal Procedure.
12.Remove TPS. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor
Removal Procedure.
Inspection Procedure
NOTE:Do not use solvent of any type when you clean the
gasket surfaces on the intake manifold and the throttle
body assembly. The gasket surface and the throttle body
assembly may be damaged as results.
1.If the throttle body gasket needs to be released,
remove any gasket material that may be stuck to the
mating surfaces of the manifold.
2.Do not leave any scratches in the aluminum casting.
014RX041
Installation Procedure
1.Install IAC valve onto the throttle body. Refer to Idle
Air Control Valve Solenoid Installation Procedure. 2.Install TPS onto the throttle body if necessary. Refer
to TPS Installation Procedure.
3.Place the gasket then the throttle body on the
manifold.
4.Install four mounting bolt. Tighten the throttle body
mounting bolt to 13.5 Nm (10 lb ft).
014RX041
5.Connect coolant line and secure them with clamps.
6.Connect all vacuum hoses and secure them with
clamps if necessary.
7.Install accelerator control cable bracket onto the
throttle body.
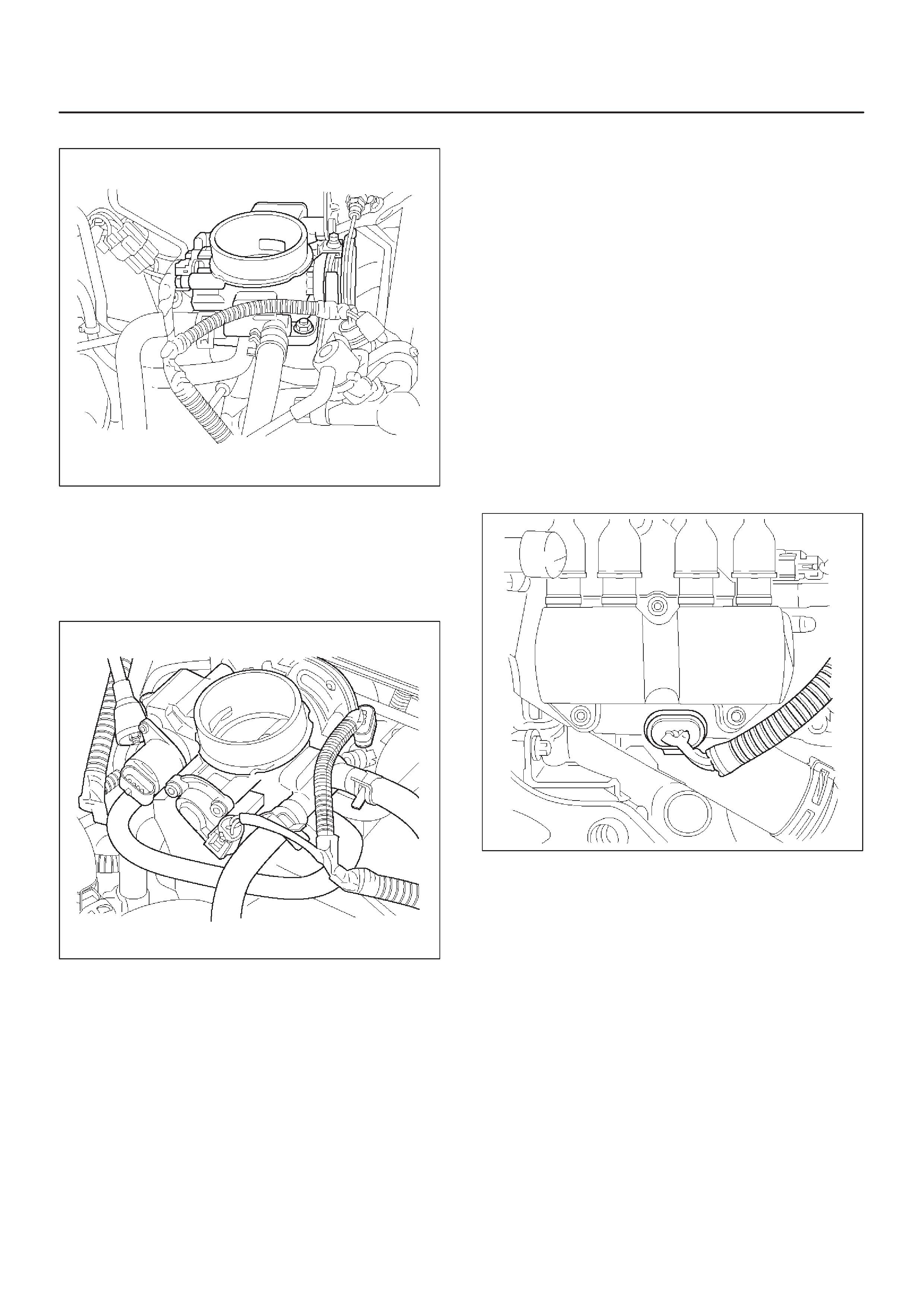
8.Connect accelerator control cable to throttle plate.
014RX025
9.Connect electrical connector at IAC valve and TPS.
10.Install the air intake duct. Refer to Air Intake DuctInstallation Procedure. 11.Fill the cooling system with required coolant. Refer to
Engine Cooling System.
12.Connect the negative battery cable.
101RX002
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
Ignition Control Module (ICM)
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Disconnect the electrical connector from the ignition
control module.
3.Remove the two attaching screws.
4.Remove the ignition control module from the engine
block.
Installation Procedure
1.Fasten the module to the engine block with two
screws.
2.Reconnect the electrical connector.
3.Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
041RX042
Ignition Coil
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Drain the cooling system. Refer to Engine Cooling
System.
3.Remove the heater supply and return hose.
4.Remove the coolant return hose.
5.Disconnect all four spark plug cables from the coil.
6.Disconnect electrical connector from the ignition coil.
7.Remove three mounting bolt from the ignition coil.
8.Remove the ignition coil from the bracket.
014RX043
Installation Procedure
1.Install the ignition coil onto the bracket with three
mounting bolts.
2.Connect electrical connector at the ignition coil.
3.Connect spark plug cable to the ignition coil.
4.Connect heater supply and return hose and secure
them with clamps.
5.Connect coolant return line and secure them with
clamps.
6.Fill the cooling system with required coolant. Refer to
Engine Cooling System.
7.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX044
Spark Plugs
Removal Procedure
Type: NGK BPR6ES–11
Spark Gap : 1.05 MM (0.040”)
Spark Plug Torque : 25 Nm (2.6 kg·m/18 lb ft)
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Remove four bolt holding spark plug cover plate to top
of valve cover, and remove the cover plate.
3.Pull ignition wire using hocks attached to end of spark
plug cable.
014RX043
4.Remove the spark plug.
014RX045
Inspection Procedure
1.Check the insulator for cracks. Replace the spark
plug if crack are present.
2.Check the electrode condition and replace the spark
plug if necessary.
014RX046
If the spark plug electrodes and insulators are fouled with
carbon or oil, the engine will not operate efficiently.
There are number of possible causes:
DFuel mixture is too rich.
DOil in the combustion chamber.
DThe spark plug gap is not set correctly.
If spark plug fouling is excessive, check the fuel and
electrical system for possible causes of trouble. If fuel and
electrical system are normal, install spark plug of a higher
heat range which have the same physical dimensions as
the original equipment spark plug.
The following symptoms are characteristics of spark
plugs that are running too hot:
DFuel mixture is too lean.
DHeat range is incorrect.
014RX047
If vehicle usage does not conform to normal driving
conditions, a more suitable spark plug may be
substituted.
If fuel and electrical system are normal, in most cases of
this sort, the problem can be corrected by using a colder
type spark plug with the same physical dimensions as the
original equipment spark plug.
3.Check the gaskets for damage and replace if
necessary.
4.Measure the spark plug gap. The specification is 1.05
mm (0.040”).
5.Adjust the spark gap by bending the grounded
electrode.
014RX048
Installation Procedure
1.Tighten the spark plug to the 25 Nm (2.6 kg·m/18 lb ft).
2.Push the spark plug cable in until it snaps in.

3.Install spark plug cover onto valve cover and secure it
with four retaining bolts.
014RX049
Spark Plug Cables
Spark Plug Cables
The cable contains a synthetic conductor which is easily
damaged. Never stretch or kink the cable. Disconnect the
cable from spark plug and the ignition coil.
The original equipment cables and the ignition coil are
marked to show correct location of the cables. If spark
plug cables or the ignition coil are replaced previously,
before cables are removed from the ignition coil, mark the
cables and the coil so they can be reconnected in the
same position.
014RX050
Inspection Procedure
NOTE:Never puncture the spark plug cable’s insulation
with a needle or the pointed end of a probe into the cable.
An increase in resistance would be created which would
cause the cable to become defective.
1.If the cable has broken or cracked insulation, it must
be replaced.
2.If the terminals are corroded or loose, the cable must
be replaced.
3.Check that the cable resistance does not exceed 10 k
W per foot.
014RX051
EMISSIONS Catalytic Converter
Refer to Engine Exhaust.
Air Conditioning Relay
Removal Procedure
1.Remove the fuse and relay box cover at right side of
engine room.
2.Refer to the diagram on the cover to determine which
is the correct relay.
3. Insert small screwdriver or use thumb pressure to
release the retainer of the relay.
4.Pull the relay straight up and out of the fuse and relay
box.
014RX052
Installation Procedure
1.Insert the relay into the correct place in the fuse and
relay box with the catch slot aligned to retainer.
2.Press down until the catch of retainer engages.
3.Install fuse and relay box cover.
Ignition Timing Adjustment
Ignition Timing Adjustment
There is no timing adjustment. The timing signal is
furnished by the CKP and the CMP signal. ECM control
the ignition timing.
EVAP Canister Hoses
EVAP Canister Hoses
To see the routing of the EVAP canister hoses, refer to
Vehicle Emission Control Information in Diagnosis or
Emission Label located bottom side ofthe hood. Use
6148M or equivalent when you replace the EVAP canister
hoses.
EVAP Canister
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect all hoses.
2.Remove two mounting bracket nuts.
Inspection Procedure
1.Inspect the hoses for cracks, damage and leaks.
2.Inspect the canister for damages.
014RX001
Installation Procedure
1.Install EVAP canister onto crossmember with two
mounting bolts.
2.Connect all hoses and secure them with clamps.
014RX054
Linear Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) Valve
Removal Procedure
1.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2.Disconnect electrical connector at EGR valve.
3.Disconnect the electrical connector at Intake Air
Temperature Sensor.
4.Remove air intake duct. Refer to Air Intake Duct
Removal Procedure.
5.Remove crankshaft breather hose.
6.Remove two bolts holding EGR valve.
7.Remove EGR valve and gasket from the manifold.
057RX001
Inspection Procedure
1.Inspect the air passage for a restrtiction. If there is
restriction, remove the object. Do not use any type of
solvent, it may damage electrical system of EGR
valve.
2.Inspect restriction for valve movement. If there is
restriction remove the object.
014RX056
Installation Procedure
1.Place the gasket and EGR valve on to the intake
manifold.
2.Install mounting bolts and tighten.
3.Connect electrical connector at EGR valve
4.Connect the crankshaft breather hose and secure it
with clamps.
5.Install the air intake duct. Refer to Air Intake Duct
Installation Procedure.
6.Connect the negative battery cable.
014RX057
Wiring and Connectors
Wiring Harness Service
The control module harness electrically connects the
control module to the various solenoids, switches and
sensors in the vehicle engine compartment and
passenger compartment.
Replace wire harnesses with the proper part number
replacement.
Because of the low amperage and voltage levels utilized
in powertrain control systems, it is essential that all wiring
in environmentally exposed areas be repaired with crimp
and seal splice sleeves.
The following wire harness repair information is intended
as a general guideline only. Refer to Chassis Electrical for
all wire harness repair procedures.
ECM Connectors And Terminals
Removal Procedure
1.Remove the connector terminal retainer.
2.Push the wire connected to the affected terminal
through the connector face so that the terminal is
exposed.
3.Service the terminal as necessary.
Installation Procedure
1.Bend the tab on the connector to allow the terminal to
be pulledinto position within the connector.
2.Pull carefully on the wire to install the connector
terminal retainer.
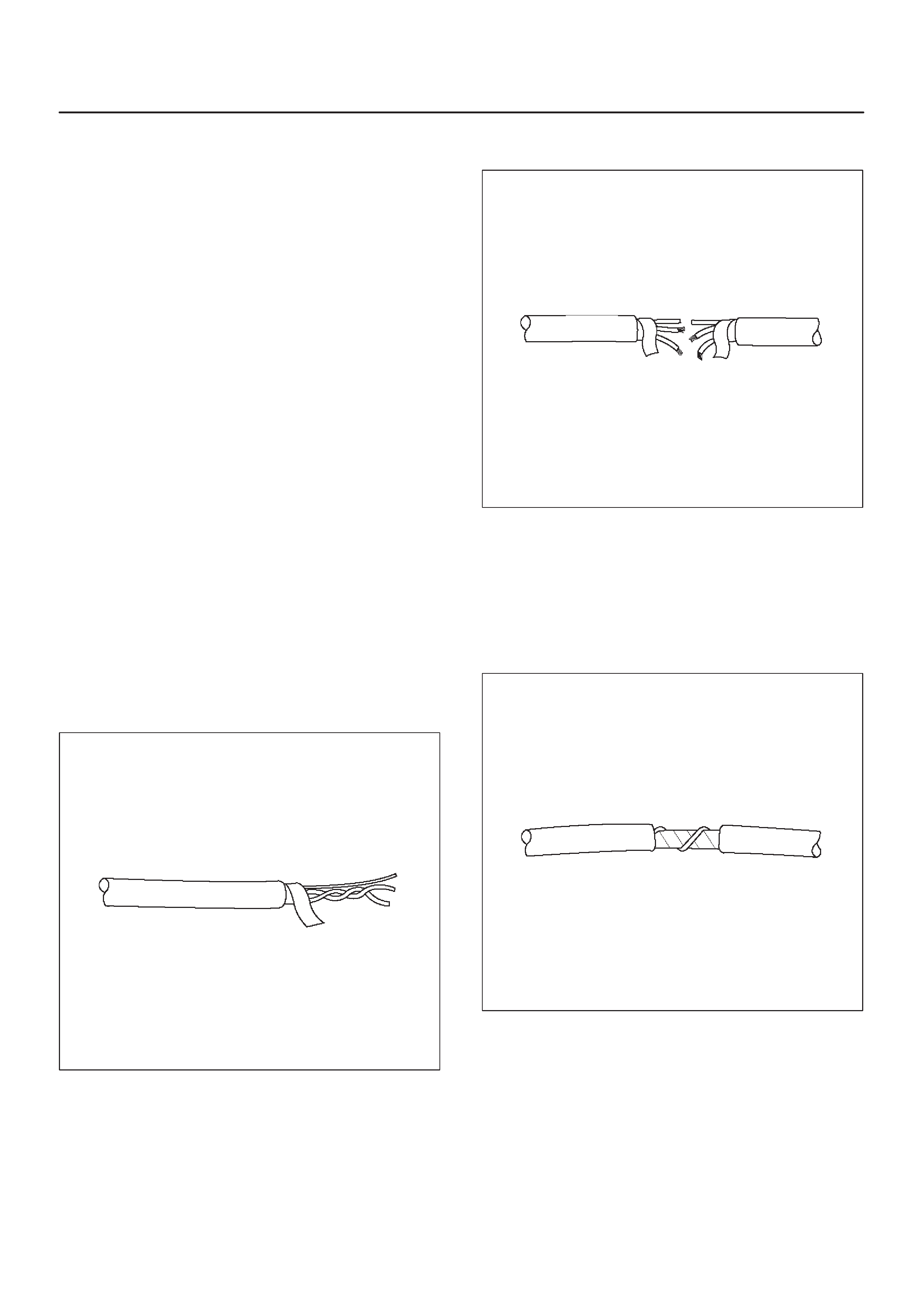
Connectors And Terminals
Connectors And Terminals
Use care when probing a connector and when replacing
terminals. It is possible to short between opposite
terminals. Damage to components could result. Always
use jumper wires between connectors for circuit
checking. NEVER probe through Weather–Pack seals.
Use an appropriate connector test adapter kit which
contains an assortment of flexible connectors used to
probe terminals during diagnosis. Use an appropriate
fuse remover and test tool for removing a fuse and to
adapt the fuse holder to a meter for diagnosis.
Open circuits are often difficult to locate by sight because
oxidation or terminal misalignment are hidden by the
connectors. Merely wiggling a connector on a sensor, or
in the wiring harness, may temporarily correct the open
circuit. Intermittent problems may also be caused by
oxidized or loose connections.
Be certain of the type of connector/terminal before
making any connector or terminal repair. Weather–Pack
and Com–Pack III terminals look similar , but are serviced
differently.
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted
Shielded Cable
Removal Procedure
1.Remove the outer jacket.
2.Unwrap the aluminum/mylar tape. Do not remove the
mylar.
047
3.Untwist the conductors.
4.Strip the insulation as necessary.
048
Installation Procedure
1.Splice the wires using splice clips and rosin core
solder.
2.Wrap each splice to insulate.
3.Wrap the splice with mylar and with the drain
(uninsulated) wire.
049
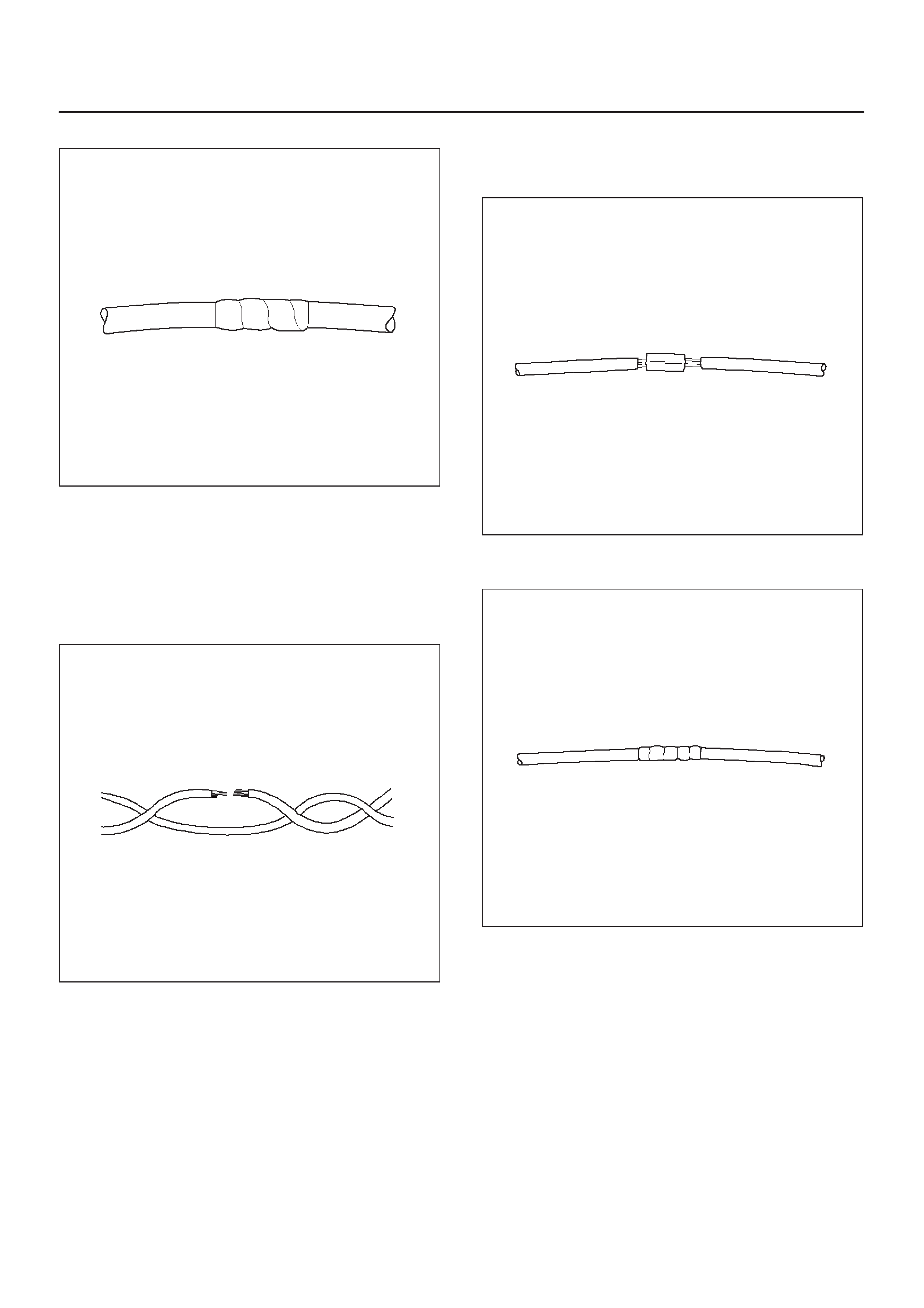
4.Tape over the whole bundle to secure.
050
Twisted Leads
Removal Procedure
1.Locate the damaged wire.
2.Remove the insulation as required.
051
Installation Procedure
1.Use splice clips and rosin core solder in order to splice
the two wires together.
052
2.Cover the splice with tape in order to insulate it from
the other wires.
053
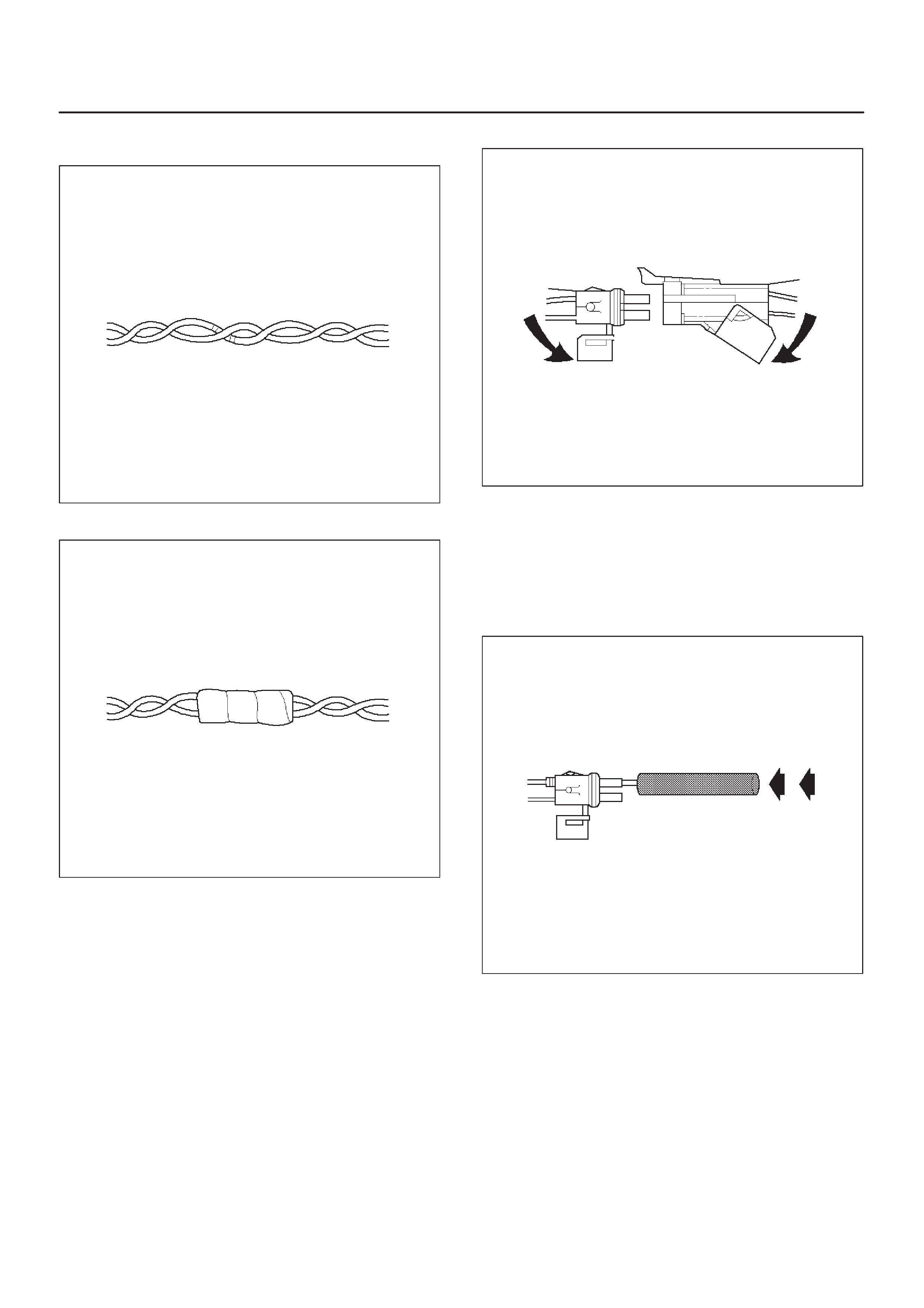
3.Twist the wires as they were before starting this
procedure.
054
4.Tape the wires with electrical tape.
055
Weather–Pack Connector
Tools Required
5-8840-0388-0 Weather–Pack II Terminal Remover
Removal Procedure
A Weather–Pack connector can be identified by a rubber
seal at the rear of the connector. This engine room
connector protects against moisture and dirt, which could
form oxidation and deposits on the terminals. This
protection is important, because of the low voltage and
the low amperage found in the electronic systems.
1.Open the secondary lock hinge on the connector.
070
2.Use tool 5-8840-0388-0 or the equivalent to remove
the pin and the sleeve terminals. Push on
5-8840-0388-0 to release.
NOTE: Do not use an ordinary pick or the terminal may
be bent or deformed. Unlike standard blade terminals,
these terminals cannot be straightened after they have
been improperly bent.
071
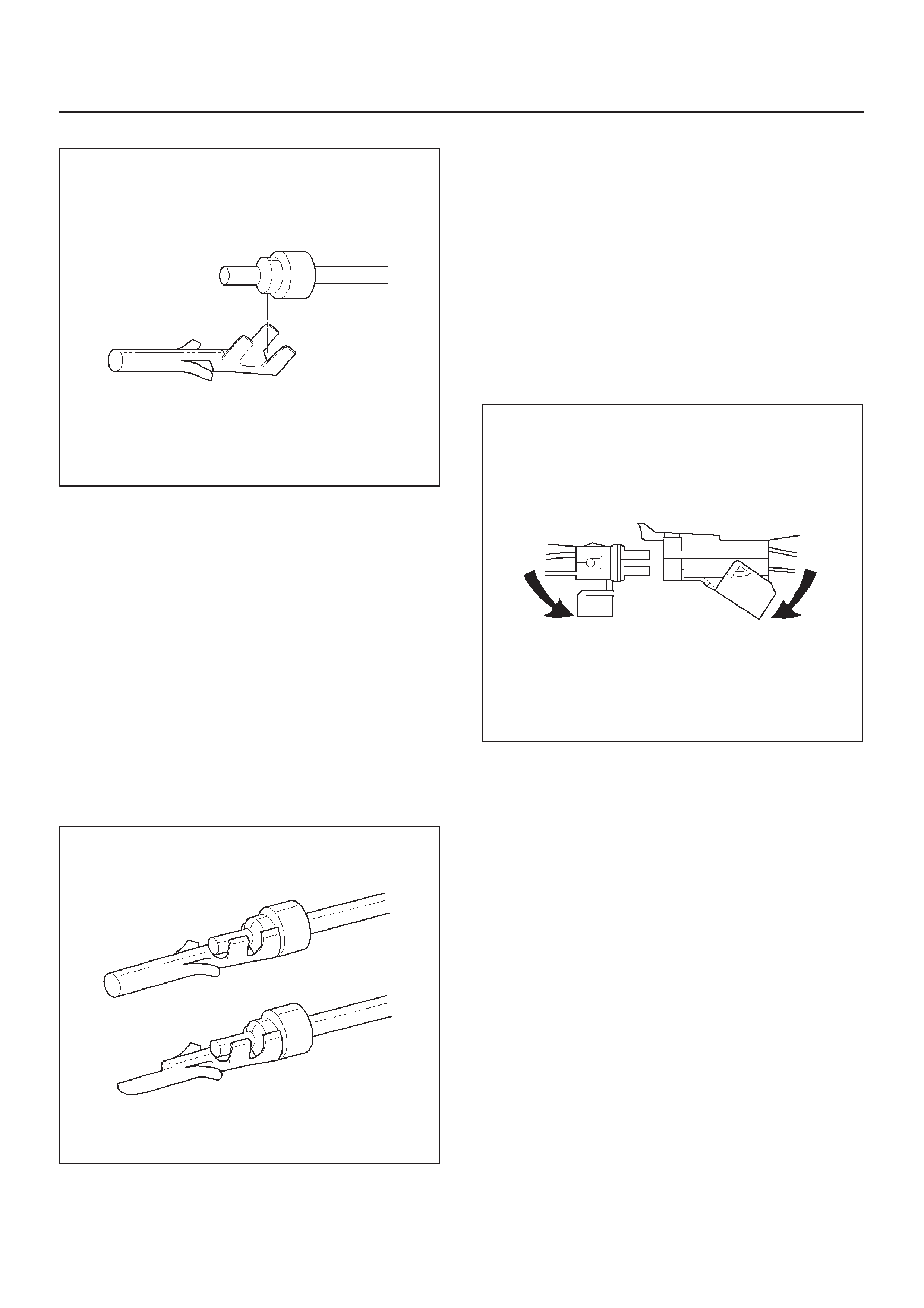
3.Cut the wire immediately behind the cable seal.
072
Installation Procedure
Make certain the connectors are properly seated and all
of the sealing rings are in place when you reconnect the
leads. The secondary lock hinge provides a backup
locking feature for the connector. The secondary lock
hinge is used for added reliability. This flap should retain
the terminals even if the small terminal lock tangs are not
positioned properly.
Do not replace the Weather–Pack connections with
standard connections. Read the instructions provided
with the Weather–Pack connector and terminal
packages.
1.Replace the terminal.
2.Slip the new seal onto the wire.
3.Strip 5 mm (0.2”) of insulation from the wire.
4.Crimp the terminal over the wire and the seal.
073
5.Push the terminal and the connector to engage the
locking tangs.
6.Close the secondary locking hinge.
Com–Pack III
Com–Pack III
The Com–Pack III terminal looks similar to some
Weather–Pack terminals. This terminal is not sealed and
is used where resistance to the environment is not
required. Use the standard method when repairing a
terminal. Do not use the Weather–Pack terminal tool
5-8840-0388-0 or equivalent. These will damage the
terminals.
070
Metri–Pack
Tools Required
5-8840-0632-0 Terminal Remover
Removal Procedure
Some connectors use terminals called Metri–Pack Series
150. These may be used at the engine coolant
temperature (ECT) sensor.
1.Slide the seal (1) back on the wire.
2.Insert the 5-8840-0632-0 tool or equivalent (3) in
order to release the terminal locking tang (2).
3.Push the wire and the terminal out through the
connector. If you reuse the terminal, reshape the
locking tang.
060
Installation Procedure
Metri–Pack terminals are also referred to as
”pull–to–seat” terminals.
1.In order to install a terminal on a wire, the wire must be
inserted through the seal (2) and through the
connector (3).
2.The terminal (1) is then crimped onto the wire.
3.Then the terminal is pulled back into the connector to
seat it in place.
061
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — ECM
AND SENSORS
58X Reference ECM Input
The engine control module (ECM) uses this signal from
the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to calculate engine
RPM and crankshaft position at all speeds. The ECM
also uses the pulses on this circuit to initiate injector
pulses. If the ECM receives no pulses on this circuit, DTC
P0337 will set. If the ECM receives a number of pulses
other than the expected amount, DTC P0336 will set. The
engine will not start and run without using the 58X
reference signal.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control switch. The ECM uses this signal to
adjust the idle speed before turning ON the A/C clutch.
The A/C compressor will be inoperative if this signal is not
available to the ECM.
For A/C wiring diagrams and diagnosis for the A/C
electrical system, refer to A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis.
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor provides a signal
used by the powertrain control module (ECM) to calculate
the ignition sequence. The CKP sensor initiates the 58X
reference pulses which the ECM uses to calculate RPM
and crankshaft position. For additional information,
refer to Electronic Ignition System.
0013
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor And
Signal
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor sends a signal to
the ECM. The ECM uses this signal as a ”sync pulse” to
trigger the injectors in the proper sequence. The ECM
uses the CMP signal to indicate the position of the #1
piston during its power stroke. The CMP allows the ECM
to calculate true sequential fuel injection (SFI) mode of
operation. If the ECM detects an incorrect CMP signal
while the engine is running, DTC P0341 will set.
If the CMP signal is lost while the engine is running, the
fuel injection system will shift to a calculated sequential
fuel injection mode based on the last fuel injection pulse,
and the engine will continue to run. It will run in the
calculated sequential mode with a 1–in–4 chance of the
injector sequence being correct.
For further information, refer to
DTC P0341
DTC P0342.
014RX007
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor (a resistor which changes value based on
temperature) mounted in the engine coolant stream. Low
coolant temperature produces a high resistance of about
100,000 W at –40°C (–40°F). High temperature causes a
low resistance of about 70 W at 130°C (266°F).
The ECM supplies a 5–volt signal to the ECT sensor
through resistors internal to the ECM and then measures
the voltage after the internal resistor. This signal voltage
will be high when the engine is cold and low when the
engine is hot. By measuring the voltage, the ECM
calculates the engine coolant temperature. Engine
coolant temperature affects most of the systems that the
ECM controls.
The Tech 2 displays engine coolant temperature in
degrees. After engine start–up, the temperature should
rise steadily to about 85°C (185°F). It then stabilizes
when the thermostat opens. If the engine has not been
run for several hours (overnight), the engine coolant
temperature and intake air temperature displays should
be close to each other. A hard fault in the engine coolant
sensor circuit will set DTC P0117 or DTC P0118. An
intermittent fault will set a DTC P1114 or P1115.
0016
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EEPROM)
The electrically erasable programmable read only
memory (EEPROM) is a permanent memory chip that is
physically soldered within the ECM. The EEPROM
contains the program and the calibration information that
the ECM needs to control powertrain operation.
Unlike the PROM used in past applications, the EEPROM
is not replaceable.
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensor (Pre
Catalyst)
The fuel control heated oxygen sensor (Bank 1 HO2S 1)
is mounted in the exhaust stream where it can monitor the
oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The oxygen present in
the exhaust gas reacts with the sensor to produce a
voltage output. This voltage should constantly fluctuate
from approximately 100 mV to 900 mV. The heated
oxygen sensor voltage can be monitored with a T ech 2. By
monitoring the voltage output of the oxygen sensor, the
ECM calculates the pulse width command for the
injectors to produce the proper combustion chamber
mixture.
DLow HO2S voltage is a lean mixture which will result in
a rich command to compensate.
DHigh HO2S voltage is a rich mixture which will result in
a lean command to compensate.
An open Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal circuit will set a DTC
P0134 and the Tech 2 will display a constant voltage
between 400–500 mV. A constant voltage below 300 mV
in the sensor circuit (circuit grounded) will set DTC
P0131. A constant voltage above 800 mV in the circuit will
set DTC P0132. The ECM can also detect HO2S
response problems. If the response time of an HO2S is
determined to be too slow , the ECM will store a DTC that
indicates degraded HO2S performance.
0012
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor
which changes its resistance based on the temperature of
air entering the engine. Low temperature produces a high
resistance of about 100,000 W at –40°C (–104°F). High
temperature causes low resistance of about 70 W at
130°C (266°F). The ECM supplies a 5–volt signal to the
sensor through a resistor internal to the ECM, and then
monitors the signal voltage. The voltage will be high when
the incoming air is cold. The voltage will be low when the
incoming air is hot. By measuring the voltage, the ECM
calculates the incoming air temperature. The IAT sensor
signal is used to adjust spark timing according to the
incoming air density.
The Tech 2 displays the temperature of the air entering
the engine. The temperature should read close to the
ambient air temperature when the engine is cold and rise
as underhood temperature increases. If the engine has
not been run for several hours (overnight), the IAT sensor
temperature and engine coolant temperature should read
close to each other. A failure in the IAT sensor circuit will
set DTC P0112, or DTC P0113.
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Control
The ECM monitors the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
actual position and adjusts the pintle position accordingly.
The ECM uses information from the following sensors to
control the pintle position:
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
DThrottle position (TP) sensor.
DManifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor.
0017
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor responds
to changes in intake manifold pressure (vacuum). The
MAP sensor signal voltage to the ECM varies from below
2 volts at idle (high vacuum) to above 4 volts with the
ignition ON, engine not running or at wide–open throttle
(low vacuum).
The MAP sensor is used to determine the following:
DManifold pressure changes while the linear EGR flow
test diagnostic is being run. Refer to DTC P0401.
DEngine vacuum level for other diagnostics.
DBarometric pressure (BARO).
If the ECM detects a voltage that is lower than the
possible range of the MAP sensor, DTC P0107 will be set.
A signal voltage higher than the possible range of the
sensor will set DTC P0108. The ECM can detect a shifted
MAP sensor . The ECM compares the MAP sensor signal
to a calculated MAP based on throttle position and
various engine load factors.
014RX013
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located in the
passenger compartment below the center console. The
ECM controls the following:
DFuel metering system.
DIgnition timing.
DOn–board diagnostics for powertrain functions.
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensors. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. It can recognize
operational problems, alert the driver through the Check
Engine lamp, and store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
DTCs identify the problem areas to aid the technician in
making repairs.
014RX002
ECM Function
The ECM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power various
sensors or switches. The power is supplied through
resistors in the ECM which are so high in value that a test
light will not light when connected to the circuit. In some
cases, even an ordinary shop voltmeter will not give an
accurate reading because its resistance is too low.
Therefore, a digital voltmeter with at least 10 megW input
impedance is required to ensure accurate voltage
readings. Tool J 39200 meets this requirement.
The ECM controls output circuits such as the injectors,
IAC, cooling fan relays, etc., by controlling the ground or
the power feed circuit through transistors or through
either of the following two devices:
DOutput Driver Module (ODM)
DQuad Driver Module (QDM)
ECM Components
The ECM is designed to maintain exhaust emission levels
to government mandated standards while providing
excellent driveability and fuel efficiency. The ECM
monitors numerous engine and vehicle functions via
electronic sensors such as the throttle position (TP)
sensor, heated oxygen sensor (HO2S), and vehicle
speed sensor (VSS). The ECM also controls certain
engine operations through the following:
DFuel injector control
DIgnition control module
DEvaporative emission (EVAP) purge
DA/C clutch control
ECM Voltage Description
The ECM supplies a buffered voltage to various switches
and sensors. It can do this because resistors in the ECM
which are so high in value that a test light may not
illuminate when connected to the circuit. An ordinary shop
voltmeter may not give an accurate reading because the
voltmeter input impedance is too low . Use a 10–megohm
input impedance digital voltmeter (such as J 39200) to
assure accurate voltage readings.
The input/output devices in the ECM include
analog–to–digital converters, signal buffers, counters,
and special drivers. The ECM controls most components
with electronic switches which complete a ground circuit
when turned ON. These switches are arranged in groups
of 4 and 7, called either a quad driver module (QDM),
which can independently control up to 4 output terminals,
or Output Driver Module (ODM) which can independently
control up to 7 outputs. Not all outputs are always used.
ECM Inputs/Outputs
Inputs – Operating Conditions Read
DAir Conditioning Compressor Clutch ON or OFF
DEngine Coolant Temperature
DCrankshaft Position
DExhaust Oxygen Content
DManifold Absolute Pressure
DBattery Voltage
DThrottle Position
DFuel Tank Vapor Pressure
DFuel Tank Level
DExhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Feedback
DKnock
DVehicle Speed
DFuel Pump Voltage
DPower Steering Pressure
DIntake Air Temperature
DCamshaft Position
Outputs – Systems Controlled
DEVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
DExhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
DIgnition Control
DFuel Injector Control
DIdle Air Control
DCoolant Fan Relays
DElectric Fuel Pump Relay Compressor Clutch Relay
DAir Conditioning
DDiagnostics
–OBD II Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine
lamp)
–Data Link Connector (DLC)
–Data Output
DTachometer Signal
ECM Service Precautions
The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draws
associated with vehicle operation. Avoid over loading any
circuit. When testing for opens and shorts, do not ground
or apply voltage to any of the ECM’s circuits unless
instructed to do so. These circuits should only be tested
using digital voltmeter J 39200. The ECM should remain
connected to the ECM or to a recommended breakout
box.
014RX002
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
The throttle position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer
connected to the throttle shaft on the throttle body. The
ECM monitors the voltage on the signal line and
calculates throttle position. As the throttle valve angle is
changed (accelerator pedal moved), the TP sensor signal
also changes. At a closed throttle position, the output of
the TP sensor is about 0.25 volts. As the throttle valve
opens, the output increases so that at wide open throttle
(WOT), the output voltage should be about 4.75 volts.
The ECM calculates fuel delivery based on throttle valve
angle (driver demand). A broken or loose TP sensor may
cause intermittent bursts of fuel from an injector and
unstable idle because the ECM thinks the throttle is
moving. A hard failure in the TP sensor 5–volt reference
or signal circuits will set either a DTC P0122 or DTC
P0123. A hard failure with the TP sensor ground circuit
may set DTC P0123 and DTC P0122. Once a DTC is set,
the ECM will use an artificial default value based on
engine RPM and mass air flow for the throttle position,
and some vehicle performance will return. A high idle may
result when either DTC P0122 or DTC P0123 is set. The
ECM can detect intermittent TP sensor faults.
101RX003
Transmission Range Switch
IMPORTANT:The vehicle should not be driven with the
transmission range switch disconnected; idle quality will
be affected.
The four inputs from the transmission range switch
indicate to the ECM which position is selected by the
transmission selector lever. This information is used for
ignition timing, EVAP canister purge, EGR and IAC valve
operation.
For more information on the transmission range switch,
refer to 4L30–E Automatic Transmission.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The ECM determines the speed of the vehicle by
converting a pulsing voltage signal from the vehicle speed
sensor (VSS) into miles per hour. The ECM uses this
signal to operate the speedometer.
0008
Use of Circuit Testing Tools
Do not use a test light to diagnose the powertrain
electrical systems unless specifically instructed by the

diagnostic procedures. Use Connector Test Adapter Kit J
35616 whenever diagnostic procedures call for probing
connectors.
Aftermarket Electrical And Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add–on) electrical and vacuum equipment is
defined as any equipment which connects to the vehicle’s
electrical or vacuum systems that is installed on a vehicle
after it leaves the factory. No allowances have been made
in the vehicle design for this type of equipment.
NOTE: No add–on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add–on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle’s electrical system at the battery
(power and ground).
Add–on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any powertrain problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be diagnosed
in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become statically
charged. The most common methods of charging are by
friction and induction.
DAn example of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
DCharge by induction occurs when a person with
well–insulated shoes stands near a highly charged
object and momentarily touches ground. Charges of
the same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.
TS23793
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage, follow these guidelines:
DDo not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered
components on the ECM circuit board.
DDo not touch any electronic sensor module
component leads.
DDo not open the replacement part package until the
part is ready to be installed.
DBefore removing the part from the package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
DIf the part has been handled while sliding across the
seat, while sitting down from a standing position, or
while walking a distance, touch a known good ground
before installing the part.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — AIR
INDUCTION
Air Induction System
The air induction system filters contaminants from the
outside air, and directs the progress of the air as it is
drawn into the engine. A remote–mounted air cleaner
prevents dirt and debris in the air from entering the
engine. The air duct assembly routes filtered air to the
throttle body . Air enters the engine by the following steps:
1.Through the throttle body.
2.Into the intake manifold.
3.Through the cylinder head intake ports.
4.Into the cylinders.
028RX002
GENERAL DESCRIPTION — FUEL
METERING
Acceleration Mode
The ECM provides extra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Accelerator Controls
The accelerator control system is a cable–type system
with specific linkage adjustments.
Refer to Cable Adjustment.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the ECM will compensate for
the weak spark by increasing the following:
DThe amount of fuel delivered.
DThe idle RPM.
CMP Signal
The ECM uses the camshaft position (CMP) sensor
signal to determine the position of the number 1 piston
during its power stroke, allowing the ECM to calculate
true sequential multiport fuel injection (SFI). Loss of this
signal will set a DTC P0341 or DTC P0342. If the CMP
signal is lost while the engine is running, the fuel injection
system will shift to a calculated sequential fuel injection
based on the last fuel injection pulse, and the engine will
continue to run. The engine can be restarted and will run
in the calculated sequential mode with the fault is present,
with a 1–in–4 chance of being correct.
Clear Flood Mode
Clear a flooded engine by pushing the accelerator pedal
down all the way. The ECM then de–energizes the fuel
injectors. The ECM holds the fuel injectors de–energized
as long as the throttle remains above 80% and the engine
speed is below 800 RPM. If the throttle position becomes
less than 80%, the ECM again begins to pulse the
injectors ON and OFF, allowing fuel into the cylinders.
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air flow.
When deceleration is very fast, the ECM may cut off fuel
completely for short periods.
Engine Speed/Vehicle Speed/ Fuel Disable
Mode
The ECM monitors engine speed. It turns off the fuel
injectors when the engine speed increases above 6000
RPM. The fuel injectors are turned back on when engine
speed decreases below 5750 RPM.
Fuel Cutoff Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the ignition
is OFF. This prevents engine run–on. In addition, the
ECM suspends fuel delivery if no reference pulses are
detected (engine not running) to prevent engine flooding.
Fuel Injector
The sequential multiport fuel injection (SFI) fuel injector is
a solenoid–operated device controlled by the ECM. The
ECM energizes the solenoid, which opens a valve to allow
fuel delivery.
The fuel is injected under pressure in a conical spray
pattern at the opening of the intake valve. Excess fuel not
used by the injectors passes through the fuel pressure
regulator before being returned to the fuel tank.
A fuel injector which is stuck partly open will cause a loss
of fuel pressure after engine shut down, causing long
crank times.
0003
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts:
DThe fuel injectors.
DThe throttle body.
DThe fuel rail.
DThe fuel pressure regulator.
DThe ECM.
DThe crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
DThe camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
DThe idle air control (IAC) valve.
DThe fuel pump.
DThe fuel pump relay.
Basic System Operation
The fuel metering system starts with the fuel in the fuel
tank. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank,
pumps fuel to the fuel rail through an in–line fuel filter. The
pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure above the
pressure needed by the injectors. A fuel pressure
regulator in the fuel rail keeps fuel available to the fuel
injectors at a constant pressure. A return line delivers
unused fuel back to the fuel tank. Refer to Section 6C for
further information on the fuel tank, line filter, and fuel
pipes.
Fuel Metering System Purpose
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control the air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is delivered
to the engine by individual fuel injectors mounted in the
intake manifold near each intake valve.
The main control sensor is the heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S) located in the exhaust system. The HO2S tells
the ECM how much oxygen is in the exhaust gas. The
ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling
the amount of time that the fuel injector is ON. The best
mixture to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 parts of air
to 1 part of gasoline by weight, which allows the catalytic
converter to operate most efficiently. Because of the
constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the
fuel injection system is called a ”Closed Loop” system.
The ECM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called ”modes.”
All modes are controlled by the ECM.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm–operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the other
side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel
pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separately.
If the pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC
P0171, or DTC P1171 will be the result. If the pressure is
too high, a DTC P0172 will be the result. For information
on diagnosing fuel pressure conditions, refer to Fuel
System Diagnosis.
014RX038
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned ON, the ECM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build-up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the ECM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until
the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked and
the 58X crankshaft position signal has been detected by
the ECM, the ECM supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric in–tank fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a ”no–start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will
result in poor performance.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is delivered
to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel lines. The
fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintains a
constant fuel pressure at the injectors. Remaining fuel is
then returned to the fuel tank.
014RX036
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The purpose of the idle air control (IAC) valve is to control
engine idle speed, while preventing stalls due to changes
in engine load. The IAC valve, mounted in the throttle
body, controls bypass air around the throttle plate. By
moving the conical valve (pintle) in (to decrease air flow)
or out (to increase air flow), a controlled amount of air can
move around the throttle plate. If the RPM is too low, the
ECM will retract the IAC pintle, resulting in more air
moving past the throttle plate to increase the RPM. If the
RPM is too high, the ECM will extend the IAC pintle,
allowing less air to move past the throttle plate,
decreasing the RPM.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small steps called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the ECM based on battery voltage, coolant
temperature, engine load, and engine RPM. If the RPM
drops below a specified value, and the throttle plate is
closed, the ECM senses a near–stall condition. The ECM
will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve position to
prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with the
engine running, the idle RPM will be wrong. In this case,
the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the key is
cycled ON then OFF. When servicing the IAC, it should
only be disconnected or connected with the ignition OFF.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine
start–up and the idle characteristics of the vehicle. If the
IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be allowed into
the manifold. This results in high idle speed, along with
possible hard starting and a lean air/fuel ratio. DTC
P0507 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck closed, too little
air will be allowed in the manifold. This results in a low idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and a rich air/fuel
ratio. DTC P0506 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck
part–way open, the idle may be high or low and will not
respond to changes in the engine load.
0006
Run Mode
The run mode has the following two conditions:
DOpen Loop
DClosed Loop
When the engine is first started, the system is in ”Open
Loop” operation. In ”Open Loop,” the ECM ignores the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). It
calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the TP,
ECT, and MAP sensors.
The system remains in ”Open Loop” until the following
conditions are met:
DThe HO2S has a varying voltage output showing that
it is hot enough to operate properly (this depends on
temperature).
DThe ECT has reached a specified temperature.
DA specific amount of time has elapsed since starting
the engine.
DEngine speed has been greater than a specified RPM
since start–up.
The specific values for the above conditions vary with
different engines and are stored in the programmable
read only memory (PROM). When these conditions are
met, the system enters ”Closed Loop” operation. In
”Closed Loop”, the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio
(injector on–time) based on the signal from the HO2S.
This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7:1.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned ON, the ECM energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to allow the fuel pump
to build up pressure. The ECM then checks the engine
coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and the throttle
position (TP) sensor to determine the proper air/fuel ratio
for starting.
The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by adjusting how long the fuel injectors are
energized by pulsing the injectors for very short times.
Throttle Body Unit
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the amount
of air delivered to the engine. The TP sensor and IAC
valve are also mounted on the throttle body.
Vacuum ports located behind the throttle plate provide the
vacuum signals needed by various components. Engine
coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in the throttle
body to warm the throttle valve and to prevent icing.
014RX040
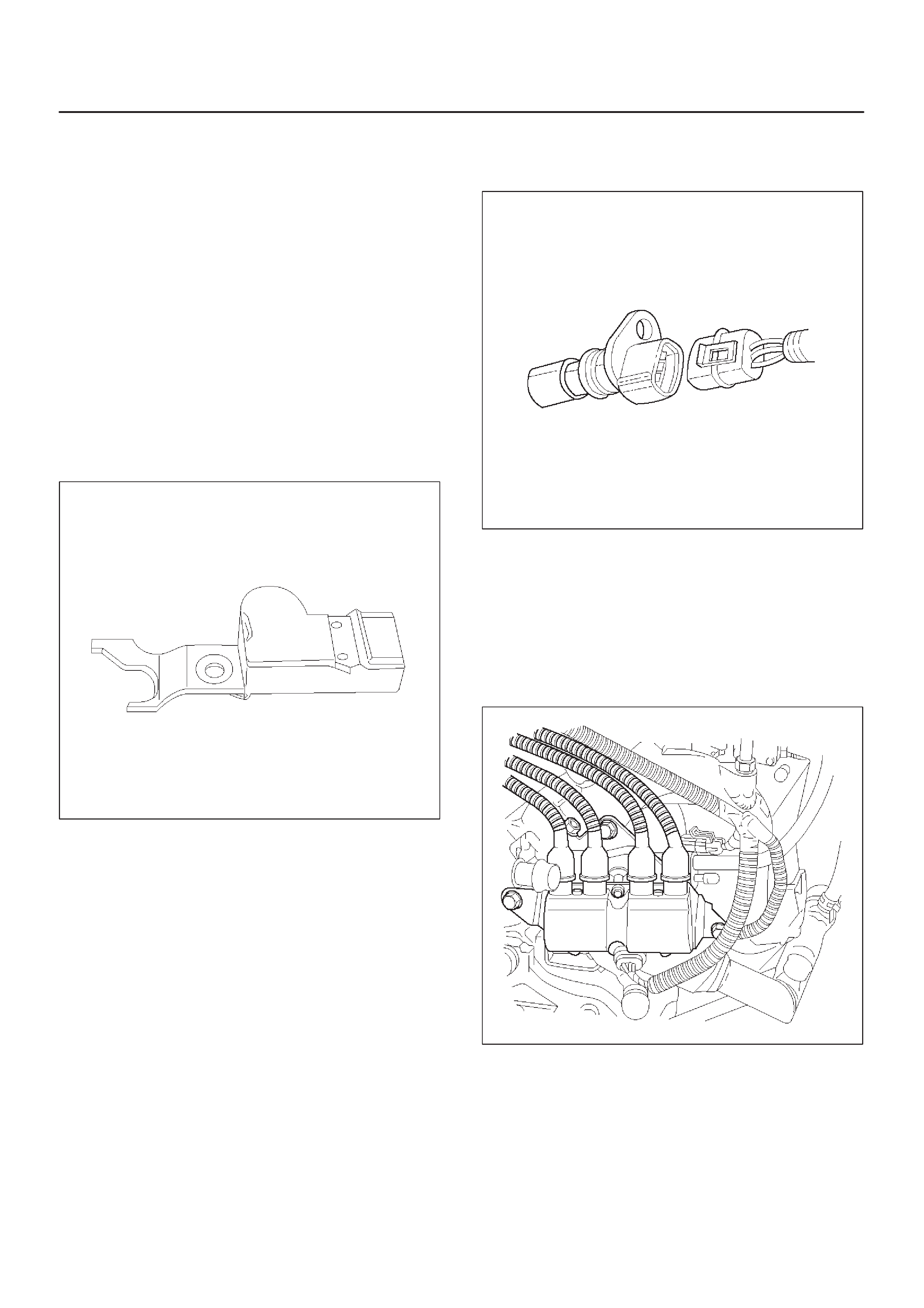
GENERAL DESCRIPTION —
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor sends a signal to
the ECM. The ECM uses this signal as a ”sync pulse” to
trigger the injectors in the proper sequence. The ECM
uses the CMP signal to indicate the position of the #1
piston during its power stroke. The CMP allows the ECM
to calculate true sequential fuel injection (SFI) mode of
operation. If the ECM detects an incorrect CMP signal
while the engine is running, DTC P0341 will set.
If the CMP signal is lost while the engine is running, the
fuel injection system will shift to a calculated sequential
fuel injection mode based on the last fuel injection pulse,
and the engine will continue to run. It will run in the
calculated sequential mode with a 1–in–4 chance of the
injector being correct.
For additional information, refer to DTC P0342.
014RX007
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor provides a signal
used by the engine control module (ECM) to calculate the
ignition sequence. The sensor initiates the 58X reference
pulses which the ECM uses to calculate RPM and
crankshaft position. For additional information, refer to
Electronic Ignition System.
Electronic Ignition
The electronic ignition system controls fuel combustion
by providing a spark to ignite the compressed air/fuel
mixture at the correct time. To provide optimum engine
performance, fuel economy, and control of exhaust
emissions, the ECM controls the spark advance of the
ignition system. Electronic ignition has the following
advantages over a mechanical distributor system:
DNo moving parts.
DLess maintenance.
DRemote mounting capability.
DNo mechanical load on the engine.
DMore coil cooldown time between firing events.
DElimination of mechanical timing adjustments.
DIncreased available ignition coil saturation time.
0013
Ignition Coils
The 2.2L engine uses 2 ignition coils, 1 per 2 cylinders. A
two–wire connector provides a 12–volt primary supply
through the 15–amp ignition coil fuse, and the ground wire
is connected to a ground–switching ignition module.
Radio frequency interference produced by the coil is
controlled by a condenser which is mounted near the
ignition coil.
014RX044
Ignition Control
The ignition control (IC) spark timing is the ECM’s method
of controlling the spark advance and the ignition dwell.
The IC spark advance and the ignition dwell are
calculated by the ECM using the following inputs:
DEngine speed.
DCrankshaft position (58X reference).
DCamshaft position (CMP) sensor.
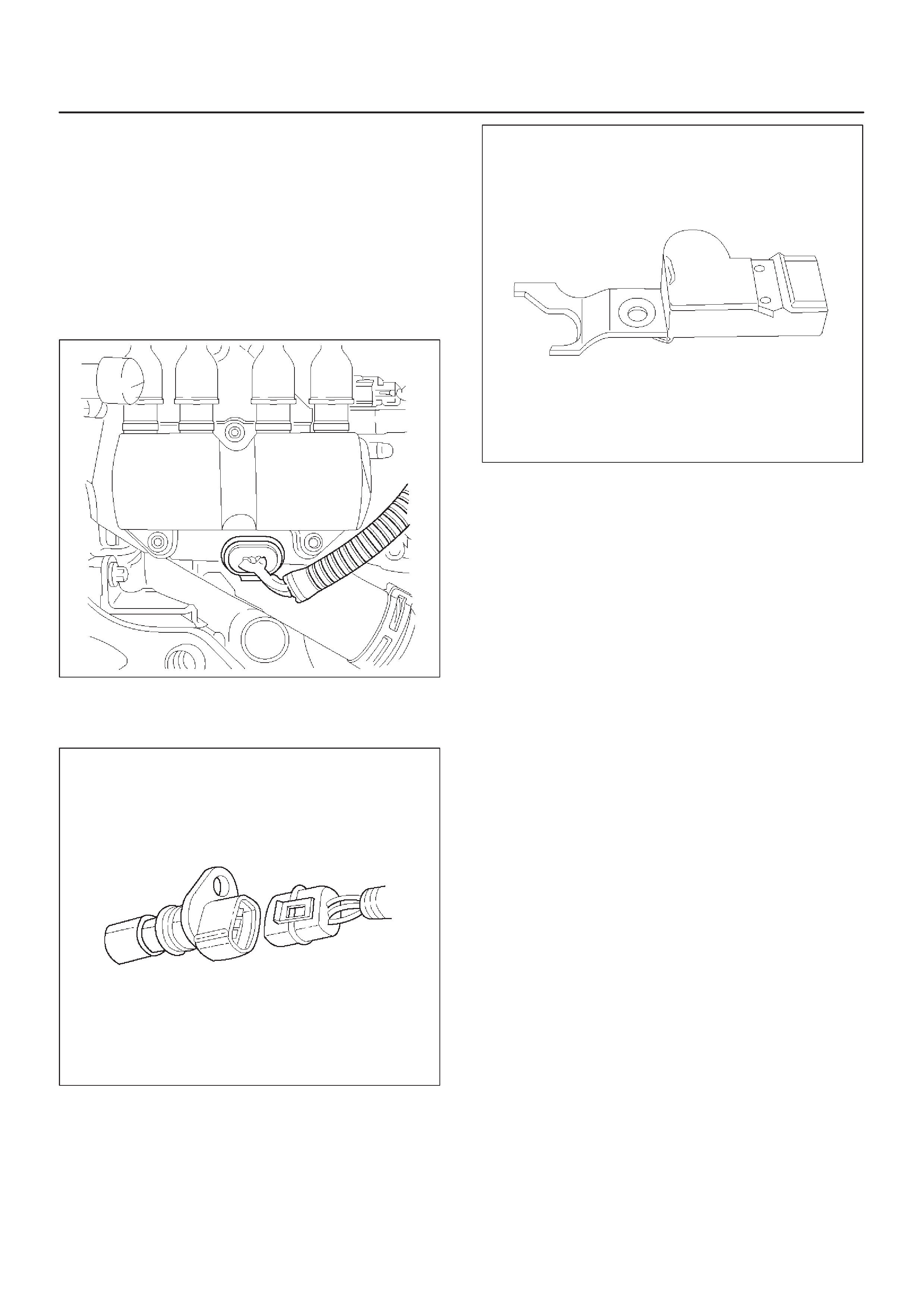
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
DThrottle position (TP) sensor.
DVehicle speed (vehicle speed sensor).
DECM and ignition system supply voltage.
Ignition Control Module (ICM)
The engine control module (ECM) controls engine ignition
through a solid–state switching unit called the ignition
control module (ICM). The software in the ECM uses
input from several sensors to determine the timing,
duration, and strength of the spark.
014RX042
DThe crankshaft position (CKP) sensor sends the ECM
a 58X signal related to the exact position of the
crankshaft.
0013
DThe camshaft position (CMP) sensor sends a signal
related to the position of the camshaft.
014RX007
Based on these sensor signals, as well as engine load
and engine coolant temperature information, the ECM
controls the switching function of the ICM by sending it a
5V signal. As long as the ICM receives the signal, it allows
battery voltage to the ignition coil. That voltage allows a
magnetic field to build in the coil.
When the ECM requires a spark plug to fire, it shuts off the
5V signal to the ICM grounding it internally. This triggers
the ICM to switch off the battery voltage to the ignition coil,
which causes the field to collapse. The lines of magnetic
force pass through the secondary portion of the coil as
they collapse. As they intersect the coil, they induce high
voltage in the secondary ignition circuit which travels
toward ground through the spark plug.
Ignition Control ECM Output
The ECM provides a zero volt (actually about 100 mV to
200 mV) or a 5–volt output signal to the ignition control
(IC) module. When the ignition control (IC) module
receives the 5–volt signal from the ECM, it provides a
ground path for the B+ supply to the primary side of the
coil and creates a magnetic field in the coil. When the
ECM shuts off the 5–volt signal to the ignition control
module, the ground path for the primary coil is broken.
The magnetic field collapses and induces a high voltage
secondary impulse which fires the spark plug and ignites
the air/fuel mixture.
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The ECM is responsible for maintaining proper spark and
fuel injection timing for all driving conditions. To provide
optimum driveability and emissions, the ECM monitors
the input signals from the following components in order
to calculate spark timing:
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
DIntake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
DThrottle position (TP) sensor.
DVehicle speed sensor (VSS).
DCrankshaft position (CKP) sensor.

Spark Plug
Although worn or dirty spark plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, they frequently fail at higher
engine speeds. Faulty spark plugs may cause poor fuel
economy, power loss, loss of speed, hard starting and
generally poor engine performance. Follow the
scheduled maintenance service recommendations to
ensure satisfactory spark plug performance. Refer to
Maintenance and Lubrication.
Normal spark plug operation will result in brown to
grayish–tan deposits appearing on the insulator portion of
the spark plug. A small amount of red–brown, yellow , and
white powdery material may also be present on the
insulator tip around the center electrode. These deposits
are normal combustion by–products of fuels and
lubricating oils with additives. Some electrode wear will
also occur.
Carbon fouling of the spark plug is indicated by dry , black
carbon (soot) deposits on the portion of the spark plug in
the cylinder. Excessive idling and slow speeds under light
engine loads can keep the spark plug temperatures so
low that these deposits are not burned off. Very rich fuel
mixtures or poor ignition system output may also be the
cause.Refer to DTC P0172.
Oil fouling of the spark plug is indicated by wet oily
deposits on the portion of the spark plug in the cylinder,
usually with little electrode wear. This may be caused by
oil during break–in of new or newly overhauled engines.
Deposit fouling of the spark plug occurs when the normal
red–brown, yellow or white deposits of combustion
by–products become sufficient to cause misfiring. In
some cases, these deposits may melt and form a shiny
glaze on the insulator around the center electrode. If the
fouling is found in only one or two cylinders, valve stem
clearances or intake valve seals may be allowing excess
lubricating oil to enter the cylinder, particularly if the
deposits are heavier on the side of the spark plug facing
the intake valve.
TS23995
Excessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the spark
plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be due to
improper gap adjustment or to excessive wear of the
electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too wide.
A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an unstable
idle condition. Excessive gap wear can be an indication of
continuous operation at high speeds or with engine loads,
causing the spark to run too hot. Another possible cause
is an excessively lean fuel mixture.
TS23992
Low or high spark plug installation torque or improper
seating can result in the spark plug running too hot and
can cause excessive center electrode wear. The plug and
the cylinder head seats must be in good contact for proper
heat transfer and spark plug cooling. Dirty or damaged
threads in the head or on the spark plug can keep it from
seating even though the proper torque is applied. Once
spark plugs are properly seated, tighten them to the
torque shown in the Specifications T able. Low torque may
result in poor contact of the seats due to a loose spark
plug. Overtightening may cause the spark plug shell to be
stretched and will result in poor contact between the
seats. In extreme cases, exhaust blow–by and damage
beyond simple gap wear may occur.
Cracked or broken insulators may be the result of
improper installation, damage during spark plug
re–gapping, or heat shock to the insulator material. Upper
insulators can be broken when a poorly fitting tool is used
during installation or removal, when the spark plug is hit
from the outside, or is dropped on a hard surface. Cracks
in the upper insulator may be inside the shell and not
visible. Also, the breakage may not cause problems until
oil or moisture penetrates the crack later.
TS23994
A broken or cracked lower insulator tip (around the center
electrode) may result from damage during re–gapping or
from ”heat shock” (spark plug suddenly operating too
hot).
TS23993
DDamage during re–gapping can happen if the
gapping tool is pushed against the center electrode or
the insulator around it, causing the insulator to crack.
When re–gapping a spark plug, make the adjustment
by bending only the ground side terminal, keeping the
tool clear of other parts.
D”Heat shock” breakage in the lower insulator tip
generally occurs during several engine operating
conditions (high speeds or heavy loading) and may be
caused by over–advanced timing or low grade fuels.
Heat shock refers to a rapid increase in the tip
temperature that causes the insulator material to
crack.
Spark plugs with less than the recommended amount of
service can sometimes be cleaned and re–gapped, then
returned to service. However, if there is any doubt about
the serviceability of a spark plug, replace it. Spark plugs
with cracked or broken insulators should always be
replaced.
A/C CLUTCH DIAGNOSIS
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation
A 12–volt signal is supplied to the A/C request input of the
ECM when the A/C is selected through the A/C control
switch.
The A/C compressor clutch relay is controlled through the
ECM. This allows the ECM to modify the idle air control
position prior to the A/C clutch engagement for better idle
quality. If the engine operating conditions are within their
specified calibrated acceptable ranges, the ECM will
enable the A/C compressor relay. This is done by
providing a ground path for the A/C relay coil within the
ECM. When the A/C compressor relay is enabled, battery
voltage is supplied to the compressor clutch coil. The
ECM will enable the A/C compressor clutch whenever the
engine is running and the A/C has been requested. The
ECM will not enable the A/C compressor clutch if any of
the following conditions are met:
DThe engine speed is greater than 6315 RPM.
DThe ECT is greater than 119°C (246°F).
DThe throttle is more than 80% open.
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose
The A/C compressor operation is controlled by the engine
control module (ECM) for the following reasons:
DIt improves idle quality during compressor clutch
engagement.
DIt improves wide open throttle (WOT) performance.
DIt provides A/C compressor protection from operation
with incorrect refrigerant pressures.
The A/C electrical system consists of the following
components:
1.The A/C control switch.
2.The A/C refrigerant pressure switches.
3.The A/C compressor clutch.
4.The A/C compressor clutch relay.
5.The ECM.
A/C Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM when the A/C mode is selected
at the A/C control switch. The ECM uses this input to
adjust the idle speed before turning on the A/C clutch. The
A/C compressor will be inoperative if this signal is not
available to the ECM.
For A/C wiring diagrams and diagnosis for the A/C
electrical system, refer to A/C Clutch Circuit Diagnosis.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION —
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION (EVAP)
SYSTEM
EVAP Emission Control System Purpose
The basic evaporative emission (EVAP) control system
used on all vehicles is the charcoal canister storage
method. Gasoline vapors from the fuel tank flow into the
canister through the inlet labeled ”TANK.” These vapors
are absorbed into the activated carbon (charcoal) storage
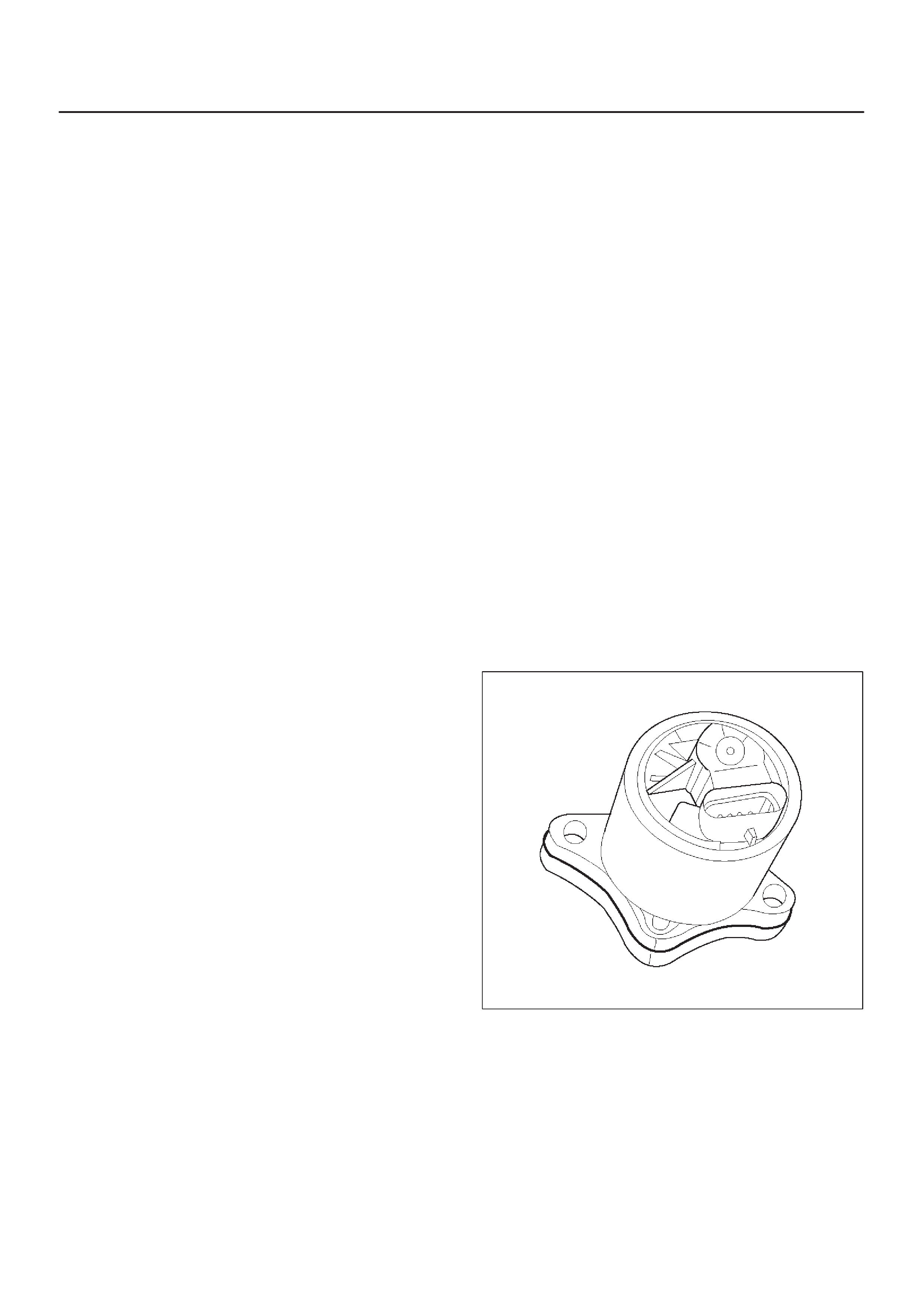

device (canister) in order to hold the vapors when the
vehicle is not operating. The canister is purged by ECM
control when the engine coolant temperature is over 60°C
(140°F), the IAT reading is over 10°C (50°F), and the
engine has been running. Air is drawn canister through
the air inlet grid. The air mixes with the vapor and the
mixture is drawn into the intake manifold.
EVAP Emission Control System Operation
The EVAP canister purge is controlled by a solenoid valve
that allows the manifold vacuum to purge the canister.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) supplies a ground to
energize the solenoid valve (purge on). The EV AP purge
solenoid control is pulse–width modulated (PWM) (turned
on and off several times a second). The duty cycle (pulse
width) is determined by engine operating conditions
including load, throttle position, coolant temperature and
ambient temperature. The duty cycle is calculated by the
ECM. The output is commanded when the appropriate
conditions have been met. These conditions are:
DThe engine is fully warmed up.
DThe engine has been running for a specified time.
DThe IAT reading is above 10°C (50°F).
Poor idle, stalling and Poor driveability can be caused by:
DA malfunctioning purge solenoid.
DA damaged canister.
DHoses that are split, cracked, or not connected
properly.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION —
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
(EGR) SYSTEM
EGR Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is used to
reduce emission levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx). NOx
emission levels are caused by a high combustion
temperature. The EGR system lowers the NOx emission
levels by decreasing the combustion temperature.
Linear EGR Valve
The main element of the system is the linear EGR valve.
The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust gas back
into the combustion chamber . The fuel/air mixture will be
diluted and combustion temperatures reduced.
Linear EGR Control
The ECM monitors the EGR actual position and adjusts
the pintle position accordingly. The ECM uses information
from the following sensors to control the pintle position:
DEngine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
DThrottle position (TP) sensor.
Linear EGR Valve Operation And Results
Of Incorrect Operation
The linear EGR valve is designed to accurately supply
EGR to the engine independent of intake manifold
vacuum. The valve controls EGR flow from the exhaust to
the intake manifold through an orifice with a
ECM–controlled pintle. During operation, the ECM
controls pintle position by monitoring the pintle position
feedback signal. The feedback signal can be monitored
with a Tech 2 as ”Actual EGR Pos.” ”Actual EGR Pos.”
should always be near the commanded EGR position
(”Desired EGR Pos.”). The ECM also tests for EGR flow.
If incorrect flow is detected, DTC P0401 will set. If DTC
P0401 is set, refer to the DTC charts.
The linear EGR valve is usually activated under the
following conditions:
DWarm engine operation.
DAbove–idle speed.
Too much EGR flow at idle, cruise or cold operation may
cause any of the following conditions to occur:
DEngine stalls after a cold start.
DEngine stalls at idle after deceleration.
DVehicle surges during cruise.
DRough idle.
DDTC P0300 (misfire detected).
Too little or no EGR flow may allow combustion
temperatures to get too high. This could cause:
DSpark knock (detonation).
DEngine overheating.
DEmission test failure.
DDTC P0401 (EGR Flow Insufficient detected).
DPoor fuel economy.
0017
EGR Pintle Position Sensor
The ECM monitors the EGR valve pintle position input to
ensure that the valve responds properly to commands
from the ECM and to detect a fault if the pintle position
sensor and control circuits are open or shorted. If the
ECM detects a pintle position signal voltage outside the
normal range of the pintle position sensor, or a signal
voltage that is not within a tolerance considered
acceptable for proper EGR system operation, the ECM
will set DTC P0404.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION —
POSITIVE CRANKCASE
VENTILATION (PCV) SYSTEM
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose
The crankcase ventilation system is used to consume
crankcase vapors in the combustion process instead of
venting them to the atmosphere. Fresh air from the
throttle body is supplied to the crankcase and mixed with
blow–by gases. This mixture is then passed through the
positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) port into the intake
manifold.
While the engine is running, exhaust gases and small
amounts of the fuel/air mixture escape past the piston
rings and enter the crankcase. These gases are mixed
with clean air entering through a tube from the air intake
duct.
028RX003
During normal, part–throttle operation, the system is
designed to allow crankcase gases to flow through the
PCV valve into the throttle body to be consumed by
normal combustion.
A plugged valve or PCV hose may cause the following
conditions:
DRough idle.
DStalling or slow idle speed.
DOil leaks.
DSludge in the engine.
A leaking PCV hose would cause:
DRough idle.
DStalling.
DHigh idle speed.
SPECIAL TOOLS
ILLUSTRATION TOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
5-8840-0285-0
(J 39200)
High Impedance
Multimeter (Digital
Voltmeter – DVM)
(1) PCMCIA Card
(2) RS232 Loop Back
Connector
(3) SAE 16/19 Adapter
(4) DLC Cable
(5) TECH–2
5-8840-0607-0
(J 34142-B)
Unpowered Test Light
5-8840-0385-0
(J 35616-A/BT-8637)
Connector Test Adapter
Kit
5-8840-0383-0
(J 26792/BT-7220-1)
Spark Tester
5-8840-0279-0
(J 23738-A)
Vacuum Pump with
Gauge
ILLUSTRATION TOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
5-8840-2640-0
(J 39194-B)
Heated Oxygen Sensor
Wrench
5-8840-0632-0
(J 35689-A)
Terminal Remover
5-8840-0388-0
(J 28742-A)
Weather Pack II
Terminal Remover
5-8840-2606-0
(J 39021-45)
Injector Test Light