Problem Possible Cause Correction
GENERAL INFORMATION
Since the problems in steering, suspension,
wheels and tyres involve several systems, they
must all be considered when diagnosing a
complaint. To identify the symptom, always road
test the vehicle first.
Proceed with the following preliminary inspections
and correct any defects which are found.
1. Inspect tyres for proper pressure and uneven
wear.
2. Raise vehicle on a hoist and inspect front and
rear suspension and steering linkage for loose
or damaged parts.
3. Spin front wheels. Inspect for out-of-round
tyres, out-of-balance tyres, loose and/or rough
wheel bearings.
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING
Vehicle Pulls
Abnormal or Excessive
Tyre Wear
Shimmy, Shake or
Vibration
1. Mismatched or uneven tyres.
2. Tyres not adequately inflated.
3. Broken or sagging springs.
4. Radial tyre lateral force.
5. Improper wheel alignment.
6. Brake dragging in one wheel.
7. Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts.
8. Faulty shock absorbers.
1. Sagging or broken spring.
2. Tyre out of balance.
3. Improper wheel alignment.
4. Faulty shock absorber.
5. Hard driving.
6. Overloaded vehicle.
7. Tyres not rotated periodically.
8. Worn or loose road wheel bearings.
9. Wobbly wheel or tyres.
10. Tyres not adequately inflated.
1. Tyre or wheel out of balance.
2. Loose wheel bearings.
3. Worn steering linkage ball joints.
4. Worn upper or lower end ball joints.
5. Excessively upper wheel runout.
6. Blister or bump on tyre.
7. Excessive loaded radial run out of
tyre/wheel assembly.
8. Improper wheel alignment.
9. Loose or worn steering linkage.
10. Loose steering gear.
11. Tyres not adequately inflated.
12. Loose, bent or broken front or rear
suspension parts.
13. Faulty shock absorber.
14. Hub bearing preload misadjustment.
Replace tyre.
Adjust tyre pressure.
Replace spring.
Replace tyre.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Repair brake.
Tighten or replace the
appropriate suspension part(s).
Replace shock absorber.
Replace spring.
Balance or replace tyre.
Check front end alignment.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace tyre.
Replace tyre and reduce load.
Replace or rotate tyre.
Replace wheel bearing.
Replace wheel or tyre.
Adjust the pressure.
Balance wheels or replace
tyre/or wheel.
Replace wheel bearing.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Repair or replace wheel
and/or tyre.
Replace tyre.
Replace tyre or wheel.
Check wheel alignment.
Tighten or replace steering
linkage.
Tighten housing bolts.
Adjust tyre pressure.
Tighten or replace the
appropriate suspension parts.
Replace shock absorber.
Adjust preload.
Problem Possible Cause Correction
Wheel Tramp or Hop
Hard Steering
Too Much Play In
Steering
Poor Steering Wheel
Returnability
Abnormal Noise
1. Blister or bump on tyre.
2. Improper shock absorber operation
1. Bind in steering linkage ball studs,
upper or lower end ball joint.
2. Improper wheel alignment.
3. Steering gear misadjustment.
4. Tire not adequately inflated.
5. Bind in steering column or shaft.
6. Improper power steering system
operation.
1. Wheel bearings worn.
2. Loose steering gear or linkage.
3. Steering gear misadjustment.
4. Worn or loose steering shaft universal
joint.
5. Worn steering linkage ball joints.
6. Worn upper or lower end ball joints.
1. Bind in steering linkage ball joints.
2. Bind in upper or lower end ball joints.
3. Bind in steering column and shaft.
4. Bind in steering gear.
5. Improper wheel alignment.
6. Tires not adequately inflated.
7. Loose steering wheel nut.
8. Worn wheel bearing.
1. Worn, sticky or loose upper or lower
end ball joint, steering linkage ball
joints or drive axle joints.
2. Faulty shock absorbers.
3. Worn upper or lower control arm bushing.
4. Loose stabilizer bar.
5. Loose wheel nuts.
6. Loose suspension bolts or nuts.
7. Broken or otherwise damaged wheel
bearings.
8. Broken suspension springs.
9. Loose steering gear.
10. Faulty steering gear.
Replace tyre.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace ball joints.
Check wheel alignment.
Check and adjust steering gear
preload.
Inflate tires to proper pressure.
Repair or replace.
Repair or replace.
Refer to "Power steering
system troubleshooting."
Replace wheel bearings.
Retighten or repair.
Inspect and adjust steering
gear preload.
Retighten or replace steering
shaft.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Replace ball joints.
Repair or replace.
Check and repair steering gear.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Adjust tire pressure.
Retighten.
Replace.
Replace.
Replace or repair.
Replace.
Retighten bolts.
Tighten nuts. Check for
elongated wheel nut holes.
Replace wheel if required.
Retighten suspension bolts or
nuts.
Replace wheel bearing.
Replace spring.
Retighten mounting bolt.
Check and adjust steering gear.
Problem Possible Cause Correction
Wandering or Poor
Steering Stability
Erratic Steering When
Bracking
Low or Uneven Trim
Height
Suspension Bottoms
Body Leans
Cupped Tires
1. Mismatched or unevenly worn tyres.
2. Loose steering linkage ball joints.
3. Faulty shock absorbers.
4. Loose stabilizer bar.
5. Broken or sagging springs.
6. Steering gear misadjustment.
7. Improper wheel alignment.
1. Worn wheel bearings.
2. Broken or sagging springs.
3. Leaking caliper.
4. Warped discs.
5. Badly worn brake pads.
6. Tyres are inflated unequally.
1. Broken or sagging springs.
2. Vehicle overloaded.
3. Incorrect springs.
1. Vehicle overloaded.
2. Faulty shock absorber.
3. Incorrect, broken or sagging springs.
1. Loose stabilizer bar.
2. Faulty shock absorbers, struts or
mounting.
3. Broken or sagging springs.
4. Vehicle overloaded.
1. Worn wheel bearings.
2. Excessive tire or wheel runout.
3. Worn ball joints.
4. Tyre out of balance.
Replace tyre or inflate tires to
proper pressure.
Replace ball joints.
Replace shock absorber.
Tighten or replace stabilizer bar
or bushings.
Replace spring (pairs).
Check or adjust steering gear.
Adjust wheel alignment.
Replace wheel bearings.
Replace spring (pairs).
Repair or replace caliper.
Replace brake disc.
Replace brake pads.
Inflate tyres to proper pressure.
Replace springs (In pairs)
Reduce load.
Adjust or replace torsion bar.
Reduce load.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace springs.
Tighten stabilizer bar bolts or
replace bushings.
Replace shock absorber.
Replace springs (In pairs)
Reduce load.
Replace wheel bearings.
Replace tire or wheel.
Replace ball joints.
Balance tyres.
TYRES
IRREGULAR AND PREMATURE WEAR
-Hard cornering
- Under inflation
- Lack of rotation
- Incorrect Wheel alignment
- Tyre unevenly worn
- Heavy acceleration
- Over inflation
Irregular and /or premature wear has many cases.
Some of them are incorrect inflation pressures,
lack of tyre rotation, poor driving habits or
improper alignment. Incorrect inflation is common
cause of tyre premature wear.
NOTE:
Due to their design, radial tyres tend to wear
faster in the shoulder area, particularly on the
front tyres.
This makes regular rotation especially necessary.
After rotation, be sure to check wheel nut torque,
and set tyre pressures.
If the following conditions are noted, rotation is
required.
1. Front tyre wear is different from rear.
2. Uneven wear exists across the tread of any
tyre.
3. Left front and right front tyre wear is unequal.
4. Left rear and right rear tyre wear is unequal.
Refer to "Servicing" in this section.
If the following conditions are noted, check the
wheel alignment.
1. Left front and right front tyre wear is unequal.
2. Uneven wear exists across the tread of any
tyre.
3. Front tyre treads have scuffed appearance with
"feather" edges on one side of tread ribs or
blocks.
4. There is cupping, flat spotting etc.
Refer to "Front End Alignment" in section 3A.
Higher than recommended pressure can cause:
1. Hard ride.
2. Poor steering stability.
3. Rapid and uneven wear at center of the tread.
Refer to "Servicing" in this section.
Lower than recommended pressure can cause:
1. Tyre squeal on turns.
2. Hard steering.
3. Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the
tread.
4. Tyre rim bruises and rupture.
5. Tyre cord breakage.
6. High tyre temperatures.
7. Reduced handling.
8. Reduced fuel economy.
Refer to "Servicing" in this section.
Unequal pressure on same axle can cause:
1. Uneven braking.
2. Steering lead.
3. Reduced handling.
4. Swerve on acceleration.
Refer to "Servicing" in this section.
WEAR INDICATORS
The original equipment tyres have built-in tread
wear indicators to show when tyres need
replacement. These indicators may appear as wide
bands. When the indicators, tyre replacement is
recommended.
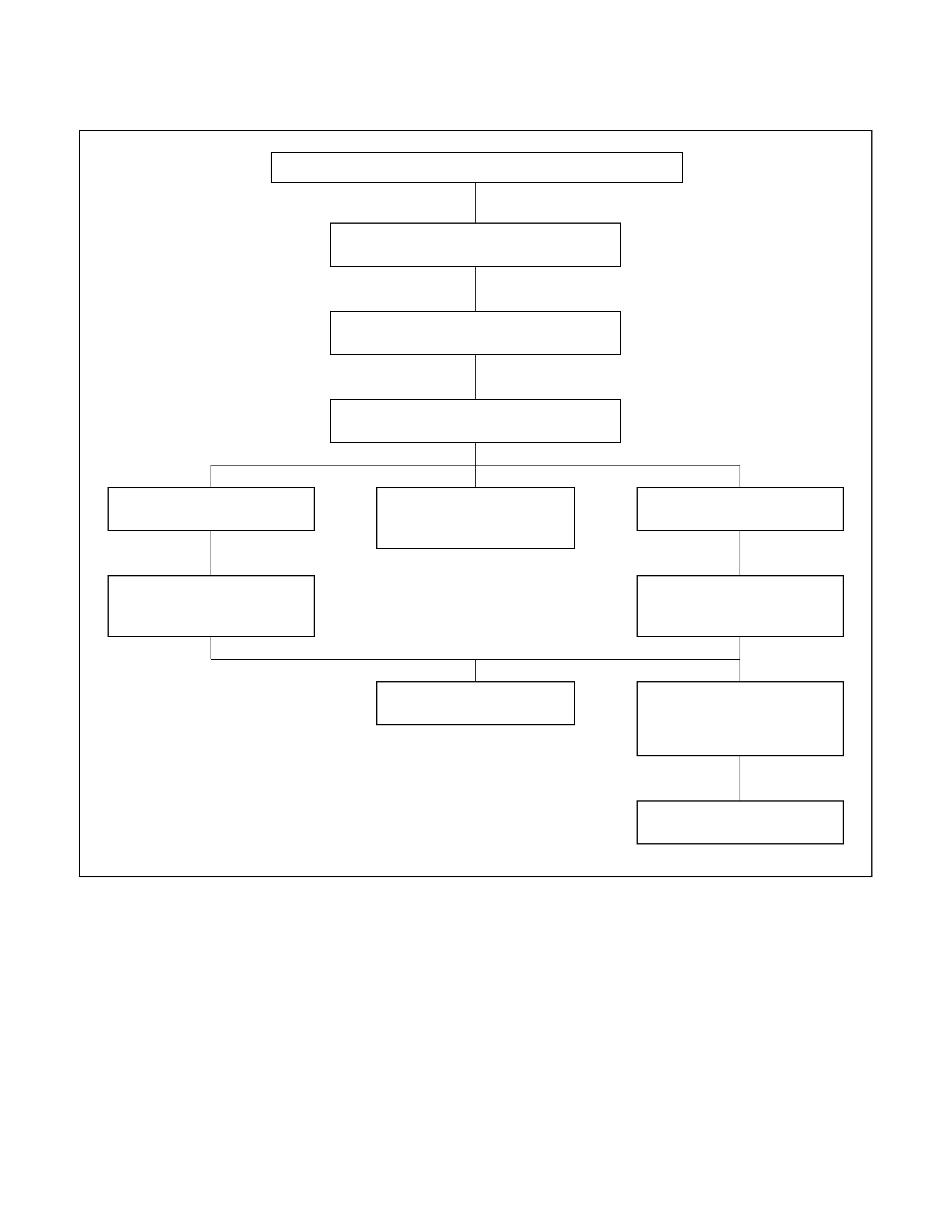
RADIAL TYRE LEAD/PULL
RADIAL TYRE LEAD/PULL CORRECTION CHART
INFLATE TYRES TO RECOMMENDED
PRESSURE
ROAD TEST VEHICLE ON LEVEL
UNCROWNED ROAD
SWITCH FRONT TYRES SIDE TO SIDE
AND ROAD TEST AGAIN
LEAD CORRECTED IF
ROUGHNESS RESULTS,
REPLACE TYRES.
LEAD CORRECTED
REPLACE TYRE
LEADS IN SAME
DIRECTION
PUT TYRES BACK IN
ORIGINAL POSITION AND
CHECK ALIGNMENT
LEAD REVERSES
DIRECTION
INSTALL KNOWN GOOD
TYRE ON
ONE FRONT SIDE
LEAD REMAINS.
INSTALL A KNOWN GOOD
TYRE IN PLACE OF OTHER
FRONT TYRE
LEAD CORRECTED
REPLACE TYRE
"Lead/Pull" is vehicle deviation from a straight
path, on a level road with no presure on the
steering wheel. Lead is usually caused by:
1. Poorly manufactured radial tyres.
2. Uneven brake adjustment.
3. Wheel alignment.
The way in which a tyre is built can produce lead in
a car. An example of this is placement of the belt.
Off-center belts on radial tyres can cause the tyre to
develop a side force while rolling straight down
the road and the tyre will tend to roll like a cone.
The "Radial Tire Lead/Pull Correction" chart should
be used to make sure that front wheel alignment is
not mistaken for tyre lead.
Rear tyres will not cause lead/pull.
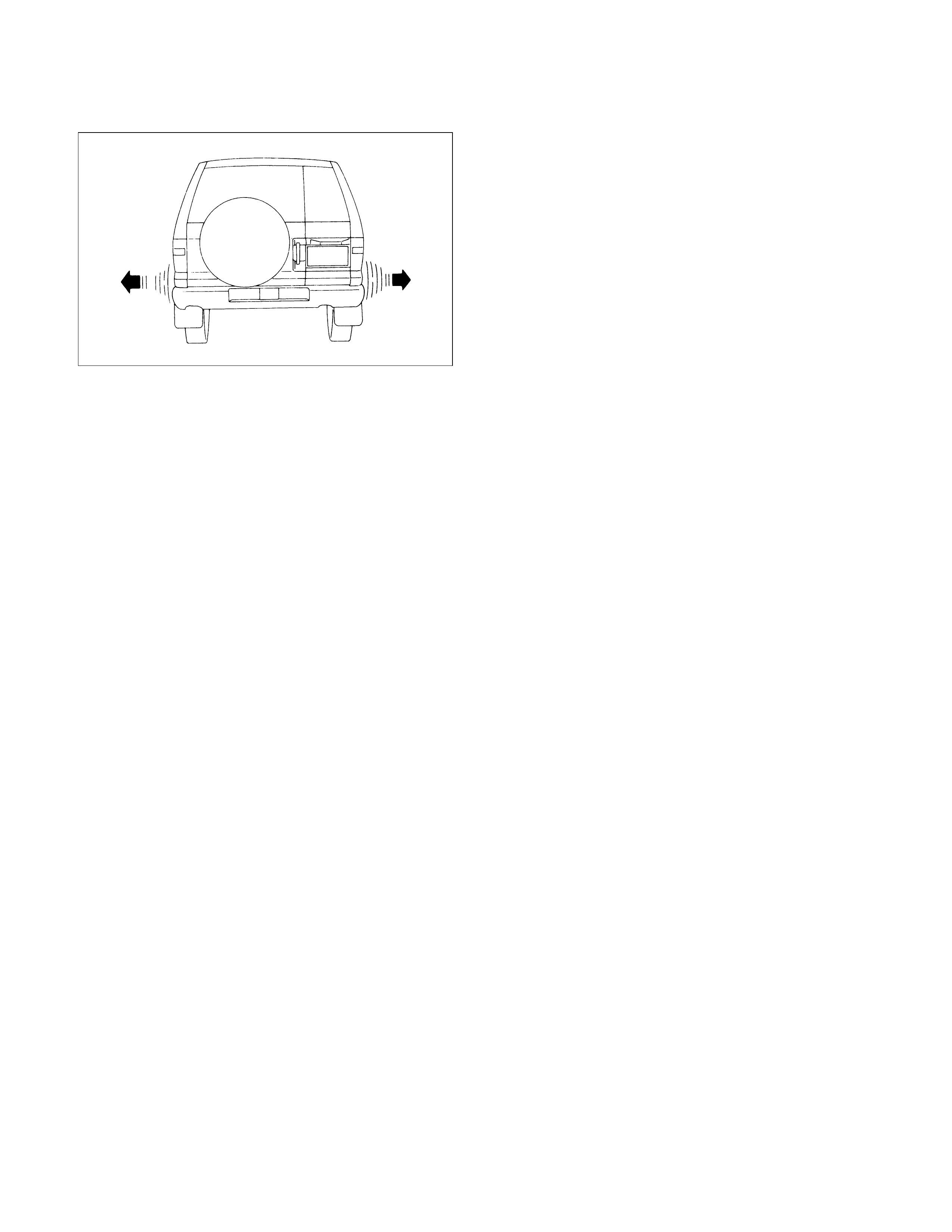
RADIAL TYR E WADDLE
Waddle is side-to-side movement at the front and
/or rear of the car. It can be caused by the steel
belt not being straight within the tyre, or by
excessive lateral runout of the tyre or wheel. It is
most noticeable at low speed, about 8 to 48 km/h
(5 to 30mph). It may also cause rough ride at 80 to
113 km/h (30 to 70mph). The car can be road
tested to see which end of the car has the faulty
tyre. If the tyre causing the waddle is on the rear,
the rear end of the car will "waddle". Front the
driver's seat, it feels as if someone is pushing on
the side of the car.
If the faulty tyre is on the front, the waddle is more
easily seen. The front sheet metal appears to be
moving back and forth. It feels as if the driver's
seat is the pivot point in the car.
Another more time-consuming method of
determining the faulty tyre is substituting tyre and
wheel assemblies that are known to be good.
Follow these steps:
1. Drive the car to determine if the waddle is
coming from the front or rear.
2. Install tyre and wheel assemblies known to be
good (from a similar car) in place of those on
the end of the car which is waddling. If the
waddle cannot be isolated to front or rear, start
with the rear tyres.
3. Road test again. If improvement is noted, install
the original tyre and wheel assemblies one at a
time until the faulty tyre is found. If no
improvement is noted, install tyres known to be
good in place of all four. Then, install the
originals one at a time until the faulty tyre is
found.
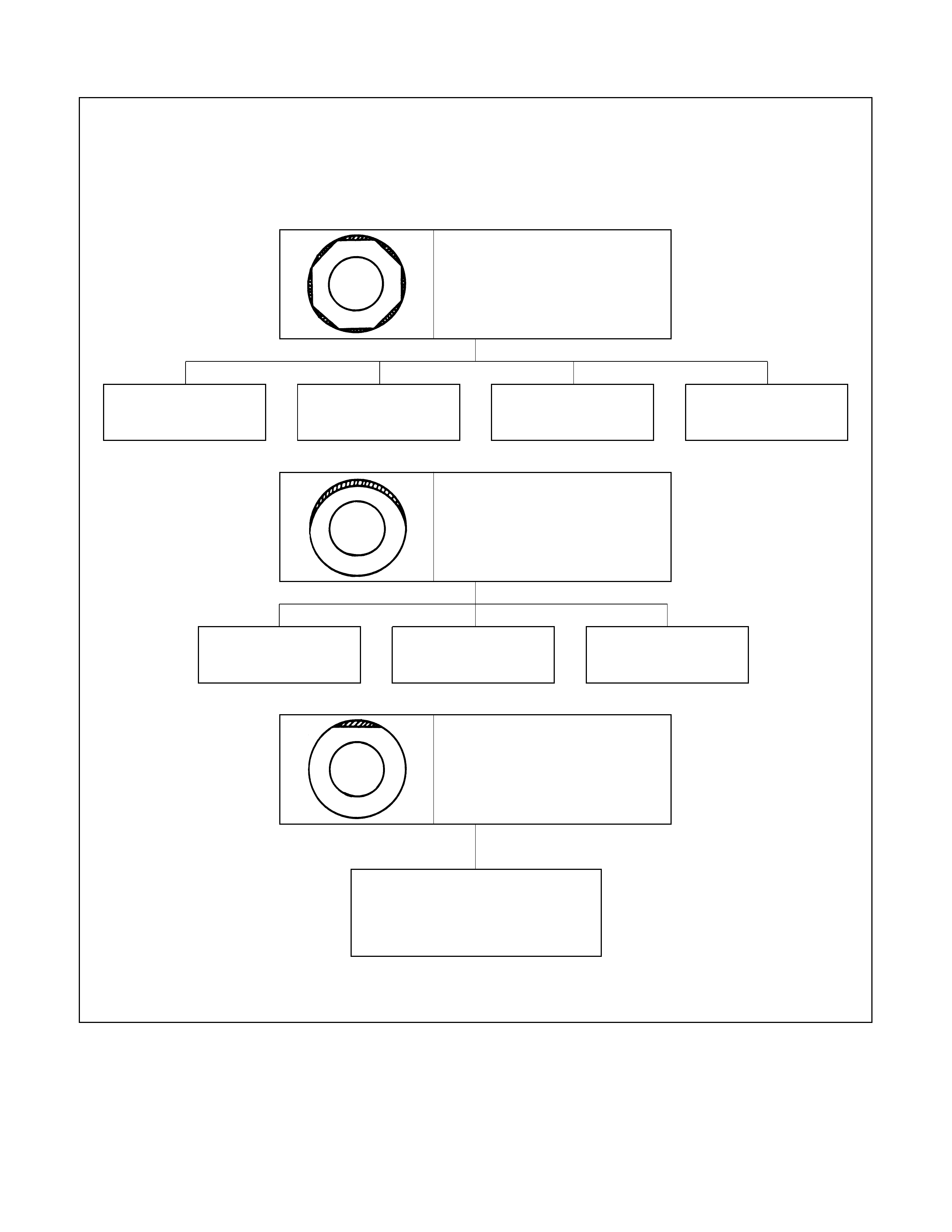
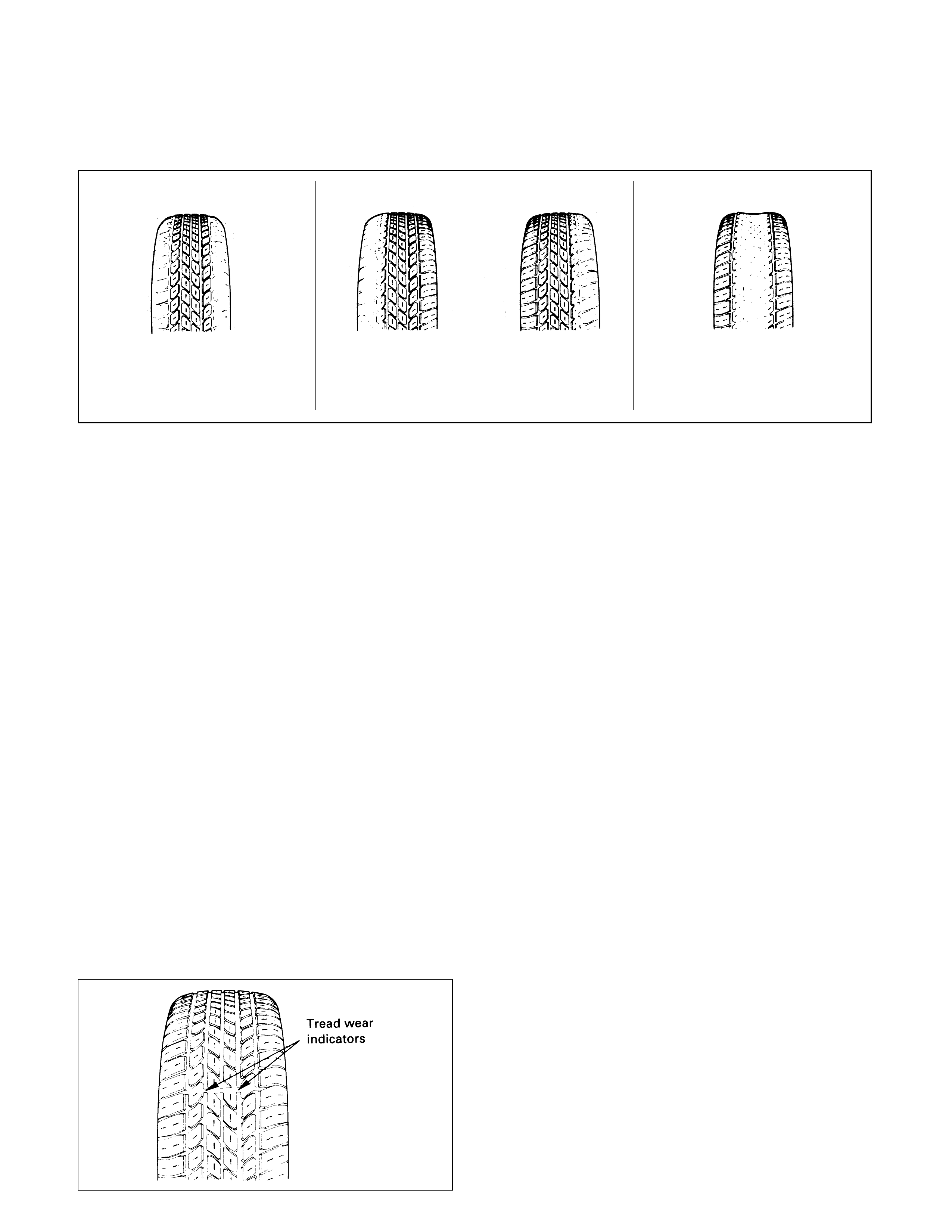
Typical examples of abnormal tyre tread wear and major causes:
CAUTION: Similar wear patterns can be caused by worn suspension parts, misalignment or whee ls
and tyres, and other suspension related problems.
Spotty wear localised on
shoulder sections, and in an
extreme case, the tyre becomes
polygonal in shape.
Tyre or wheel out of
round or distorted.
Hub or knuckle out of
round or distorted.
Play in hub bearing
or ball joint
Rotating parts out of
balance
Tread wear one-sided
Rotating parts out of
balance
Tyre or wheel out of
round
Localised tread wear
Once spotty wear develops in
tread due to hard braking or
abrupt starting. localised wear
tends to be promoted.
Hub or knuckle out of
round or distorted
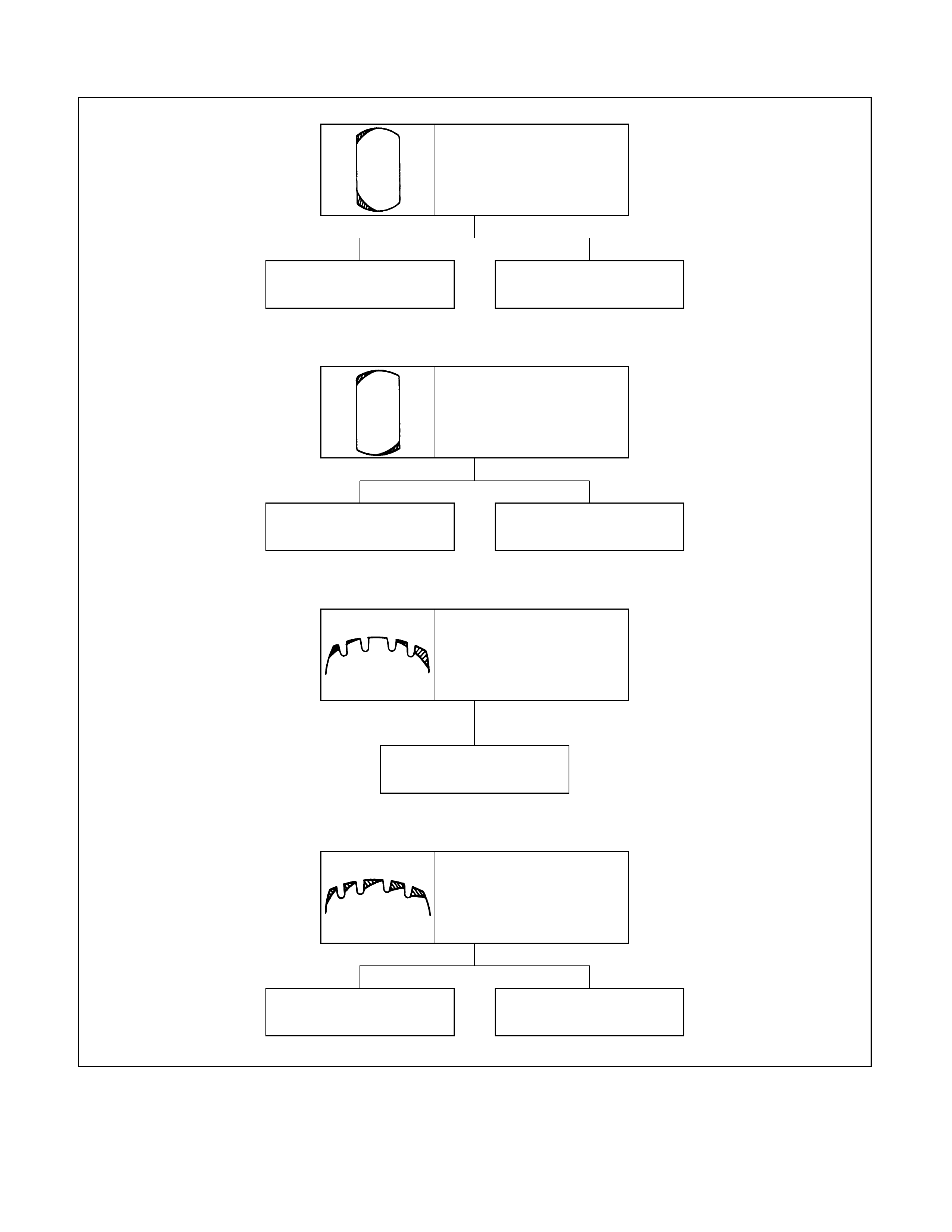
Camber or toe-in incor-
rect Shoulder wear caused by
repeated hard-cornering
Shoulder wear (generally
wear develops in outer
shoulder).
Tyre or wheel out of
round or distorted Play in bearings or ball
joint
Wear in shoulders at
points opposed to each
other
Flexing of tyre excessive
due to under-inflation
Premature wear in
shoulders
Wear caused by repeated
hard-cornering Camber or toe-in incor-
rect
One-sided feather edging
Type
Torsion bar spring
Length mm (in)
Diameter mm (in)
Front shock absorber
Type
Piston diameter mm (in)
Stroke mm (in)
Compressed length mm (in)
Extended length mm (in)
Stabiliser bar
Diameter mm (in)
Independent double wishbone arms,
torsion bar spring with stabilizer bar
Wide Tread Narrow Tread
LWB SWB LWB SWB
1217 (47.9) 1217 (47.9) 1217 (47.9) 1217 (47.9)
29.0 (1.14) 28.6 (1.13) 28.2 (1.11) 27.0 (1.06) ∗
∗ 28.2 (1.11) Australia only
Gas filled, double acting, telescopic
30.0 (1.18)
130.0 (5.12)
390.0 (15.35)
260.0 (10.24)
Wide Tread Narrow Tread
LWB SWB LWB SWB
28.0 (1.10) 28.0 (1.10) 27.0 (1.06) 26.0 (1.02) ∗
∗ 28.2 (1.11) Australia only
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
FRONT SUSPENSION
REAR SUSPENSION: COIL SPRING
LWB SWB
Type 4-Link, coil spring type with stabilizer bar
Shock absorber
Type Gas filled, double acting, telescopic
Piston diameter mm (in) 25.0 (0.98)
Stroke mm (in) 185.0 (7.28) 170.0 (6.69)
Extended length mm (in) 504.0 (19.84) 489.0 (19.25)
Compressed length mm (in) 319.0 (12.56)
Stabilizer bar
Diameter mm (in) 20.0 (0.79) 20.0 (0.79)
19.0 (0.75) GME only
WHEELS
Size 16 × 7JJ 16 × 6JJ 16 × 5.50F
Offset mm (in) 38.0 (1.50) 30.0 (1.18) 20.0 (0.79)
P.C.D., wheel studs mm (in) 139.7 (5.50)
P. C. D.= Pitch circle diameter.
STANDARD TIRE
Size 245 / 70R16 215 / 80R16 7.00-16-6PR
Pressure
Front kPa (kg / cm2/ psi) 210 (2.1 / 30) 220 (2.2 / 31)
Rear kPa (kg / cm2/ psi) 240 (2.4 / 34) 230 (2.3 / 33) 250 (2.5 / 36)
Items Service Standard Service Limit
SERVICE STANDARD
FRONT SUSPENSION
Upper ball joint preload N·m (kg·m/lb·in)
Lower ball joint preload N·m (kg·m/lb·in)
WHEELS
Wheel run-out at rim vertical play mm (in)
Wheel run-out at rim horizontal play mm (in)
0.5 – 3.2 (0.05 – 0.33 / 4.3 – 28.6)
0.5 – 6.4 (0.05 – 0.65 / 4.3 – 56.4)
––––––––
––––––––
––––––––
––––––––
––––––––
––––––––
1.5 (0.059) Steel
0.7 (0.028) Aluminum
1.5 (0.059) Steel
0.7 (0.028) Aluminum
SER VICING
SUSPENSION
INSPECTION
Visual check
Check the following parts:
- Spring for damage.
- Mount for looseness or damage.
- Shock absorbers for oil leakage.
- Shock absorbers mount for looseness.
- Rubber bushes of suspension wear or damage.
- Spring action for loss of balance.
- Joint ball rubber boot for damage.
WHEELS AND TYRES
INSPECTION
Visual check
Check the following parts:
- Wheel pins.
- Wheel disc for damage.
- Hub bearing grease.
- Front and rear hub bearing for looseness.
INFLATION OF TYRES
Tyre pressure, in cold condition (after vehicle has set for
three hours or more, or driven less than one mile), should
be checked monthly or before any extended trip. Tyre
pressure increases approximately 15% when the tyres
become hot during driving. Tyre pressure specification is
shown on the label located on the left door lock pillar.
NOTE:
Check the tyre pressure whenever irregular wear is found.
Tyre inflation greatly affects tyre wear. If the alignment
check does not reveal any alignment problems, check the
condition of the shock absorbers and balance.
TYRE ROTATION
Tyre rotation is recommended to equalize wear for longer
tyre life.
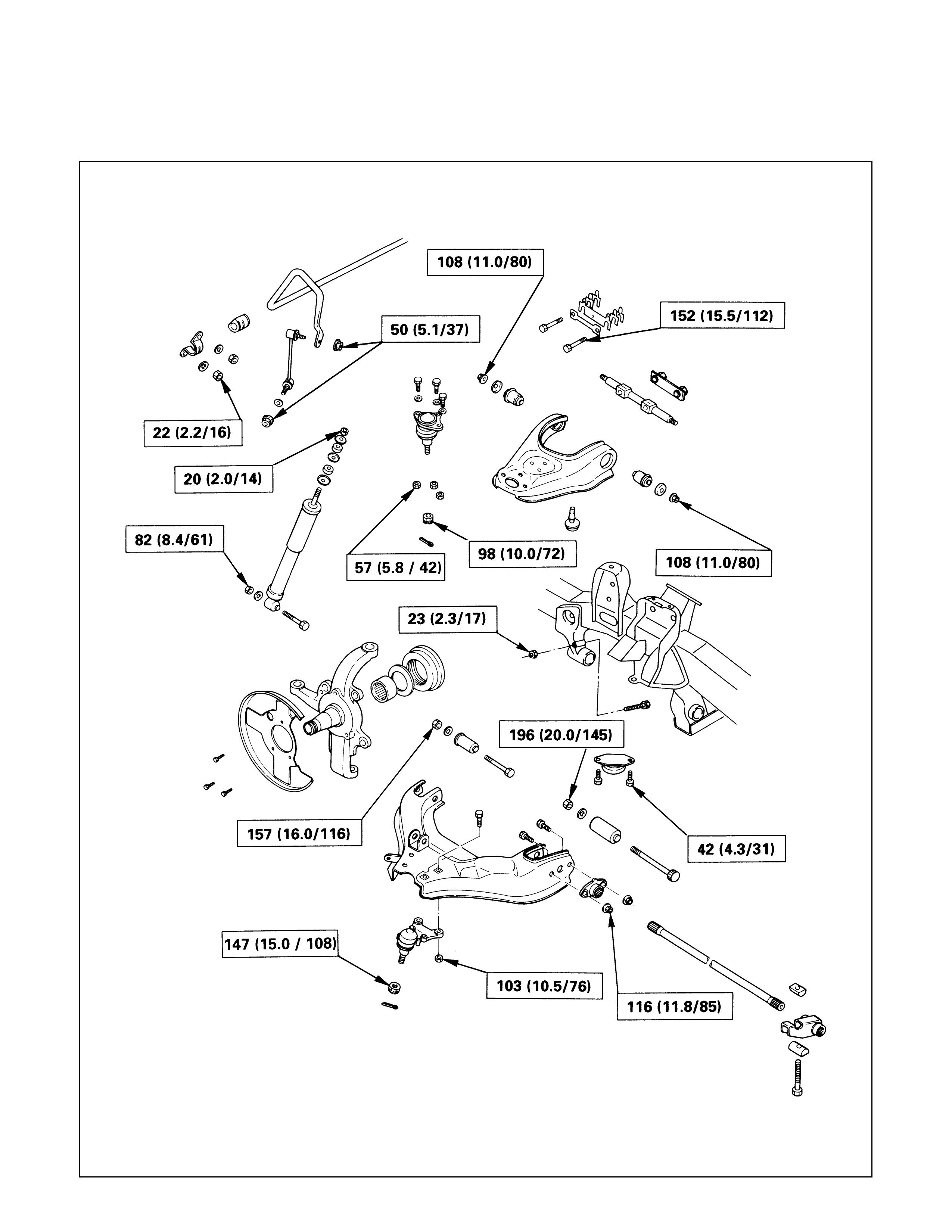
FIXING TORQUE
Front Suspension N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
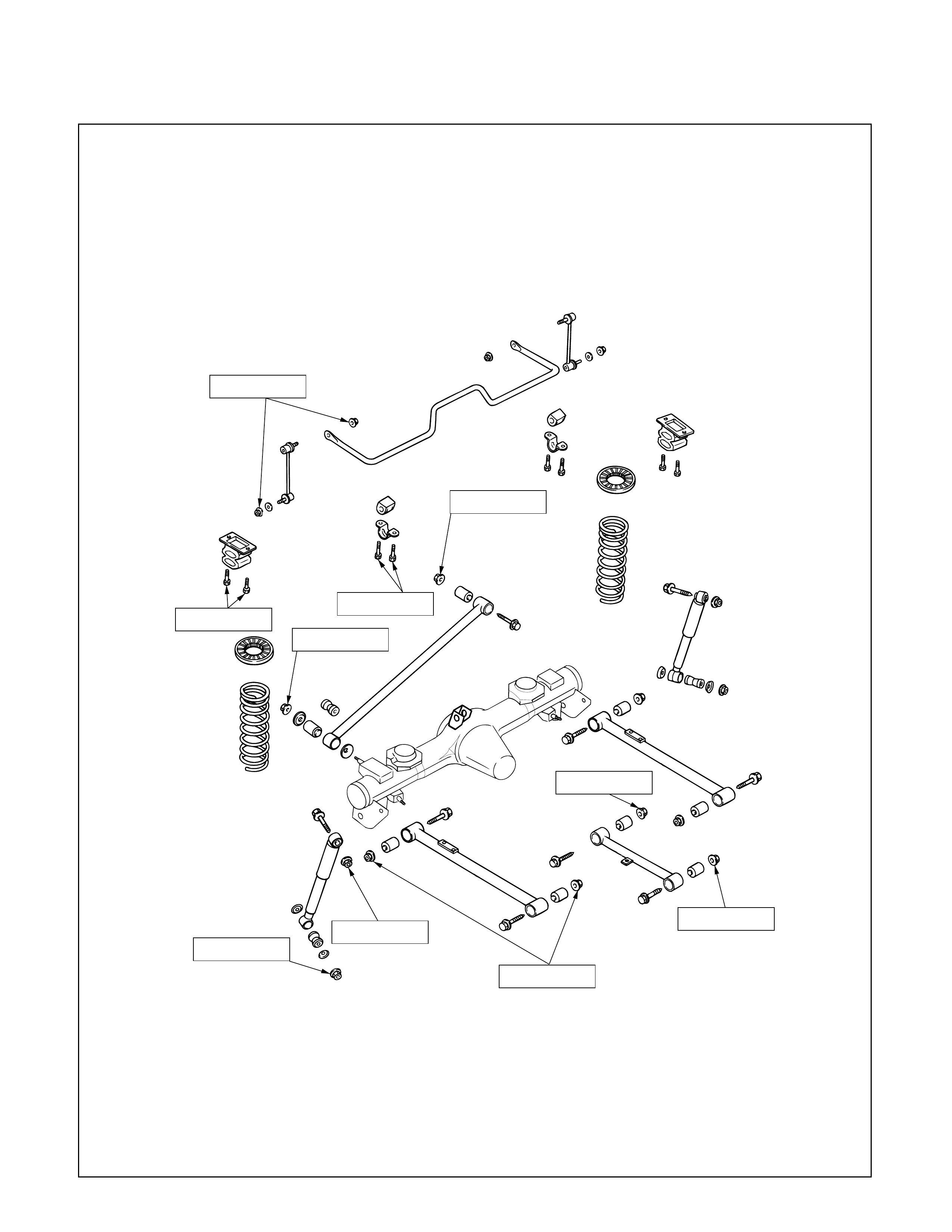
Rear Suspension ; Coil Spring N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
78(8.0/58)
137(14.0/101)
95(9.7/70)
37(3.8/27)
50(5.1/37)
137(14.0/101)
137(14.0/101)
137(14.0/101)
78(8.0/58)
22(2.2/16)
E03RW009
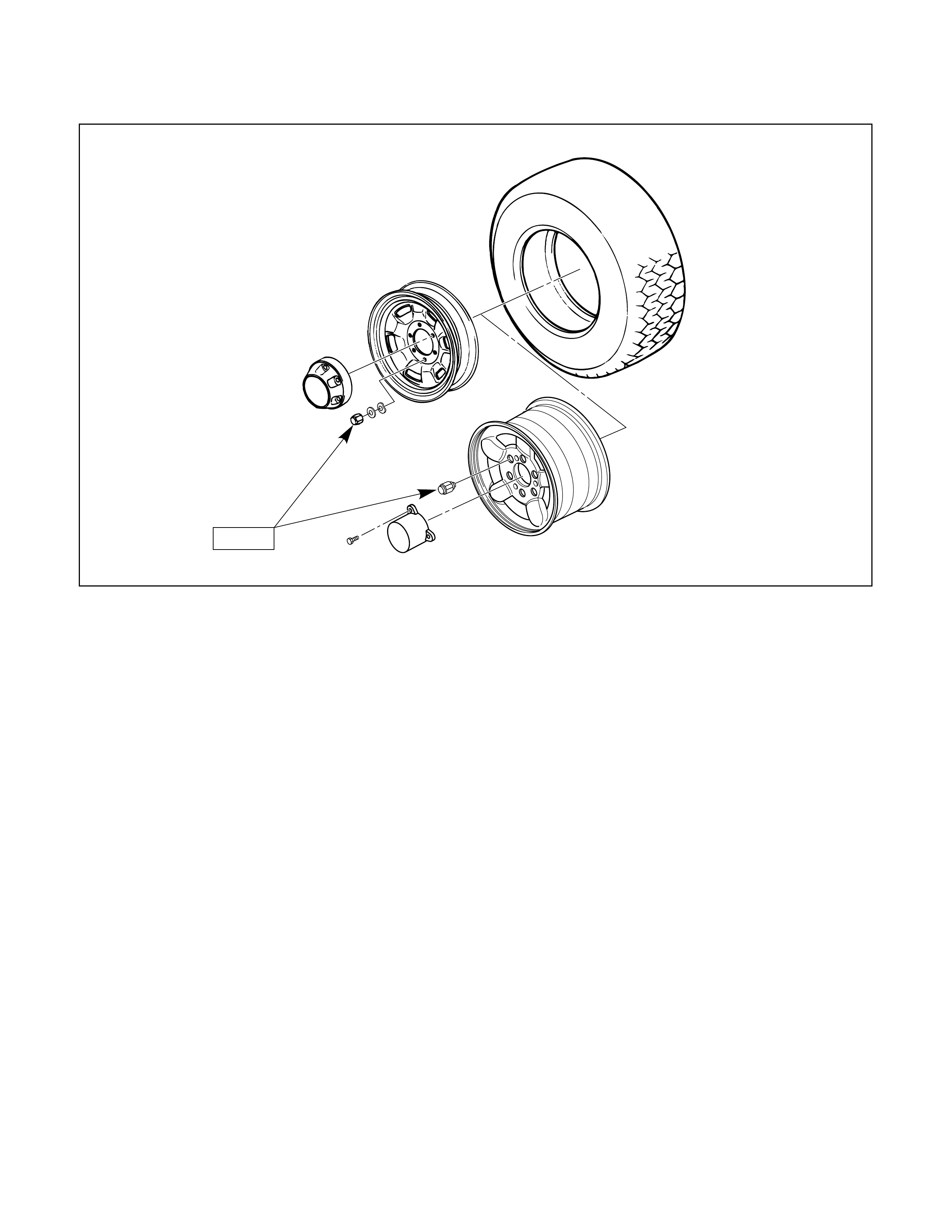
Wheels and Tyres N·m (kg·m/lb·ft)
118 (87)
E03RV001
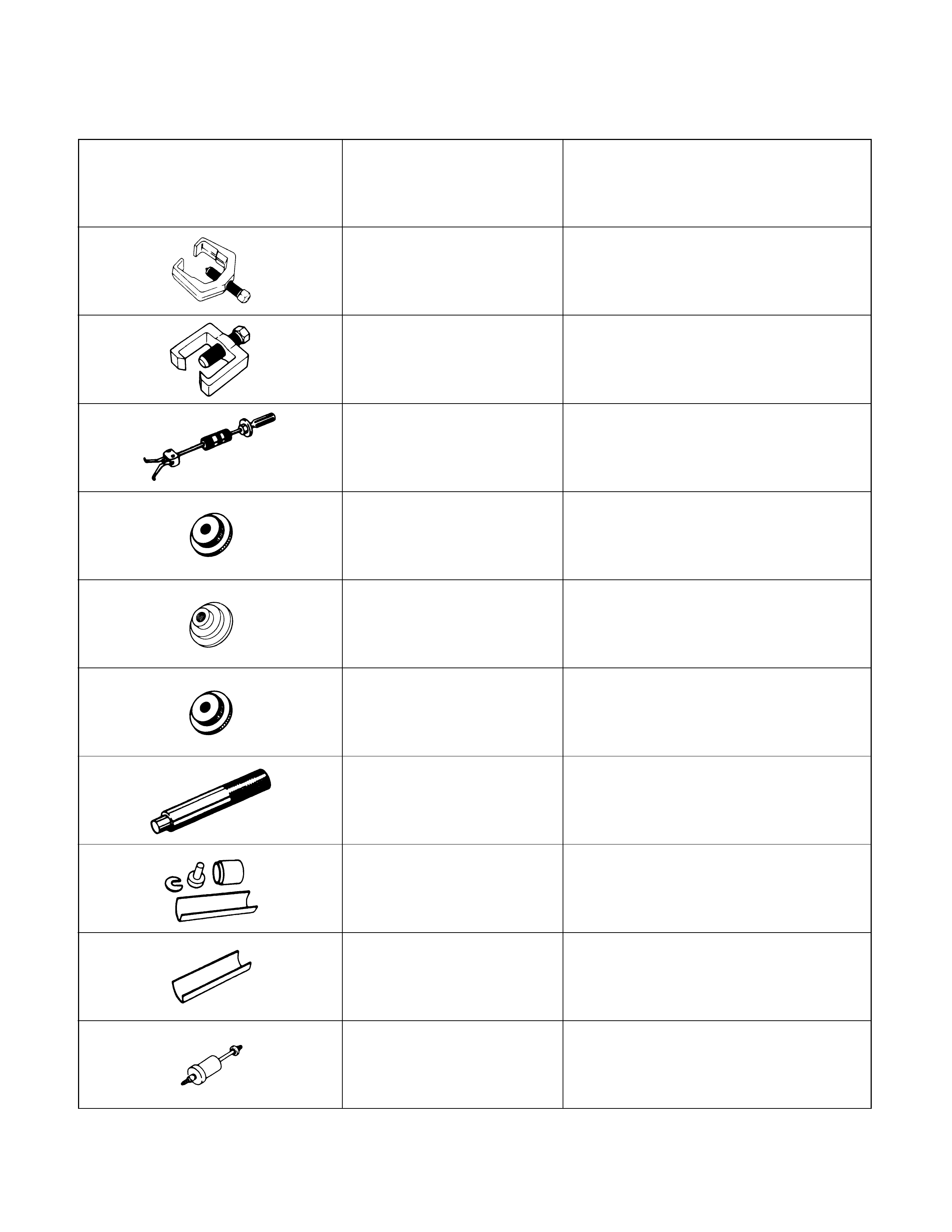
Illustration Part No. Part Name
SPECIAL TOOLS
5–8840–2121–0
(J–36831)
5–8840–0019–0
(J–23907)
5–8840–2127–0
(J–36387)
5–8840–2406–0
(J–41468)
Remover:
Pitman arm
Remover:
Tie rod end
Remover:
Needle bearing
Installer:
Oil seal
Installer:
Oil seal
5–8840–2005–0
(J–29107)
5–8840–0007–0
(J–8092)
5–8840–0256–0
(J–29755)
5–8840–2307–0
(J–39376)
5–8840–2123–0
(J–36833)
Grip
Remover and Installer:
Upper arm bushing
Installer:
Upper arm bushing
Remover and Installer kit:
Lower arm front bushing
5–8840–2128–0
(J–36838) Installer.
Needle bearing
Illustration Part No. Part Name
5–8840–2124–0
(J–36834)
5–8840–2298–0
(J–39214)
5–8840–2327–0
(J–39792)
5–8840–2299–0
(J–39215)
Remover and Installer kit:
Lower arm rear bushing
Remover and Installer:
Trailing and Center link bushing
Remover and Installer:
Lateral rod bushing (Axle side)
Remover and Installer:
Lateral rod bushing

