Main Data And Specifications
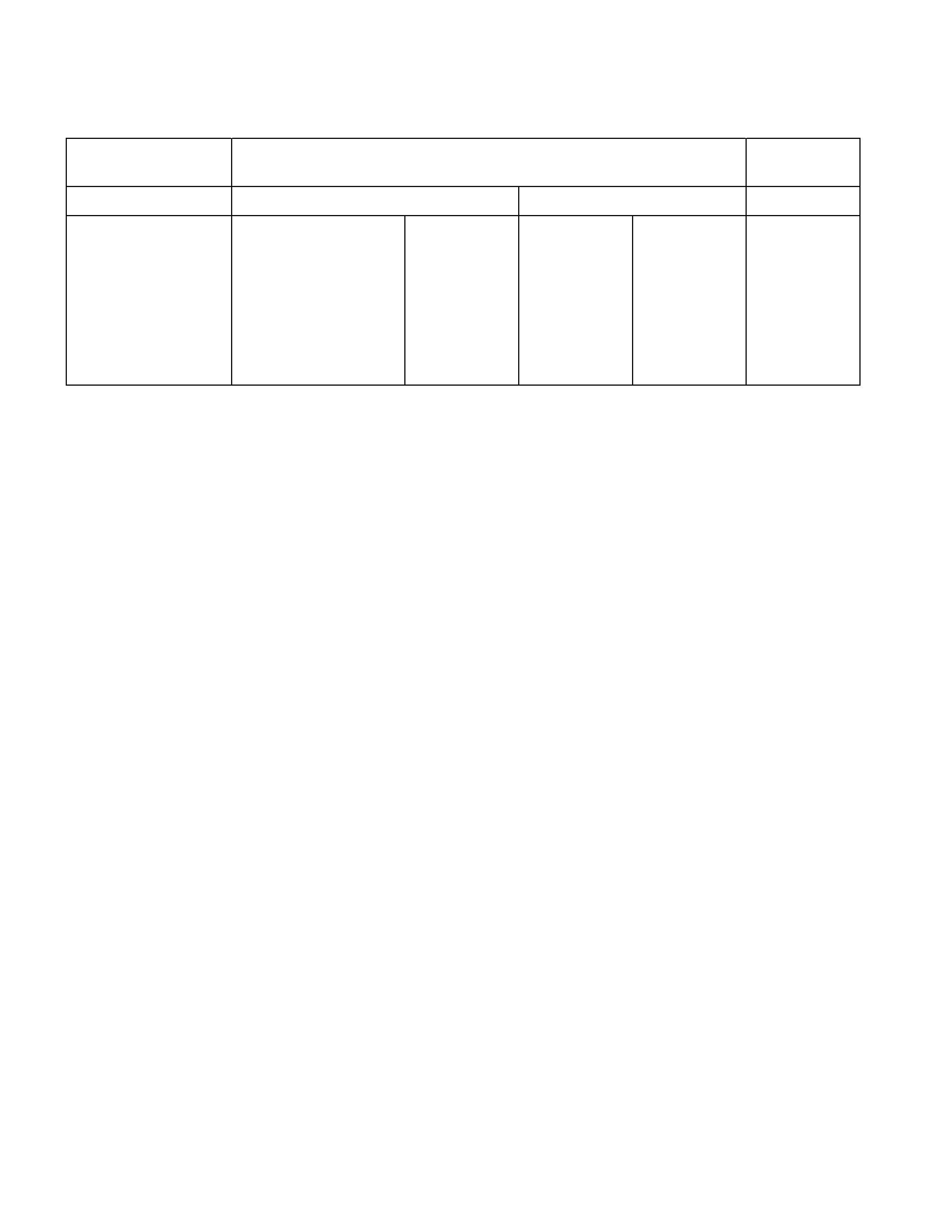
Tire Size and Pressure
Item 4×2 Model 4×4 Model
EXC HIGH RIDE SUS HIGH RIDE SUSPENSION
Tyre Size
Wheel Size
Tyre Pressure
Front (kPa)
Rear (kPa)
195R14C
8PR 106/104Q
14 x 5.5J
250 kPa
450 kPa
215/70R15C
106/104S
15 x 6.5JJ
225 kPa
375 kPa
225/75R15C
110/108S
15 x 6.5JJ
225 kPa
325 kPa
245/70R16
111S
16 x 7JJ
200 kPa
280 kPa
245/70R16
111S
16 x 7JJ
200 kPa
280 kPa
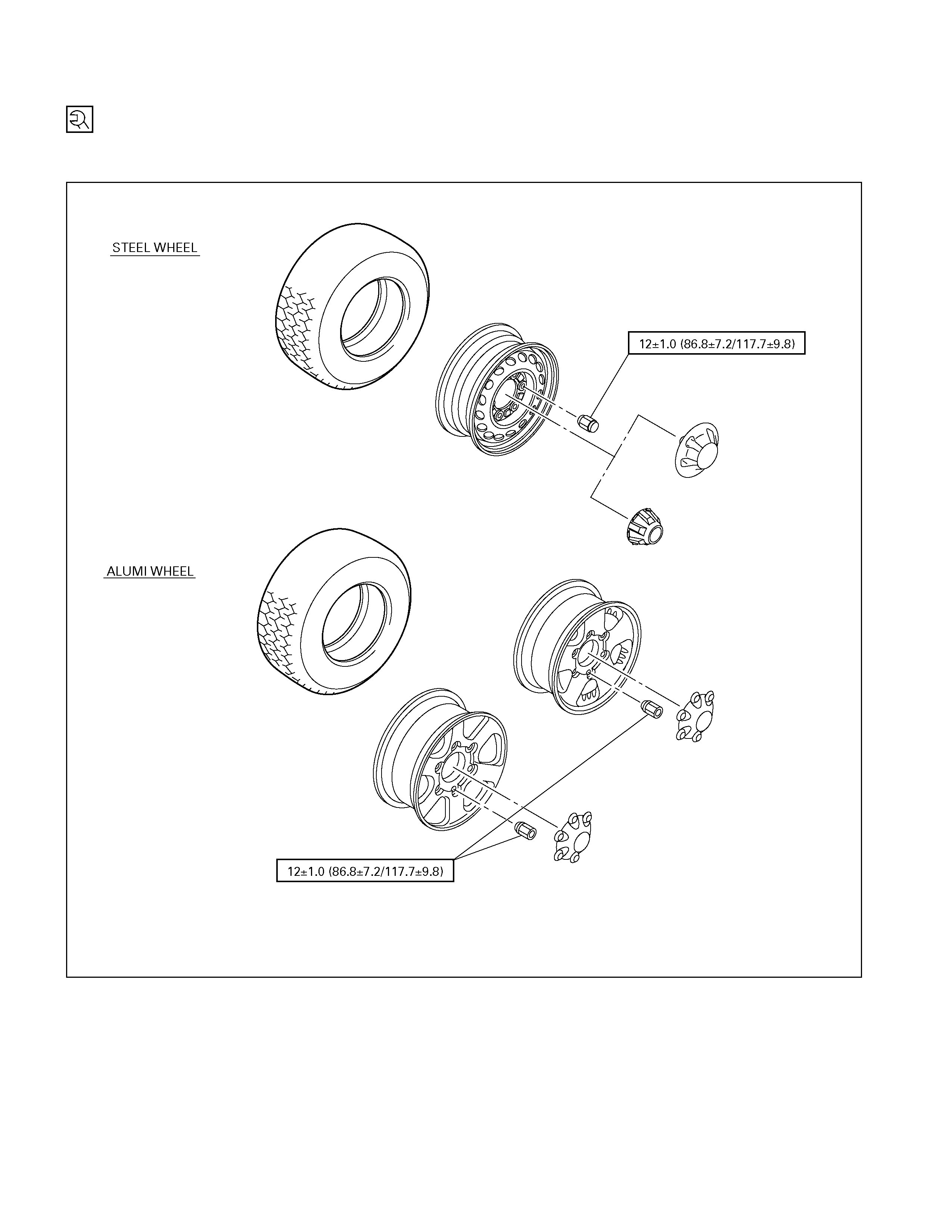
Torque Specifications
Special Parts Fixing Nuts And Bolts
WHEELS AND TIRES kgf⋅m (lb⋅ft/N⋅m)
Wheels And Tires
General Description
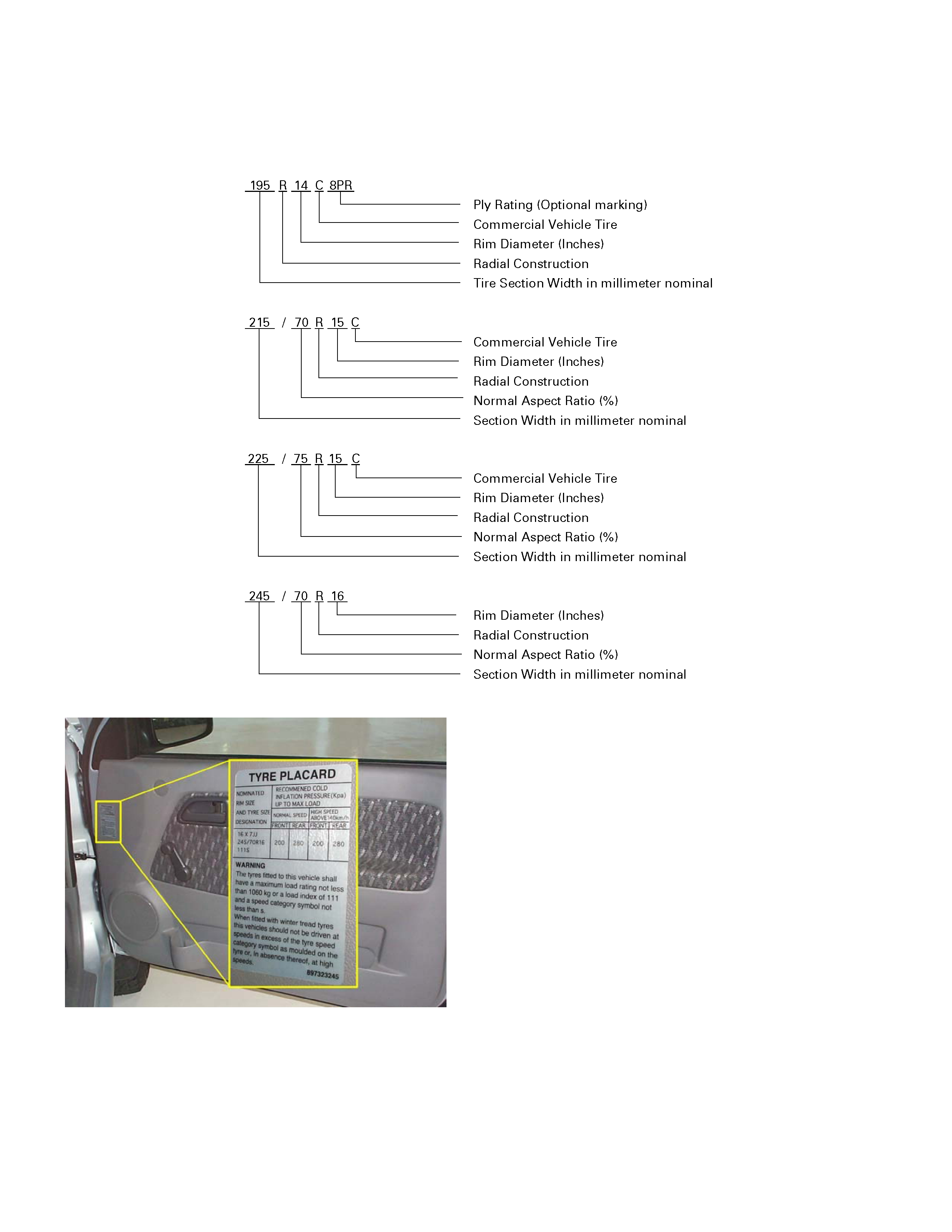
TIRE DESIGNATION
TYRE PRESSURE LABEL (LOCATION : DRIVERS DOOR TRIM)
Note :
• The air pressure of the tire should be maintained as indicated in the label instruction on the driver's door or
frame of driver's door.
Lower pressure can cause burst and adverse vehicle handling.
On the other hand, higher pressure can cause shock-burst and reduce gripping effect.
Servicing
Servicing refers to general maintenance procedures to be performed by qualified service personnel.
WHEEL NUT TORQUES
Wheel Nut Torque kgf⋅m(lb⋅ft/N⋅m)
12.0 ± 1.0 (86.8 ± 7.2 / 117.7 ± 9.8)
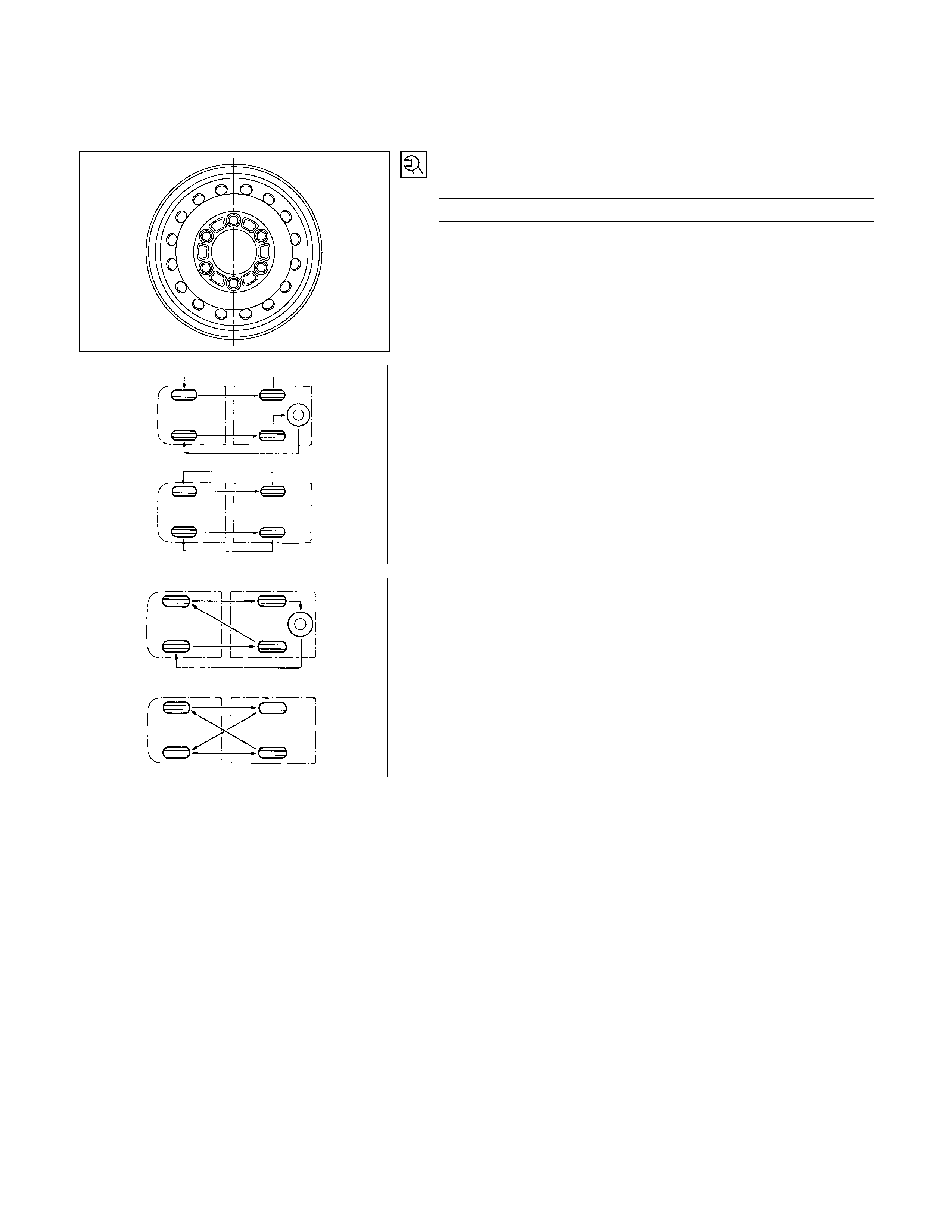
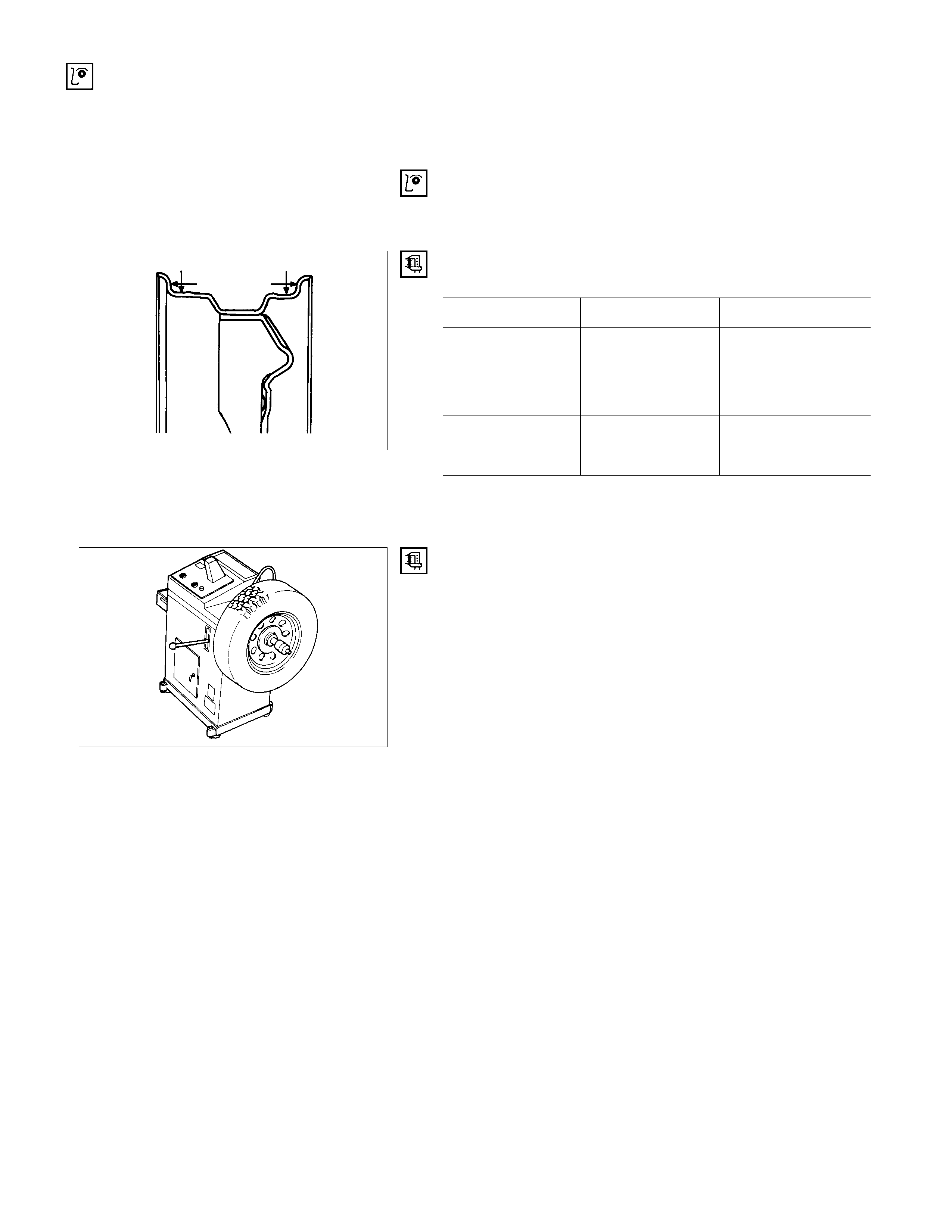
TIRE ROTATION
For rotation of radial tires, interchange the front and the rear
wheels on the same side as shown in the figure.
If one-sided tire wear appears on radial tires, rotate the wheels
as shown in the figure.
Note:
After rotation, adjust the front and rear tire pressure and be sure to check wheel nut tightness.
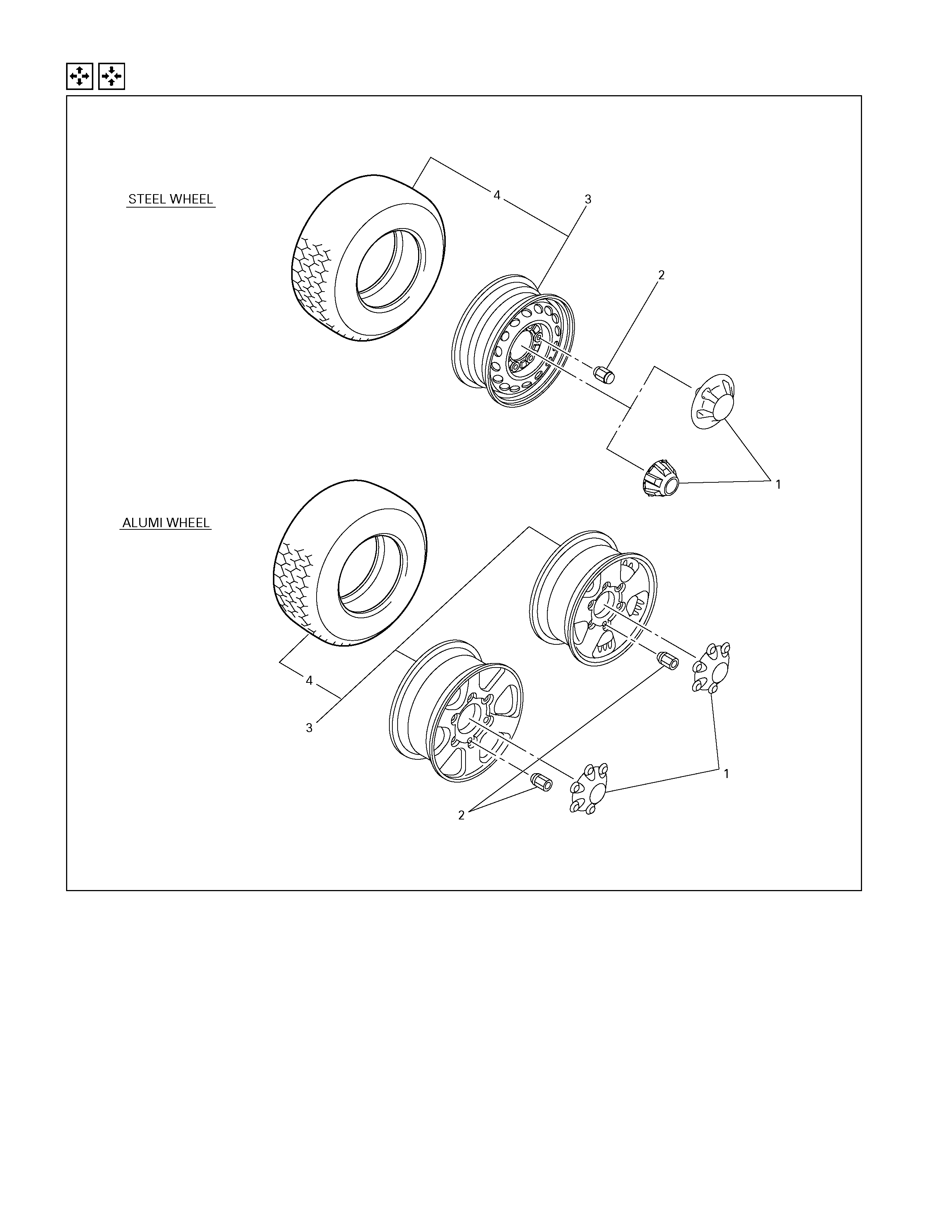
Disassembly And Reassembly
Disassembly Steps
(for Alumi models)
1. Wheel cap
2. Wheel nut
3. Wheel and tire assembly
4. Tire assembly
(for Steel models)
1. Wheel nut
2. Wheel cap
3. Wheel and tire assembly
4. Tire assembly
Reassembly Steps
(for Alumi models)
4. Tire assembly
3. Wheel and tire assembly
2. Wheel nut
1. Wheel cap
(for Steel models)
4 Tire assembly
3. Wheel and tire assembly
2. Wheel cap
1. Wheel nut
Inspection And Repair
Carryout necessary repairs or parts replacement if wear, damage or any other abnormal conditions are found through
inspection.
Visual Check
Inspect all disassembled parts for wear, damage or other
abnormal conditions.
Measure Wheel Runout
mm
Wheel Ty pe Radial Lateral
14 inch St eel
15 inch St eel
16 inch St eel
Less than 1.0 Less than 1.0
15 inch Alumi
16 inch Alumi Less than 0.4 Less than 0.55
If the measured value exceed the specified limit, the wheel
must be replaced.
Balancing Wheel and Tire
On-vehicle Balancing
On-Vehicle balancing methods very with equipment and tool
manufacturers. Be sure to follow each manufacturer’s
instructions during balancing operation.
Off- vehicle Balancing
Most electronic off-vehicle balancers are more accurate than
the on-vehicle spin balancers. They are easy to use and give
a dynamic balance. Although they do not correct for drum or
disc unbalance (as on-vehicle spin balancing does), they are
very accurate.
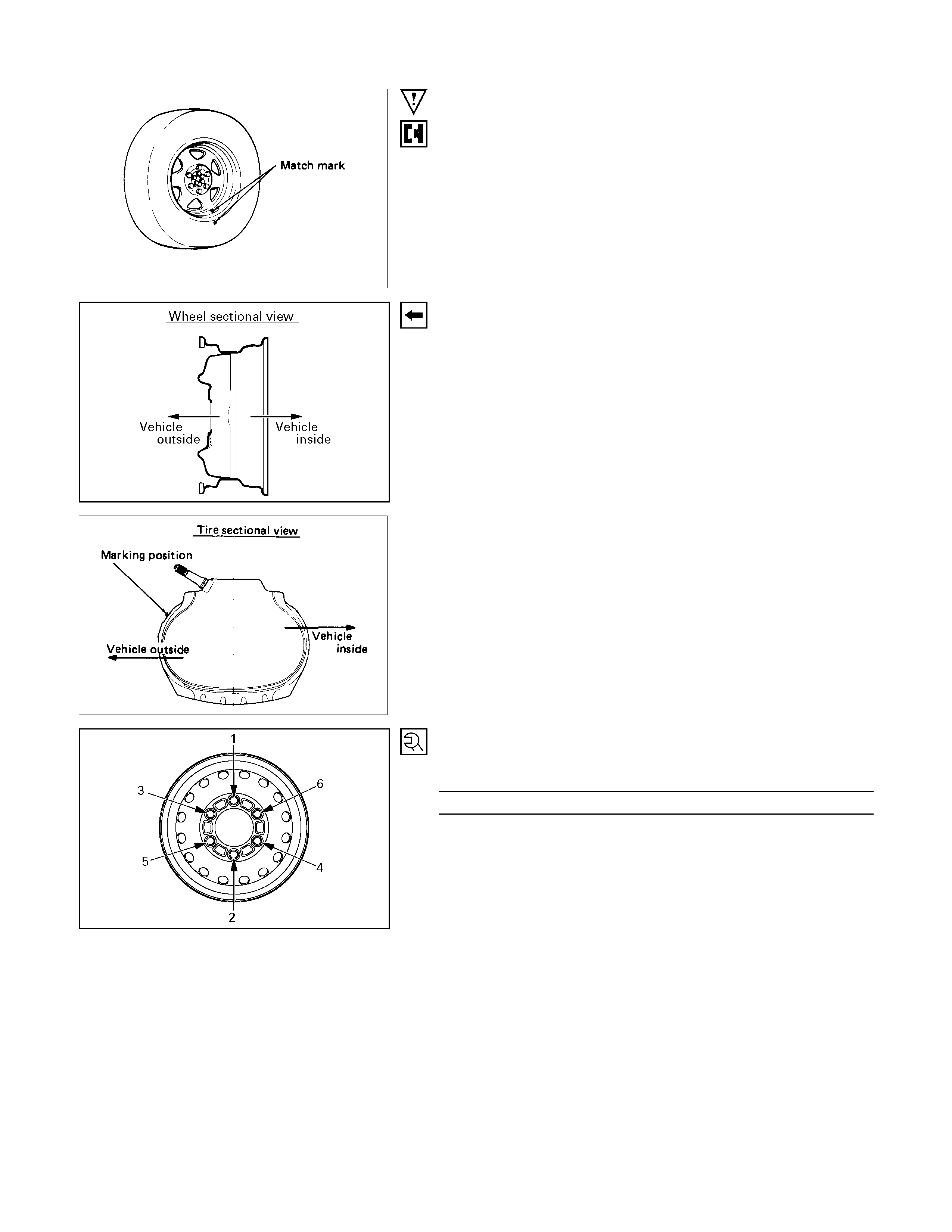
Important Operations
1. Tire Assembly
To assemble align the match mark (approx. 10mm diameter
paint mark) of wheel with the match mark (approx. 8mm
diameter red paint mark) of tire. If the match mark at wheel
has disappeared, align with air valve.
2. Wheel and Tire Assembly
3. Wheel Nut
Tighten wheel nuts in numerical order.
Wheel Nut Torque kgf⋅m (lb⋅ft/N⋅m)
12.0 ± 1.0 (86.8 ± 7.2 / 117.7 ± 9.8)
Troubleshooting
Typical examples of abnormal tire tread wear and major causes :
CAUTION:
Similar wear patterns can be caused by worn suspension parts, misalignment of wheels and tires, and other
suspension related problems.
Spotty wear - wear localized
on shoulder section. In
extreme cases, the tire
becomes polygonal in shape.
Tire or wheel out of
round or distorted. Hub or knuckle out
of round or distorted. Play in hub bearings
or ball joints. Rotating parts out of
balance.
Tread wear one-sided.
Rotating parts out of
balance. Tire or wheel out of
round. Hub or knuckle out
of round or distorted.
Localized tread wear.
Once spotty wear develops in
tread due to hard braking or
abrupt starting, localized wear
tends to be accelerated.
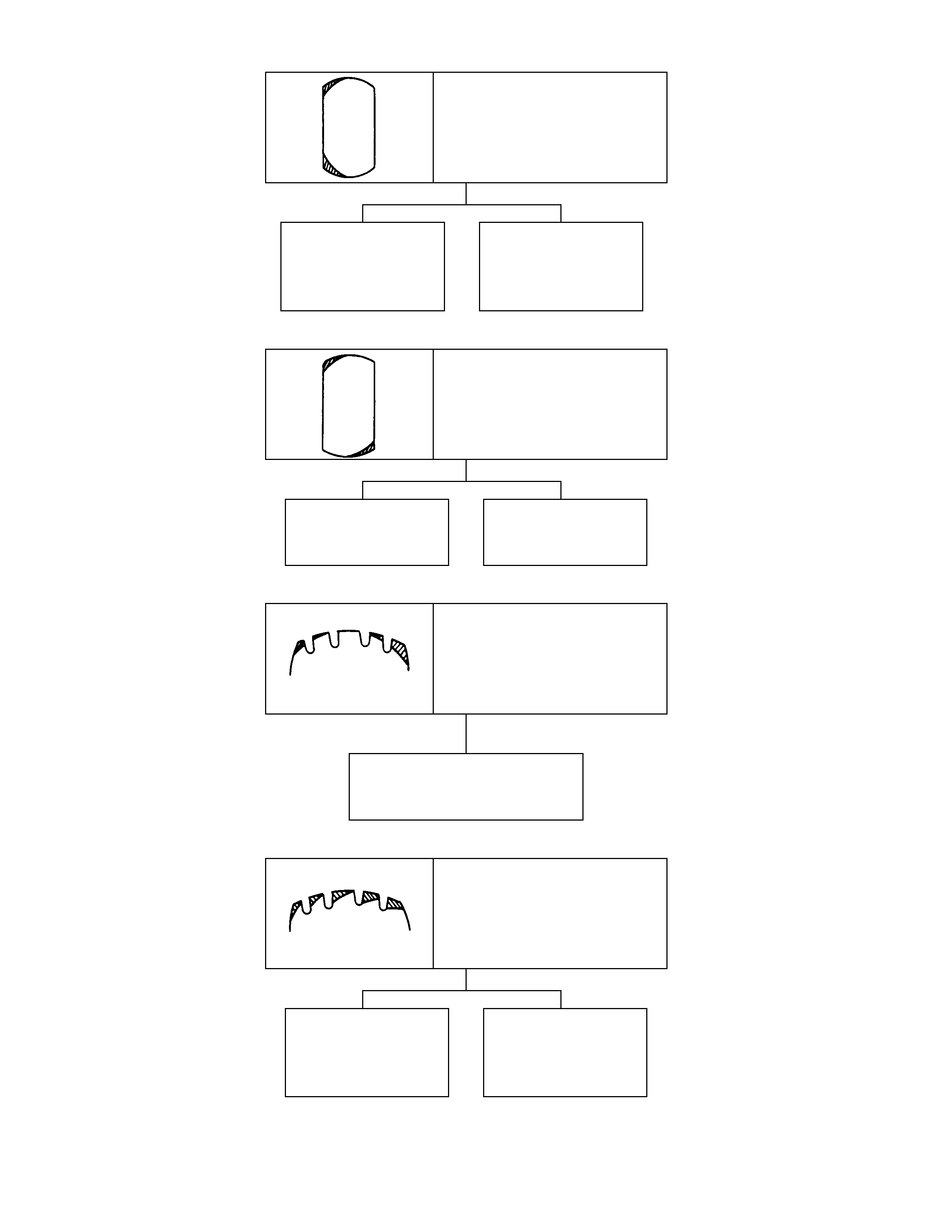
Shoulder wear (generally
wear develops on outer
shoulder).
Camber or toe-in
incorrect. Shoulder wear
caused by repeated
hard-cornering.
Wear on shoulders at points
opposed to each other.
Tire or wheel out of
round or distorted. Play in bearings or
ball joint.
Premature wear on
shoulders.
Flexing of tire excessive due
to under-inflation.
One-sided feather edging.
Wear caused by
repeated hard-
cornering.
Camber or toe-in
incorrect.
