GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Replacement wheels or tyres must be equivalent to
the originals in load capacity, specified dimension
and mounting configuration. Improper size or type
may affect bearing life, brake performance,
speedometer/odometer calibration, vehicle ground
clearance and tyre clearance to the body and
chassis.
All models are equipped with metric sized steel
belted radial tyres. Correct tyre pressures and
driving habits have an important influence on tyre
life. Heavy cornering, excessively rapid
acceleration and unnecessary sharp braking
increase premature and uneven wear.
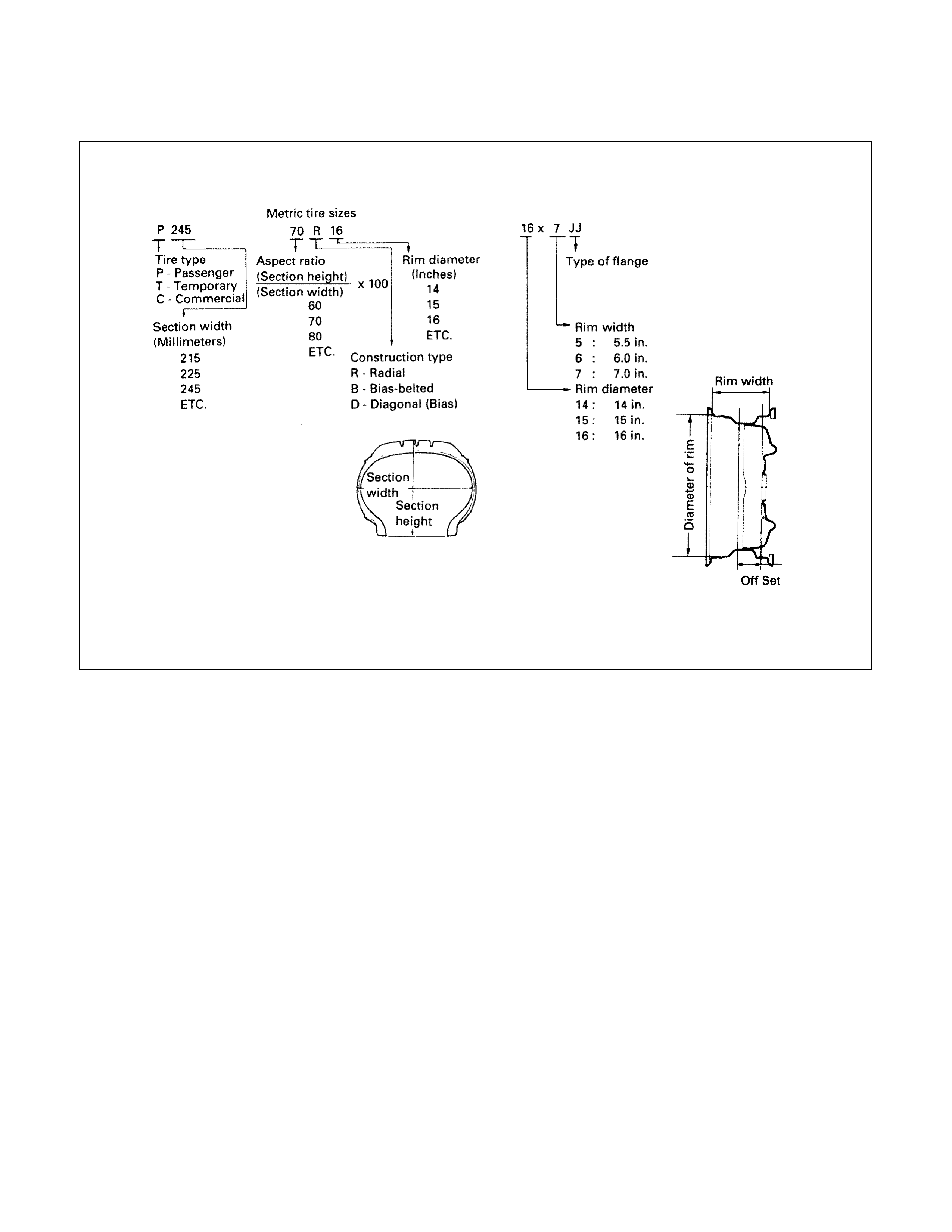
Metric Tyre Size Format Rim Size Format
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
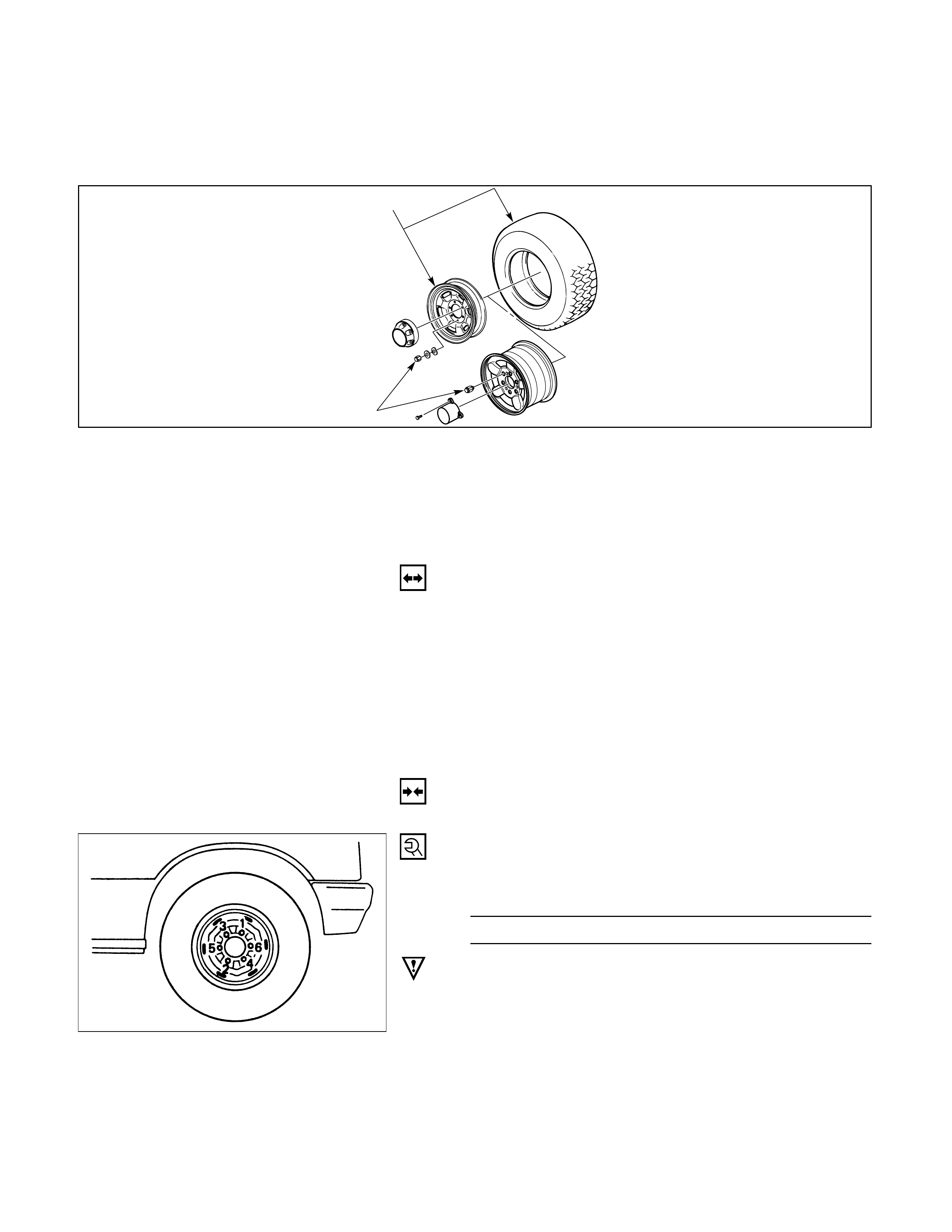
WHEELS
2. Wheel and tire
1. Wheel lug nut
Removal Steps
1. Wheel lug nut
2. Wheel and tyre
Installation Steps
2. Wheel and tyre
1. Wheel lug nut
480R V004
REMOVAL
1. Wheel Lug Nut
Loosen wheel nut by approximately 180¡ (half a
rotation) and raise the vehicle. Then remove the nuts.
2. W heel and tyre
NOTE:
Never use heat to loosen a tight w heel lug nut. The
application of heat to the hub can shorten the life of
the w heel and may cause damage to w heel bearings.
INSTALLATION
1. Wheel and tyre
2. Wheel Lug Nut
Tighten the wheel lug nuts to the specified torque in
numerical order.
W heel Lug Nut Torque Nm (kg m/lb ft)
118 (12.0 / 87)
CAUTION:
Before installing wheels, remove any build-up of
corrosion on the wheel mounting surface and brake
disc mounting surface by scraping and wire brushing.
Installing wheels without good metal-to-metal
contact at mounting surfaces can cause wheel nuts to
loosen, which can later allow a wheel to come off
while the vehicle is moving.
NOTE:
Valve caps should be on the valve stems to keep dust
and water out.
TYRES
REPLACEMENT
When replacement is necessary, the original metric size
should be used. Most metric tyre sizes do not have exact
corresponding alphanumeric tyre sizes. It is recommended
that new tyres be installed in pairs on the same axle. If
necessary to replace only one tyre, it should be paired with
tyre having the most tread, to equalize braking traction.
CAUTION:
Do not mix different types of tyres such as radial, bias and
bias-belted tyres except in emergencies, because vehicle
handling may be seriously affected and may result in loss
of control.
TYRE MOUNTING
Remove valve cap on valve stem and deflate the tyre.
Then use a tyre changing machine to mount or dismount
tyres.
Follow the equipment manufacturers instruction. Do not
use hand tools or tyre lever alone to change tyres as they
may damage the tyre beads or wheel rim.
TYRE DISMOUNTING
Rim bead seats should be cleaned with a wire brush or
coarse steel wool to remove lubricants, and light rust.
Before mounting a tyre, the bead area should be well
lubricated with an approved tyre lubricant.
After mounting, inflate the tyre to 196 kPa (28 psi) so that
beads are completely seated. Inflate the air to specified
pressure and install valve cap to the stem
WARNING:
NEVER STAND OVER TYRE WHEN INFLATING. BEAD MAY
BREAK WHEN BEAD SNAPS OVER RIMS SAFETY HUMP
AND CAUSE SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY.
NEVER EXCEED 240 kPa (35 psi) PRESSURE WHEN
INFLATING. IF 240 kPa (35 psi) PRESSURE WILL NOT
SEAT BEADS, DEFLATE, RE-LUBRICATE AND RE-INFLATE.
OVER INFLATION MAY CAUSE THE BEAD TO BREAK AND
CAUSE SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY.
TYRE REPAIR
There are many different materials on the market used to
repair tyres.
Manufacturers have published detailed instructions on
how and when to repair tyres. These instructions can be
obtained from the tyre manufacturer if they are not
included with the repair kit.
UNIT REPAIR
WHEELS
REPLACEMENT
Damaged wheels and wheels with excessive runout must
be replaced.
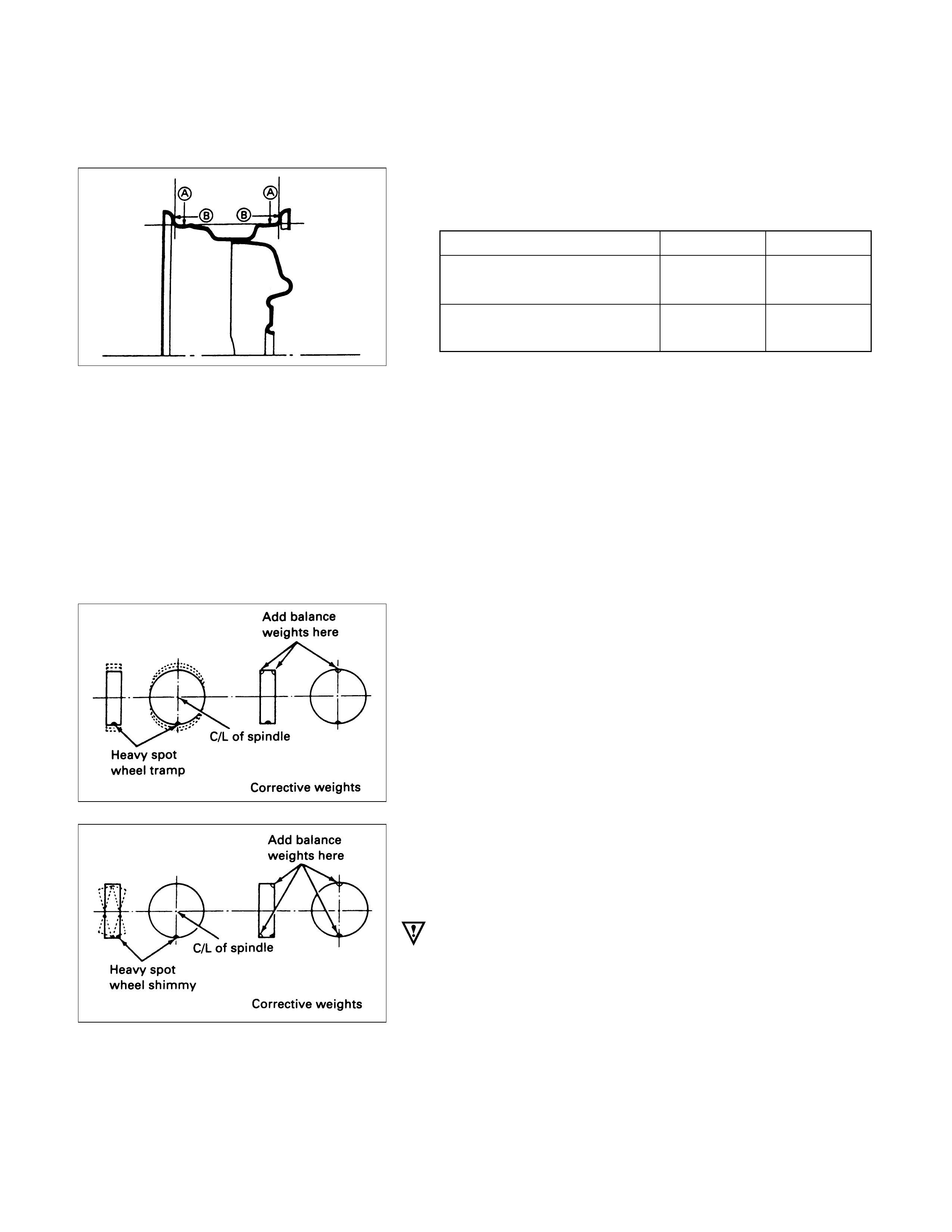
Wheel Runout at Rim (Based on Hub bore.)
GENERAL BALANCE PROCEDURE
Deposits of mud, etc. must be cleaned from the inside of
the rim.
The tyre should be inspected for the following: match
mount paint marks, bent rims, bulges, irregular tyre wear,
proper wheel size and inflation pressure. Then balance
according to the equipment manufacturer’s
recommendations.
There are two types of wheel and tire balance.
Static balance is the equal distribution of weight around
the wheel.
Assemblies that are statically unbalanced cause a
bouncing action called tramp. This condition will
eventually cause uneven tire wear.
Dynamic balance is the equal distribution of weight on
each side of the wheel center-line so that when the tyre
spins there is not tendency for the assembly to move from
side to side. Assemblies that are dynamically unbalanced
may cause shimmy.
WARNING:
STONES SHOULD BE REMOVED FROM THE TREAD TO
AVOID OPERATOR INJURY DURING SPIN BALANCING
AND TO OBTAIN A GOOD BALANCE.
Steel Aluminum
AVertical play:
Less than mm(in) 1.5 (0.059) 0.7 (0.028)
BHorizontal play:
Less than mm(in) 1.5 (0.059) 0.7 (0.028)
BALANCING
ON-VEHICLE BALANCING
On-Vehicle balancing methods vary with equipment and
tool manufacturers. Be sure to follow each manufacturer’s
instructions during balancing operation.
OFF-VEHICLE BALANCING
Most electronic off-vehicle balancers are more accurate
than the on-vehicle spin balancers. They are easy to use
and give a dynamic balance. Although they do not correct
for drum or disc unbalance (as on-vehicle spin balancing
does), they are very accurate.
