
SECTION 7D1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM (4L30–E)
Service Precaution
General Description
Electronic Control Diagram
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Control System Diagram
Shift Control
Band Apply Control
Torque Converter Clutch Control
Line Pressure Control
On–Board Diagnostic System
Fail Safe Mechanism
Torque Management Control
ATF Warning Control
ABS Control (If equipped)
Shift Mode Control
Gear Shift Control
Winter Drive Mode
Backup Mode
Functions of Input / Output Components
Diagnosis
Electronic Diagnosis
Check Trans Indicator
Diagnostic Check
“Check Trans” Check
Tech2 OBD II Connection
Using Tech 2 On The Vehicle
Transmission Application Menu
THM 4L30E Transmission Functions
F0: Transmission Data
F1: PC Solenoid Data
OBD II Diagnostic Management System
16 – Terminal Data Link Connector (DLC)
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Clear DTC
DTC Check
PCM Precaution
Information On PCM
Intermittent Conditions
UBS Jackaroo
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Identification
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode
Switch) Illegal Position
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch (Mode
Switch) Performance
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
Sensor Circuit Low Input
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
Sensor Circuit High Input
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck
On)
DTC P0722 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
(OSS) Low Input
DTC P0723 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
(OSS) Intermittent
DTC P0730 Transmission Incorrect Gear Ratio
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force
Motor) Circuit Electrical
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical
DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical
DTC P1790 ROM Transmission Side Bad Check
Sum
DTC P1792 EEPROM Transmission Side Bad
Check Sum
DTC P1835 Kickdown Switch Always On
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid Malfunction
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor
Specifications

Service Precaution
WARNING: IF SO EQUIPPED WITH A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS),
REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND WIRING
LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON
OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING. WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE
ON OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING, REFER TO THE SRS SERVICE
INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW WARNINGS
COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
HOLDEN will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. HOLDEN will also call
out the fasteners that require thread lockers or
thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED,
do not use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases,
or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners
or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such
coatings adversely affect the fastener torque and
the joint clamping force, and may damage the
fastener. When you install fasteners, use the correct
tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to
parts and systems.
General Description
The 4L30–E is a 4–speed fully automatic transmission.
It uses a microcomputer as a control unit to judge
running conditions including throttle opening rate and
vehicle speed, then it sets the shifting point in the
optimum timing so that best driving performance can be
achieved.
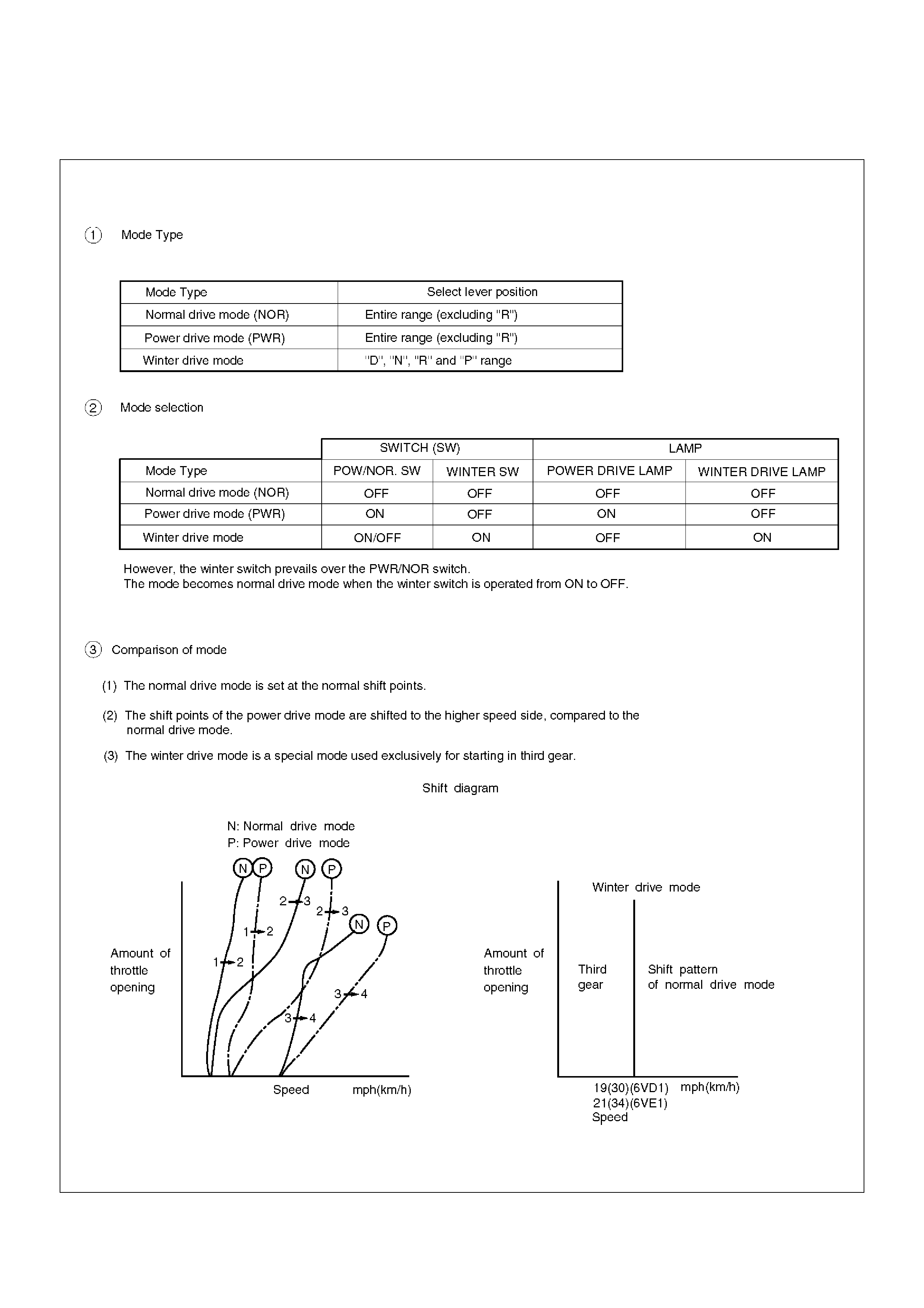
In addition, the built–in shift mode select function can
select three shift modes according to the driver's
preference:
• Normal mode –Normal shift pattern.
• Winter mode –Starts in 3rd gear to reduce slippage
on ice or snow.
• Power mode has a delayed upshift for when more
powerful acceleration is required.
Also, the built–in fail safe function (“backup mode”)
assures driving performance even if the vehicle speed
sensor, throttle signal or any solenoid fails.
Further, the self–diagnostic function conducts diagnosis
in a short time when the control system fails, thus
improving serviceability.
The major features of 4L30–E are as follows:
• A compact structure consisting of 2 sets of planetary
gears and flat torque converter.
• Electronic control selects the optimum shift mode
according to the driving conditions.
• Electronic control maintains the optimum hydraulic
pressure for clutch, band brake as well as
transmission so that shift feeling is improved.
• Two sets of planetary gears reduce friction of power
train.
Also, a lockup mechanism in the torque converter
reduces fuel consumption.
• Wide gear ratio and high torque rate of torque
converter provide excellent starting performance.
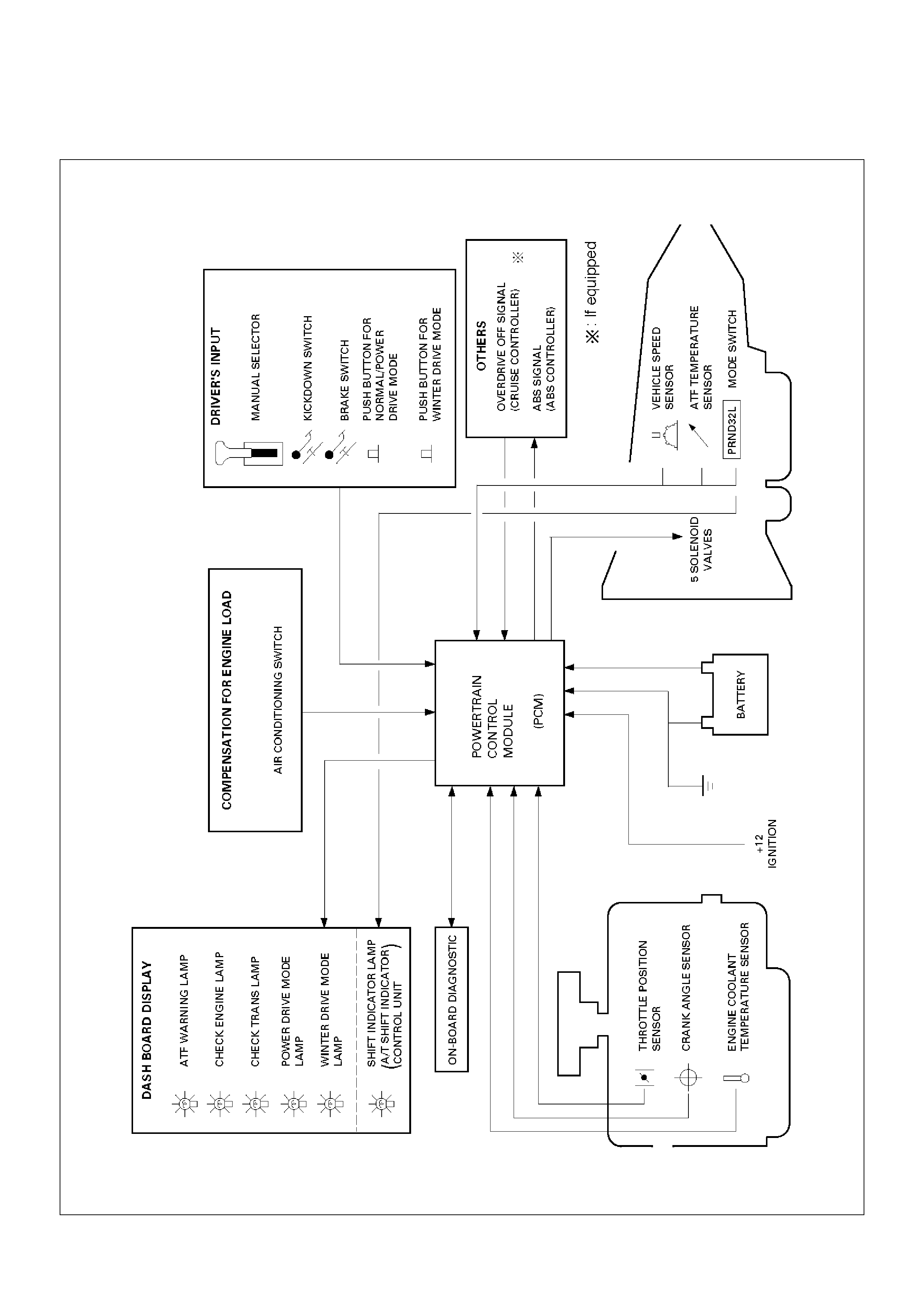
Electronic Control Diagram
C07RW052
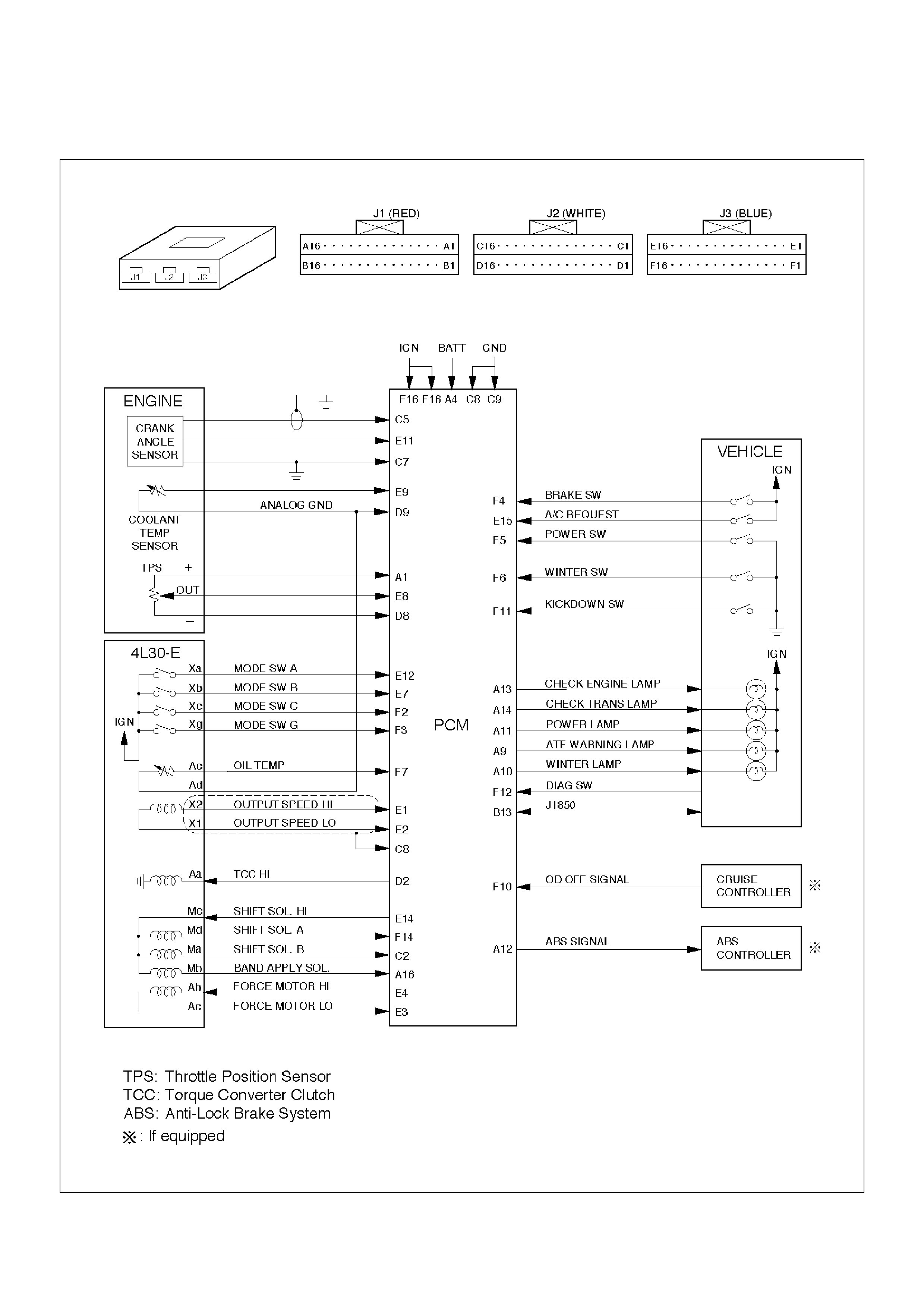
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
C07RW051
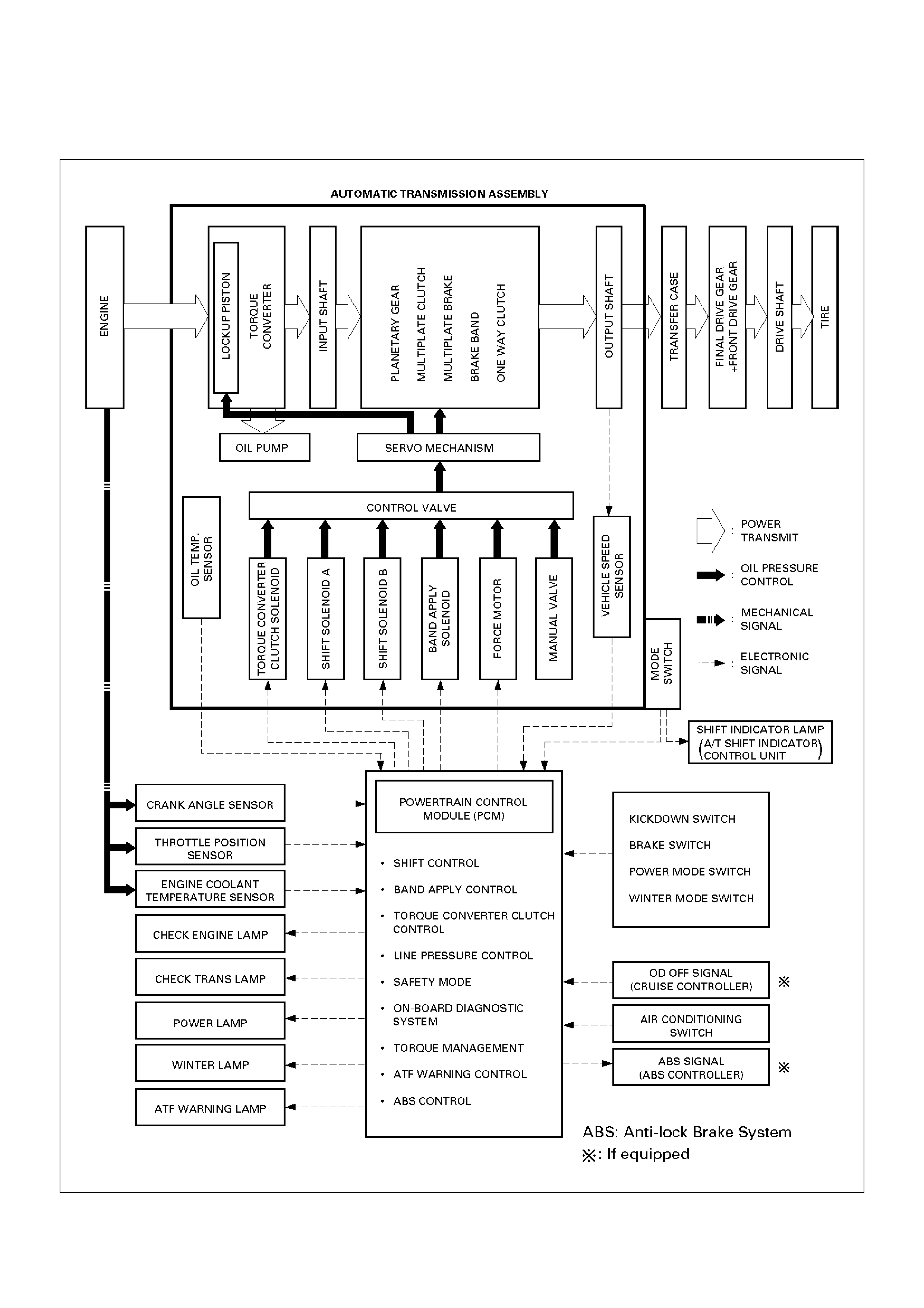
Control System Diagram
C07RY00031

Shift Control
The transmission gear is shifted according to the shift
pattern selected by the driver. In shifting gears, the
gear ratio is controlled by the ON/ OFF signal using the
shift solenoid A and the shift solenoid B.
Band Apply Control
The band apply is controlled when in the 3–2 downshift
(engine overrun prevention) and the garage shift
(shock control).
The band apply solenoid is controlled by the signal from
the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the flow
of the oil.
Torque Converter Clutch Control
The clutch ON/OFF is controlled by moving the
converter clutch valve through shifting Torque Converter
Clutch (TCC) solenoid using the ON/OFF signal.
Line Pressure Control
The throttle signal allows the current signal to be sent to
the force motor. After receiving the current signal, the
force motor activates the pressure regulator valve to
regulate the line pressure.
On–Board Diagnostic System
Several malfunction displays can be stored in the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) memory, and read
out of it afterward.
The serial data lines, which are required for the testing
of the final assembly and the coupling to other
electronic modules, can be regulated by this function.
Fail Safe Mechanism
If there is a problem in the transmission system, the
PCM will go into a “backup” mode.
The vehicle can still be driven, but the driver must use
the select lever to shift gears.
Torque Management Control
The transmission control side sends the absolute spark
advance signal to the engine control side while the
transmission is being shifted. This controls the engine
spark timing in compliance with the vehicle running
condition to reduce the shocks caused by the change
of speed.
ATF Warning Control
The oil temperature sensor detects the ATF oil
temperature to control the oil temperature warning,
TCC, and the winter mode.
ABS Control (If equipped)
When the select lever is at “L” or “R” range, a signal is
sent to the ABS controller as one of the ABS control
conditions.
Shift Mode Control
C07RY00012
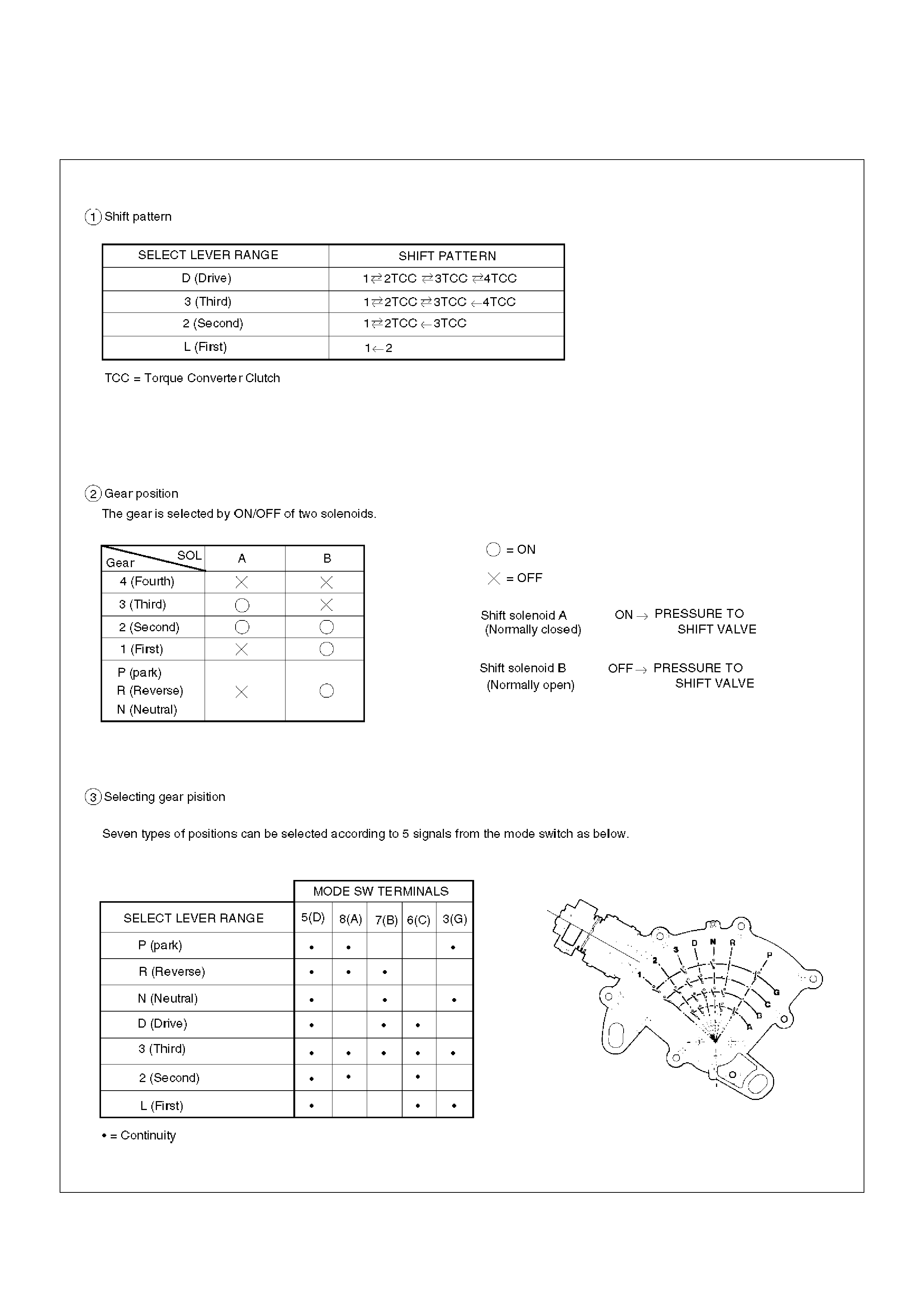
Gear Shift Control
F07RT034

Winter Drive Mode
1. Operation
The winter switch will operate when switched on
after all of the following conditions are present:
a The gear select position is“D”, “N”, “R”and “P”
range.
b Vehicle speed is 7mph (11km/h) or less.
c Transmission oil temperature is 130°C (266°F)
or less.
d Kickdown switch is off.
e Accelerator opening is at 8% or less.
2. Cancel Release
1. Cancellation by driver
a Turning off the winter drive mode switch
b Shifting select position to“3”, “2”, or “L”
(Winter drive mode is not canceled by
selecting“N”, “R”, or “P” from“D”)
c Ignition key is turned off.
2. Automatic cancellation
a When vehicle runs at 19mph (30 km/h)
(6VD1) or 21 mph (34 km/h) (6VE1) or more
for 1 second or more
b When transmission oil temperature reaches
130°C (266°F) or above
NOTE: The mode returns to normal drive mode or
power drive mode after the winter drive mode is
canceled.
Backup Mode
If a major system failure occurs which could affect
safety or damage the transmission under normal vehicle
operation, the diagnostic system detects the fault and
overrides the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The “CHECK TRANS” light flashes to alert the driver,
and the transmission must be manually shifted as
follows:
Shifts are firmer to prevent clutch slip and consequent
wear. The fault should be corrected as soon as
possible.
Select lever position Gear Ratio Selected
D 4 (Fourth)
Manual 3 4 (Fourth)
Manual 2 3 (Third)
Manual L 1 (First)
R Reverse
Functions of Input / Output Components
* If equipped
Components Function
I
N
P
U
T
S
I
G
N
A
L
Speed sensor
(fixed to transmission (T/M))
Senses rotation of output shaft and feeds the data to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
Throttle position sensor
(TPS)
(fixed to engine)
Senses the extent of throttle valve opening and the speed of the throttle valve
lever motion to open the valve. Feeds the data to PCM.
Brake Switch (SW)
(fixed to brake pedal)
Senses whether the driver has pressed the brake pedal or not and feeds the
information to PCM.
Kickdown SW
(fixed to accelerator pedal)
Senses whether the driver has pushed the accelerator pedal fully or not, and
feeds the information to PCM.
Mode SW (fixed to T/M) Senses the select lever position, and feeds the information to PCM.
Power drive SW
(fixed to front console)
Senses whether the driver has selected the power mode, and feeds the
information to PCM.
T/M oil temp. sensor Senses the T/M oil temperature and feeds the data to PCM
Engine coolant temperature
sensor
Senses the engine coolant temperature, and feeds the data to PCM.
Engine speed signal Feeds the signals monitoring engine speed to PCM from crank angle sensor.
Air conditioning information Senses whether the air conditioner has been switched on or not, and feeds the
information to PCM.
Winter switch (fixed to front
console)
Senses whether the driver has selected the winter mode, and feeds the
information to PCM.
Cruise controller *
(Overdrive OFF signal)
Downshift takes place when Overdrive OFF signal is received from auto cruise
control unit.
O
U
T
P
U
T
S
I
G
N
A
L
S
O
L
E
N
O
I
D
Shift solenoid A, B Selects shift point and gear position suited to the vehicle running condition on the
basis of PCM output.
Band apply solenoid Controls oil flow suited to the vehicle running condition on the basis of PCM
output.
Torque Converter Clutch
solenoid
Controls clutch engagement/disengagement suited to the vehicle running
condition on the basis of PCM output.
Force motor
(Pressure regulator
valve)
Adjusts the oil pump delivery pressure to line pressure suited to the vehicle
running condition on the basis of PCM output.
Power drive mode lamp Informs the driver whether the vehicle is in power mode or not.
Winter drive mode lamp Informs the driver whether the vehicle is in winter mode or not.
T/M monitor lamp
(“CHECK TRANS”)
Informs the driver of failure in the system.
ATF warning lamp Lights when ATF oil temperature rises.
ABS signal * When the select lever is at “Reverse” or “L” range, sends a signal to the ABS
controller as one of the ABS control conditions.
Diagnosis
Electronic Diagnosis
How To Diagnose The Problem
1. To avoid incorrect diagnostics, this book needs to be
followed accurately. Unless stated, do not jump
directly to a section that could contain the solution.
Some important information may be missed.
2. The sections in CAPITALS and bold are the main
sections that can be found in the contents.
3. The GOTO “SECTION” means to continue to check
going to the“section”.
4. The GOTHROUGH “SECTION” means to go
through the “section” and then to go back to the
place the GOTHROUGH was written.
5. BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS:
You should understand the basic theory of
electricity. This includes the meaning of voltage,
amps, ohms, and what happens in a circuit with an
open or shorted wire. You should also be able to
read and understand wiring diagrams.
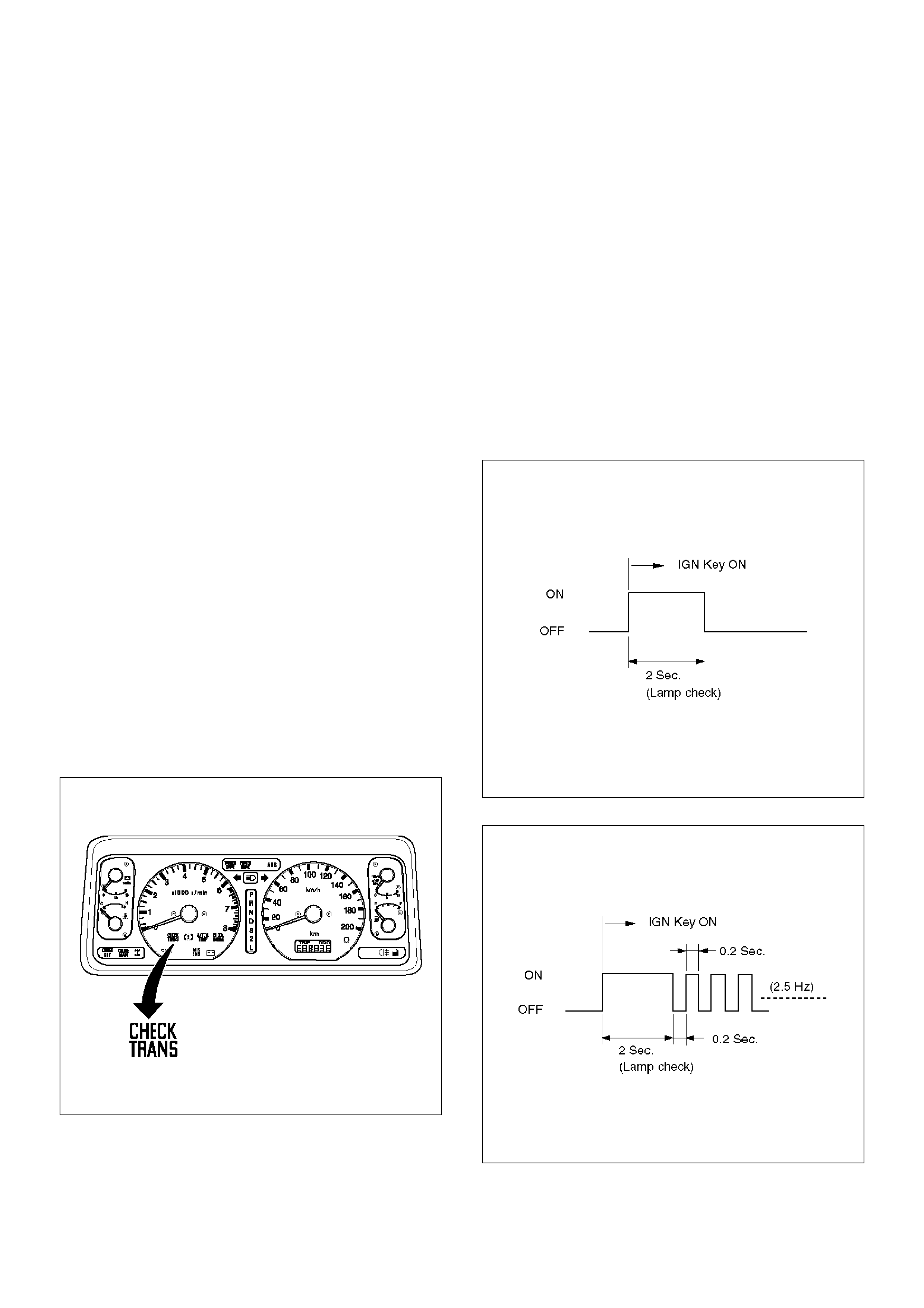
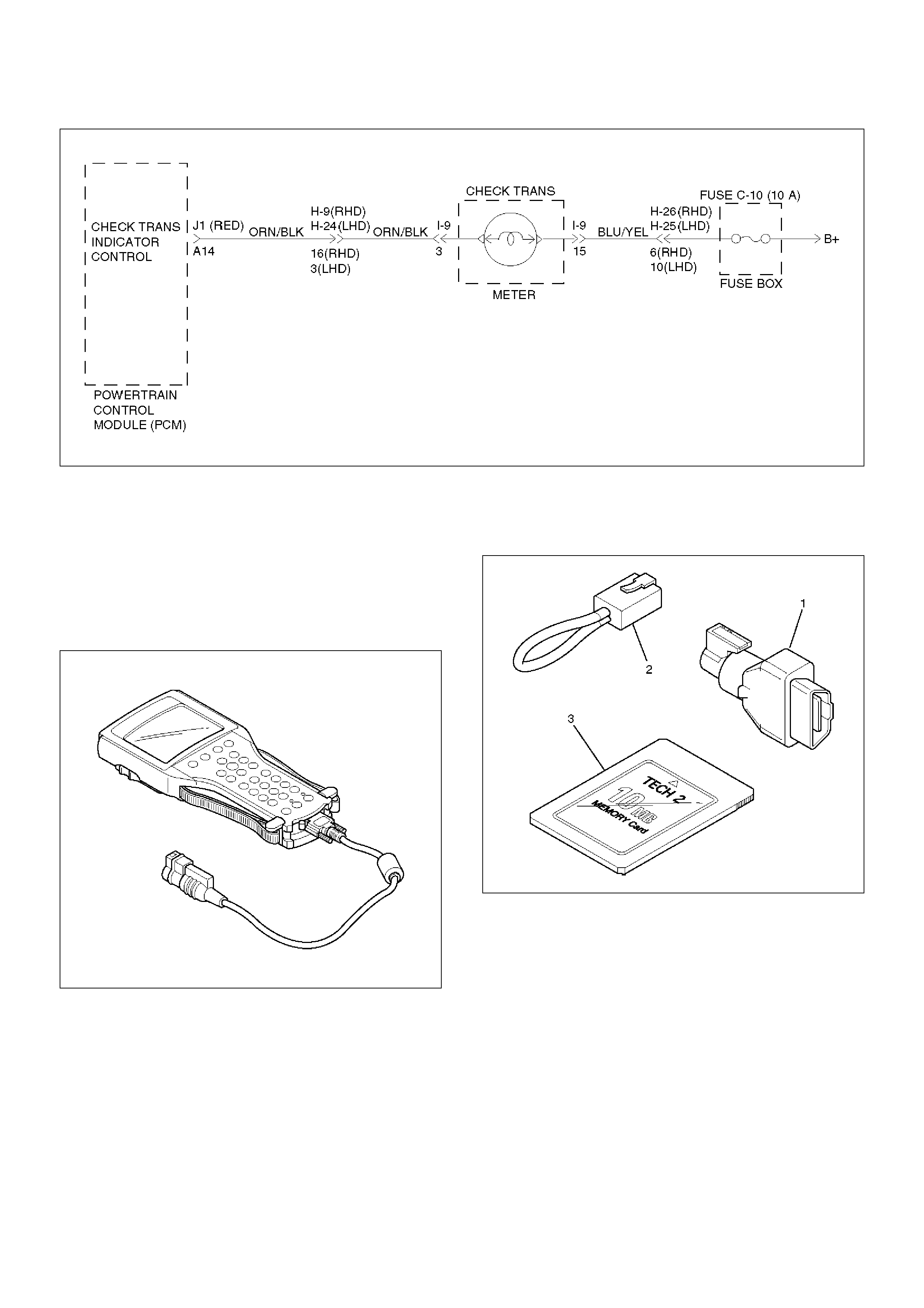
Check Trans Indicator
Find CHECK TRANS indicator and verify if it is
A Flashing: GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
B Staying on: GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS
CHECK.
C Is never ON when the ignition key is turned on:
GOTHROUGH CHECK TRANS CHECK
D Is ON during 2 seconds at ignition but OFF after:
Normal operation. No DTC or malfunction.
821RW261
Diagnostic Check
This test determines if the transmission or its inputs,
outputs, connections, or sensors are failing.
1. Connect the Tech2: GOTHROUGH Tech2 OBD II
CONNECTION.
2. Turn on the ignition but not the engine.
3. Push “F2” on Tech2 to see the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC):
4. Do you have a DTC?
YES: write down all code numbers and do the DTC
CHECK
NO: the DTC can not help you finding the problem.
1. GOTHROUGH “CHECK TRANS” CHECK
2. IF it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds ON
and 0.2 seconds OFF, this means that you
should have a DTC stored. Please recheck
GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK and if you find
the same problem, replace the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM).
Normal
C07RW047
Abnormal
C07RW048
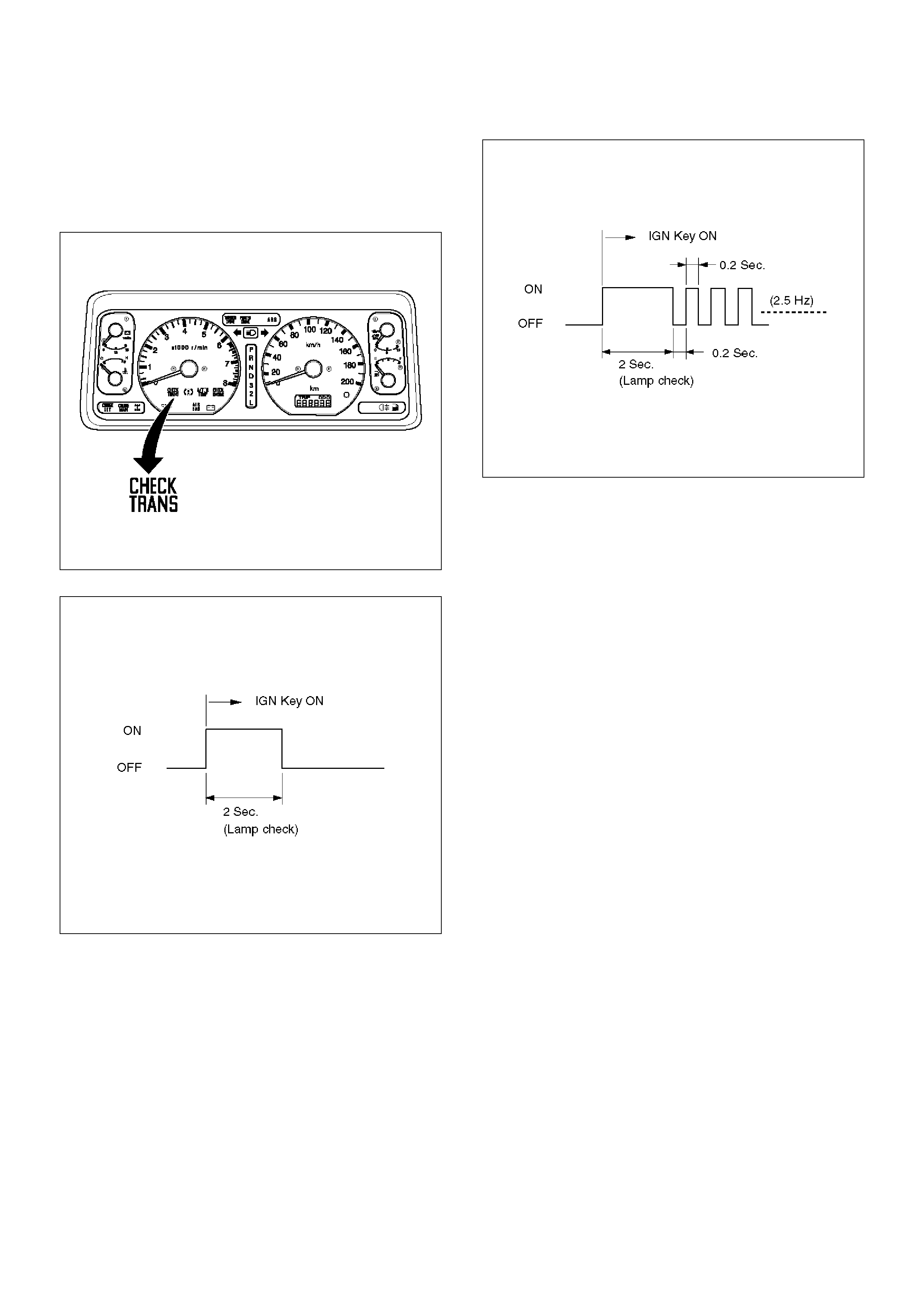
“Check Trans” Check
1. Indicator it is ON during 2 seconds at ignition (or
when the engine is cranked) but it is OFF after the
engine starts. The indicator is working normally
GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
821RW261
Normal
C07RW047
2. Indicator it is flashing and the flash is 0.2 seconds
ON and 0.2 seconds OFF always when ignition is
on (engine cranked or not). This means that there is
a malfunction. GOTO DIAGNOSTIC CHECK.
Abnormal
C07RW048
3. Indicator it is staying ON always when Ignition is
ON.
1. This means that connection between the lamp
and the PCM is shorted to ground.
2. Verify if instrument panel terminal 3 of connector
I–9 is shorted to ground.
3. Verify if the PCM connector J1 (RED) terminal
A14 is shorted to ground.
4. Verify that the instrument panel terminal 15 of
connector I–9 is connected to battery.
5. IF problem solved: GOTO CHECK TRANS
INDICATOR.
NO:Replace Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
4. Indicator it is staying OFF with the ignition ON
(engine OFF).
1. This means that connection between the lamp
and the PCM is shorted to battery or opened.
2. Verify if instrument panel terminal 3 of connector
I–9 is shorted to battery or open.
3. Verify if the PCM connector J1 (RED) terminal
A14 is shorted to battery or open.
4. Verify that the instrument panel terminal 15 of
connector I–9 is connected to battery. If not,
check the fuses and the connections voltage.
5. IF problem solved: GOTO CHECK TRANS
INDICATOR.
NO: Replace Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
D07RW028
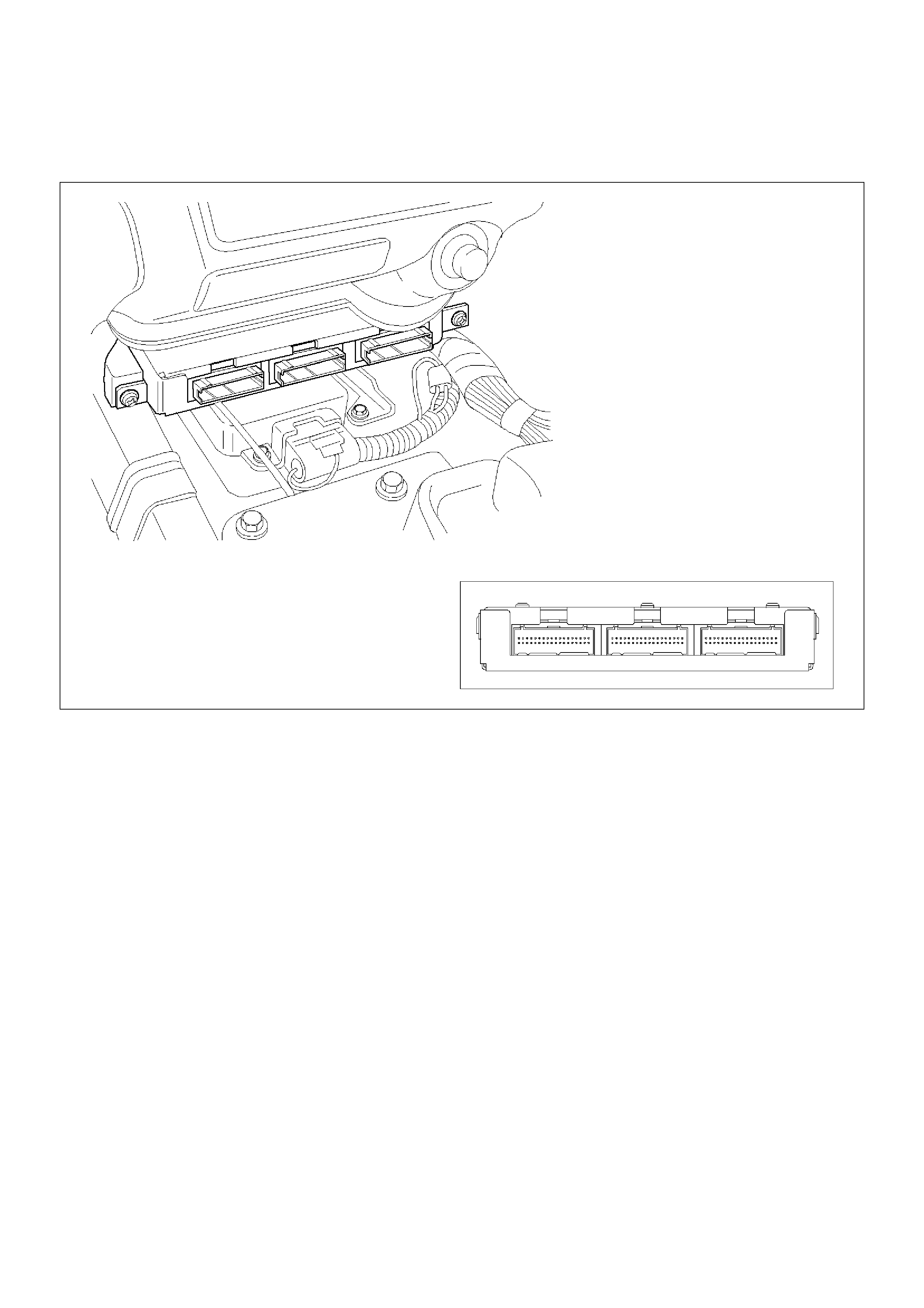
Tech2 OBD II Connection
In order to access OBD II Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) data, use of the Tech2 scan tool kit (7000086) is
required.
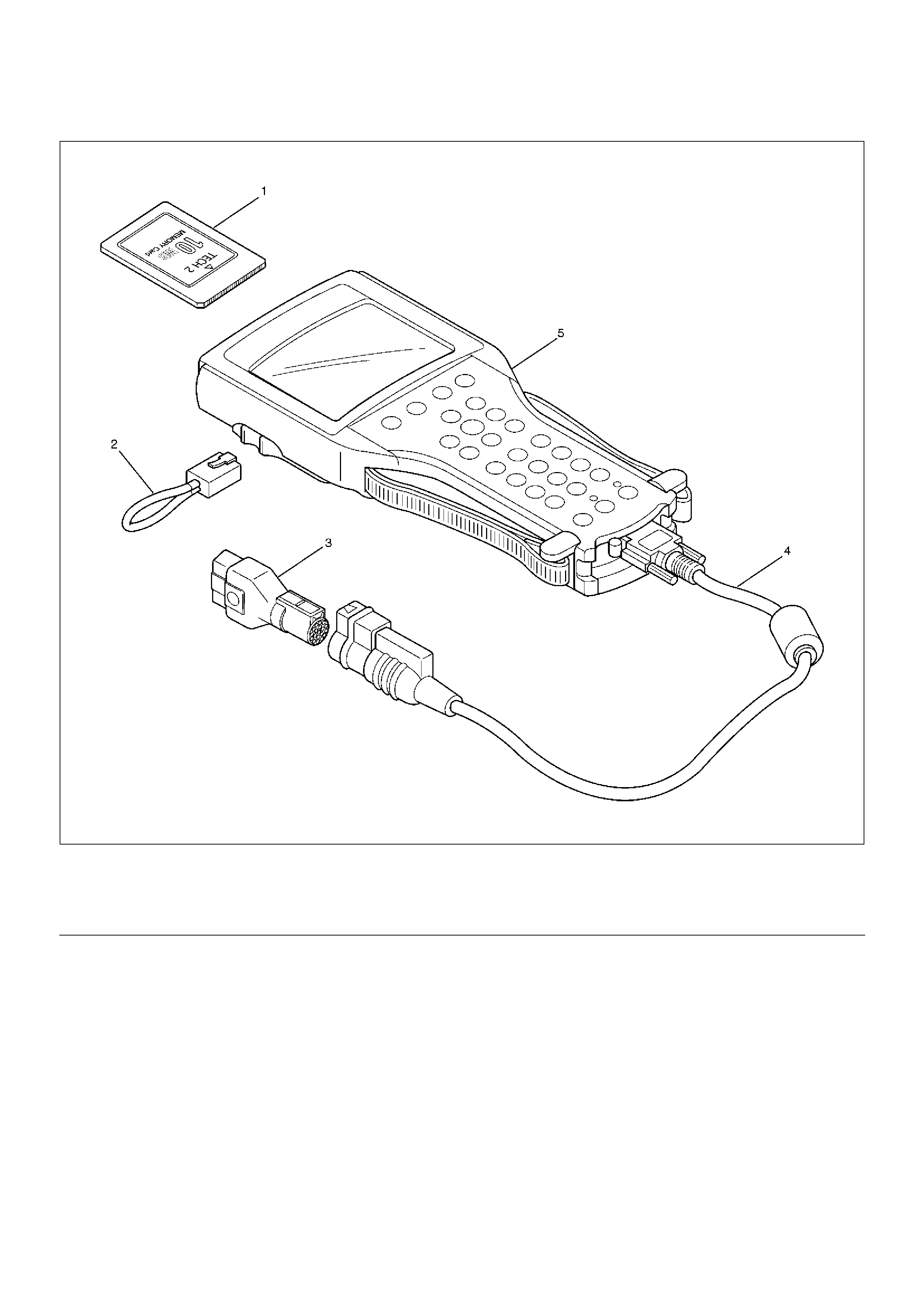
1. The electronic diagnosis equipment is composed of:
1. Tech2 (7000057) hand–held scan tool unit and
DLC cable (3000095).
901RW176
2. SAE 16/19 adapter (3000098) (1), RS 232 loop
back connector (3000112) (2), and PCMCIA
card (3000117) (3).
F07RW033
2. Connecting the TECH2
901RW180
EndOFCallout
Legend
(1) PCMCIA Card
(2) RS 232 Loop Back Connector
(3) SAE 16/19 Adapter
(4) DLC Cable
(5) Tech2
Using Tech 2 On The Vehicle
NOTE: Due to the constant evolution of TECH 2
software, the screens shown in this section may
differ slightly from those displayed for the vehicle
being tested.
Connecting TECH 2 To The Vehicle
1. Connect Tech 2 to the vehicle DLC, with the DLC
cable and the 16/19 pin adapter.
2. Switch the unit on by pressing the power button (2).
A green light (1) should come on indicating that the
tool is receiving power.
NOTE: At this time the technician should see the Power
On Self Test (POST) run. The POST is a built in
diagnostic self test for the TECH 2 that should find most
common system faults. The POST is run on every
power up to ensure the best operation of the tool. After
the completion of the POST, the TECH 2 unit will briefly
show the POST results. If POST passes, the tool will
continue onto the title screen. If POST fails, results of all
tests will be displayed, and this should show which test
failed. POST failures may be classified as fatal or non-
fatal. A fatal error will not allow the user to continue
using the tool. Failure of the keypad would be an
example of a fatal error. Non-fatal errors found during
the POST will allow continued use of the TECH 2, but
with some limitations. If either a fatal or non-fatal error
occurs, refer to the Troubleshooting section of the
TECH 2 User's Guide.
1. Power Status Indicator Light
2. PWR (Power) Key
3. SHIFT Key
4. SHIFT Key Status Indicator Light
3. At the Tech 2 title screen press the ENTER key to
continue.
PWR
F0
F3
F6
F9
F1
F4
F7
F2
F5
F8
?
GM
TECH 2
2
2
Tech
10 Megabyte
Press [ENTER] to continue
Software Version 11.010
Holden 1997 - 2002
2
1
4
3

4. A selection can be made from the Main Menu,
either by using a function key or by using the arrow
keys to highlight a menu choice and pressing
ENTER.
•NOTE: You will then need to supply some additional
information to the TECH 2. This requires navigation
through a series of lists (called picklists). On some
menus or picklists, the user can use a function key to
make a menu selection, but most of the picklists
require using the selection and action keys. If a
mistake is made in the selection process, or if a
different application or function is desired, press EXIT
to back up one level. Within an application, there may
be soft keys which are available for use. These soft
keys allow access to additional tool functions without
exiting a current tool function. Soft keys are made up
of sets which will appear together. To see the next set
of soft keys, select the More soft key.
The TECH 2 Main Menu contains the following:
F0: Diagnostics
Contains all functions to test, diagnose, monitor and
program the different vehicle systems.
F1: Service Programming System (SPS)
SPS is used in conjunction with Technical
Information System (TIS) 2000 to program vehicle
control units.
F2: View Capture Data
Contains all functions to work with one or two
previously recorded snapshots on one or two
vehicles. This function is to enable the viewing of
captured data without a vehicle.
F3: Tool Options
Contains the TECH 2 self test, set clock, set units,
set screen contrast and Getting Started.
F4: Download/Upload Help
Contains help information on the downloading and
uploading from the TECH 2 to the TIS 2000 CD-
ROM.
Main Menu
UBS2000a
F0: Diagnostics
F1: Service Programming System (SPS)
F2: View Capture Data
F3: Tool Options
F4: Download/Upload Help

5. Select the correct Model Year with the arrow keys
and the press ENTER. The Vehicle identification
screen will then be displayed.
6. Select the correct Vehicle Type with the arrow keys
and the press ENTER. The System Select Menu
will then be displayed.
7. The desired system can be selected from the
System Select Menu with the function keys or with
arrow keys and then press ENTER.
F0:Powertrain contains all functions to test,
diagnose, and monitor the engine and transmission
systems that communicate with the Tech 2 via the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
F1: Chassis contains all functions to test,
diagnose, monitor the vehicles chassis systems;
TOD and ABS modules.
F2: Body contains all functions to test, diagnose,
monitor the instruments and Supplemental
Restraint System.
Main Menu
Select one of the following
Model Year(s)
TF2001a
(2)
(1)
(Y)
(X)
(W)
(V)
(2)
2002
2001
2000
1999
1998
1997
1 / 6
2002
Main Menu
Select one of the following
Vehicle Type(s)
Frontera
Jackaroo
Rodeo
VX Commodore
VU Utility
WH Statesman & Caprice
Corsa-B
Corsa-C
Astra-F
Astra-G
Jackaroo
1 / 10
UBS2001
System Select Menu
(1) 2001 Jackaroo
F0: Powertrain
F1: Chassis
F2: Body
UBS2002


Transmission Application Menu
1. Select the correct transmission from the Vehicle
Identification menu with the arrow keys, then press
ENTER and follow the screen instructions.
2. Turn on the ignition and press the Confirm soft key.
3. The Transmission Identification screen will then
display the Part Number and Identifier. This
information will vary with engine type and software
level. Press the Confirm soft key, the transmission
application menu will then be displayed.
NOTE: If Tech 2 is able to communicate with the
PCM the Engine identification information will be
displayed. If Tech 2 is unable to communicate with
the PCM, Tech 2 will display “Waiting for Data”.
The following functions are available in the
transmission application menu:
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes
F1: Data Display
F2: Snapshot
F3: Miscellaneous Tests
Vehicle Identification
Select one of the following
Powertrain
3.0L L4 4JX1
3.5L V6 6VE1
4L30E
AW30-40LE
4L30E
3 / 4
UBS2005
Powertrain
(2) 2002 Jackaroo
Electronic System: 4L30E
Turn Ignition On!
UBS2005k
Confirm

THM 4L30E Transmission Functions
F0: DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
In this test mode, DTCs stored by the TCM can be displayed or cleared. When F0: Diagnostic Trouble Codes is
selected, there are an additional two modes:
F0: Read DTC Info By Priority: All current DTC(s) will be displayed.
F1: Clear Current DTC: Clears all current DTC(s) in the PCM memory.
F1: DATA DISPLAY
In this mode, TECH 2 continuously monitors transmission data. When F1: Data Display is selected, there are
additional two modes:
F0: Transmission Data: TECH 2 continuously monitors transmission data.
F1: TCC Data: TECH 2 continuously monitors torque converter clutch data.
F2: SNAPSHOT
In this test mode, the TECH 2 scan tool captures data before and after a snapshot triggering condition which may or
may not set a DTC.
F3: MISCELLANEOUS TESTS
In this test mode, the TECH 2 performs software override commands of the TCM, to assist in problem isolation during
diagnostics.
F0:Check Light: Allows the user to turn the ‘CHECK TRANS’ Lamp ON & OFF.
F1:Power Lamp: Allows the user to turn the ‘Power’ Lamp ON & OFF.
F2: Solenoid 1-2/3-4 test: Allows the user to turn the 1-2/3-4 shift solenoid ON & OFF.
F3: Solenoid 2-3 test: Allows the user to turn the 2-3 shift solenoid ON & OFF.
F4: Band Apply Solenoid: This test allows the user to turn the Band Apply solenoid ON & OFF.
F5: TCC Solenoid: Allows the user to turn the TCC solenoid ON & OFF.
F6: Power Control Driver Test: Allows the user to all turn solenoids ON & OFF simultaneously.
F7: Pressure Reg.Solenoid test: Allows the user to turn the Pressure Regulator Solenoid ON & OFF.
F8: Pressure Reg. Solenoid: Allows the user to increase and decrease the current through the PRS.
F0: Transmission Data
Item Unit Engine running at idle
Engine Speed RPM 750 ~ 900 RPM
Vehicle Speed km/h, MPH 0 MPH
Throttle Position % 0 %
Throttle Position Sensor V 0.5 ~ 1.0 V
Manifold Absolute Pressure kPa approx. 40 kPa
Barometric Pressure kPa approx. 102 kPa
AT Output Speed (Automatic Transmission) RPM 0 RPM
AT Input Speed Ratio (Automatic Transmission) 0.0
Ignition Voltage V 12.8 ~ 14.1 V
AT Oil Temperature (Automatic Transmission) °C, °F 70 ~ 80°C (158 ~ 176°F)
AT Oil Life Monitor (Automatic Transmission) % 100 %
Commanded Gear 1
Current Gear 1
Mode Switch C Inactive, Active Inactive
Mode Switch B Inactive, Active Inactive
Mode Switch A Inactive, Active Active
Mode Switch G Inactive, Active Active
Actual Gear Park
1–2 Shift Solenoid A Off, On Off
2–3 Shift Solenoid B Off, On On
Brake Switch Off, On Off
Solenoid Brake Band Off, On Off
TCC Slip Speed RPM 750 ~ 900 RPM
TCC Status Disabled, Enabled Enabled
TCC Solenoid Off, On Off
TCC Duty Cycle % 0 %
TCC Apply Mode No Apply, In Apply No Apply
TCC Release Mode No, Yes No
TCC On Mode No, Yes No
TCC Off Mode No, Yes Yes
Default Gear No, Yes No
Engine Warm No, Yes Yes
A/C Request Yes, No Yes
A/C Clutch Relay Off, On On
Winter Switch Off, On Off
Winter Drive Lamp Off, On Off
Kickdown Switch Off, On Off
ATF Lamp (Automatic Transmission) Off, On Off
Power Switch Normal, Power Normal
Power Drive Lamp Off, On Off
ABS Status On, Off Off
F1: PC Solenoid Data
Item Unit Engine running at idle
Engine Speed RPM 750 ~ 900 RPM
Vehicle Speed km/h, MPH 0 MPH
Throttle Position % 0 %
Throttle Position Sensor V 0.5 ~ 1.0 V
Manifold Absolute Pressure kPa approx. 40 kPa
Barometric Pressure kPa approx. 102 kPa
PCS Current (Pressure Control Solenoid) A approx. 1.0 A
PCS Actual Current (Pressure Control Solenoid) A approx. 1.0 A
PCS Duty Cycle (Pressure Control Solenoid) % approx. 45 %
Desired PCS Pressure (Pressure Control Solenoid) kPa 43 ~ 52 kPa
Shift Pressure (Line Pressure) kPa 43 ~ 52 kPa
Transmission Temperature °C, °F 75 ~ 110°C (167 ~ 230°F)
OBD II Diagnostic Management System
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Location
C07RW005
Class 2 Serial Data Bus
OBD II technology requires a much more sophisticated
PCM than does OBD I technology. The OBD II PCM
diagnostic management system not only monitors
systems and components that can impact emissions,
but they also run active tests on these systems and
components. The decision making functions of OBD II
PCMs have also greatly increased. To accommodate
this expansion in diagnostic complexity, Holden
engineers have designed the Class 2 serial data bus,
which meets SAE J1850 recommended practice for
serial data.
“Serial Data” refers to information which is transferred in
a linear fashion – over a single line, one bit at a time. A
“Data Bus” is an electronic pathway through which serial
data travels.
TROOPER previously used a 5 volt data bus called
UART, which is an acronym for“Universal
Asynchronous Receive and Transmit”. When neither the
vehicle's control module nor the diagnostic tool, such as
a Tech2, are “talking,” the voltage level of the bus at rest
is 5 volts. The two computers talk to each other at a rate
of 8,192 bits per second, by toggling or switching the
voltage on the data bus from 5 volts to ground.
Class 2 data, which is used on OBD II vehicles, is quite
different. Data is transferred at a rate of 10.4 kilobits
per second, and the voltage is toggled between zero
and 7 volts.
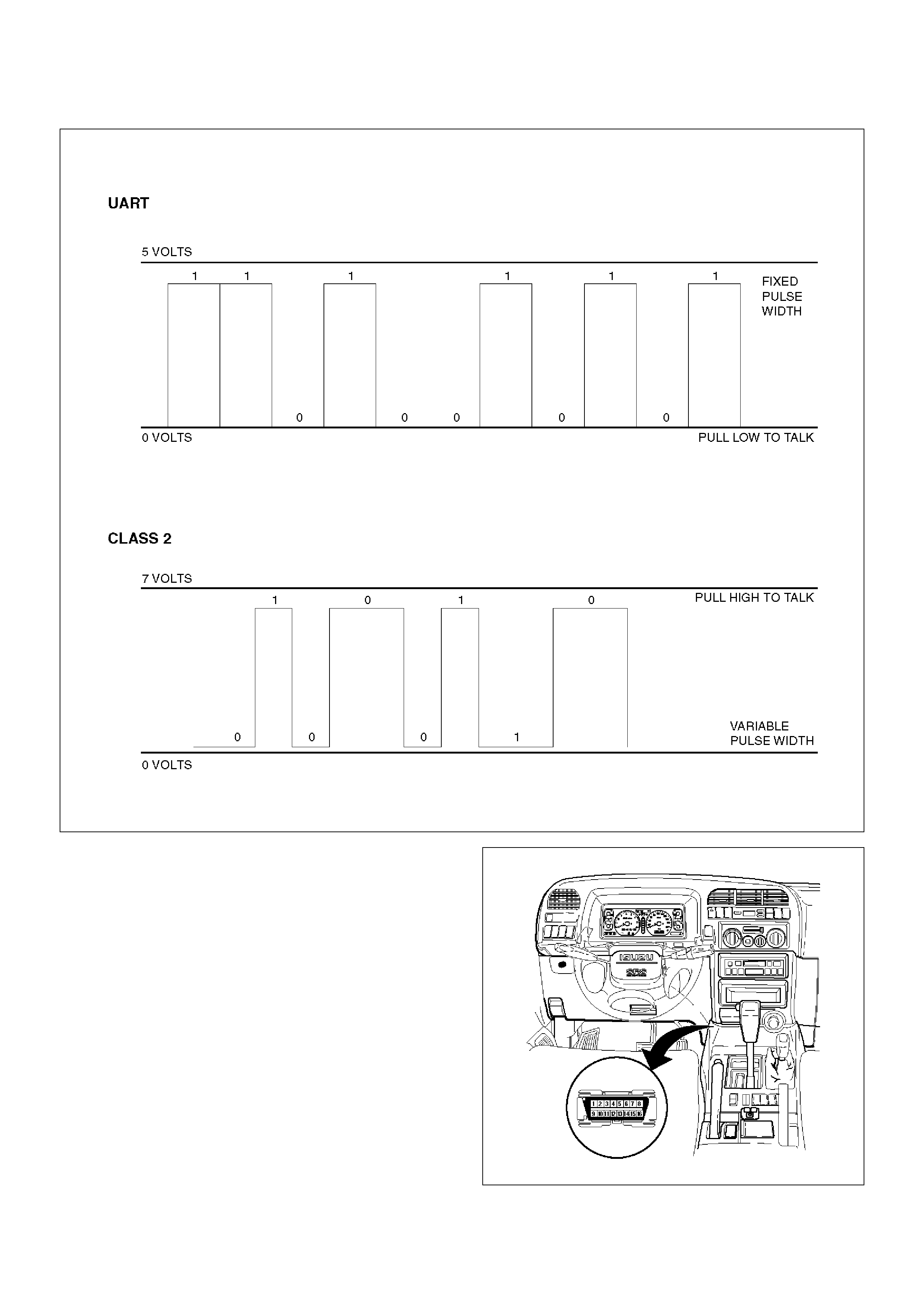
C07RT006
Class 2 data is also pulse width modulated. Each bit of
information can have one of two lengths: long or short.
On the other hand, UART data bits come in only one
length (short). The pulse width modulation of Class 2
data allows better utilization of the data line.
The message carried on Class 2 data streams are also
prioritized. This means that if two devices try to
communication on the data line at the same time, only
the higher priority message will continue. The device
with the lower priority message must wait.
NOTE: The Class 2 data wire is always terminal 2 of
the new 16–terminal Data Link Connector (DLC).
16 – Terminal Data Link Connector (DLC)
OBD II standardizes Data Link Connector (DLC)
configurations. The DLC, formerly referred to as the
ALDL, will be a 16–terminal connector found on the
lower left side of the driver's side instrument panel. All
manufacturers must conform to this 16–terminal
standard.

821RW262
821RW263
810RT022
EndOFCallout
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) looks the same
as the MIL you are already familiar with (“CHECK
ENGINE”lamp). However, OBD II requires that it
illuminate under a strict set of guidelines. Basically, the
MIL is turned on when the PCM detects a DTC that will
impact the vehicle's emissions.
The MIL is under the control of the Diagnostic
Executive. The MIL will be turned on if a component or
system which has an impact on vehicle emissions
indicates a malfunction or fails to pass an emissions–
related diagnostic test. It will stay on until the system or
component passes the same test, for three consecutive
trips, with no emissions–related faults.
Types Of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The Diagnostic Executive classifies Diagnostic Trouble
Codes (DTCs) into certain categories. Each type has
different requirements to set the code, and the
Diagnostic Executive will only illuminate the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp (MIL) for emissions–related DTCs.
DTCs fall into four categories: A, B, C, and D; only
types A and B are emission–related The following
descriptions define these categories:
TYPE A
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL (“Check
Engine”lamp) on the first trip in which an emission–
related diagnostic test has run and reported a “test
failed” to the Diagnostic Executive.
TYPE B
Will store the DTC and turn on the MIL on the second
consecutive trip in which an emission–related
diagnostic test has run and reported a “test failed” to the
Diagnostic Executive. After one failure, the type B DTC
is “armed,” or prepared to store a history code and turn
on the MIL if a second failure occurs. One passed test
will disarm a type B DTC. Some special conditions
apply to misfire and fuel trim DTCs. For a type B DTC
to store and turn on the MIL, two ignition cycles are
required.
TYPE C
Will store the DTC and turn on a “SERVICE” lamp
(“Check Trans”lamp) on the first trip that a non–
emission–related diagnostic test has run and reported a
“test failed” to the Diagnostic Executive. This type of
DTC will be used in future applications.
TYPE D
Will store a DTC but will not turn on the MIL on the first
trip that a non–emission–related diagnostic test has
run and reported a “test failed” to the Diagnostic
Executive. These codes can be very helpful for vehicle
service when the driver may comment about a
condition, but the MIL did not turn on.
PIN 1 – (Not used)
PIN 2 – J1850 Bus + L line on 2–wire systems, or
single wire (Class 2)
PIN 3 – (Not used)
PIN 4 – Chassis ground pin
PIN 5 – Signal ground pin
PIN 6 – PCM diagnostic enable
PIN 7 – (Not used)
PIN 8 – (Not used)
PIN 9 – Primary UART
PIN 10 – (Not used)
PIN 11 – (Not used)
PIN 12 – ABS diagnostic or CCM diagnostic enable
PIN 13 – SIR diagnostic enable
PIN 14 – (Not used)
PIN 15 – (Not used)
PIN 16 – Battery power from vehicle unswitched (4
AMP MAX.)

Clear DTC
NOTE: If you clear the DTC (Diagnostic Trouble
Codes) you will not be able to read any codes recorded
during the last occurrence.
NOTE: To use the DTC again to identify a problem, you
will need to reproduce the fault or the problem. This
may require a new test drive or just turning the ignition
on (this depends on the nature of the fault).
1.IF you have a Tech2:
1.Connect the Tech2 if it is still not connected
GOTHROUGH Tech2 OBD II CONNECTION.
2.Push “F1= Clear DTC Info” in the Application
Menu and answer “Yes” to the question “Do you
want to clear DTC's?”
aWhen a malfunction remains as it is the
Tech2 displays“4L30E CODES NOT
CLEARED”. This means that the problem
is still there or that the recovery was not
done. Please GOTO DTC CHECK.
bWhen a malfunction has been repaired and
the recovery is done. The Tech2
displays“4L30E CODES CLEARED”.
2.IF you have no Tech2:
To clear the DTC, remove Fuse “Stop, A/T CONT”
(C–14, 15A) for at least 10 seconds.
DTC Check
1.Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) have been
identified by Tech2.
2.You have written the list of the DTCs. The order of
the malfunctions has no meanings for this PCM.
Usually only one or two malfunctions should be set
for a given problem.
3.Check directly the DTCs you identified. The DTCs
are sorted by number. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) Identification in this section.
PCM Precaution
The PCM can be damaged by:
1. Electrostatic discharge
2. The short circuit of some terminals to voltage or to
ground.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage Description:
1. Electronic components used to control systems are
often designed to carry very low voltage, and are
very susceptible to damage caused by electrostatic
discharge. It is possible for less than 100 volts of
static electricity to cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as
4,000 volts for a person to even feel the zap of a
static discharge.
2. There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction. An example
of charging by friction is a person sliding across a
car seat, in which a charge of as much as 25,000
volts can build up. Charging by induction occurs
when a person with well insulated shoes stands
near a highly charged object and momentarily
touches ground. Charges for the same polarity are
drained off, leaving the person highly charged with
the opposite polarity. Static charges of either type
can cause damage, therefore, it is important to use
care when handling and testing electronic
components.
NOTE: To prevent possible electrostatic discharge
damage:
1. Do not touch the PCM connector pins or soldered
components on the PCM circuit board.
2. Be sure to follow the guidelines listed below if
servicing any of these electronic components:
3. Do not open the replacement part package until it is
time to install the part.
4. Avoid touching electrical terminals of the part.
5. Before removing the part from its package, ground
the package to a known good ground on the vehicle.
6. Always touch a known good ground before handling
the part. This step should be repeated before
installing the part if the part has been handled
while sliding across the seat, while sitting down from
a standing position or while walking some distance.
Information On PCM
1. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is located in
the center console and is the control center of the
electronic transmission control system.
2. The PCM must be maintained at a temperature
below 85°C (185°F) at all times. This is most
essential if the vehicle is put through a paint baking
process. The PCM will become inoperative if its
temperature exceeds 85°C (185°F). Therefore, it is
recommended that the PCM be removed or that
temporary insulation be placed around the PCM
during the time the vehicle is in a paint oven or other
high temperature process.
3. The PCM is designed to process the various inputs
and then respond by sending the appropriate
electrical signals to control transmission upshift,
downshift, shift feel and torque converter clutch
engagement.
4. The PCM constantly interprets information from the
various sensors, and controls the systems that
affect transmission and vehicle performance. By
analyzing operational problems, the PCM is able to
perform a diagnostic function by displaying DTC(s)
and aid the technician in making repairs.
Intermittent Conditions
If the Tech2 displays a diagnostic trouble code as
intermittent, or if after a test drive a DTC does not
reappear though the detection conditions for this DTC
are present, the problem is most likely a faulty
electrical connection or loose wiring. Terminals and
grounds should always be the prime suspect.
Intermittents rarely occur inside sophisticated electronic
components such as the PCM.
Use the DTC information to understand which wires and
sensors are involved.
When an intermittent problem is encountered, check
suspect circuits for:
1. Poor terminal to wire connection.
2. Terminals not fully seated in the connector body
(backed out).
3. Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
4. Loose, dirty, or corroded ground connections:
HINT: Any time you have an intermittent in more
than one circuit, check whether the circuits share a
common ground connection.
5. Pinched or damaged wires.
6. Electro–Magnetic Interference (EMI):
HINT: Check that all wires are properly routed away
from spark plug wires, distributor wires, coil, and
generator. Also check for improperly installed
electrical options, such as lights, 2–way radios, etc.
Use the F3 SNAPSHOT mode of the Tech2 to help
isolate the cause of an intermittent fault. The snapshot
mode will record information before and after the
problem occurs. Set the snapshot to “trigger” on the
suspect DTC. If you notice the reported symptom
during the test drive, trigger the snapshot manually.
After the snapshot has been triggered, command the
Tech2 to play back the flow of data recorded from each
of the various sensors. Signs of an intermittent fault in a
sensor circuit are sudden unexplainable jump in data
values out of the normal range.
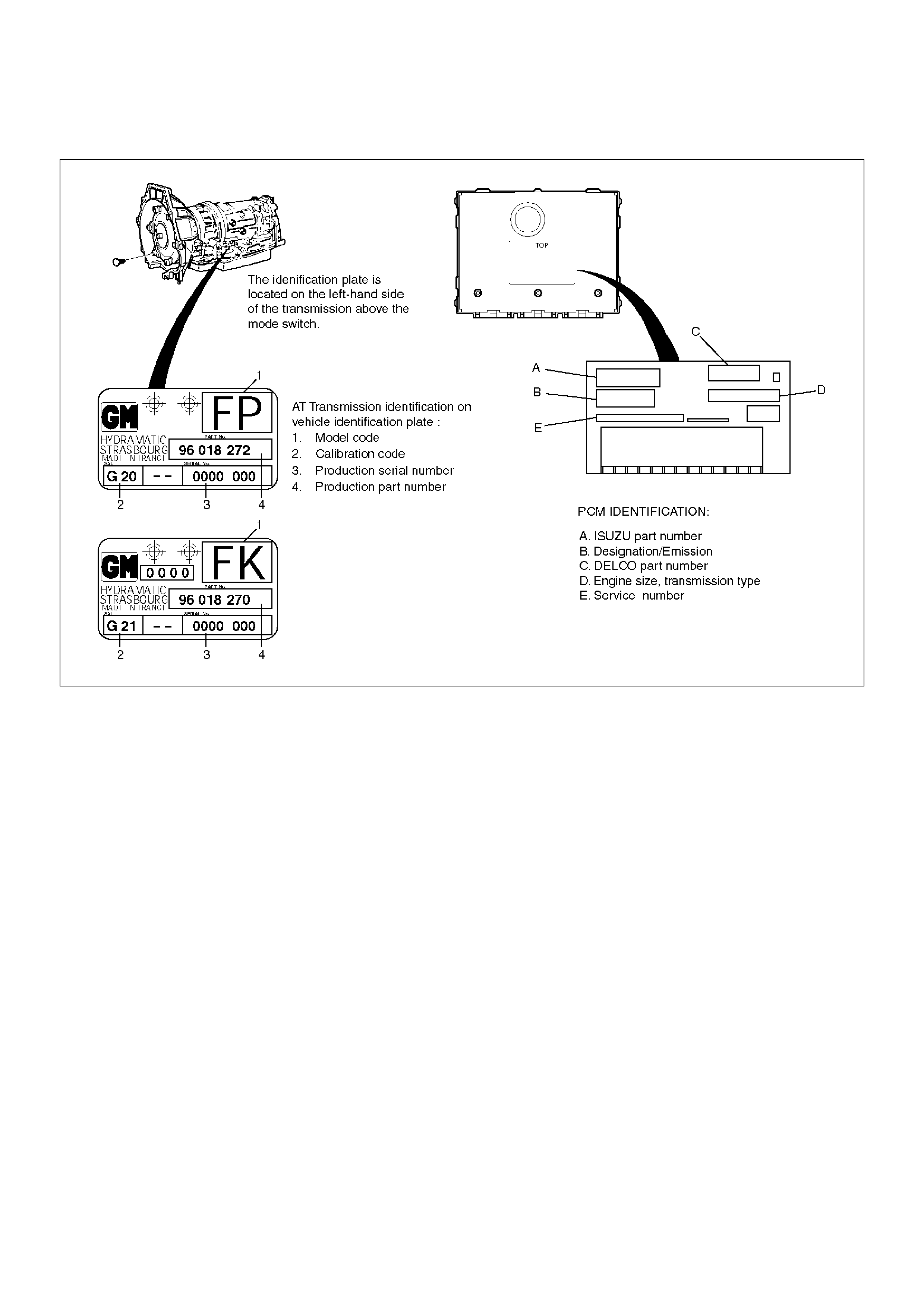
Transmission And PCM Identification
The chart below contains a list of all important
information concerning rear axle ratio, Powertrain
Control Module (PCM), and transmission identification.
Rr axle
Ratio
PCM TRANSMISSION
HOLDEN Parts No. Calibration
Code Holden Part No. Model Code
4.300
8–16254–019–1
8–16254–959–1
8–09376–619–1
G21 8–96018–270–4 FK (4X4)
UBS Jackaroo
240RY00031
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Identification
NOTE: On the following charts, refer to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) section for the Wiring System,
and the 12B1 or 12B2 section for circuit
diagram details, parts location, and connector
configuration.
DTC
NUMBER DTC NAME DTC TYPE “CHECK
TRANS”
P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature D
P0560 System Voltage Malfunction C Flash
P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal Position D
P0706 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Performance D
P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input
(TFT) D
P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High
Input D
P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck ON) D
P0722 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Low Input C Flash
P0723 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Intermittent C Flash
P0730 Transmission Incorrect Gear Ratio C Flash
P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit
Electrical CFlash
P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical C Flash
P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical C Flash
P1790 ROM Transmission Side Bad Check Sum C Flash
P1792 EEPROM Transmission Side Bad Check Sum C Flash
P1835 Kickdown Switch Always ON D
P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid Malfunction D
P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical D
DTC TYPE DEFINITION
C Flashing Check Trans on 1st failure
DNo lamps
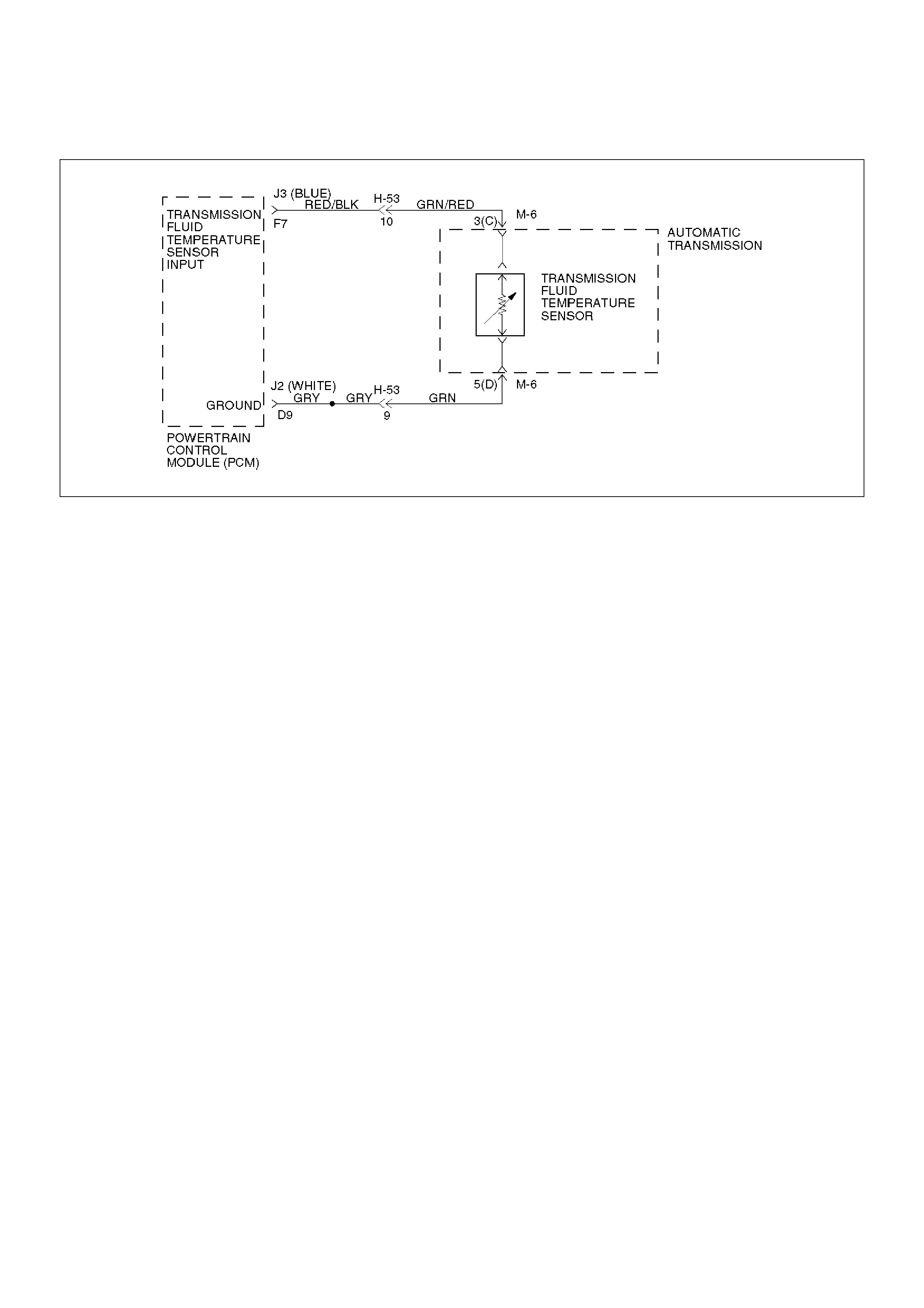
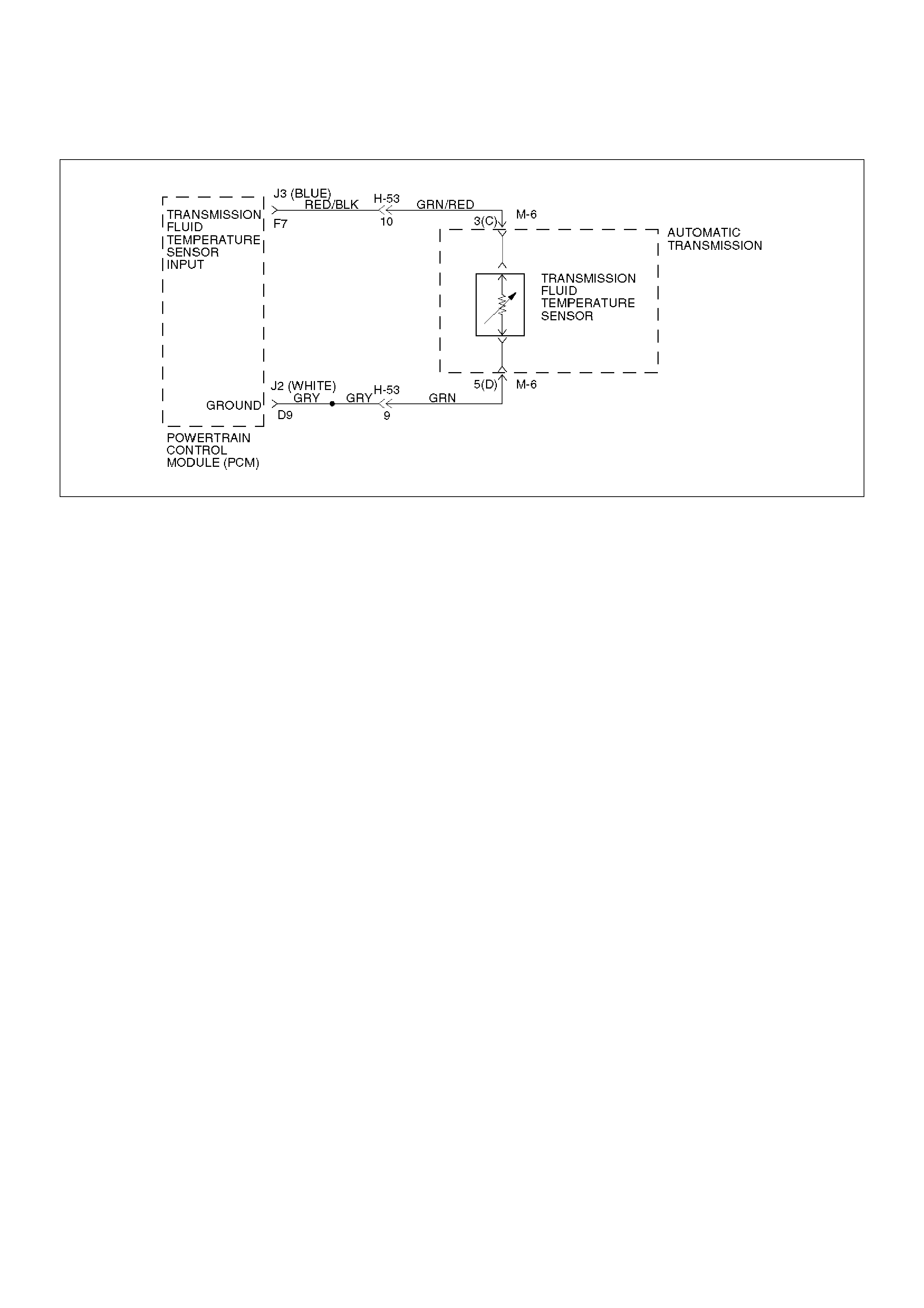
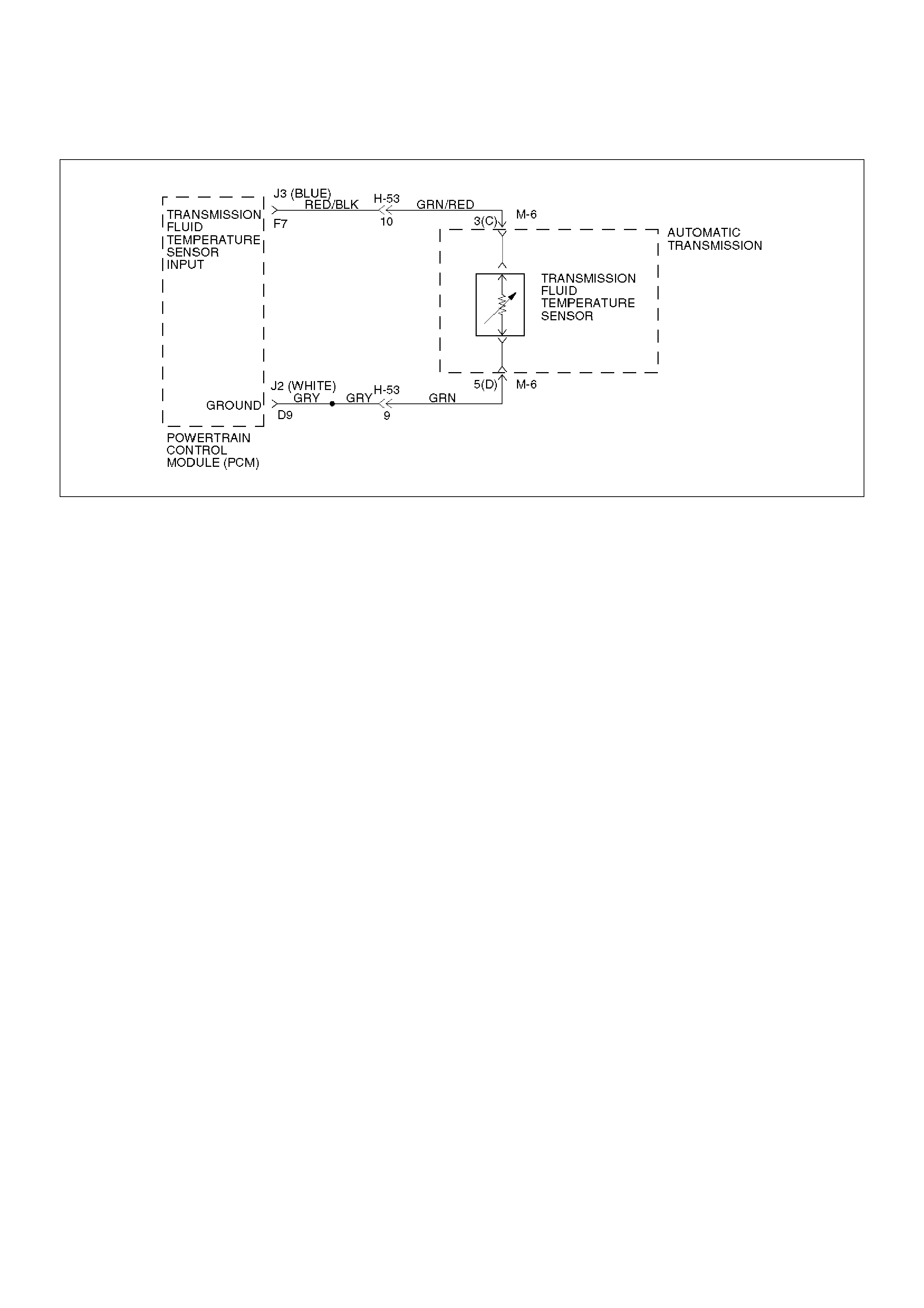
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor is a
thermister that controls the signal voltage to the PCM.
The PCM supplies a 5–volt reference to the sensor on
circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED. When the transmission
fluid is cold, the sensor resistance is high and the PCM
will sense high signal voltage. As the fluid temperature
warms to a normal transmission operating temperature
of 100°C (212°F), the sensor resistance becomes less
and the voltage decreases to 1.5 to 2.0 volts.
This DTC detects a high transmission temperature for a
long period of time. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• No TFT DTCs P0712 or P0713.
• TFT is greater than 135°C (275°F).
• All conditions met for 21 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Hot mode TCC Shift Pattern.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
• ATF Lamp ON. (TFT is greater than 145°C (293°F).)
• Disable E–side TCC OFF request.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warm–up cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed, or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well.
Also check for a chafed wire that could short to bare
metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside
the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• Check harness routing for a potential short to ground
in circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED.
• Scan tool TFT sensor temperature should rise
steadily to about 100°C (212°F), than stabilize.
• Check for a “skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor by
comparing the TFT sensor temperature to the
ambient temperature after a vehicle cold soak. A
“skewed” sensor can cause delayed garage shifts or
TCC complaints.
• Check for a possible torque converter stator problem.
• Verify customer driving habits, trailer towing, etc.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart.
2. This test checks for a “skewed” sensor or shorted
circuit.
3. This test simulates a TFT DTC P0713.
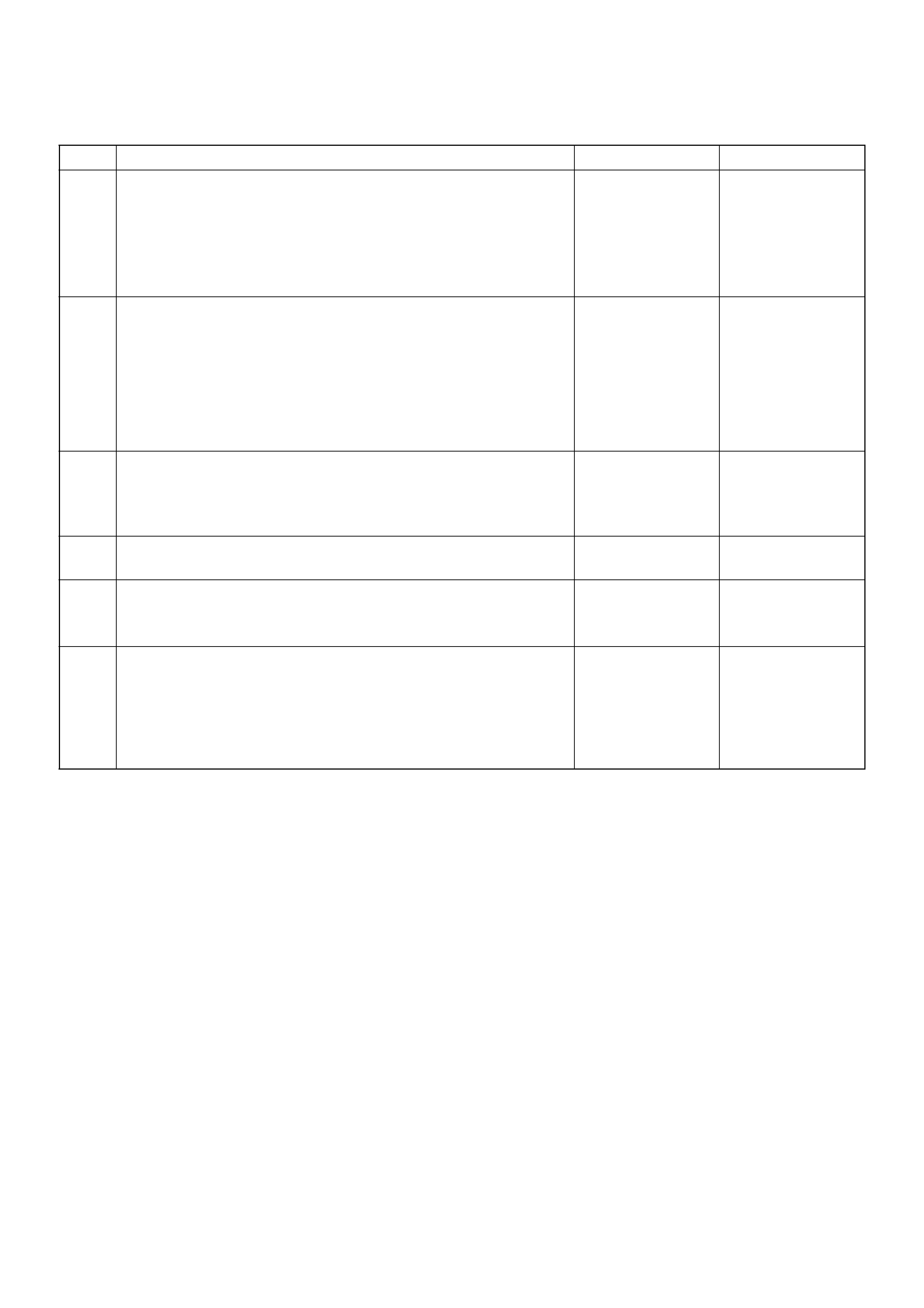
DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature
Step Action Yes No
1 Perform the following checks:
• Check for possible engine system problems.
• Transmission fluid checking procedure. Refer to Checking
Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) Section.
Were the checks performed? Go to Step 2 —
2 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when “Clear
Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Is the TFT sensor signal voltage less than 1.54 volts? Go to Step 3
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53
(additional DTCs may set).
Is the TFT sensor signal voltage greater than 4.92 volts?
Go to Internal
Wiring Harness
Check. Go to Step 4
4 Inspect/repair circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED for a short to ground.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 1. Inspect the PCM for poor connections.
2. Replace the PCM if no poor connections were found.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 6 —
6 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
TFT is less than 125°C (257°F) for at least 10 seconds.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction
D07RW030
Circuit Description
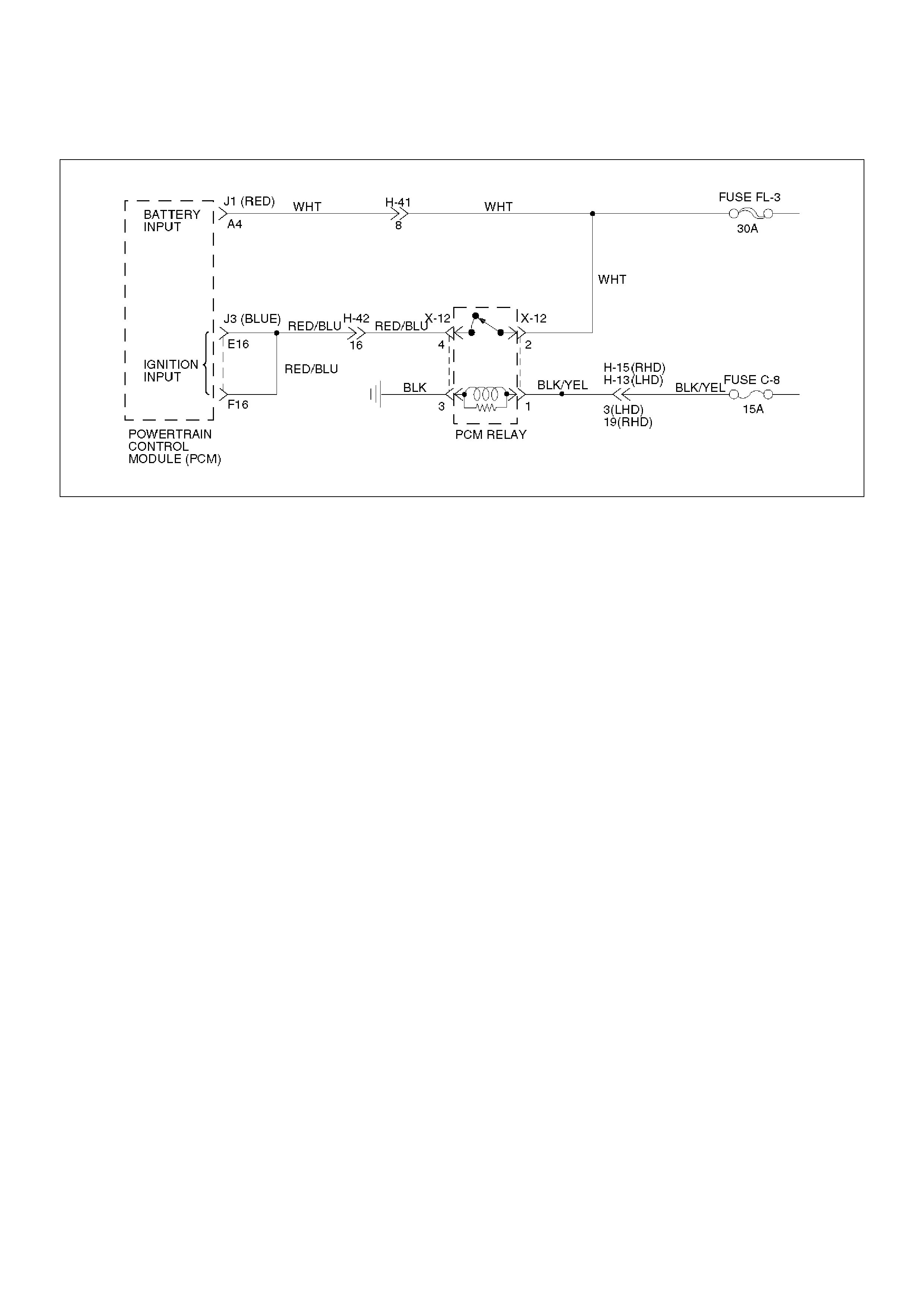
Circuit WHT is the battery voltage feed for the PCM.
Circuit RED/BLU is the ignition voltage feed for the
PCM.
This DTC detects a low voltage or a high voltage. This
is a type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
System Voltage Low:
• Engine speed is greater than 1,000 rpm.
• System voltage is less than 10 volts at a maximum
transmission temperature of 150°C (302°F).
• System voltage is less than 7.3 volts at a minimum
transmission temperature of –40°C (–40°F).
• All conditions met for 4 seconds.
System Voltage High:
• System voltage is greater than 16 volts for 2 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Fixed to 4th gear.
• Maximum line pressure.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Charging the battery with a battery charger and jump
starting an engine may set DTC(s). If DTC(s) set
when an accessory is operated, check for faulty
connections or excessive current draw.
• Check for faulty connections at the starter solenoid or
fusible link.
• Check for loose/damaged terminals at generator.
• Check belt wear/tension.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart.
3. This test checks charging system voltage.
4. This test checks battery voltage input at the PCM.
6. This test checks ignition voltage input at the PCM.
DTC P0560 System Voltage Malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”. Note: If any other DTCs
are present, refer to their applicable diagnostic charts before
continuing.
4. Using the J–39200 DVOM, measure the battery voltage
across the battery terminals. Record the measurement for
future reference.
Is the voltage higher than 10.5 volts? Go to Step 2
Go to Engine
Electrical in Engine
section
2 Start the engine and warm to normal operating temperature.
Is the generator/check engine light“on”?
Go to Starting and
Charging System
in Engine section Go to Step 3
3 1. Increase the engine speed to 1,000–1,500 rpm.
2. Observe scan tool system voltage.
Is the system voltage within 13–15 volts. Go to Step 4
Go to Starting and
Charging System
in Engine section
4 1. Turn the ignition switch“off”.
2. Disconnect the J1(RED) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connector
(additional DTCs will set).
3. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
4. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the battery voltage input
at PCM connector terminals J1–A4 and J3–E16.
Is there a voltage variance between the voltage measured at the
battery (taken in Step 1) and at terminals J1–A4 and J3–E16 that
is greater than 0.5 volts? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the high resistance condition in circuit WHT.
Was the circuit repaired? Go to Step 10 —
6 1. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Measure the ignition voltage input at PCM connector
terminals J3–E16 and J3–F16.
Is there a voltage variance between the voltage measured at the
battery (taken in Step 1) and at terminals J3–E16 and J3–F16
that is greater than 0.5 volts? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7 Repair the high resistance condition is circuit RED/BLU.
Was the circuit repaired? Go to Step 10 —
8 Check PCM connector terminals J1–A4, J3–E16 and J3–F16 for
bent, damaged, or backed out connector pins. Also check for
weak terminal tension.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9 Replace the PCM.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 10 —
10 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle under the
following conditions:
Start the vehicle and warm to normal operating temperature.
The PCM must see a system voltage between 10 and 16
volts.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
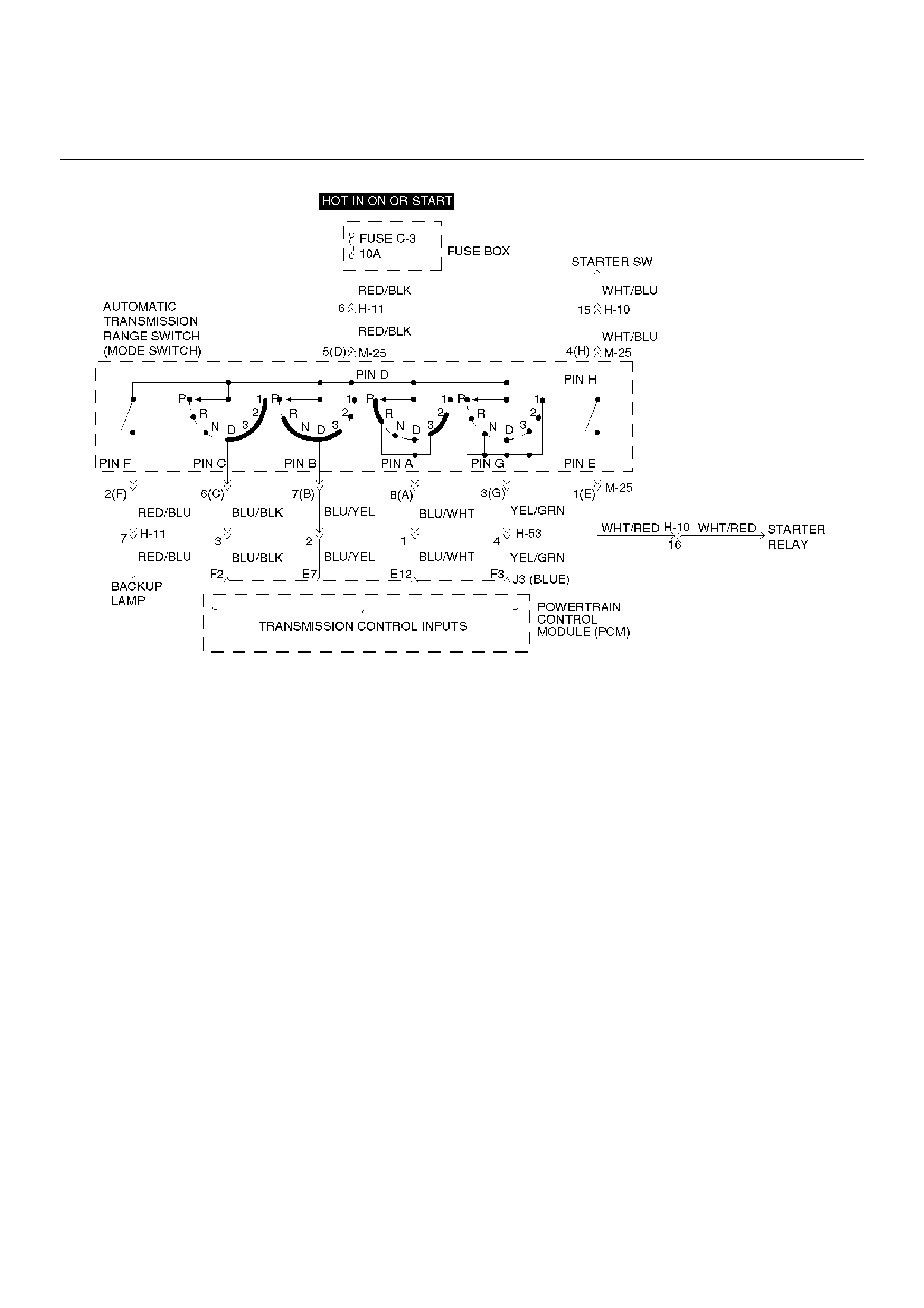
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal Position
D07RW031
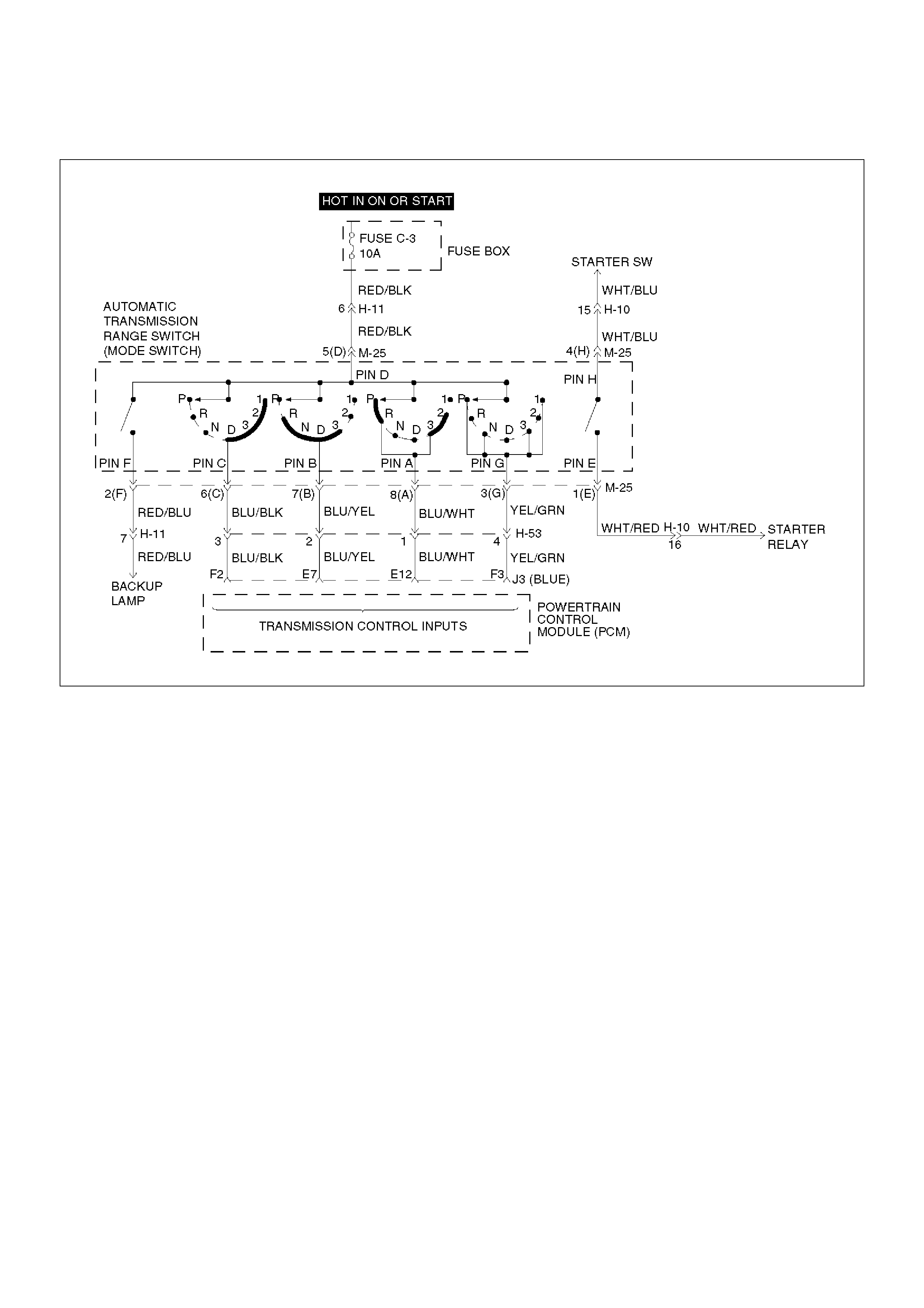
Circuit Description
• The range switch supplies the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) with information regarding the selector
lever position: P, R, N, D 3, 2 or L. The selector lever
position is indicated by the state of four ON/OFF
contracts. The range switch is located on one side of
the transmission. It is on the transmission manual
shaft and is fixed to the main case.
• The range switch is also used to provide the
information P or N to the engine crank wiring. The
engine can be cranked only if connector M–25
terminal 4(H) is connected to terminal 1(E) which is
connected to ground.
• The range switch is also used to provide the backup
lamp power in reverse. This is why the range switch
is supplied through a 10A fuse (C–3). This fuse can
burn due to a short circuit in the backup lamp.
This DTC detects when a fuse is open or the range
switch circuit does not work. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Range switch illegal positions met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Default to D position.
• Inhibit torque management.
• Maximum line pressure.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Refer to accompanying chart for the normal range
signals and the illegal combinations.
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 8–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken
wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• Refer to the “Range Switch Logic Table” or
“Functional Test Procedure” for further information.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks the indicated range signal to the
manual valve actually selected.
5. This test checks for continuity between each selected
range switch connector terminals.
Range Switch Logic Table
DTC P0705 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Illegal Position
Range
Position
Range Switch Pin
ABCP(G)
Park ON OFF OFF ON
Reverse ON ON OFF OFF
Neutral OFF ON OFF ON
D4 OFF ON ON OFF
D3 ON ON ON ON
2ONOFFONOFF
LOFFOFFONON
Illegal OFF OFF OFF OFF
Illegal OFF OFF OFF ON
Step Action Yes No
1 Perform the following checks:
• The transmission linkage from the select lever to the manual
valve is adjusted properly.
• Diagnostic circuit check.
Were the checks performed? Go to Step 2 —
2 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
4. Select each transmission range: DL, D2, D3, D4, N, R, and
P.
Does each selected transmission range match the scan tool
“Range Switch” display?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
3 Are all range switch pin displays incorrect? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Check fuse and wiring to the 8–way connector terminal 5(D) for
opens.
Refer to Mode Switch in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
If no problem was found, replace the range switch.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 8 —
5 1. Disconnect the 8–way range switch connector.
2. Using ohmmeter, check continuity between terminal 5(D) and
respectively terminals 3(G), 6(C), 7(B) and 8(A) of the 8–way
range switch connector.
3. Move shift selector lever through all positions and compare
results with“Range Switch Logic Table”.
Is one range switch pin display incorrect? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6 Check the affected wiring and connector, and repair.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 8 —
7 Check the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) connectors for poor
connection.
If no problem was found, replace the PCM.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 8 —

8 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and road test the vehicle.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Performance
D07RW031
Circuit Description
• The range switch supplies the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) with information regarding the selector
lever position: P, R, N, D, 3, 2 or L. The selector lever
position is indicated by the state of four ON/OFF
contracts. The range switch is located on one side of
the transmission. It is on the transmission manual
shaft and is fixed to the main case.
• The range switch is also used to provide the
information P or N to the engine crank wiring. The
engine can be cranked only if connector M–25
terminal 4(H) is connected to terminal 1(E) which is
connected to ground.
• The range switch is also used to provide the backup
lamp power in reverse. This is why the mode switch
is supplied through a 10A fuse (C–3). This fuse can
burn due to a shot circuit in the backup lamp.
• This DTC detects an invalid state of the range switch
or the range switch circuit by deciphering the range
switch inputs. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
This DTC will set if any of the following conditions
occurs:
Condition 1 (“R”bad position):
• Engine is running.
• No output speed DTCP0722, P0723.
• Output speed greater then 3,200 RPM.
• Range switch indicates“R”.
• All conditions met for 4 seconds.
Condition 2 (“P”or “N” bad position):
• Engine is running.
• No TPS codes.
• Engine speed is less than 3,000 RPM.
• TP angle is greater than 20%.
• Range switch indicates “P” or“N”.
• All conditions met for 4 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Default to “D” position.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Refer to the accompanying chart for the normal range
signals and the illegal combinations.
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 8–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for
a broken wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• Refer to the “Range Switch Logic Table” for further
information.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks the indicated range signal to the
manual valve actually selected.
5. This test checks for continuity between each selected
range switch connector terminals.
Range Switch Logic Table
DTC P0706 Transmission Range Switch (Mode Switch) Performance
Range
Position
Range Switch Pin
ABCP(G)
Park ON OFF OFF ON
Reverse ON ON OFF OFF
Neutral OFF ON OFF ON
D4 OFF ON ON OFF
D3 ON ON ON ON
2ONOFFONOFF
LOFFOFFONON
Illegal OFF OFF OFF OFF
Illegal OFF OFF OFF ON
Step Action Yes No
1 Perform the following checks:
• The transmission linkage from the select lever to the manual
valve is adjusted properly.
• Diagnostic circuit check.
Were the checks performed? Go to Step 2 —
2 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
4. Select each transmission range: DL, D2, D3, D4, N, R, and
P.
Does each selected transmission range match the scan tool
“Range Switch” display?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 3
3 Are all range switch pin displays incorrect? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Check fuse and wiring to the 8–way connector terminal 5(D) for
opens.
Refer to Mode Switch in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
If no problem was found, replace the range switch.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 8 —
5 1. Disconnect the 8–way range switch connector.
2. Using ohmmeter, check continuity between terminal 5(D) and
respectively terminals 3(G), 6(C), 7(B) and 8(A) of the 8–way
range switch connector.
3. Move shift selector lever through all positions and compare
results with“Range Switch Logic Table”.
Is one range switch pin display incorrect? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6 Check the affected wiring and connector, and repair.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 8 —
7 Check the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) connectors for poor
connection.
If no problem was found, replace the PCM.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 8 —
8 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and road test the vehicle.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit Low Input
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The TFT sensor is a thermister that controls the signal
voltage to the PCM. The PCM supplies a 5–volt
reference signal to the sensor on circuit RED/BLK–
GRN/RED. When the transmission fluid is cold, the
sensor resistance is high. The PCM detects high signal
voltage. As the transmission fluid temperature
increases to the normal operating temperature of 100°C
(212°F), the sensor resistance becomes less and the
voltage decreases to 1.5 to 2 volts. With transmission
fluid over temperature and DTC P0218 also set, check
the transmission cooling system.
This DTC detects a continuous short to ground in the
TFT signal circuit or the TFT sensor. This is a type “D”
DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• Ignition is“on”.
• TFT sensor indicating a voltage less than 0.4 volts.
• All conditions met for 20 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Transmission default temperature will be:
80°C (176°F) if engine temperature code is set.
100°C (212°F) if engine temperature is warm.
80°C (176°F) if engine run time is greater than 5
minutes.
21°C (69.8°F) if engine run time is less than 5
minutes.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Check harness routing for a potential short to ground
in circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED. Scan tool TFT display
should rise steadily to about 100°C (212°F), then
stabilize.
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken
wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• The temperature to resistance value scale may be
used to test the TFT sensor at the various
temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
“skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor.
A “skewed” sensor could result in delayed garage
shifts or TCC complaints.
• Verify customer driving habits, trailer towing, etc.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks for a short to ground or a “skewed”
sensor.
3. This test checks for an internal fault within the
transmission by creating an open.
Resistance Chart
DTC P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit Low Input
°C°F Resistance (kW)
–40 –40 672
032 65
20 68 25
80 176 2.5
120 248 0.78
150 304 0.37
Step Action Yes No
1 Perform the transmission fluid checking procedure. Refer to
Checking Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was the fluid checking procedure performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to Checking
Transmission Fluid
Level and
Condition in
Automatic
Transmission
(4L30–E) section
2 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Does the scan tool display a TFT sensor signal voltage less than
0.4 volts? Go to Step 3
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
3. Turn the ignition“on”.
Does the TFT signal voltage change to match the voltage 4.92
volts? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 9
4 Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5 (D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 5
5 1. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5(D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 6
6 1. Remove the transmission oil pan. Refer to Transmission Oil
Temperature Sensor (Adapter Case) in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) section.
2. Check the internal wiring harness for a short to ground.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
7 1. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the TFT sensor.
2. Measure the resistance of the TFT sensor.
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 8
8 Replace the TFT Sensor.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 12 —
9 Check circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED for a short to ground.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 10
10 Check the PCM for faulty connections.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 12 —
12 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
TFT sensor indicates a voltage greater than 0.33 volts for 2
seconds.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High Input
D07RW029
Circuit Description
The TFT sensor is a thermistor that controls the signal
voltage to the PCM. The PCM supplies a 5–volt
reference signal to the sensor on circuit RED/BLK–
GRN/RED. When the transmission fluid is cold, the
sensor resistance is high and the PCM will sense high
signal voltage. As the transmission fluid temperature
warms to the normal operating temperature of 100°C
(212°F), the sensor resistance becomes less and the
voltage decreases to about 1.5 to 2 volts.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to power
in the TFT signal circuit or the TFT sensor. This is a
type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• Ignition is“on”.
• TFT sensor indicating a voltage greater than 4.86
volts.
• All conditions met for 20 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Transmission default temperature will be:
80°C (176°F) if engine temperature code is set.
100°C (212°F) if engine temperature is warm.
80°C (176°F) if engine run time is greater than 5
minutes.
21°C (69.8°F) if engine run time is less than 5
minutes.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for
a broken wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• Scan tool displays transmission fluid temperature in
degrees. After transmission is operating, the
temperature should rise steadily to about 100°C
(212°F), then stabilize.
• The temperature to resistance value scale may be
used to check the TFT sensor at the various
temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
“skewed” (mis–scaled) sensor.
A “skewed” sensor could result in hard shifts or TCC
complaints.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This check verifies problem in the TFT sensor circuit.
3. This test simulates a TFT sensor DTC P0712. If the
PCM recognizes the low signal voltage (high
temperature), and the scan tool displays 146°C
(295°F) or greater, the PCM and wiring are OK.
5. This test checks the TFT sensor and internal wiring
harness.
Resistance Chart
DTC P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit High Input
°C°F Resistance (kW)
–40 –40 672
032 65
20 68 25
80 176 2.5
120 248 0.78
150 304 0.37
Step Action Yes No
1 Perform the transmission fluid checking procedure.
Refer to Checking Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was the fluid checking procedure performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to Checking
Transmission Fluid
Level and
Condition in
Automatic
Transmission
(4L30–E) section
2 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Does the scan tool display a TFT sensor signal voltage greater
than 4.86 volts? Go to Step 3
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
3. Install a fused jumper wire from terminal 3(C) to 5(D) on the
engine harness.
4. Turn the ignition“on”.
Does the TFT signal voltage drop to less than 0.4 volts? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 9
4 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5(D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 5
5 1. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals 3(C) and 5(D).
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 6
6 1. Remove the transmission oil pan.
2. Check the internal wiring harness for an open. Refer to
Transmission Oil Temperature Sensor (Adapter Case) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 7
7 1. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the TFT sensor.
2. Measure the resistance of the TFT sensor.
Is the resistance within specifications? (See Resistance Chart.)
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 8
8 Replace TFT sensor. Refer to Transmission Oil Temperature
Sensor (Adapter Case) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 13 —

9 Check circuit RED/BLK–GRN/RED for an open or short to B+.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 10
10 Check circuit GRY–GRN for an open.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 11
11 Check the PCM for faulty or intermittent connections.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
12 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 13 —
13 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
2. TFT sensor indicates a voltage less than 4.92 volts for 2
seconds.
3. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No

DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck On)
D07RW032
Circuit Description
The TCC brake switch is used to indicate brake pedal
status. The normally opened brake switch signal
voltage circuit is opened.
Brake switch supplies a B+ signal on circuit GRN/YEL
to the PCM when the brakes are applied. The PCM
uses this signal to deenergize the TCC solenoid when
the brakes are applied.
This DTC detects a closed brake switch during
accelerations. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• No OSS DTCs P0722 or P0723.
• The PCM detects a closed brake switch/circuit (12
volts) for 2 seconds, and the following events occur
seven consecutive times: vehicle speed is less than 8
km/h (5 mph); then vehicle speed is between 8 and
32 km/h (5 and 20 mph) for 4 seconds; then vehicle
speed is greater than 32 km/h (20 mph) for 4
seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• If throttle opening is greater than 10% and vehicle
speed is greater than 45 km/h (28 mph), then
disregard brake switch contingency for TCC off
mode.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and TCC brake switch. Look for possible
bent, backed out, deformed or damaged terminals.
Check for weak terminal tension as well. Also check
for a chafed wire that could short to bare metal or
other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside the
insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• Check customer driving habits and/or unusual driving
conditions (i.e. stop and go, highway).
• Check brake switch for proper mounting and
adjustment.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks for voltage at the brake switch.
5. This test checks the brake switch.
8. This test checks circuit GRN/YEL at the PCM.
DTC P0719 TCC Brake Switch Circuit High (Stuck On)
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”. If ABS code
is set, check applicable fuse.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
4. Apply then release the brake pedal.
Does the scan tool display “TCC Brake Switch” as “closed” with
the brake pedal applied, and then display “open” when the brake
pedal is released?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 2
2 1. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Back probe ignition feed circuit terminal B13–1 at the brake
switch.
Is the test light“on”? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 1. Connect the test light to ground.
2. Back probe circuit terminal B13–4 at the brake switch.
Is the test light“off”? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
4 Repair the open in battery feed circuit terminal B13–1 to the
brake switch.
If fuse is open, check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to ground.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 13 —
5 Disconnect brake switch connector B–13 and ignition switch“on”.
Is the test light“on”? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 6
6 Check the brake switch short (B13–1 and B13–4).
Was a problem found? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
7 Check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to voltage.
Ignition switch“on”.
Is the test light“on”? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 10
8 1. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Check circuit terminal B13–4 for a short to voltage.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 10
9 Replace the brake switch.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 13 —
10 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Reconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Turn the ignition“on”.
Does the scan tool display “TCC Brake Switch” as “open” with
the brake applied, then display “closed” with the brake pedal
released?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 11
11 Check the PCM for faulty or intermittent connections.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
12 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 13 —
13 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
The PCM brake switch signal must indicate 0 volts for 1
seconds with the brake pedal applied.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
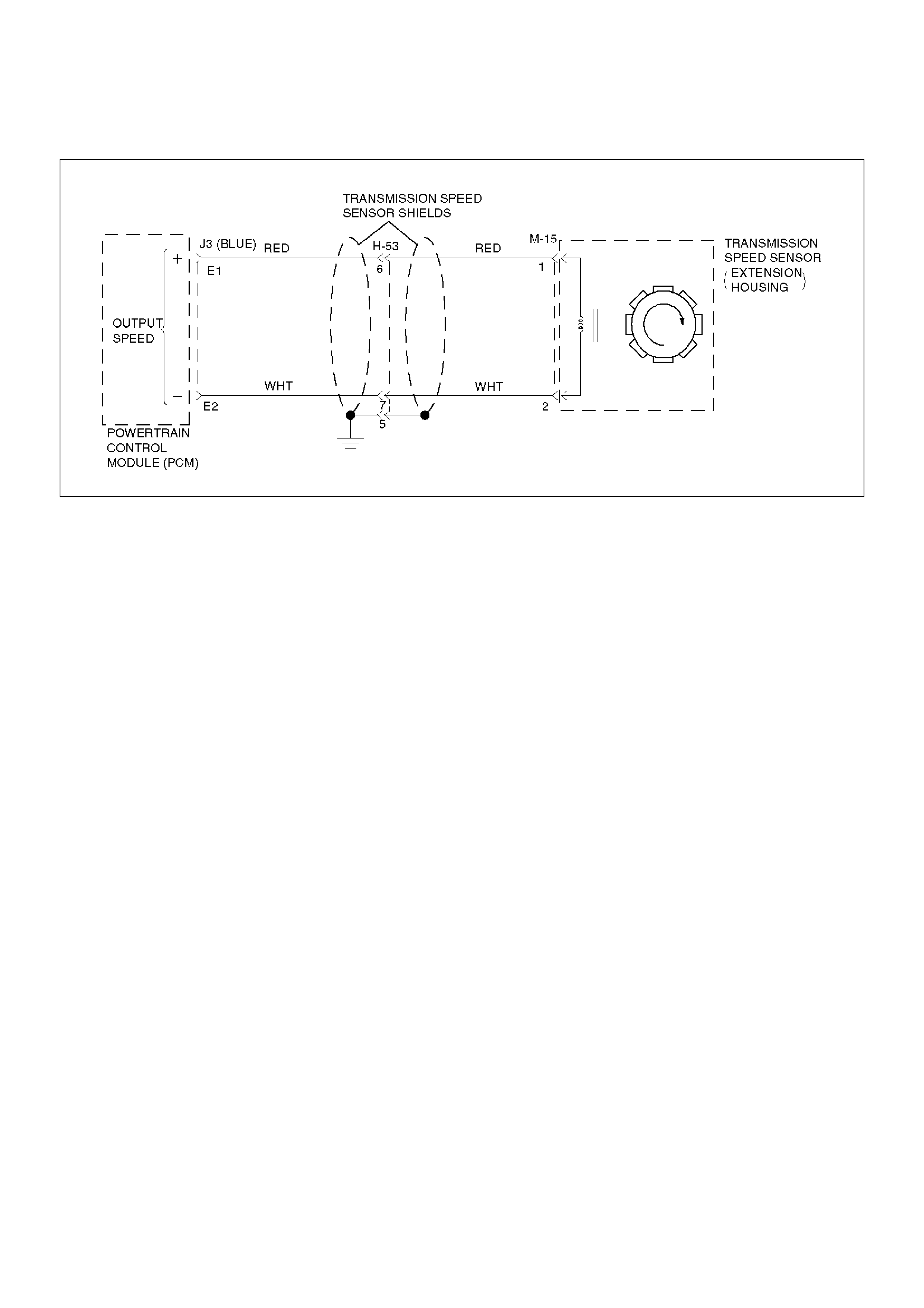
DTC P0722 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Low Input
D07RW006
Circuit Description
Output speed information is provided to the PCM by the
OSS, which is a permanent magnet (PM) generator.
The PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The
AC voltage level and number of pulses increases as the
speed of the vehicle increases. The PCM then converts
the pulsing voltage to output speed, which is used for
calculations. The vehicle speed can be displayed with a
scan tool.
This DTC detects a low output speed when there is a
high engine speed in a drive gear range. This is a type
“C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• No MAP DTCs P0107 or P0108, P0106, P1106,
P1107.
• No TPS DTCs P0122 or P0123.
• Not in Park or Neutral.
• TP angle is greater than 10%.
• Engine vacuum is between 0 and 70kPa.
• Engine speed is between 3,000 and 7,000 rpm.
• Transmission output speed is less than 0 rpm.
• All conditions met for 5 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Fixed to 4th gear.
• Maximum line pressure.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool. The DTC will be cleared from
history when the vehicle has achieved 40 warmup
cycles without a failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• An OSS DTC P0722 will set when no output speed is
at detected at start off.
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM. Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed
or damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for
a broken wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
4. This test checks the OSS circuit.
5. This test checks the integrity of the OSS.
7. This test checks the 5–volt and ground circuit of the
PCM.

DTC P0722 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Low Input
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
4. Raise the drive wheels.
5. Start the engine.
6. Place the transmission in any drive range.
With the drive wheels rotating, does the “Trans Output Speed”
increase with the drive wheel speed?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 2
2 Does the speedometer work? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Check for the most current and/or incorrect calibration.
Is the calibration current? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
harness connector terminals J3–E1 and J3–E2.
Is the reading 3,000 ohms? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1. Select AC volts.
2. Rotate the rear wheels, ensuring the driveshaft is turning.
Is the voltage greater than 0.5 volts? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
6 Inspect circuits RED and WHT for a poor connection or an open
circuit.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 8
7 1. Reconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Disconnect the OSS harness from the OSS.
3. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition“on”.
4. Using the J 39200 DVOM, measure the voltage at the OSS
harness connector terminals M15–1 and M15–2.
Is the reading between 4.0 to 5.1 volts? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 10
8 1. Remove the OSS.
2. Check the output shaft speed sensor rotor for damage or
misalignment. Refer to Speed Sensor (Extension Housing) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 9
9 Replace the OSS.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 17 —
10 Was the reading in step 7 less than 4.0 volts? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Was the reading in step 7 greater than 5.1 volts? Go to Step 15 —
12 Using the J 39200 DVOM to chassis ground, measure the
voltage on circuit RED.
Is the reading between 4.0 to 5.1 volts? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
13 Repair the open in circuit WHT.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 17 —
14 Check circuit RED for a short to ground or open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 16
15 Repair the short to B+ in circuit RED.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 17 —

16 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 17 —
17 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle under the
following conditions:
Transmission output speed is greater than 101 rpm for 3
seconds.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
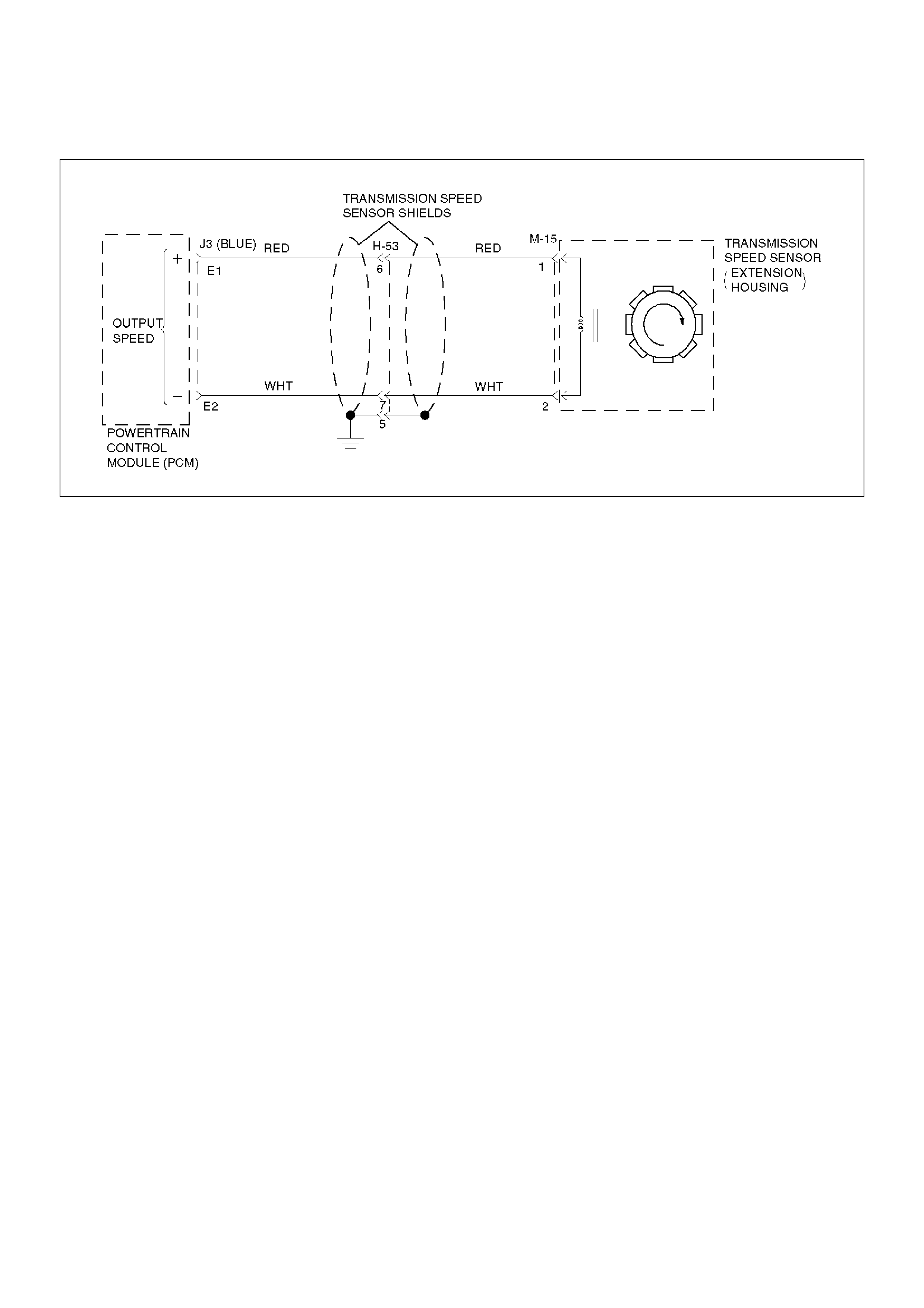
DTC P0723 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Intermittent
D07RW006
Circuit Description
Output speed information is provided to the PCM by the
OSS, which is a permanent magnet (PM) generator.
The PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The
AC voltage level and number of pulses increases as the
speed of the vehicle increases. The PCM then converts
the pulsing voltage to output speed, which is used for
calculations. The vehicle speed can be displayed with a
scan tool.
This DTC detects a low output speed when there is a
high engine speed in a drive gear range. This is a type
“C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
In Park or Neutral:
• Transmission output speed change is greater than
10,000 rpm.
• Conditions met for 6 seconds.
• Engine running time is greater than 2 seconds.
Not in Park or Neutral:
• Transmission output speed change is greater than
512 rpm.
• Conditions met for 0.075 seconds
• Engine running time is greater than 2 seconds.
• Engine vacuum is less than 70 kPa.
• Output speed is greater than 1,380 rpm for 1 second.
• NORAW–NOLAST < 60 rpm for 6 seconds.
NORAW: Latest raw data of output shaft speed.
NOLAST: Filtered pervious data of output speed.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Fixed to 4th gear.
• Maximum line pressure.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• A OSS DTC P0723 will set when output speed has
been detected and is lost.
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM. Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed
or damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal
tension as well. Also check for a chafed wire that
could short to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for
a broken wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
4. This test checks the OSS circuit.
5. This test checks the integrity of the OSS.
7. This test checks the 5–volt and ground circuit of the
PCM.
DTC P0723 Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) Intermittent
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
4. Raise the drive wheels.
5. Start the engine.
6. Place the transmission in any drive range.
With the drive wheels rotating, does the “Trans Output Speed”
increase with the drive wheel speed?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 2
2 Does the speedometer work? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Check for the most current and/or incorrect calibration.
Is the calibration current? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
harness connector terminals J3–E1 and J3–E2.
Is the reading 3,000 ohms? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1. Select AC volts.
2. Rotate the rear wheels, ensuring the driveshaft is turning.
Is the voltage greater than 0.5 volts? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
6 Inspect circuits RED and WHT for a poor connection or an open
circuit.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 8
7 1. Reconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
2. Disconnect the OSS harness from the OSS.
3. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition“on”.
4. Using the J 39200 DVOM, measure the voltage at the OSS
harness connector terminals M15–1 and M15–2.
Is the reading between 4.0 to 5.1 volts? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 10
8 1. Remove the OSS.
2. Check the output shaft speed sensor rotor for damage or
misalignment. Refer to Speed Sensor (Extension Housing) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 9
9 Replace the OSS.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 17 —
10 Was the reading in step 7 less than 4.0 volts? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Was the reading in step 7 greater than 5.1 volts? Go to Step 15 —
12 Using the J 39200 DVOM to chassis ground, measure the
voltage on circuit RED.
Is the reading between 4.0 to 5.1 volts? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
13 Repair the open in circuit WHT.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 17 —
14 Check circuit RED for a short to ground or open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 16
15 Repair the short to B+ in circuit RED.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 17 —
16 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 17 —
17 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle under the
following conditions:
Transmission output speed is greater than 101 rpm for 3
seconds.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
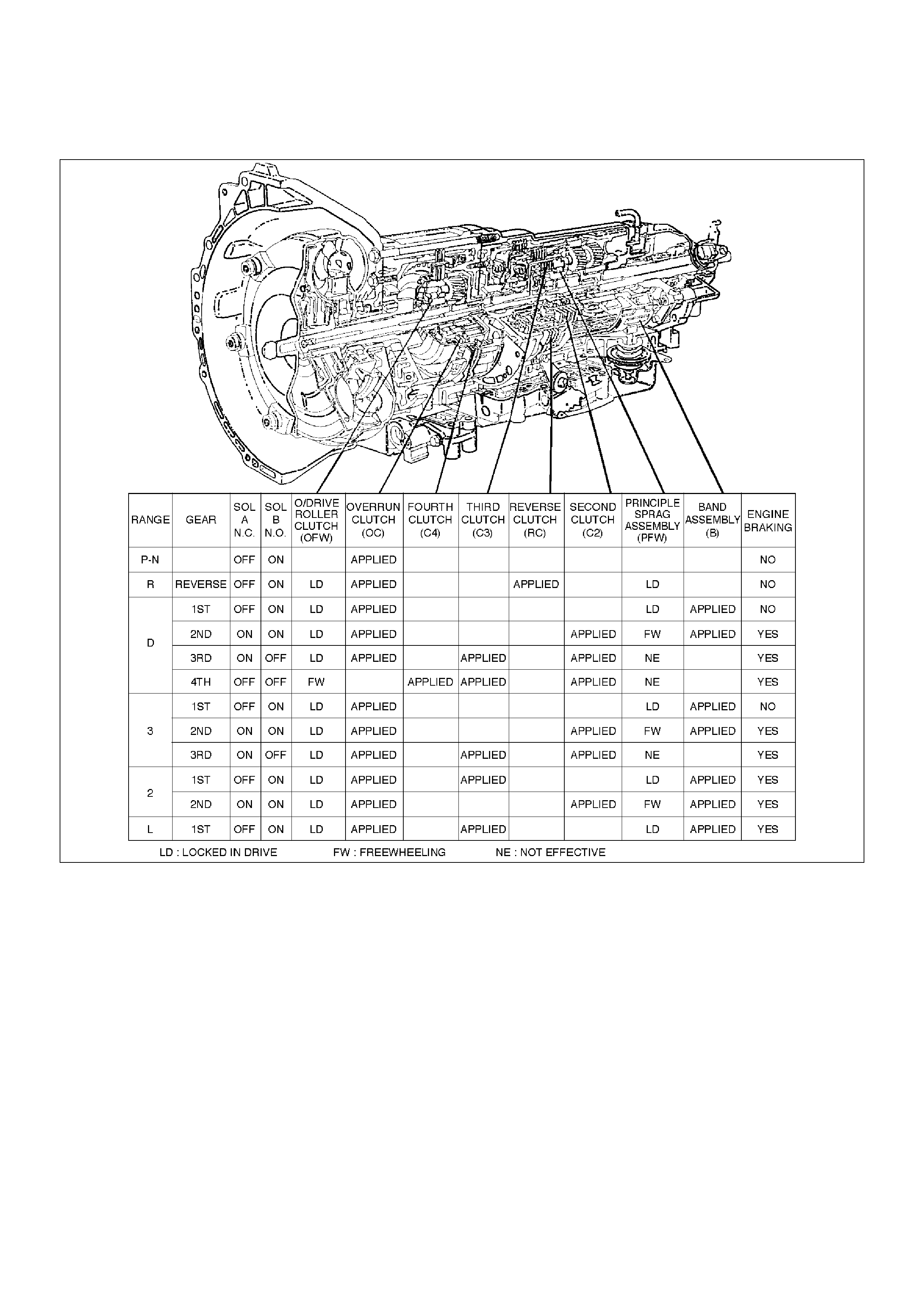
DTC P0730 Transmission Incorrect Gear Ratio
D07RT015
Circuit Description
• The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) calculates the
slippage of the converter and transmission based
upon the engine speed, the output speed, and the
current gear ratio.
• The slippage of the converter at a high enough
engine speed is low. The transmission should not
slip more than a given value when there is no shift.
• This DTC detects a slip at each gear. This is a type
“C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• No Output Speed Sensor DTC(s) P0722, P0723.
• Not in Park, Neutral, or Reverse.
• Engine speed is greater than 3,500 rpm.
• 3 seconds since upshift.
• 3 seconds since downshift.
• 3 seconds since garage shift (N®D).
• And one of the following conditions occur:
– Slip is greater than 508 rpm in 1st gear.
– Slip is greater than 468 rpm in 2nd gear.
– Slip is greater than 449 rpm on 3rd gear.
– Slip is greater than 440 rpm on 4th gear.
• All conditions met for 5.5 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Maximum line pressure.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn “off” the CHECK TRANS Lamp
after three consecutive ignition cycles without a
failure reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from PCM memory by using
a scan tool.
• The DTC can also be cleared from memory when the
vehicle has made 40 warmup cycles without a failure
reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC Actions Taken items
when the fault conditions no longer exist and the
ignition is cycles “off” long enough to power down the
PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Check for intermittent output speed sensor circuit
problems.
• Check for possible incorrect calibration. (PCM part
No., tire specification, and rear axle ratio)
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This step checks for possible low fluid level causing
slipping resulting in an undefined gear ratio.
3. This step checks for correct gear ratios for
commanded gears.
4. This step checks for low line pressure.
DTC P0730 Transmission Incorrect Gear Ratio
Step Action Yes No
1 Visually inspect the transmission cooling system for fluid leaks.
• Refer to Chart 16: Possible Causes of Transmission Fluid
Leaks of Mechanical/Hydraulic Diagnosis Symptoms Index in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section
Was condition found and corrected? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 2
2 Refer to Checking Transmission Fluid Level and Condition in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Has transmission fluid checking procedure been performed?
Go to Step 3
Go to Checking
Transmission Fluid
Level and
Condition in
Automatic
Transmission
(4L30–E) section
3 1. Install the scan tool.
2. Turn the ignition switch to the “on” position.
3. Engine not running.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s) use the scan tool to record the
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
4. Record the Failure Record data.
5. Use the scan tool snapshot mode to record transmission gear
ratios.
6. Drive vehicle in transmission gear ranges L, 2, 3, and D with
the engine speed is greater than 3,500 rpm for 5.5 seconds.
7. Record each transmission gear.
1st:2.73 – 2.99
2nd:1.54 – 1.71
3rd:0.93 – 1.05
4th:0.66 – 0.78
Does commanded gear ratio match ranges as shown?
Refer to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 4
4 Perform line pressure check.
• Refer to Line Pressure Test in Automatic Transmission (4L30–
E) section.
Was condition found and corrected? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
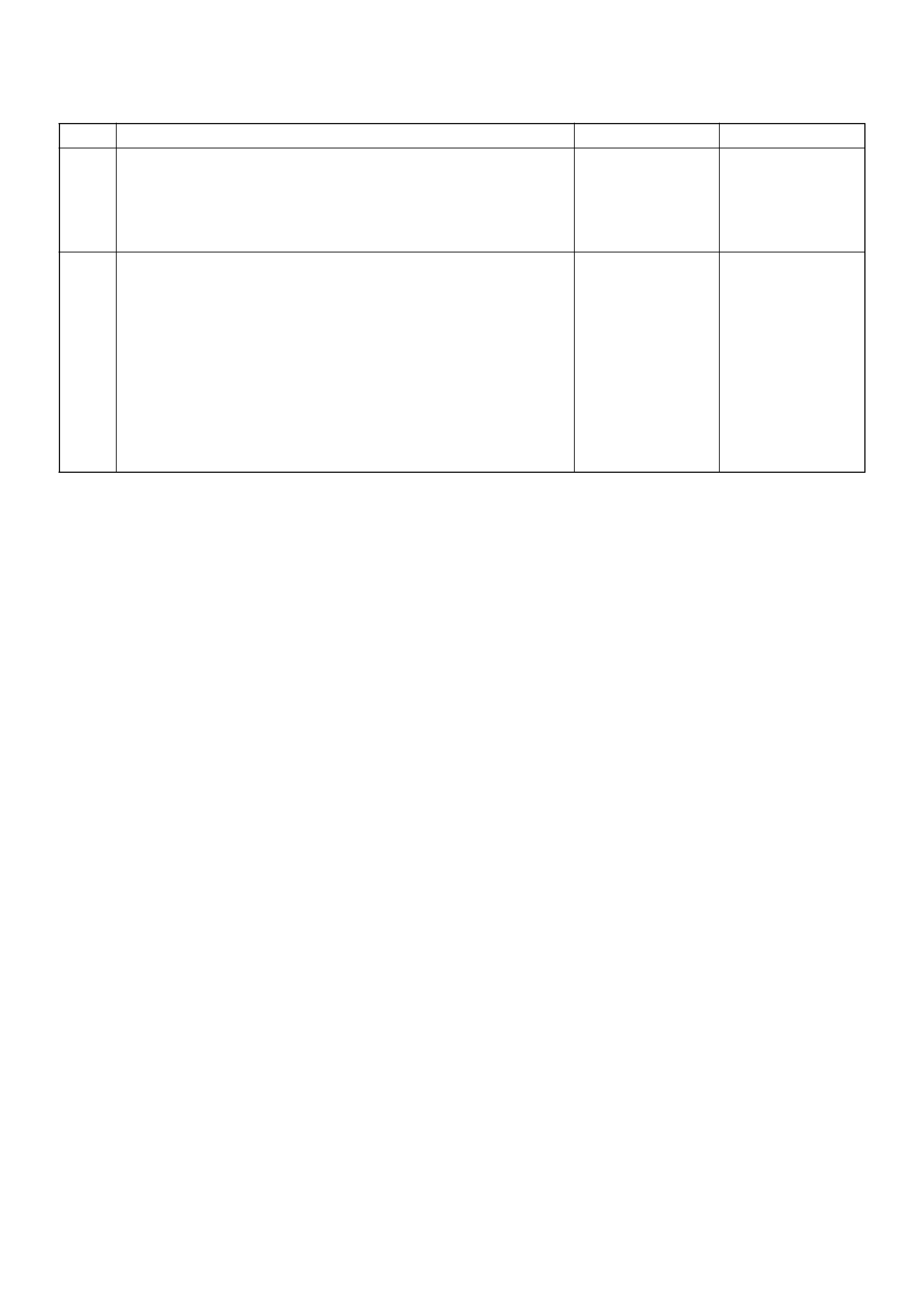
5 Check for possible clutch slippage.
• Refer to Chart 6: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0730 of
Mechanical/Hydraulic Diagnosis Symptoms Index in Automatic
Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Was condition found and corrected? Go to Step 6 —
6 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear info” function.
2. Operate the vehicle under the following conditions:
• Drive the vehicle in D4 with the engine speed greater than
3,500 rpm to obtain anyone of the following gear ratios for
seven seconds.
1st 1:2.73 – 1:2.99
2nd 1:1.54 – 1:1.71
3rd 1:0.93 – 1:1.05
4th 1:0.66 – 1:0.78
Has the last test failed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical
D07RW008
Circuit Description
The PCS is a PCM–controlled device used to regulate
transmission line pressure. The PCM compares TPS
voltage, engine rpm, and other inputs to determine the
line pressure appropriate for a given load. The PCM will
regulate the pressure by applying a varying amperage
to the PCS. The applied amperage can vary from 0.1
to 1 amp, and is monitored by the PCM.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground
in the PCS circuit or the PCS. This is a type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• The PCM detects that the different between
commanded and actual current is 200 milliampere
(mA) for over 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• Maximum line pressure.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn “off” the CHECK TRANS Lamp
after three consecutive ignition cycles without a
failure reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from PCM history by using a
scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from memory when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 5–way connector. Look
for possible bent, backed out, deformed or damaged
terminals. Check for weak terminal tension as well.
Also check for a chafed wire that could short to bare
metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken wire inside
the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
1. This test checks the ability of the PCM to command
the PCS.
2. This test checks the PCS and internal wiring harness
for incorrect resistance.
DTC P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) (Force Motor) Circuit Electrical
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
4. While the engine is operating, put the transmission in Park.
5. Using the scan tool, apply 0.1 amp through 1.0 amp while
observing “PC Ref. Current” and“PC Act. Current”.
Is the “PC Act. Current” reading always within 0.16 amp?
Go to Diagnostic
Aids Go to Step 2
2 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the transmission 5–way connector M–6.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M6–2(B) and M6–1(E).
Is the resistance within 3–7 ohms? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 3
3 1. Remove the transmission oil pan. Refer to Solenoid (Adapter
Case Valve Body) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E)
section.
2. Disconnect the internal wiring harness at the PCS.
3. Measure the resistance of the PCS.
Is the resistance within 3–7 ohms? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 Replace the PCS.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 9 —
5 Repair the internal wiring harness for an open.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 9 —
6 Inspect/repair circuits J3–E4, M6–2(B), J3–E3, and M6–1(E).
Was a problem found? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 7
7 Inspect/repair circuits J3–E4, M6–2(B), J3–E3, and M6–1(E) for
a short to ground or poor connections.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 9 —
9 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
The PCS duty cycle is not at its electrical high or low limit.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
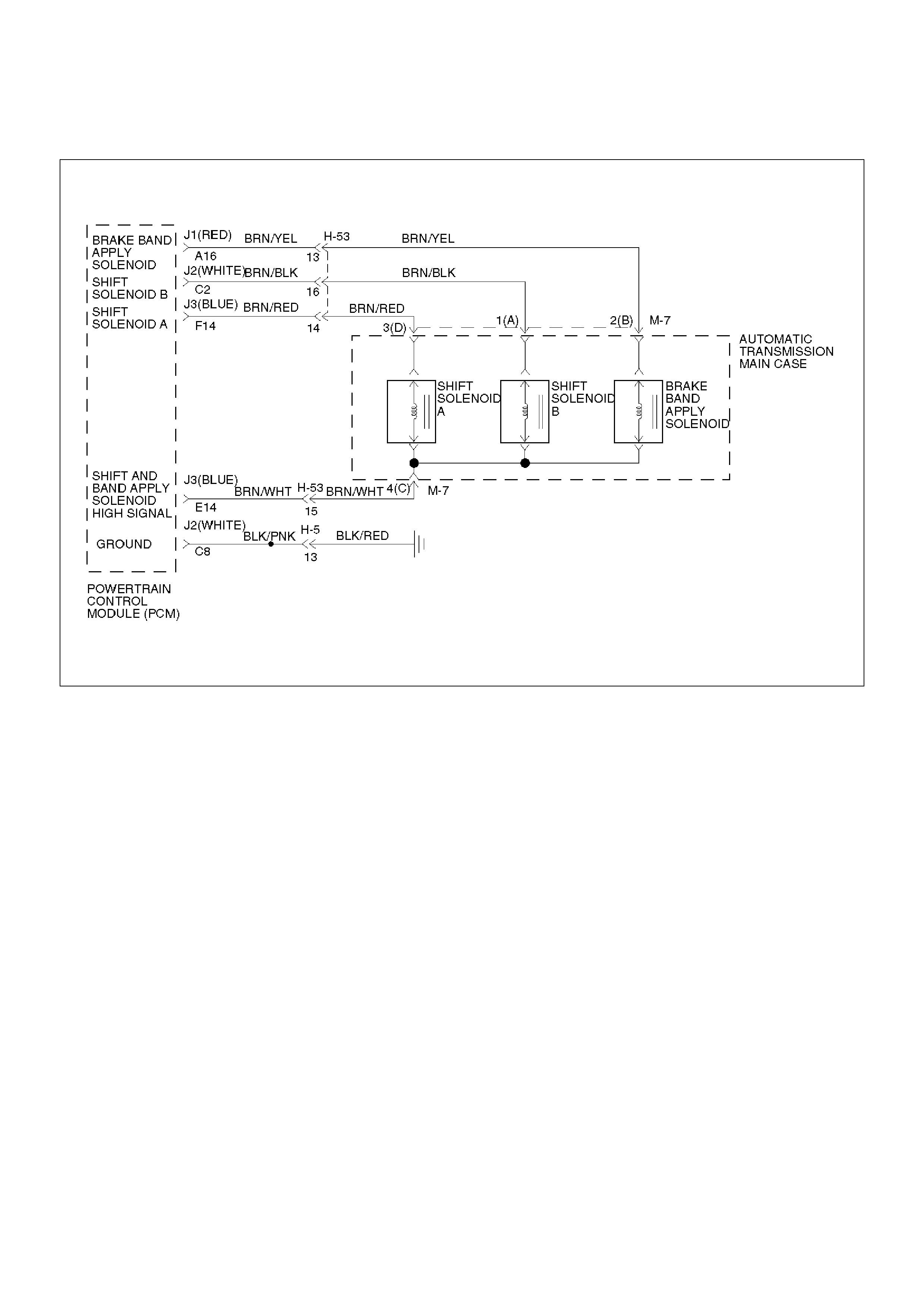
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical
D07RW009
Circuit Description
• The shift solenoid A is a simple on/off solenoid
located in the main case valve body. The solenoid is
the normally closed type. In second or third gear, the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes the
solenoid to open a fluid inlet port. When the port is
open, fluid pressure actuates the shift valve.
• The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
produced by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
• The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage, except in
BACKUP MODE or when ignition is off the HSD is
turned off.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground
in the shift solenoid A circuit or the shift solenoid A.
This is a type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Ignition is“on”, Engine“run”.
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+) or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
• All conditions met for 0.33 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Maximum line pressure.
• Immediate landing to 4th gear.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken
wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
• An open ignition feed circuit can cause multiple DTCs
to set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks for power to the shift solenoid A from
the ignition through the PCM.
4. This test measures the resistance of the component.
8. This test checks the function of the shift solenoid A
and the transmission internal wiring harness.
Shift Solenoid Status Chart
DTC P0753 Shift Solenoid A Electrical
Gear Shift solenoid A Shift solenoid B
1st OFF ON
2nd ON ON
3rd ON OFF
4th OFF OFF
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“on”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Were DTCs P0753, P0758, P1860 set? Go to Step 2
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
2 1. Turn the ignition“on”.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the voltage between
PCM connector terminals J3–E14 and J2–C8 (GND).
Is the voltage within 10–12 volts? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Turn the ignition“on”.
4. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the voltage between
PCM connector terminals J3–F14 and ground.
Is the voltage within 10 – 12 volts? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J3–E14 and J3–F14.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1. Disconnect the J1 (RED) and J2 (WHITE) PCM connectors.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, check a continuity between PCM
terminals J3–F14 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 7
6 1. Disconnect the 16–way harness connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals H53–14 and H53–15.
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 8
7 Using the J39200 DVOM, check a continuity between J3 (BLUE)
PCM terminal E14 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 9
8 1. Disconnect the transmission main case 4 pin connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M7–3(D) and M7–4(C).
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 15
9 Check every connection at the PCM connector.
Was a problem found? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 16
10 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminals J3–F14
and transmission harness terminal M7–3(D) is shorted to voltage.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 —
11 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal
J3–F14 and transmission harness terminal M7–3(D) is shorted to
ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 —
12 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminals J3–E14
and transmission harness terminal M7–4(C) is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 —
13 The wiring harness between PCM connector J3 and transmission
16–way connector H–53 is open or poor connection.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 —
14 The wiring harness between transmission 16–way connector H–
53 and transmission main case connector M–7 is open or has a
poor connection.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 —
15 The shift solenoid A is faulty.
Replace the shift solenoid A. Refer to Solenoid (Main Case Valve
Body) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 18 —
16 The PCM may be faulty.
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 18 —
17 Repair the PCM connector connection.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 —
18 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle under the
following conditions:
• The shift solenoid A is commanded “on” and voltage drops
to zero.
• The shift solenoid A is commanded “off” and voltage
increases to B+.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified
Exit DTC table
Step Action Yes No

DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical
D07RW009
Circuit Description
• The shift solenoid B is a simple on/off solenoid
located in the main case valve body. It is normally
open. When the port is open, fluid pressure actuates
the shift valve. In first or second gear, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) energizes the solenoid to
close a fluid inlet port.
• The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
procuded by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
• The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage. In BACKUP
MODE or when the ignition is off, the HSD is turned
off.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground
in the shift solenoid B circuit or shift solenoid B. This is
a type “C” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Ignition is“on”, Engine“run”.
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+) or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
• All conditions met for 0.33 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Fixed to 4th gear.
• Maximum line pressure.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.

Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken
wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
4. This test measures the resistance of the component.
6. This test checks the function of the shift solenoid B
and the transmission internal wiring harness.
10.This test checks for power to the shift solenoid B
from the ignition through the PCM.
Shift Solenoid Status Chart
DTC P0758 Shift Solenoid B Electrical
Gear Shift solenoid A Shift solenoid B
1st OFF ON
2nd ON ON
3rd ON OFF
4th OFF OFF
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“on”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Were DTCs P0753, P0758, P1860 set? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 2
2 1. The engine“on”.
2. Apply brake pedal and select transmission range“D”.
3. Press and hold down the winter switch and select
transmission mode“winter”.
Does the scan tool display DTC P0758 at 3rd gear? Go to Step 7
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J2 (WHITE) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connectors.
3. Turn the ignition“on”.
4. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the voltage between
PCM connector terminals J2–C2 and J2–C8.
Is the voltage within 10 – 12 volts? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J2–C2 and J3–E14.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 5
5 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals H53–16 and H53–15.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 6
6 1. Disconnect the transmission main case connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M7–1(A) and M7–4(C).
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
7 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J2 (WHITE) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connectors.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J2–C2 and J3–E14.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8 Using the J39200 DVOM, check a continuity between PCM
connector terminal J2–C2 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 19 Go to Step 10
9 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals H53–16 and H53–15.
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms? Go to Step 20 Go to Step 11
10 Using the J39200 DVOM, check a continuity between PCM
connector terminal J3–E14 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 21 Go to Step 12
11 1. Disconnect the transmission main case connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M7–1(A) and M7–4(C).
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 22 Go to Step 23
12 Check every connection of the PCM and transmission 16–way
connector H–53.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 Go to Step 13
13 1. Connect the J2 (WHITE) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connectors to
the PCM.
2. Turn the ignition“on”, the engine“on”.
3. Repeat Step 2.
Does the scan tool display DTC P0758 at 3rd gear? Go to Step 24
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
14 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal
J2–C2 and transmission main case terminal M7–1(A) is shorted
to voltage.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
15 The PCM internal terminal J2–C2 is shorted to voltage.
Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 25 —
16 The wiring harness between PCM connector and transmission
16–way connector is shorted.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
17 The wiring harness between transmission 16–way connector and
transmission main case connector is shorted.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
18 The shift solenoid B is faulty, or the internal wiring harness from
the shift solenoid B is shorted.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
19 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal
J2–C2 and transmission main case connector terminal M7–1(A)
is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
20 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal J2–C2 and
transmission 16–way connector terminal H53–16, or between
PCM connector terminal J3–E14 and 16–way connector terminal
H53–15 is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
21 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal J3–E14
and transmission main case connector terminal M7–4(C) is
shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
Step Action Yes No
22 The wiring harness between transmission 16–way connector
terminal H53–16 and transmission main case connector terminal
M7–1(A), or between H53–15 and M7–4(C) is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
23 The internal wiring harness from the shift solenoid B is open, or
the shift solenoid B is faulty.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 25 —
24 Replace the PCM.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 25 —
25 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle under the
following conditions:
• The shift solenoid B is commanded “on” and voltage drop
to zero.
• The shift solenoid B is commanded “off” and voltage
increases to B+.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
DTC P1790 ROM Transmission Side Bad Check Sum
Circuit Description
Transmission Side Read Only Memory (ROM) and
Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM) is an electronic circuit that controls
the transmission control in the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).
This DTC detects a check sum error. This is a type “C”
DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Detects check sum error for 1 second.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Maximum line pressure.
• Immediate landing to 4th gear.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
DTC P1790 ROM Transmission Side Bad Check Sum
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Was DTC P1790 set? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 2
2 Was DTC P1792 set? Go to Step 3 —
3 1. Remove the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
2. Using the ITCS, make a reprogramming the transmission
EEPROM.
Was the reprogramming complete? Go to Step 5 —
4 Replace the PCM.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 5 —
5 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
DTC P1792 EEPROM Transmission Side Bad Check Sum
Circuit Description
Transmission Side Read Only Memory (ROM) and
Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only
Memory (EEPROM) is an electronic circuit that controls
the transmission control in the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).
This DTC detects a check sum error. This is a type “C”
DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Detects check sum error for 1 second.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Maximum line pressure.
• Immediate landing to 4th gear.
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will illuminate the CHECK TRANS Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC/CHECK
TRANS Lamp
• The PCM will turn off the CHECK TRANS Lamp after
three consecutive ignition cycles without a failure
reported.
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
DTC P1792 EEPROM Transmission Side Check Bad Check Sum
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“off”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Was DTC P1790 set? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 2
2 Was DTC P1792 set? Go to Step 3 —
3 1. Remove the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
2. Using the ITCS, make a reprogramming the transmission
EEPROM.
Was the reprogramming complete? Go to Step 5 —
4 Replace the PCM.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 5 —
5 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and operate the vehicle.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
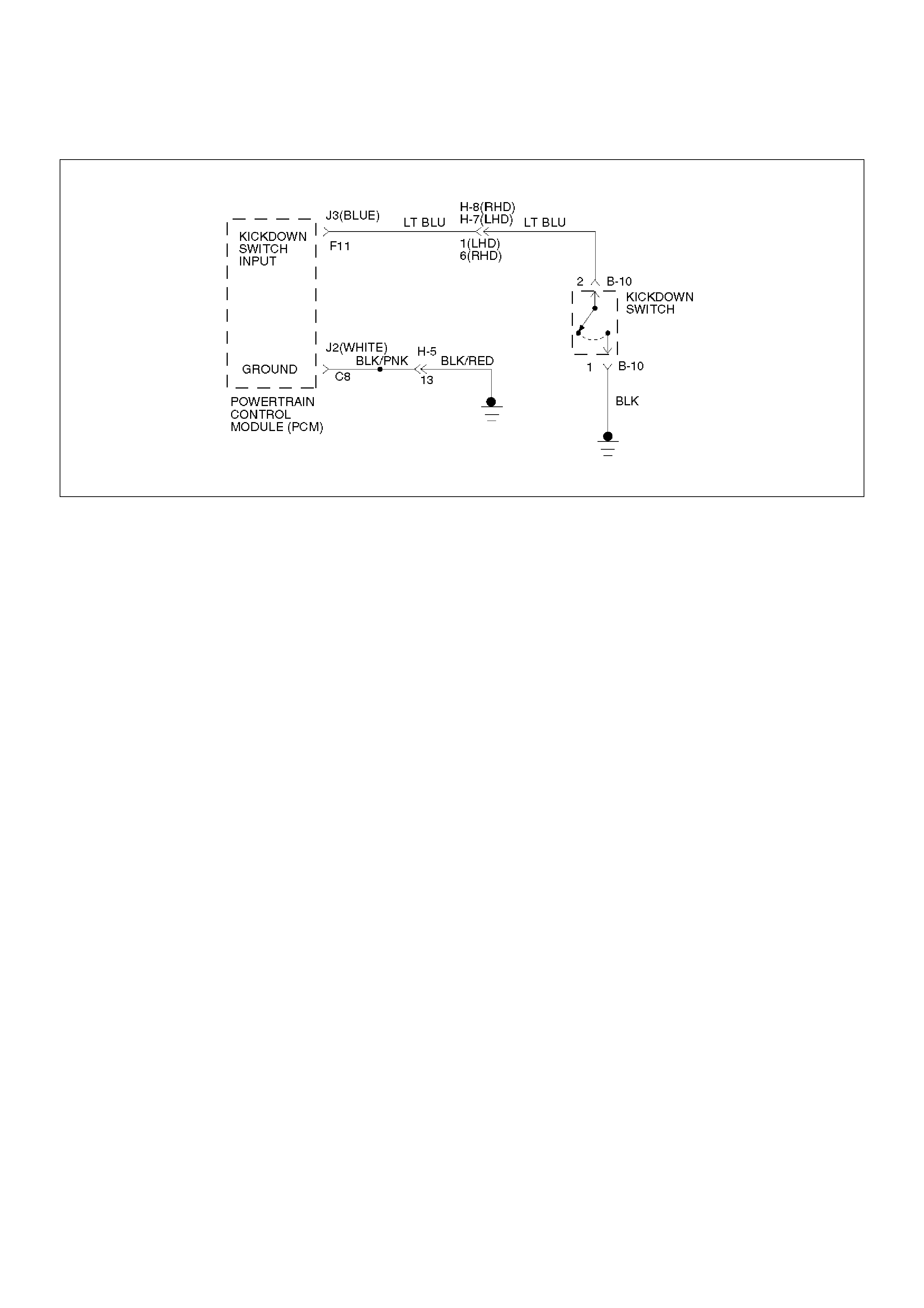
DTC P1835 Kickdown Switch Always On
D07RW033
Circuit Description
• When the driver presses the accelerator pedal down
fully, the kickdown switch closes, sending a ground
signal to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
• This information is used to perform shifts at high
engine speed.
• When the kickdown switch is closed, the Throttle
Position Sensor (TPS) is already is at 100%.
• This DTC detects a closed kickdown switch when TP
angle is less than 70%.
• This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• No TPS DTCs P0122 or P0123.
• TP angle is less than 70%.
• Kickdown switch is“on”.
• All conditions met for 1 second.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets.
• Kickdown mode control is off.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Check the wiring harness for a short to ground
between the PCM and kickdown switch.
• Check the kickdown switch for failure.
• Check kickdown adjustment.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
1. This test checks for short to ground or kickdown
switch failure.
3. This test checks for regulation kickdown switch.
DTC P1835 Kickdown Switch Always On
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“on”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Does the scan tool display “Kickdown switch” “low”(closed
switch)? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J3 (BLUE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, check a continuity between PCM
connector terminal J3–F11 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
3 The TP angle goes from 0% to 100% with the accelerator pedal
depressed.
Is the kickdown switch “on” when TP angle is below 70%? Go to Step 5
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
4 1. Disconnect the kickdown switch connector B–10.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, check a continuity between
terminals B10–1 and B10–2.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
5 Adjust the kickdown switch.
Is the kickdown switch “on” when TP angle is above 95%? Go to Step 9 —
6 Replace the kickdown switch.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 9 —
7 Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) in
Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 9 —
8 Repair the short to ground in circuit LT BLUE.
Is the repair complete? Go to Step 9 —
9 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following condition
is met:
The torque converter stator temperature switch circuit does
not indicate a hot mode when the transmission fluid
temperature is less than 60°C (140°F) for at least 5 seconds.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
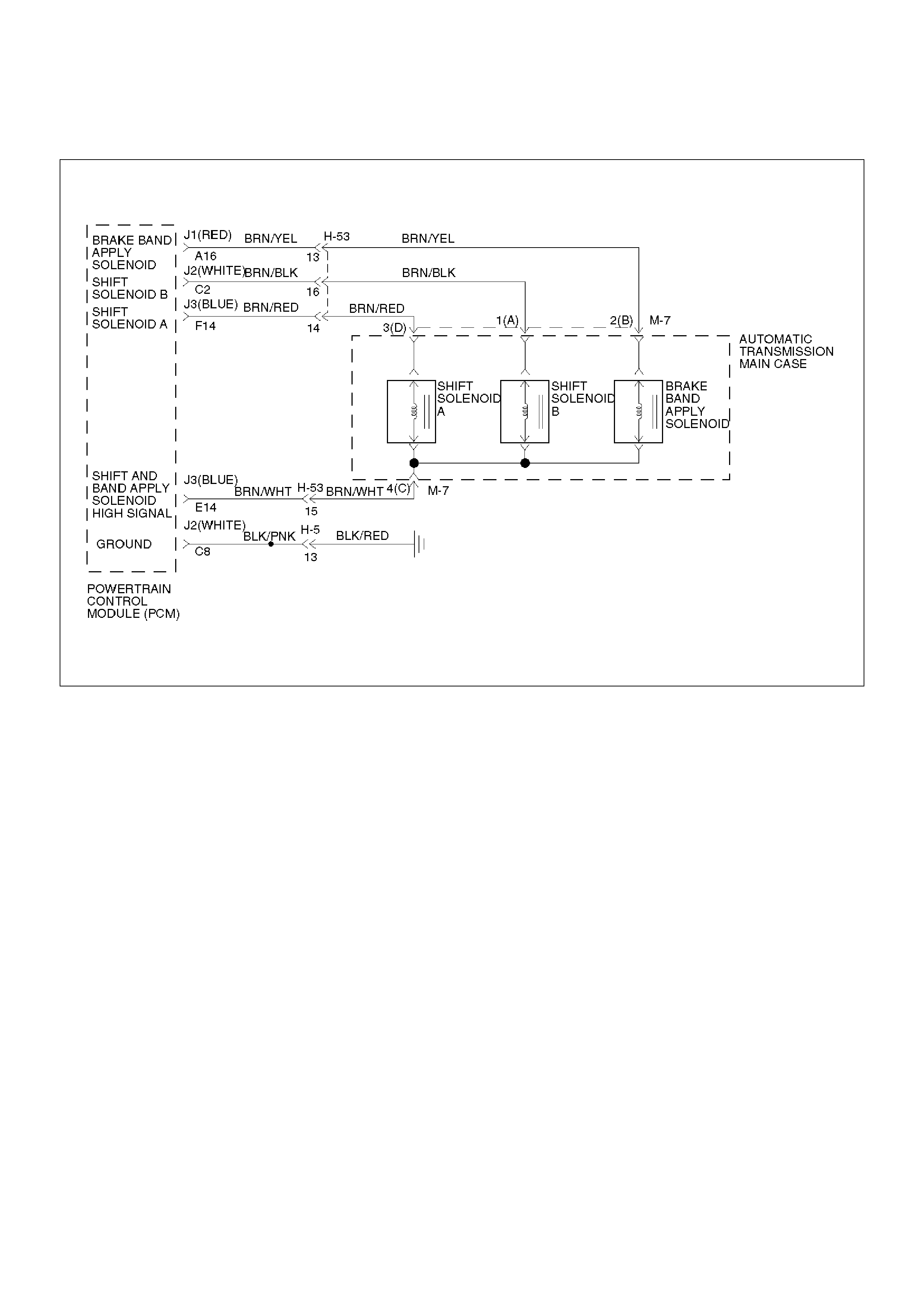
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid Malfunction
D07RW009
Circuit Description
• The brake band apply solenoid is a normally open
solenoid which controls the flow of fluid for brake
band application. The Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) uses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and
changes the duty cycle to control the solenoid. The
PCM turns the solenoid on (energized) and off
(deenergized) at a constant frequency. The length of
time the solenoid is energized during each on/off
cycle is called the pulse width. By varying or
“modulating” the pulse width, the solenoid output
pressure is changed. Since the solenoid is normally
open, increasing the pulse width increases the duty
cycle and decreases the output pressure. PWM
control provides smooth band application without an
accumulator. The band is only applied in first and
second gears.
• In the event of an electrical failure (open), the
solenoid regulates at the maximum oil flow (0% duty
cycle).
• The solenoid is activated by current. This current is
produced by applying a voltage to one side (the High
side) and a ground to the other side (Low side).
• The High Side Driver (HSD) is a circuit of the PCM
that acts as a switch between the solenoids and the
supply voltage. The High side of the solenoid is
permanently supplied with voltage. When the ignition
is off, the HSD is turned off.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground
in the brake band apply solenoid circuit or the brake
band apply solenoid. This is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• Ignition is“on”, Engine“run”.
• The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains high (B+) or the PCM commands the
solenoid “off” and the voltage remains low (zero
volts).
• All conditions met in 1.3 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Inhibit brake band apply solenoid.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connection at the
PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken
wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks for power to the brake band apply
solenoid from the ignition through the PCM.
3. This test checks the resistance of the transmission
internal wiring harness and brake band apply
solenoid.
4. This test checks the ability of the PCM and wiring to
control the ground circuit.
DTC P1850 Brake Band Apply Solenoid Malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“on”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when the
“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Were DTCs P0753, P0758 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2 Using the J39200 DVOM, back probe between PCM connector
terminals J3–E14 and J2–C8.
Is the voltage between 10 to 12 volts? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
3 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J1 (RED) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connectors.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J1–A16 and J3–E14.
Is the resistance within 10–12 ohms? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
4 Using the J39200 DVOM, back probe between PCM connector
terminals J1–A16 and J2–C8.
Is the voltage between 10 to 12 volts? Go to Step 25 Go to Step 3
5 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J1 (RED) and J3 (BLUE) PCM connectors.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, check continuity between PCM
terminal J3–E14 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, check continuity between
connector H53–13 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 16
7 1. Disconnect the transmission main case connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, check continuity between the
terminal M7–2(B) and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
8 1. Disconnect the J1 (RED) PCM Connector.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J1–A16 and J3–E14.
Is the resistance within 10–12 ohms? Go to Step 25 Go to Step 9
9 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal H53–13 and H53–15.
Is the resistance within 10–12 ohms? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 10
10 1. Disconnect the transmission main case connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M7–2(B) and M7–4(C).
Is the resistance within 10–12 ohms? Go to Step 19 Go to Step 20
11 Using the J39200 DVOM, check continuity between PCM
terminal J1–A16 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 25
12 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal H53–13 and H53–15.
Is the resistance within 10–12 ohms? Go to Step 23 Go to Step 14
13 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, check continuity between terminal
H53–13 and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 21
14 1. Disconnect the transmission main case connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals M7–2(B) and M7–4(C).
Is the resistance within 10–12 ohms? Go to Step 24 Go to Step 20
15 1. Disconnect the transmission main case connector M–7.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, check continuity between the
terminal M7–2(B) and ground.
Is there a continuity? Go to Step 17 Go to Step 22
16 The wiring harness between PCM terminal J3–E14 and
transmission 16–way connector terminal H53–15 is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
17 The brake band apply solenoid is faulty, or the internal wiring
harness from the brake band apply solenoid is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
18 The wiring harness between the transmission 16–way connector
terminal H53–15 and the transmission main case connector
terminal M7–4(C) is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
19 The wiring harness between the transmission 16–way connector
terminal H53–15 and the transmission main case connector
terminal M7–4(C) is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
20 The brake band apply solenoid is faulty, or the internal wiring
harness from the brake band apply solenoid is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
21 The wiring harness between the PCM connector terminal J1–A16
and transmission 16–way connector terminal H53–13 is shorted
to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
22 The wiring harness between the transmission 16–way connector
terminal H53–13 and the transmission main case connector
terminal M7–2(B) is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
Step Action Yes No
23 The wiring harness between the PCM connector terminal J1–A16
and the 16–way connector terminal H53–13 is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
24 The wiring harness between the transmission 16–way connector
terminal H53–13 and the transmission main case connector
terminal M7–2(B) is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 26 —
25 Check every connection at the PCM.
If OK, replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 26 —
26 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
• The brake band apply solenoid is commanded “on” and
the volts drop to zero.
• The brake band apply solenoid is commanded “off” and the
volts increase to B+.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
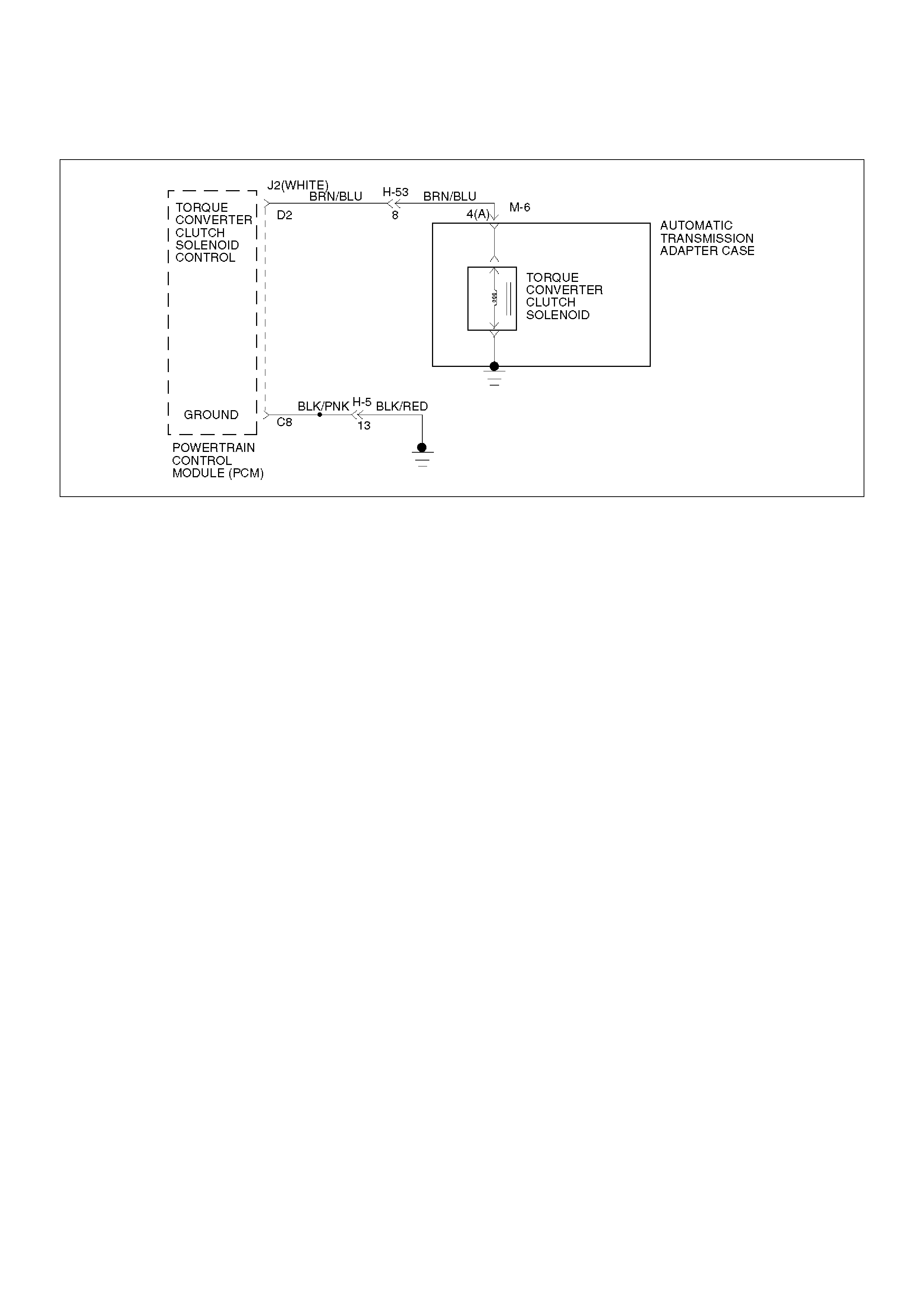
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical
D07RW010
Circuit Description
The PCM allows current to flow through the solenoid
coil according to the duty cycle (percentage of “on” and
“off” time). This current flow through the solenoid coil
creates a magnetic field that magnetizes the solid core.
The magnetized core attracts the check ball to seat
against spring pressure. This blocks the exhaust for the
TCC signal fluid and allows 2–3 drive fluid to feed to
TCC signal circuit. The TCC signal fluid pressure acts
on the TCC regulator valve to regulate line pressure and
to apply fluid pressure to the torque converter clutch
shift valve. When the TCC shift valve is in the apply
position, regulated apply fluid pressure is directed
through the TCC valve to apply the torque converter
clutch. The TCC solenoid is used in conjunction with
the TCC solenoid to regulate fluid to the torque
converter. The TCC solenoid is attached to the valve
body within the transmission.
This DTC detects a continuous open or short to ground
or ignition in the TCC circuit or the TCC solenoid. This
is a type “D” DTC.
Conditions For Setting The DTC
• Battery voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• No shift solenoid A DTC P0753.
• No shift solenoid B DTC P0758.
• Ignition is“on”, Engine“run”.
• The PCM commands the solenoid “on” and the
voltage remains low (zero volts).
• The PCM commands the solenoid “off” and the
voltage remains high (B+).
• All conditions met for 0.25 seconds.
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
• Inhibit TCC engagement.
• The PCM will not illuminate the CHECK TRANS
Lamp.
Conditions For Clearing The DTC
• The DTC can be cleared from the PCM history by
using a scan tool.
• The DTC will be cleared from history when the
vehicle has achieved 40 warmup cycles without a
failure reported.
• The PCM will cancel the DTC default actions when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition is cycled
“off” long enough to power down the PCM.
Diagnostic Aids
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the PCM and at the transmission 16–way connector.
Look for possible bent, backed out, deformed or
damaged terminals. Check for weak terminal tension
as well. Also check for a chafed wire that could short
to bare metal or other wiring. Inspect for a broken
wire inside the insulation.
• When diagnosing for a possible intermittent short or
open condition, move the wiring harness while
observing test equipment for a change.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test checks for voltage to the solenoid.
3. This test checks the ability of the PCM and wiring to
control the ignition circuit.
8. This test checks the resistance of the TCC solenoid
and the internal wiring harness.
DTC P1860 TCC Solenoid Electrical
Step Action Yes No
1 1. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine“on”, turn the ignition switch“on”.
NOTE: Before clearing DTC(s), use the scan tool to record
“Failure Records” for reference, as data will be lost when
the“Clear Info” function is used.
3. Record the DTC“Failure Records”.
Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2 Using the J39200 DVOM, back probe between PCM connector
terminals J2–D2 and J2–C8.
Is the voltage 0 ? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
3 1. Apply brake pedal and select transmission range“D”.
2. Do a test drive, and increase the vehicle speed to TCC “on”
at 4th.
Does the scan tool display DTC P1860 at TCC“ON”? Go to Step 9
Go to Diagnostic
Aids
4 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J2 (WHITE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
PCM connector terminals J2–D2 and J2–C8.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
5 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal J2–D2 and
transmission adapter case connector terminal M6–4(A) is
shorted to voltage.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 Go to Step 19
6 Intermittent condition.
Check the wiring harness and terminals between PCM connector
J2 and transmission adapter case connector M–6.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 18 Go to Step 19
7 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal H53–8 and ground.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 8
8 1. Disconnect the transmission adapter case connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal M6–4(A) and ground.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 16 Go to Step 17
9 1. Turn the ignition“off”.
2. Disconnect the J2 (WHITE) PCM connector.
3. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminals J2–D2 and J2–C8.
Is the resistance within 18 – 20 ohms? Go to Step 18 Go to Step 10
10 1. Disconnect the transmission 16–way connector H–53.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal H53–8 and ground.
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 1. Disconnect the transmission adapter case connector M–6.
2. Using the J39200 DVOM, measure the resistance between
terminal M6–4(A) and ground.
Is the resistance within 18–20 ohms? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
12 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal J2–D2 and
transmission 16–way connector terminal H53–8 is shorted to
ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
13 The wiring harness between transmission 16–way connector H–
53 and adapter case connector M–6 is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
14 The TCC solenoid is faulty, or the internal wiring harness from the
TCC solenoid is shorted to ground.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
15 The wiring harness between PCM connector terminal J2–D2 and
transmission 16–way connector terminal H53–8 is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
16 The wiring harness between transmission 16–way connector
terminal H53–8 and adapter case terminal M6–4(A) is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
17 The TCC solenoid is faulty, or the internal wiring harness from the
TCC solenoid is open.
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
18 Check every connection at the PCM.
If OK, replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) in Automatic Transmission (4L30–E) section.
Is the replacement complete? Go to Step 20 —
19 Check the PCM connector terminal J2–D2, transmission 16–way
connector terminal H53–8 and transmission adapter case
connector terminal M6–4(A).
Was a problem found and corrected? Go to Step 20 —
20 1. After the repair is complete, use the scan tool to select“DTC”,
then “Clear Info” function and ensure the following conditions
are met:
• The TCC solenoid is commanded “on” and the volts
increase to B+.
• The TCC solenoid is commanded “off” and the volts drop
to zero.
2. Review the scan tool“DTC Info”.
Has the last test failed or is the current DTC displayed?
Begin diagnosis
again
Go to Step 1
Repair verified Exit
DTC table
Step Action Yes No
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Specifications
Temperature Temperature Minimum
Resistance
Nominal
Resistance
Maximum
Resistance
Signal
°C°FWWWVolts
-40 -40 600500 664200 731100 5.00
-30 -22 319800 350400 382400 4.65
-20 -4 177400 192700 208600 4.41
-10 14 102200 110100 118300 4.00
0 32 60870 65110 69450 3.52
10 50 37410 39750 42120 2.98
20 68 23660 24980 26300 2.40
30 86 15270 16120 16970 1.85
40 104 10040 10660 11290 1.43
50 122 6758 7211 7673 4.29
60 140 4645 4980 5324 4.04
70 158 3255 3506 3765 3.69
80 176 2323 2513 2710 3.34
90 194 1685 1831 1982 3.04
100 212 1242 1355 1472 2.58
110 230 929 1017 1109 2.24
120 248 704 773 846 1.97
130 266 540 595 653 1.67
140 284 419 464 511 1.42
150 302 329 365 403 1.16