
SECTION 0A - GENERAL INFORMATION
General Repair Instruction
Illustration Arrows
Identification
Lifting Instructions
Loading & Towing
Standard Bolts Torque Specifications
Abbreviations Charts
General Repair Instruction
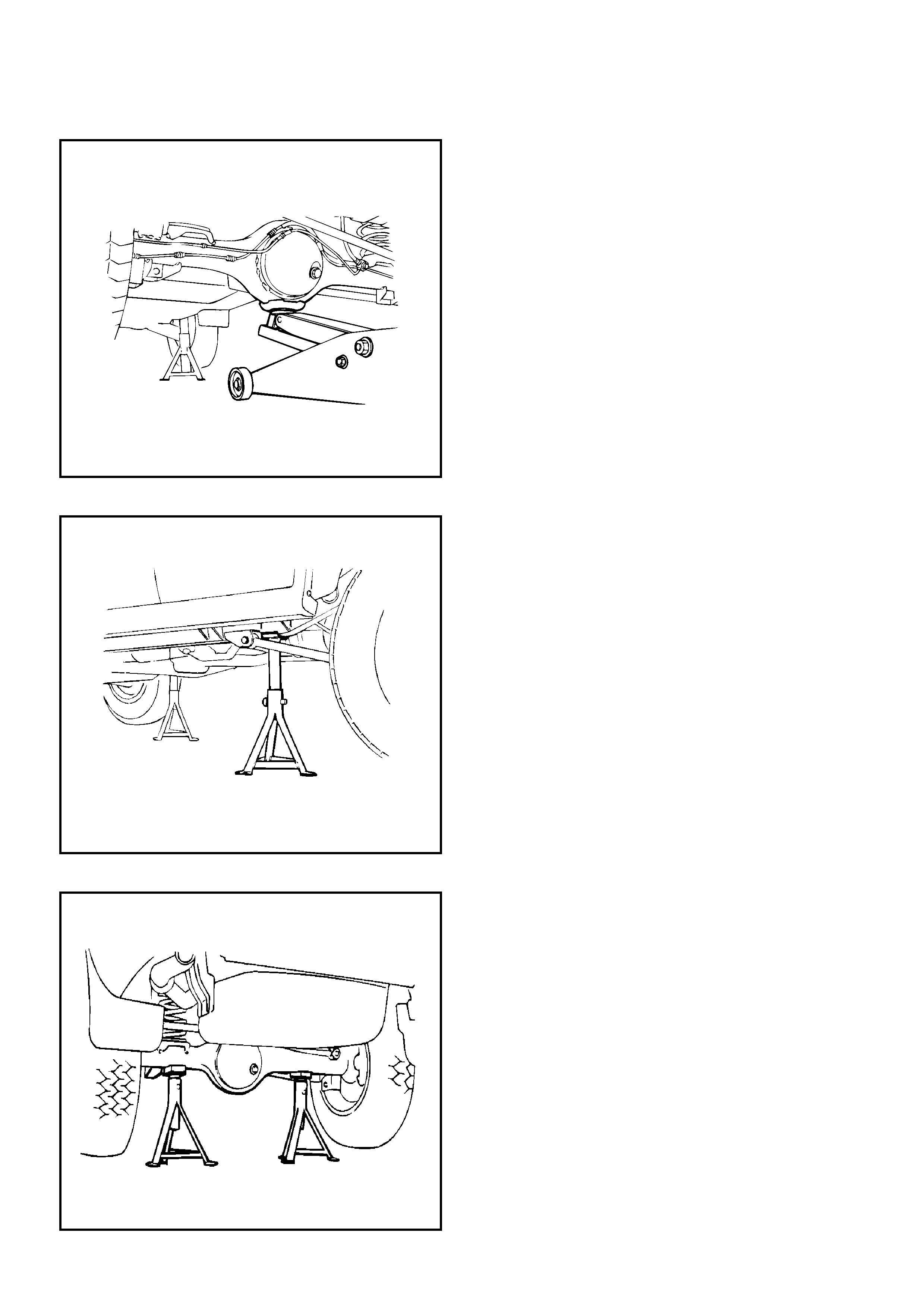
1. If a floor jack is used, the following precautions are
recommended.
Park vehicle on level ground, “block" front or rear
wheels, set jack against the recommended lifting
points (see “Lifting Instructions" in this section),
raise vehicle and support with chassis stands and
then perform the service operations.
2. Before performing service operations, disconnect
ground cable from the battery to reduce the chance
of cable damage and burning due to short circuiting.
3. Use a cover on body, seats and floor to protect them
against damage and contamination.
4. Brake fluid and anti–freeze solution must be
handled with reasonable care, as they can cause
paint damage.
5. The use of proper tools and recommended essential
and available tools, where specified, is important
for efficient and reliable performance of service
repairs.
6. Use genuine Holden parts.
7. Used cotter pins, plastic clips, gaskets, O–rings, oil
seals, lock washers and self–locking nuts should be
discarded and new ones should be installed, as
normal function of the parts cannot be maintained if
these parts are reused.
8. To facilitate proper and smooth reassembly
operation, keep disassembled parts neatly in
groups. Keeping fixing bolts and nuts separate is
very important, as they vary in hardness and design
depending on position of installation.
9. Clean the parts before inspection or reassembly.
Also clean oil ports, etc. using compressed air, and
make certain they are free from restrictions.
10. Lubricate rotating and sliding faces of the parts with
oil or grease before installation.
11. When necessary, use a sealer on gaskets to
prevent leakage.
12. Carefully observe all specifications for bolt and nut
torques.
13. When removing or replacing parts that require
refrigerant to be discharged from the air
conditioning system, be sure to use the Vehicle
Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling Equipment
(VRRRE) to recover and recycle Refrigerant–134a.
14. When a service operation is completed, make a final
check to be sure the service has been done
properly and the problem has been corrected.
15. SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM
The vehicle is equipped with a Supplemental
Restraint System (SRS) – Air Bags. This system is
not to be serviced without consulting the appropriate
service information. Consult Section 12M if work is
to be done on the front of the vehicle such as
bumper, sheet metal, seats, wiring, steering wheel
or column. Also review SRS system information if
any arc welding is to be done on the vehicle. The
SRS system equipped vehicle can be identified by:
1. “AIR BAG" warning light on the instrument
cluster.
2. “SRS” embossed on the steering wheel horn
pad.
3. SRS warning labeling on the interior sunvisor.
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline
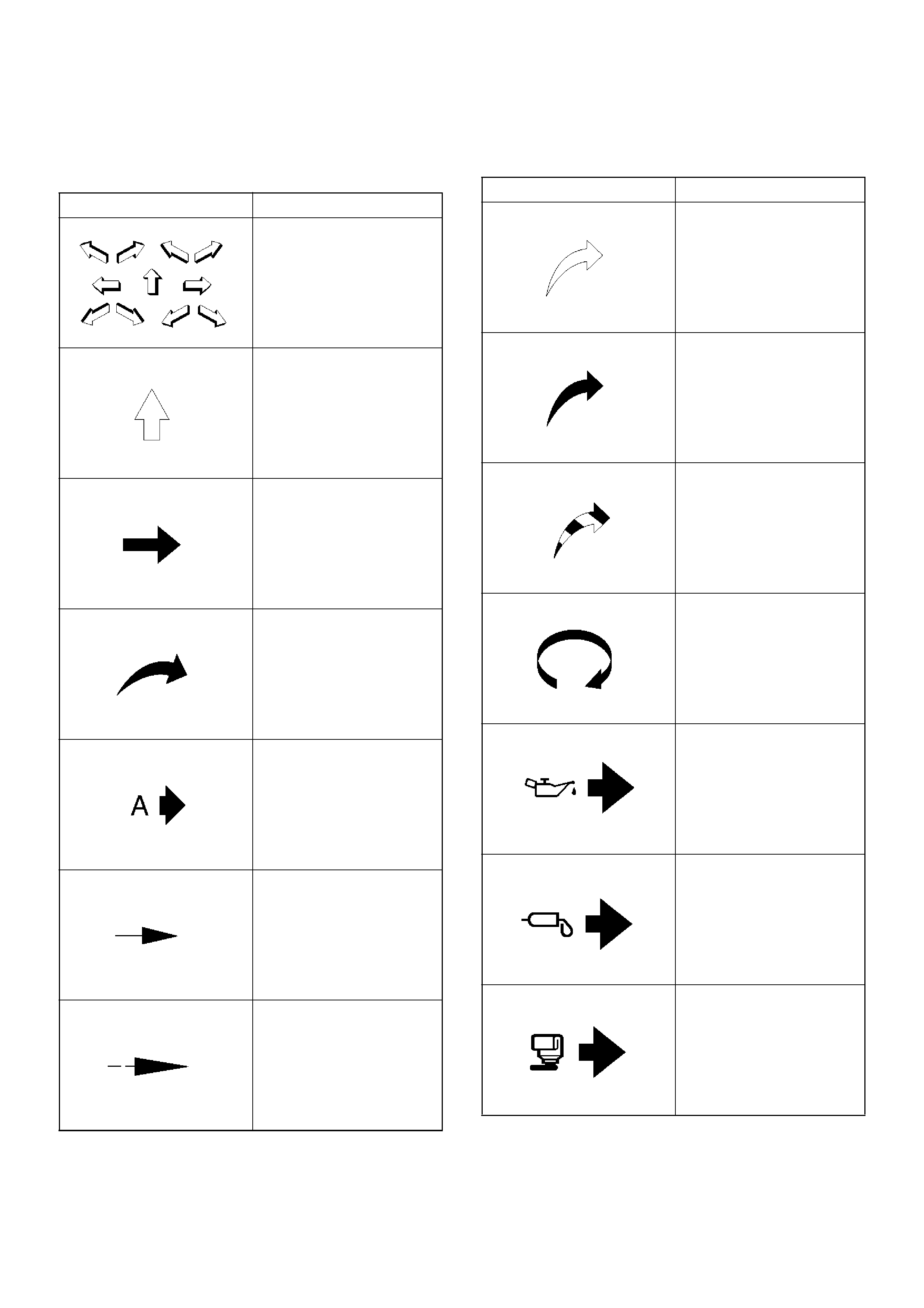
Illustration Arrows
Arrows are designed for specific purposes to aid your understanding of technical illustrations.
Arrow Type Application
Front of vehicle
Up Side
Task Related
View Detail
View Angle
Dimension (1:2)
Sectioning (1:3)
• Ambient/Clean air flow
• Cool air flow
• Gas other than
ambient air
• Hot air flow
• Ambient air mixed with
another gas
• Can indicate
temperature change
Motion or direction
Lubrication point oil or
fluid
Lubrication point grease
Lubrication point jelly
Arrow Type Application
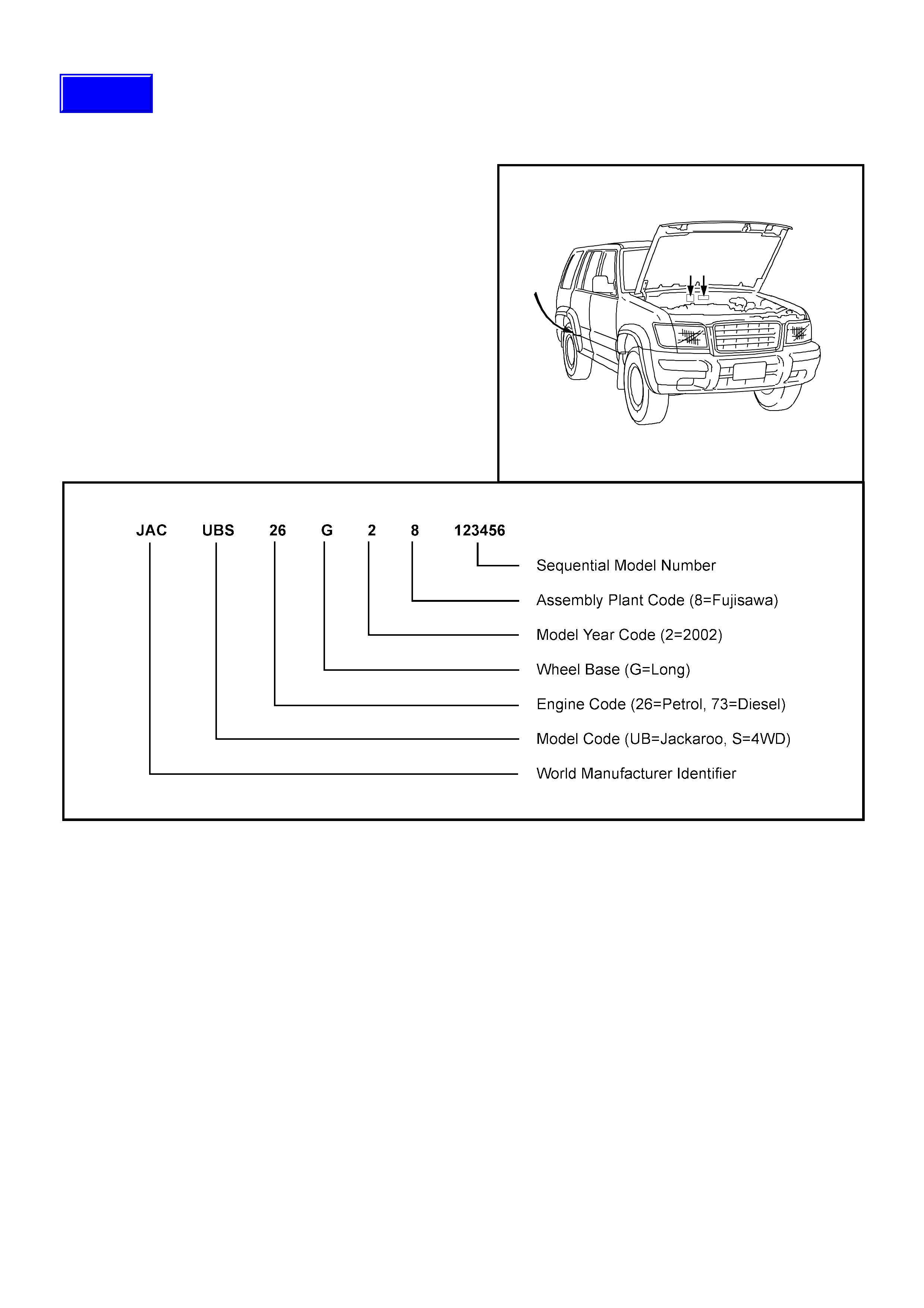
Identification
Vehicle Identification Number (ISO VIN)
This is the legal identification of the vehicle. The ISO
VIN is stamped in three locations on the vehicle;
1. On the chassis rail, just ahead of the driver side rear
wheel.
2. On the Body and Option (Service ID) Plate.
3. On the Safety Compliance Plate.
An explanation of the ISO VIN is shown below.
23
1
Techline
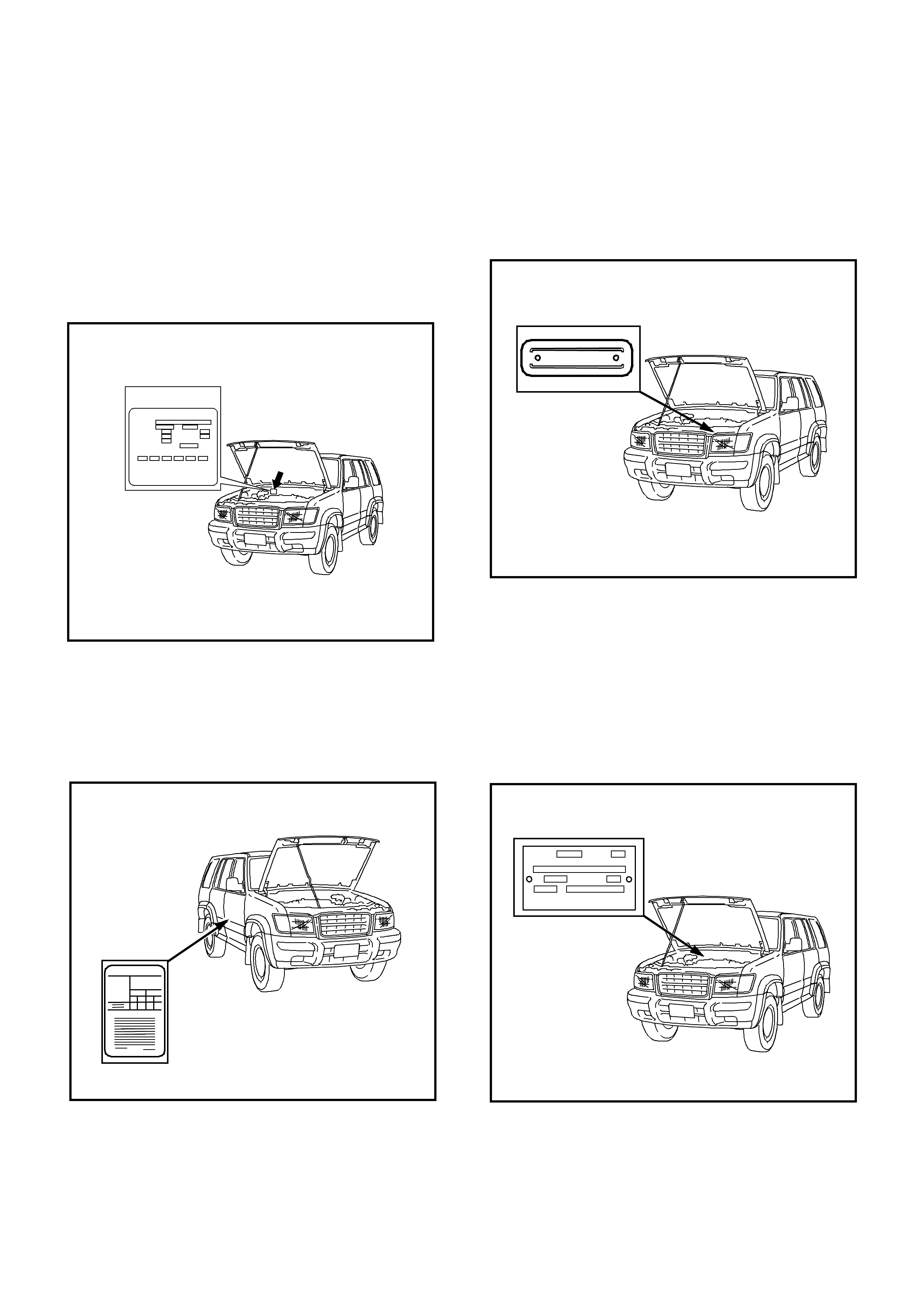
Body and Options (Service Parts)
Plate
The Body and Options plate is located on the passenger
side of the dash panel in the engine compartment.
It displays the VIN and codes for options that have been
built into the vehicle. For example, the body type, body
paint colour, trim level, engine and transmission codes
and model designation.
Tyre Placard
The Tyre Placard is located on the driver’s door lock
pillar, and is visible when the door is open.
Holden Identification Plate
The Holden identification Plate is riveted to the centre of
the radiator support panel in the engine compartment
It is used for warranty identification, roadside assistance
identification etc.
Safety Compliance (ADR) Plate
The ADR plate is riveted to the passenger side of the
dash panel in the engine compartment.
It displays the approval numbers, category,
manufacturers name, model name and code, Gross
Vehicle Mass (GVM), seating capacity, build date and
VIN.
Service parts ID plate
ISUZU MOTORS L T D. JAPAN
V. I .N .
M.D.
ENGINE
GRADE
TRANS.
TIRE
BODY TYPE
B. COLOR/TRIM
OPTION
TYRE PLACARD
WAR NI NG
RECOMMENDED C OLD
INFLATION PRESSURE
UP TO MAX LOAD
NOMINATED
RIM SIZE
A ND
TYRE S IZE
DESIGNATION
200
FRONT
NORMAL SPEED HIGH SPEED
FRONTREAR REAR
200 200 200
8MT35 2673294
APPROVAL No
THIS VEHICLE WAS MANUFACTURED TO COMPLY
WITH THE M OTOR VEHIC LE STANDA RD ACT 1996
GYM KG
VN
SE ATS
JACUBS26G28123456
HOLDEN LIM ITED
CATEGORY
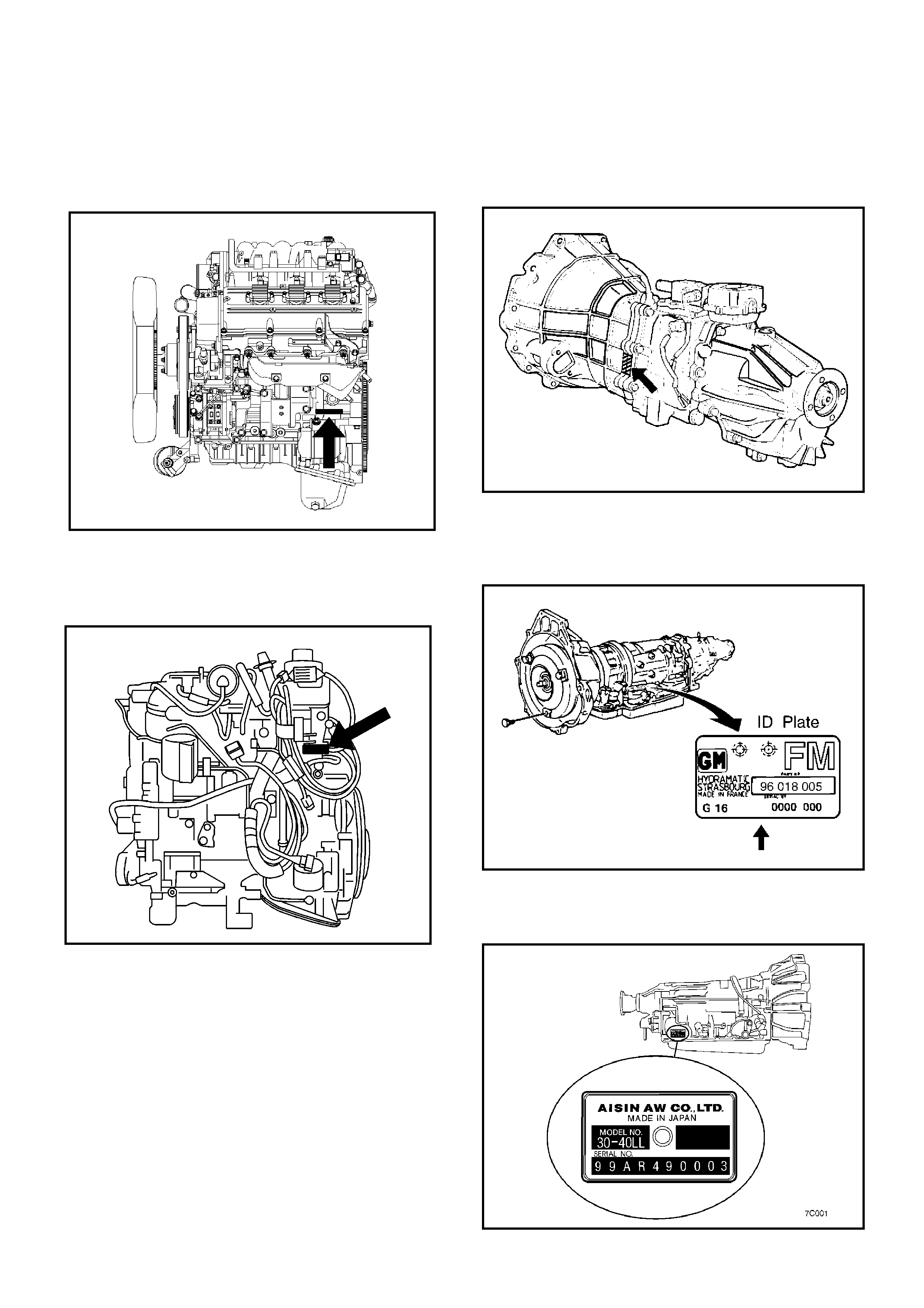
Engine Serial Number
• 6VE1 Engine
Stamped on the left rear lower area of the cylinder block
above the starter.
• 4JX1-TC Engine
On the left rear area of the cylinder block above the
starter.
Transmission Serial Number
• Manual - MUA Series
Stamped on the passenger side of the transmission
intermediate plate.
• Automatic - THM 4L30E
Stamped on the identification plate, located on the
passenger side of the transmission above the mode
switch.
• Automatic - AW 30-40 LE
Stamped on the identification plate, located on the driver
side of the transmission.
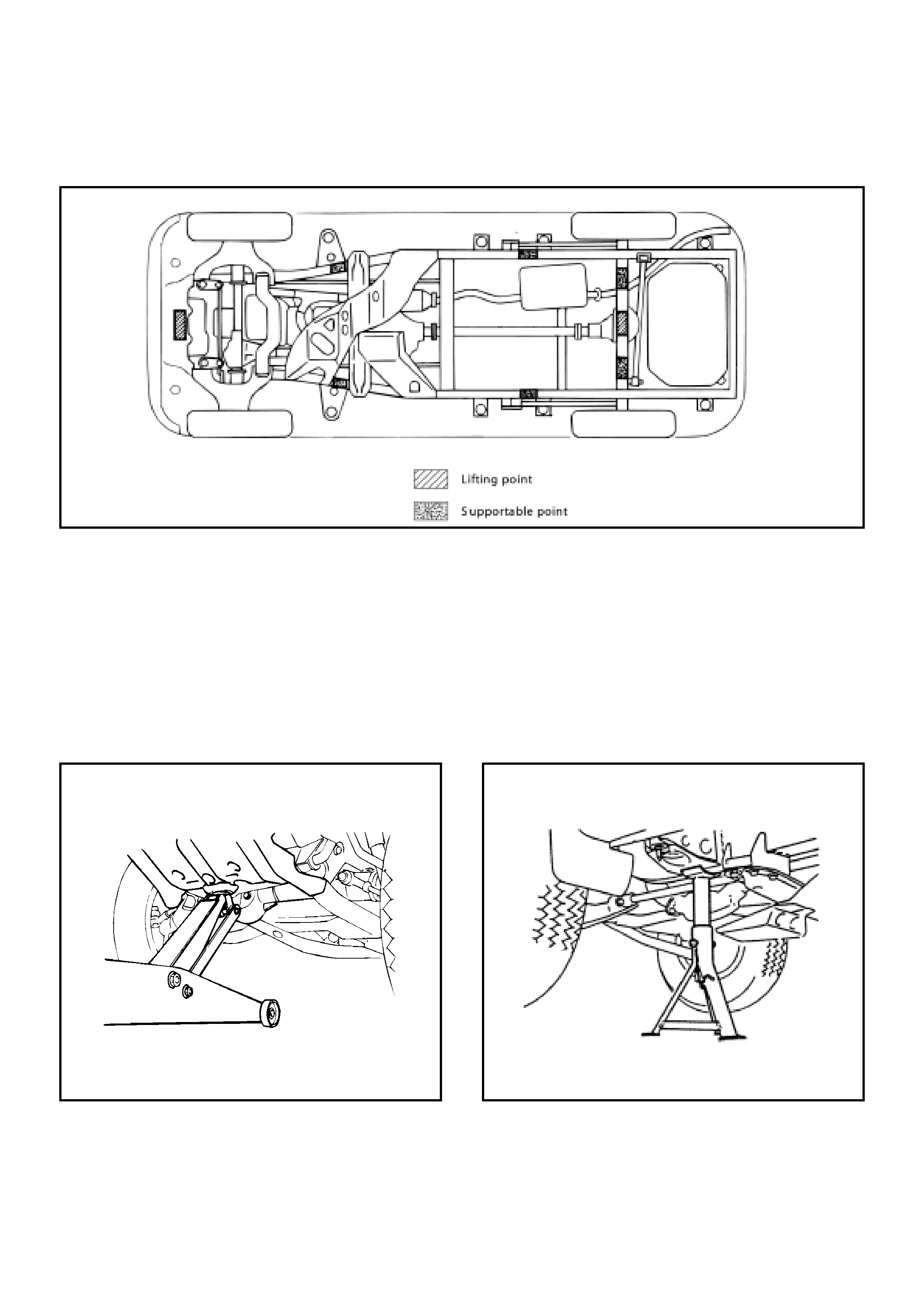
Lifting Instructions
Lifting Points and Supportable Point Locations
CAUTION:
• If a lifting device other than the oem jack is used, raising the vehicle from any other point other than those
shown may result in serious damage.
• When jacking or lifting a vehicle at the frame side rail or other prescribed lift points, be certain that the lift
pads donot contact the catalytic converter, brake pipes, fuel lines or cables. Such contact may result in
vehicle damage or unsatisfactory vehicle
C00RX002
• Lift Point: Front • Support Point: Front
• Lift Point: Rear
• Support Point: Rear
• Support Point: Rear
Loading & Towing
Trailers
The word “trailer” is used throughout this section. The word “trailer” is intended to include all types of towed vehicle,
such as a caravan, boat trailer or any other special purpose trailer, etc.
Overloading
Overloading is a safety hazard and could also shorten the life of the vehicle. Never exceed the loads specified for the
vehicle or trailer, as specified below.
Vehicle Capacities
Unladen Mass – the mass of the vehicle in running order, unoccupied and unladen with all fluid reservoirs filled to
nominal capacity (including fuel) and with all standard equipment fitted. Refer to the following table.
Gross Vehicle Mass Rating (GVMR) – the maximum allowable laden mass of the vehicle. Refer to the following
table.
Gross Combination Mass Rating (GCMR) – the maximum allowable sum of the masses of the towing vehicle and
the towed trailer. Refer to the following table.
Gross Towed Mass Rating (GTMR) – the maximum allowable mass of a trailer (including load) that may be towed by
the vehicle. Refer to the following table.
Front Axle Capacity and Rear Axle Capacity – the maximum allowable loads on the ground at the front and rear
axles. Refer to the following table.
Note: It may not be possible to tow a fully laden trailer (total trailer mass near or equal to the GTMR) with a fully
laden vehicle (total vehicle mass near or equal to the GVMR), because the total combined weight of the vehi-
cle–trailer combination may exceed the Gross Combination Mass Rating (GCMR). In such cases it is neces-
sary to reduce the load in either or both the towing vehicle and the trailer so that the combined mass of the
towing vehicle and trailer is less than the GCMR.
When towing, the driver must take into account the additional load the trailer puts on the vehicle. Particular
attention must be given to how the trailer changes the loads at the vehicle’s front and rear axles.
When the vehicle and trailer are at or near full load, it may be necessary to use a public weighbridge to check
that none of the vehicle’s, trailer’s or towing equipment’s capacities have been exceeded.
Handling, durability and economy may be affected by towing a trailer.
Jackaroo Jackaroo SE Monterey
Engine 3.5 V6 3.0 T/D 3.5 V6 3.0 T/D 3.6 V6 3.0 T/D
Transmission MAMAMAMAAA
Unladen Mass (kg) 1925 1940 2045 2045 2030 2045 2150 2150 2084 2189
All Models
GVMR (kg) 2600
GCMR (kg) 5100
GTMR (kg) 2500
Max. Ball Load (kg) 250
Front Axle Capacity (kg) 1250
Rear Axle Capacity (kg) 1500
Roof Rack Capacity (kg) 50
Country/State Regulations
Note that there are various regulations related to towing, and that these can vary between the different countries/
states. These regulations normally cover the maximum allowable mass of the trailer and the maximum allowable
driving speeds. You must be familiar with the regulations for towing for each of the states in which you intend to tow.
Details of the regulations are available from the relevant state road traffic authorities or motoring associations.
Towing Equipment
The following table shows which towing equipment is essential, according to the total mass to be towed.
For occupant safety and the vehicle’s durability, all equipment marked “Essential” must be correctly installed and used.
Otherwise you may void the New Vehicle Warranty, to the extent that Holden considers the overloading, missing
equipment or misuse to have affected the specifications or quality of the vehicle.
The Holden Dealer can supply and install towing equipment to suit the towing needs.
The Holden towing package for UBS Jackaroo includes the tow bar, tow bar “tongue” and wiring harness. A Load Dis-
tribution Hitch if required, is sold separately.
Caution: Holden towing equipment is recommended where it is available. Where it is not available, no recommenda-
tion is made as to the make of equipment to be used. Holden will not accept liability for defects occurring in
towing equipment not marketed by Holden or for defects in the vehicle arising from the use of such equip-
ment. The use of such equipment may void the New Vehicle Warranty, to the extent that Holden considers
the overloading or missing equipment to have affected the specifications or quality of the vehicle.
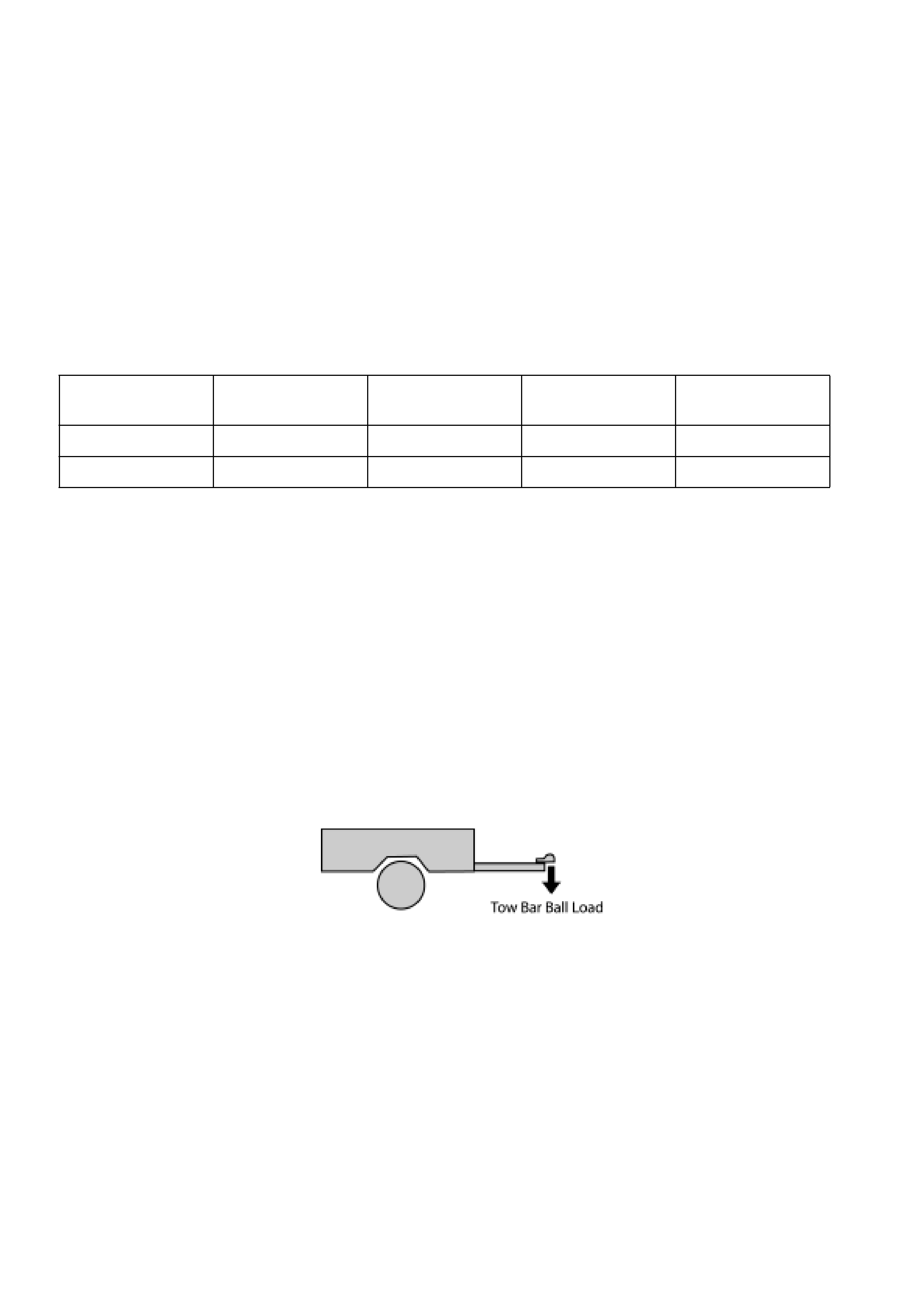
Tow Bar Ball Load
When a trailer is connected to the towing vehicle, some of the weight of the trailer is applied through the tow “ball” to
the tow bar and towing vehicle. This weight is called the “tow bar ball weight” or “ball load”. The maximum ball load is
200kg.
If the “ball load” is too light or too heavy the steering, handling and ride characteristics of the vehicle can be adversely
affected.
As a general guideline, for single axle trailers, the “ball load” should be approximately 10% of the loaded trailer mass.
For heavy trailers with more than one axle, the “ball load” should be in the range 5% - 10% of the loaded trailer mass.
Check the “ball load” capacity of the towing equipment. This may be called the “Maximum Down Load”, “Maximum
Vertical Load”, “Maximum Ball Load” or similar and will be specified on the tow bar.
Establish a target “ball load” that is in accordance with the recommendations (above) and within the capacity of the
towing equipment.
Check the “ball load” (compare with the target) before coupling the trailer to the towing vehicle.
The “ball load” can be adjusted by redistributing the contents of the trailer ie. by moving the contents of the trailer for-
ward or backward within the trailer so as to change the trailer’s balance.
Total Trailer Mass 1800 kg Tow Bar Trailer Wiring Har-
ness
Trailer Brakes Load Distribution
Hitch
Up to 900kg Essential Essential Check State Laws -
Above 900kg Essential Essential Essential Essential

For further information contact the roads authority in the relevant country/state.
Load Equalising Hitch
A Load Distribution Hitch (sometimes called a “Load Equalising Hitch”) is designed to transfer some of the load from
the vehicle’s rear axle to the vehicle’s front axle and the axle(s) of the trailer.
A load distribution hitch can also be used to restore the towing vehicle to a more normal (level) “attitude”. This
reduces the need to adjust headlight alignment and should provide the towing vehicle with more “normal” ride and
handling. For these reasons, the use of load distributing devices can make towing safer, more comfortable and more
convenient.
Adjust the load distribution hitch so that the vehicle is has about the same “attitude” (“stance” or “angle to the ground”)
as when it is unladen.
Roof Racks
For occupant safety, and to avoid damaging the vehicle’s roof, there is no released Holden approved roof rack system
for TF Rodeo.
Fitting Accessories (Bull Bars, Driving Lamps, Insect Screens, etc.)
When fitting accessories take care not to restrict airflow through the air conditioner’s condenser and the radiator, oth-
erwise engine overheating and/or poor air conditioning performance may result.
The mass of all accessories must be considered when evaluating the vehicle’s overall loaded condition.
Remember that bull bars may affect air bag operation.
Running In Before Towing
Holden recommends driving the new vehicle for at least 1,500km before towing. If it is required to tow in the first 1,500
km of the vehicle’s life, the maximum vehicle speed should not exceed 80 km/h.
The same applies if the vehicle is equipped with a new or reconditioned engine, transmission or axle.

Off Road Loading And Towing
Driving the vehicle off-road may induce higher loads than normal on-road driving. To reduce the risk of damage to the
vehicle (and trailer) and improve safety when operating off-road, reduce the vehicle speed and minimise the load
being carried (and towed).
TOWING PRECAUTIONS
•The vehicle will handle differently when towing. It is a good idea to for the driver to make a couple of short-distance
trips with the trailer to become familiar with the handling characteristics of the vehicle when towing.
•The vehicle must be correctly maintained and serviced.
•Have the trailer maintained and serviced, with particular attention to the condition of the brakes, tyres, suspension,
wheel bearings, lighting and the towing equipment.
•Driving speed should be reduced when towing.
•If the trailer has poor directional stability seek qualified advice eg. the trailer’s manufacturer or retailer. The use of
stabilising equipment should be considered.
•Ensure that all loads – in or on the towing vehicle and in the trailer - are properly secured.
•Use extended-arm rear vision mirrors when the trailer is wider than the towing vehicle.
•Headlights may need realignment after the loaded trailer has been hitched. The use of a load distribution hitch will
reduce the need for headlight realignment, making towing safer and more convenient.
•Slow the vehicle and select a lower gear before descending steep hills.
•When towing, inflate the vehicle’s tyres to the maximum recommended pressure.
•Be familiar with the regulations for towing for each of the states in which you intend to tow. Contact the road traffic
authority in each state for specific advice.
•The brakes on the trailer must be adequate for the braking needs of the trailer and must not adversely affect the
performance of the brakes of the towing vehicle.
•When a tow bar is removed, be certain to seal any mounting holes in the chassis frame or vehicle body to prevent
the possible entry of exhaust fumes, dust and water. Sealing mounting holes in the chassis frame will ensure that
the tow bar can be properly refitted at a later date.
•Ensure that no part of the tow bar (including the tongue or tow ball obscures the vehicle’s licence plate. If necessary,
remove the tow bar tongue when it is not in use.
•More frequent vehicle maintenance is required when using the vehicle to pull a trailer. Refer to Section 0B -
Lubrication and Servicing.
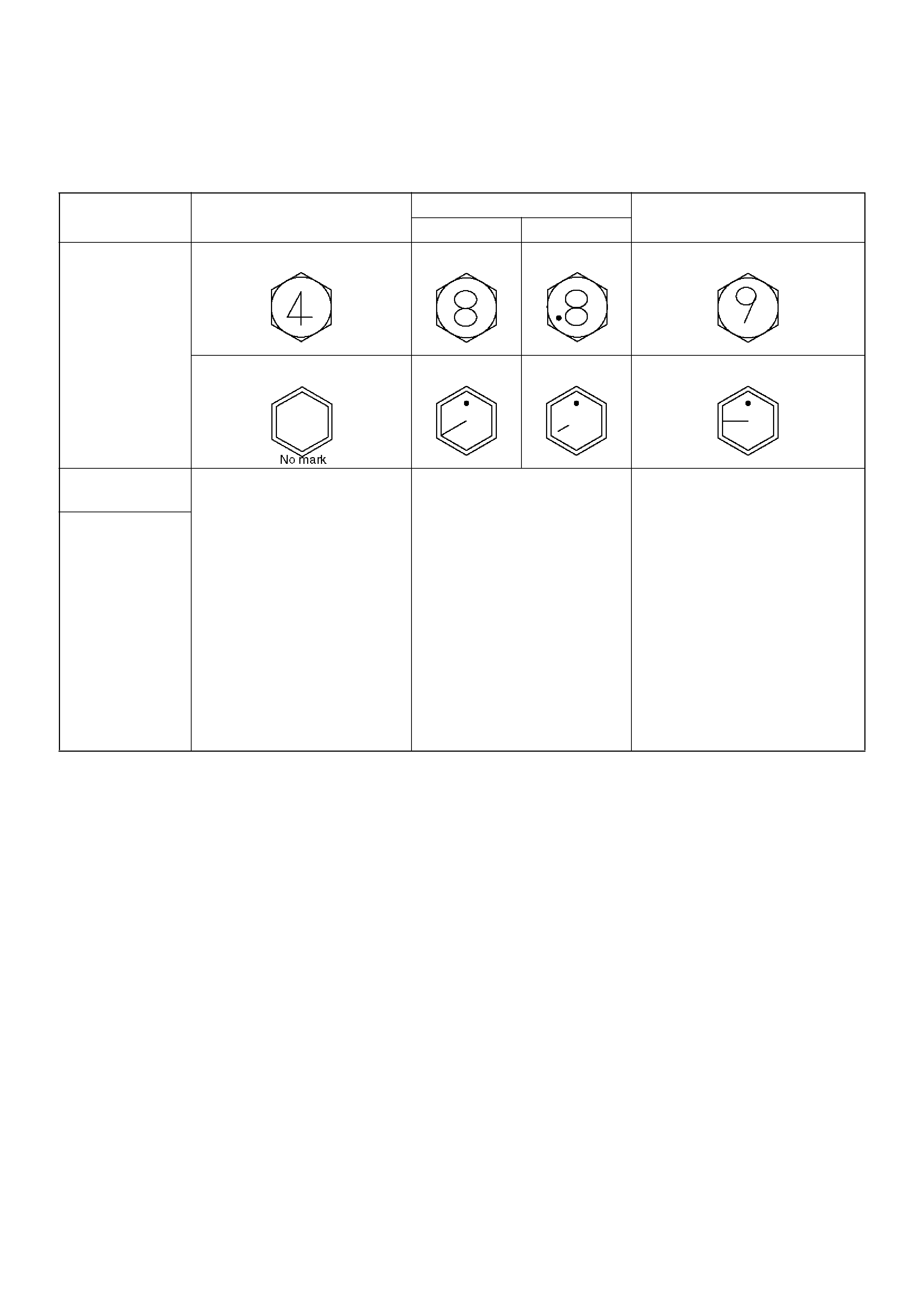
Standard Bolt Torque Specifications
The torque values given in the following table should be applied where a particular torque is not specified.
The asterisk * indicates that the bolts are used for
female–threaded parts that are made of soft materials
such as casting, etc.
Strength Class 4.8 8.8 9.8
Refined Non-Refined
Bolt
Identification
Bolt Diameter ´
Pitch (mm)
M 6X1.0
M 8X1.25
M 10X1.25
* M10X1.5
M12X1.25
* M12X1.75
M14X1.5
* M14X2.0
M16X1.5
* M16X2.0
M18X1.5
M20X1.5
M22X1.5
M24X2.0
4 – 8 N·m (3 – 6 lb ft)
8 – 18 N·m (6 – 13 lb ft)
21 – 34 N·m (15 – 25 lb ft)
20 – 33 N·m (14 – 25 lb ft)
49 – 74 N·m (36 – 54 lb ft)
45 – 69 N·m (33 – 51 lb ft)
77 – 115 N·m (56 – 85 lb ft)
72 – 107 N·m (53 – 79 lb ft)
104 – 157 N·m (77 – 116 lb ft)
100 – 149 N·m (74 – 110 lb ft)
151 – 226 N·m (111 – 166 lb ft)
206 – 310 N·m (152 – 229 lb ft)
251 – 414 N·m (185 – 305 lb ft)
359 – 539 N·m (265 – 398 lb ft)
5 – 10 N·m (4 – 7 lb ft)
12 – 23 N·m (9 – 17 lb ft)
28 – 46 N·m (20 – 34 lb ft)
28 – 45 N·m (20 – 33 lb ft)
61 – 91 N·m (45 – 67 lb ft)
57 – 84 N·m (42 – 62 lb ft)
93 – 139 N·m (69 – 103 lb ft)
88 – 131 N·m (65 – 97 lb ft)
135 – 204 N·m (100 – 150 lb ft)
130 – 194 N·m (95 – 143 lb ft)
195 – 293 N·m (144 – 216 lb ft)
270 – 405 N·m (199 – 299 lb ft)
363 – 544 N·m (268 – 401 lb ft)
431 – 711 N·m (318 – 524 lb ft)
–
17 – 30 N·m (12 – 22 lb ft)
37 – 63 N·m (27 – 46 lb ft)
36 – 60 N·m (27 – 44 lb ft)
76 – 114 N·m (56 – 84 lb ft)
72 – 107 N·m (53 – 79 lb ft)
114 – 171 N·m (84 – 126 lb ft)
107 – 160 N·m (79 – 118 lb ft)
160 – 240 N·m (118 – 177 lb ft)
153 – 230 N·m (113 – 169 lb ft)
230 – 345 N·m (169 – 255 lb ft)
317 – 476 N·m (234 – 351 lb ft)
425 – 637 N·m (313 – 469 lb ft)
554 – 831 N·m (409 – 613 lb ft)

Abbreviations Charts
List of automotive abbreviations which may be used
in this manual
A — Ampere(s)
ABS — Antilock Brake System
AC — Alternating Current
A/C — Air Conditioning
ACCEL — Accelerator
ACC — Accessory
ACL — Air Cleaner
Adj — Adjust
A/F — Air Fuel Ratio
AIR — Secondary Air Injection System
Alt — Altitude
AMP — Ampere(s)
ANT — Antenna
ASM — Assembly
A/T — Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
ATDC — After Top Dead Center
ATF — Automatic Transmission Fluid
Auth — Authority
Auto — Automatic
BARO — Barometric Pressure
Bat — Battery
B+ — Battery Positive Voltage
Bbl — Barrel
BHP — Brake Horsepower
BPT — Backpressure Transducer
BTDC — Before Top Dead Center
° C — Degrees Celsius
CAC — Charge Air Cooler
Calif — California
cc — Cubic Centimeter
CID — Cubic Inch Displacement
CKP — Crankshaft Position
CL — Closed Loop
CLCC — Closed Loop Carburetor Control
CMP — Camshaft Position
CO — Carbon Monoxide
Coax — Coaxial
Conn — Connector
Conv — Converter
Crank — Crankshaft
Cu. In. — Cubic Inch
CV — Constant Velocity
Cyl — Cylinder(s)
DI — Distributor Ignition
Diff — Differential
Dist — Distributor
DLC — Data Link Connector
DOHC — Double Overhead Camshaft
DTC — Diagnostic Trouble Code
DTM — Diagnostic Test Mode
DTT — Diagnostic Test Terminal
DVM — Digital Voltmeter (10 meg.)
DVOM — Digital Volt Ohmmeter
EBCM — Electronic Brake Control Module
ECM — Engine Control Module
ECT — Engine Coolant Temperature
EEPROM — Electronically Erasable Programmable
Read Only Memory
EGR — Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EI — Electronic Ignition
ETR — Electronically Tuned Receiver
EVAP — Evaporation Emission
Exh — Exhaust
° F — Degrees Fahrenheit
Fed — Federal (All States Except Calif.)
FF — Front Drive Front Engine
FL — Fusible Link
FLW — Fusible Link Wire
FP — Fuel Pump
FRT — Front
ft — Foot
FWD — Front Wheel Drive
4WD — Four Wheel Drive
4 x 4 — Four Wheel Drive
4 A/T — Four Speed Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
Gal — Gallon
GEN — Generator
GND — Ground
Gov — Governor
g — Gram
Harn — Harness
HC — Hydrocarbons
HD — Heavy Duty
Hg — Hydrargyrum (Mercury)
HiAlt — High Altitude
HO2S — Heated Oxygen Sensor
HVAC — Heater–Vent–Air–Conditioning
IAC — Idle Air Control
IAT — Intake Air Temperature
IC — Integrated Circuit / Ignition Control
ID — Identification / Inside Diameter
IGN — Ignition
INJ — Injection
IP — Instrument Panel
IPC — Instrument Panel Cluster
Int — Intake
ISC — Idle Speed Control
J/B — Junction Block
kg — Kilograms
km — Kilometers
km/h — Kilometer per Hour
kpa — Kilopascals
kV — Kilovolts (thousands of volts)
kW — Kilowatts
KS — Knock Sensor
L — Liter
lb ft — Foot Pounds
lb in — Inch Pounds
LF — Left Front
LH — Left Hand
LR — Left Rear
LS — Left Side
LWB — Long Wheel Base
L–4 — In–Line Four Cylinder Engine

MAF — Mass Air Flow
MAN — Manual
MAP — Manifold Absolute Pressure
Max — Maximum
MC — Mixture Control
MFI — Multiport Fuel Injection
MIL — Malfunction Indicator Lamp
Min — Minimum
mm — Millimeter
MPG — Miles Per Gallon
MPH — Miles Per Hour
M/T — Manual Transmission/Transaxle
MV — Millivolt
N — Newtons
NA — Natural Aspirated
NC — Normally Closed
N·M — Newton Meters
NO — Normally Open
NOX — Nitrogen, Oxides of
OBD — On-Board Diagnostic
OD — Outside Diameter
O/D — Over Drive
OHC — Overhead Camshaft
OL — Open Loop
O2 — Oxygen
O2S — Oxygen Sensor
PAIR — Pulsed Secondary Air Injection System
P/B — Power Brakes
PCM — Powertrain Control Module
PCV — Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PRESS — Pressure
PROM — Programmable Read Only Memory
PNP — Park/Neutral Position
P/S — Power Steering
PSI — Pounds per Square Inch
PSP — Power Steering Pressure
Pt. — Pint
Pri — Primary
PWM — Pulse Width Modulate
Qt. — Quart
REF — Reference
RF — Right Front
RFI — Radio Frequency Interference
RH — Right Hand
RPM — Revolutions Per Minute
RPM Sensor — Engine Speed Sensor
RPO — Regular Production Option
RR — Right Rear
RS — Right Side
RTV — Room Temperature Vulcanizing
RWAL — Rear Wheel Antilock Brake
RWD — Rear Wheel Drive
SAE — Society of Automotive Engineers
Sec — Secondary
SFI — Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection
SI — System International
SIR — Supplemental Inflatable Restraint System
SOHC — Single Overhead Camshaft
Sol — Solenoid
SPEC — Specification
Speedo — Speedometer
SRS — Supplemental Restraint System
ST — Start / Scan Tool
Sw — Switch
SWB — Short Wheel Base
SYN — Synchronize
Tach — Tachometer
TB — Throttle Body
TBI — Throttle Body Fuel Injection
TCC — Torque Converter Clutch
TCM — Transmission Control Module
TDC — Top Dead Center
Ter m — Termina l
TEMP — Temperature
TOD— Torque On Demand
TP — Throttle Position
TRANS — Transmission/Transaxle
TURBO — Turbocharger
TVRS — Television & Radio Suppression
TVV — Thermal Vacuum Valve
TWC — Three Way Catalytic Converter
3 A/T — Three Speed Automatic Transmission/
Transaxle
2WD — Two Wheel Drive
4 x 2 — Two Wheel Drive
U–joint — Universal Joint
V — Volt(s)
VAC — Vacuum
VIN — Vehicle Identification Number
VRRRE — Vehicle Refrigerant Recovery and Recycling
Equipment
V–ref — ECM Reference Voltage
VSS — Vehicle Speed Sensor
VSV — Vacuum Switch Valve
V–6 — Six Cylinder “V" Engine
V–8 — Eight Cylinder "V" Engine
W — Watt(s)
w/ — With
w/b — Wheel Base
w/o — Without
WOT — Wide Open Throttle