SECTION 6C2-2A - DIAGNOSTIC CHARTS
CAUTION
This vehicle will be equipped with a Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). A SRS
will consist of either seat belt pre-ten sioners and a driv er’s side air bag, or seat b elt
pre-tensioners and a driver’s and front passenger’s side air bags. Refer to
CAUTIONS, Section 12M, before performing any service operation on or around SRS
components, the steering mechanism or wiring. Failure to follow the CAUTIONS
could result in SRS deployment, resulting in possible personal injury or
unnecessary SRS system repairs.
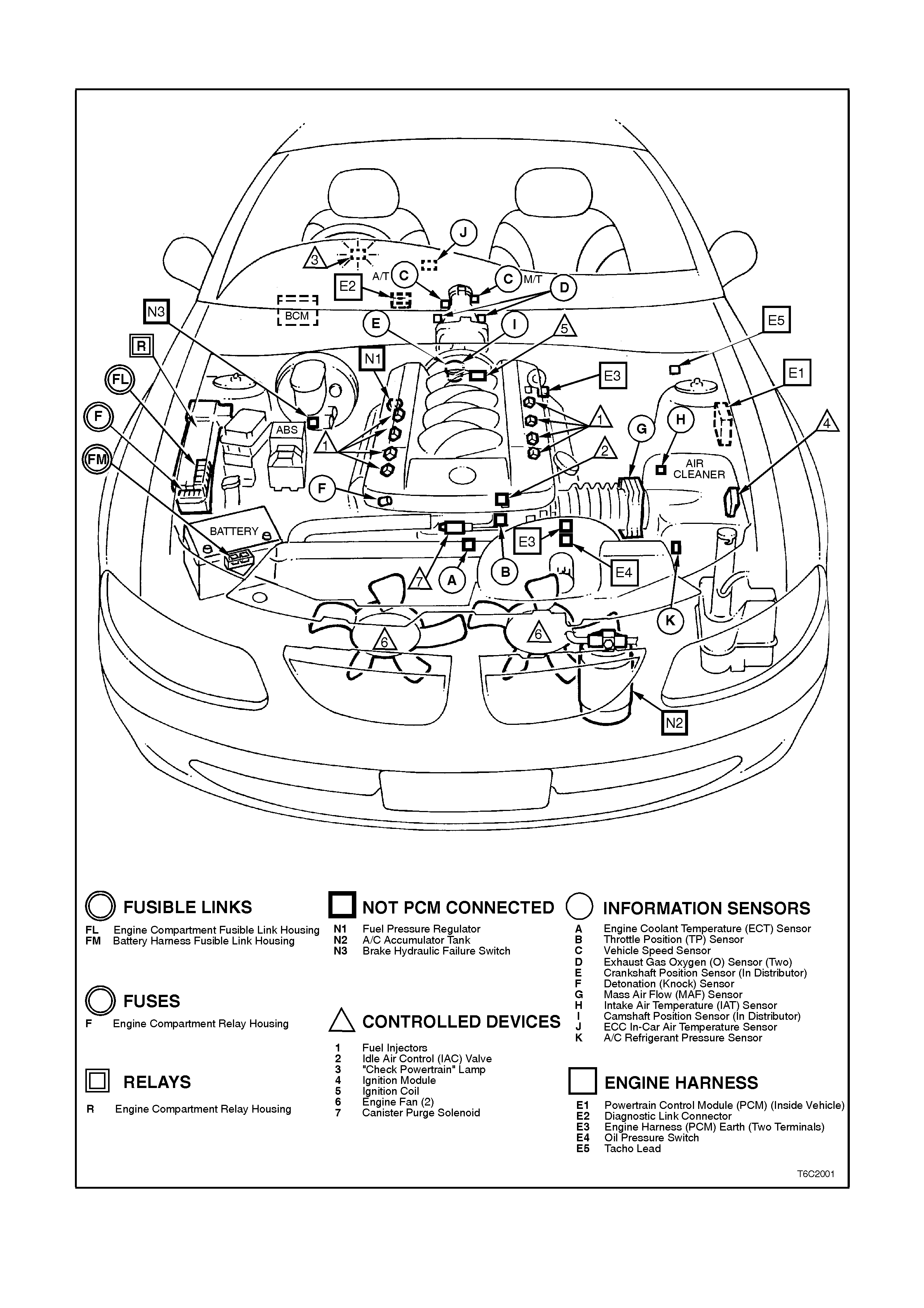
SYSTEM COMPONENT LOCATIONS
Figure 6c2-2A-1 Engine Compartment Component Locations
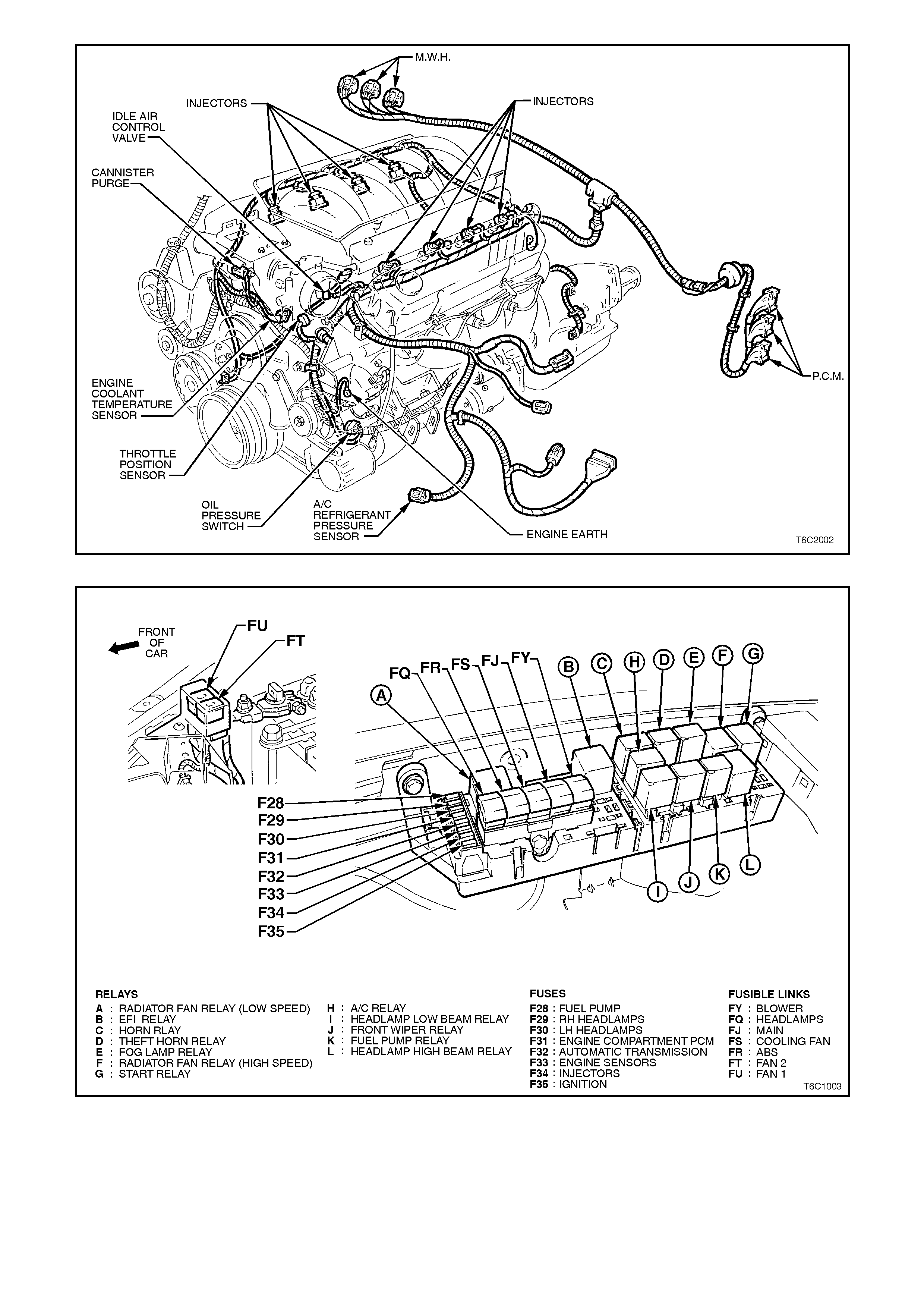
Figure 6C2-2A-2 System Component Locations
Figure 6C2-2A-3 Power Distribution Center
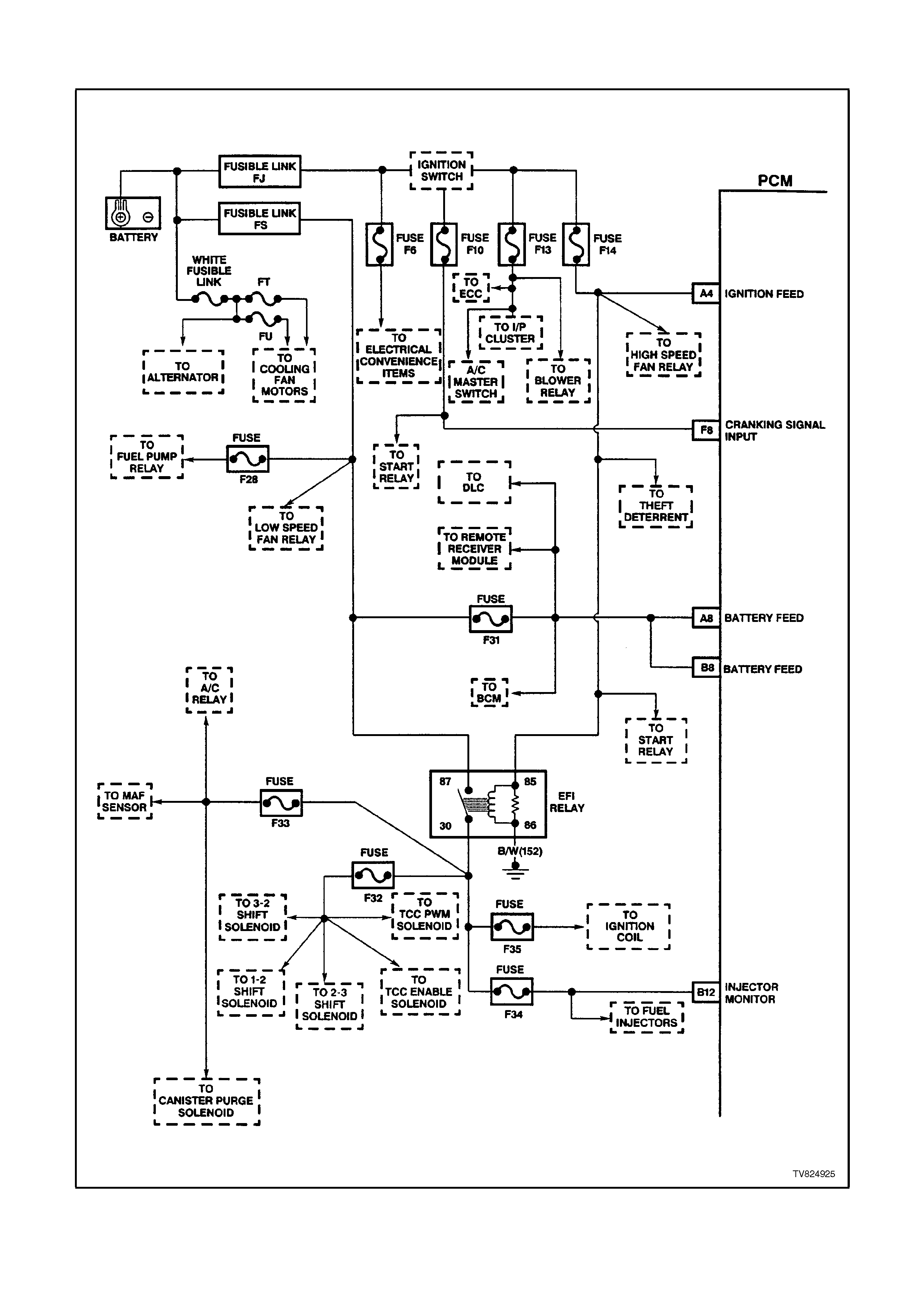
PCM WIRING DI AGRAMS
Figure 6C2-2A-4 PCM wiring diagram 1 of 8
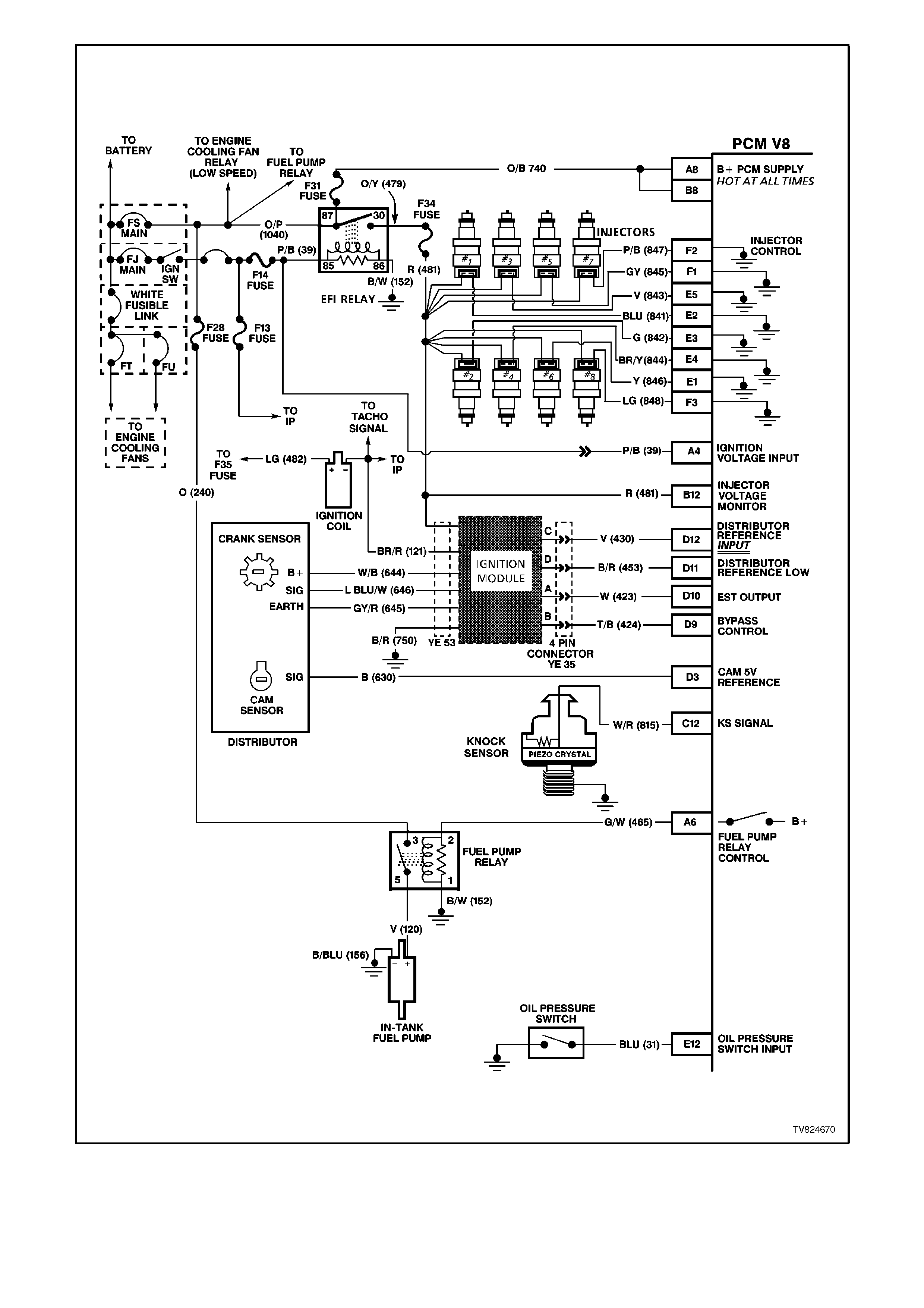
Figure 6C2-2A-5 PCM Wiring Diagram 2 of 8
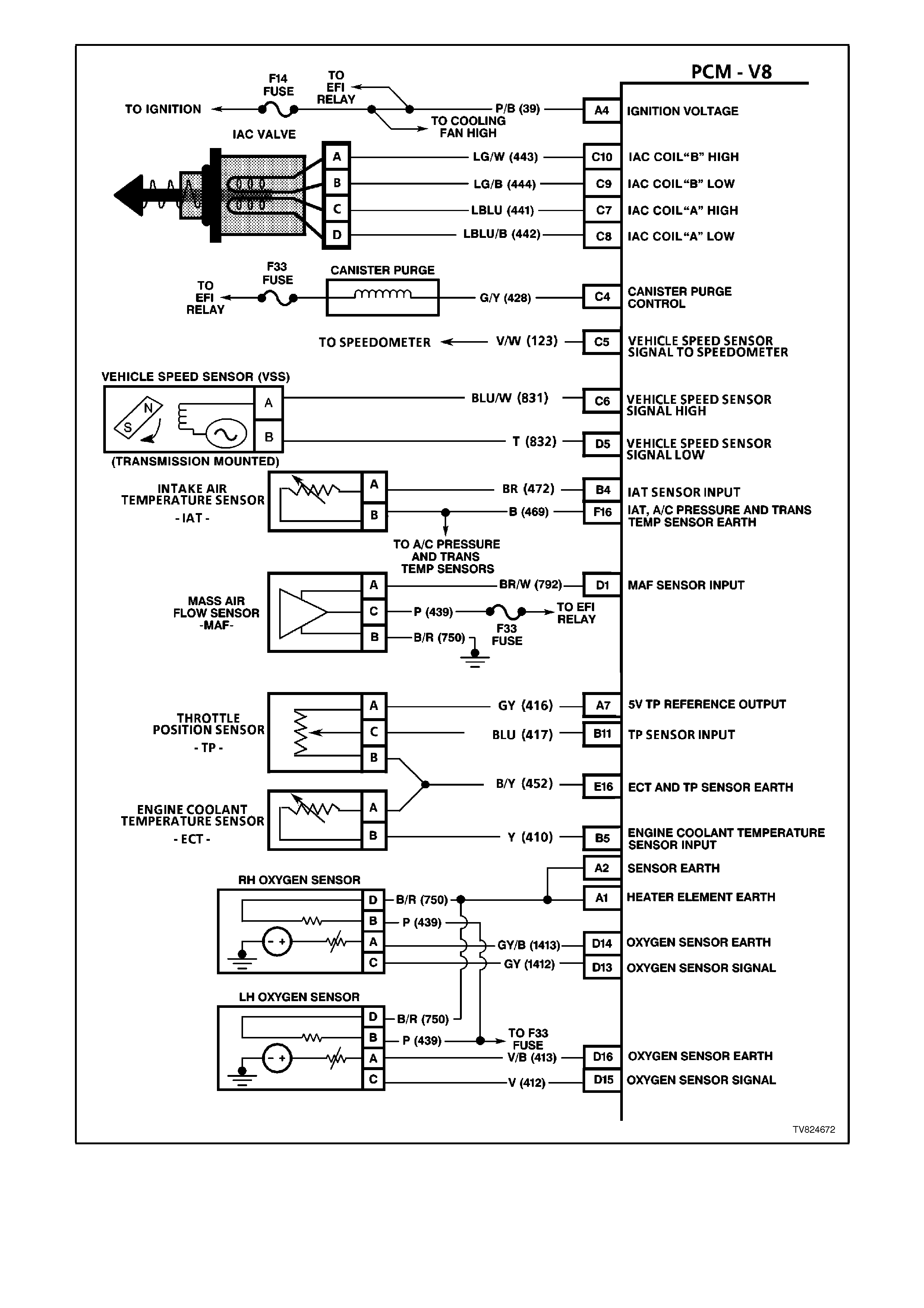
Figure 6C2-2A-6 PCM Wiring Diagram 3 of 8
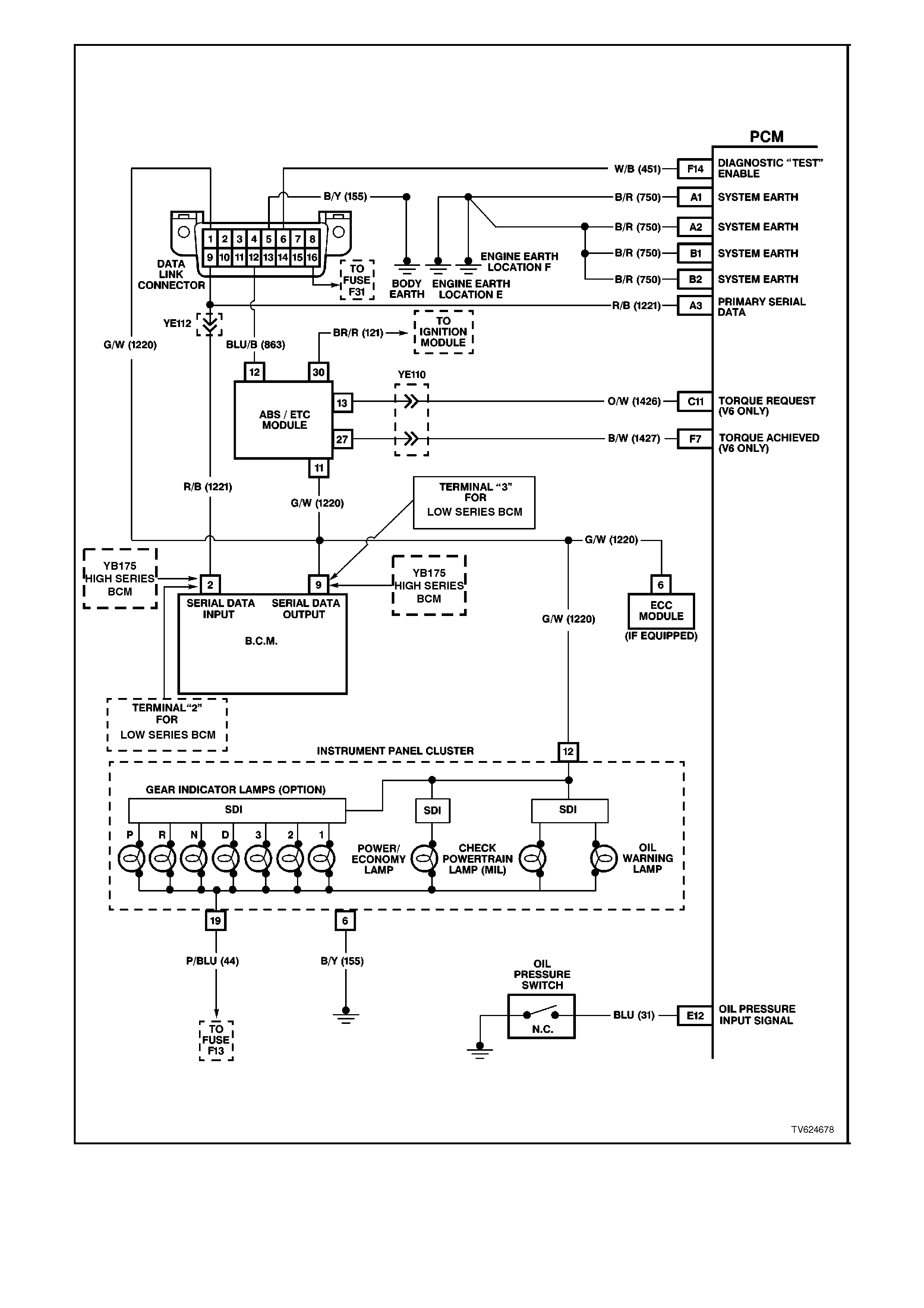
Figure 6C2-2A-7 PCM Wiring Diagram 4 of 8
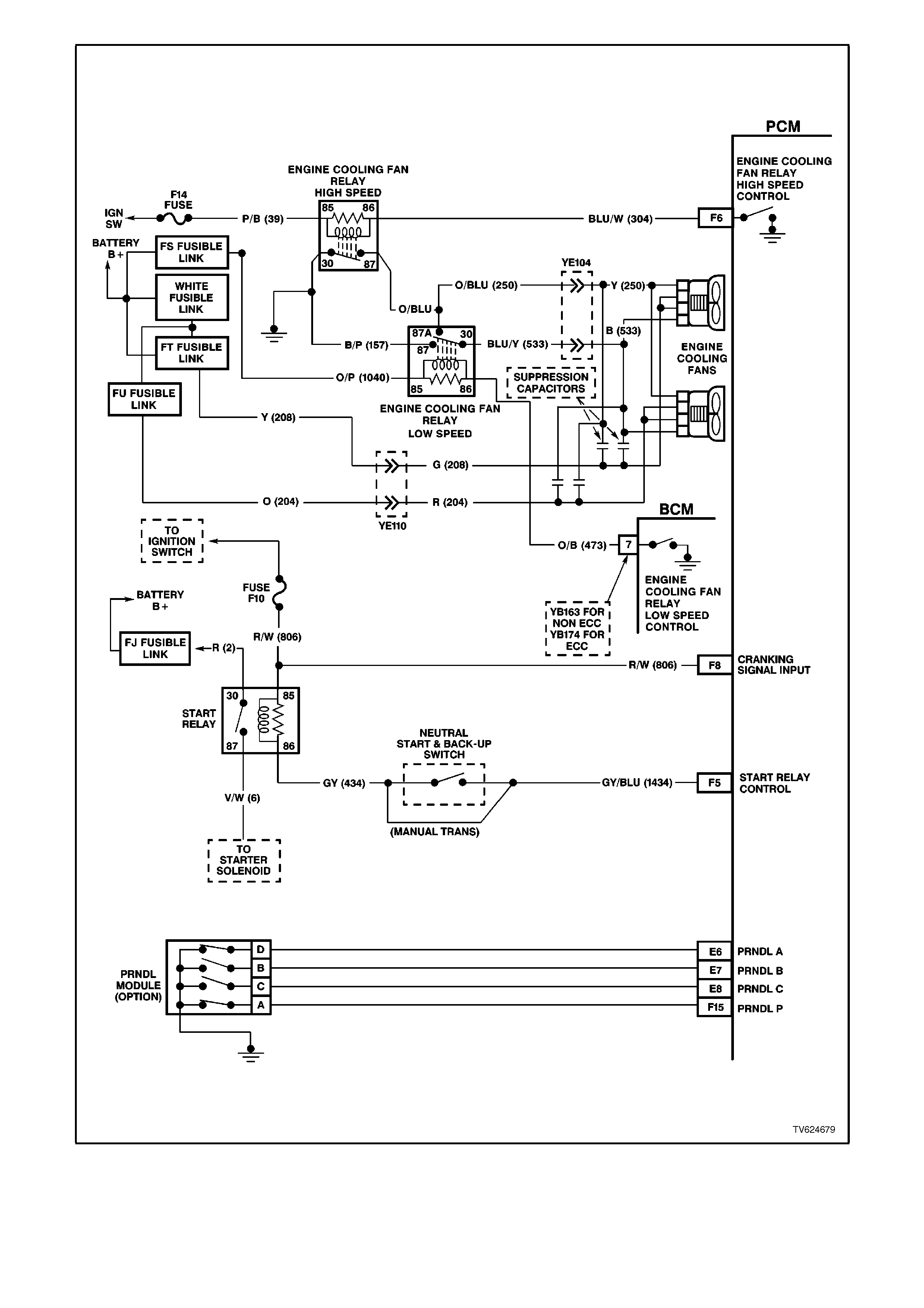
Figure 6C2-2A-8 PCM Wiring Diagram 5 of 8
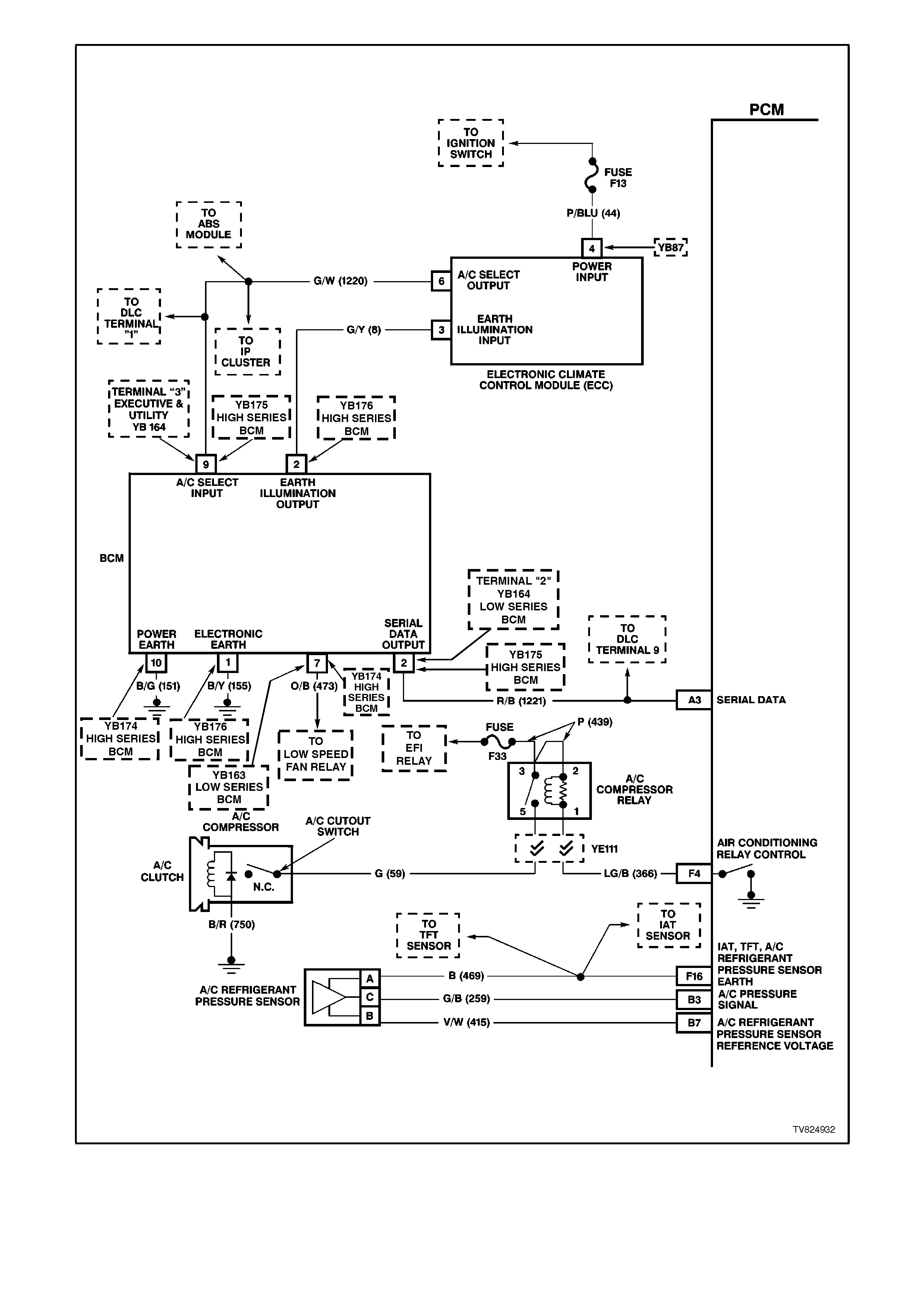
Figure 6C2-2A-9 PCM Wiring Diagram 6 of 8
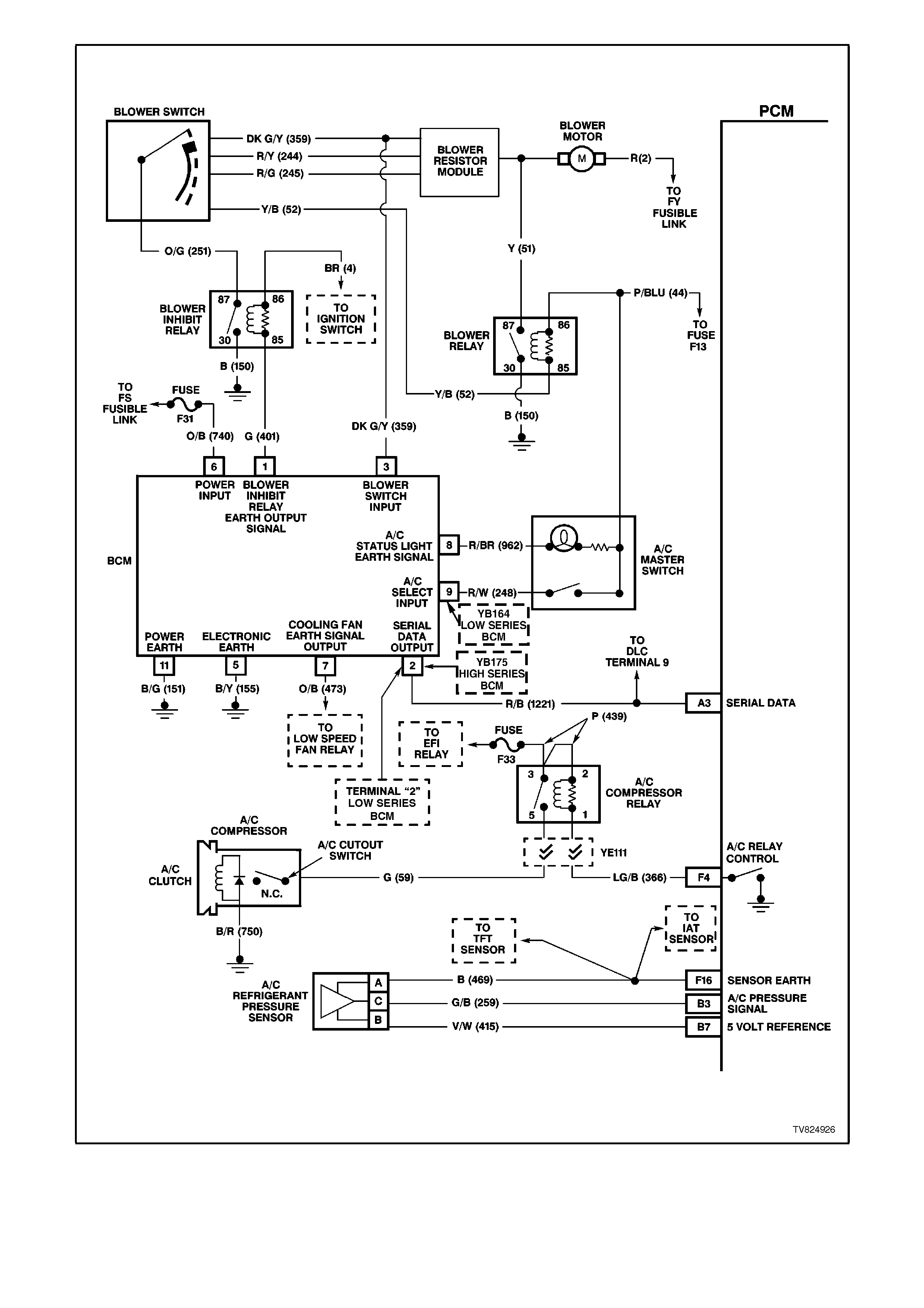
Figure 6C2-2A-10 PCM Wiring Diagram 7 of 8
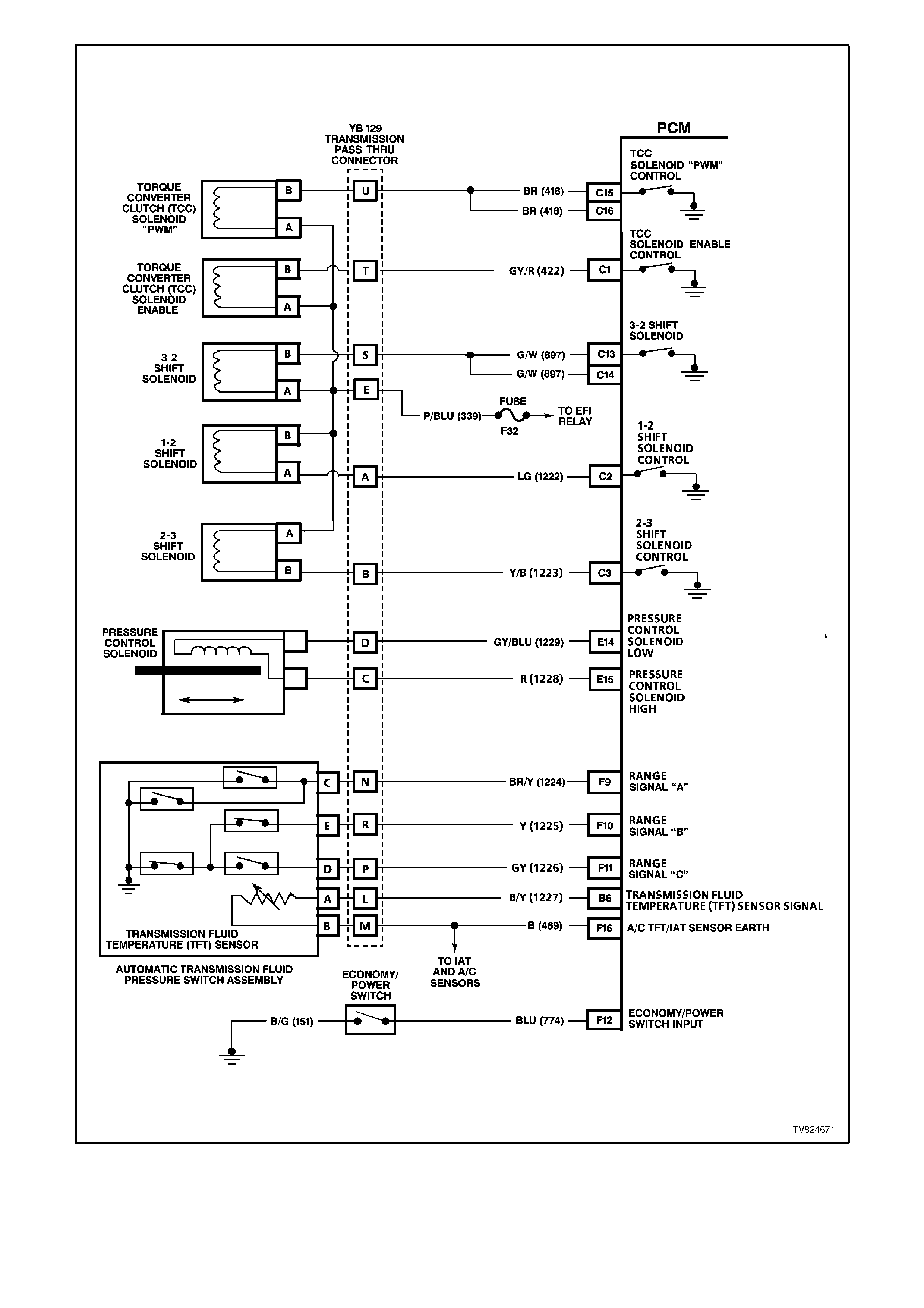
Figure 6C2-2A-11 PCM Wiring Diagram 8 of 8
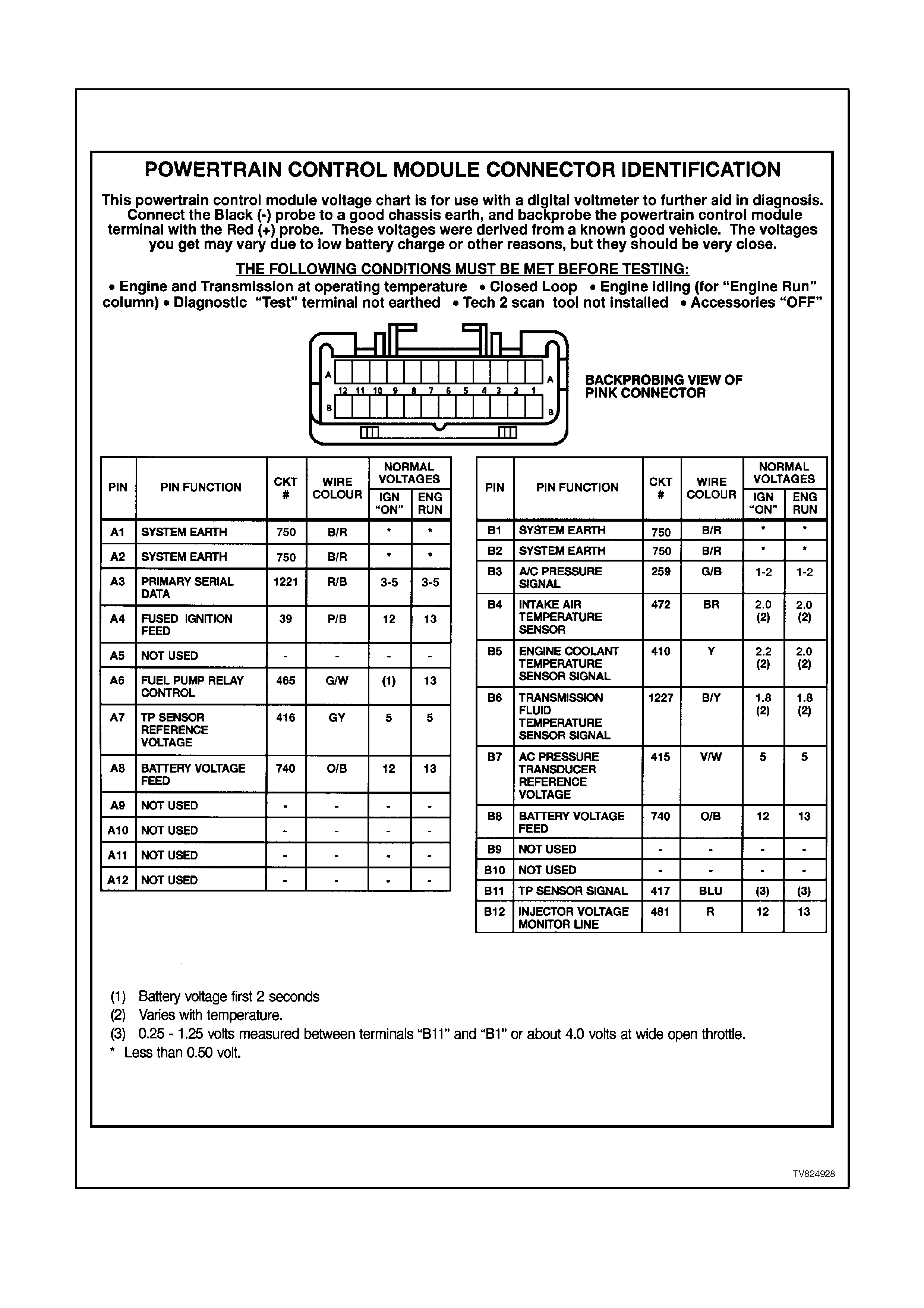
PCM CONNECTOR IDENTIFICATION AND VOLTAGES
Figure 6C2-2A-12 PCM Connector Identification and Voltages 1 of 3
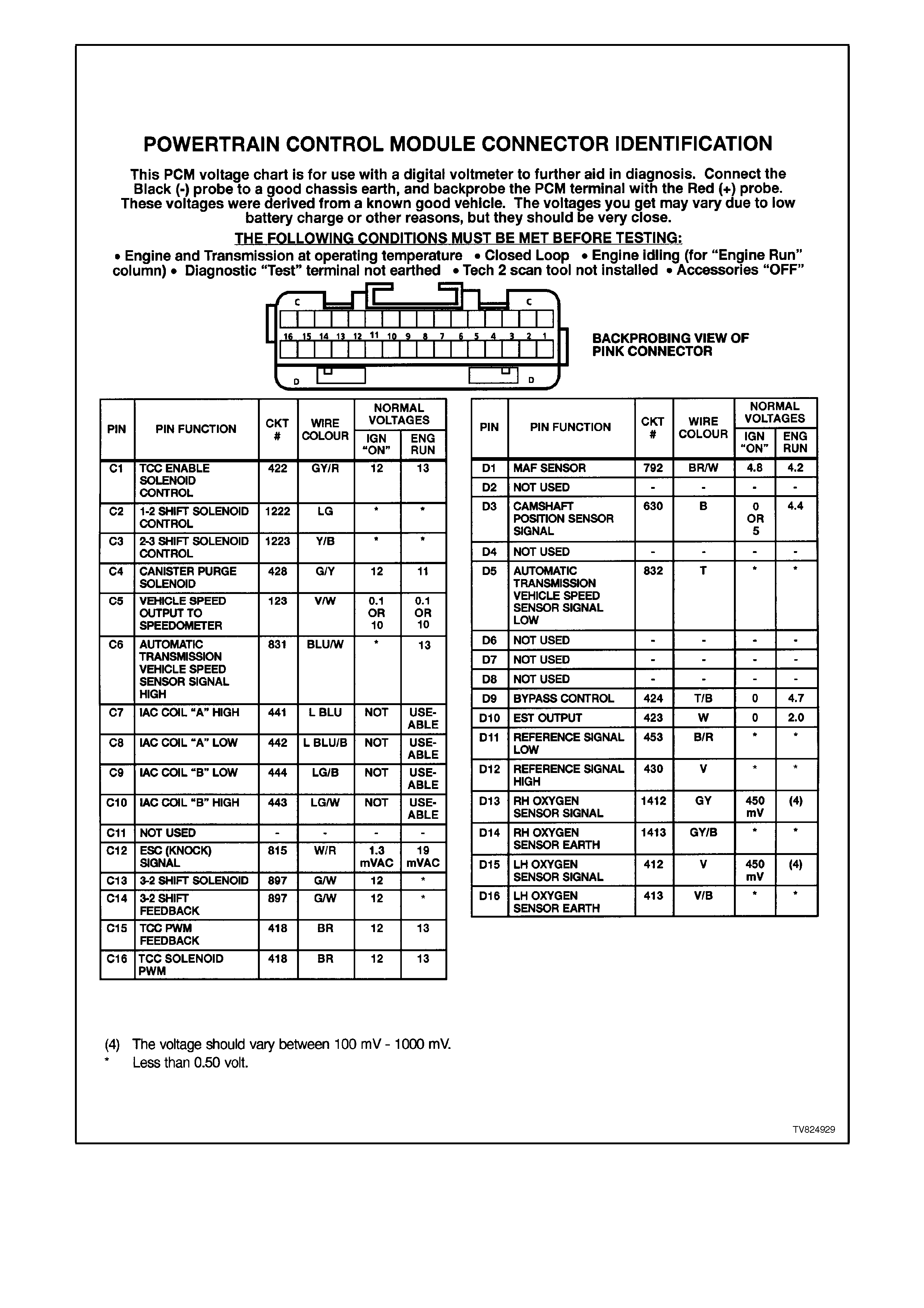
Figure 6C2-2A-13 PCM Connector Identification and Voltages 2 of 3
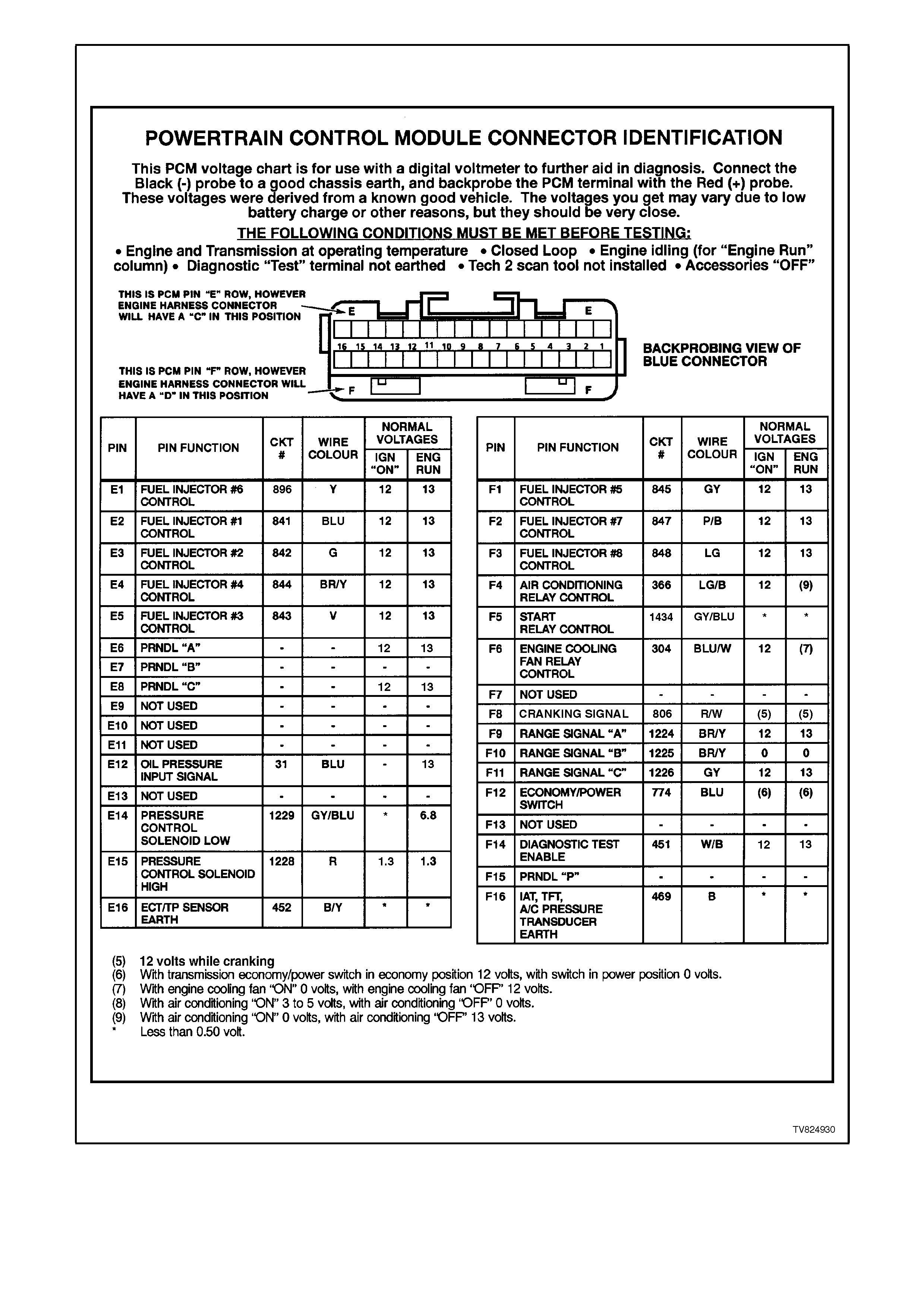
Figure 6C2-2A-14 PCM Connector Identification and Voltage 3 of 3

PCM CONNECTOR TERMI NAL DEFINITIONS
PINS A1 - A12
A1 SYSTEM EARTH - This terminal should have zero volts. This circuit is connected directly to the engine earth.
A2 SYSTEM EARTH - This terminal should have zero volts. This circuit is connected directly to the engine earth.
A3 SERIAL DATA - This is a dedicated line for the Tech 2 scan tool communications. The circuit connects the
PCM, the ABS and the BCM together. The Tech 2 scan tool communicates to these modules by sending a
message to the module and requesting the module to respond. The normal voltage on this circuit is about 5
volts. When the Tech 2 scan tool is communicating with a module the voltage will be around 2.5V.
A4 IGNITION FEED - This is the ON signal to the PCM from the ignition switch circuit. The ignition feed is not the
"power supply" to the PCM. The ignition feed only tells the PCM that the ignition switch is "ON." The voltage
should be equal to the battery voltage when the key is in either the "run" or the "crank" position.
A5 NOT USED
A6 FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL - Whenever the ignition is turned ON the PCM energises the fuel pump
relay. If no crankshaft reference input pulses are received, the PCM turns OFF the relay. As soon as the PCM
receives crankshaft reference pulses, the PCM will turn the fuel pump relay back on.
A7 TP SENSOR 5V REFERENCE VOLTAGE - This voltage should always be 5 volts whenever the ignition is
"ON." The reference voltage is a regulated voltage from the PCM, and supplies 5 volts to the TP sensor.
A8 BATTERY VOLTAGE FEED - This supplies the PCM with full-time B+ volts. This circuit stays hot even when
the ignition is turned off. The battery voltage feed circuit receives it's voltage from the ENGINE fuse circuit.
A9 NOT USED
A10 NOT USED
A11 NOT USED
A12 NOT USED
PINS B1 - B12
B1 SYSTEM EARTH - This terminal should have zero volts. This terminal is connected directly to the engine
earth.
B2 SYSTEM EARTH - This terminal should have zero volts. The terminal is connected directly to the engine earth.
B3 A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER INPUT SIGNAL - The signal that is sent from the pressure transducer to the
PCM indicates to the PCM what the A/C pressure is. Depending on the A/C pressure, this signal will indicate
to the PCM if the A/C pressure is to low or to high.
B4 IAT SENSOR SIGNAL INPUT - The PCM sends a 5 volt reference to the IAT sensor. The sensor is connected
to earth. The signal voltage will vary according to incoming air temperature.
B5 ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL INPUT - The PCM sends a 5 volt signal voltage to
the engine coolant temperature sensor. The ECT sensor is also connected to earth. The voltage will vary with
engine coolant temperatures.
B6 TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR SIGNAL - The PCM sends out a 5 volt signal
voltage to the transmission fluid temperature sensor. The sensor, being also connected to earth, will cycle the
voltage according to transmission fluid temperature. As the fluid temperature increases, the voltage seen on
terminal D15 will decrease.
B7 A/C SENSOR 5V REFERENCE VOLTAGE - This voltage should always be 5 volts whenever the ignition is
ON. It is a regulated voltage output from the PCM, and supplies 5 volts to the A/C sensor.
B8 BATTERY VOLTAGE FEED - This supplies the PCM with full time B+. This circuit stays hot even when the
ignition is turned off. It receives its voltage from the "ENGINE" fuse circuit.
B9 B10 - NOT USED
B11 TP SENSOR SIGNAL INPUT - The TP Sensor input voltage varies from 0 to 5 volts. Typically the voltage is
less than 1.25 volt at idle, and greater than 4-volts at wide open throttle.
B12 INJECTOR VOLTAGE MONITOR LINE - The injector voltage monitor line is used so that the PCM will know
the exact voltage that the fuel injectors are operating. This voltage is used to control the pulse width modulation
of the fuel injectors.

PINS C1 - C16
C1 NOT USED
C2 1-2 SHIFT SOLENOID CONTROL - The PCM either opens or earths the 1-2 shift solenoid. When the PCM
provides a path to earth, the 1-2 shift solenoid is considered ON and the voltage should read 0 volts.
C3 2-3 SHIFT SOLENOID CONTROL - The PCM either opens or earths the 2-3 shift solenoid. When the PCM
provides a path to earth, the 2-3 shift solenoid is considered ON and the voltage should read 0 volts.
C4 CANISTER PURGE - Grounds the canister purge valve circuit to enable the purging of the canister.
C5 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL - The PCM alternately earths this signal when the drive wheels are
turning. This pulsing action takes place about 6250 times per kilometre. The speedometer, the BCM and the
trip computer will calculate the vehicle speed based on the time between pulses.
C6 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED INPUT SIGNAL HIGH
The transmission has an output shaft speed sensor used by the PCM to calculate vehicle speed, and to help
determine various automatic transmission shifting functions. It is a magnetic inductive sensor that generates an
AC voltage signal sent to the PCM. If measured with the digital AC voltmeter, no voltage will appear until the
output shaft begins turning.
C7, C8, C9,C10
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE - These circuits control the positioning of the pintle valve which is located
inside the IAC valve. The voltage on this circuit is difficult to predict because of so many variables.
C11 NOT USED
C12 ESC (KNOCK) SIGNAL - The knock sensor is used to detect engine detonation, and the PCM will retard the
Electronic Spark Timing (EST) based on the signal being received.
C13 3-2 SHIFT SOLENOID - The 3-2 shift solenoid is normally closed, and is pulse width modulated. The 3-2
control solenoid controls the 3-2 down shift. The PCM operates the 3-2 shift solenoid at a frequency of 50 Hz.
The solenoid is constantly fed B+ voltage. The PCM controls the time the path to earth is closed or opened.
C14 3-2 SHIFT SOLENOID FEEDBACK CIRCUIT The 3-2 shift solenoid is a normally closed solenoid which is
used to control the 3-2 down shift. The solenoid is constantly fed B+ and the PCM controls the time the path to
earth is closed. The PCM does this to provide a smooth 3-2 down shift. If the PCM senses an incorrect voltage
on this circuit when controlling the 3-2 down shift solenoid (i.e. - 0 volts with the solenoid OFF, or 12 volts with
the solenoid ON) a DTC 66 will set.
C15 TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ENABLE SOLENOID - The Torque converter clutch apply solenoid is used
to smoothly engage the torque converter clutch. By varying the solenoids duty cycle, the PCM can slowly
engage the torque converter clutch, which allows a smooth TCC engagement. If the PCM senses an incorrect
voltage on this circuit when controlling the TCC PWM solenoid (i.e. - 0 volts with the solenoid OFF, or 12 volts
with the solenoid ON) a DTC 83 will set.
C16 TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH - PULSE WIDTH MODULATED APPLY SOLENOID CONTROL
AUTO TRANS ONLY
The PCM uses the pulse width modulated TCC apply solenoid to smoothly engage the torque converter clutch,
after the TCC enable solenoid is energised. By varying the duty cycle pulse width modulation, the PCM can
slowly engage the torque converter clutch, allowing very smooth TCC engagement.

PINS D1 - D16
D1 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) INPUT SIGNAL -
The PCM supplies a 5-volt signal voltage to the mass air flow sensor on this circuit. The mass air flow sensor
pulses the 5-volt signal to earth. These ground pulses occur at a very fast rate - from less than 500 per second
(500 Hz) with no airflow through the sensor, to upwards of many thousands of pulses per second at high air
flow rates such as during acceleration. If measured, the voltage seen will be between 0.5 and 4.5 volts,
depending on air flow through the sensor.
D2 NOT USED
D3 CAMSHAFT POSITION INPUT SIGNAL -
This signal is used by the PCM to sequence the fuel injectors, similar to the firing order of an engine. This
allows the PCM to operate the fuel injectors in a sequential fuel injection mode.
D4 NOT USED
D5 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED INPUT SIGNAL LOW -
The transmission has an output shaft speed sensor used by the PCM to calculate vehicle speed, and to help
determine various automatic transmission shifting functions. It is a magnetic inductive sensor that generates an
AC voltage signal sent to the PCM. If measured with the digital AC voltmeter, no voltage will appear until the
output shaft begins turning.
D6 NOT USED
D7 NOT USED
D8 NOT USED
D9 IGNITION MODULE BYPASS CONTROL - With the ignition ON and the engine OFF this terminal will have
very low voltage. As soon as the PCM receives engine RPM over 450 RPM (engine "run" threshold) the PCM
twill send 5 volts to the Ignition Module Bypass Circuit.
D10 ELECTRONIC SPARK TIMING (EST) OUTPUT - This terminal will have very low voltage with the ignition ON
and engine OFF. With the engine at idle, the voltage should be slightly more than 1 volt. As the engine RPM
increases, this voltage will also increases.
D11 REFERENCE SIGNAL LOW - This terminal should always be zero volts. This circuit is connected through the
ignition module to engine earth.
D12 REFERENCE SIGNAL HIGH - This terminal could be called the tach input. It provides the PCM with RPM and
crankshaft position information. With the ignition ON and engine OFF, the voltage will be either high or low,
depending on crankshaft position. As the crankshaft turns, the voltage will be an average of the two readings.
D13 R/H OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL INPUT - With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, the voltage should be
between 350 and 450 millivolts (.350 -.450 volts). This is the PCM-supplied O2 circuit "bias" voltage. With the
engine running and the O2 sensor in closed loop, the voltage should be changing between 10 - 1000 millivolts
(.010 - 1.000 volt).
D14 R/H OXYGEN SENSOR EARTH CIRCUIT - This terminal should have zero volts. This circuit is connected
directly to the engine earth. This terminal earths the PCM circuitry for the O2 voltage inside the PCM.
D15 L/H OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL INPUT - With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, the voltage should be
between 350 and 450 millivolts (.350 -.450 volts). This is the PCM-supplied O2 circuit "bias" voltage. With the
engine running and the O2 sensor in closed loop, the voltage should be changing between 10 - 1000 millivolts
(.010 - 1.000 volt).
D16 L/H OXYGEN SENSOR EARTH CIRCUIT - This terminal should have zero volts. This circuit is connected
directly to the engine earth. This terminal earths the PCM circuitry for the O2 voltage inside the PCM.

PINS E1 - E16
E1 FUEL INJECTOR CONTROL - With the engine OFF and the ignition ON, the voltage should be B+. With the
engine running at idle, the charging system increases the battery voltage slightly, so this voltages will increase.
With higher engine RPM or more engine load, the resulting increase in injector pulse frequency or injector
pulse width will cause this voltage to become slightly less.
E2 SAME AS E1
E3 SAME AS E1
E4 SAME AS E1
E5 SAME AS E1
E6 RANGE SIGNAL "A" - The PCM sends out a buffered B+ signal to the pressure switch assembly. The B+
signal must pass through a series of switches to earth. When the switch(es) are closed, the voltage should be
near 0. The PCM monitors this voltage to calculate the position of the manual valve.
E7 RANGE SIGNAL "B"- SAME AS E6
E8 RANGE SIGNAL "C"- SAME AS E6
E9 NOT USED
E10 NOT USED
E11 NOT USED
E12 OIL PRESSURE SWITCH - This is a earth input to the PCM from the Oil Pressure Switch indicating proper oil
pressure when the engine is running. If oil pressure is lost while the engine is running, the oil switch will open
its contacts and the earth signal to the PCM will be removed. When the PCM sees this loss of earth signal, the
PCM will command the oil lamp ON.
E13 NOT USED
E14 TRANSMISSION PRESSURE CONTROL
SOLENOID (PCS) - LOW
AUTO TRANS ONLY
The 4L60-E automatic transmission uses an electrical solenoid to control hydraulic pressure inside the
transmission. This electrical solenoid allows the PCM to control "line pressure", similar to other automatic
transmissions that use a "throttle valve" cable or vacuum modulator. The duty cycle, and amount of current
flow to the PCS, are both controlled by the PCM. By monitoring this line, the PCM can determine if the
commanded amperage has gone to the PCS and returned to the PCM.
E15 TRANSMISSION PRESSURE CONTROL
SOLENOID (PCS) - HIGH
AUTO TRANS ONLY
The duty cycle, and amount of current flow to the PCS, are controlled by the PCM. This circuit is the B+ supply
line from the PCM to the PCS. The duty cycle and amperage are controlled by the PCM.
E16 ECT/TP SENSOR EARTH - This terminal should be zero volts. This circuit is connected through the PCM to
the engine earth.

PINS F1 - F16
F1 FUEL INJECTOR CONTROL - With the engine OFF and the ignition ON, the voltage should be B+. With the
engine running at idle, the charging system increases the battery voltage slightly, so this voltages will increase.
With higher engine RPM or more engine load, the resulting increase in injector pulse frequency or injector
pulse width will cause this voltage to become slightly less.
F2 SAME AS F1
F3 SAME AS F1
F4 AIR CONDITIONING RELAY CONTROL -
When the A/C is requested, the BCM will communicate to the PCM via the serial data line, requesting A/C. The
PCM supplies the earth path on this terminal to energise the A/C control relay. The voltage will be less than 1
volt when the PCM energises the relay. When the PCM does energise the A/C control relay, the voltage will be
more than 0.1, but less than 1 volt.
F5 START RELAY CONTROL - When the PCM receives the ignition voltage from the Cranking Signal Input
circuit, the PCM will then supply the earth signal needed to energise the Start Relay Control. Once this Start
Relay Control is energised, power is supplied to the starter.
F6 ENGINE COOLING FAN - HIGH SPEED RELAY CONTROL -This terminal will have B+ until the PCM
energises the high speed cooling fan relay. The input that causes the PCM to energise the high speed fan relay
is the engine coolant temperature sensor. The PCM will also energise the high speed fan relay in the
Diagnostic Mode - i.e., ignition ON, engine stopped, and DLC diagnostic "test" enable terminal earthed.
F7 NOT USED
F8 NOT USED
F9 RANGE SIGNAL A INPUT SIGNAL
F10 RANGE SIGNAL B INPUT SIGNAL
F11 RANGE SIGNAL C INPUT SIGNAL
AUTO TRANS ONLY
Range signal "A", "B" and "C". The PCM sends out a buffered 12 volt signal to the pressure switch assembly,
located in the automatic transmission valve body. The 12 volt signal must pass through either a normally open
or normally closed switch to reach earth. When the switch(es) are closed, the signal should be near 0 volts.
The PCM monitors the status of these signals to determine which gear servo is actually receiving hydraulic
apply pressure.
F12 NORMAL / ECONOMY INPUT SIGNAL
AUTO TRANS ONLY
The PCM sends a signal of about 12 volts, and monitors the status of this circuit. In the ECONOMY position
the switch is open, the PCM voltage status signal remains high - about 12 volts, and the PCM does not allow
shift point changes. When the transmission switch is pressed to the POWER position the switch is closed and
the PCM voltage status signal is pulled low - about 0 volts. The PCM senses the zero voltage signal, and
enables power mode shifting only if other criteria are met. These criteria include throttle position and engine
speed.
F13 NOT USED
F14 DIAGNOSTIC TEST ENABLE INPUT - This terminal is connected to the DLC. When the diagnostic test
terminal is not earthed, this terminal will read 5 volts. When the DLC diagnostic test enable terminal is earthed,
the resulting zero voltage at the PCM will cause the PCM to operate in the Diagnostic Mode.
F15 PRNDL P - This circuit along with PCM circuits E6, E7, E8 indicate to the PCM what transmission gear the
driver has selected. The PCM will then send a command via the serial data line to the instrument panel cluster
to indicate to the driver what gear has been selected.
F16 INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE / TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE /A/C PRESSURE SENSOR
EARTH CIRCUIT - This terminal should be zero volts. It is connected through the PCM circuitry to engine
earth.

TECH 2 SCAN ENGINE DATA
The Tech 2 scan Data listed in the table may be used for comparison
1. After completing the " ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM CHECK"
2. Finding the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly and
3. No diagnostic DTCs are displayed.
A TECH 2 SCAN TOOL THAT DISPLAYS FAULTY DATA SHOULD NOT BE USED, AND THE PROBLEM
SHOULD BE REPORTED TO THE MANUFACTURER. THE USE OF A FAULTY TECH 2 SCAN TOOL CAN
RESULT IN MISDIAGNOSIS AND UNNECESSARY PARTS REPLACEMENT.
Only the parameters listed are used in this Volume for diagnosis. For more description on the values and use of the
Tech 2 scan tool to diagnosis PCM inputs, refer to the applicable diagnosis chart in this Section. If all values are
within the range illustrated, refer to "Symptoms" Charts in Section 6C2-2B.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to number(s) on the Tech 2 Scan Data Engine Stream chart.
1. The Tech 2 scan tool "FO: DATA LIST" will display scan position's that will be displayed in order. The Tech 2
can tool will display nine (9) scan position parameters at a time. The "DOWN ARROW" button will scroll down
through all of the scan positions one at a time. After "Time From Start" parameter is displayed, pressing the
"DOWN ARROW" button again, will display scan position parameters starting at the top of the list again.
2. "Units Displayed" are the available ways of displaying what each parameter is currently operating in, or a value
that is being sensed or being output by the PCM.
3. "Typical Data Value" is separated into two parts. These displayed values are typical of a normally operating
vehicle. The ignition "ON" comparison should be performed first as this may lead to a quick identification of a
failure. The engine running data should be compared to the ignition "ON" data as a diagnostic check to make
sure the component or system is operating properly.
4. Ignition "ON" values are the typical values that should be seen on the Tech 2 scan tool with the ignition "ON,"
and engine stopped. Temperature sensors should be compared to the actual temperatures by letting the
sensor sit overnight and then comparing their values. A difference of 3-5 degrees C from the actual
temperature may indicate a problem with the sensor. Use the diagnostic aids chart for that sensor to compare
the resistance to temperature values.
5. "ENGINE RUNNING" typical data values are an average of display values recorded from normally operating
vehicles at normally operating temperature. They are intended to represent what a normally functioning system
would typically display.
TECH 2 SCAN DATA ENGINE STREAM
TYPICAL DATA VALUE !
!!
!
SCAN POSITION "UNITS
DISPLAYED # IGNITION
"ON" $ENGINE RUNNING %
ENGINE SPEED RPM 0 RPM ± 100 RPM FROM DESIRED
RPM
(± 50 RPM IN DRIVE)
DESIRED IDLE
SPEED RPM 0 RPM PCM IDLE COMMAND
(VARIES WITH
TEMPERATURE)
ECT SENSOR VOLTS VOLTS Varies 1.96 V
ENG. COOLANT
TEMP DEGREES C Varies +96 C
IAT VOLTAGE VOLTS Varies Varies
IAT DEGREES C Varies Varies
MAF SENSOR
FREQUENCY Hz 0 Hz 2600-2900 Hz
MASS AIR FLOW GRAM /SEC 0 G/S 5 -10 G/S
MASS AIR FLW/CYL mG/S 0.0 mG/S 150-170 mG/S
TPS SIGNAL
VOLTAGE VOLTS 0.32 V 0.47 V
TPS ANGLE 0-100 % 0 % 0 %
RH O2 SENSOR
READY YES / NO NO YES
LH O2 SENSOR
READY YES / NO NO YES
RH O2 SENSOR mV 447
mV(varies) 100 - 1000 mV AND
VARYING
LH O2 SENSOR mV 447
mV(varies) 100 - 1000 mV AND
VARYING
ST FUEL TRIM R + 0 - 100 % 0 % + 0 % to 10%
ST FUEL TRIM L + 0 - 100 % 0 % + 0 % to 10 %
LT FUEL TRIM R + 0 - 100 % 0% + 0 % to 10%
LT FUEL TRIM L + 0 - 100 % 0 % + 0 % to 10 %
LTFT ENABLE YES / NO NO NO
FUELLING MODE OPEN /
CLOSED LOOP OPEN LOOP CLOSED LOOP
LTFT CELL CELL # 0 0
RH O2 STATUS RICH / LEAN LEAN Rich
LH O2 STATUS RICH / LEAN LEAN Rich
RH O2 CROSS CNTS COUNTS 0 0
LH O2 CROSS CNTS COUNTS 0 0
STFT DELTA 0 - 100 % 0 % 0 - 10%
LTFT DELTA 0 - 100 % 0 % 0 - 10%
DECEL FUEL CUT-
OFF NO/YES NO NO
INJ. PULSE TIME mS 27.5 mS 3-5 mS
INJECTOR VOLTAGE VOLTS 11.4 V 14.0 V
AIR / FUEL RATIO % 0.0 : 1 14.0 : 1
PURGE PWM % 0 % 0 -15 %
BATTERY VOLTAGE VOLTS 11.3 V 14.0 V
REFERENCE VOLTS VOLTS 4.99 V 4.99 V
CRANK SWITCH CRANKING/OF
FOFF OFF
TYPICAL DATA VALUE !
!!
!
CAM SIGNAL MISSING
/PRESENT MISSING PRESENT
IAC POSITION STEPS 30-50
STEPS 25 -50 STEPS
LITRES / Hr LITRES/Hr 00.00 2.50 L/Hour
IDLE RPM VARIANT RPM 0 RPM 9 RPM
SPARK MODE BYPASS/EST BYPASS EST
SPARK ADVANCE DEGREES
BTDC + 0° BTDC + 18 ° BTDC
KNOCK SIGNAL KNOCK/NONE NONE NONE
KNOCK RETARD # OF DEGREES 0 ° 0 °
TCC SOLENOID ON / OFF OFF OFF
VEHICLE SPEED KM / H 0 KM/H 0 KM/H
A/C REQUEST ON /OFF OFF OFF
A/C CLUTCH ON /OFF OFF OFF
A/C PRESSURE
VOLTS VOLTS 1-2 V 1-2 V
A/C PRESSURE kPa 400 - 600
kPa 400 -600 kPa A/C OFF
800 -1000 kPa A/C ON
HIGH SPEED FAN ON / OFF OFF OFF
LOW SPEED FAN
REQUEST ON / OFF OFF ON or OFF
THEFT STATUS NO
START/START START START
STARTER RELAY OFF/ON ON ON
FUEL PUMP RELAY ON / OFF OFF ON
CRANK TIME SEC 0.0 SEC 0.5 SEC
DTC STATUS NO
DTC(s)/DTC(s)
SET
NO DTC(s) NO DTC(s)
TIME FROM START TIME 0:00:00 VARIES FROM START
PROM I.D. FOUR DIGITS Varies with
Prom
Updates
Varies with PROM Updates
CHECK
POWERTRAIN LAMP ON/OFF ON OFF

TECH 2 SCAN ENGINE DATA DESCRIPTIONS
A list of explanations for each data message displayed on the Tech 2 scan tool is listed below. This information will
assist in diagnosing emission or driveability problems. The displays can be viewed while the vehicle is being driven.
Refer to the " On-Board Diagnostic System Check" for additional informational.
ENGINE SPEED - Range 0-9999 RPM - The engine speed is computed by the PCM from the fuel control reference
input. It should remain close to desired idle under various engine loads with engine idling.
DESIRED IDLE SPEED- Range 0-3175 RPM - The idle speed that is commanded by the PCM. The PCM will
compensate for various engine loads to keep the engine at the desired idle speed.
ECT SENSOR VOLTS/ENG COOLANT TEMP- Range -40 degrees to 151 degrees C / 0 - 5 VOLTS - The
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is mounted in the inlet manifold. The ECT sensor measures the engine
temperature. The PCM supplies a 5 volts reference and a earth circuit to the engine coolant temperature sensor.
When the sensor is cold (internal resistance high), the PCM reads a high signal voltage. As the sensor warms
(internal resistance decreases), the voltage signal will decrease.
IAT SENSOR VOLTS/IAT - Range -40 degrees to 151 degrees C / 0 - 5 VOLTS - The PCM converts the
resistance of the intake air temperature sensor to degrees. Intake Air Temp (IAT) is used by the PCM to adjust fuel
delivery and spark timing according to incoming air density.
MAF Sensor - Range 0-10,192 Hz - The signal that is sent from the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor to the PCM is in
the form of a frequency output. This frequency output changes as the demand of engine air intake changes.
MASS AIR FLOW - Range 0-246 Grams/Sec. - The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the change in the
intake air flow which results from engine load and speed changes. As intake air flow increases, the air in the inlet
manifold also increases and addition fuel is required.
MASS AIR FLOW/CYL - Range 0-1000 mG/S. - Calculated air flow per each cylinder.
TPS VOLTAGE - Range 0-5.10 Volts - Used by the PCM to determine the amount of throttle demanded by the
driver. The TPS voltage should read between 0.25 - 1.25 volts at idle to greater than 4 volts at wide open throttle.
TPS ANGLE - Range 0-100% - Computed by the PCM from the TP sensor voltage. The TP angle should read 0%
at idle to greater than 80% at Wide Open Throttle.
(RIGHT) AND (LEFT) O2 SENSOR READY - Tech 2 display s "YES" or "NO". Indicating if the oxygen sensor has
reached operating temperature.
(RIGHT or LEFT) O2 SENSOR - Range 0-1192 mV - Represents the exhaust sensor output voltage. The O2
sensor voltage should fluctuate constantly between 100 mV (Lean exhaust) and 1000 mV (Rich exhaust) when
operating in "Closed Loop."
(LEFT or RIGHT) SHORT TERM FUEL TRIM - Range -100% -0% -+ 100% - Short Term Fuel Trim represents a
short-term correction for fuel delivery by the PCM in response to the amount of time the oxygen sensor voltage is
above or below the 450 mV threshold. If the oxygen sensor voltage has mainly been below 450 mV, indicating a
lean air/fuel mixture, STFT will increase to request the PCM to reduce fuel delivery to compensate for the indicated
rich condition. Under certain conditions such as extended idle and high ambient temperatures, canister purge may
cause STFT to read less than -10%.
(LEFT or RIGHT) LONG TERM FUEL TRIM -100% - 0% - +100% - LTFT is derived by the PCM from the STFT
value and is used for long-term correction of fuel delivery. A value of 0% indicates that fuel delivery requires no
compensation to maintain a 14.7:1 air/fuel ratio. A value below 0% means that the fuel system has been rich and
fuel delivery is being reduced decreased injector pulse width to maintain a 14.7 to 1 A/F ratio. A value above 0%
indicates that a lean condition exists and the PCM has been compensating by adding fuel. LTFT tends to follow
STFT.
LTFT ENABLE - Tech 2 Displays "YES" or "NO". - The Long Term Fuel Trim is enable by the PCM when a long
term fuel correction is required. A YES indicates that the LTFT is enabled, a NO indicates that is not.
FUELLING MODE - Displays OPEN or CLOSED- "Closed Loop" displayed indicates that the PCM is controlling
the fuel delivery from the oxygen sensor voltage. In Open Loop, the PCM ignores the oxygen sensor voltage and
bases the amount of fuel to be delivered on TP Sensor, coolant, and the IAT sensor inputs only. At extremely high
temperatures, it is possible for the system to remain in Open Loop to control the catalytic converter temperatures.
LTFT CELL - Range 0-23 - LTFT cell is dependent upon engine speed and mass air flow readings. A plot of RPM
vs MAF is divided into 24 cells. LTFT cell indicates which cell is currently active.
O2 SENSOR STATUS (Left or Right) - RICH or LEAN - Indicates whether the exhaust oxygen sensor voltage is
above (rich) or below (lean) the 450 mV oxygen sensor threshold voltage. This voltage should change constantly
indicating that the PCM is controlling the air/fuel mixture properly.
O2 SENSOR CROSS COUNTS (Left or Right) - Displays the number of times the O2 Sensor voltage switches from
less than 450 mV to greater than 450 mV and then from greater than 450 mV to less than 450 mV.
STFT/LTFT DELTA - Range 0-100%. - The difference (Delta) in % of the STFT/LTFT counts from each bank. This
value is used by the PCM to determine bank to bank fuel trim balance.
DEC. FUEL CUT-OFF - Displays OFF or ON - Indicates if the PCM is in the Decel Fuel Cut-off Mode.
INJ. PULSE WIDTH - Range 0.0 - 999.9 mS. - The ON time of the injector as determined by the PCM.

INJECTOR VOLTAGE - Range 0 - 14.0 Voltage -The voltage commanded from the PCM to open the injector.
AIR FUEL RATIO - Range 0.00 : 99.99 - The reading reflects the commanded value. This should be at or near
14.7. A lower value indicates a richer commanded air fuel mixture while a higher value indicates a leaner mixture.
PURGE PWM - Range 0-100%. The duty cycle of the purge solenoid as being commanded by the PCM.
BATTERY VOLTAGE - Range 0-25.5 volts - This represents the system voltage measured by the PCM at the
ignition No. 1 feed.
REFERENCE VOLTS - Range 0-5 Volts - Indicates the voltage that is supplied to various sensors from the PCM.
CRANK SWITCH - Displays Cranking or OFF. - Indicates that the engine is cranking. The signal is used by the
PCM to prevent backfire.
CAM SIGNAL - Range MISSING/PRESENT- A signal generated by the cam sensor then sent to the PCM. The
PCM then uses this signal for piston positioning for sequential fuelling.
IDLE SPEED VARIANT - RANGE 0-9999 RPM - Indicates the variation in RPM between sampling of engine
speeds.
IAC POSITION - Range 0-255 Counts - Displays the commanded position of the idle air control pintle in counts.
The higher the number of counts, the greater the commanded idle speed. The Idle air control valve should respond
quickly to changes in engine load.
LITRES/100km - Range 0-100 - Indicates fuel consumption per litres per 100 km.
SPARK MODE - Displays "BYPASS" or "EST" - Indicates what mode of ignition timing the vehicle is operating.
SPARK ADVANCE - Range -90 Degrees to +90 Degrees - This displays the spark advance (EST) calculation
which the PCM is programming into the ignition system. The PCM computes the desired spark advance using data
such as engine temperature, engine rpm, engine load, vehicle speed, and operating mode.
KNOCK SIGNAL - Displays "KNOCK" or "NONE" - Indicates whether or not a knock signal is being detected by
the PCM. Should read "NONE" at idle.
KNOCK RETARD - Range 0 Degrees - 90 Degrees - Indicates the amount of spark advance the PCM is removing
from EST in response to the Knock sensor (ESC) signal. Should read 0 degrees at idle.
TCC ENABLE SOLENOID - Displays ON or OFF. - Indicates if the TCC enable Solenoid is commanding the TCC
ON or OFF.
VEHICLE SPEED - Range 0-255 km/h - The vehicle speed sensor signal is converted into kph and mph for
display.
A/C REQUEST - Displays YES or NO - Represents the state of the A/C request serial data input from the BCM.
A/C CLUTCH - Displays ON or OFF - Represents the commanded state of the A/C clutch control relay. Clutch
should be engaged when ON is displayed.
A/C PRESSURE SENSOR - Tech 2 Displays 0.0 - 5.0 Volts - Represents the A/C refrigerant pressure sensor
signal. The amount of pressure indicates the amount of load that the A/C compressor is placing on the engine. The
PCM uses this information to adjust idle speed and to control the cooling fan.
A/C PRESSURE - Range 0 - 3195 kPa - The kPa displayed indicates that the PCM is monitoring an A/C
Refrigerant Pressure signal voltage which is too high or too low to allow the A/C compressor clutch to engage.
HIGH SPEED FAN - Tech 2 Displays "ON" or "OFF - Indicates if the engine cooling fan high speed relay has
been commanded ON or OFF.
LOW SPEED FAN REQUEST - Tech 2 Displays "ON" or "OFF - Indicates if the engine cooling fan low speed
relay has been commanded ON or OFF.
THEFT STATUS - Displays "NO START" or " START". - Indicates the status of the Theft Deterrent System.
FUEL PUMP STATUS - Displays ON or OFF. - Indicates if the fuel pump is ON or OFF.
ENGINE CRANK TIME - Range 0 - 99.9 Seconds. - Indicates the duration of the engine crank time.
DTC STATUS - Indicates if there are any DTC's in
TIME FROM START - Displays 0:00:00. - Indicates the hours, minutes and seconds the engine has been running.
PROM I.D. - Displays a four digit number - Indicates the numerical identification of the PROM stored in the PCM.
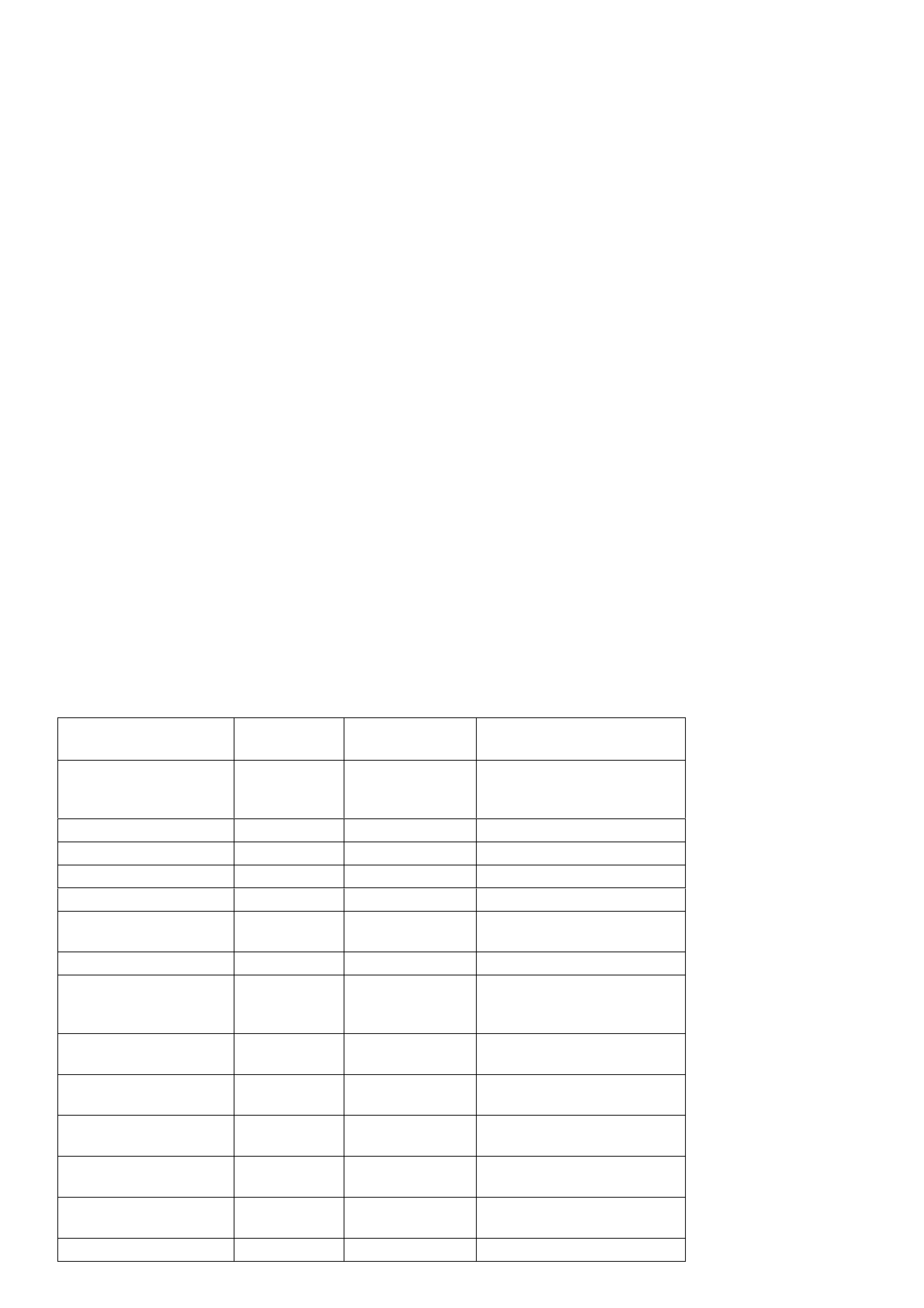
TECH 2 SCAN TOOL TRANSM ISSION DATA
The Tech 2 scan Data listed in the table may be used for comparison
1. After completing the " ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM CHECK".
2. Finding the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly and
3. No diagnostic DTCs are displayed.
A TECH 2 SCAN TOOL THAT DISPLAYS FAULTY DATA SHOULD NOT BE USED, AND THE PROBLEM
SHOULD BE REPORTED TO THE MANUFACTURER. THE USE OF A FAULTY TECH 2 SCAN TOOL CAN
RESULT IN MISDIAGNOSIS AND UNNECESSARY PARTS REPLACEMENT.
Only the parameters listed are used in this manual for diagnosis. For more description on the values and use of the
Tech 2 scan tool to diagnosis PCM inputs, refer to the applicable diagnosis chart in this Section. If all the values are
within the range illustrated, refer to "Symptoms" Charts in Section 6C2-2B.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to circled number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. The scan position refers to the Tech 2 scan tool DATA LIST that will be displayed in order.
2. "Units Displayed" are the available ways of displaying what each parameter is currently operating in, or a value
that is being sensed or being out putted by the PCM.
3. "Typical Data Value" is separated into two parts. These displayed values are typical of a normally operating
vehicle. The ignition ON comparison should be performed first as this may lead to a quick identification of a
fault. The engine running data should be compared to the ignition ON data as a diagnostic check to make sure
the component or the system is operating properly.
4. Ignition ON values are the typical values that should be seen on the Tech 2 scan tool with the ignition ON, and
the engine OFF. The temperature sensors should be compared to the actual temperatures by letting the
sensor sit overnight and then comparing their values. A difference of 3 to 5 degrees C from the actual
temperature may indicate a problem with the sensor. Use the diagnostic aids chart for that sensor to compare
the resistance to temperature values.
Some ON or OFF switches may display an abnormal state. If the chart states this position is abnormal, than
this may be caused by an open or short to earth, depending upon the normal state of the switch. Refer to the
proper Section or more information on diagnosis.
5. "ENGINE RUNNING" typical data values are an average of display values recorded from normally operating
vehicles at normally operating temperature. They are intended to represent what a normally functioning system
would typically display.
TECH 2 SCAN DATA - TRANSMISSION
DISPLAY POSITION UNITS
DISPLAYED TYPICAL DATA
IGNITION ON TYPICAL VALUE ENGINE
RUNNING
ENGINE SPEED RPM 0 RPM ± 100 RPM FROM
DESIRED RPM
(± 50 RPM IN DRIVE)
VEHICLE SPEED km/h 0 km/h 0 km/h
TPS SIGNAL VOLTS 0.50 V 0.50 V
THROTTLE ANGLE 0-100 % 0 % 0 %
ECT SENSOR V Varies Varies
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE °C Varies 96°C
TFT SENSOR V Varies Varies
TRANSMISSION
FLUID
TEMPERATURE
°C Varies Varies
TFP SWITCH A OPEN/
CLOSED OPEN 12V OPEN 12V
TFP SWITCH B OPEN/
CLOSED CLOSED 0V CLOSED 0V
TFP SWITCH C OPEN/
CLOSED OPEN 12V OPEN 12V
TFP GEAR P-N-
1-2-3-D-RP/N P/N
PRNDL SELECTED
POSITION INVALID/
P-R-N-D-LPP
1-2 SHIFT SOLENOID ON/OFF OFF ON
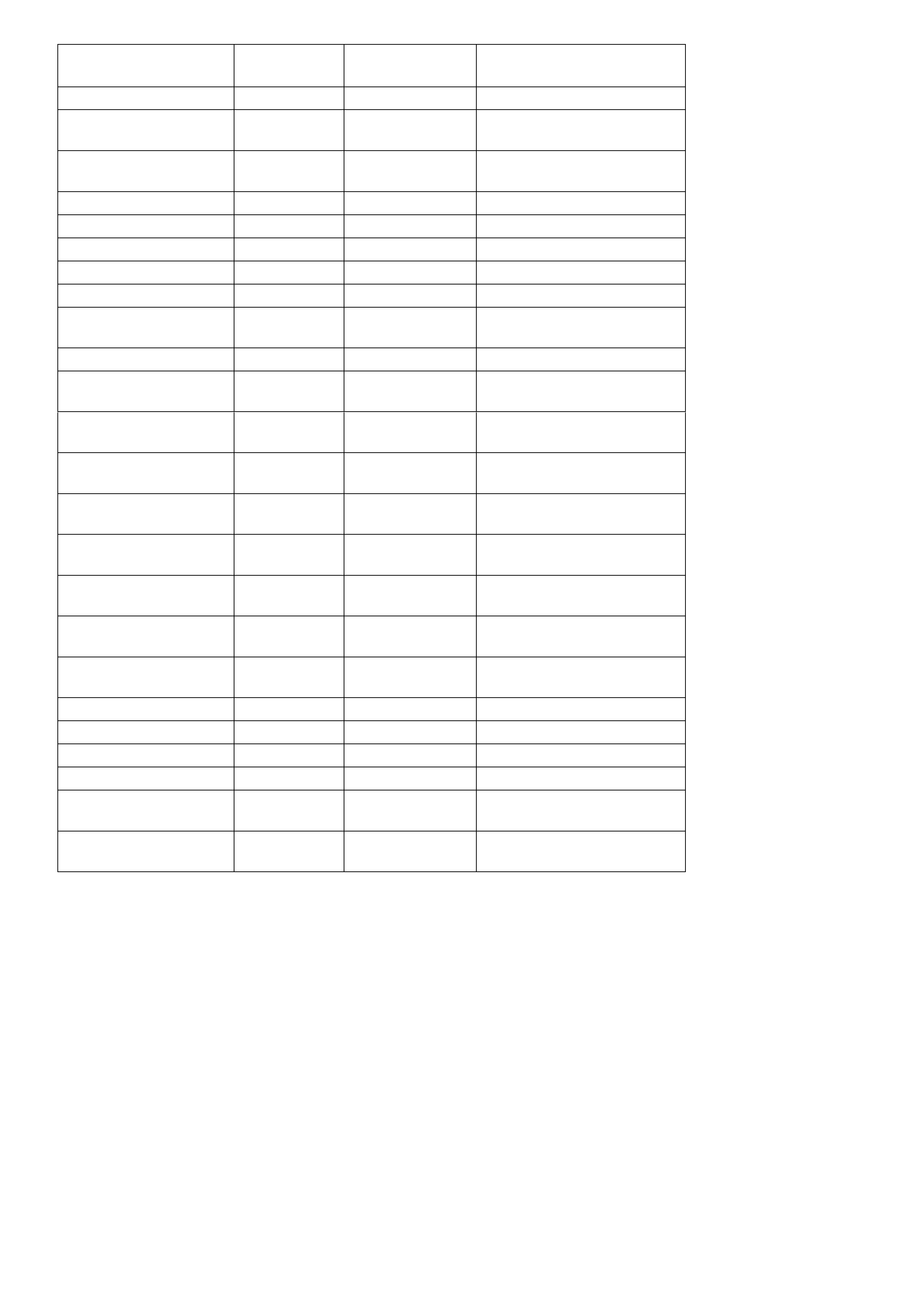
DISPLAY POSITION UNITS
DISPLAYED TYPICAL DATA
IGNITION ON TYPICAL VALUE ENGINE
RUNNING
2-3 SHIFT SOLENOID ON/OFF OFF ON
1-2 SHIFT SOLENOID
FEEDBACK ON/OFF OFF ON
2-3 SHIFT SOLENOID
FEEDBACK ON/OFF OFF ON
1-2 SHIFT TIME sec 0 sec 0 sec
2-3 SHIFT TIME sec 0 sec 0 sec
COMMANDED PCS Ma 0 mA 950 mA
ACTUAL PCS mA 0 mA 950 mA
PCS DUTY CYCLE % 0 mA 60%
TCC ENABLE
SOLENOID ON/OFF OFF OFF
TCC PWM SOLENOID % 0% 0%
TRANSMISSION SLIP
SPEED RPM 0 650 RPM
ECONOMY/POWER
SHIFT SWITCH Economy/
Power Economy Economy
3-2 DOWNSHIFT
ENABLED YES/NO NO NO
3-2 DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID ON/OFF OFF ON
LONG TERM 1-2
SHIFT ADAPT kPa 0 kPa 0
LONG TERM 2-3
SHIFT SOLENOID kPa 0 kPa 0
SHORT TERM SHIFT
ADAPT kPa 0 kPa 0 kPa
ADAPT SHIFT
STATUS Enabled/
Disabled Enabled Enabled
SHIFT ADAPT CELL 0 0 0
GEAR RATIO :1 1 3.06:1
COMMANDED GEAR 1-2-3-4 3 1
BATTERY VOLTAGE V 12V 12V
TIME FROM START HH:MM:SS Varies with
engine run time Varies with
engine run time
CHECK
POWERTRAIN LAMP OFF/ON ON OFF

TECH 2 SCAN TOOL TRANSM ISSION DATA DESCRIPTIONS
A list of explanations for each data message displayed on the Tech 2 scan tool begins as follows. This information
will assist in tracking emission or driveability problems, since the displays can be viewed while the vehicle is being
driven. Refer to the " On-Board Diagnostic System Chec k " for additional informational.
ENGINE SPEED - Range 0-9999 RPM - Displays the actual engine speed, as received from the reference input
signal. Displays in increments of 1 RPM.
VEHICLE SPEED - Range 0-255 KM/H - Displays the PCM's calculation of vehicle speed as received from the
PCM. Useful for checking speedometer accuracy.
TPS SIGNAL - Range 0-5 VOLTS - This position shows the Throttle Position sensor signal input to the PCM. The
values read will be in voltage. The PCM then will calculate the throttle opening. The TP sensor voltage should be
between 0.25 - 1.25 volts with the throttle closed and greater than 4 volts at Wide Open Throttle .
TPS THROTTLE ANGLE - Range 0-100% - This display is the PCM's calculation of the percentage of throttle
opening. The TPS angle should display zero (0%) with the throttle closed and greater than 80% at Wide Open
Throttle.
ECT SENSOR VOLTS/ENG COOLANT TEMP - Range -40 degrees C to 151 degrees C/0 - 5 Volts - The PCM
supplies 5 volts to the ECT sensor circuit. The sensor is a thermistor which changes internal resistance as
temperature changes. When the sensor is cold (internal resistance high), the PCM receives a high signal voltage
which it interprets as a cold engine. As the sensor warms (internal resistance decreases), the voltage signal will
increase indicating a warm engine.
TFT SENSOR VOLTS/TRANS FLUID TEMP - Range -40 degrees C to 151 degrees C/0 - 5 VOLTS - This
displays the temperature of the fluid in the transmission.. The TECH 2 scan tool will display TFT in voltage and in
degrees Celsius. The TFT sensor reading should read close to the air temperature when the transmission is cold,
and increases as the transmission fluid temperature increases. After the engine is started the temperature should
rise steadily to between 82 degrees C and 94 degrees C then stabilise.
TFP SWITCHES A/B/C RANGE VOLTS - Range 0-12 VOLTS - These values represent the three fluid pressure
switch assembly signals. These lines are normally high and are taken low as the fluid pressure switch interprets the
manual valve position. The sequence of these signals is decoded by the PCM to determine the appropriate gear
range.
PRNDL SELECTED POSITIONS - This value represents the decoded sequence of the Transmission Fluid
Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch Assembly (TFP). The TFP is used to determine the manual valve position.
The manual valve position is an input to the PCM used to control line pressure, TCC, and shift solenoid operation.
1-2 SHIFT SOLENOID, AND 2-3 SHIFT SOLENOID This displays the ON or OFF state of the two shift solenoids.
The shift solenoids are turned OFF or ON to change gears.
1-2 AND 2-3 SHIFT SOLENOID FEEDBACK - These values represent the true electrical state of the solenoids.
The PCM uses this information to set malfunction DTC's.
1-2 SHIFT TIME - This value represents the time taken to shift from first gear to second gear. This information is
only accurate if the shift was adaptable.
2-3 SHIFT TIME - This value represents the time taken to shift from second gear to third gear. This information is
only accurate if the shift was adaptable.
COMMANDED TFP - This value represents the commanded pressure control solenoid current. The commanded
current is determined from the manual valve position, transmission fluid temperature, transmission output speed,
shift solenoid state, TCC, A/C status, engine speed, TCC slip and the throttle position sensor. The commanded
pressure control solenoid current is then used to control the transmission line pressure.
ACTUAL TFP - This value represents the actual transmission fluid pressure control solenoid current. This value
should always be close to the desired pressure control solenoid current.
TFP DUTY CYCLE - This value represents the pressure control solenoid duty cycle. This value is determined by the
desired pressure control solenoid current.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) SOLENOID-
This value represents the status of the Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) solenoid. This status is determined by
throttle position, transmission output speed, transmission range, engine coolant temperature, transmission fluid
temperature, and TCC slip.
TCC PWM SOLENOID - Range 0-100%. This parameter is the commanded percentage of ON time of the TCC
PWM solenoid . Approximately 90% represents an ON (energised) commanded state. Zero percent represents an
OFF (non-energised) commanded state. This commanded state is applied at a vehicle speed between
approximately 0 -16 km/h (0-10 mph).
TRANSMISSION SLIP SPEED - This displays the calculated difference between the engine RPM and the
transmission input shaft RPM. This TCC slip RPM should be within ±30 RPM to the actual engine RPM whenever
the TCC is applied.
ECONOMY/POWER SHIFT SW - This display shows the state of the economy/power switch.

3-2 SHIFT SOLENOID PWM- This value represents the duty cycle of the 3-2 downshift solenoid. This device
regulates the release of the 3-4 clutch and the apply of the 2-4 band. The duty cycle is normally about 90%, except
during a 3-2 downshift when the duty cycle drops. The duty cycle will be 0% in first gear. The duty cy cle is
determined by throttle position, vehicle speed, and the commanded gear.
3-2 SHIFT SOLENOID FEEDBACK - These values represent the true electrical state of the solenoid and circuit.
The PCM uses this information to set a DTC.
ADAPT SHIFT STATUS- This value indicates if the current shift will update the 1-2 adapt tables which are used to
modify line pressure.
SHIFT ADAPT CELL - This value displays the cell that the PCM is operating. There are three cells to adapt the
shift, these cells are: Light throttle, Medium throttle and Full throttle. These three cells are very similar to LTFT cell
used by the engine.
GEAR RATIO - This display represents the gear ratio of the commanded gear. 1st 3.06:1, 2nd 1.63:1, 3rd 1.00:1,
4th 0.69:1, Rev 2.29 :1.
COMMANDED GEAR - The gear that the PCM is commanding the transmission. In Park, the Tech 2 scan tool will
display, the commanded state of the shift.
BATTERY VOLTAGE - Range 0-25.5 VOLTS - This represents the system voltage measured by the PCM at its
ignition No. 1 feed.
TIME FROM START - Tech 2 Displays 0:00:00 - Indicates the hours, minutes and seconds the engine has been
running.
CHECK POWERTRAIN LAMP - ON/OFF - Indicates whether the lamp on the instrument panel is illuminated.
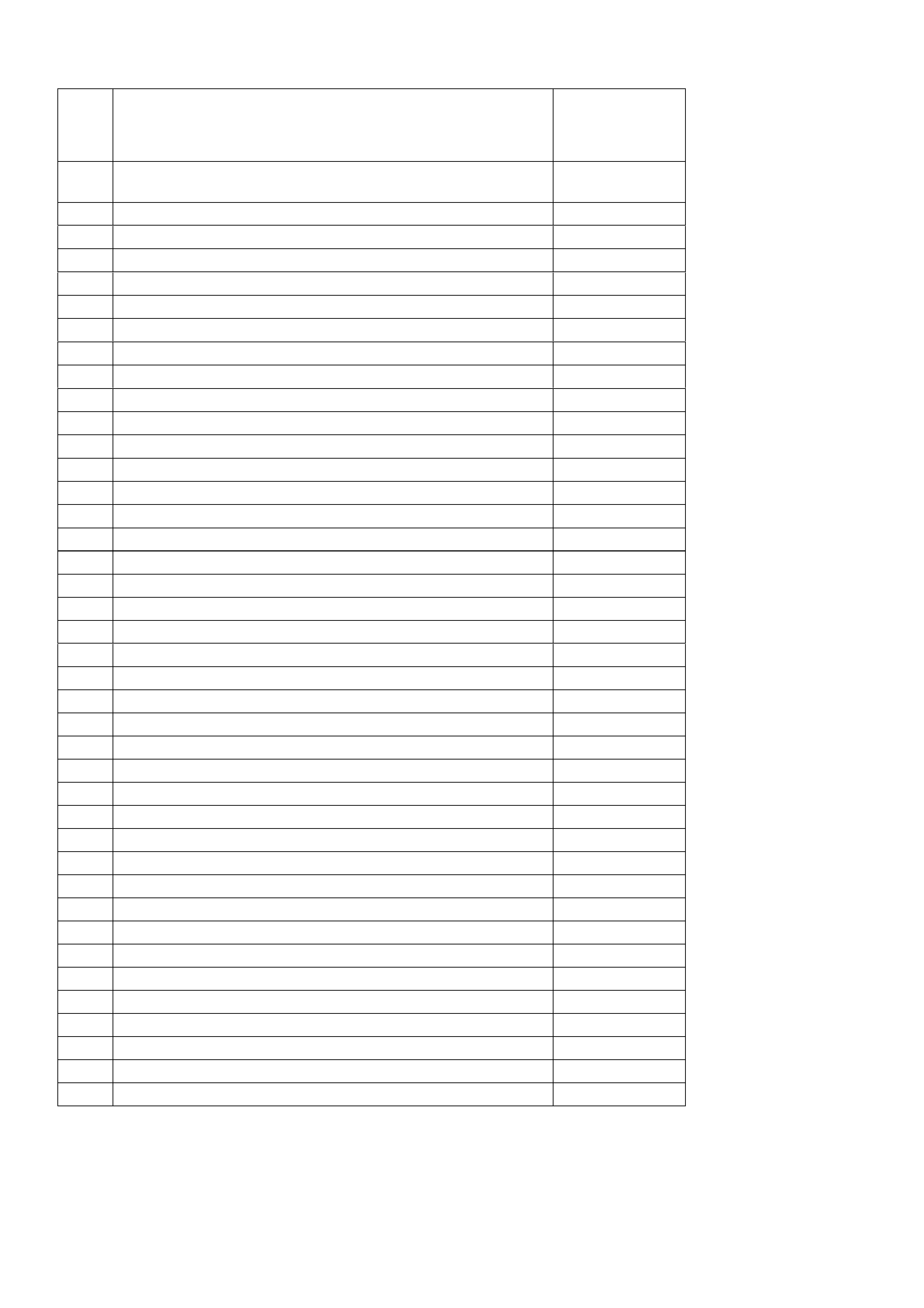
PCM V8 ENGINE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)
DTC DESCRIPTION ILLUMINATE
“CHECK
POWERTRAIN”
LAMP
12 No revolutions per minute signal - normal when engine is not
running No
13 Right Hand (RH) No Oxygen Sensor Signal Yes
14 Engine Coolant Temperature ECT - Signal Voltage Low Yes
15 Engine Coolant Temperature ECT - Signal Voltage High Yes
16 Engine Coolant Temperature ECT - Signal Voltage Unstable Yes
17 PCM Error - ECT Circuit No
19 Throttle Position (TP) Sensor Stuck No
21 Throttle Position (TP) - Signal Voltage High Yes
22 Throttle Position (TP) - Signal Voltage Low Yes
23 Intake Air Temperature (IAT) - Signal Voltage High No
24 No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal Yes
25 Intake Air Temperature (IAT) - Signal Voltage Low No
26 Intake Air Temperature (IAT) - Signal Voltage Unstable No
31 Theft Deterrent Signal Missing Yes
32 Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor- Out Of Range Yes
35 Idle Speed Error No
36 Vacuum Leak No
41 Ignition Electronic Spark Timing (EST) Circuit Fault Yes
42 Bypass Circuit Fault Yes
43 Knock Sensor Circuit Fault No
44 Right Hand (RH) Lean Exhaust Indication Yes
45 Right Hand (RH) Rich Exhaust Indication Yes
46 No Reference Pulses While Cranking Yes
48 Camshaft Position Sensor Signal Missing No
49 Cam/Crank Sensor Signal Intermittent No
51 PROM Error Yes
54 System Voltage Unstable Yes
55 PCM Analog to Digital (A/D) Conversion Error Yes
57 Injector Voltage Monitor Fault No
63 Left Hand (LH) No Oxygen Sensor Signal Yes
64 Left Hand (LH) Lean Exhaust Indication Yes
65 Left Hand (LH) Rich Exhaust Indication Yes
76 Short Term Fuel Trim (STFT) Delta High No
78 Long Term Fuel Trim (LTFT) Delta High No
91 QDSM (Quad Driver Module) Circuit Fault No
92 Low Speed Fan No BCM Response No
93 SNEF Circuit Fault No
94 No Vehicle Speed Sensor - Manual Transmission Yes
96 A/C Pressure Sensor Circuit No
97 Canister Purge Circuit Fault No
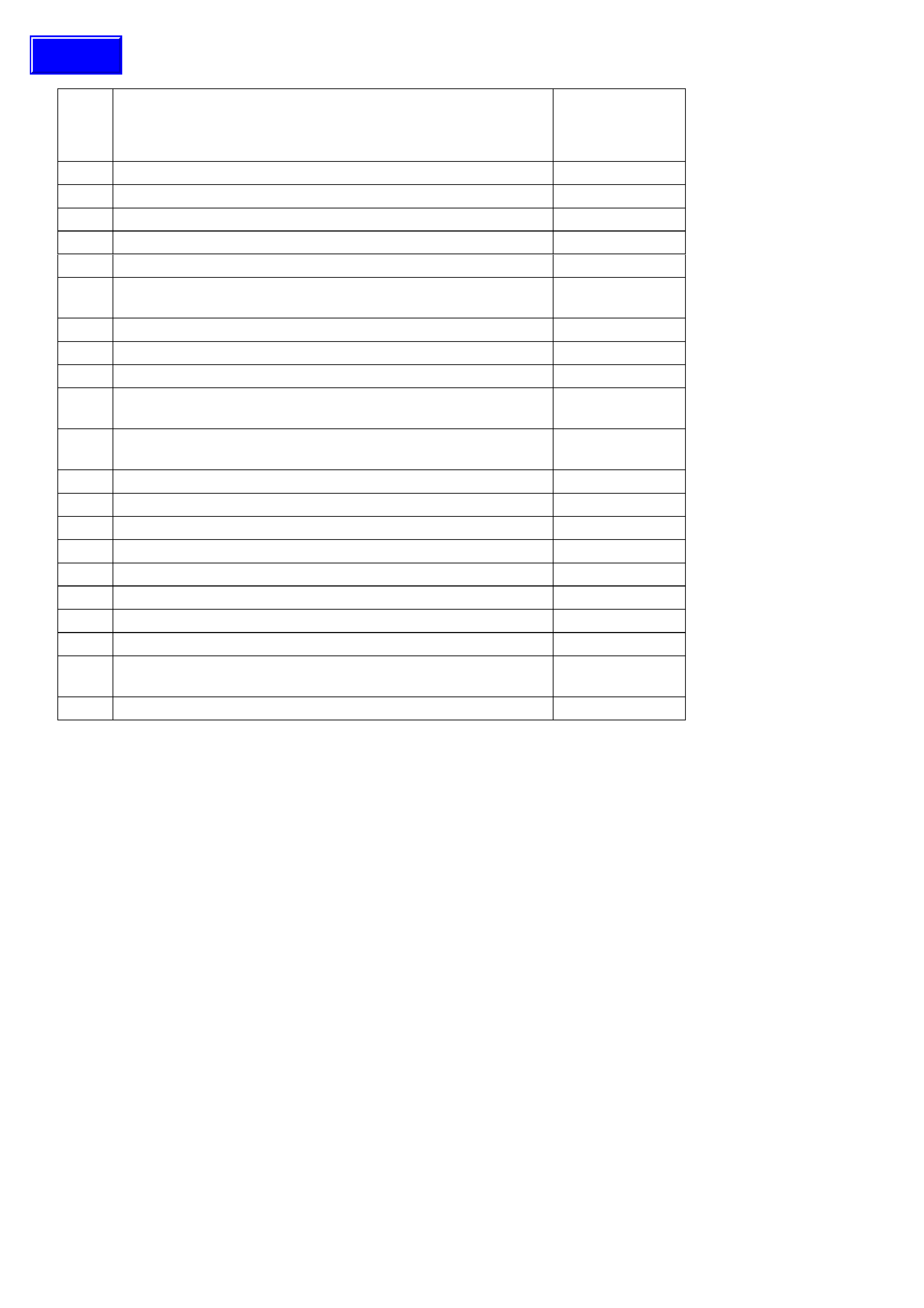
PCM V8 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)
DTC DESCRIPTION ILLUMINATE
“CHECK
POWERTRAIN”
LAMP
14 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) - Signal Voltage Low Yes
15 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) - Signal voltage High Yes
21 Throttle Position (TP) Signal Voltage High Yes
22 Throttle Position (TP) Signal Voltage Low Yes
24 No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal Yes
28 Transmission Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch
Assembly Circuit Yes
52 System Voltage Too High - Long Time Yes
53 System Voltage Too High Yes
55 PROM - Analog - Digital (A/D) Conversion Error Yes
58 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit - Low
Input Yes
59 Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor Circuit - High
Input Yes
66 3-2 Downshift Solenoid Circuit - Fault Yes
67 Torque Converter Clutch Enable Solenoid Circuit - Electrical Yes
69 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Stuck ON No
73 Pressure Control Solenoid Circuit - Error No
75 System Voltage Low Yes
79 Transmission Fluid Over-Temperature Yes
81 2-3 Shift Solenoid Circuit - Error Yes
82 1-2 Shift Solenoid Circuit - Error Yes
83 Torque Converter Clutch Pulse Width Modulation Solenoid
Circuit No
85 Transmission Component Slipping No
Techline

4L60E TRANSMISSION FLUID CHECKING PROCEDURE
GENERAL INFORMATION
When adding or changing the transmission fluid, use only Dexron III. Refer to the VT Series Owner’s Handbook for
the recommended servicing intervals.
Because Dexron II transmission fluid changes colour and odour very easily, these indicators should not necessarily
be relied upon to diagnose either transmission internal condition or fluid deterioration.
Reference to the table under ‘ Transmission Fluid Checking Procedure” shows that a dark brown fluid colour,
with a delayed shift pattern, may only indicate that the fluid requires replacement and, is not a definite indication of a
potential transmission problem.
NOTE:
Do not overfill the transmission. Overfilling may cause foaming of the fluid, loss of fluid, shift complaints and
possible damage to the transmission.
TRANSMISSION FLUID COLOUR
Transmission fluid colour when new, is red. A red dy e is added so that it can be distinguished from other oils and
lubricants. The red dye is not an indicator of fluid quality and is not permanent. As the vehicle is driven, the
transmission fluid will quickly begin to look darker. The colour will then appear light brown. A dark brown colour with
a distinctively burnt odour may indicate fluid deterioration and a need for the fluid to be changed.
NOTE:
As the temperature affects the transmission fluid levels, this operation must only be performed when the
transmission is at normal operating temperature 82 - 94 followed, the result could be a false reading of the fluid
level on the dipstick. Degrees C. If the vehicle is not at normal operating temperature, and the proper checking
procedures are not
TRANSMISSION FLUID CHECKING PROCEDURE
1. Start the engine and drive the vehicle for a maximum of 24 km, or until the transmission’s normal operating
temperature is reached.
2. Park the vehicle on a level surface.
3. Move the gear selector into PARK.
4. Apply the park brake.
5. Let the engine idle for 3 minutes with all the accessories turned off.
6. Locate the red coloured dipstick in the engine compartment. Lift the locking lever then remove the dipstick.
Check the fluid colour, the fluid condition and the fluid level.
Do not check the fluid levels immediately after the vehicle has been operated under any of the following conditions.
• In high ambient temperatures above 32 °C.
• At sustained high speeds.
• In heavy city traffic during hot weather.
• Towing
• In commercial use (e.g. taxi).
If the vehicle has been operated under these conditions, turn the engine off and allow the vehicle to cool for
approximately thirty minutes. After a cool-down period, re-start the vehicle and continue from step 2.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Check the fluid colour.
Is the fluid colour red? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
2Is the fluid level correct? Go to Step 20 Go to Step 3
3Check the fluid.
Is the fluid foamy? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 4
4Check the fluid level. The
proper fluid level should
be In the middle of the X-
hatch.
Is the fluid level high?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5Fluid will be low.
Add fluid to the proper
fluid level.
Is the fluid level
satisfactory?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 1
6Check for external leaks.
Were any leaks found? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 20
7Correct the fluid leak
condition.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 20
8Is the fluid level too high? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
9Remove the excess fluid
to adjust to the proper
fluid level.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 20
10 1. Check for
contaminants in the
fluid.
2. Drain the fluid in order
to determine the
source of the
contamination.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
11 Is the fluid colour non-
transparent pink? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 13
12 Replace the cooler.
Is the action complete? Go to Step 15
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
13 The fluid colour should be
light brown. The
Transmission fluid may
turn dark with normal use.
This does not always
indicate oxidation or
contamination.
Is the fluid colour light
brown?
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 1
14 Drain the fluid in order to
determine if the fluid is
contaminated. A very
small amount of material
in the bottom of the pan is
normal, but large pieces
of metal or other material
in the bottom of the pan
requires a transmission
overhaul.
Was the fluid
contaminated?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 18
15 Overhaul the
transmission. Refer to
Section 7C5, UNIT
REPAIR.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 16
16 Flush the cooler.
Is the action complete? Go to Step 17
17 Add the new fluid.
Is the action complete? Go to Step 19
18 Change the fluid and the
filter.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
19 Is the fluid level
satisfactory, If not, correct
as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 20
20 Refer to 4L60-E
Transmission Functional
Test Procedure, in
Section 7C3, Diagnosis.
Is the action complete?
Fluid Checking
Procedure
Completed
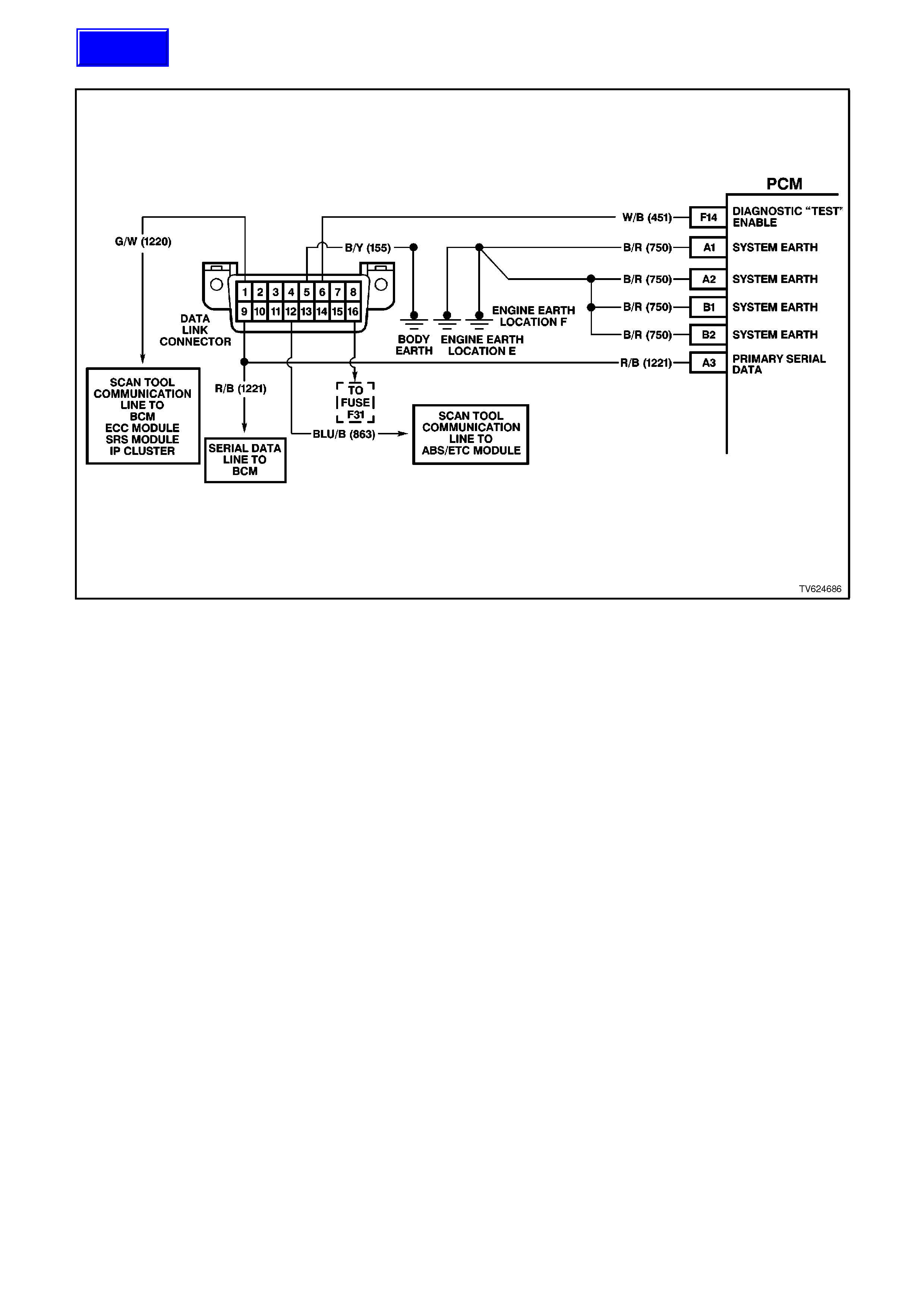
CHART A - ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM CHECK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The On-Board Diagnostic System Check is an organised approach in identifying a problem created by a powertrain
control system malfunction. It must be the starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis, because it directs
the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. Understanding the chart and using it
correctly will reduce diagnostic time and prevent the unnecessary replacement of good parts.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. This step is a check for the proper operation of the "Check Powertrain" lamp (MIL). The PCM should provide
serial data communication path for the "Check Powertrain" lamp, this is a bulb check. The "Check Powertrain"
lamp should be "ON." If it can do this, it confirms that the PCM has power, earth and is capable of some
functions.
If the "Check Powertrain" lamp is "OFF," this indicates a problem in the "Check Powertrain" lamp fuse circuits
or the PCM earth circuits or the PCM's serial data communication circuit or a problem with the PI cluster. Chart
A-1 will check for both ignition feed and constant battery power to the PCM and the PCM earth.
2. This check is done to see if the PCM has the capability of performing internal diagnostics. With the diagnostic
"test" terminal earthed, the "Check Powertrain" lamp, should flash a DTC 12 three times, followed by any
DTC(s) stored in memory. DTC 12 means there is no crankshaft reference signal coming to the PCM, this is
normal because the engine is not running.
3. This check is used to see if the PCM can supply serial data for Tech 2 scan tool use. If a PROM error is
present, the PCM may have been able to flash DTC 12 but not enable serial data.
4. This check is to see there are any Theft Deterrent DTC stored. If Theft Deterrent sy stem is enabled, this may
be the cause of the no crank condition.
5. This test determines if the vehicle is able to crank. If the vehicle will not crank, refer to Chart A-4.0 to diagnosis
starter cranking circuit.
7. This test is used to determine the cause of a "Cranks But Will Not Run," although the PCM is powered up, a
"Cranks But Will Not Run" symptom could exist because of a PCM problem or the vehicle electrical system.
8. Look at all the parameters to determine if one is not in a normal state with just the ignition "ON" and engine
stopped. Look at the ECT value to see if the value is shifted above or below where it should be. If so, refer
"Diagnostic Aid Chart" on DTC 14.
9. Look at all the parameters to determine that all values are within typical ranges for normal operating
temperatures at idle. Keep in mind that a basic engine problem may alter sensor value.
Techline
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
If the Serial Data circuit is shorted to voltage or earth, the vehicle will not crank. Check Serial Data circuit from PCM
to BCM, and from BCM to all other controllers.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
11. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
2. Observe the "CHECK
POWERTRAIN" lamp.
Is the "CHECK
POWERTRAIN" lamp ON
steady?
Go to Step 2 If No "CHECK
POWERTRAIN"
lamp, Go to Chart
A-1 in this Section
----------------------
If "CHECK
POWERTRAIN"
lamp is flashing
DTC 12, Go to
Step 10
2Jumper the Data Link
Connector terminal "6" to
terminal "5".
Does the "CHECK
POWERTRAIN" lamp
flash DTC 12?
Go to Step 3 Go to Chart A-1
in this section
31. Remove the Data Link
Connector jumper.
2. Install a Tech 2 Scan
tool.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the Tech 2 tool
display PCM serial data?
Go to Step 4 Go to Chart A-2
in this section
41. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
2. Use the Tech 2 to
check for Theft
Deterrent DTC(s).
Are any Theft Deterrent
DTC(s) stored?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
chart
Go to Step 5
5Does the engine crank? Go to Step 6 Go to Chart A-4.0
in this Section
6Use the scan tool to
check for any other
DTC(s).
Are Any Diagnostic
Trouble Codes set?
Refer To
Applicable DTC
Chart in this
Section.
Start with lowest
DTC Number
Go to Step 7
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Does the engine start? Go to Step 8 Go to chart A-3.1
in this section
81. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Compare the Tech 2
Scan tool data values
with the typical values
shown on the Tech 2
scan data page.
Are the values within the
typical ranges?
Go to Step 9 Refer to indicated
Component(s)
System checks in
this Section
91. Run the engine until
the specified operating
temperature is
reached.
2. Run the engine at
1500 RPM's for two
minutes, then let the
engine idle.
3. Compare the Tech 2
scan data with the
typical values shown
on the scan data page.
Are all the values normal
or within their typical
ranges?
85°C Refer to
"Symptom
Diagnosis Charts"
in Section 6C1-2B
Refer to indicated
"Component(s)
System " checks
in this Section
10 Check for an earthed
diagnostic "TEST"
terminal circuit.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 11
11 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
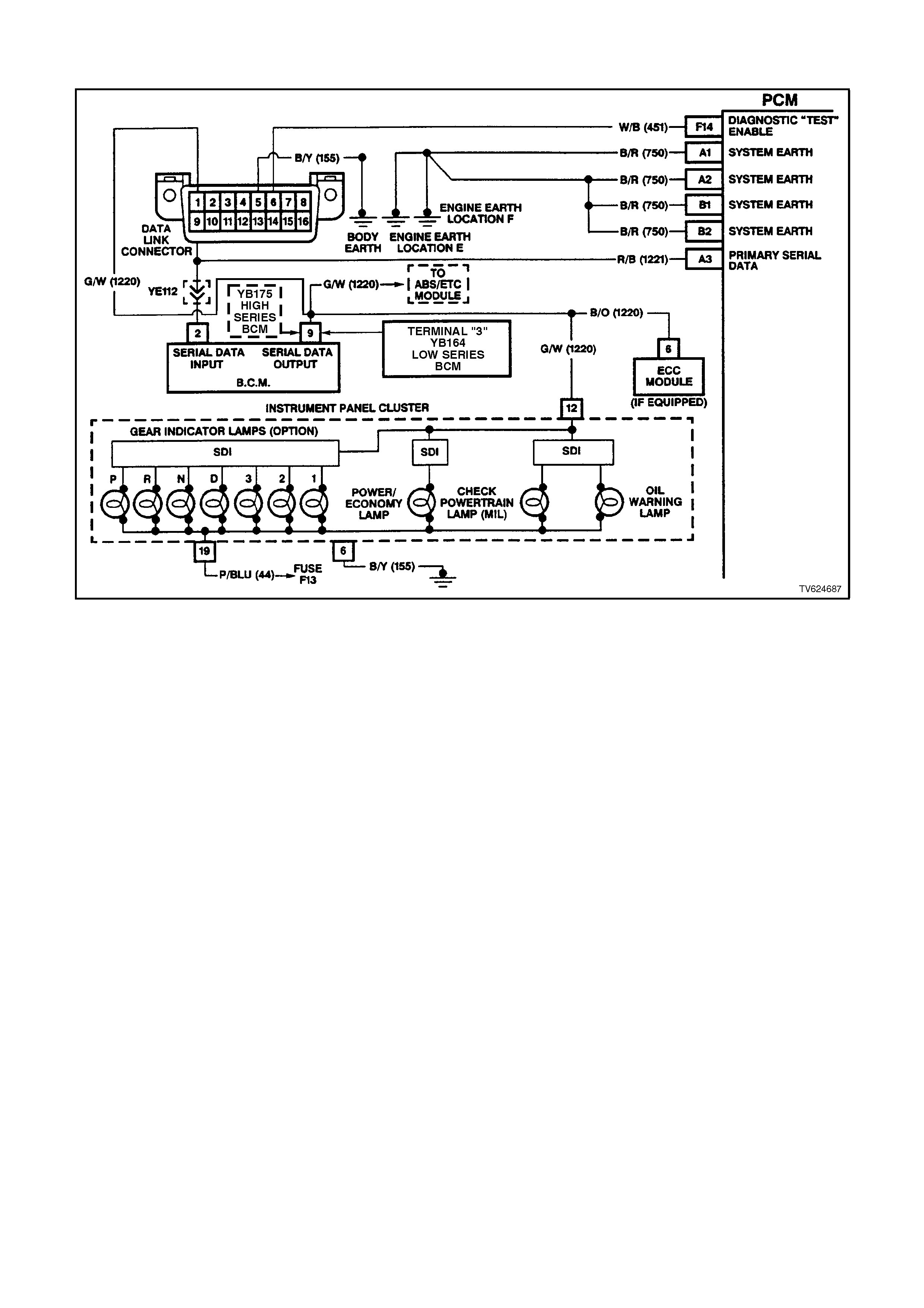
CHART A-1 - NO CHECK POWERTRAIN LAMP
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
There should always be a steady "Check Powertrain" (MIL) lamp with the ignition ON and engine OFF. The Battery
supplies voltage directly to the "Check Powertrain" (MIL) lamp through a fused circuit. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) will control the (MIL) over the serial data communication circuit to the Body Control Module (BCM).
When the PCM requests the "Check Powertrain" lamp ON, the PCM will send a message over the serial data circuit
to the BCM requesting that the (MIL) be turned ON. The BCM in return will then send a message through the serial
data circuit to the instrument panel (PI) Cluster. The PI Cluster will then determine what message the BCM is
sending, and will then turn ON the "Check Powertrain" lamp when commanded.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. Fuse F13 supplies the power to the instrument panel cluster. If fuse F13 is open, the instrument panel cluster
lamps will not light.
5. If the Tech 2 scan tool can not communicate with the vehicle, there may be a problem in the serial data line.
Chart A-2 will check the serial data line.
6. If the Tech 2 scan tool is capable of commanding the MIL ON and OFF, the PCM may be at fault.
7. This checks for the proper serial data voltage to the instrument panel (PI) cluster.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Check the PI cluster fuse
(F13).
Is the fuse OK?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 9
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
4. Probe the PCM battery
feed circuits (A8 and
B8) and then the
ignition feed circuit
(A4) with a test light
connected to earth on
the harness side.
Is the test light ON for all
three circuits?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 15
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. With a test light
connected to B+,
probe the PCM earth
circuits (A1, A2 , B1,
B2).
Is the test light ON for all
four circuits?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 16
51. Reconnect the PCM
connectors.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
Does the Tech 2 scan tool
display PCM serial data?
Go to Step 6 Go to Chart A-2
6With the scan tool still
connected to the DLC,
command the MIL ON
using the scan tool.
Does the MIL turn ON
when commanded ON
with the scan tool?
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 7
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the PI Cluster
from the dash panel.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Using a DVM, probe
the PI Cluster
connector terminal 12
with the DVM
connected to earth.
Does the DVM display
voltage at the specified
value?
4-5 volts Go to Step 8 Go to Step 10
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
8Check for poor connection
at the PI Cluster
connector.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 11
91. Repair the short to
earth in the PI cluster
fuse circuit.
2. Replace the fuse.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Repair the open in the
serial data circuit from the
BCM to the PI Cluster.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Check the "Check
Powertrain " (MIL) bulb for
an open.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 13
12 Replace the "Check
Powertrain " (MIL) bulb.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Replace the instrument
panel cluster.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
14 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Check for an open or a
short to earth in the power
circuit that did not light the
test light. Repair as
necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
16 Repair the open in the
earth circuit that did not
light the test light.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
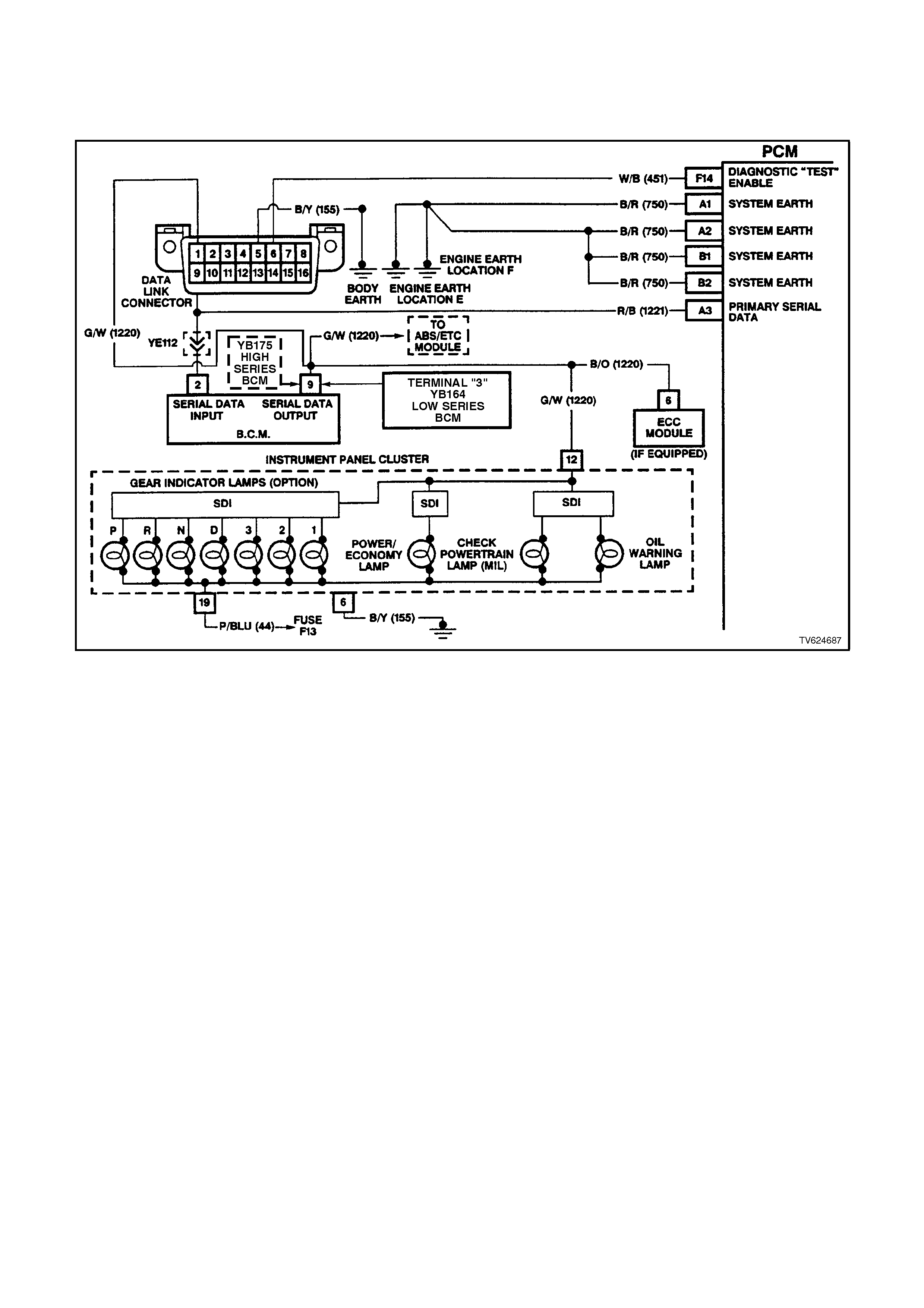
CHART A-2 - NO SERIAL DATA OR WILL NOT FLASH DTC 12,
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAM P (MI L) "CHECK POWERTRAIN" LAMP ON
STEADY
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
There should always be a steady (MIL) "Check Powertrain" lamp when the ignition is ON and the engine is OFF.
The battery voltage is supplied directly to the (MIL) "Check Powertrain" lamp bulb. The Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) will control the "Check Powertrain" lamp and turn ON via the serial data communication circuit.
With the ignition ON, and the engine OFF and the diagnostic test terminal earthed, the "Check Powertrain" lamp
should flash a DTC 12, followed by any diagnostic trouble code(s) that are stored.
With the Tech 2 scan tool connected to the DLC and the ignition switch ON, the scan tool should display serial data.
If the scan tool does not display serial data, then the serial data circuit may be open or shorted.
There are several other control modules that are connected to the serial data circuit (PCM, BCM, ABS module, ECC
module, SRS module and PI cluster). Any one of these controllers could cause a fault in the serial data line. This
fault could result in the scan tool not being able to display serial data.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This step checks if the PCM will flash a DTC 12.
3. This checks if the Tech 2 scan tool will communicate with the PCM.
4. There should be 4 to 5 volts at the DLC, terminal 9. If the voltage is higher or lower, then serial communication
will be effected. This serial data circuit is also connected to several other controllers. A problem with any one of
these other controllers, may cause serial data communication fault.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
A fault with the serial data circuit, could be caused by one or more of the several controllers connected to this serial
data circuit. Isolate the fault by disconnecting each controller one at a time until the serial data communication is
restored.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section.
21. Ignition" ON" engine
stopped.
2. Earth diagnostic
"TEST" terminal No. 6.
Does "CHECK
POWERTRAIN" lamp
flash DTC 12?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
31. Connect Tech 2 scan
tool to DLC.
2. Ignition "ON", engine
stopped.
Does the Tech 2 scan tool
display PCM serial data?
No trouble found Go to Step 4
41. Ignition "ON" engine
stopped.
2. Using DVM, probe
DLC terminal 9 with
DVM connected to
earth.
Does the DVM display
voltage varying between
the
specified value?
3-5 volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
5Check connections
between the DLC and the
PCM. If not OK repair, if
connection are OK,
Replace PCM,
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
PCM Security link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
61. Ignition "ON" engine
stopped.
2. Using DVM, probe
DLC terminal 6 with
DVM connected to
earth.
Does the DVM display
voltage at specified
value?
B+ Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
7Replace the PI cluster.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
8Is the voltage steady at or
above the specified
value?
5 volts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
91. Connect a Tech 2 scan
tool to DLC.
2. Ignition ON, engine
stopped.
Does the Tech 2 scan tool
display BCM serial data?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
10 Repair the open or the
short to earth in the serial
data circuit between the
PCM and the DLC.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Repair the short to voltage
on the serial data circuit.
NOTE:
Assure that none of the
other controllers on the
serial data circuit are
causing this voltage
problem. Unplug each
controller one at a time to
isolate a short to voltage.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
12 Check for an open in the
Diagnostic Test circuit
from the PCM to the DLC.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 5
13 Check for a short to earth,
a short to voltage, or an
open in the serial data
line. Refer to Diagnostic
Aids.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 7
NOTE:
For additional PCM wiring information refer to PCM Wiring Diagram - 2 of 8 in this section.
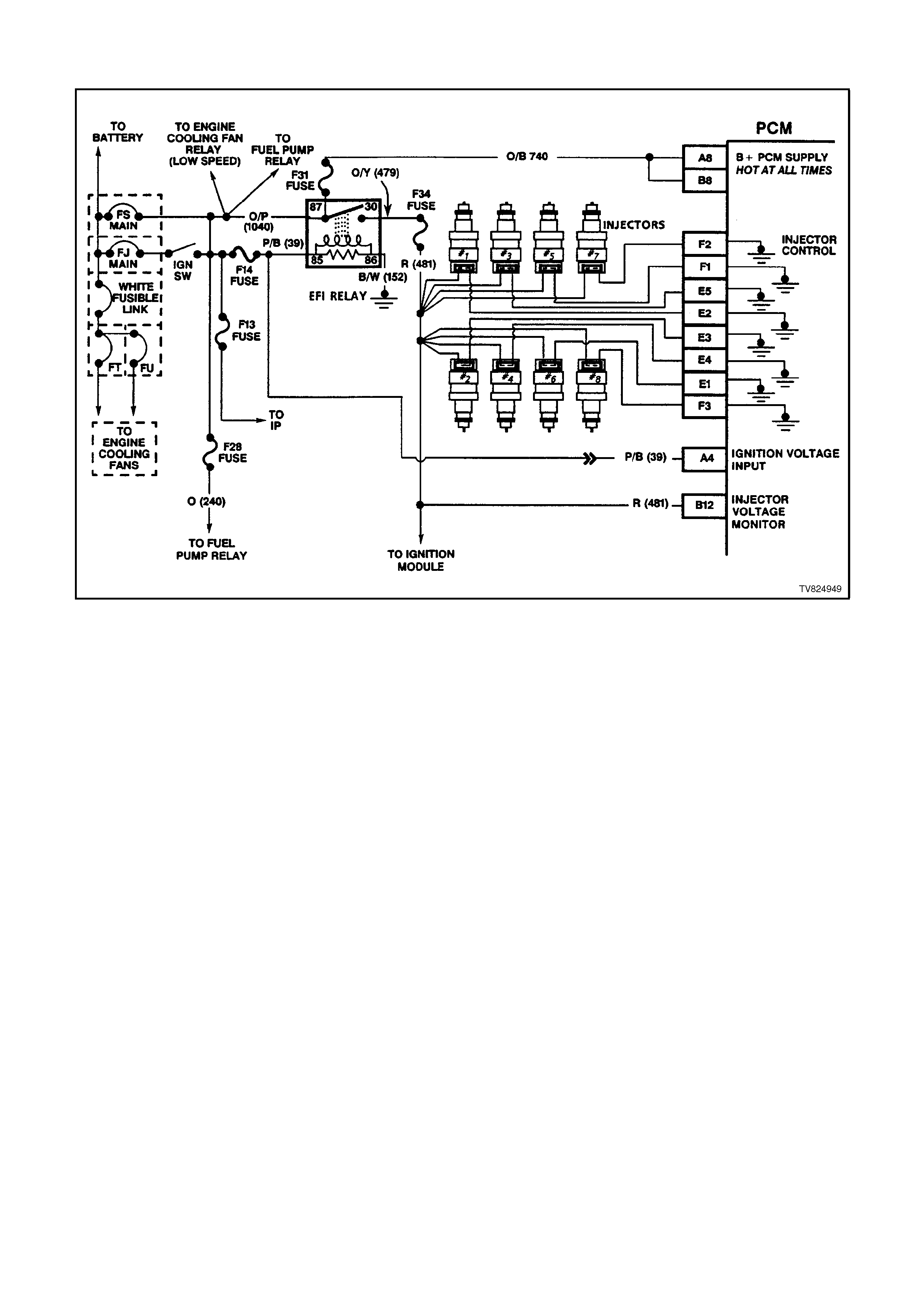
CHART A-3.1 - ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
This is the first of several diagnostic charts that must be followed in order to find the cause of a no-start. These
charts assume, that the cranking motor circuit is in good working order, and that the engine will crank with adequate
RPM. These charts also assume that Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 31 or DTC 46 are not set. The On-Board
Diagnostic System Check is always the starting point for all diagnostic procedures.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. There are a few cases where the PCM could cause a no-start. The On-Board Diagnostic System Check will
uncover any problems in the PCM power circuit and the earth circuit.
4. This is a quick check of the fuel system. The easiest place to install the pressure gauge is where the fuel pipes
come up into the engine compartment. There are 2 hoses, and the gauge must be connected to the hose or
pipe leading directly to the fuel rail. This connection is on the left (passenger) side of the fuel rail. The other
hose or pipe leads to the pressure regulator, and no pressure testing is done there. If the pressure is not as
specified, or continues to drop after the pump stops running, the Fuel System Diagnostic Chart A-4.2 in this
Section must be used.
6. Note that this check is for sufficient voltage at the spark plug wire. If, the spark plug electrodes are wet with fuel
(engine flooded), the engine may not start. A flooded engine is a symptom of some other problem. There is no
normal condition that should ever be able to flood the engine.
NOTE:
Use ST 125 spark checker or equivalent. An ST 125 requires about 25,000 volts (25 kilovolts, or 25 kV) to "spark".
Do not use a spark plug in open air earthed to the engine as an indication of sufficient "spark". Only a few kilovolts
are required to jump the gap of a spark plug outside of the engine, and that would be an inadequate test of the
ignition coil output ability.
8. At this point the Fuel system and the ignition system are OK. Continue to inspect the rest of the PCM input
sensors and outputs. Use the typical scan tool value charts, the functional test charts, and the voltage pin out
charts for additional information.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Check the power feed
fuses F14, F28, F34
and F35.
2. Check the FS Main
fuse, the FJ main fuse,
and the white fusible
link wire.
Are all of the above circuit
protectors OK?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 7
31. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
3. Remove the fuel filler
cap.
4. Use the Tech 2 to
command the fuel
pump ON and OFF
while listening at the
fuel filler neck for the
fuel pump to turn ON
and OFF.
Does the fuel pump turn
ON and OFF when
commanded?
Go to Step 4 Go to Chart A-4.1
in this Section
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the EFI relay
from the engine
compartment FUSE
AND RELAY CENTRE,
then crank the engine
for 15 seconds to
relieve the fuel
pressure.
3. Ignition OFF, install a
fuel pressure gauge
(Gauge to be installed
in the pressure line,
between the fuel feed
hose and the fuel inlet
line to the fuel rail, at
left rear of fuel rail.)
4. Reinstall the fuel pump
relay.
5. Turn the ignition ON
for 10 seconds.
Does the fuel pressure
hold steady between the
specified value for two
minutes?
270-350
kPa Go to Step 5 Go to Chart A-4.2
in this Section
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the fuel
injector electrical
connectors.
3. Connect a test light
across the No.1
cylinder fuel injector
harness terminals.
4. Have a helper crank
the engine while you
observe the light.
5. Repeat the test on
cylinders No. 2 through
No. 8.
Did the test light flash on
all eight cylinders while
cranking the engine?
Go to Step 6 Go to Chart A-3.2
in this section
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the spark plug
wire from the No. 1
spark plug.
3. Connect an ST125
spark tester to the No.
1 cylinder (see note
above).
4. Check for spark while
cranking the engine. A
few sparks and then
nothing is considered
no spark.
5. Continue to check for
spark on the remaining
cylinders.
Was their spark on all
eight cylinders?
Go to Step 8 Go to Chart A-8.1
in this Section
71. Repair the short to
earth in the circuit that
the circuit protector
was found open.
2. Replace the open
circuit protector.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
8At this point, the fuel
control system, the fuel
delivery system, and
ignition system are OK.
Check For:
• Fouled spark plugs.
The proper MAF
sensor operation. If the
engine will start with
the MAF sensor
electrical connector
disconnected refer
Chart A-6.1 in this
Section.
The proper TP sensor
circuit operation. Use
the Tech 2 scan tool to
monitor the TP sensor
signal. If the voltage is
over 2.5 volts with the
throttle closed, refer to
Chart A-6.2 in this
Section.
• A restricted exhaust
system. Loosen the
front pipe from the
exhaust manifold(s). If
the engine will start,
refer to Chart A-13 in
this Section.
An improper Engine
Coolant Temperature
(ECT) sensor
resistance. Refer to
DTC 14 DIAGNOSTIC
AIDS to check the
resistance of the ECT
sensor.
• The camshaft timing
chain slipped or
stripped, causing the
camshaft to be out-of-
time.
• Inadequate engine
compression.
• Measure the
resistance across the
terminals of each fuel
injector. Replace any
fuel injector that does
not measures between
14 and 16 Ohms.
Verify Repair
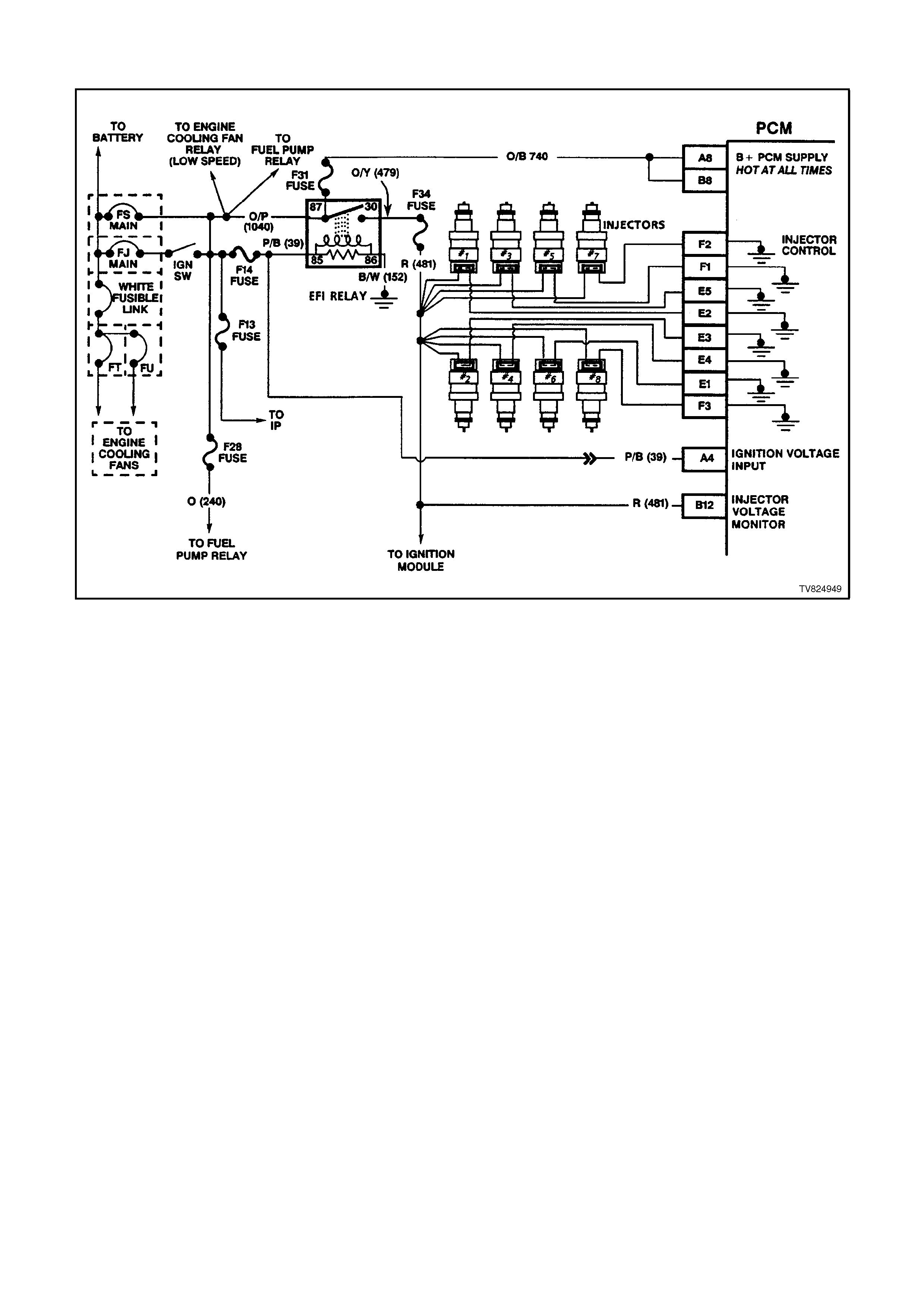
CHART A-3.2 - ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
These charts assume, that the cranking motor circuit is in good working order, and that the engine will crank with
adequate RPM. These charts also assume that Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 31 or DTC 46 are not set. The On-
Board Diagnostic System Check is always the starting point for all diagnostic procedures.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. Do not use this chart unless sent here from Chart A-3.1. There must be some preliminary checks done before
continuing with this chart. Failure to perform these steps could lead to an incorrect diagnosis.
2. This test both circuits for an open. Repair the open in the circuit that did not light the light.
3. This test CKT 152 for an open in the EFI relay circuit.
6. The Security Link procedure must be performed whenever the PCM or the PROM is replaced. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 SERVICE OPERATION for the Security Link procedures.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2From Table A-3.1
1. Ignition OFF.
2. Reconnect the fuel
injector's electrical
connectors.
3. Disconnect the EFI
relay.
4. Ignition ON.
5. With a test light
connected to earth,
probe the EFI relay
harness connector
CKT 39, then CKT
1040.
Is the test light ON at both
circuits?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 8
31. Ignition OFF.
2. EFI relay
disconnected.
3. With a test light
connected to B+,
probe EFI relay CKT
152.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 9
41. Ignition OFF.
2. EFI relay
disconnected.
3. Using a fused jumper
wire, jumper across
terminal 87 to terminal
30 on the EFI harness
connector.
4. Attempt to start the
engine.
Does the engine start and
continue to run?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
51. Inspect CKT 481 for an
open, or a short to B+
between the EFI relay
and the fuel injectors.
2. Repair as necessary.
Was a fault found in CKT
481?
Verify Repair Go to Step 6
6Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
7Replace the EFI relay.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
81. Inspect the circuit that
did not turn ON the
test light for an open.
2. Repair as necessary
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Repair the open in the EFI
relay earth CKT 152.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
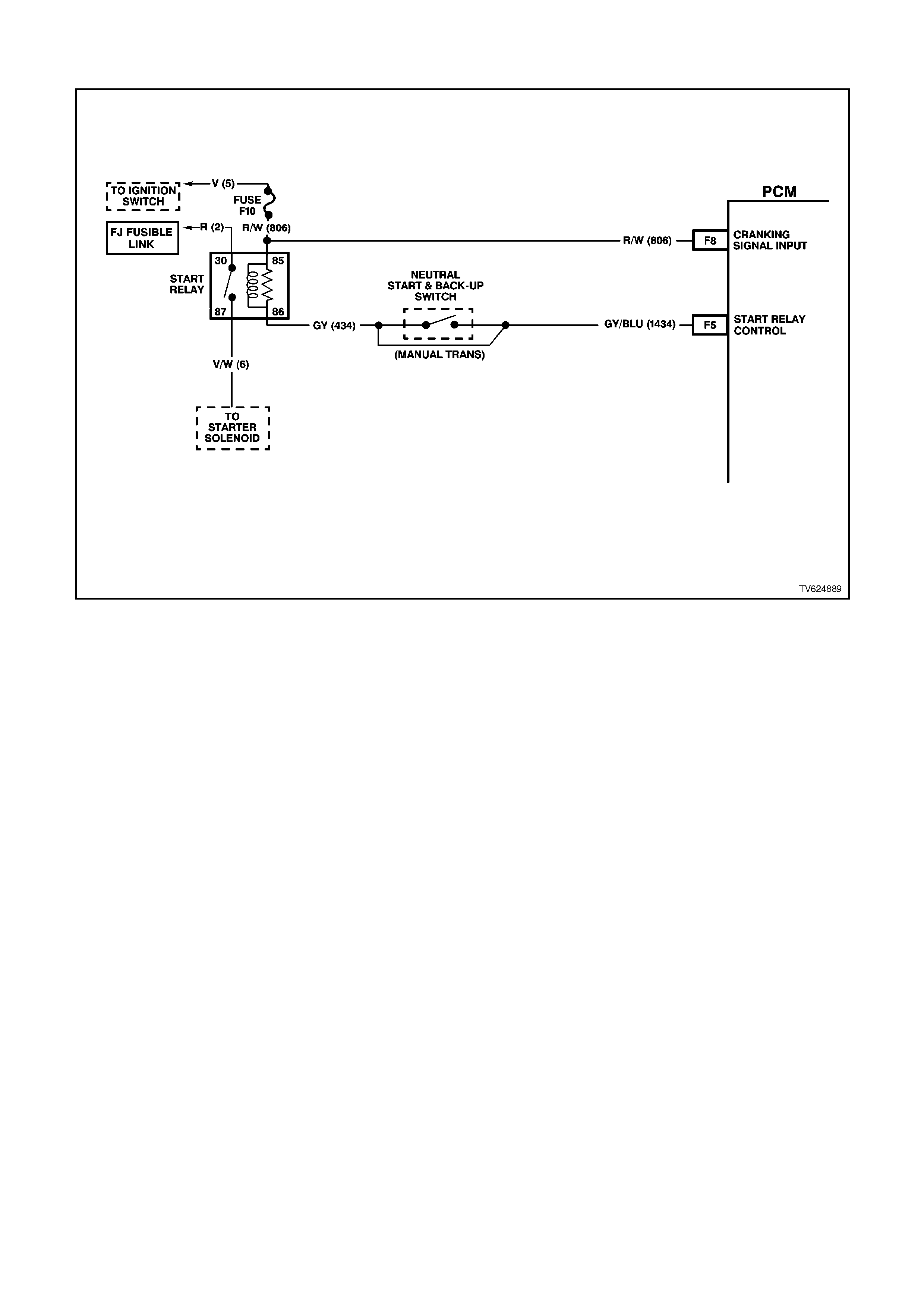
CHART A-4.0 - STARTER CRANKING CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
When the ignition is turned to the ON position, battery power is supplied from a fusible link to the Start Relay
terminal "30". As the ignition switch is turned to the START position, power is also supplied from the ignition switch
to the PCM Cranking Signal Input terminal, and to the Start Relay terminal "85". The PCM supplies the earth signal
needed to energise the Start Relay and allows power to the starter motor.
When the PCM receives this voltage input at the Cranking Signal Input terminal, the PCM will then look for the
proper Theft Deterrent signal sent from the BCM. If the PCM has determined that the proper Theft Deterrent signal
is present, the PCM will allow the vehicle to crank. If the PCM determines that a improper Theft Deterrent signal
was sent from the BCM, or no Theft Deterrent signal was sent, the PCM will not supply a earth signal from the PCM
terminal to the Start Relay terminal "86". When the Start Relay receives this earth signal from the PCM, the relay will
be energised, allowing the starter motor to operate. This removed earth signal to the Start Relay w ill cause the
vehicle not to crank.
The cranking signal provides an input for enabling fuel cut off during a possible backfire situation. During an engine
start, when the ignition switch is released from the crank position before the engine is running, the engine may
backfire. The PCM stops all injector 12.5 milliseconds. pulses when the engine speed is less than 450 RPM, the
coolant temperature is greater than -4 degrees C, and a cranking signal is not received, but was received within the
previous 12.5 milliseconds.
If there is a fault with the PCM Start Relay circuit a DTC 91 will set.
If there is a problem with the Theft Deterrent signal from the BCM to the PCM, a DTC 31 will set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This step checks to see if DTC 31 or 91 is set. Either of these DTC could prevent the vehicle from cranking.
This step also verifies that if a PCM was replaced, that the Security Link procedure was performed.
3. This step checks to see if power is being applied to the starter motor. If test light lights, the problem is with the
starter motor.
12. This step checks the adjustment of the Neutral start switch.
18. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Use the scan tool to
check for a DTC 31 or
a DTC 91.
Is a DTC 31 or a DTC 91
set?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
chart
Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Using a test light,
probe the starter
solenoid terminal "S"
with test light
connected to earth.
3. Have a helper turn the
ignition switch to the
START position, note
the test light.
Does the test light
illuminate when the
ignition switch is turned to
the START position?
Refer to Section
6D2-2 ENGINE
ELECTRICAL -
STARTING
SYSTEM
Go to Step 4
4Check fuse F10 for an
open.
Was an open fuse found?
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 5
51. Remove the start relay.
2. With a test light
connected to earth
probe the start relay
harness terminal 30.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
Does the test light
illuminate??
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 16
61. With the start relay still
removed and the test
light connected to
earth probe the start
relay harness
terminal 85.
2. Turn the ignition to the
start position.
Did the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 15
7Check for an open circuit
between the starter
solenoid and the Start
Relay.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 9
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the Start
Relay.
3. Connect a test light
between the relay
harness terminal 85
and terminal 86.
4. Turn the ignition switch
to the START position.
Does the test light
illuminate when the
ignition switch is turned to
the START position?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 10
9Replace the Start Relay.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
10 Is the vehicle equipped
with a manual
transmission?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 13
11 1. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
2. With a test light
connected to B+,
probe both of the
circuits at the neutral
start switch.
Did the test light illuminate
at both terminals?
Go to Step 17 Go to Step 12
12 Check the adjustment of
the neutral start switch. If
the adjustment is OK,
replace the neutral start
switch.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Check for open circuit
from the neutral start
switch to the Start Relay.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 18
14 Repair the short to earth
in the faulty circuit.
Replace the fusible link or
the fuse as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Repair the open in the
ignition circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
16 Check for an open circuit
2 including the fusible link.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
17 Repair the open in circuit
434.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
18 Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6D2-3
Service Operations, for
PCM Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
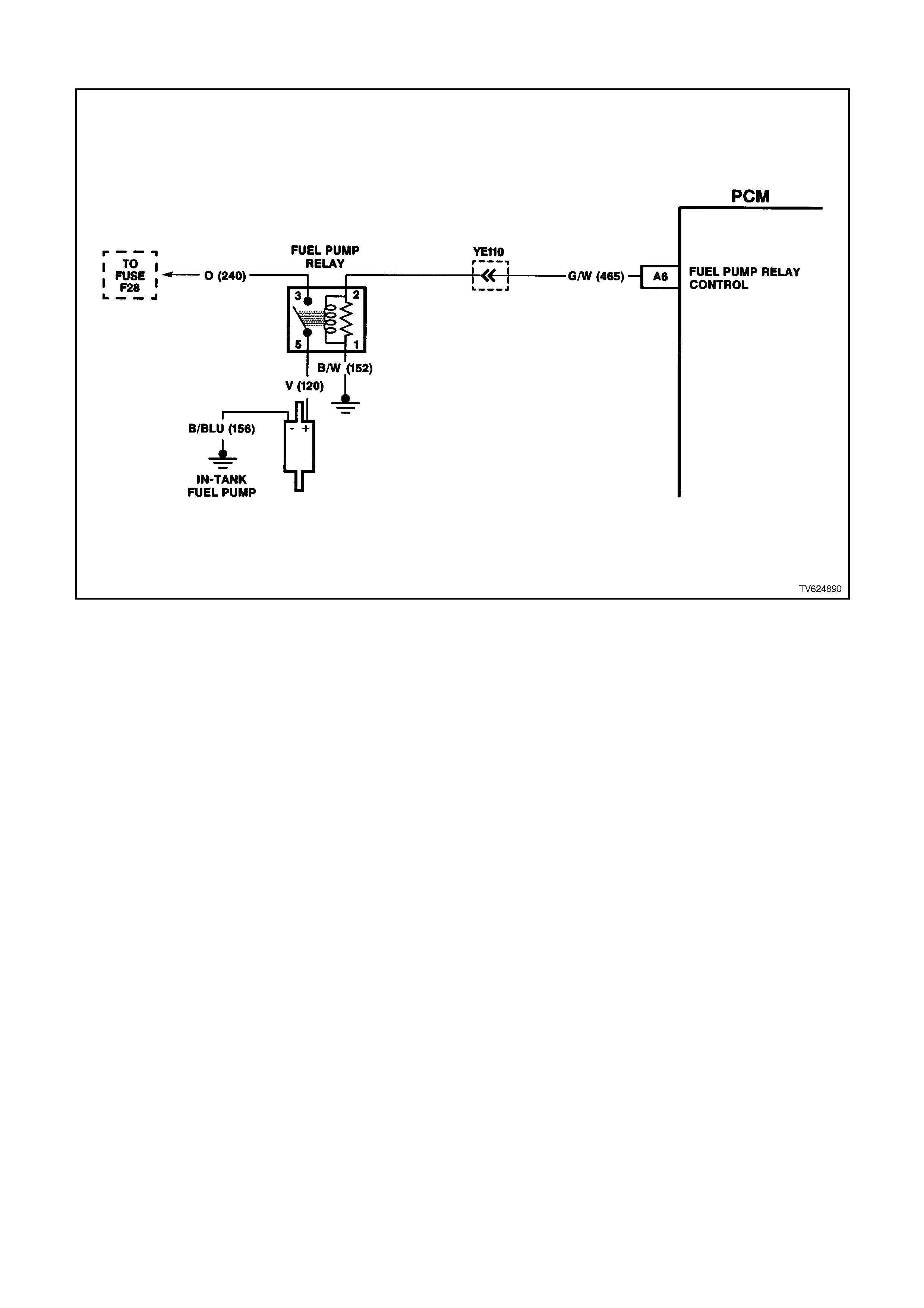
CHART A-4.1 - FUEL PUMP ELECTRI CAL CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the Power Control Module (PCM) energises the Fuel Pump Relay control
output. The PCM will provide a B+ voltage to the Fuel Pump Relay, as long as the engine is cranking or running,
and the PCM is receiving crankshaft reference input signal pulses.
If there are no distributor reference pulses (ignition ON, engine OFF - or - engine stalled), the PCM will shut OFF
the Fuel Pump Relay within 2 seconds.
Improper electrical control of the pump will result in one or more of the following symptoms:
• Cranks, but won't run.
• Hard start.
• Cuts out, may feel like an ignition problem.
• Excessive cranking ti me.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. Do not use this chart unless sent here from another chart. It is important to follow this sequence.
2. The test light should light on both power feed circuits.
5. If the B+ voltage is not being supplied to the fuel pump inspect for an open circuit. The fuel pump will not
operate if B+ voltage is not supplied
13. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the fuel pump
relay.
3. Ignition ON.
4. With a test light
connected to earth,
probe the fuel pump
relay power feed
circuits (CKT 240 and
CKT 465) on the
harness side of the
fuel pump relay
connector.
Did the test light illuminate
on both of the circuits?
Go to step 3 Go to step 7
31. Ignition ON.
2. Fuel pump relay
disconnected.
3. With a test light
connected to B+,
probe the fuel pump
relay earth circuit (CKT
152) on the harness
side of the fuel pump
relay connector.
Did the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 4 Go to step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Relay disconnected.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Using a fused jumper,
jumper the power feed
circuit, CKT 240
(terminal 3) to CKT
120 (terminal 5).
4. Listen for the fuel
pump to turn ON.
Does the fuel pump turn
ON?
Go to Step 9 Go to step 5
51. Reinstall the fuel pump
relay.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Raise the vehicle and
suitably support.
4. Disconnect the fuel
pump motor electrical
connector.
5. Ignition ON.
6. With a test light
connected to earth,
probe the fuel pump
motor power feed
circuit (CKT 120) on
the fuel pump motor
electrical connector
side.
7. Using the Tech 2, turn
the fuel pump ON and
OFF.
Does the test light turn
ON and OFF when the
fuel pump
is commanded ON and
OFF?
Go to step 6 Go to Step 10
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the fuel
pump motor electrical
connector.
3. Using a test light
connected to B+,
probe the fuel pump
motor earth circuit
(CKT 156) on the
connector side.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Inspect the power feed
circuit that did not light the
test light for an open or a
short to earth.
Was an open circuit
found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 13
8Repair the open, or the
short to B+ in the fuel
pump relay earth circuit
(CKT 152).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Replace the Fuel Pump
Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Repair the open or the
short to earth, in the fuel
pump motor power feed
circuit (CKT 120).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Repair the open or the
short to B+ in the Fuel
Pump motor earth circuit
(CKT 156).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
12 Replace the fuel pump
motor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
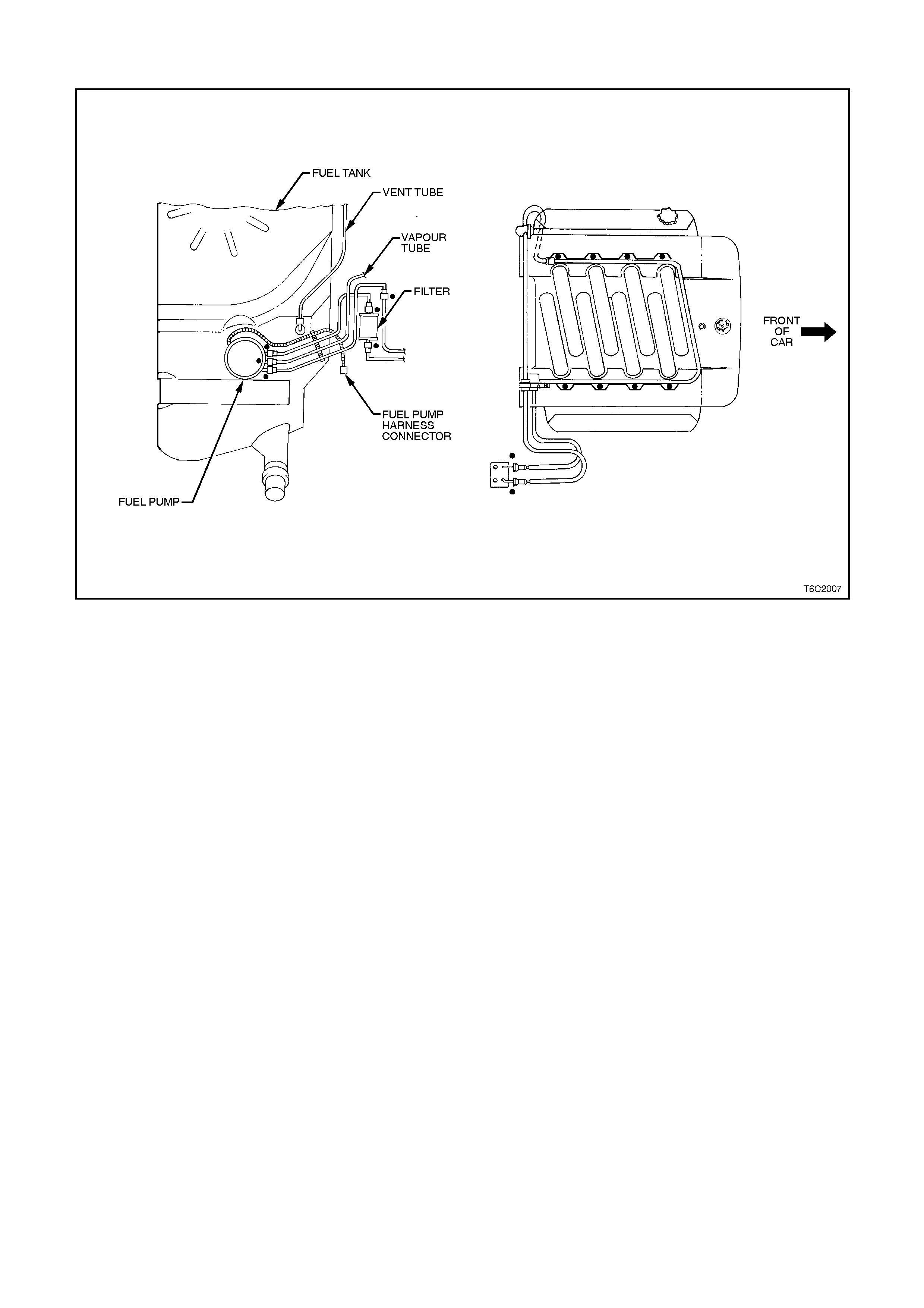
CHART A-4.2 - FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Fuel is drawn from the tank by the electric fuel pump and is fed under pressure through a fuel filter. The fuel then
continues to the fuel rail and then is injected into the ports by the fuel injectors.
Fuel pressure in the system is governed by the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the
pressure between the fuel pressure inlet and the intake manifold. Excess fuel is returned to the fuel tank through
the fuel return line.
The fuel pump has a check valve to maintain pressure at the fuel rail after the pump stops running. The check valve
plays an important part in the fuel delivery system. The check valve keeps the fuel rail pressurised with fuel after the
pump is turned off. The check valve is inside the fuel pump, and is not serviceable.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. Do not use this chart unless instructed to do so from chart A-3.1. There are some preliminary procedures that
must be done before continuing on with this chart.
5. Thoroughly inspect the components mentioned for any restrictions. Even the slightest restriction can cause a
problem with the fuel flow and the fuel pressure.
6. Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 414 kPa as damage to the system can occur from excessive
pressures.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS
Inspect for any obvious signs of fuel leakage. Such as fuel odours and wet spots. Also inspect the underbody fuel
lines for any sort of damage.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check
2From Table A-3.1
Did the fuel pressure read
between the specified
value than begin to lose
pressure.
270-350
kPa Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3Did the fuel pressure read
less than the specified
value
270 kPa Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
41. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Turn the ignition OFF
for 10 seconds then
ON.
3. Use the Tech 2 to turn
the fuel pump ON for
10 seconds, while
observing the fuel
pressure gauge.
4. After the fuel pump is
turned OFF, and while
the pressure is
dropping, pinch shut
the pressure side hose
at the fuel gauge
sender unit
connection.
Does the fuel pressure
hold steady?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
5Inspect for a restriction in
the following components
or systems.
• A fuel pressure line
restricted between the
fuel pump and the fuel
rail.
• A fuel supply line
restricted in the fuel
tank.
• A restricted fuel filter.
• A restricted in-tank fuel
strainer.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
61. Ignition OFF for 10
seconds.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Release the pressure
(supply) hose to the
fuel rail.
4. While y ou observe the
pressure gauge, turn
ON the fuel pump for
10 seconds, using the
Tech 2.
5. While the pressure is
dropping, pinch shut
the fuel return hose at
the fuel gauge sender
unit.
CAUTION:
Do not allow the fuel
pressure to exceed 414
kPa when performing this
test.
Is the fuel pressure
greater than the specified
value?
350 kPa Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Replace the fuel pressure
regulator.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Locate and replace the
leaking fuel injector(s).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Repair or replace any
leaky parts in the
pressure-side of the fuel
system.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Repair or replace the
faulty component or
system.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Replace the fuel pump
motor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
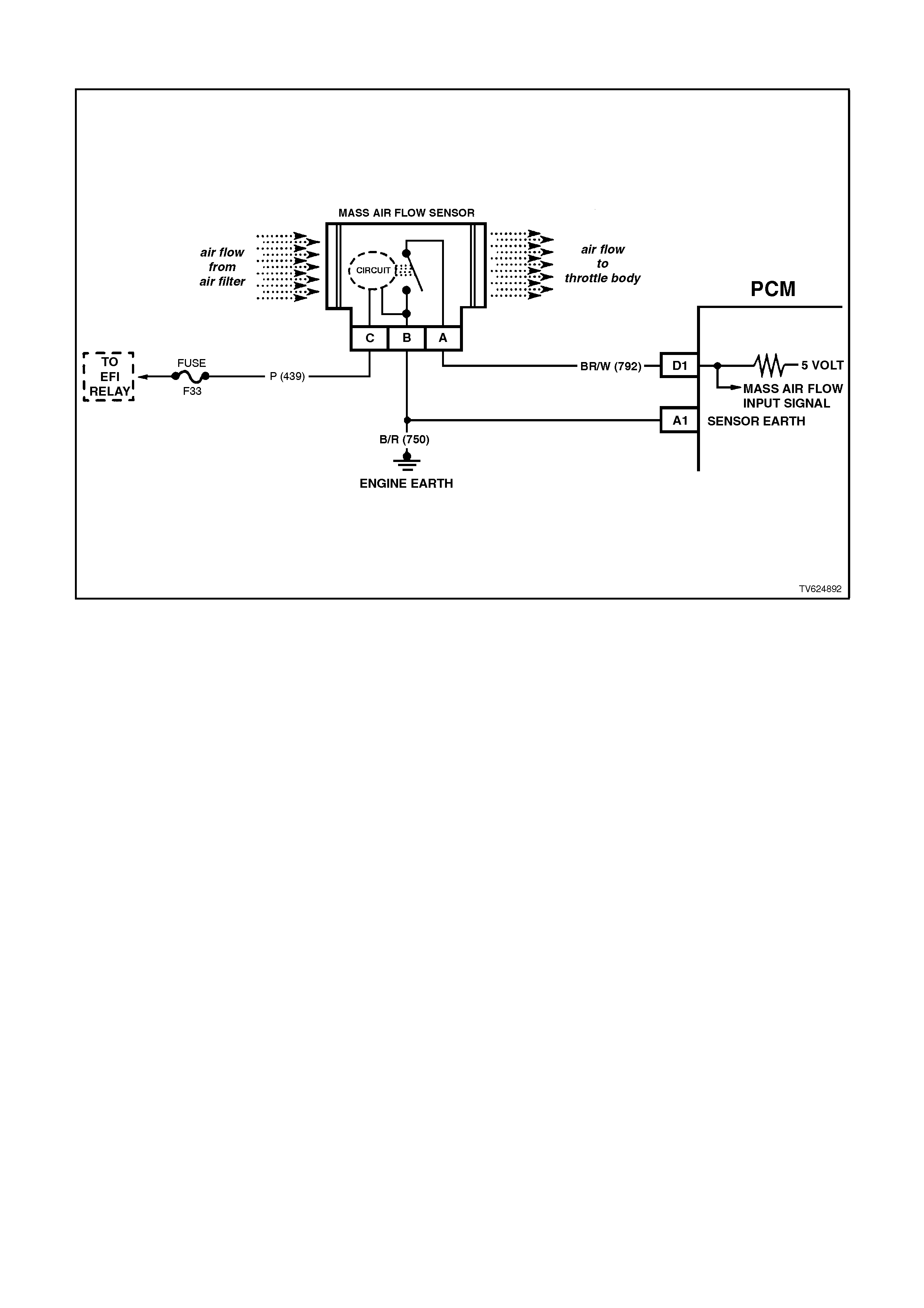
CHART A-6.1 - MAF SENSOR OUTPUT CHECK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The signal that is sent from the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is sent in the form of a frequency output. A large
quantity of air passing through the MAF sensor will be indicated as a high frequency output (such as when under
acceleration). A small quantity of air passing through the sensor will be indicated as a low frequency output (such as
when decelerating or at idle). The Tech 2 "Scan" tool displays this information both as air flow in grams per second,
grams per cylinder and frequency. A normal reading is approximately 6-10 grams per second at idle and increases
with RPM.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to Step number(s) on the Diagnostic Chart.
3. This checks for the proper Mass Air Flow in grams per second at idle.
4. This checks for the proper Mass Air Flow in grams per second at 2500 RPM.
5. This checks the Mass Air Flow sensor for a steady decrease in grams per second as the RPM changes from
2500 to idle.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Check the air intake ducts for any restrictions.
• Check the air intake ducts for leaks between the MAF sensor and the intake manifold.
• Check for a partially restricted exhaust system.
• Check for any other source that would allow air into the engine after the MAF sensor.
• This would include:
inlet manifold gasket
inlet manifold
throttle body and or gasket
PCV system, this includes the oil dipstick for proper seating
injector o-rings
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Is a DTC 32 present? Go to DTC 32 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, the engine
running at the normal
operating temperature
(90°C).
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Using the Tech 2;
select "Mass Air Flow
G/S".
Is the reading between
the specified value at
idle?
6-10
Grams
Per
Second
(G/S)
at Idle
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
41. Increase the engine
speed to 2500 RPM
and hold the speed
steady.
2. Monitor the Tech 2
MAF sensor reading.
Is the reading between
the specified value?
20-30
Grams
Per
Second
(G/S) at
2500
RPM
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Release the throttle, and
watch the MAF sensor
readings on the scan tool.
Does the Mass Air Flow
G/S decrease at a steady
rate between the specified
value at idle?
6-10
Grams
Per
Second
(G/S)
at idle
No trouble found
with Mass Air
Flow sensor
Go to Step 6
6Check for a restriction in
the Mass Air Flow
induction system. Also
check for air leaks after
the MAF sensor or a
possible restricted
exhaust system.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids
above.
If all checks OK, replace
the Mass Air Flow sensor.
Is the action complete ?
Verify Repair
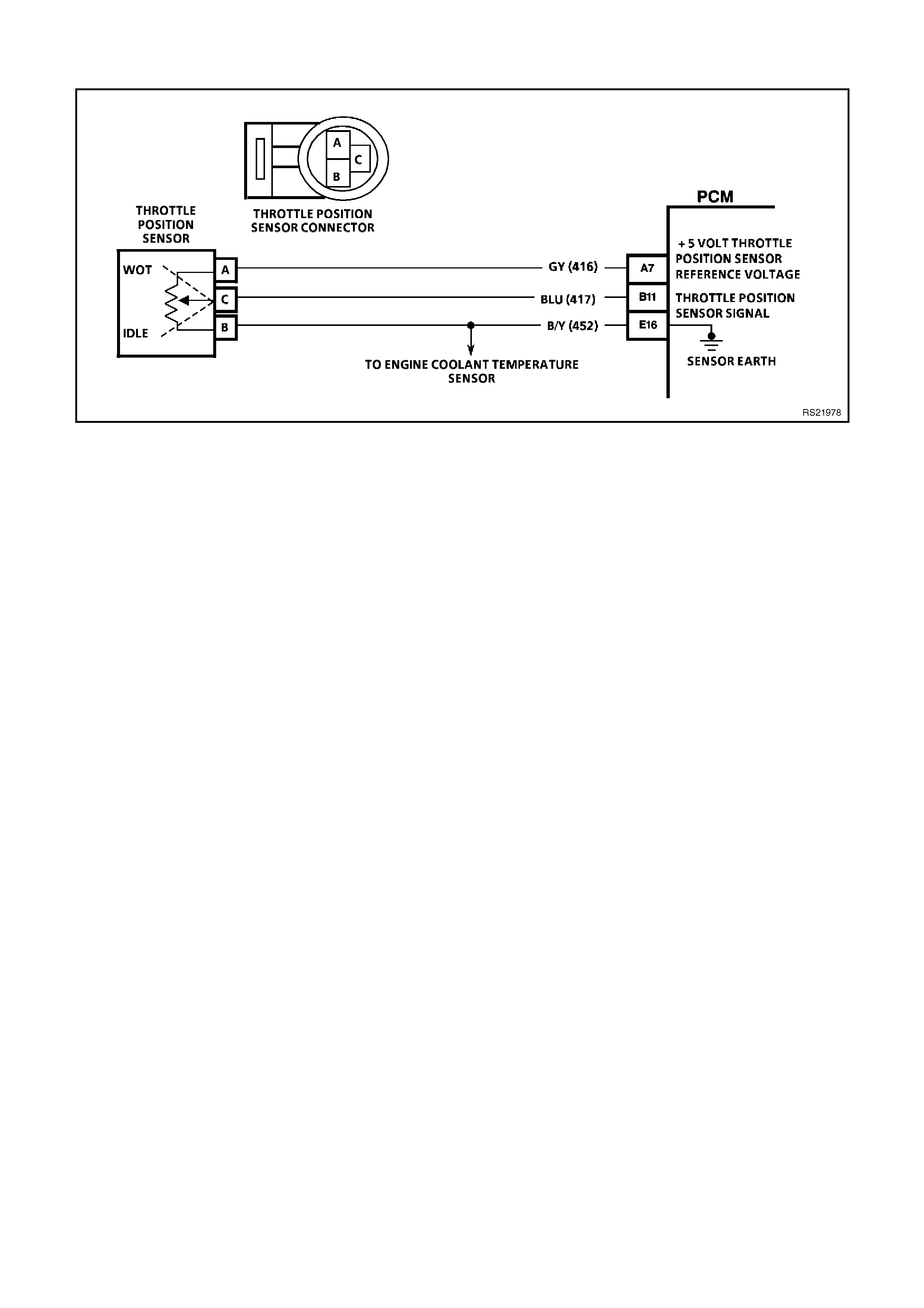
CHART A-6.2 - TP SENSOR OUTPUT CHECK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The TP sensor is a potentiometer which is mounted to the throttle body. The TP sensor is rotated by the throttle
body shaft. The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference and an earth circuit to the TP sensor. The TP sensor will send a
voltage signal back to the PCM based on the throttle angle position.
At a closed throttle position, the output voltage is usually less than 1.0 volt. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that, at wide-open throttle, the output should be greater than 4.0 volts. By monitoring the output voltage
from the TP sensor, the PCM can determine the fuel needs based on throttle opening (driver demand).
If the PCM receives a high voltage when the engine is running at less than 400 RPM, a hard start may result (clear-
flood mode). Once a Diagnostic Trouble Code is set, the PCM will use a default value for TP sensor based on
engine RPM to enable the vehicle to be driven, although performance could be less than normal.
The TP sensor is not adjustable. The PCM uses the reading at idle as 0% throttle, so no adjustment is necessary.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This checks the voltage in the idle position. The voltage is usually less than 1.0 volt.
3. The voltage should increase at the same steady rate in which the throttle is opened.
6. With the throttle valve wide open, the TP sensor output should be greater than 4 volts.
7. If the throttle stop screw has been inadvertently reset, the TP sensor output at idle could be out of limit.
9. If the closed-throttle voltage is over 2.5 volts, hard starting may be encountered (worse cold) due to "clear-
flood" mode. This mode occurs when engine RPM is less than 400, and TP sensor input indicates the throttle
is more than 80% open. Possible causes: short to voltage on input signal circuit 417, open earth circuit 452, or
a faulty sensor.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check
21. Ignition ON, engine
OFF, throttle plate
closed.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Monitor the TP sensor
Voltage.
Is the voltage on Tech 2
Scan tool between the
specified values?
0.25 to
1.25
volts
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
2. While monitoring the
Tech 2 Scan tool,
slowly and steadily
depress the
accelerator pedal to a
wide open position.
Did the voltage increase
at a steady rate w ith the
throttle movement?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
41. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. With a Tech 2 Scan
monitor the TP sensor
voltage.
Is the TP sensor voltage
within the specified value?
1.25 to
2.5 volts Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5Is the TP sensor voltage
greater than the specified
value?
2.5 volts Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
61. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
2. With the Tech 2 Scan
tool still connected,
monitor the voltage as
the throttle valve is
opened to a wide open
position.
Have a helper ensure that
the throttle valve is fully
open when accelerator
pedal is fully depressed.
If throttle valve does not
fully open when pedal is
depressed, check for
extra floor mats or carpet
under accelerator pedal.
Then refer SERVICE
OPERATIONS, Section
6C2-2 - "Throttle Cable -
Adjust".
Is the TP sensor voltage
greater than the specified
value?
4 volts TP sensor is
working properly
Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section.
Go to Step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
71. Check the throttle stop
screw, refer to Section
6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS. Reset
if incorrect.
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
3. Recheck the TP
sensor voltage.
Is the TP sensor voltage
within the specified value?
0.25 to
1.25
volts
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
8Replace the TP sensor.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
91. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the TP
sensor.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
4. Monitor the TP sensor
voltage with the Tech 2
scan tool.
Is the TP sensor voltage
below the specified value?
1.25 volt Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
10 Check for an open in the
TP sensor earth circuit.
Was problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 8
11 Repair the short to voltage
in the TP sensor signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
12 The voltage is below 0.25
volts
Repair the short to earth
in the TP sensor signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
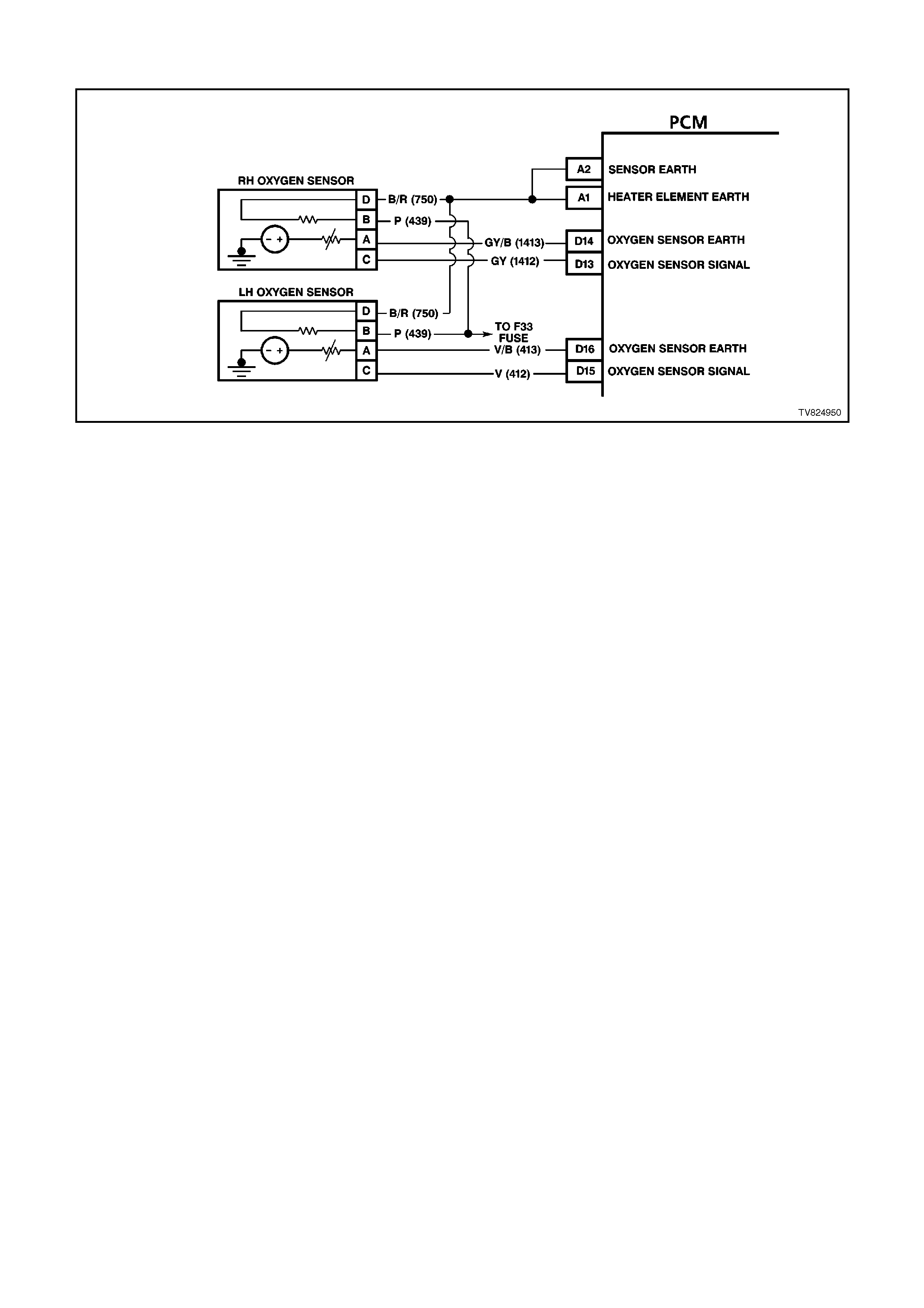
CHART A-6.3 - OXYGEN SENSOR CHECK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The O2 sensor is located in the exhaust stream near the engine. The O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the
exhaust gases in the exhaust stream then sends an output voltage to the PCM relative to the oxygen content. This
voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean mixture) to greater than 900 mV(low O2
exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM should always supply the O2 sensor with a constant 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins
heating up its internal resistance begins to decrease. The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing
voltage that differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2
sensor the PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
When the ignition is turned ON, B+ is applied to the O2 sensor’s heater element. Approximately 30 seconds after
the B+ is applied to the heater portion of the O2 sensor, the O2 sensor should reach a temperature greater than
500°C. The heated O2 sensor becomes active much quicker than a non-heated O2 sensor. This allows the PCM to
control the air/fuel ratio more consistent over a wider range of operating conditions.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the Diagnostic Chart.
2. Never perform this test on a cold engine. The oxygen sensor must be near normal operating temperature for
this chart to work. It is important to see a low voltage because this means the oxygen sensor is only monitoring
oxygen in the exhaust pipe.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Start the engine.
2. Run the engine
between 1600 and
1800 RPM for 2
minutes or until the
engine coolant
temperature is above
85° C, then let the
engine idle.
3. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
4. Monitor the O2 sensor
voltages.
5. With the engine idling,
Press the Down arrow
button on the Tech 2
"Scan" tool until 11.7
A/F ratio is displayed,
at the same time note
the response of the O2
Sensor.
6. The O2 Sensor should
display above the
specified value.
7. Then press the button
on the Tech 2 "Scan"
tool until 17.7 A/F ratio
is displayed, at the
same time note the
response of the O2
Sensor.
Did the O2 Sensor display
above and below the
specified value?
Above
700 mV
Below
100 mV
No trouble found Go to Step 3
3Replace the O2 Sensor.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
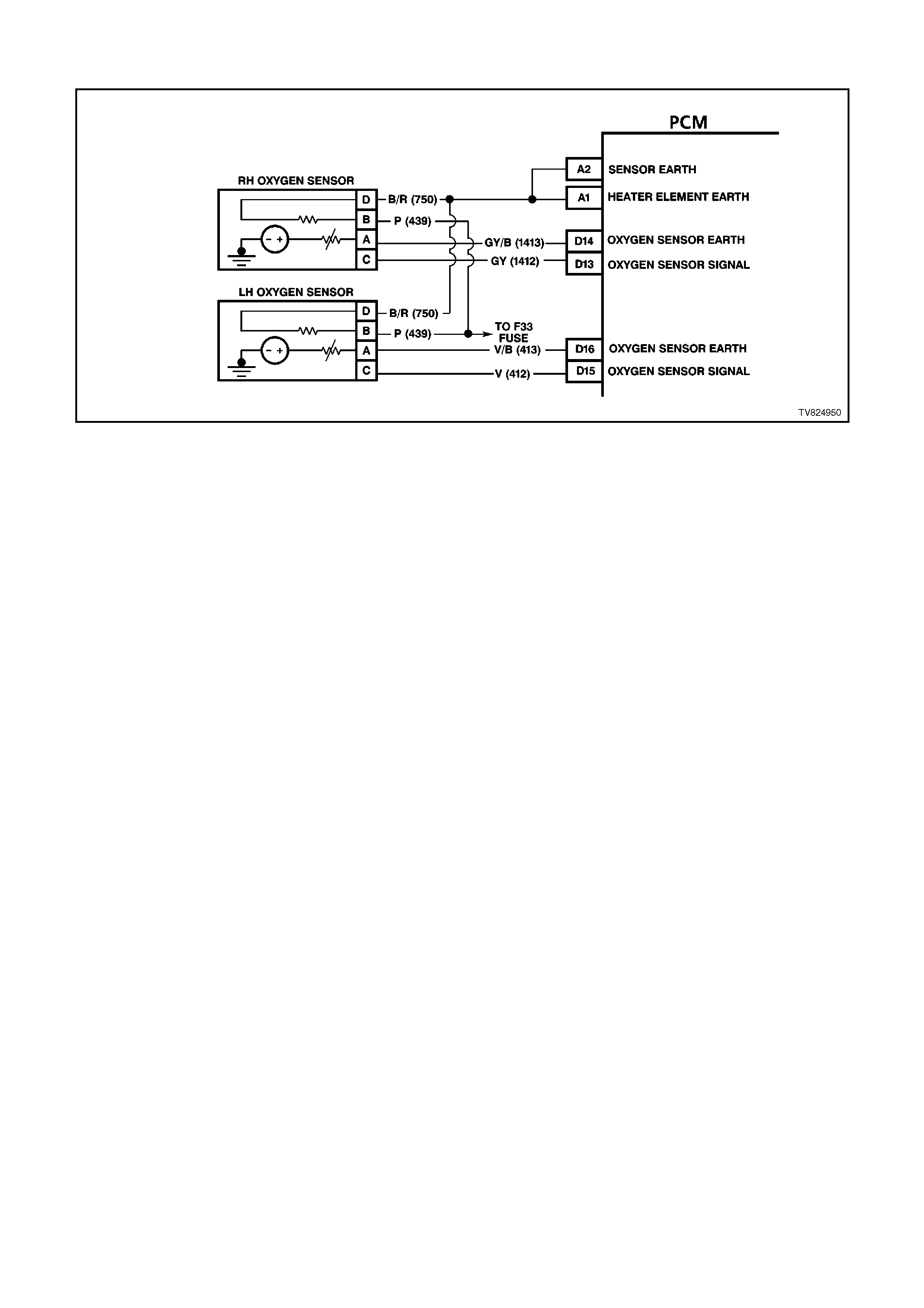
CHART A-6.3A - OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER CHECK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The O2 sensor is located in the exhaust stream near the engine. The O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the
exhaust gases in the exhaust stream then sends an output voltage to the PCM relative to the oxygen content. This
voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean mixture) to greater than 900 mV(low O2
exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM should always supply the O2 sensor with a constant 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins
heating up its internal resistance begins to decrease . The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing
voltage that differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2
sensor the PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
When the ignition is turned ON, B+ is applied to the O2 sensor’s heater element. Approximately 30 seconds after
the B+ is applied to the heater portion of the O2 sensor, the O2 sensor should reach a temperature greater than
500°C. The heated O2 sensor becomes active much quicker than a non-heated O2 sensor. This allows the PCM to
control the air/fuel ratio more consistent over a wider range of operating conditions.
TEST DESCRIPTION
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the Diagnostic Chart.
2. Never perform this test on a cold engine. The oxygen sensor must be near normal operating temperature for
this chart to work.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this section
21. Ignition ON.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool and monitor the
LH and RH O2
sensors.
3. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
Did LH and RH O2 Sensor
voltages drop to specified
value within 40 seconds?
450 mV
to less
than 100
mV
No problem
found.
Oxygen Sensor
Heater is OK
If both dropped
to the specified
value, Go to
Step 8
---------------------
If only one
dropped to the
specified value,
Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the oxygen
sensor harness
connector from the
sensor that did not
drop.
3. Connect a test light
between the oxygen
sensor connector on
the powertrain
harness, circuit 439,
and circuit 750.
4. Ignition ON.
Did the Test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Using a DVM, measure
the resistance of the
oxygen sensor heater
between circuits 439
and circuit 750.
Is the resistance within
the specified value?
3.5 -
13.2
ohms
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Replace the heated
oxygen sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
6Repair the poor
connection at oxygen
sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Connect a test light to
B+.
3. Probe the oxygen
sensor connector on
the powertrain harness
connector, circuit 750.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Repair the open or the
short to earth in circuit
439 between fuse F9 and
the oxygen sensor.
Replace the fuse if the
fuse is open.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Repair the open in circuit
750.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
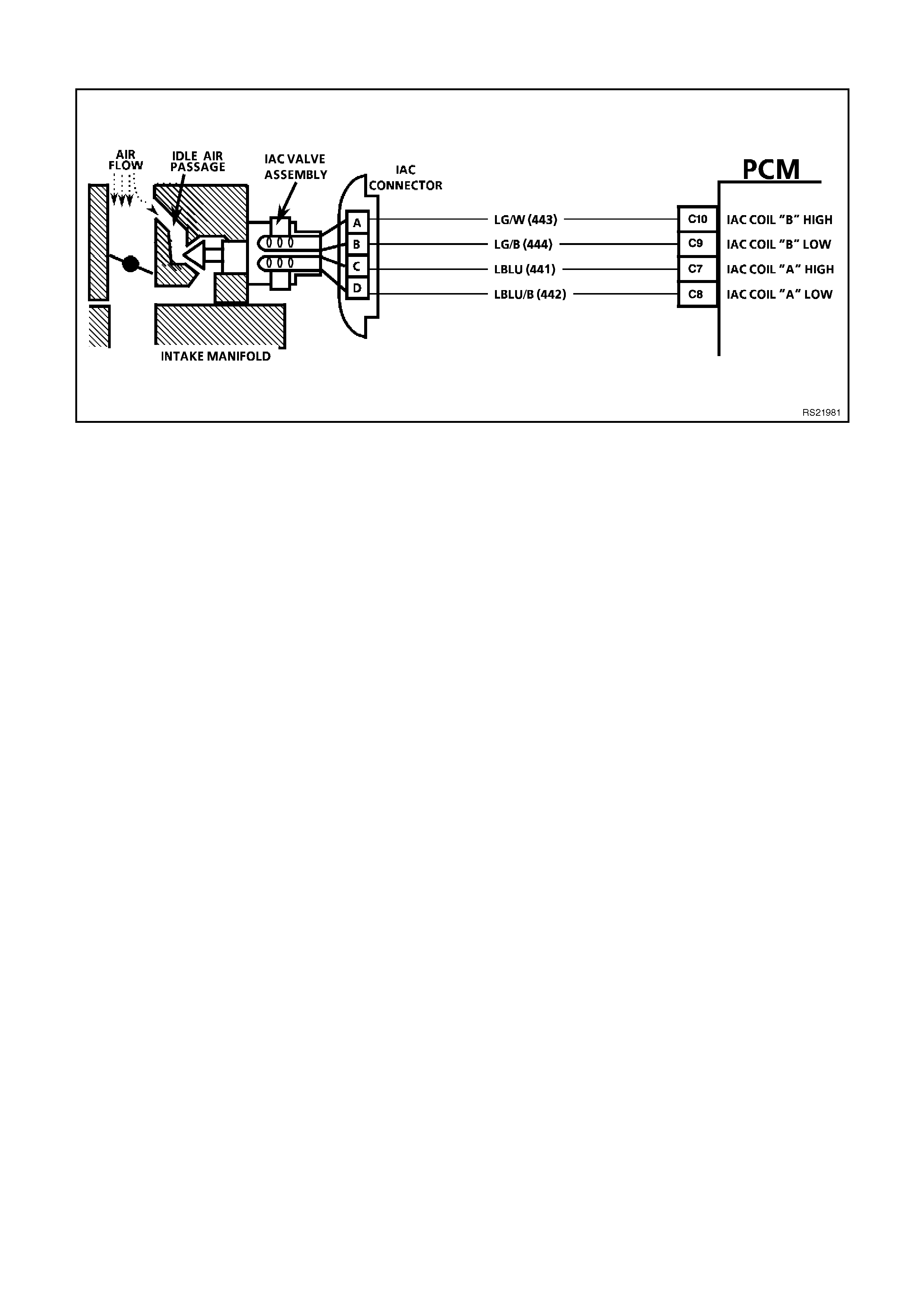
CHART A-7.1 - IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The IAC valve contains a bi-directional motor driven by two coils. The PCM controls the IAC valve by sending
voltage pulses (called counts or steps to the IAC motor windings. The PCM controls the air entering the engine by
adjusting a pintle inside the IAC valve inward or outward from the valves seat. The pintle valve moves a given
distance for each pulse received.
TO INCREASE THE IDLE SPEED: The PCM sends pulses to retract the pintle valve, this allows more air to bypass
the throttle plate through an idle air passage, until the PCM commanded idle speed reaches the PCM-desired idle
speed.
TO DECREASE THE IDLE SPEED: The PCM sends pulses to extend the pintle valve , this reduces the airflow
bypassing the throttle plate through an idle air passage, until The PCM commanded idle speed reaches the PCM-
desired speed.
The PCM desired idle speed, and the PCM commanded IAC position, is based on the following conditions.
• The Engine Coolant Temperature.
• The actual engine RPM (crankshaft reference input).
• The engine load (A/C request input, engine fan command).
• The battery voltage.
• The vehicle speed (VSS).
• The throttle position (TP) sensor angle.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This tests the PCM's ability to control IAC valve.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Remove the IAC valve and check for a frozen or a sticking IAC valve. Check that the TP sensor is within an
acceptable range.

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a TECH 2 scan
tool.
2. Start the engine and
allow the engine to
idle.
3. With the up/down
arrows, vary the
engine speed from 600
RPMs to 1675 RPMs.
Does the engine speed
increase and decrease
when
Commanded?
Go to Step 3 Go to Chart A-7.2
in this Section

3No trouble found with IAC
system.
Check For:
• Vacuum leaks (causes
fast idle speeds).
• Sticking or binding
throttle shaft, cables,
or linkages.
• Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor
resistance.
• Refer to DTC 14 in this
Section.
• The TP sensor
operation, refer to
CHART A-6.2 in this
Section.
• System earth circuit
terminals at the engine
for being clean and
tight.
• Spark plugs that are
excessively worn, mis-
gapped, or cracked.
• Initial base ignition
timing , refer to Section
6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
• Inspect all the
accessory drive
pulleys. They should
spin freely.
• For high or low fuel
pressure, or leaking
injectors - refer
CHART A-4.2 in this
Section
• A/C clutch control
circuit fault, refer to
CHART A 11.1 or
CHART A 11.3 in this
Section
• Generator output - if
less than 9 volts or
greater than 17 volts,
the PCM will not
command the IAC.
• Throttle body -
remove the IAC and
inspect the bore for
foreign material or
evidence of IAC valve
"dragging" in the bore.
• Throttle stop screw,
refer. SERVICE
OPERATIONS,
SECTION 6C2-3.
Refer to "rough, unstable,
or incorrect idle" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
Verify Repair
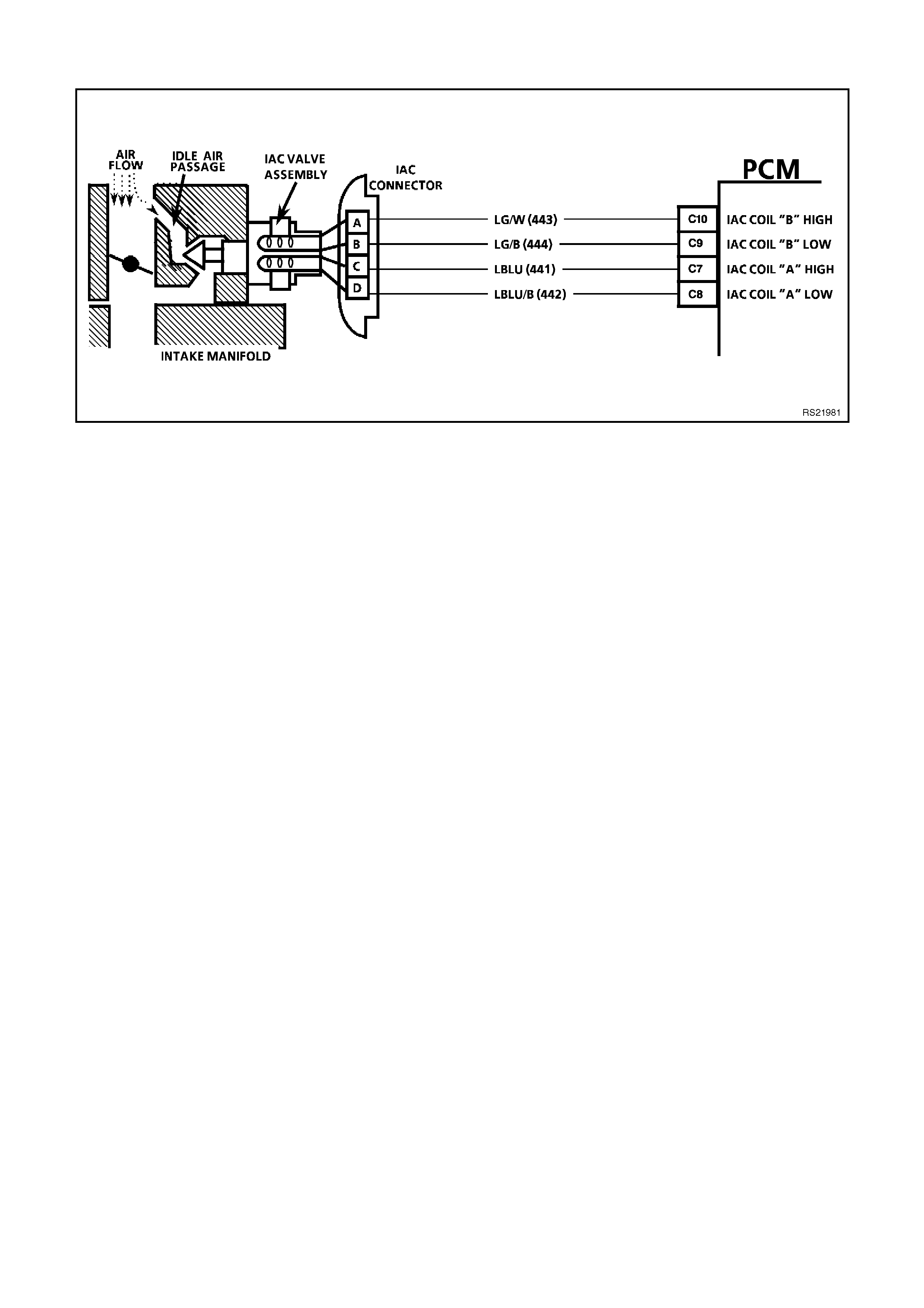
CHART A-7.2 - IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) SYSTEM
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM controls engine idle speed by moving the IAC valve to control closed-throttle air flow around the throttle
plate. It does this by sending voltage pulses (called "counts" or "steps") to the IAC motor windings. The motor shaft
and conical valve move a given distance for each pulse received.
TO INCREASE IDLE SPEED: The PCM sends enough pulses to retract the IAC valve and allow more air to bypass
the throttle plate through the idle air passage, until idle speed reaches the PCM - desired idle RPM.
TO DECREASE IDLE SPEED: The PCM sends enough pulses to extend the IAC valve and reduce the air flow
bypassing the throttle plate through the idle air passage, until idle speed reaches the PCM-desired RPM.
The PCM desired idle RPM, and the commanded IAC position, is based on:
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
• Actual engine RPM (crankshaft reference input)
• Engine load (A/C request input, engine fan command
• Battery voltage (voltage at PCM terminal A4
• Vehicle Speed (VSS)
• Throttle Position (TPS
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. The Tech 2 IAC reset, the PCM should issue electrical "extend/retract" signals to the IAC valve. With the IAC
disconnected, each connector terminal should have a "pulsing" voltage, noted by a flashing or flickering test
light. The rate of flashing or flickering is not important.
8. There are 2 separate windings in the IAC motor. Each winding (A - to - B, and C - to- D) should have between
40 and 80 ohms resistance. Also, there should be no continuity between the two windings.
NOTE:
When performing this test, ensure that a standard low power test light is used.
Do not use a "High-Wattage" test light, as the PCM could be damaged. A high wattage test light will either give
inaccurate test results, damage the PCM, or both.
A low-power test light must be used for any circuit testing. While a particular brand of test light is not suggested, a
simple test on any test light will ensure it to be OK for PCM circuit testing. Connect an accurate ammeter (such as
the digital multimeter) in series with the test light being tested, and power the test light-ammeter circuit with the
vehicle battery (See above). If the ammeter indicates less than 3/10 amp current flow (0.3 A or 300 ma), the test
light is OK to use. If more than 0.3A (300 ma), do not use.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2From Chart A-7.1
1. Disconnect the IAC
valve electrical
connector.
2. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
3. Using the TECH 2;
Reset the IAC valve.
4. Probe each IAC
harness connector
terminal for five
seconds with the test
light connected to
earth.
• See note above for
proper test light usage.
Does the test light flash
on all the terminals while
the IAC valve is being
reset?
Go to Step 3 If No light one or
more terminals,
go to Step 6
-----------------------
If steady light one
or more terminals,
go to Step 13
3Check for faulty IAC valve
terminals.
Were any faulty terminals
found?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4Repair the faulty
terminals.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
5Replace the IAC valve.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
6Check for an open or a
short to earth in the
circuit(s) that did not light
the test light.
Were any opens or shorts
found?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Repair any opens or
shorts found.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
81. Remove the throttle
body, refer to Section
6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
2. Check the resistance
across the IAC coils.
3. Check all of the IAC
terminals opposite of
the harness connector
terminals "A" to "B"
and "C" to "D".
Are all of the IAC coils
within the specified value?
40 to 80
ohms Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
9Using a DVM measure the
resistance between the
IAC valve terminals "A"
and "D".
Is the reading at the
specified value?
Infinite Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
10 Check for faulty PCM
terminals.
Were any faulty terminals
found?
Go to Step 17 Go to Step 11
11 Check for faulty IAC
terminals.
Were any faulty terminals
found?
Go to Step 16 Go to Step 12
12 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
electrical connector.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
4. Check for a short to
voltage on the circuit
that the light was on
steady.
Was a short to voltage
found?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
14 Check for faulty IAC valve
connections.
Were any faulty
connections found?
Go to Step 16 Go to Step 5
15 Repair the short to
voltage.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
16 Repair the faulty IAC
valve connections.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
17 Repair the faulty PCM
terminals.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
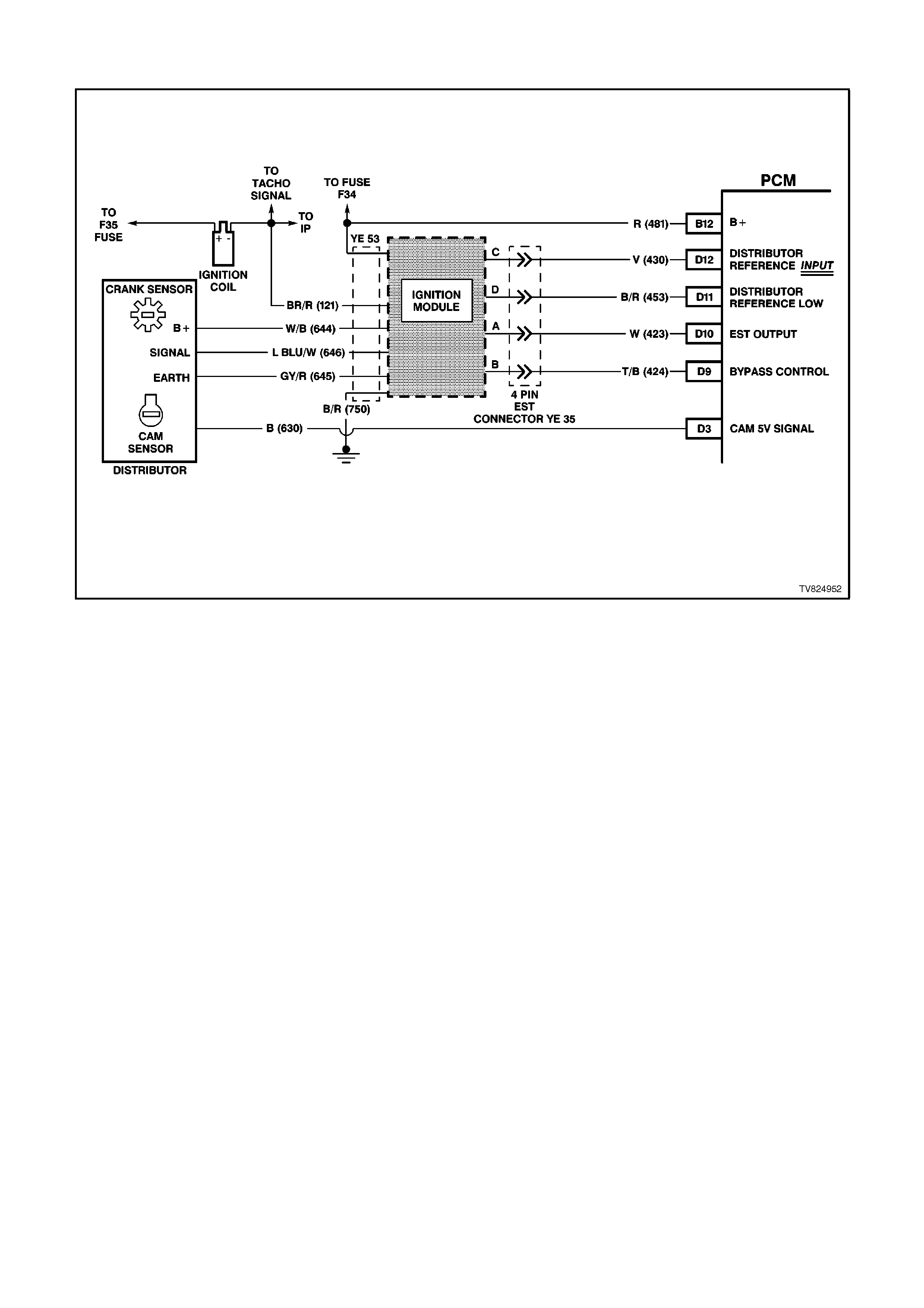
CHART A-8.1 - IGNITION SYSTEM CHECK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The ignition system controls the fuel combustion by providing a spark to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder at
the correct time. This provides good engine performance, fuel economy, and control exhaust emissions. The PCM
controls the spark advance and the ignition dwell when the ignition system is operating in the EST mode.
The main components that make up the ignition system for the V8 engine are:
• The Distributor Assembly
• The Ignition Coil
• The Ignition Module
• The PCM
• The Spark Plugs
• The Spark Plug Wires
• The Cam sensor
• The Crankshaft Sensor
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. Do not use this chart unless sent here from chart A-3.1
3. The tachometer lead is only intended for service use. If the tachometer lead is connected, the lead most likely
connects to equipment not installed at the factory. A factory-installed tachometer is connected to circuit 121 at
a different location.

NOTE:
When performing this test, ensure that a standard low-power test light is used. Do not use a high wattage test light,
as the distributor hall switch could be damaged. A high wattage test light will either give inaccurate test results or
damage the hall switch.
5. Thoroughly inspect the distributor cap for any carbon build up or contamination that could effect the current
flow. Also, inspect the cap and the rotor for any cracks or signs of water intrusion.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Remove the spark plugs and inspect for the following conditions.
• Fuel fouling
• Contamination
• Cracks
• Excessive wear
• Improper gap
• Carbon tracking
• Improper heat range
Replace any plugs that are in question. Refer to Diagnosis in Section 6D2-3 for additional checks.
Spray a fine coat of water on the distributor and the wires while listening for a change in engine speed. This could
help find a crack in the component.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
2From Chart A-3.1
Was spark found on any
of the cylinders?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 3
31. Locate the tachometer
lead behind the left
front shock tower.
2. Connect a test light to
B+, and probe the tach
terminal lead.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ignition
coil wire at the
distributor cap.
3. Connect an ST-125
tester to the ignition
coil wire lead .
4. Crank the engine and
look for spark.
CAUTION:
Do not touch the ignition
coil wire while cranking
the engine.
Was there a crisp blue
spark observed?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
51. Check for
contamination or
cracks in the distributor
cap and rotor.
2. Replace or repair any
component that was
found at fault.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 6
6Check the resistance in all
the spark plug wires.
Replace any wires that
show more than the
specified value of
resistance.
Is the action complete?
30,000
ohms Verify Repair
7Replace the ignition coil.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
8Repair the short in the
tacho lead circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
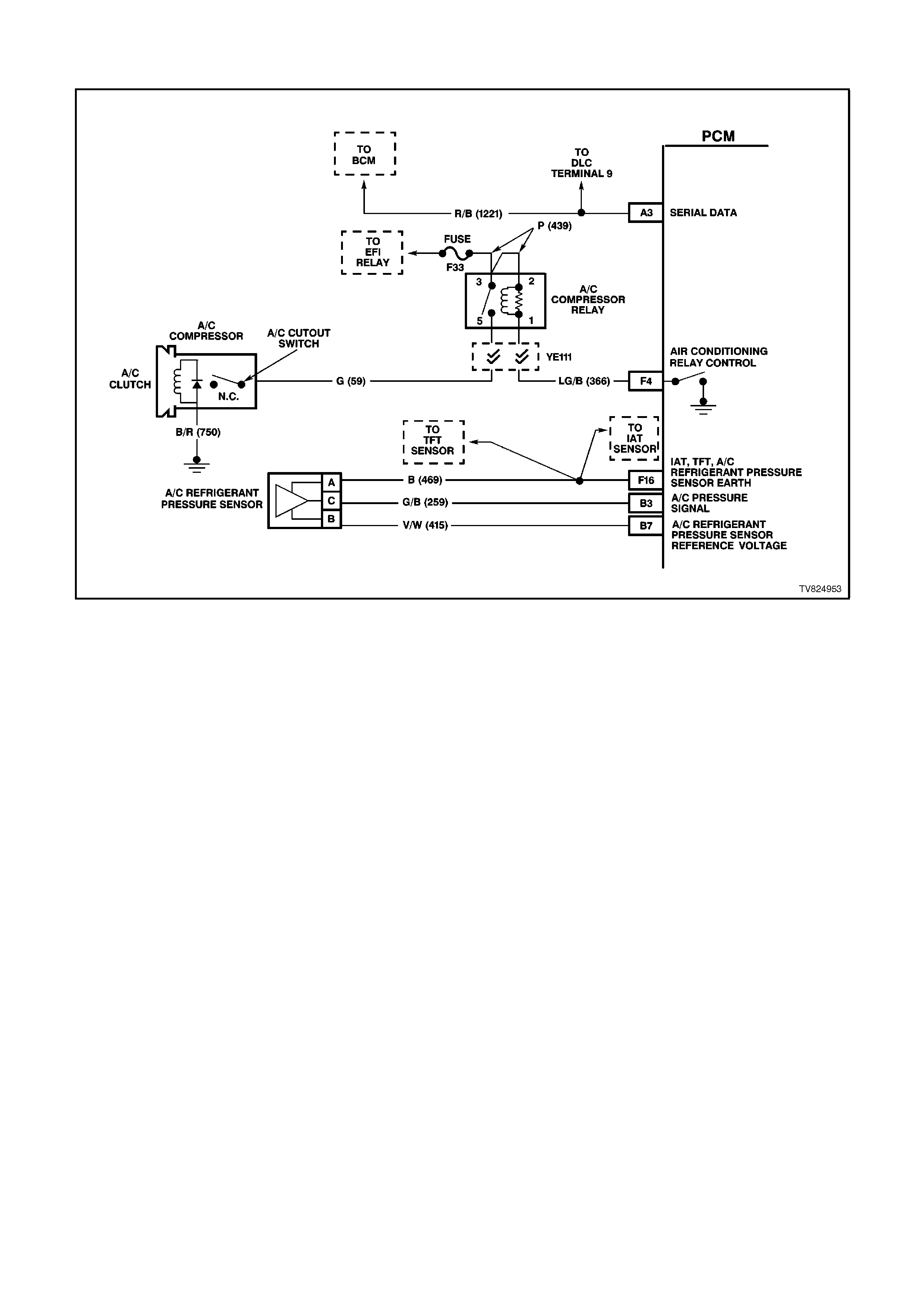
CHART A-11.1 - A/C CLUTCH CONTROL (NON ECC SYSTEM)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
With the blower fan ON, and the air conditioning ON, the switched ignition voltage is supplied from fuse F13 through
the A/C master switch, and then to the BCM. The BCM will then supply a serial data signal to the PCM requesting
A/C. If the BCM does not receive a earth signal from the blower switch to BCM terminal "3", the BCM will not supply
the serial data request for the A/C. Once the PCM receives the serial data signal, the PCM will energise the A/C
compressor relay by supplying a earth signal (A/C Relay Control ). The BCM also supplies a earth signal from BCM
terminal "7" to the low speed cooling fan relay .
This serial data signal to the PCM is also used to adjust the idle speed before turning ON the A/C compressor relay.
If this signal is not available to the PCM, the A/C compressor will be inoperative.
This system also incorporates a A/C Pressure Transducer. The A/C Pressure Transducer signal indicates low side
and high side refrigerant pressure to the PCM. The PCM uses this information to adjust the idle air control valve to
compensate for the higher engine loads present with high A/C refrigerant pressures. A fault in the A/C Pressure
Transducer signal will cause DTC 96 to set.
The purpose of the A/C Pressure Transducer is to protect the system from damage due to either the refrigerant
pressure being too low (which could damage the compressor due to insufficient lubrication), or too high (which
could result in a leak in the sealed refrigerant R134a system).
The PCM will NOT energise the A/C control relay if any of the following conditions are present:
• A DTC 91, or 96 is set.
• The engine speed is greater than 4,800 RPM. If de-energised because of RPM,
• the A/C will re-energise when the engine speed falls below 4,000 RPM for at least seconds.
• The Throttle Position angle is greater than 90%.
• The A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor voltage is too Low or too High

TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. The PCM's diagnostic circuits must be proven before any further testing is performed.
2. The PCM does not normally energise the A/C control relay unless the engine is running.
4. This checks for operation of the condenser fan.
20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 26, 28.
There are no terminal identification on the relay connector (although the relay has terminal numbers). Make
certain the correct relay connector terminal (not the relay) is being probed.
39. The most likely cause of an automotive air conditioner not working is a discharged refrigerant R134a system,
due to a refrigerant leak.
CHECK FOR:
If fuse F13 is open, check for short to earth on all the circuits associated with this fuse.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section.
21. Ignition ON, engine
stopped.
2. Disconnect the A/C
compressor clutch
electrical connector
and reconnect, and
note the compressor
clutch.
Did the compressor clutch
cycle OFF then ON with
the electrical connector
disconnected and
reconnected?
If the A/C clutch
cycled OFF then
ON or will not
disengage
Go to Step 6
Go to Step 3
31. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Blower Switch turned
ON.
3. Cycle the A/C switch
ON and OFF, waiting a
few seconds between
positions.
Listen to the A/C
compressor clutch. Does
the A/C compressor
clut ch cycle ON and
"OFF?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 14
41. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. The A/C switch in the
ON position.
Does the A/C condenser
fan operate when the A/C
switch is turned ON?
Go to Step 5 Go to Chart A-12
in this Section
51. A/C clutch control
circuits OK.
2. If the complaint is
insufficient cooling,
review the symptoms.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the A/C
compressor electrical
connector.
2. Observe the A/C
clutch.
Is the A/C clutch engaged
to the A/C compressor?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Replace the A/C
compressor clutch. Refer
to Section 2B AIR
CONDITIONING -
REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION for
details.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
81. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Using a test light
connected to B+,
backprobe PCM
terminal for A/C Relay
Control.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 11
9Check for a short to earth
in circuit for A/C Relay
Control from the PCM to
A/C Compressor Relay.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
10 Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
PCM Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 1. Ignition ON.
2. Disconnect the A/C
compressor electrical
connector.
3. Using a test light
connected to earth,
probe the A/C
compressor electrical
connector power
circuit.
4. With the test light ON,
remove the A/C
Compressor Relay and
note the test light.
Did the test light turn
OFF?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 13
12 Replace the A/C
Compressor Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Repair the short to voltage
on the A/C compressor
power feed circuit from
the A/C Compressor
Relay to the A/C
compressor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
14 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Observe the A/C
Refrigerant Pressure
Sensor voltage display
on the scan tool.
Is the indicated A/C
Refrigerant Pressure
Sensor voltage at or
between the specified
value?
0.35V -
4.2V Go to Step 15 Go to Step 39
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
15 Check the power supply
fuse to the A/C master
switch.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 16 Go to Step 17
16 Repair the short to earth
in the fuse circuit, and
replace the fuse.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
17 1. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Turn the A/C Master
Switch to the ON
position.
2. Using a test light
connected to earth,
backprobe the BCM
terminal to the A/C
Select Input circuit.
Does the test light
illuminate??
Go to Step 20 Go to Step 18
18 Check for an open or a
poor connection in the
circuit from the A/C
Master Switch to the BCM
A/C Select Input, or an
open in power feed circuit
to the A/C Master Switch.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 19
19 Replace the A/C Master
Switch.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
20 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Remove the Blower
Inhibit Relay from
Relay center, leave
harness connector
connected to the relay.
3. Using a test light
connected to B+,
backprobe the relay
harness connector
terminal 30.
4. Turn the A/C Master
Switch to the ON
position.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 21 Go to Step 26
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
21 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Using a test light
connected to B+,
backprobe the BCM
terminal for the Blower
Switch Input Signal.
3. Turn the A/C Master
Switch to the ON
position.
4. Turn the Blower Switch
to the ON position.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 22 Go to Step 33
22 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the A/C
Compressor Relay
from the relay center.
3. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
4. Turn the A/C Master
Switch to the ON
position.
5. Turn the Blower Switch
to the ON position.
6. Using a test light
connected to B+,
probe terminal "2" of
the A/C Compressor
Relay harness
connector.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 23 Go to Step 35
23 1. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Using test light
connected to earth ,
probe A/C Compressor
Relay harness
terminals 1 and 3.
Does test light illuminate
on both circuits?
Go to Step 24 Go to Step 36
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
24 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Reinstall Blower Inhibit
Relay and A/C
Compressor Relay.
3. Disconnect electrical
connector at A/C
compressor.
4. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
5. Turn A/C Master
Switch to the ON
position.
6. Turn Blower Switch to
the ON position.
7. Using test light
connected to earth,
probe A/C compressor
harness power feed
circuit from A/C
Compressor Relay to
compressor.
Dose test light illuminate?
Go to Step 25 Go to Step 37
25 Check A/C compressor
earth circuit for an open, if
open repair. If earth circuit
is OK, Replace A/C
compressor. Refer to
Section 2B AIR
CONDITIONING -
REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
26 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Using a test light
connected to B+,
backprobe the Blower
Inhibit Relay terminal
85 for Blower Inhibit
Relay Earth Output
Signal from BCM.
3. Turn the A/C master
switch ON.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 28 Go to Step 27
27 Check for open in circuit
from BCM to Blower
Inhibit Relay or poor
connection at BCM. If OK,
replace BCM.
Is action complete?
Verify Repair
28 1. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Disconnect the Blower
Inhibit Relay from the
harness connector.
3. Using a test light
connected to earth,
probe the relay
harness terminal 86.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 30 Go to Step 29
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
29 Repair the open in the
circuit from the Blower
Inhibit Relay terminal 86
to the Ignition Switch.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
30 1. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. With the Blower Inhibit
Relay still
disconnected, probe
the relay harness
terminal 87 with a test
light connected to B+.
Does the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 31 Go to Step 32
31 Replace the Blower Inhibit
Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
32 Repair the open in the
earth circuit to the Blower
Inhibit Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
33 Check for open circuit
from the Blower Switch to
the BCM Blower Switch
Input terminal.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 34
34 Check for an open in the
circuit from the Blower
Inhibit Relay terminal 30
to the Blower Switch.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 38
35 Check for an open in the
circuit from the A/C
Compressor Relay to the
PCM terminal for the A/C
Relay Control.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
36 Repair the open in the
circuit that did not light.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
37 Check for an open in the
circuit from the A/C
Compressor to the A/C
Compressor Relay.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 12
38 Replace the Blower
Switch.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
39 Check the A/C Pressure
Sensor signal circuit for
short to earth.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 40
40 Check the A/C refrigerant
(R-134a) system for being
undercharged, or
overcharged.
Is the action complete.
Verify Repair
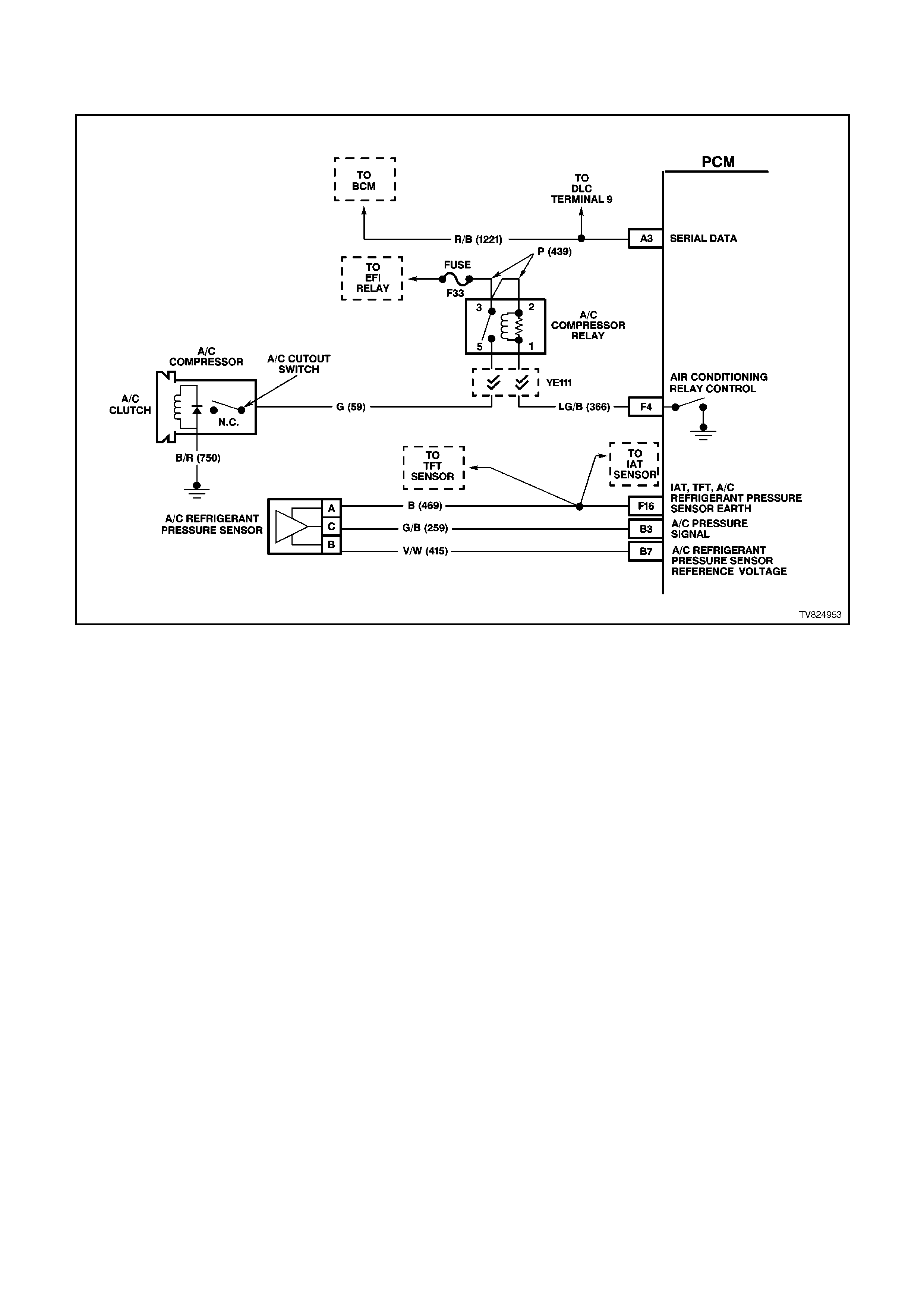
CHART A-11.3 - A/C CLUTCH CONTROL WITH ELECTRONI C CLIM ATE
CONTROL (ECC)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
When the A/C is requested, the Electronic Climate Control Module will supply a signal to the BCM. The BCM will
then send a serial data request to the PCM. When the PCM receives the serial data request on PCM terminal B12,
it indicates that air conditioning has been requested and approximately 1/2 second after the PCM receives this
signal, it will energise the A/C control relay . This serial data signal to the PCM is also used to adjust the idle speed
before turning ON the A/C compressor relay. If this signal is not available to the PCM, the A/C compressor will not
operate. If there is a problem with the A/C Relay Control circuit, QDSM DTC 91 will set. The BCM also supplies the
earth signal from BCM terminal "7" to the low speed cooling fan relay.
This A/C system also incorporates an A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (A/C Pressure Transducer). The A/C
Refrigerant Pressure Sensor signal indicates low and high side refrigerant pressures to the PCM. The PCM uses
this information to adjust the idle air control valve to compensate for the higher engine loads present with high A/C
refrigerant pressures., and not allow A/C operation if pressure is to low A fault in the A/C Refrigerant Pressure
Sensor signal will cause DTC 96 to set.
The PCM will NOT energise the A/C control relay if any of the following conditions are present.
• A DTC 91, or a DTC 96 is set.
• The engine speed is greater than 4,800 RPM. If disabled because of RPM, the fan will re-enable when the
engine speed falls below 4000 RPM for at least 10 seconds.
• The throttle angle is greater than 90%.
• The A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor is less than.2V or greater than 4.9V.

TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
1. The PCM's diagnostic circuits must be proven before any further testing is performed.
3. The PCM does not normally energise the A/C control relay unless the engine is running.
4. When the Tech 2 scan tool is installed, and the A/C switch is turned ON, the scan tool should display "A/C
Requested".
6. This checks for operation of the condenser fan.
7. The most likely cause of an automotive air conditioner not cooling properly is a discharged or overcharged
refrigerant R134a system.
18, 19, 20 There are no terminal identification on the relay connector (although the relay itself has terminal
numbers). Make certain the correct relay connector terminal (not the relay) is being probed.
CHECK FOR:
If fuse F13 is open, check for short to earth on all circuit associated with this fuse.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Check the Electronic
Climate Control module
fuse.
Is the fuse OK?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 18
31. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Cycle the A/C master
switch ON and OFF,
waiting a few seconds
between positions.
3. Observe the A/C
compressor clutch.
Did the compressor clutch
cycle ON and OFF?
If either engages
or will not
disengage Go to
Step 15
Go to Step 4
41. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Turn the A/C switch
ON.
Does the Tech 2 scan
tool display "A/C
Requested"?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 10
51. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Cycle the A/C switch
ON and OFF, waiting a
few seconds between
positions.
3. Listen to the A/C
compressor clutch.
Does the A/C compressor
clutch cycle ON and OFF?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 19
61. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Turn the A/C switch
ON for 5 to 10
seconds.
3. The A/C clutch should
stay engaged ON for
the same time.
Does the compressor
clutch stay engaged ON?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 9
7Ignition ON, engine idling.
Does the A/C condenser
fan operate when the A/C
is turned ON?
Go to Step 8 Go to Chart A-12
in this Section
8The A/C clutch control
circuits OK. If complaint is
insufficient A/C cooling,
review sympto m section.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
9Check the A/C refrigerant
(R 134a) system for being
undercharged. Recharge
as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Check for a poor
connection or an open
circuit between the BCM
and the Electronic Climate
Control Module.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 11
11 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the BCM
connectors.
3. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
4. With a DVM connected
to earth, probe the
BCM harness
connector terminal for
the A/C Select Input
from the Electronic
Climate Control
module.
5. Turn ON the A/C
switch.
Is the voltage between the
specified value?
2 - 4
volts Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
12 Check for an open or a
short to earth in the A/C
Select circuit between the
BCM and the Electronic
Climate Control module.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 14
13 Replace the BCM.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
14 Check for poor connection
at the Electronic Climate
Control module, if the
connection is OK, replace
the Electronic Climate
Control Module.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Check for a short to earth
from the A/C Relay
Control circuit to the A/C
Compressor Relay.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 16
16 Check for a short to
voltage in the power feed
circuit to the A/C
compressor.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 17
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
17 Replace the defective A/C
compressor relay.
NOTE:
If the compressor clutch
still will not disengage,
replace the A/C
compressor clutch. Refer
to Section 2B AIR
CONDITIONING -
REMOVAL AND
OPERATION for details.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
18 1. Repair the short to
earth in the fuse
circuit.
2. Replace the fuse.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
19 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Disconnect the A/C
compressor relay.
3. Probe both relay
terminals "3" and "1" of
the harness connector,
with a test light
connected to earth.
Is the test light ON at both
terminals?
Go to Step 20 Go to Step 26
20 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Probe the A/C
compressor relay
socket circuit for the
A/C Relay Control with
a test light connected
to B+.
3. Turn the A/C switch
ON.
Is the test light ON when
the A/C switch is ON?
Go to Step 21 Go to Step 24
21 1. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
2. Reconnect the A/C
compressor relay.
3. Backprobe relay
harness terminal "5"
circuit with a test light
connected to earth.
4. Turn the A/C switch
ON.
Is test light ON when A/C
switch is turned ON?
Go to Step 22 Go to Step 28
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
22 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the A/C
compressor electrical
connector.
3. Ignition ON, engine
idling.
4. Probe the compressor
harness connector
terminal power feed
circuit with a test light
connected to earth.
5. Turn the A/C switch
ON.
Is the test light ON when
the A/C switch is turned
ON?
Go to Step 23 Go to Step 29
23 1. Check for a defective
"Discharge Gas
temperature" switch in
the compresso r, or a
defective A/C clutch.
2. Repair or replace as
necessary.
Is the action complete ?
Verify Repair
24 Check for a faulty
connection at the A/C
compressor relay.
Was a poor connection
found ?
Verify Repair Go to Step 25
25 Check for an open in the
PCM A/C Relay Control
circuit, from the PCM to
the A/C compressor relay.
Was a problem found ?
Verify Repair Go to Step 27
26 Repair the open in the
circuit that did not light the
test light.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
27 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
28 Replace the A/C
compressor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
29 Repair the open in circuit
59 to the A/C compressor
clutch.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
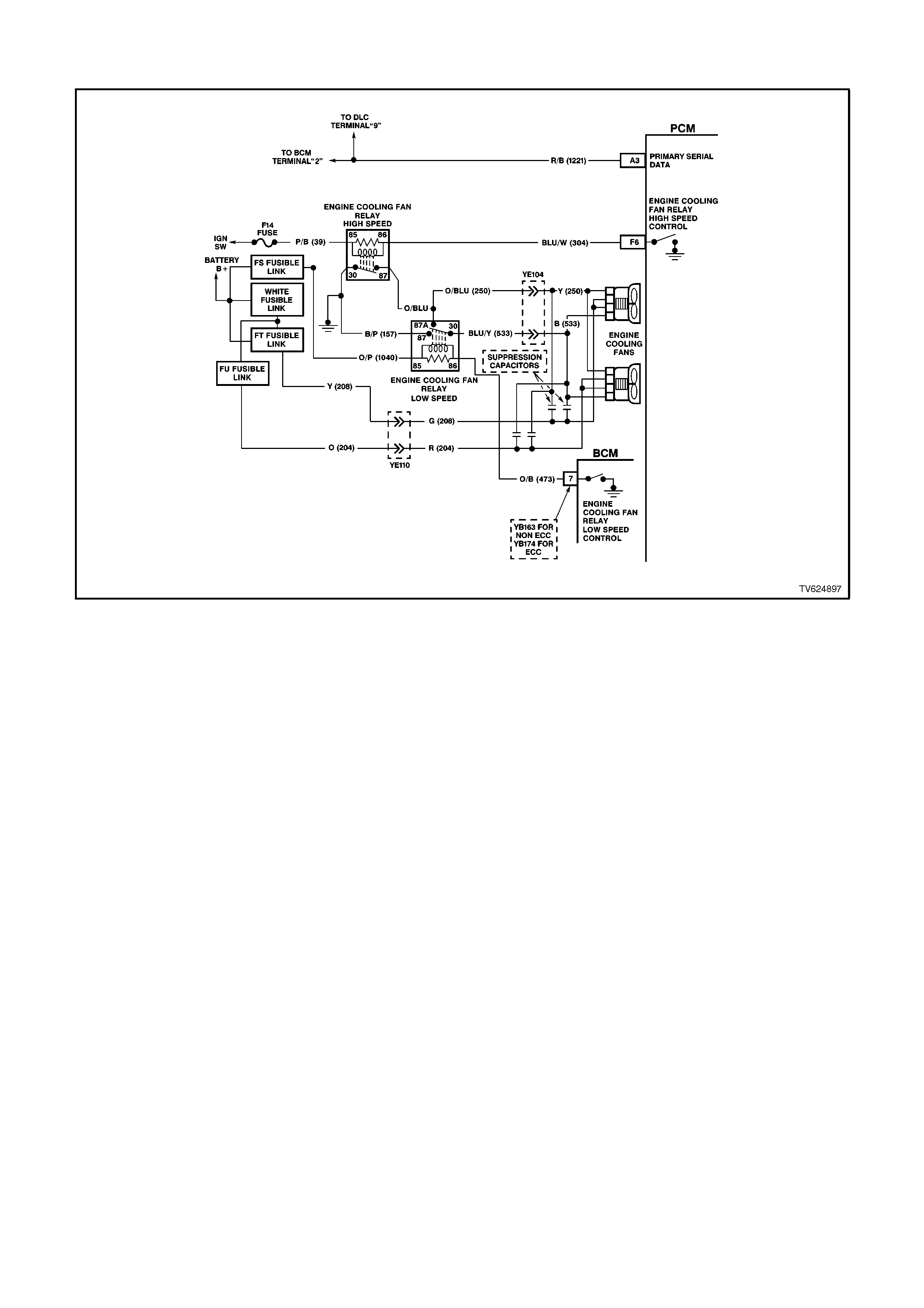
CHART A-12.1 - ELECTRIC FAN CONTROL
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The V8 engine has two duel speed electric fan which provides the primary means of moving air through the engine
radiator. The engine cooling fan high speed relay is controlled by the PCM. The PCM controls the earth path for the
engine cooling fan high speed relay.
The low speed of the electric fan is controlled by the PCM through special Data Communication to the BCM. The
BCM controls the earth path for the engine cooling fan low speed relay.
Both relays are used to control the earth paths to the electric motor that drives the five blade fan.
The engine cooling fan low speed relay is energised by the BCM. The PCM determines when to enable the engine
cooling fan low speed based on inputs from the A/C request signal, vehicle speed and engine coolant temperature.
The engine cooling low speed fan will be turned ON when.
• The A/C request indicated (YES).
• The Vehicle speed is less than 54 Km/h.
- OR -
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 104 degrees C. The fan will remain on until the coolant
temperature goes below 99 degrees C.

ENGINE COOLING FAN HIGH SPEED
The engine cooling fan high speed is controlled by the PCM based on input from the Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor (ECT). The PCM will only turn ON the engine cooling fan high speed if the engine cooling low speed fan has
been ON for 2 seconds and the following conditions are satisfied.
• There is a BCM message response fault which will cause a DTC 92.
• An engine coolant temperature sensor fault is detected, such as DTC 14,15,16,17, or 91.
• An engine coolant temperature greater than 109 degrees C.
If the fan low speed was OFF when the criteria was met to turn the fan high speed ON, the fan high speed will come
ON 5 seconds after the fan low speed is turned ON. The engine cooling fan High speed relay can also be enable by
the A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor. The A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor will provide a signal to the PCM when
A/C pressure becomes to high approximately 1770 kPa.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This entire diagnostic procedure must begin with a "cold" engine - at ambient air temperature. If the coolant is
hot when diagnosis is performed, replacement of good parts will result. Fan should not be running if engine
coolant temperature is less than 99 degrees C and air conditioning is not ON.
10. On A/C equipped vehicles, the engine cooling fan High speed relay should energise by the PCM, as soon as
the PCM energises the A/C clutch.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Engine coolant
temperature below 99
degrees C.
Is the electric fan
running ?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 9
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the Radiator
Fan High Speed Relay.
3. Ignition ON.
Does the fan continue to
run ?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
41. Ignition ON, Engine
OFF.
2. Remove the Fan Low
Speed Relay.
Does the fan continue to
run ?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 16
51. Ignition ON.
2. Probe the Radiator
Fan High Speed Relay
harness connector
circuit 304 with a test
light to B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Probe the Fan High
Speed Relay harness
connector circuit 304
with a test light
connected to B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 7
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Replace the Radiator Fan
High Speed Relay. Verify Repair
91. Ignition ON.
2. Using the scan tool,
Select HIGH FAN
relay control.
3. Turn ON the HIGH
FAN with up/down
arrow keys.
Does the cooling fan
operate in high fan mode?
Go to Step 20 Go to
Chart A-12.2 in
this Section
10 Is the vehicle equipped
with A/C? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 1. Start engine, allow to
idle.
2. Turn A/C ON.
3. Electric fan should run
when the A/C clutch
engages.
NOTE:
If A/C clutch will not
engage, refer Chart A-
11.1 or Chart A-11.3 in
this Section.
Does the fan run when the
A/C clutch is engaged?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 9
12 The electric fan circuit is
OK. Verify Operation
13 1. Connect a test light to
B+.
2. Probe circuit 533 of
Radiator Fan Low
Speed Relay.
Is the test light ON ?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 18
14 Repair the short to earth
in circuit 304. Verify Repair
15 Repair the short to earth
in circuit 533. Verify Repair
16 1. Ignition ON.
2. Probe the Fan Low
Speed Relay harness
connector circuit 473
with a test light
connected to B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 17 Go to Step 21
17 Check for short to earth
on circuit 473.
Was a short to earth
found ?
Verify Repair Go to Step 18
18 Replace the BCM.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
19 1. Reinstall the Radiator
Fan High Speed Relay.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Use the scan tool to
turn on the "LOW FAN
" with the up/down
arrow keys.
Does the radiator fan
motor run?
Go to Step 10 Go to
Chart A-12.3 in
this Section
20 1. Ignition ON.
2. Use the scan tool in
order to turn on the
high fan with the
up/down arrow keys.
3. While the fan is
running, remove the
Radiator Fan High
Speed Relay.
Did the cooling fan motor
go to a lower running
speed ?
Go to Step 19 If the radiator fan
motor is turned
OFF,
Go to Chart
A-12.2 in this
Section
21 Check for short to earth in
circuit 250.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 22
22 Replace the Radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
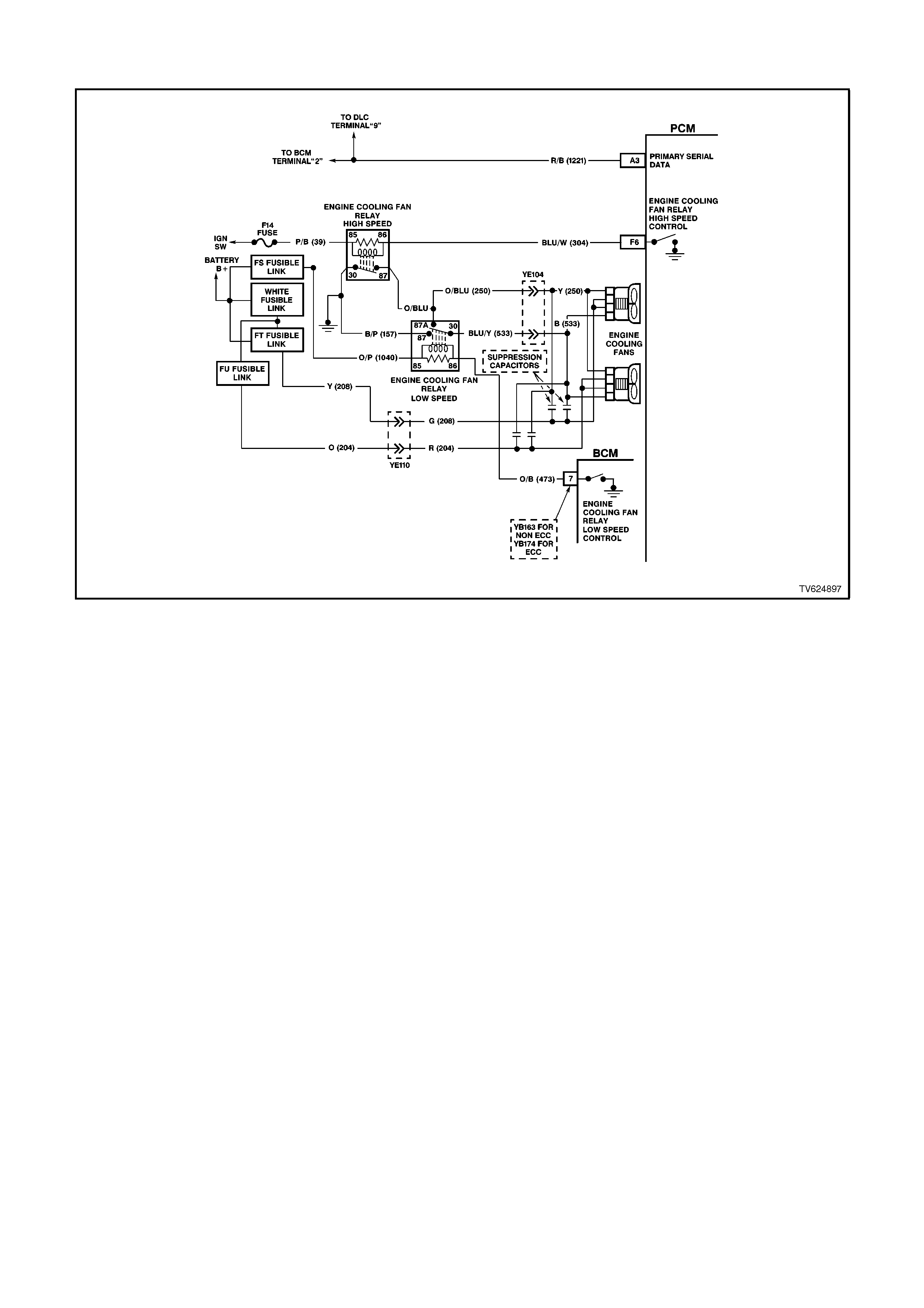
CHART A-12.2 - ELECTRIC FAN CONTROL
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The engine has a water pump driven radiator fan incorporating a semi-fluid hydraulic fan clutch. This engine-driven
fan provides the primary means of moving air through the engine radiator. On vehicles equipped with air
conditioning, an additional electric motor driven fan is placed in front of the A/C condenser.
• The electric fan(s) will turn ON when the engine cooling fan relay is energised by the PCM.
• The electric fan(s) will turn ON, if any of the following conditions are present;
• The engine coolant temperature exceeds 110 degrees C. (After the PCM turns the fan ON, it will run until the
coolant temperature is below 105 degrees C.).
• An engine coolant temperature sensor DTC is detected (refer DTC 14 or 15 Chart in this Section).
• An A/C request signal is received and the vehicle speed (VSS input) is less than 64 km/h.
• The Field service mode is active. (Ignition ON, engine OFF, and the DLC diagnostic test enable terminal
earthed.)
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This checks for B+ to the fan relay on both supply circuits.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check.
2From Chart A-12.1
Check fusible links FS,
FT, FU, and White fusible
link for open. Was a
problem found?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove Radiator Fan
High Speed Relay.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Probe relay socket,
circuit 39 with test light
connected to earth.
Is test light ON?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 10
41. Ignition ON.
2. Probe Radiator Fan
High Speed Relay
socket circuit 304 with
a test light connected
to B+.
3. Using scan tool,
Select HIGH FAN,
enable fan ON with
up/down arrows.
Is test light ON?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 9
51. Ignition ON.
2. Reinstall Radiator Fan
High Speed Relay.
3. Back-probe Radiator
Fan High Speed Relay
harness connector
circuit 250 with test
light connected to B+.
4. Using scan tool, Select
HIGH FAN, enable fan
ON with the up/down
arrow keys.
Is the test light ON.
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 11
61. Ignition ON.
2. Disconnect both
electric cooling fan
wiring harness
connector.
3. Probe both fan
harness connector,
circuits 533 and 250
with a test light to B+.
4. Using scan tool, Select
HIGH FAN, enable fan
ON by pressing the
up/down arrow keys.
Is the test light ON for
both circuits ?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Probe both fan harness
connector power feed
circuits, with a test light
connected to earth.
Is the test light ON for all
circuits ?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 15
81. Check for short to
earth that caused
fusible link to blow.
2. Check the engine
cooling fan motor for
drawing to much
current. Is the action
complete ?
Verify Repair
91. Ignition ON.
2. Using scan tool,
Select HIGH FAN,
enable output by
pressing the up/down
arrow keys.
3. Backprobe PCM
terminal "F6" with a
test light connected to
B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 16
10 Repair the open or the
short to earth in circuit 39.
Replace the fuse if blown.
Verify Repair
11 With test light connected
to B+, backprobe Radiator
Fan High Speed Relay
harness connector circuit
157.
Does test light illuminate?
Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
12 Check for poor a
connection at both fan
motors. If OK, replace the
electric fan motor that did
not operate.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Check for open in circuits
533 or 250.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 18
14 Repair open in circuit 304. Verify Repair
15 Repair open in fan motor
power circuit that did not
light test light.
Verify Repair
16 Check for short to voltage
in circuit 304, or faulty
connection at PCM, if OK
replace PCM.
Verify Repair
17 Replace Radiator Fan
High Speed Relay. Verify Repair
18 Check for open in earth
circuit 157.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 19
19 Replace the Radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay. Verify Repair
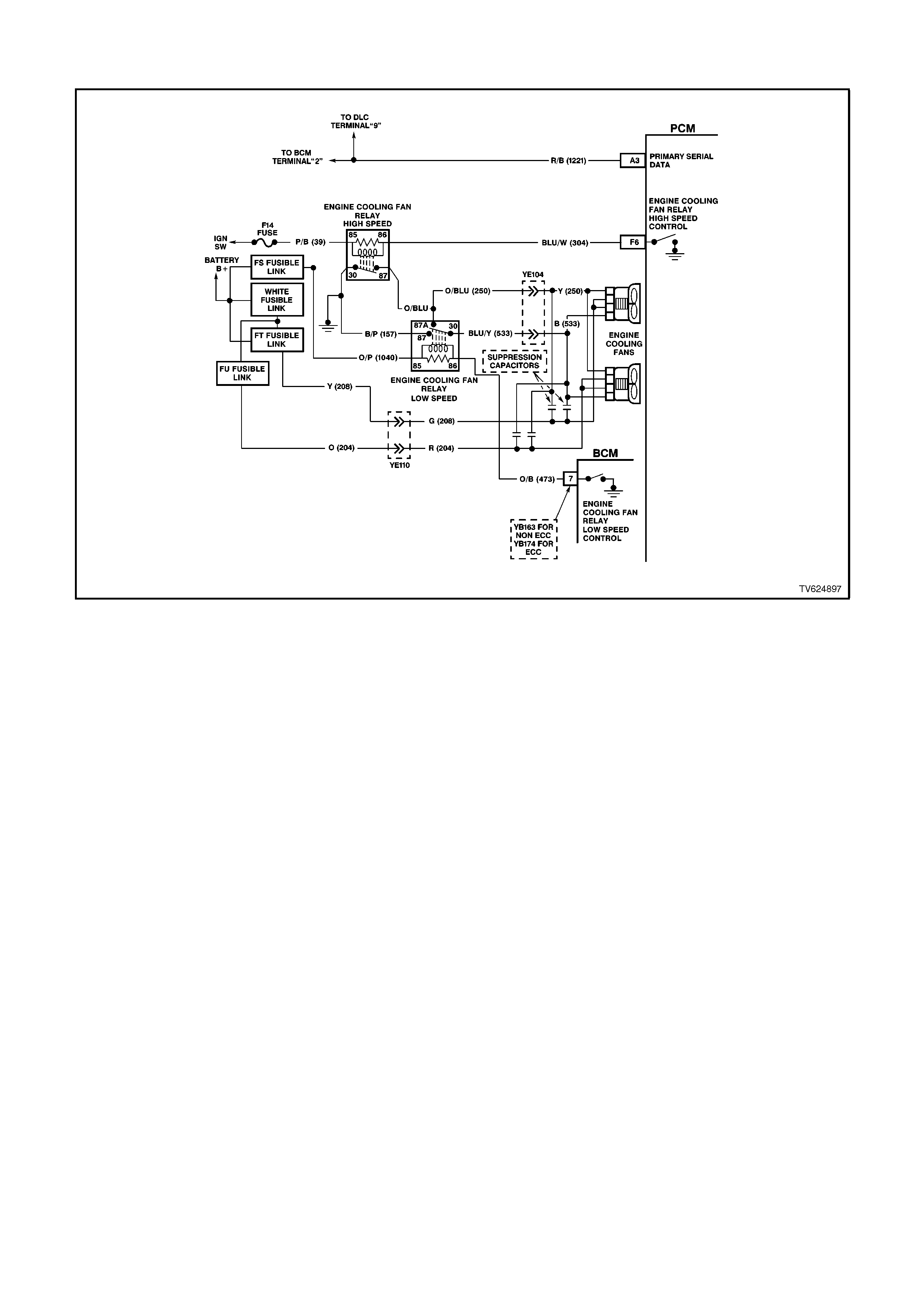
CHART A-12.3 - ELECTRIC FAN CONTROL
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The V8 engine has two (2) two speed electric fan which provides the primary means of moving air through the
engine radiator. The two speed electric cooling fan are used to cool engine coolant flowing through the radiator. It is
also used to cool the refrigerant flowing through the A/C condenser.
The engine cooling fan high speed relay is controlled by the PCM. The PCM controls the earth path for the engine
cooling fan high speed relay.
The low speed of the electric fan is controlled by the PCM through special Data Communication to the BCM. The
BCM controls the earth path for the engine cooling fan low speed relay.
Both relays are used to control the earth paths to the electric motor's that drives both five bladed fan's.
ENGINE COOLING FA N LOW SPEED:
The engine cooling fan low speed relay is energised by the BCM. The PCM determines when to enable the engine
cooling fan low speed based on inputs from the A/C request signal, vehicle speed and engine coolant temperature.
The engine cooling low speed fan will be turned ON when:
• The A/C request indicates (YES).
• The vehicle speed is less than 54 Km/h.
- OR -
• The coolant temperature is greater than 104 degrees C and will remain on until the coolant temperature goes
below 99 degrees C

ENGINE COOLING FAN HIGH SPEED
The engine cooling fan high speed is controlled by the PCM based on input from the Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor (ECT). The PCM will only turn ON the engine cooling fan high speed if the engine cooling low speed fan has
been ON for 2 seconds and the following conditions are satisfied:
• There is a BCM message response fault which will cause a DTC 92.
• An engine coolant temperature sensor fault is detected, such as DTC 14,15,16,17, or 91.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 109 degrees C.
If the fan low speed was off when the criteria was met to turn the fan high speed on the fan high speed will come on
5 seconds after the fan low speed is turned on. The engine cooling fan High speed relay can also be enable by the
A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor. The A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor will provide a signal to the PCM when A/C
pressure becomes to high approximately 1770 kPa.
TEST DESCRIPTION
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This checks the FS fusible link power supply to the Radiator Fan Low Speed Relay.
4. This step checks for proper BCM operation for the Radiator Fan Low Speed Relay.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2. Go to OBD
System Check.
21. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove Radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay.
3. Probe the relay socket,
circuit 250 with a test
light connected to B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove Radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Probe relay socket,
circuit 1040 with test
light connected to
earth
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 9
41. Ignition ON.
2. Probe the radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay
socket, circuit 473 with
a test light connected
to B+.
3. Using a scan tool,
Select LOW FAN,
enable the fan ON with
the up/down arrow
keys.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
51. Ignition ON.
2. Reinstall Radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay.
3. Back-probe the low
speed relay wiring
harness connector,
circuit 533 with test
light connected to B+.
4. Using a scan tool,
Select LOW FAN,
enable the fan ON with
the up/down arrow
keys.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect both the
electric cooling fan
wiring harness
connectors.
3. Probe both wiring
harness connector
circuit's 533 with a test
light connected to B+.
4. Using a scan tool,
Select LOW FAN,
enable the fan ON with
the up/down arrow
keys.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 12
7Repair the short to earth
in circuit 250.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
81. Ignition ON.
2. Using a scan tool,
Select LOW FAN,
enable fan ON.
3. Backprobe BCM
terminal "7" with a test
light connected to B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 15
9Repair the open in the
circuit which causes the
test light not to come ON.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Replace the Radiator Fan
Low Speed Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Repair the short to earth.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
12 Repair the open in circuits
533 or 250.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Repair the open in circuit
473 between the BCM
and the Radiator Fan Low
Speed Relay.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
14 Replace the Radiator fan
motor that did not operate.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Check for a faulty
connection at the BCM, if
OK replace the BCM.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
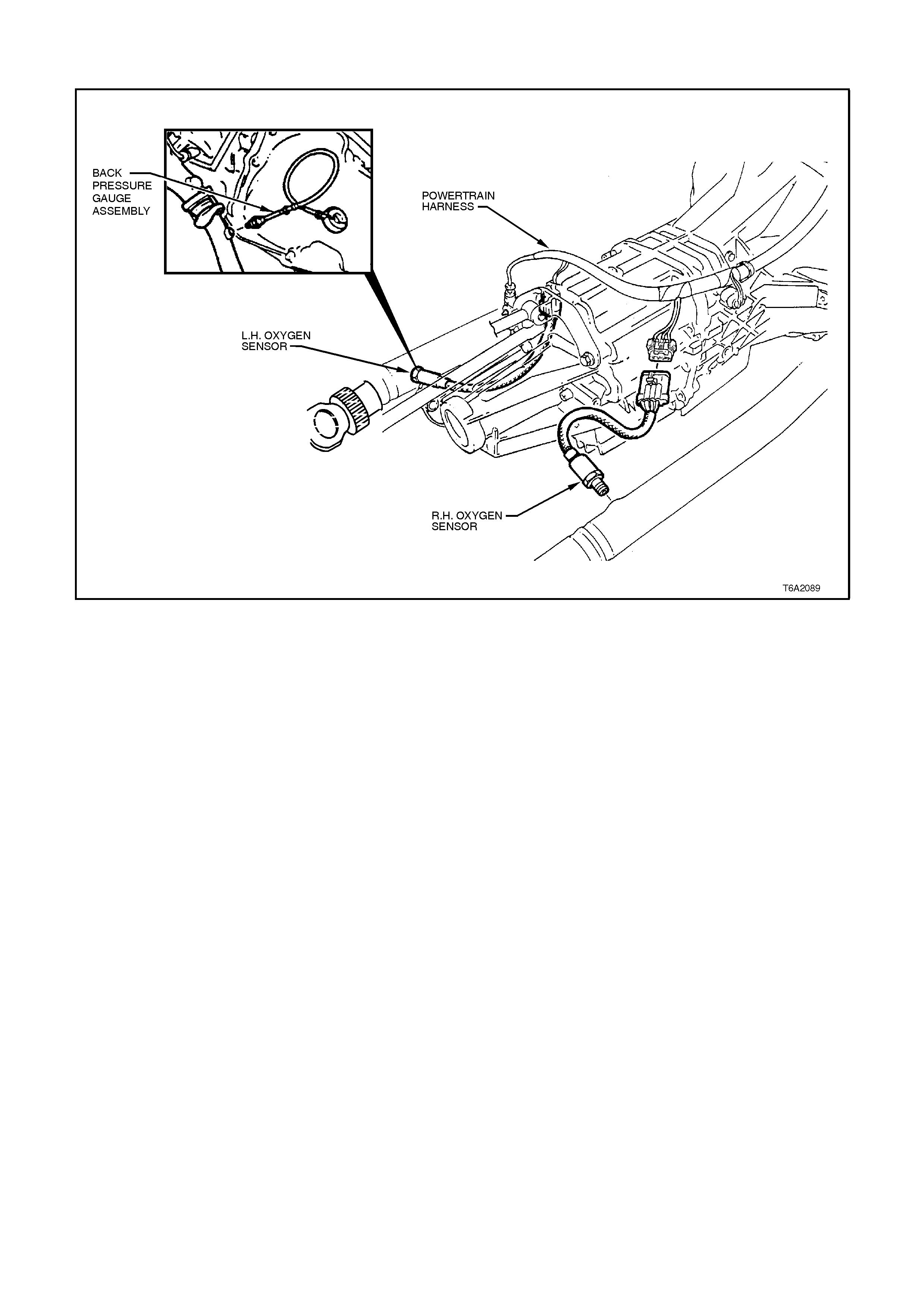
CHART A-13 - RESTRICTED EXHAUST CHECK
A restricted exhaust can cause a variety of symptoms. Below is a list of some of these symptoms.
• No power, sluggish
• Hesitation on acceleration
• Surges while driving
• Poor fuel economy
• Stalling
• Hard starting
Conditions that could cause a restricted exhaust;
• A collapsed exhaust pipe.
• Loose baffles in the muffler can cause an internal restriction.
• Catalytic converter.
Things that can cause a catalytic converter to become restricted are; 1. The use of LEADED FUEL (2) A very
rich-running engine. This rich-running condition could be caused by fuel pressure to high, or by a malfunction in the
engine control system (3) Engine in a bad state of tune. Worn parts in the ignition system can cause an engine
misfire, which sends unburned fuel into the exhaust system. The catalytic converter sees this unburned fuel as a
rich-running condition. (4) Push-starting the engine can send a tremendous amount of unburned fuel into the
exhaust system.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Carefully remove the O2
sensor.
Could the O2 sensor be
removed from the exhaust
system?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
31. Install an exhaust back
pressure gauge in
place of the removed
O2 sensor.
2. Start the engine and
allow to idle.
3. Observe the exhaust
system back pressure
reading on the gauge.
Is the reading less than
the specified value?
8.6 kPa Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4Rev the engine to 2000
RPM and observe the
reading on the gauge.
Is the reading on the
gauge less than the
specified value?
20.7
kPa Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5No problem found with the
exhaust system.
Is the action complete?
Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
6If the O2 sensor will not
remove from the exhaust
system, run the engine
until the exhaust system
temperature is greater
than 60°C.
Was the removal of the
O2 sensor successful?
Go to Step 3 Verify Repair
7NOTE:
If there are no obvious
reasons for the excessive
back pressure, a
restricted catalytic
converter should be
suspected and replaced
using the current
recommended
procedures.
Refer above, for things
that could cause a
restricted exhaust: for
possible causes.
Is the action complete?
Verify the Repair
and Go to the
OBD System
Check in this
Section
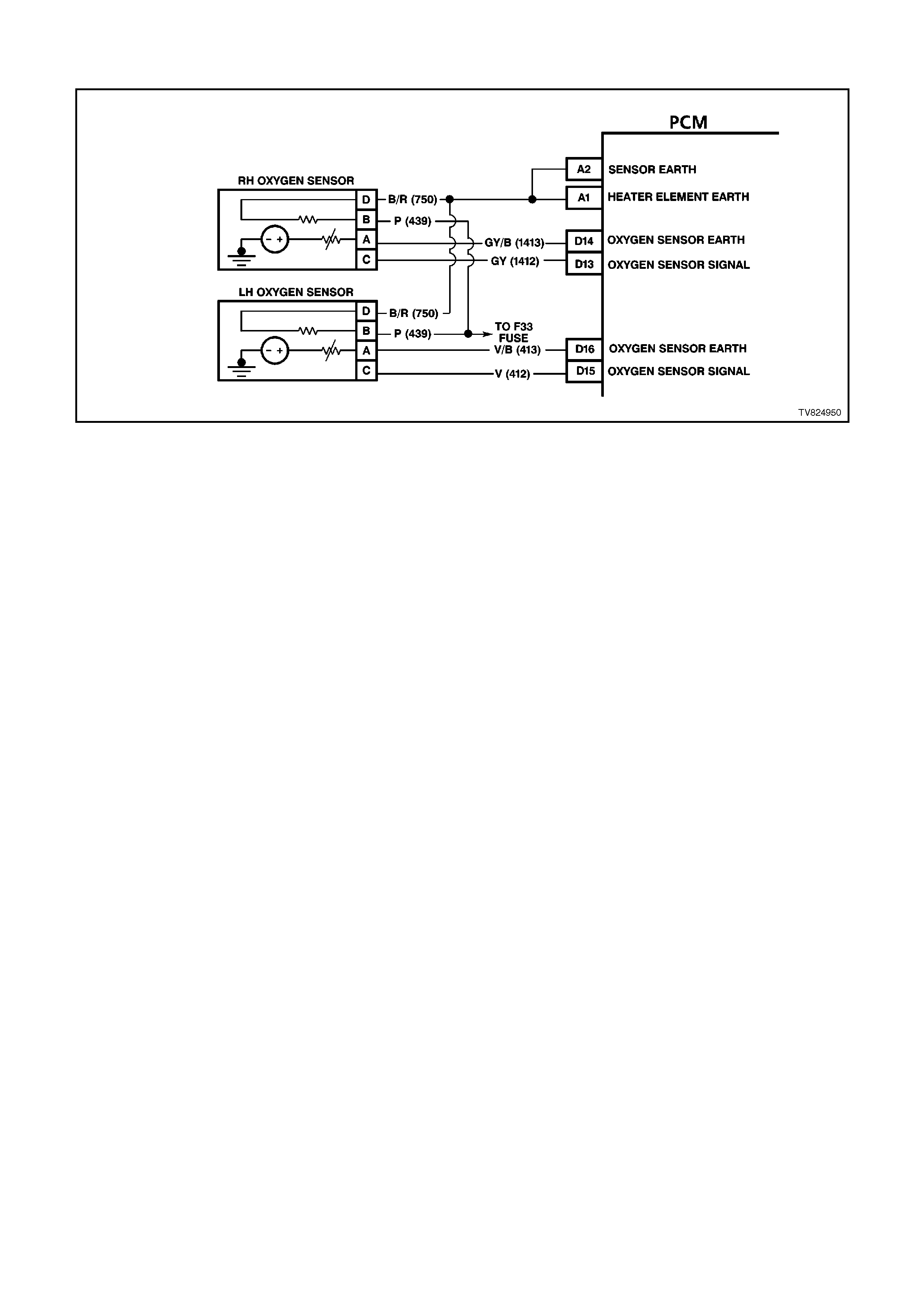
DTC 13 - RIGHT HAND (RH) NO OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The right side O2 sensor is located in the exhaust stream forward of the catalytic converter. The O2 sensor monitors
the oxygen content of the exhaust gas in the exhaust stream then sends a voltage to the PCM relative to the oxygen
content. This voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean mixture) to greater than 900 mV
(low O2 exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM provides the O2 sensor with a constant 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins heating up its
internal resistance begins to decrease . The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing voltage that
differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2 sensor the
PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
When the ignition is turned ON, B+ is applied to the O2 sensor’s heater element. Approximately 30 seconds after
the B+ is applied to the heater portion of the O2 sensor, the O2 sensor should reach a temperature greater than
500°C. The heated O2 sensor becomes active much quicker than a non-heated O2 sensor. This allows the PCM to
control the air/fuel ratio more consistent over a wider range of operating conditions.
DTC 13 WILL SET IF:
• One or more of the following DTCs are not set. DTC 19, 21, or DTC 22 is not set.
• The engine run time is greater than 2 minutes.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 85°C.
• The Throttle Position (TP) sensor angle is greater than 6.25%.
• The O2 sensor voltage stays between 347 and 551 mV.
• The above conditions have been present for 20 seconds.
When a DTC 13 is active, the PCM will operate the fuel system in the open-loop mode.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. The Tech 2 Scan tool allows you to read the same oxygen sensor voltage the PCM is using for its calculations.
3. This step simulates a lean exhaust indication to the PCM. If the PCM and wiring are OK, the PCM will see the
lean indication and the Tech 2 Scan tool should display the O2 sensor voltage below 200 mV.
8. In doing this test, use only a high impedance digital volt-ohm meter. This test checks the continuity of circuits
412 and 150. If circuit 150 is open, the PCM voltage on circuit 412 will be over 0.6 volts.
9. The earth circuit is a separate wire from the PCM to the engine. The PCM uses this circuit to compare it with
the voltage on circuit 412. It completes the earth path for the PCM's oxygen sensor circuitry. This circuit must
be complete, clean, and tight connection to the engine.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Normal Tech 2 Scan tool voltage varies between 100 mV and 999 mV when in Closed Loop.
Carbon deposits caused by a rich running of the engine can cause a temporary poisoning of the sensor. This will
result in a slow or sluggish O2 sensor. The sensor can be cleaned by running the vehicle for several minutes at
operating temperature while not in the rich condition. If a rich condition is present find the problem causing the rich
condition before attempting to clean the O2 sensor.
Check for other forms of contamination.
• Silica from gasket forming material.
• Lead from the use of leaded gasoline.
• Metallic compounds from the use of inferior or low grades of petrol or engine oil.
Some of these contaminants will clean themselves from continuous running of the engine. Do not attempt to clean
the O2 sensor with any form of cleaner solvent this may cause permanent damage.
Check the O2 sensor pigtail wire for proper routing. If the O2 sensor pigtail wire contacts the exhaust manifold the
wire insulation can burn and short itself to the exhaust manifold.
Also, check the O2 sensor for any leaks around its sealing surface or any exhaust leaks. Refer to "Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS. To diagnose the oxygen sensor, refer to CHART A-6.3 in this Section.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Run the engine until
the engine coolant
temperature reaches
85°C.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Monitor the RH O2
sensor voltage on the
scan tool.
Is the Right Hand O2
sensor voltage between
the specified values?
347-
551 mV Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS
31. Turn the engine OFF.
2. Disconnect the Right
Hand O2 sensor
electrical connector.
3. Jumper the harness
circuit (PCM side) to
earth.
4. Start the engine and
allow the engine to
idle.
5. Monitor the RH O2
sensor voltage on the
scan tool.
Is the RH O2 sensor
voltage below the
specified value?
0.2 Volt
(200
mV)
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4Check for a faulty
connection at the oxygen
sensor pigtail wire
connector.
Was a poor connection
found?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
51. Turn the engine OFF.
2. Remove the jumper.
2. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
3. Using a DVM check
the voltage in the RH
O2 sensor signal circuit
(PCM side) at the RH
O2 sensor harness
connector.
Is the RH O2 sensor
voltage between the
specified values?
0.3 - 0.6
Volts
(300-
600 mV)
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
61. Turn the engine OFF.
2. Remove the jumper
wire.
3. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
4. Use a DVM to check
the voltage in the RH
O2 sensor signal circuit
(PCM side) at the RH
O2 sensor harness
connector.
Is the RH O2 sensor
voltage greater than the
specified value?
0.6 Volts
(600
mV)
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Check for an open or a
faulty connection in the
RH O2 sensor ground
circuit (3 total).
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
8Check for an open or a
faulty connection in the
RH O2 sensor signal
circuit.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
9Replace the RH O2
sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Repair the fault in the RH
O2 sensor pigtail
connector.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
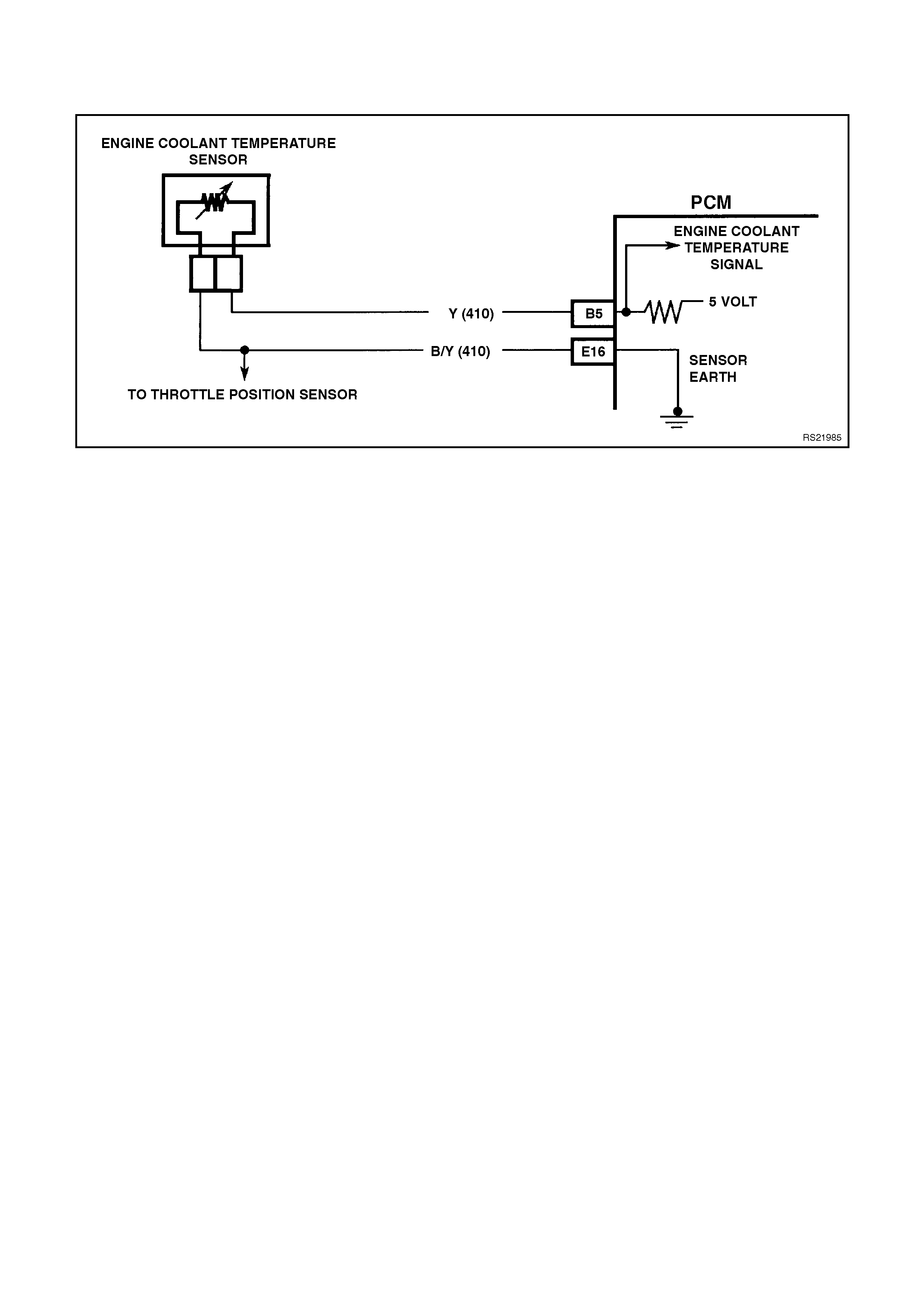
DTC 14 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR - SIGNAL
VOLTAGE LOW
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference and a earth circuit to the ECT sensor. The ECT sensor in turn will send an
output voltage to the PCM based on engine coolant temperature. When the engine coolant temperature is cold, the
ECT sensor (thermistor) resistance will be high, therefore the PCM voltage signal will be high. As the engine coolant
temperature warms up, the sensor resistance decreases, and the PCM will see a lower signal voltage. At engine
operating temperature (85 °C to 95 °C), the voltage should be between .9 and 1.5 volts.
DTC 14 WILL SET IF:
The engine coolant temperature voltage is less than 0.3V (140°C) for one second.
• The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
• The PCM will use a default value of 90°C whenever a DTC 14 is set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This test will determine if circuit 410 is shorted to earth which will cause the conditions for DTC 14.
4. If checking the resistance at the engine coolant temperature sensor is difficult because of sensor location,
disconnect the PCM connectors and check the resistance between the engine coolant temperature signal
circuit and the sensor earth circuit.
Whenever replacing the PCM perform the security link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Check the harness routing for a potential short to earth in circuit 410.
Check the terminals at the ECT sensor for a good connection.
After the engine is started, the temperature should rise steadily to about 90°C then stabilise when the thermostat
opens.
The "Temperature vs Resistance Value" chart may be used to compare the engine coolant temperature sensor at
various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of a shifted sensor. A shifted ECT sensor could result in a
driveability problem. Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR TEMPERATURE VS. RESISTANCE VALUES(APPROXIMATE)
COHMS
110 110
100 190
90 250
70 450
40 1,200
30 1,800
20 2,500
0 6,000
-10 8,750
-20 15,000
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Start the engine and
monitor the Engine
Coolant Temperature
until the coolant
temperature reaches
the specified
temperature.
Does the engine coolant
temperature reach the
specified temperature?
140°C Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
31. Ignition Off.
2. Disconnect the engine
coolant temperature
sensor electrical
connector.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
4. Monitor the engine
coolant temperature.
Is the engine coolant
temperature less than the
specified value?
-30°C Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4Check the resistance
across the engine coolant
temperature sensor
terminals.
Does the resistance
values match the
specified values for the
ECT sensor vs resistance,
refer above ?
See
table
above
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
5Check for an intermittent
or loose terminal in the
sensor harness
connector.
Was a faulty connection
found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 7
6Check the ECT sensor
signal circuit for a short to
earth.
Was a short found?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 7
7Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
9Repair the ECT sensor
connector terminals.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Repair the short to earth
in the ECT sensor signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
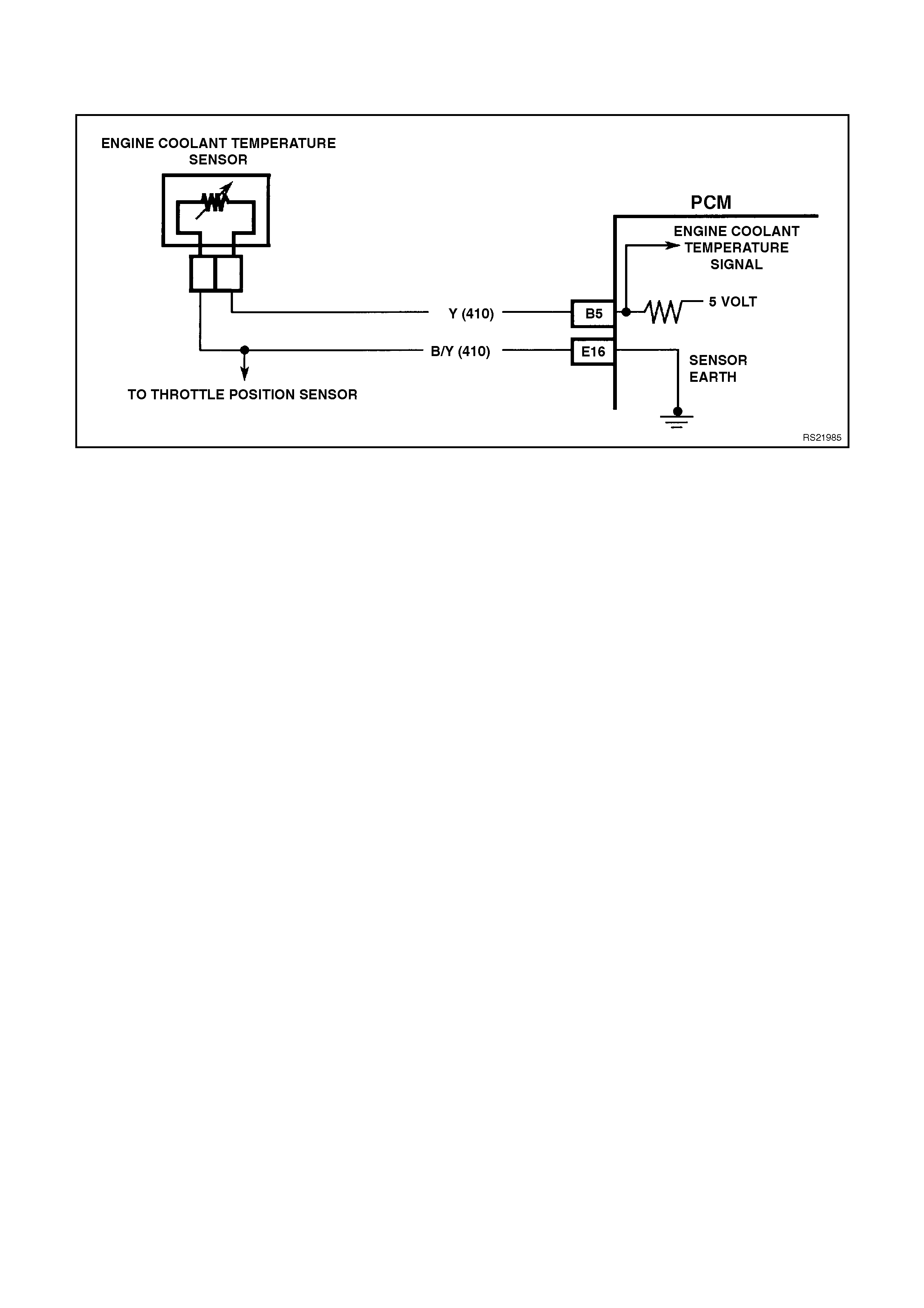
DTC 15 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR - SIGNAL
VOLTAGE HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference and a earth circuit to the ECT sensor. The ECT sensor in turn will send an
output voltage to the PCM based on engine coolant temperature. When the engine coolant temperature is cold, the
ECT sensor resistance will be high, therefore the PCM voltage will be high. As the engine coolant temperature rises,
the sensor resistance decreases, and the PCM sees a lower signal voltage. At normal engine operating
temperature (85 °C to 95 °C), the voltage should be between .9 and 1.5 volts.
DTC 15 WILL SET IF:
• The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
• The ECT input signal voltage is greater than 4.7 volts, indicating an engine coolant temperature less than about
-35 degrees C for one second.
The PCM will use a default value of 90°C whenever a DTC 14 is set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This test simulates a Diagnostic Trouble Code 14. If the PCM recognises the low signal voltage, (high
temperature) and the Tech 2 "Scan" tool reads 130 degrees C or above, then the PCM and wiring are OK.
4. This test will determine if circuit 410 is open. There should be an open circuit voltage of 5 volts at the Engine
Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor harness connector. By jumping the 5 volt signal to earth, the PCM should
recognise this change.
9. Whenever the PCM is replaced, perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
A Tech 2 scan tool reads engine coolant temperature in degrees Celsius. After the engine is started, the
temperature should rise steadily to about 90 degrees C then stabilise when the thermostat opens.
A faulty connection, an open in circuit 410 or an open in circuit 452 will result in a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
15 to set.
If a DTC 21 or a DTC 59 are also set, check circuit 452 for faulty wiring or connections. Check terminals at the
sensor for a good connection.
The "Temperature vs Resistance Value" scale may be used to test the engine coolant temperature sensor at
various temperature to evaluate the possibility of a shifted sensor. A shifted sensor could result in poor driveability.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR TEMPERATURE VS. RESISTANCE VALUES (APPROXIMATE)
COHMS
110 110
100 190
90 250
70 450
40 1,200
30 1,800
20 2,500
0 6,000
-10 8,750
-20 15,000
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Is the ECT sensor
temperature at or between
the specified value?
-35°C to
-40°C Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ECT
sensor electrical
connector.
3. Jumper the harness
terminals together.
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Is the ECT sensor
temperature greater than
the specified value?
130°C Go to Step 8 Go to Step 4
41. Engine OFF.
2. Jumper the ECT
sensor signal circuit to
earth.
Does the Scan tool
display ECT sensor
temperature greater than
the specified value?
130°C Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5Check the resistance
across the engine coolant
temperature sensor
terminals.
Does the DVM reading
match the specified
values for the
temperatures vs sensor
resistance table, refer
above ?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 10
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
6Check for a faulty
connection in the sensor
harness connector.
Was a faulty connection
found?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
7Check the ECT sensor
signal circuit for an open
or a faulty connection at
the PCM.
Was a fault connection
found?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
8Check for a faulty ECT
sensor connection.
Was a faulty connection
found?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Replace the ECT sensor.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
11 Repair the faulty
connection or circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
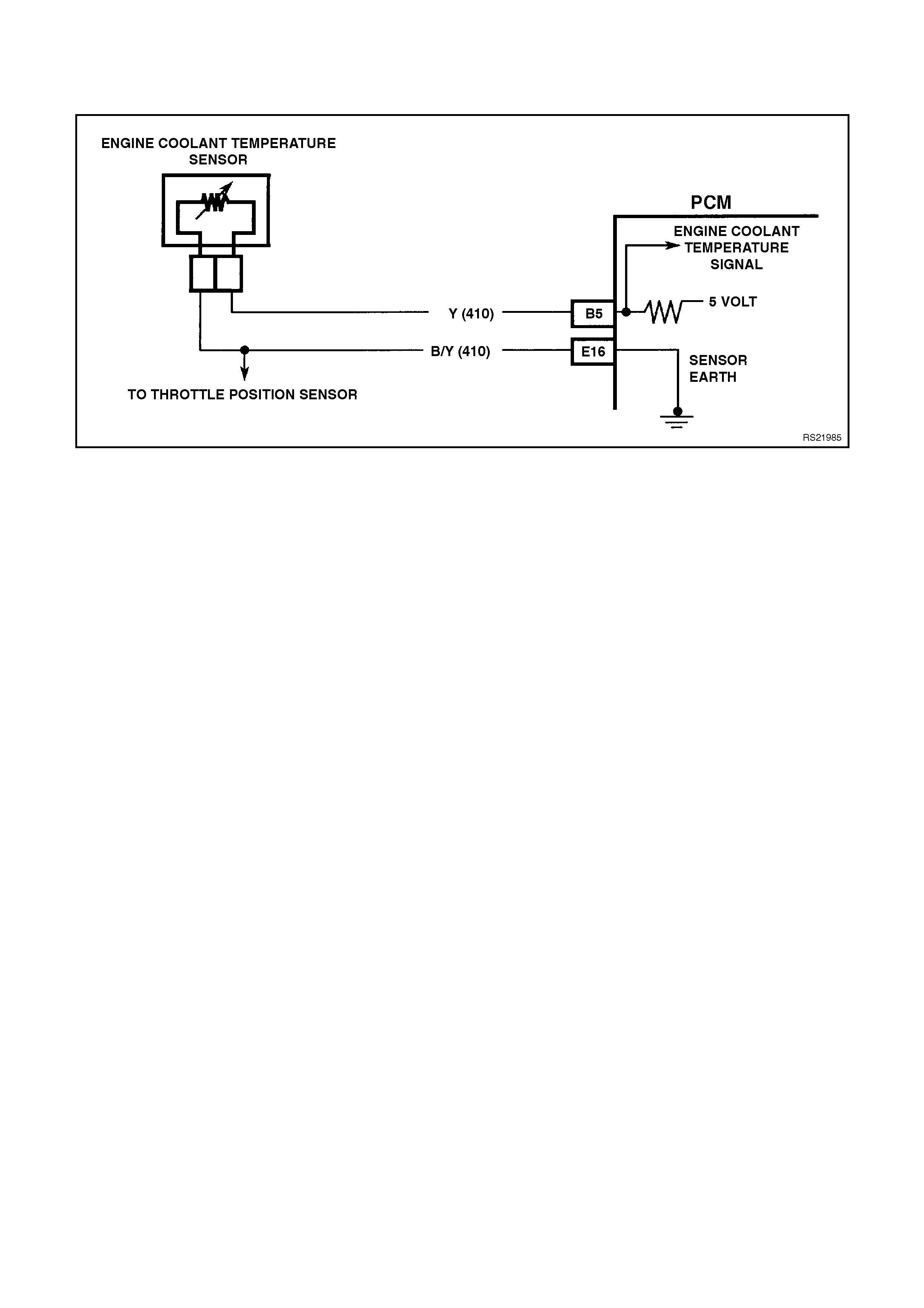
DTC 16 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE (ECT) SENSOR - SIGNAL
VOLTAGE UNSTABLE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference and a earth circuit for the ECT sensor. The ECT sensor in turn will send an
output voltage to the PCM based on engine coolant temperature. When the engine coolant temperature is cold, the
ECT sensor (thermistor) resistance will be high, therefore the PCM voltage signal will be high. As the engine coolant
temperature warms up, the sensor resistance decreases, and the PCM will see a lower signal voltage. At normal
engine operating temperature (85 °C to 95 °C), the voltage should be between 0.9 and 1.5 volts.
DTC 16 WILL SET IF:
• The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
• A DTC 14, 15 or 17 is not set.
• The ECT temperature changes more than 20 in 400 milliseconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Numbers below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. The cause of an unstable ECT sensor is most likely caused from a bad connection causing intermittent voltage
spikes. By moving the wires and watching for a change in voltage on the scan tool can help identify the
problem area.
7. Whenever the PCM is replaced, perform the Security Link Procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
When attempting to diagnose an intermittent problem, use the snapshot mode of the Tech 2 scan tool, to review
diagnostic information.
This DTC is most likely to set on a cold engine than on a hot engine because of the pull up resistors in the PCM.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 Scan
tool.
2. Set up the snapshot
mode to trigger on
DTC 16.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
4. Monitor the Scan tool
while wiggling the
ECT sensor connector.
Does the “Eng Coolant
Temp” reading change
sharply while wiggling the
wires?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 3
3Wiggle and tug the ECT
sensor harness.
Does the "Eng Coolant
Temp" reading change
sharply while wiggling the
harness?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 4
4Wiggle and tug the
harness at the PCM.
Does the "Eng Coolant
Temp" reading change
sharply while wiggling the
wires at the PCM
harness?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
5Lightly tap on the PCM.
Does the "Eng Coolant
Temp" reading change
sharply when tapping on
the PCM?
Go to Step 6 DTC 16 is
intermittent.
Refer to
diagnostic Aids
above.
6Make sure the PCM is
mounted securely to the
vehicle.
Was a mounting fault
found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 7
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
81. Check the ECT sensor
connector.
2. Check the tension of
the female terminal
grip with a spare male
terminal.
3. Inspect the connectors
for corrosion. If the
connectors are
corroded, clean the
connectors with
electronic part cleaner
and retest.
4. If these repairs do not
resolve the problem,
replace the terminals.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
91. Check for broken
strands of wire in the
ECT sensor harness.
2. Check for cuts and
pinches in the ECT
sensor harness.
3. Repair as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 1. Check the ECT sensor
connection at the
PCM.
2. Check the tightness of
the female terminal
grip with a spare male
terminal.
3. Inspect the connectors
for corrosion. If the
connectors are
corroded, clean them
with electronic parts
cleaner and retest.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

DTC 17 - PCM ERROR - ECT CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM uses two different internal pull-up resistors to increase the resolution throughout the entire range of
engine operating temperatures. When the engine coolant temperature is less than 50 degrees C, the 4K ohm
resistor is used. When temperature is above 50 degrees C, the PCM switches to the 348 ohm resistor. If the pull-up
resistor does not switch, a DTC 17 will set.
DTC 17 WILL SET IF:
• The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
• The pull-up resistor inside the PCM switches and the ECT voltage changes less than 60 mV.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart
2. Whenever the PCM is replaced perform the Security Link procedure in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
DTC 17 is an internal fault within the PCM. Replace the PCM.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
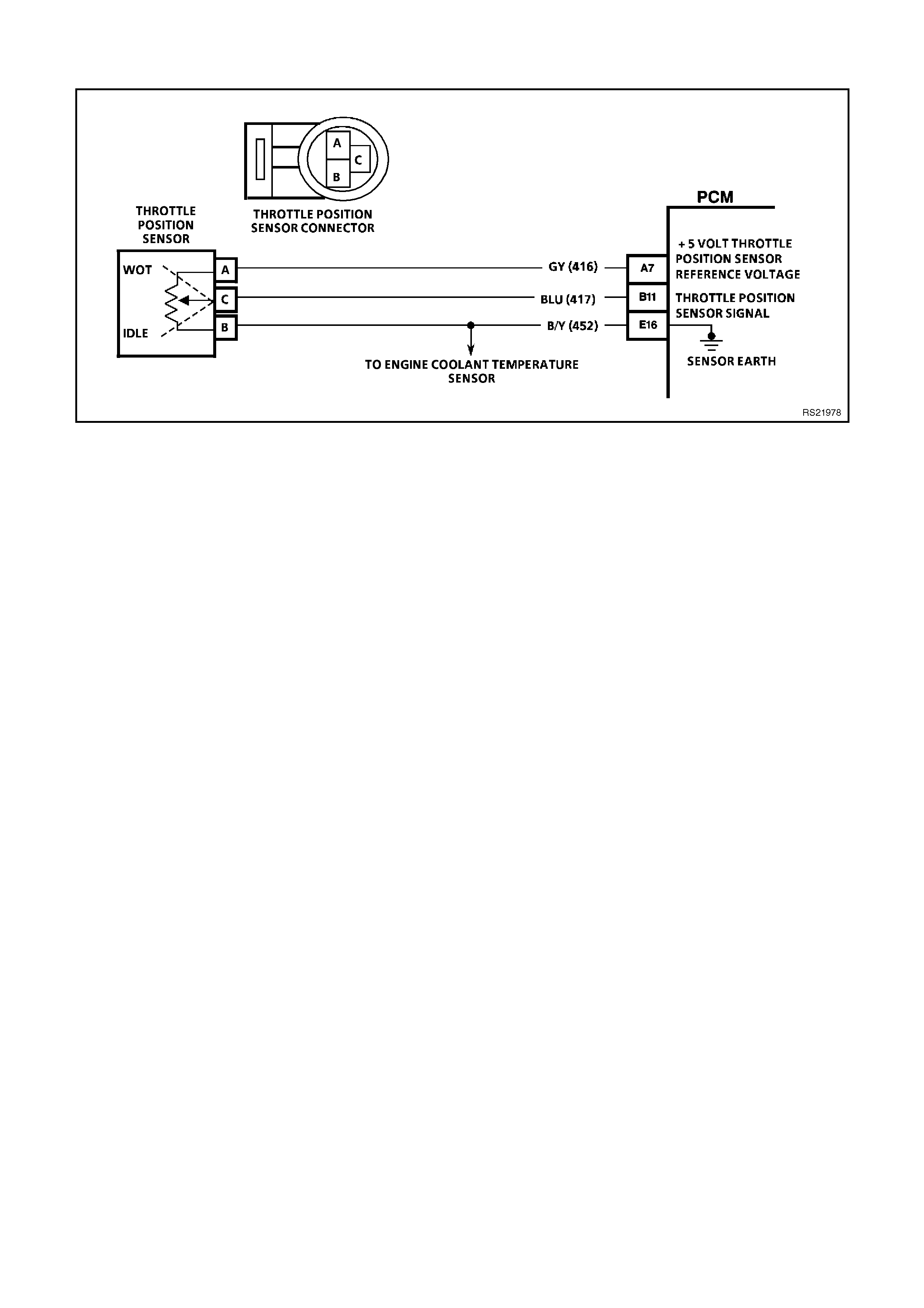
DTC 19 - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR - STUCK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor provides a voltage signal to the PCM that changes relative to the throttle blade
angle. The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage and an earth circuit to the TP sensor. The TP sensor in return
sends a voltage to the PCM based on throttle blade angle (driver demand).The TP signal voltage will vary between
0.25 and 1.25 volts at idle to greater than 4 volts at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
DTC 19 WILL SET IF:
• The throttle position (TP) sensor angle changes less than 2% during 100ms of airflow below 300mg/cyl.
The PCM will use a default value of 35% during the time the fault is present.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
The scan tool reads throttle position in volts. The TP sensor signal voltage should be between 0.25 to 1.25 volts
when the throttle is closed. The TP sensor voltage should increase at a steady rate as the throttle is opened.
The Tech 2 scan tool will also read throttle angle. 0%=closed throttle; 100%=WOT.
If the voltage is steady above the DTC 22 voltage criteria and below the DTC 21 voltage criteria, look for a short to
voltage on the TP signal circuit.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
DTC 19 CRITERIA TABLE (APPROXIMATE)
TPS% RPM
13 800
16 1,200
19 1,600
23 2,000
26 2,400
29 2,800
32 3,200
34 3,600
39 4,000
43 4,400
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Inspect the movement of
the throttle cable, the
throttle linkage, and the
throttle blade.
Are any of the
components binding or
sticking?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3Is the Throttle Position
(TP) sensor binding or
sticking during its
movement from closed
throttle too wide open
throttle and back to closed
throttle position?
Go to Step 5
4Repair or replace the
binding or the sticking
component as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair Go to Step 5
5Replace the Throttle
Position (TP) sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

DTC 21 - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR - SI GNAL VOLTAGE HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor provides a voltage signal to the PCM that changes relative to the throttle blade
angle. The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage and an earth circuit to the TP sensor. The TP sensor in return
sends a voltage to the PCM based on throttle blade angle (driver demand). The TP signal voltage will vary between
0.25 and 1.25 volts at idle to greater than 4 volts at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
DTC 21 WILL SET IF:
• The TP sensor throttle angle is greater than 4.8V for 2 seconds.
When a DTC 21 is set the PCM will default to a 35% throttle angle for engine operation.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. With the TP sensor disconnected, the TP sensor signal voltage should go low if the PCM and wiring are OK.
4. Probing circuit 452 with a test light connected to B+ checks the sensor’s earth circuit. A faulty TP sensor earth
circuit will set a DTC 21.
8. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
The scan tool reads throttle position in volts. The TP sensor signal voltage should be between 0.25 to 1.25 volts
when the throttle is closed. The TP sensor voltage should increase at a steady rate as the throttle is opened.
The Tech 2 scan tool will also read throttle angle. 0%=closed throttle; 100%=WOT.
When a DTC 21 is set, the PCM does not receive the proper signal from the TP sensor. The PCM can still
determine the TP sensor value with a default value based on MAF and engine RPM. If DTC 21 is set, the
transmission will have; no TCC, high line pressure, harsh shifts and no 4th gear (if in hot mode).
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Throttle closed.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the Tech 2 scan
tool display Throttle
Position voltage over the
specified value?
2.5 volts Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the TP
sensor electrical
connector.
Does the scan tool display
throttle position voltage
less than specified value?
0.2 volts
(200 mV) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4Probe the TP sensor earth
circuit with a test light
connected to battery
voltage.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5Check for a faulty
connection.
Was faulty connection
found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
6Check for a short to
voltage in the TP sensor
signal circuit.
Was a fault found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7Check for an open in the
TP sensor earth circuit.
Is the TP sensor earth
circuit open?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operation, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Repair the faulty
connection or the faulty
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Replace the Throttle
Position Sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
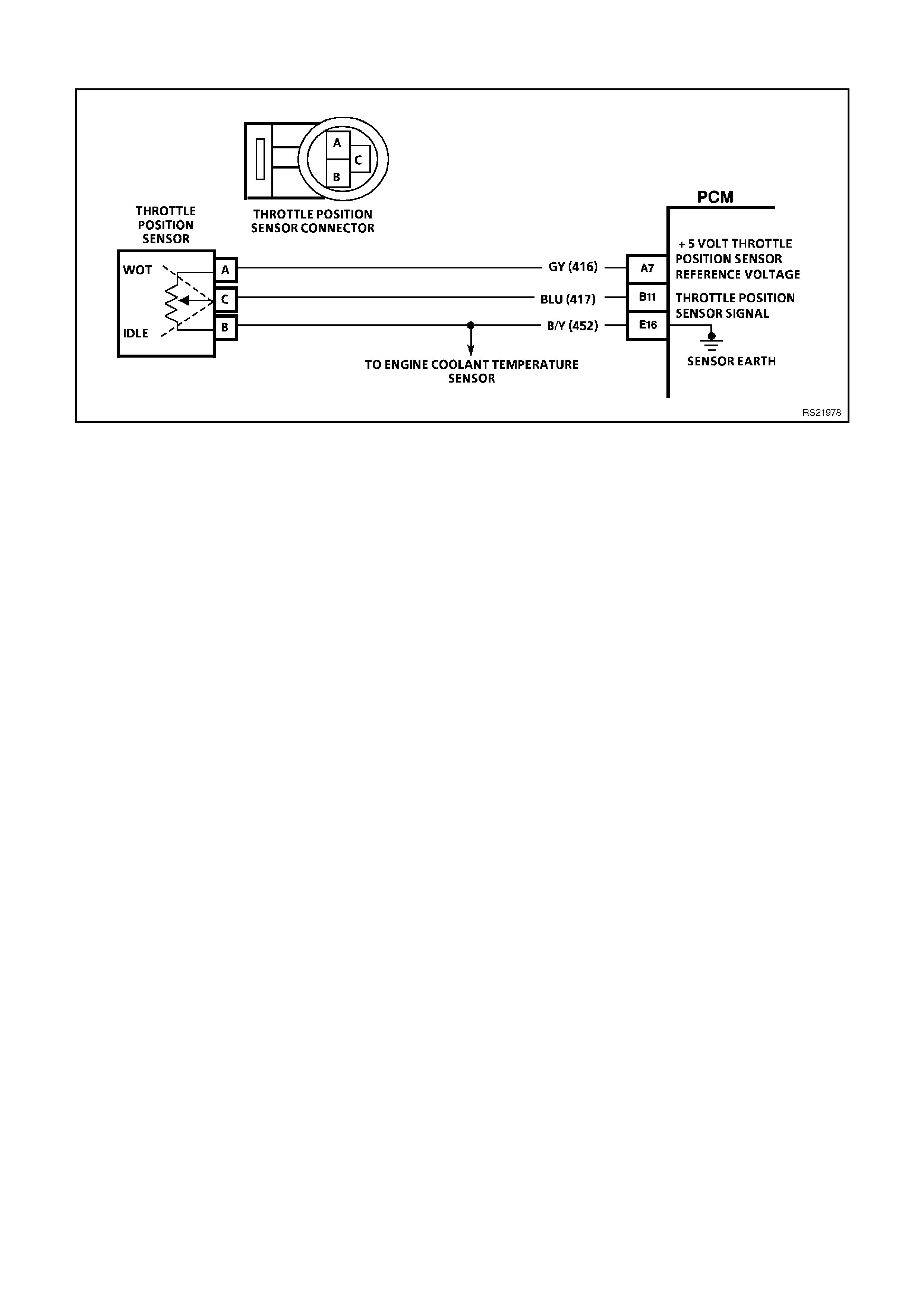
DTC 22 - THROTTLE POSITION (TP) SENSOR - SI GNAL VOLTAGE LOW
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor provides a voltage signal to the PCM that changes relative to the throttle blade
angle. The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference and an earth circuit to the TP sensor. The TP sensor in return sends a
voltage to the PCM based on throttle blade angle(driver demand).The TP signal voltage will vary between 0.25 and
1.25 volts at idle to greater than 4 volts at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
DTC 22 WILL SET IF:
• The TP sensor angle is less than 120 mV for 2 seconds.
The PCM will use a default value of 35% for the TP sensor whenever a DTC 22 sets.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This test simulates a Diagnostic Trouble Code 21 (high voltage). If the PCM recognises the high signal voltage
and the Scan tool reads over 4 volts, then the PCM and wiring are OK.
4. This simulates a high signal voltage to check for an open in circuit 417. The Tech 2 Scan tool will not read 12
volts, but what is important is that the PCM recognises the signal.
8. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
A Tech 2 scan tool reads throttle position in volts. With the ignition ON or at an idle, the TP sensor voltage should
read between 0.25 and 1.25 volts with the throttle closed. The voltage should increase at a steady rate as the
throttle is moved toward Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
The Tech 2 Scan tool will read throttle angle. 0%=closed throttle; 100%=WOT.
When a DTC 22 is set, the PCM does not receive the proper signal from the TP sensor. The PCM can still
determine the TP sensor value with a default value based on MAF and engine RPM. If DTC 22 is set, the
transmission will have no TCC high line pressure, harsh shifts and no 4th gear (if in hot mode).
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Throttle closed.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the Tech 2 scan tool
display TP sensor voltage
below the specified value?
0.12 volt
(120 mV) Go to Step 3 DTC 22 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored, refer
to "Intermittents"
in Section 6C2-
2B SYMPTOMS.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the TP
sensor electrical
connector.
3. Jumper circuits 416
and 417 together.
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the scan tool display
throttle position voltage
greater than the specified
value?
4.0 volts
(4000
mV)
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Remove the jumper
wire.
3. Probe the TP sensor
signal circuit with a test
light connected to B+.
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the scan tool display
TP sensor voltage greater
than the specified value?
4.0 volts
(4000
mV)
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Check for an open or a
short in the TP sensor’s
5V reference circuit or a
faulty connection.
Was a fault found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6Check for an open or a
short in the TP sensor
signal circuit or a faulty
connection.
Was a short, open or
faulty connection found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7Replace the Throttle
Position Sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Repair the fault in the
circuit or the connection.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

DTC 23 - INTAKE AIR TEM PERATURE (IAT)
SENSOR - SIGNAL VOLTAGE HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor used to control the signal voltage to the PCM. The PCM
supplies a 5 volt reference voltage and a earth circuit to the IAT sensor. The IAT sensor in turn will send a signal
voltage back to the PCM based on intake air temperature. When the intake air is cold, the IAT sensor output voltage
and resistance will be high. If the intake air is warm, the IAT sensor output voltage and resistance will be low.
DTC 23 WILL SET IF:
• The IAT sensor signal voltage is greater than 4.9 volts,(indicating an intake air temperature below -38 degrees
C) for one second.
The PCM will use a default value of 25°C during the time the fault is present.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. A Diagnostic Trouble Code 23 will set, due to an open sensor, wire or connection. This test will determine if the
wiring and the PCM are OK.
6. This will determine if the IAT sensor signal circuit or the IAT sensor earth circuit is open.
11. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS
A Tech 2 scan tool indicates the temperature of the air in the intake. When the PCM detects a fault in the IAT
sensor circuit, a default value of 46 degrees C will be used by the PCM.
Carefully check the harness and the connections for possible open circuit 472 or circuit 469.
An open circuit 469 will set DTC 23 and DTC 33, if the engine has been allowed to sit overnight, then the intake air
temperature and engine coolant temperature values should be within a few degrees of each other. After the engine
is started, the IAT sensor will increase due to engine compartment temperatures.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
IAT SENSOR TABLE TEMPERATURE VS RESISTANCE VALUES (APPROXIMATE)
°C OHMS
100 185
70 450
38 1,800
20 3,400
4 7,500
-7 13,500
-18 25,500
-40 100,700
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
3. Monitor the IAT sensor
temperature.
Does the scan tool display
the IAT sensor
temperature at or between
the specified value?
-35°C to
-40°C Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the IAT
sensor electrical
connector.
3. Jumper the harness
terminals together
(PCM side).
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the Scan tool
display the IAT sensor
temperature greater than
the specified value?
130°C Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4Measure the resistance
across the IAT sensor
terminals.
Is the value within the
specified range?
See IAT
table
above
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 10
5Check for an intermittent
or a loose terminal in the
IAT sensor harness
connector.
Is a problem found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 9
61. Ignition OFF engine
ON.
2. Jumper the IAT sensor
5V reference/signal
circuit to earth.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Is the IAT sensor
temperature greater than
the specified value?
130°C Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Check for an open in the
IAT sensor earth circuit or
for faulty connection.
Was an open or faulty
connection found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
8Check for an open in the
IAT sensor circuit 5V
reference/signal circuit or
for a faulty connection.
Wan an open or faulty
connection found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
91. Remove the jumper
from the IAT sensor
harness.
2. Ignition OFF.
3. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
5. Check for short to
voltage in the IAT
sensor 5V
reference/signal circuit.
Was a fault found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
10 Replace the intake air
temperature sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6c2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
12 Repair the faulty circuit or
the faulty connection.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
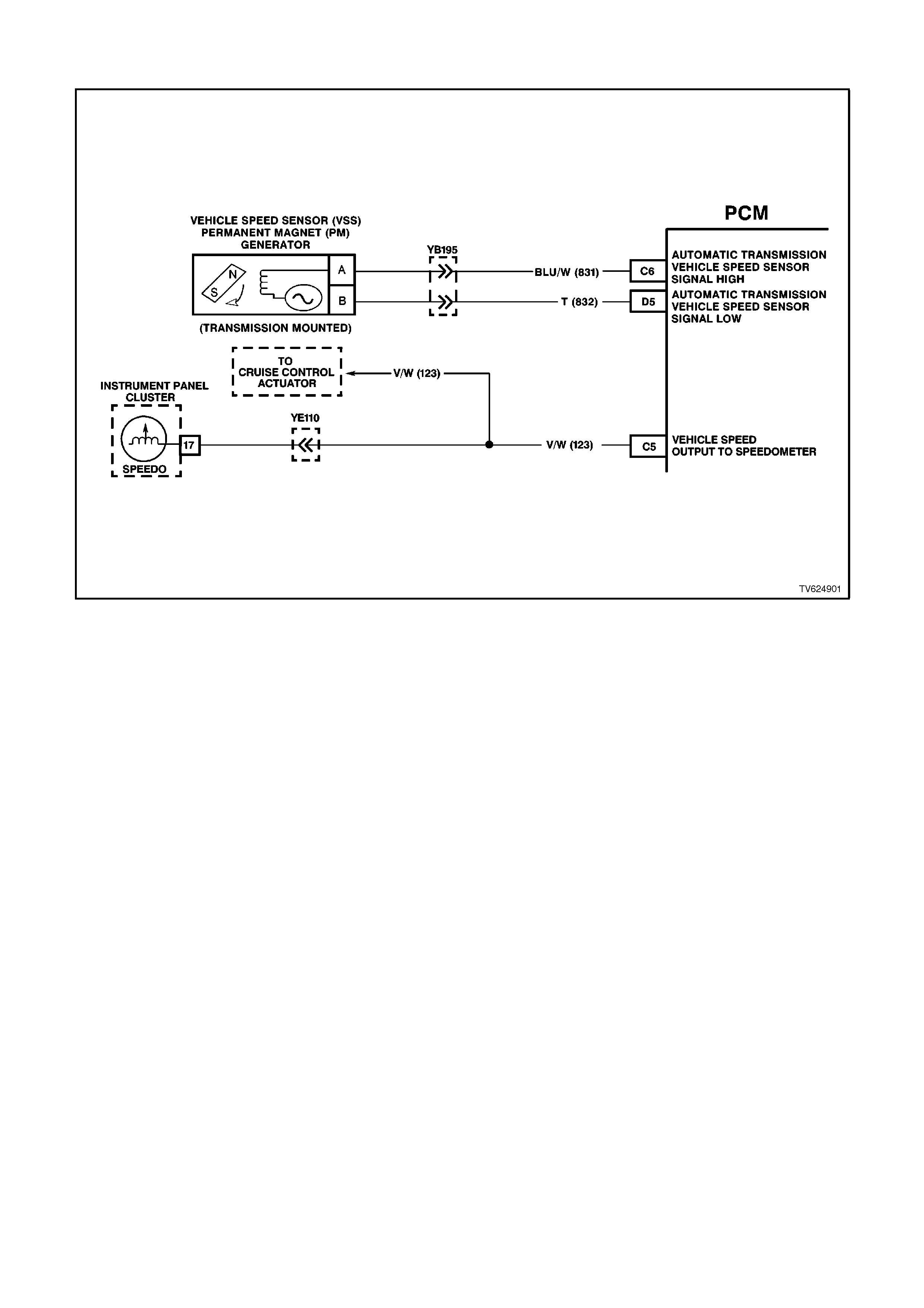
DTC 24 - NO VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Assembly provides vehicle speed information to the PCM. The VSS Assembly is
a Permanent Magnet (PM) generator. The PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The AC voltage level and
the number of pulses increase with the speed of the vehicle. The PCM then converts the pulsing voltage to vehicle
speed. The PCM uses this information for calculations. A scan tool can display the vehicle speed.
When the PCM detects a low or no vehicle speed, when there is high engine speed in a drive range and a low
throttle position voltage, then a DTC 24 sets.
DTC 24 WILL SET IF:
• One of the following DTC's are set. DTC 19, 21, 22, or DTC 32.
• Circuit 123 voltage is constant - that is, NOT pulsing.
• The engine RPM is between 1400 and 3000 RPM.
• The throttle position sensor angle is less than 1%.
• The engine load is low (MAF sensor) 95 mg/cyl.
DTC 24 will set if the VSS circuit is open from a standing stop. As the vehicle is accelerated the transmission will
shift from 1st to 2nd gear at approximately 54 km/h. If a VSS signal is not present, a DTC 24 will set.

TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. This tests the integrity of the VSS Assembly.
4. This tests the VSS Assembly circuit.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
Corrosion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• Check circuits 831 and 832 for the proper connections to be sure they are clean and tight and the harness is
routed correctly.
• The scan tool should indicate vehicle speed whenever the drive wheels are turning greater than 3 km/h.
• The vehicle speed sensor resistance should be between 1470-2140 Ohms at 20°C, and 2270-2820 Ohms at
100° C.
• Refer to 'intermittents' in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
When a DTC 24 sets, the PCM will command second gear only, commands maximum line pressure, freeze shift
adapts from being updated and inhibit TCC engagement.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check.
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Clear the DTC.
5. Raise the drive wheels.
NOTE:
Do not perform this test
without supporting the
rear axle assembly or the
lower control arms on
vehicles with independent
rear suspension so that
the drive shafts are in a
normal horizontal position.
6. Start the engine.
7. Place the transmission
in any drive gear.
With the rear wheels
rotating, does the scan
tool Vehicle Speed
increase with the drive
wheel speed?
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch
to the OFF position.
2. Disconnect the VSS
connector from the
VSS assembly.
3. Using the J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, connect
the J 39200 DVM to
the VSS terminals.
4. Select AC volts.
5. Place the transmission
selector in the neutral
position.
6. Rotate the drive
wheels by hand,
ensuring that the
driveshaft is turning.
With rear wheels rotating,
is the DVM voltage
greater than the specified
value?
0.5 volts
AC Go to Step 4 Go to Step 11

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Turn the ignition switch
to the OFF position.
2. Reconnect the VSS
connector to the VSS
Assembly.
3. Disconnect the PCM
connector 1 (Pink-32
pin) from the PCM.
4. Connect the DVM test
leads to the connector
terminals D5 (T) and
C6 (Blu/W).
5. Place the transmission
selector in the neutral
position.
6. Rotate the drive
wheels by hand,
ensuring that the
driveshaft is turning.
With rear wheels rotating,
is the DVM voltage
greater than the specified
value?
0.5 volts
AC Go to Step 13 Go to Step 5
51. Select W (Ohms), on
the DVM.
2. Measure the
resistance between the
connector terminals D5
(T) and C6 (Blu/W).
Is the circuit resistance
within the specified
range?
1470-
2820 ohm Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6Connect the DVM
between the connector
terminal C6 and earth.
Is the circuit resistance
less than the specified
value?
250k ohm Go to Step 7 Go to Diagnostic
Aids above
71. Check circuit 831 and
circuit 832 for a short
to earth.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Was the short to earth
condition found and
corrected?
Go to Step 14 Go to Diagnostic
Aids above
8Is the resistance reading
in step 6 greater than the
specified value?
2820 ohm Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
91. Check circuit 831 and
circuit 832 for a
shorted together
condition.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Was a shorted together
condition found and
corrected ?
Go to Step 14 Go to Diagnostic
Aids above
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
10 1. Check circuit 831 and
circuit 832 for an open
condition.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Was an open condition
found and corrected ?
Go to Step 14 Go to Diagnostic
Aids above
11 1. Remove the VSS
Assembly.
2. Inspect the VSS
Output Sensor Rotor
for damage or
misalignment.
Did you find a condition?
Refer to
Section 7B-2
MANUAL
TRANSMISSION
- V8 or
Section 7C-4
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Go to Step 12
12 Replace the VSS
Assembly. Refer to
Service Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 14
13 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations. For the
Security Link procedure
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 14
14 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
ensuring that the
vehicle speed is
greater than 10 km/h
and observe the scan
tool Vehicle Speed.
Is the scan tool Vehicle
Speed greater than the
specified value?
10 km/h System OK Begin the
Diagnosis Again
Go to Step 1
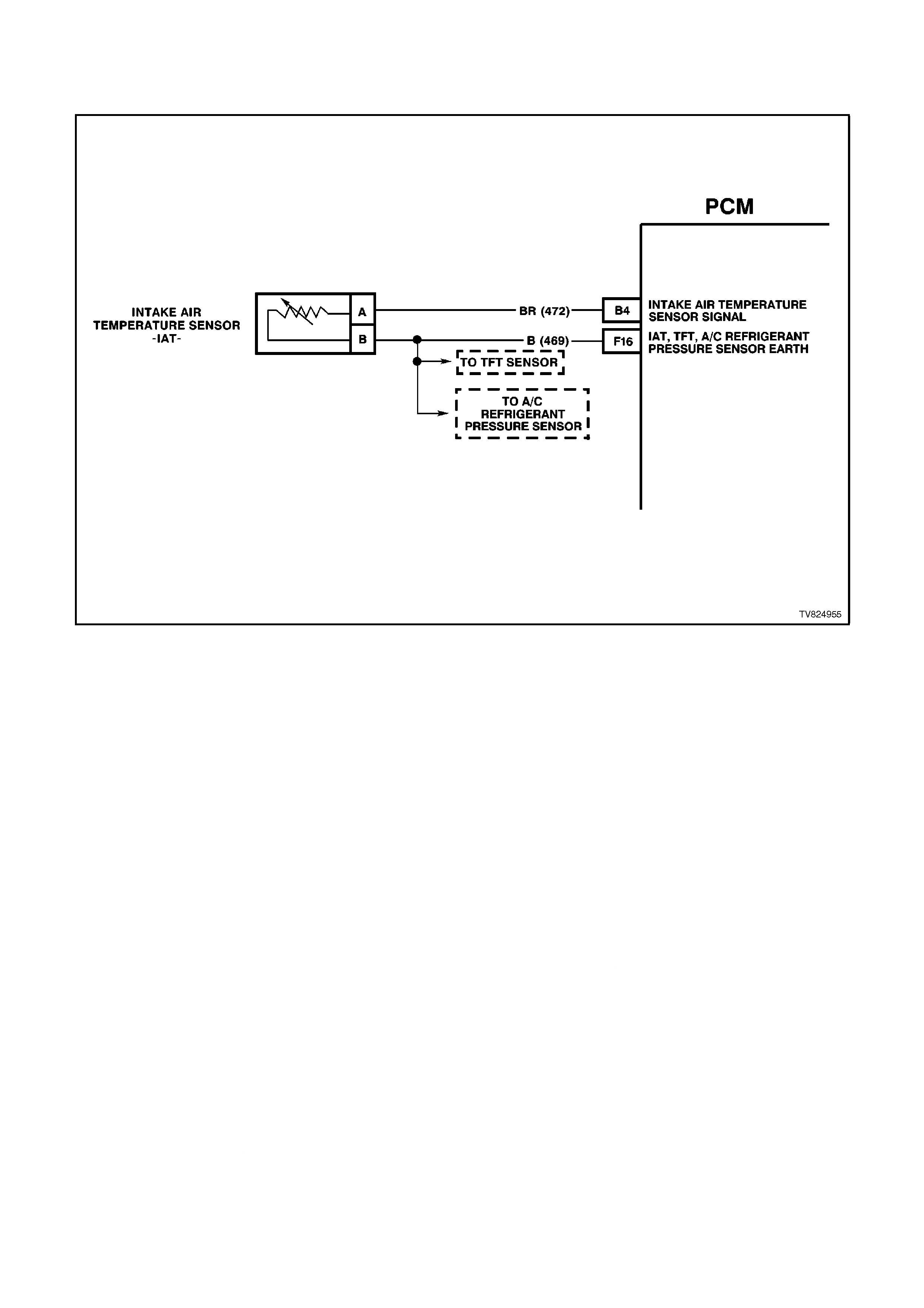
DTC 25 - INTAKE AIR TEM PERATURE (IAT) SENSOR - SIGNAL VOLTAGE
LOW
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor that is used to control the signal voltage to the PCM. The
PCM supplies a 5 volt reference voltage and a earth circuit to the IAT sensor. The IAT sensor in turn will send a
signal voltage back to the PCM based on intake air temperature. When the intake air is cold, the IAT sensor output
voltage and resistance will be high, therefore, the PCM will sense a high signal voltage. If the intake air is warm, the
IAT sensor output voltage and resistance will be low, therefore, the PCM will sense a low signal voltage.
DTC 25 WILL SET IF:
• The engine run time is greater than 60 seconds.
• The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) signal voltage is less than 0.1 volts, for one second.
• The PCM will use a default value of 25°C for IAT during the time the fault is present.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This will verify the if the DTC still is present.
3. The range should be between -30 degrees C and - 40 degrees C if the fault condition exists.
4. The values listed are approximates and should be close.
8. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) on a Tech 2 scan tool indicates the temperature of the air entering into the
engine. If the engine has been allowed to sit overnight, the IAT sensor and engine coolant temperature sensor
values should be within a few degrees of each other. After the engine is started, the IAT will increase due to engine
compartment temperatures, however, the IAT sensor will rarely exceed 80 degrees C.
When the PCM detects a fault in the IAT circuit, a default value of 25° C will be used.
Check harness routing for possible short to earth in circuit 469.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
IAT SENSOR TABLE TEMPERATURE VS RESISTANCE VALUES (APPROXIMATE)
deg. C OHMS
100 185
70 450
38 1,800
20 3,400
4 7,500
-7 13,500
-18 25,500
-40 100,700
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the scan tool display
IAT sensor temperature
greater than the specified
temperature?
134°C Go to Step 3 DTC 25 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored, refer
to "Diagnostic
Aids" above
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the IAT
sensor electrical
connector.
3. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Does the scan tool
display IAT sensor
temperature below the
specified value?
-30°C to
-40°C Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Measure the
resistance across the
IAT sensor terminals.
Does the value
correspond to the
specified value?
See IAT
table
above
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5Check for a loose terminal
in the harness connector,
or terminals being shorted
together.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
6Check for a short in the
IAT sensor 5V reference/
signal circuit.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7Replace the IAT sensor.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
8Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Repair the circuit as
necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
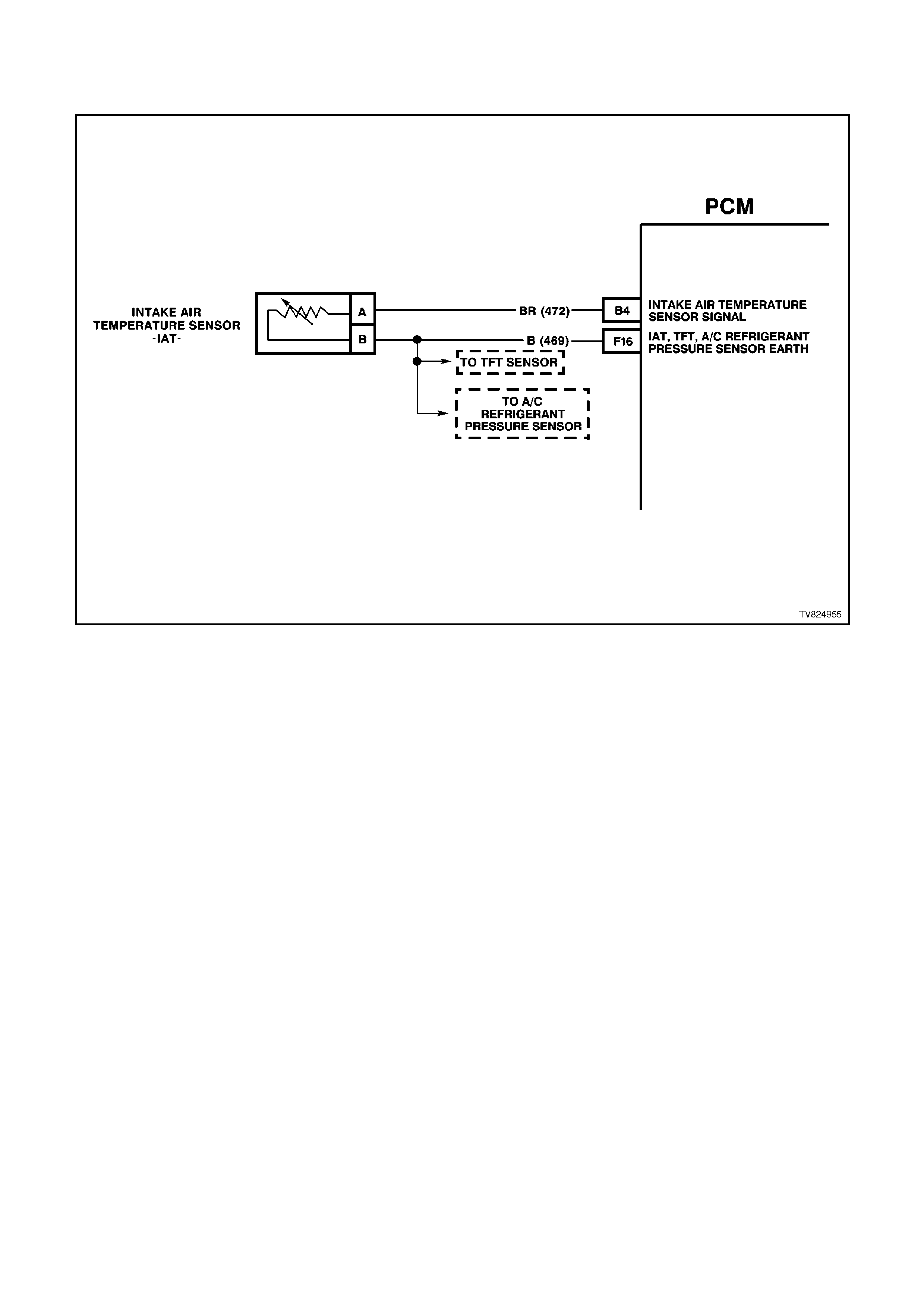
DTC 26 - INTAKE AIR TEM PERATURE (IAT) SENSOR - SIGNAL VOLTAGE
UNSTABLE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor used to control the signal voltage to the PCM. The PCM
supplies a 5 volt reference voltage and a earth circuit to the IAT sensor. The IAT sensor in turn will send a signal
voltage back to the PCM based on intake air temperature. When the intake air is cold, the IAT sensor output voltage
and resistance will be high. If the intake air is warm, the IAT sensor output voltage and resistance will be low .
DTC 26 WILL SET IF:
• The IAT sensor reading changes more than .14V (140 mV) in 100 milliseconds.
• The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
The PCM will use a default value of 25°C for IAT during the time the fault is present.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. By gently moving the wires while watching the Tech 2 for a voltage change can help identify the location of the
problem.
7. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
When attempting to diagnose an intermittent problem, use the snapshot mode on the Tech 2 "Scan" tool to review
the diagnostic information.
IAT SENSOR TABLE TEMP. TO RESISTANCE VALUES (APPROXIMATE)
COHMS
100 185
70 450
38 1,800
20 3,400
4 7,500
-7 13,500
-18 25,500
-40 100,700
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Scan tool.
2. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
3. Monitor the Tech 2
Scan tool while
wiggling the IAT
sensor connector.
Does the IAT sensor
reading change sharply?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 3
3Wiggle and tug the IAT
sensor harness.
Does the IAT sensor
reading change sharply?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 4
4Wiggle and tug the
harness at the PCM.
Does the IAT sensor
value change sharply?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
5Lightly tap on the PCM.
Does the IAT sensor
value change sharply?
Go to Step 6 DTC 26 is
intermittent.
Refer Diagnostic
Aids above.
6Check that the PCM is
mounted securely to the
vehicle.
Was a mounting fault
found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 7
7Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
81. Inspect the IAT sensor
connector.
2. Check the tension of
the female terminal
with a spare male
terminal.
3. Inspect connectors for
corrosion. If the
connectors are
corroded clean them
with electronic part
cleaner and retest.
4. If these repairs do not
resolve the problem,
replace the terminals.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
91. Check for an open in
the IAT harness.
2. Check for broken
strands of wire in the
IAT sensor harness.
3. Check for cuts or
pinches in the IAT
sensor harness.
4. Make any repairs as
necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repairs
10 1. Check the IAT sensor
connection at the
PCM.
2. Check the tension of
the female terminal
grip with a spare male
terminal.
3. Inspect the connectors
for corrosion. If
connectors are
corroded, try cleaning
with them electronic
parts cleaner and
retest.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repairs

DTC 28 - TRANSMISSION FLUID PRESSURE (TFP)
MANUAL VALVE POSITION SWITCH ASSEMBLY CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Automatic Transmission Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch (TFP Valve Position Switch) consists of
five pressure switches (two normally-closed and three normally-open) and a Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
sensor combined into one unit. The combined unit mounts on the valve body. The PCM supplies the battery voltage
for each range signal. By earthing one or more of the circuits through various combinations of the pressure
switches, the PCM detects which manual valve position you select. The PCM compares the actual voltage
combination of the switches to a TFP Valve Position Switch combination chart stored in memory. The TFP Valve
Position Switch. cannot distinguish between Park and Neutral because the monitored valve body pressures are
identical. With the engine OFF and the ignition switch in the RUN position, the TFP Valve Position Switch indicates
Park/Neutral. Disconnecting the transmission pass-through connector removes the earthing potential for the three
range signals to the PCM. In this case, with the engine OFF, and the ignition switch in the RUN position, D2 will be
indicated.
When the PCM detects an invalid state of the TFP Valve Position Switch or the TFP Valve Position Switch circuit by
deciphering the TFP Valve Position Switch inputs, then DTC 28 set.
DTC 28 WILL SET IF:
DTC 28 sets when the PCM detects an illegal switch combination for 6 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. This step compares the indicated range signal to the manual valve position that is actually selected.
4. This step tests for correct voltage from the PCM to the transmission pass-through connector terminals.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Refer to the TFP Valve Position Switch Logic Table for the normal range signals and the illegal combination signals.
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the
transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions.
• A bent terminal
• A backed out terminal
• Poor terminal tension
• A chafed wire
• A broken wire inside the insulation
• Moisture intrusion
When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
Refer to Automatic Transmission Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch Resistance Check or
Functional Test Procedure for further information.
TFP VALVE POSITION SWITCH LOGIC
Gear
Position Range
Signal A Range
Signal B Range
Signal C
-P-OPEN 12V CLOSED
0V OPEN 12V
-R-CLOSED
0V CLOSED
0V OPEN 12V
-N-OPEN 12V CLOSED
0V OPEN 12V
-D-OPEN 12V CLOSED
0V CLOSED
0V
-3-OPEN 12V OPEN 12V CLOSED
0V
-2-OPEN 12V OPEN 12V OPEN 12V
-1-CLOSED
0V OPEN 12V OPEN 12V
Illegal CLOSED
0V OPEN 12V CLOSED
0V
Illegal CLOSED
0V CLOSED
0V CLOSED
0V
When DTC 28 is set, the PCM will inhibit TCC engagement, command D2 line pressure, and freeze shift adapts
from being updated
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
2Perform the following
inspections.
Ensure that the
transmission linkage from
the select lever to the
manual valve is adjusted
properly.
Perform the fluid checking
procedure/inspection.
Did you perform the
inspections?
Go to Step 3 Perform the
Inspections
31. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. While the engine is
idling at normal
operating temperature,
apply the parking
brake.
5. Select each
transmission range: P,
R, N, D, 3, 2, and 1.
Does each selected
transmission range match
the scan tool TFP Switch
A/B/C display?
Refer to the TFP Valve.
Position Switch. Logic
Table.
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 4
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
4Turn the ignition OFF.
Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector
(additional DTCs may
set).
Install the J 39775 Jumper
Harness on the engine
side of the transmission
pass-through connector.
With the engine OFF, turn
the ignition switch to the
RUN position.
Using the J 39200 DVM
and J 35616 Connector
Test Adapter Kit, check
for voltage at connector
terminals N, R, and P.
Is B+ displayed on all
three circuits?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Check the circuits that did
not indicate B+ for an
open or a short to earth.
Repair the circuits if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 7
6In order to verify that
circuit 1224, circuit 1225,
and circuit 1226 are not
shorted together, use a
fused jumper to earth, on
each circuit while
monitoring the scan tool
TFP Switch A/B/C display.
When a range signal
circuit is earthed, are any
other range signal circuits
affected?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
7Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
the Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 13
8Repair the affected wiring
as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
91. Turn the ignition switch
to the OFF position.
2. Reconnect the pass-
through connector.
3. Select the PARK
position.
4. Start the engine.
5. Apply the brakes.
6. Move the shift selector
through all gear
ranges, while
observing the A and
the C range signals on
the scan tool.
Does either range signal
always indicate 0
volts/ON?
Go to Step 10 Intermittent
Problem Go to
“Diagnostic Aids”
above
10 1. Turn the ignition switch
to the OFF position.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector.
3. Remove the
transmission pan.
4. Remove the internal
wiring harness
connector from the
TFP Valve Position
Switch.
5. Check the internal
wiring harness circuits
1224 and 1226 for a
short to earth.
Did you find a short to
earth condition on either
circuit?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Replace the TFP Valve
Position Switch. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 13
12 Replace the internal A/T
Wiring Harness
Assembly. Refer to
Service Operations in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Is the replacement
complete?
Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
13 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position for
at least 2 seconds.
• Start the vehicle and
idle for 5 seconds.
• Select each
transmission range: P,
R, N, D4, D3, D2 and
D1.
• Compare the scan tool
TFP Switch A/B/C/
display, to the TFP
Valve Position Switch
Logic Table.
Does each shifter position
range signal match the
scan tool TFP Switch
A/B/C display?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
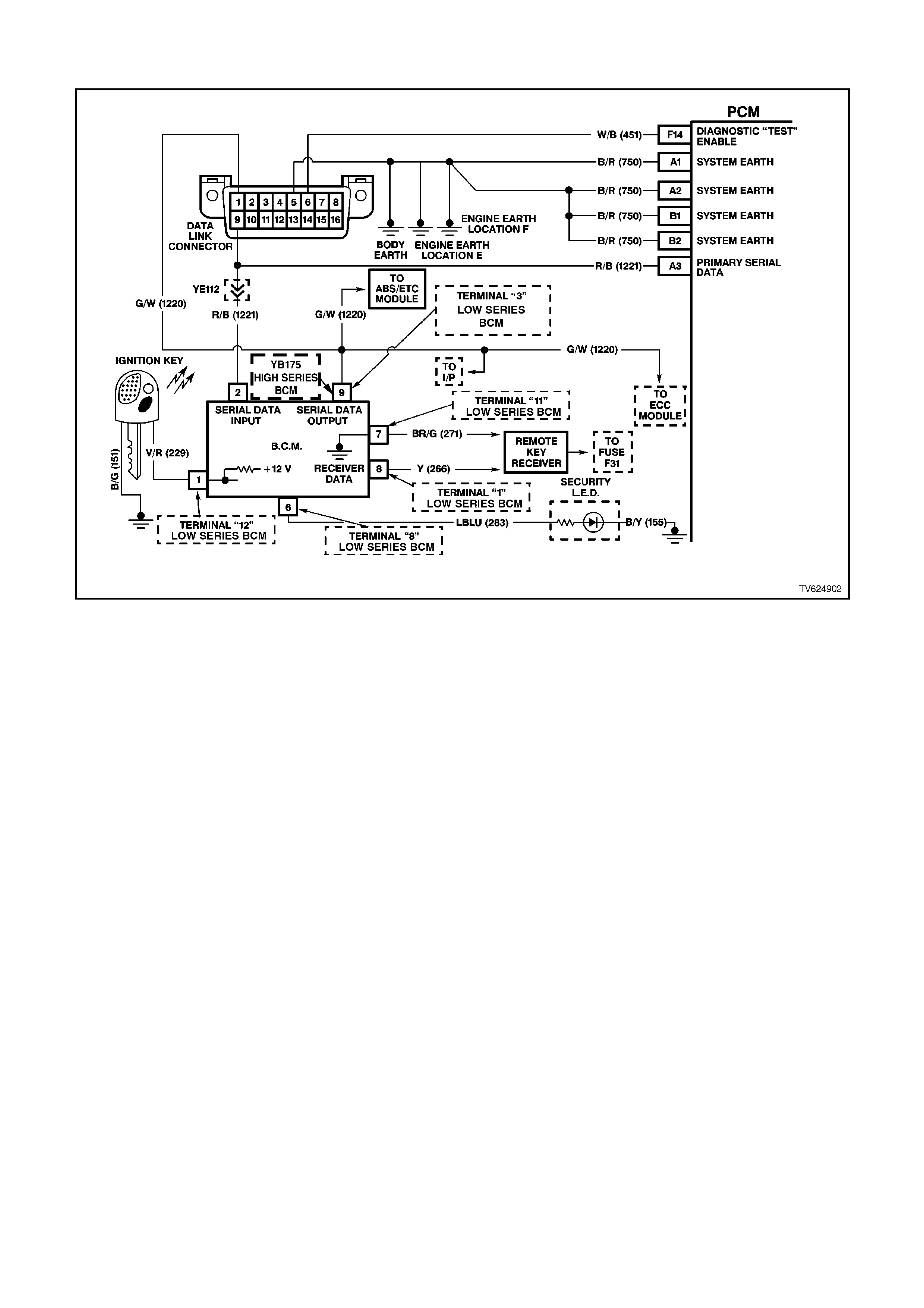
DTC 31 - THEFT DETERRENT SIGNAL MISSING
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
When the ignition is turned ON, the PCM will send a message over the Fuel Enable Input circuit to the BCM. When
the BCM receives this message, it instantly enables the starter and sends a message back to the PCM. The
message says that the proper ignition key has been used and that it is OK for the PCM to enable the fuel injectors
to start the vehicle. If the BCM does not receive communications from the PCM when the ignition is switched ON,
the starter motor will enable after a one second delay.
DTC 31 WILL SET IF:
The PCM sends 10 messages to the BCM and does not receive a message saying it is OK to start.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. If the engine cranks after a one second delay it means the BCM did not see a message from the PCM when
the ignition was turned ON.
3. An open or short to earth on circuit 1221 will disable any serial data communication.
5. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Check for any damage to the harness which could cause an intermittent open or short to earth or backed out
terminals at the PCM connectors, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this section
2Attempt to start the
vehicle.
Does the engine crank
after a one second delay
when the ignition is turned
ON?
Go to Step 3 DTC 31 is
intermittent.
Refer "Diagnostic
Aids" above
3Ignition ON engine OFF.
Is the voltage between
DLC terminal "9" and
earth between the
specified value?
4 - 6
volts Refer to Section
12F THEFT
DETERRENT
SYSTEM for
further diagnosis
Go to Step 4
41. Check for an open, a
short or a poor
connection at the PCM
terminal in the fuel
enable circuit 1221.
2. Repair as necessary.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 5
5Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

DTC 32 - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR OUT OF RANGE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the flow of air which passes through in a given time. The PCM uses
this information to monitor the operating condition of the engine for fuel delivery calculations. A large quantity of air
movement indicates acceleration, while a small quantity indicates deceleration or idle. The MAF sensor produces a
frequency signal which cannot be easily measured. The MAF sensor can be diagnosed using the procedures on this
chart. With DTC 32 set, the PCM will use a default value for air flow based on throttle position, and engine speed
and some vehicle performance will return. When DTC 32 is set the MIL "Check Powertrain Lamp" will be
illuminated.
DTC 32 WILL SET IF:
• The engine is running.
• No MAF signal for over two seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
5. Verifies that both ignition feed voltage and a good earth circuit are available.
6. The normal reading at idle should be between 5-10 grams per second.
7. A voltage reading at sensor harness connector terminal "A" of less than 4 or over 6 volts indicates a fault in
circuit 792 or poor connection.
13. Perform the Security Link procedure whenever replacing the PCM. Refer to Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS for linking procedure.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, a mis-routed harness, a rubbed through wire insulation, or a
wire broken inside the insulation.
Check the following conditions:
• A Poor Connection at PCM Pin - Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection.
• A Mis-Routed Harness - Inspect MAF sensor harness to ensure that it is not too close to high voltage wires,
such as spark plug leads.
• A Damaged Harness - Inspect the harness for damage. If the harness is OK, observe the Tech 2 scan tool while
moving the related connectors and wiring harness. A change in the display would indicate the intermittent fault
location.
• A Plugged Air Filter - A wide open throttle acceleration from a stop should cause the MAF reading on the Tech 2
scan tool to range from about 5-10 g/s at idle to 100 or greater at the time of the 1-2 shift on an automatic
transmission. If not, check for restriction.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2. Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section.
21. Ignition ON.
2. Using Tech 2 scan
tool, select MAF
frequency.
Is the "MAF frequency"
reading at the specified
value ?
0 Hz Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3Replace the MAF sensor.
Is action complete ? Verify Repair
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the MAF
sensor.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Connect a test light to
earth, and probe the
MAF sensor harness
connector terminal "C".
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 11
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the MAF
sensor.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Measure the voltage
between MAF sensor
harness connector
terminals "B" and "C" .
Is the voltage greater then
the specified value?
10 volts Go to Step 7 Go to Step 10
61. Ignition OFF.
2. Reconnect the MAF
sensor.
3. Ignition ON engine
idling.
Is the MAF sensor "MASS
AIR FLOW" reading
between specified value?
5 - 10
grams/
sec
DTC 32 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTC's
were stored, refer
to "Diagnostic
Aids" above.
Go to Step 3
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the wiring
harness connector
from the MAF sensor.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Measure the voltage at
MAF sensor harness
connector terminal "A"
with a voltmeter to
earth.
Is the measured voltage
between the specified
values?
4 - 6
Volts Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
8Is the voltage on MAF
sensor harness connector
terminal "A" less than
specified value?
4 volts Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
9Check for an open or
short to earth on circuit
792.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 13
10 Repair the open in circuit
750.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Repair the open or the
short to earth in circuit
439.
Replace the fuse F33 if
open.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
12 Repair the short to voltage
on circuit 792.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
PCM Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
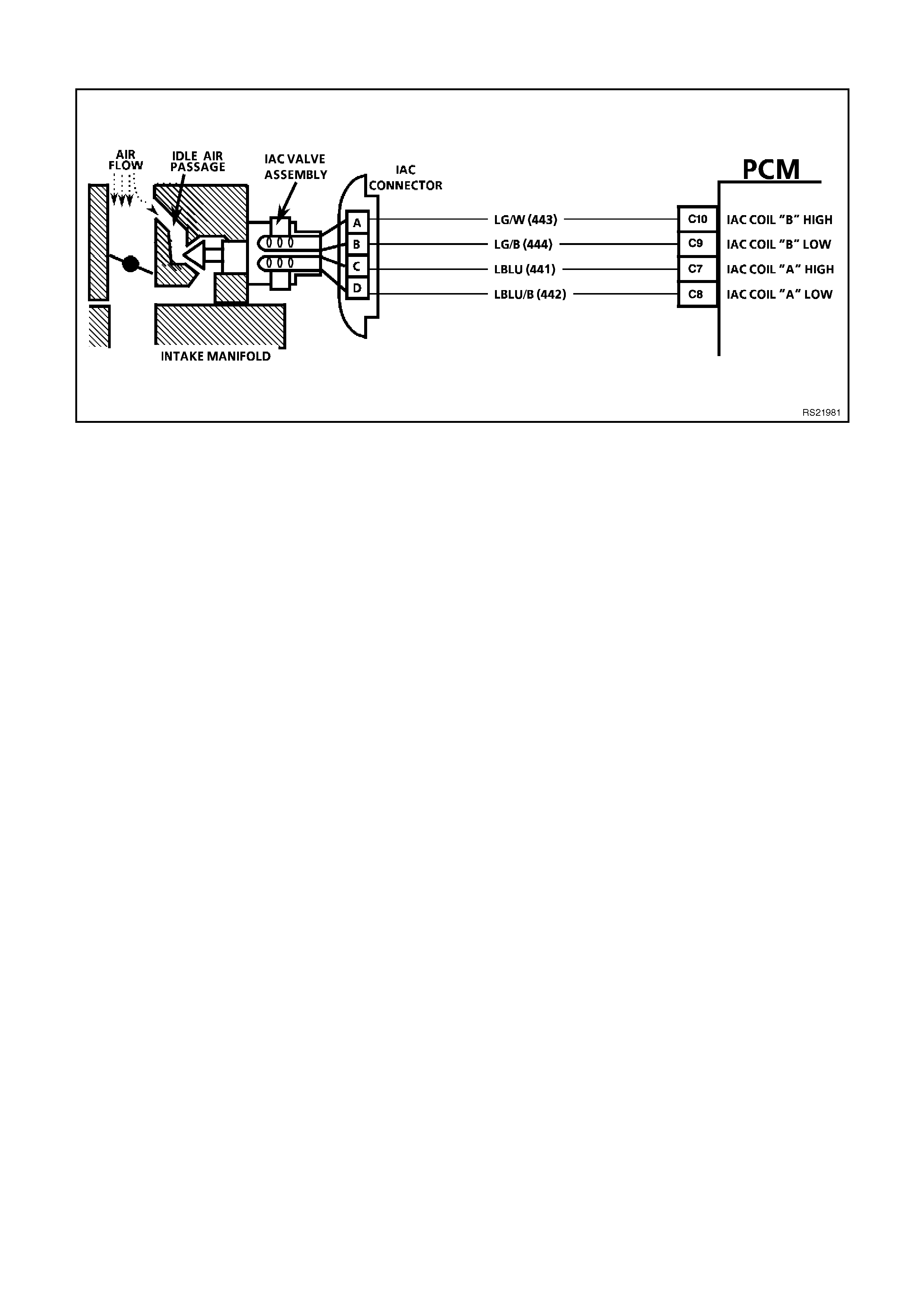
DTC 35 - IDLE SPEED ERROR
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The IAC valve is a stepper motor. Stepper motors have coils that the PCM turns ON and OFF several times per
second. This allows for an incremental clockwise and counter clockwise rotation of a pintle valve. The pintle valve
has a threaded shaft that either extends or retracts with each pulse of the PCM. The controlled pulses are called
steps or counts. The PCM controls the air entering into the engine at idle through the IAC valve. To increase the
idle speed, the PCM will command the pintle valve away from the throttle body. This allows more air to bypass the
throttle blade and thus increase engine RPM. To decrease the engine RPM at idle, the PCM will command the
pintle valve toward the throttle body seat to restrict air from entering into the engine and thus reduce engine RPM.
DTC 35 WILL SET IF:
• One or more of the following DTC's are not set. DTC 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 35, 36, 72, 94.
• The IAT sensor reading is less than 73°C.
• The engine idle speed varies more than ± 75 RPM from desired idle speed for greater than 5 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. The Tech 2 Scan tool RPM control mode is used to extend and retract the IAC valve. The valve should move
smoothly within the specified range. If the idle speed is commanded (IAC extended) too low (below 600 RPM),
the engine may stall. This may be normal and would not indicate a problem. Retracting the IAC beyond its
controlled range (above 1675 RPM) will cause a delay before the RPM's start dropping, this too is normal.
8. The test lights each should flash, to indicated a good circuit. While the sequence is not important, if either light
is OFF or does not flash, check the circuits for faults, beginning with poor terminal contacts.
14. The engine is idling at less than 75 RPM from desired idle speed for greater than 5 seconds.

DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
A slow, unstable, or fast idle may be caused by a non-IAC system problem that cannot be compensated by the IAC
valve. Out of control range IAC Tech 2 "Scan" tool counts will be above 60 if idle is too low and zero counts if idle is
too high. The following checks should be made to repair a non-IAC system problem:
• Vacuum Leak (High Idle).
• If the idle speed is above 800 RPM, locate and correct the vacuum leak. Including the PCV system. Also, check
for binding of the throttle blade or linkage.
• System too lean (High Air/Fuel Ratio).
• The idle speed may be too high or too low. Engine speed may be too high or too low. Engine speed may vary up
and down and disconnecting the IAC valve does not help. DTC 44 may be set. Tech 2 Scan tool O2 voltage will
be less than 300 mV. Check for low regulated fuel pressure, water in the fuel or a restricted injector.
• System too rich (Low Air/Fuel Ratio).
• The idle speed will be too low. The Tech 2 "Scan" tool IAC counts will usually be above 80. The system is
obviously rich and may exhibit black smoke in the exhaust. The Tech 2 "Scan" tool O2 voltage will be fixed
above 800 mV. Check for high fuel pressure, a leaking or a sticking fuel injector. A silicon contaminated O2
sensor voltage will be slow to respond.
• Throttle Body.
• Remove the IAC valve and inspect the bore for foreign material.
• IAC valve Electrical Connections.
• The IAC valve connections should be carefully checked for proper contact tension.
• PCV Valve.
• An incorrect or faulty PCV valve may result in an incorrect idle speed.
• Refer to "Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or Stalling" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS
• If the intermittent poor driveability or the idle symptoms are resolved by disconnecting the IAC valve, carefully
recheck the connections, the IAC valve terminal resistance, or replace the IAC valve.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Start the engine and
allow the engine to idle
until the specified
temperature is
reached.
3. Transmission in park
or neutral.
4. Set the park brake.
5. Turn the A/C OFF.
6. Use the Tech 2 scan
tool to cycle the IAC
valve from 600 RPM to
1675 RPM.
Does the engine speed
change smoothly when
commanded?
80°C Go to Step 3 Go to Step 5
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the IAC
valve electrical
connector.
3. Measure the
resistance across the
IAC valve terminals A
and B.
4. Measure the
resistance across the
IAC valve terminals C
and D.
Are the resistance
readings across terminals
A and B, and terminals C
and D between the
specified values?
40-80
ohms Go to Step 4 Go to Step 13
41. Measure the
resistance across the
IAC valve terminals B
and C.
2. Measure the
resistance across the
IAC valve terminals A
and D.
Are the resistance
readings across terminals
B and C, and terminals A
and D within the specified
values?
Infinite IAC valve control
circuits are OK.
Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
above.
Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
51. Disconnect the IAC
valve electrical
connector
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
3. With a test light
connected to earth,.
Probe the IAC valve
electrical connectors.
Does the test light
illuminate on two
terminals?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6With a test light
connected to B+, probe
the IAC valve electrical
connector terminals.
Does the test light
illuminate on two
terminals?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
7Check for an open or a
short in the IAC valve HI
and Lo circuits.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 14
81. Start the engine and
allow to idle.
2. With a test light
connected to earth,
probe the IAC valve
electrical terminals?
Does the test light flash
ON and OFF on all the
terminals?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9Did the test light remain
ON steady for the
terminals
that did not flash?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 11
10 Check the IAC passages
for a restriction.
Was a fault found?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 7
11 Check the PCM electrical
connector for proper
tension at the terminals.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 14
12 Repair the circuit or the
connector as necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Replace the IAC valve.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
14 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Clean the passages as
necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
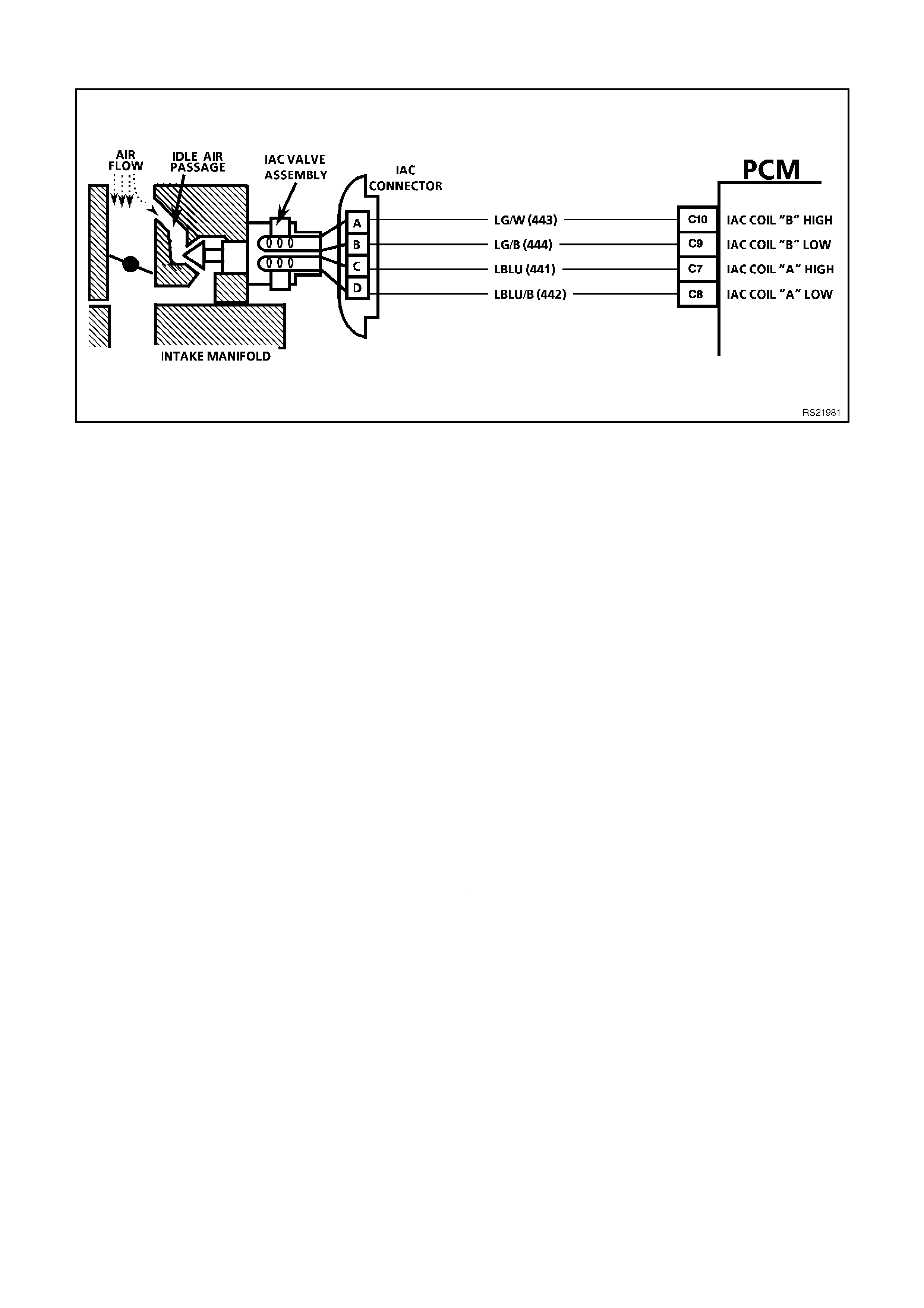
DTC 36 - VACUUM LEAK
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM controls the engine idle speed by adjusting the position of the Idle Air Control (IAC) motor pintle. The IAC
is a bi-directional motor driven by two coils. The PCM sends pulses (steps) to the IAC to extend or retract the IAC
pintle into a passage in the throttle body to decrease or increase air flow. The commanded IAC position (displayed
in counts) can be monitored on the scan tool; a lower number of counts indicates less commanded airflow (pintle
extended). This method allows highly accurate control of the idle speed and quick response to changes in engine
load. If the PCM detects a high idle speed, the PCM will send 50 counts (steps) to the IAC motor. If the RPM
increases more than 50 RPM it is accepted that the IAC motor is moving and therefore the fault is a vacuum leak,
and DTC 36 will set. If the RPM does not change when the PCM commands the IAC to respond to a commanded
count (steps), the PCM will set a DTC 35.
DTC 36 WILL SET IF:
• A DTC 35 is not set
• The actual engine idle speed varies by more than 75 RPM from desired the PCM will command the IAC valve
out 50 steps. If the idle speed increases by more than 75 RPM when command out than a DTC 36 will set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. The importance of this step cannot be stressed too strongly. It can lead to correcting a problem without further
checks and save valuable time.
4. By restricting the vacuum supply hoses, you are isolating which vacuum circuit may have a vacuum leak.
When the leak is stopped, the engine should respond immediately.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Check the IAC air passage for possible foreign material.
Code 36 may also be set by other system faults. Refer to 'Symptom Charts" for diagnostic by symptoms.

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Ignition Off.
2. Perform a
visual/physical check
of all the vacuum
hoses and air duct
between the Mass Air
Flow Sensor and the
throttle body for:
Cracks, Splits, Kinks,
Connections and in
their proper location.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 3
31. Ignition "ON", engine
running.
2. Listen for a hissing
sound as evidence of a
vacuum leak.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 4
41. Ignition "ON", engine
running.
2. Using pliers, restrict
each vacuum hose
near the intake
manifold and listen for
the engine RPM to
change when hoses
are restricted.
Did RPM change when
with vacuum hoses
restricted?
Repair vacuum
leak in hose or
vacuum circuit.
Verify Repair
Go to Step 5
5Inspect suspect areas of
the intake system such
as:
• The intake manifold
gaskets
• PCV system
• Throttle body vacuum
hose connections
• Throttle body gasket
• Oil dipstick seal and oil
fill cap for sources of
un-metered air.
• IACV O-ring
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 6
6Clear DTC and drive
vehicle.
Does DTC reset?
Go to Step 7 Repair Complete
7Replace PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
PCM Security Link
procedure.
Is action complete?
Verify Repair
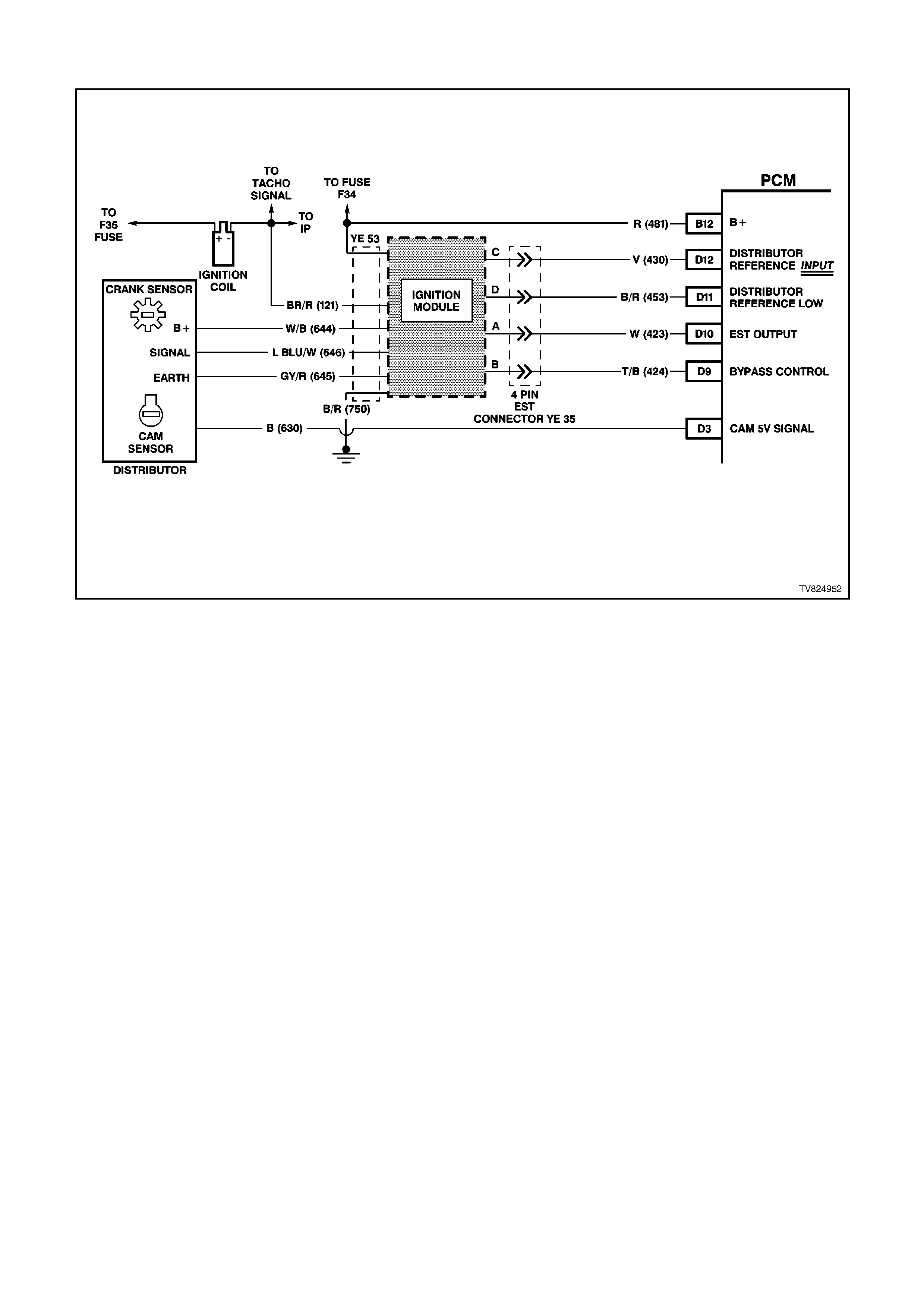
DTC 41 - IGNITION ELECTRONIC SPARK TIMING (EST) CI RCUI T
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
There are two modes of ignition system operation. The BYPASS timing mode, and the ELECTRONIC SPARK
TIMING mode. The bypass mode is normally used while cranking the engine.
The Electronic Spark Timing mode is used to allow the PCM to control the ignition system after the engine is
running. The PCM controls a "Bypass control circuit", used to control the ignition module between the different
ignition system modes.
The PCM's Electronic Spark Timing (EST) output circuitry generates EST output pulses anytime crankshaft
reference input pulses are received. The PCM also monitors it's EST output terminal, to monitor if and when EST
pulses are present.
When the ignition system is operating in the Bypass mode (such as when the engine is cranking), the ignition
module earths the EST pulses coming from the PCM. Because the EST pulses should be earthed through the
ignition module during Bypass mode operation., the PCM should not detect EST pulses on it's EST output terminal.
If the EST output circuit between the PCM and the ignition module has an "open circuit", then the ignition module
can not earth the PCM's EST output pulses. If the PCM detects three EST pulses during the first 3 crankshaft
reference input pulses, a DTC 41will set.
A DTC 41 will also set if the Bypass control circuit is shorted to voltage. If this where to happen, the PCM's EST
monitor would not sense the EST signal being earthed in the ignition module while cranking, and a DTC 41 would
set.
If CKT 423 is open, the ignition module will switch to the EST mode. If CKT 423 circuit is open, no EST pulses will
reach the ignition module, and the engine may stall. A DTC 41 may set. The engine can be restarted, but the
ignition system will operate in the bypass mode until the fault is corrected. When operating in the bypass mode, the
ignition spark timing is set to 10 ° advance, which will cause a loss of engine performance.
DTC 41 WILL SET IF:
• The ignition switch is in the ON position.
• The PCM has detected at least 3 EST output pulses, during the first 3 crankshaft reference signal pulses
received from the ignition module.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to the step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This will verify if the fault is intermittent.
3. The typical voltage on this circuit with the ignition OFF should be less than .5V.
7. The actual voltage may go as high as 2.5V. The important fact is that the voltage is at least two volts.
10. Perform the Security Link procedure whenever the PCM is replaced. Refer to Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Check all the ignition wiring and connectors to and from the PCM and the ignition module.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Clear DTC 41.
2. Start the engine.
3. Observe the DTC(s).
Did a DTC 41 set?
Go to Step 3 DTC 41 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTC's
were stored, refer
to "Diagnostic
Aids" above.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ignition
module 4 pin
connector.
3. Probe the ignition
module harness
connector terminal for
circuit 424 (T/B) with a
voltmeter connected to
earth.
4. Ignition ON.
Is the voltage greater than
the specified value?
0.5V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
C-D connector.
3. Ignition ON.
4. robe the ignition
module harness
connector terminal for
circuit 424 (T/B) with a
voltmeter connected to
earth.
Is the voltage greater than
the specified value?
0.5V Go to Step 5 Go to Step 10
5Repair the short to voltage
in the Bypass circuit 424
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
6Replace the ignition
module.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Reconnect the 4 pin
connector to the
ignition module.
3. Backprobe the PCM
connector D10 with a
voltmeter connected to
earth.
4. Start or crank the
engine.
Is the voltage
approximately at the
specified value while
cranking or with engine
running?
2 volts Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Check for a faulty
connection, or an open in
the EST circuit 423.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 6
9Check the PCM for a
faulty connection.
Was a faulty connection
found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
10 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 3 for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
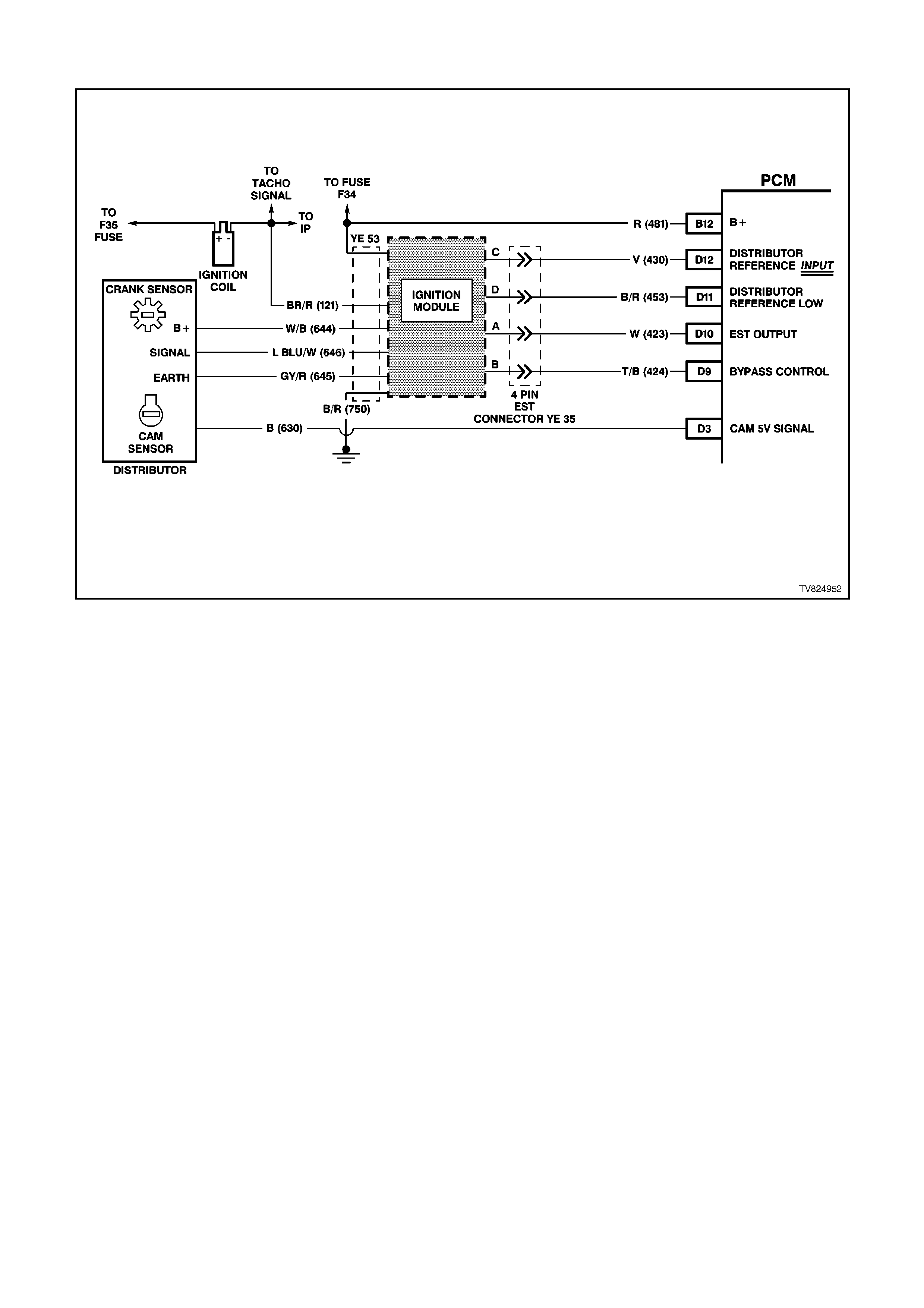
DTC 42 - IGNITION BYPASS CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
There are two modes of ignition system operation. The BYPASS timing mode, and the ELECTRONIC SPARK
TIMING mode. The bypass mode is normally used while starting the engine. The Electronic Spark Timing mode is
used to allow the PCM to control the ignition system after the engine is running. The PCM controls a "Bypass
control circuit", used to control the ignition module between the two different ignition system modes.
The PCM's Electronic Spark Timing (EST) output circuitry generates EST output pulses anytime crankshaft
reference input pulses are received. The PCM also monitors it's EST output terminal, to monitor if and when EST
pulses are present.
When the ignition system is operating in the By pass mode (such as when the engine is cranking), the ignition
module earths the EST pulses coming from the PCM. Because the EST pulses should be earthed through the
ignition module during Bypass mode operation, the PCM should not detect EST pulses on the EST output terminal.
DTC 42 WILL SET IF:
• The engine speed is greater than 1600 RPM.
• The PCM does not receive any EST pulses within 400 ms.
When a DTC 42 is set, the ignition will run in the bypass mode.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. Confirms that the DTC 42 is present.
13. Checks whether the DTC 42 is a faulty PCM or an intermittent in circuits 423 or 424.
14. Whenever the PCM is replaced perform the Security Link procedure in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Refer to "Intermittents" in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
• Check all the circuit wiring and the connections to the PCM, and the ignition module.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check.
21. Clear the DTC 42.
2. Start the engine.
3. Observe the DTC(s).
Did the DTC 42 set?
Go to Step 3 Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
above
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ignition
module 4 pin
connector.
3. Probe the ignition
module harness
connector terminal for
circuit 423(W) with a
voltmeter connected to
earth.
4. Ignition ON.
Is the voltage greater than
the specified value?
0.5V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
C-D connector.
3. Ignition ON.
Is there voltage present at
the ignition module
harness connector for
circuit 423(W)?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 15
5Repair the short to voltage
in circuit 423.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
61. Ignition ON.
2. Probe the ignition
module harness
connector for circuit
423 with a test light
connected to battery
voltage.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 9
71. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
C-D connector.
3. Probe the ignition
module connector
harness terminal for
circuit 423 with a test
light connected to B+.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 14
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
8Repair the short to earth
in circuit 423. Is the action
complete?
Verify Repair
91. Ignition ON.
2. Disconnect the ignition
module 4 pin
connector.
3. With a test light
connected to B+,
probe the ignition
module harness
connector for circuit
424.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 12
10 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
C-D connector.
3 Ignition ON.
4 Disconnect the ignition
module 4 pin
connector.
5 With a test light
connected to B+,
probe the ignition
module harness
connector for circuit
424.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 14
11 Repair the short to earth
in circuit 424.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
12 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
C-D connector.
3. Check for a faulty
connection or an open
in circuit 424.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
13 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Reconnect the ignition
control module 4 pin
connector.
3. Disconnect PCM C-D
connector.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Probe the PCM
harness connector for
circuit 423 with an
ohmmeter connected
to earth.
5. Probe the PCM
harness connector for
circuit 424 with a test
light connected to B+.
NOTE:
As the test light contacts
circuit 424, does the
resistance switch from
less than the specified
value to greater than the
specified value?
40 ohms
to
Infinity
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 15
14 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6c2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Replace the ignition
control module.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
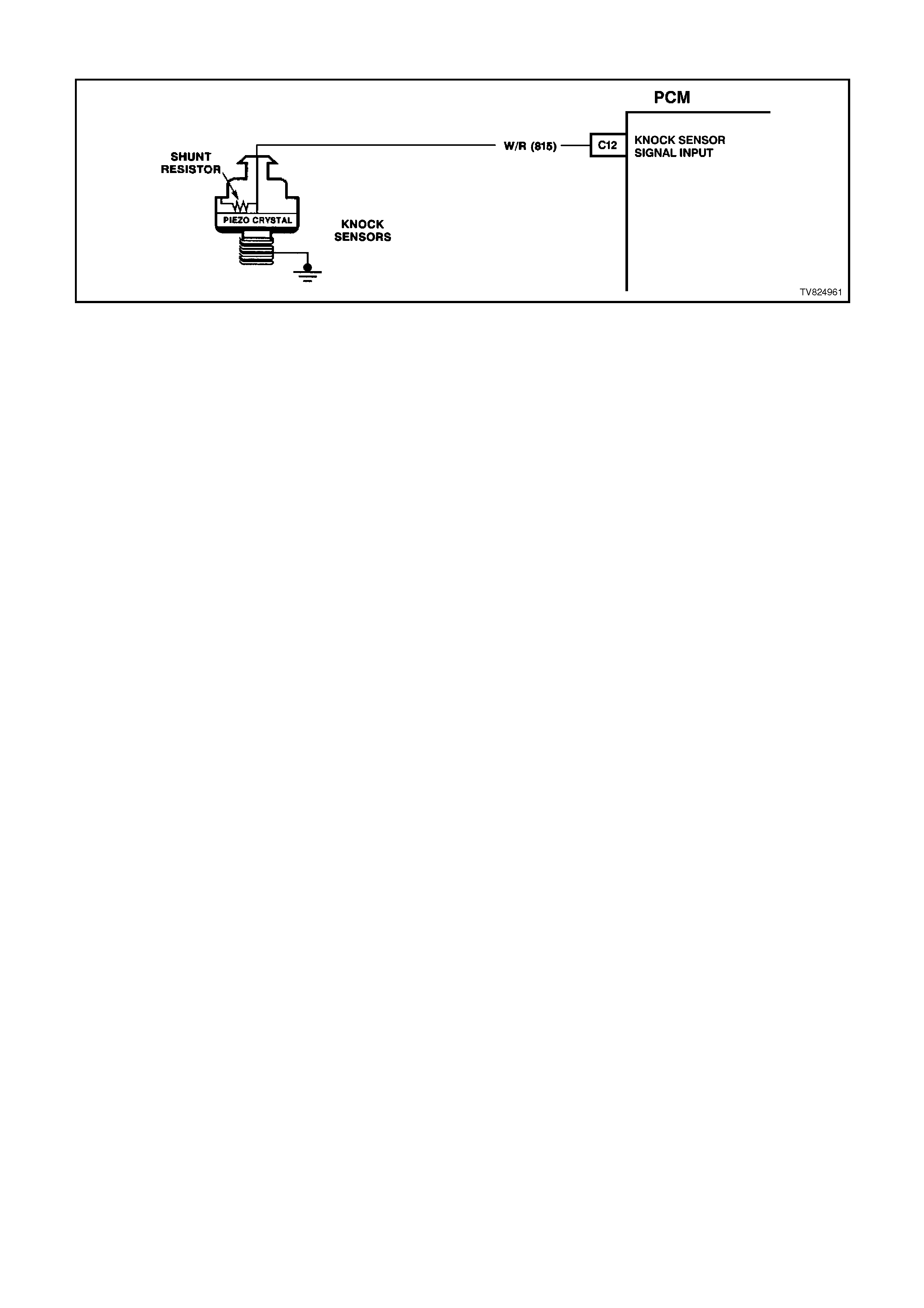
DTC 43 - KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Electronic Spark Control (ESC) system detects engine detonation. The PCM will retard the Electronic Spark
Tim ing (EST ) based on the signal being received f rom the k nock s ensor. T his input allows the EST spar k advanc e
to be optimised under all conditions. This allows the knock sensor input to reduce the total advance when
detonation is detected. T otal EST advance can be retarded by as much as 12 degrees by the knock sensor input.
This could be described as a "closed-loop" spark advance system.
A loss of this s ignal would caus e the EST advanc e to r emain at a "no detonation" level. However, if detonation were
occurring, the advance would not be retarded, and detonation could become severe enough under heavy engine
load conditions to result in pre-ignition and potential engine damage.
The knock sensor produces a small AC voltage, which goes above and below the DC voltage supplied from the
PCM. The sensor’s AC voltage output is dependent upon the level of detonation or knock. This portion of the sensor
reacts like a microphone, producing a small signal voltage based on vibration.
DTC 43 WILL SET IF
• One or more of the following DTC's are not set. DTC 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 21, 22, or 93.
• The TP sensor angle is greater than or equal to 10%.
• The ECT is greater than 65°C.
• The engine speed is greater than 2500 RPM.
• The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds.
• The PCM does not receive a knock signal.
• The above conditions are present for 3 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This step determines if conditions for DTC 43 still exist (voltage on circuit 815 above 4.4 volts or below
0.2 volt)
4. If the knock sensor is generating a knock signal, then DTC 43 is intermittent.
5. This Step determines if the knock sensor circuit is shorted to voltage.
6. This confirms that the knock sensor’s resistance is OK.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
If circuit 815 is not open or not shorted to earth the most likely cause is an open circuit in the PCM and a
replacement should be fitted. If a replacement PCM did not correct the problem, then Refer to "Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS in this Service Information.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1 Was the "On-Board Diagnostic" (OBD)
System Check performed? Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2 1. Install Tech 2 scan tool.
2. Record then clear DTC(s).
1. Ignition “ON”, engine idling.
2. Using Tech 2 scan tool, select
“Knock Signal” and “Knock
Retard”.
Is “Knock Retard” above the specified
value?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Repair short to voltage on circuit 815.
Is action complete? Verify Repair
4 1. Ignition “ON”, engine idling.
2. Lightly tap on alternator bracket
with hammer.
Is the Tech 2 scan tool indicating
“Knock Retard” above the specified
value?
0 degrees DTC 43 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTC’s
were stored, refer
to “Diagnostic
Aids” above.
Go to Step 5
5 1. Ignition “ON”, engine stopped.
2. Backprobe PCM connector
terminal for circuit 815, with DVM
connected to earth.
3. Set DVM to read DC voltage
Is voltage reading on DVM above the
specified value?
0 volts Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
6 1. Ignition “OFF”.
2. Disconnect PCM connectors.
3. Back probe PCM connector
terminal for circuit 815, with DVM
connected to earth
4. Set DVM to read resistance.
Is resistance on DVM at the specified
value?
80 kOhms
(80,000
Ohms)
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 10
7 1. Ignition “OFF”.
2. Reconnect PCM connectors.
3. Back probe PCM connector
terminal for circuit 815, with DVM
connected to earth
4. Set DVM to read AC voltage.
Is DVM indicating above specified
value?
50 mV AC Go to Step 8 Go to Step 11
8 Check for poor connection at PCM.
Was a poor connection found? Verify Repair Go to Step 9
9 Replace PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations for PCM Security Link
procedure
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Check for open or short to earth in
circuit 815.
Was a fault found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 11
11 Replace knock sensor(s)
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
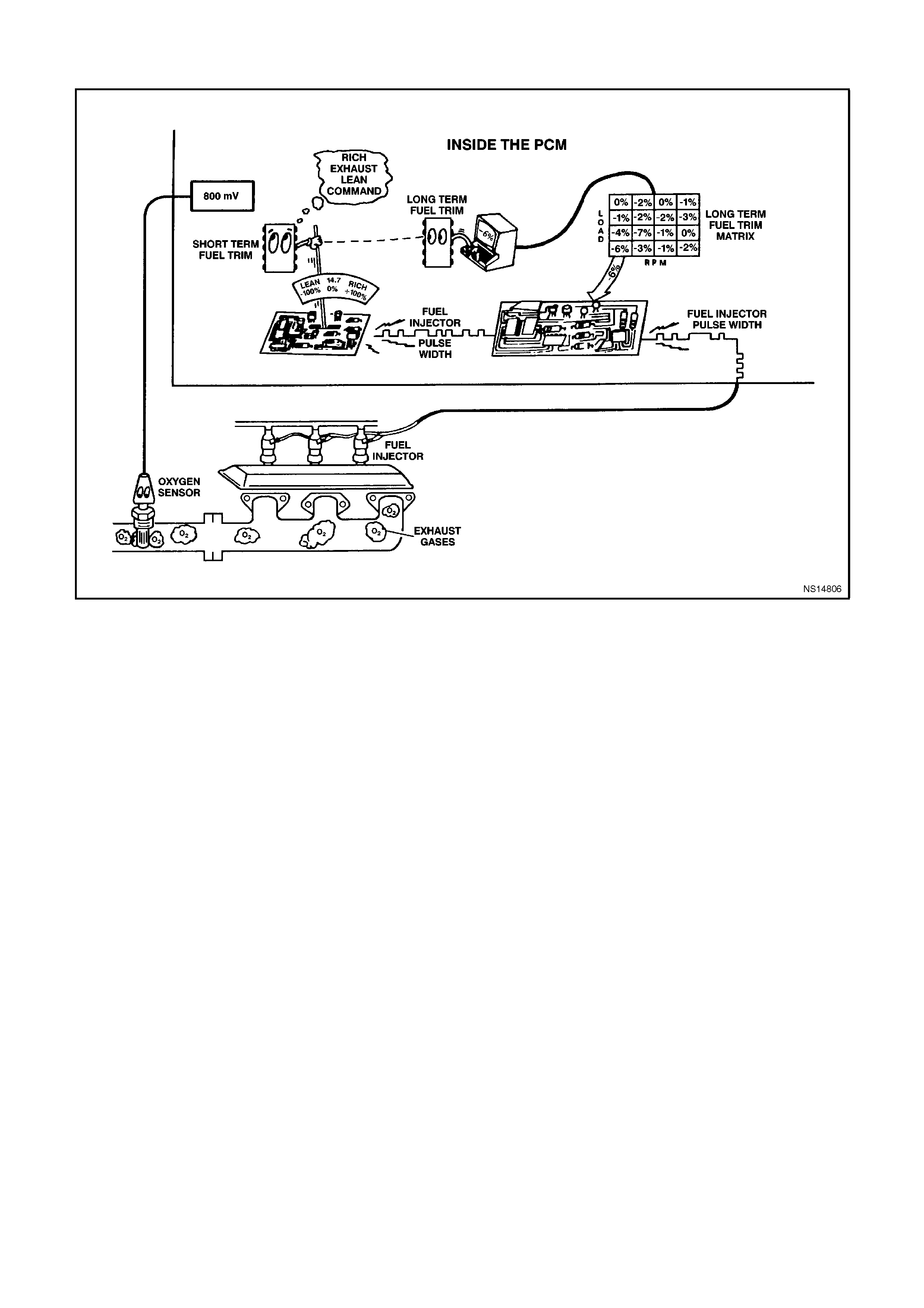
DTC 44 - RIGHT HAND (RH) LEAN EXHAUST INDICATED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the exhaust gas in the exhaust stream then sends a voltage to the
PCM relative to the oxygen content. This voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean
mixture) to greater than 900 mV(low O2 exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM provides the O2 sensor with a constant 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins heating up its
internal resistance begins to decrease . The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing voltage that
differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2 sensor the
PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
When the ignition is turned ON, B+ is applied to the O2 sensor’s heater element. Approximately 30 seconds after
the B+ is applied to the heater portion of the O2 sensor, the O2 sensor should reach a temperature greater than
500°C. The heated O2 sensor becomes active much quicker than a non-heated O2 sensor. This allows the PCM to
control the air/fuel ratio more consistent over a wider range of operating conditions.
DTC 44 WILL SET IF:
• One or more of the following DTC's are not set. DTC 23, 25, 26, 33, or 34.
• The IAT sensor is less than 90°C.
• The O2 sensor signal voltage remains below 250 mV.
• The system is operating in Closed Loop.
• The above conditions have been met for 45 seconds.
The fuel control circuit will operate in the open loop mode whenever a DTC 44 is set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
4. A DTC 44 is most likely caused by one of the following.
• An O2 Sensor Wire - Sensor pigtail may be contacting the exhaust manifold. Check for intermittent earth in the
wire between the connector and sensor.
• Fuel Contamination - Water, even in small amounts, can be delivered to the injectors.
• MAF Sensor - A shifted MAF sensor could cause the fuel system to go lean. Refer to CHART A-6.1 in this
Section.
• Fuel Pressure - System will go lean if pressure is too low. Monitor the fuel pressure while driving the vehicle at
various road speeds and/or loads to confirm. Refer CHART A-4.1 in this Section.
• Exhaust Leaks - If there is an exhaust leak, the engine can cause outside air to be pulled into the exhaust and
past the sensor. Vacuum or crankcase leaks can cause a lean condition.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Use the Tech 2 Scan tool to observe the Long Term Fuel Trim values at different RPMs and air flow conditions.
The Tech 2 "Scan" tool also displays the Long Term Fuel Trim cells, so the Long Term Fuel Trim values can be
checked in each of the cells to determine when the DTC 44 may have been set. If the conditions for DTC 44 exists,
the Long Term Fuel Trim values will be around +18%.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Start the engine.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Run the engine until it
reaches normal
operating temperature
(Above 80 degrees C).
4. Continue to run between
1600 to 1800 RPM for
two minutes.
Is the RH O2 sensor
voltage fixed below
specified value?
250 mV Go to Step 3 DTC 44 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored, refer
to "Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
3Disconnect the RH O2
sensor connector.
With the engine idling,
does the Tech 2 Scan tool
display RH O2 sensor
voltage between the
specified values?
Between
347 mV
and
551 mV
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Refer to TEST
DESCRIPTION above.
2. Perform the checks on
the items as noted.
• MAF sensor operation
• Low fuel pressure
• Contaminated fuel
• Manifold leaks ahead of
the RH O2 sensor
• Lean injector (possibly
restricted)
• O
2 sensor earth circuit.
Are all items checked
found to be OK?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. With the RH O2 sensor
still disconnected, check
the RH O2 sensor signal
for a short to earth.
Is a short to earth
detected?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
6Replace the RH O2 sensor.
Is the action complete? Verify repair
7Repair the RH O2 signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Replace the PCM. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Replace or repair the faulty
condition.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
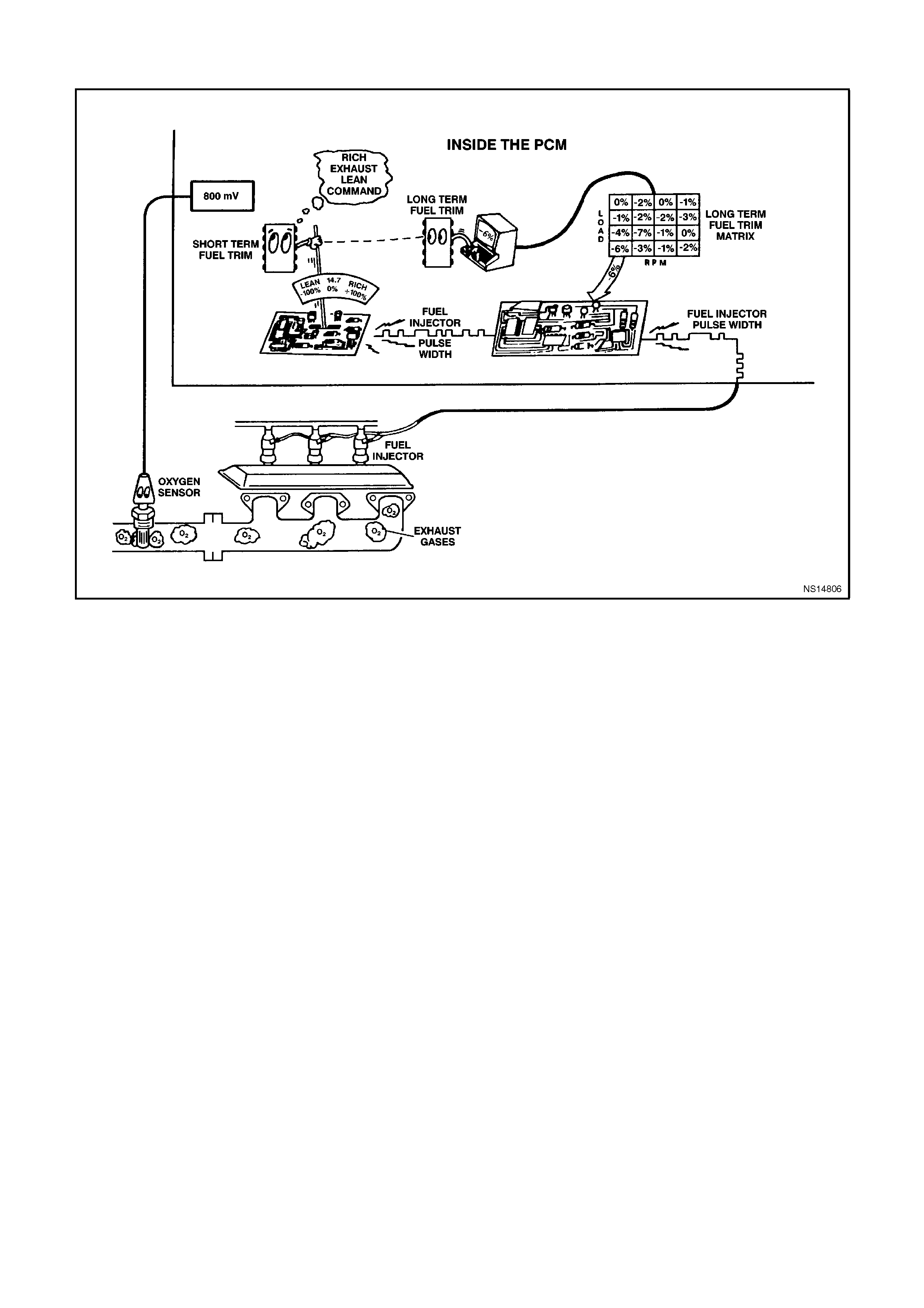
DTC 45 - RIGHT HAND (RH) RICH EXHAUST INDICATED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The O2 sensor is located in the exhaust stream near the engine. The O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the
exhaust gases in the exhaust stream then sends an output voltage to the PCM relative to the oxygen content. This
voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean mixture) to greater than 900 mV(low O2
exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM always supplies the O2 sensor with a steady 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins heating up its
internal resistance begins to decrease . The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing voltage that
differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2 sensor the
PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
DTC 45 WILL SET IF:
• The fuel system is in closed loop.
• The throttle angle is between 5% and 20%.
• The O2 sensor voltage remains greater than 750 millivolts for 30 seconds.

TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to Step numbers
4. A DTC 45 indicates a rich exhaust. Begin the diagnosis with the items listed below.
• Fuel Pressure. System will be rich, if the pressure is too high. The PCM can compensate for some increase. If
the pressure gets too high, a DTC 45 may set. Refer to the fuel system diagnosis CHART A-4.2 in this Section.
• Rich Injector.
• Leaking Injector. Refer CHART A-4.2 in this Section.
• Check for fuel contaminate oil.
• Short to voltage on circuit 412.
• HEI Shielding. An open earth circuit 453 (ignition system) may result in EMI, or induced electrical noise as
reference pulses. The additional pulses result in a higher than actual engine speed signal. The PCM than
delivers too much fuel, causing system to go rich. Engine tachometer will also show higher than actual engine
speed, which can help in diagnosing this problem.
• Canister Purge. Check for fuel saturation. If full of fuel, check canister control and hoses.
• MAF Sensor. A shifted "High" MAF sensor could cause the fuel system to go rich.
• Check for a leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to the regulator for fuel.
• TP Sensor. An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system to go rich, due to a false indication of the
engine accelerating.
11. Perform the Security Link procedure in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE OPERATIONS whenever replacing the PCM.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Using the Tech 2 Scan tool, observe the Long Term Fuel Trim values at different RPM and air flow conditions. The
Tech 2 "Scan" tool also displays the Long Term Fuel Trim cells, so the Long Term Fuel Trim values can be checked
in each of the cells to determine when the DTC 45 may have set. If the conditions for a DTC 45 exists, the Long
Term Fuel Trim values will be around - 18%.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Engine at the normal
operating temperature
(above 80 degrees C).
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Run the engine
between 1600 RPM
and 1800 RPM for two
minutes.
Is the voltage greater than
the specified value?
750 mV Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the RH O2
sensor wiring harness.
3. With an ohmmeter
connected to earth,
probe the RH O2
sensor signal circuit
wiring harness
connector.
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Is the voltmeter reading
less then the specified
value?
347 mV Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Probe the RH O2
sensor signal circuit
wiring harness
connector.
4. Ignition ON.
Is the RH O2 sensor
voltage less than the
specified value?
347 mV Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the short to voltage
in the RH O2 sensor
signal circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
6Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 3 for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
71. Disconnect the RH O2
sensor wiring harness
connector.
2. Jumper the RH O2
sensor signal circuit
harness connector to
earth.
3. Install a scan tool.
With the engine running,
does the scan tool display
the RH O2 sensor voltage
below the specified value?
347 mV Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
8Refer to Test Description
step 4 to perform
additional checks for:
• High Fuel Pressure
• MAF Sensor Operation
• Leaking Injectors
• Ignition Earth Circuit
• Canister Purge
• Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor
Circuit
• Intake Air Temperature
Sensor Circuit
• Throttle Position
Sensor Operation
Do all the additional
checks from Test
Descriptions step 8 test
OK?
Refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
Verify Repair
91. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Check the RH O2
sensor earth circuit for
continuity between the
PCM connector
terminal "D13" and the
engine earth.
Is an OPEN circuit
indicated?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
10. Check the PCM earth wire
connection at the engine.
This must be a clean and
tight connection.
Is the connection good?
Go to Step 11 Verify Repair
11 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
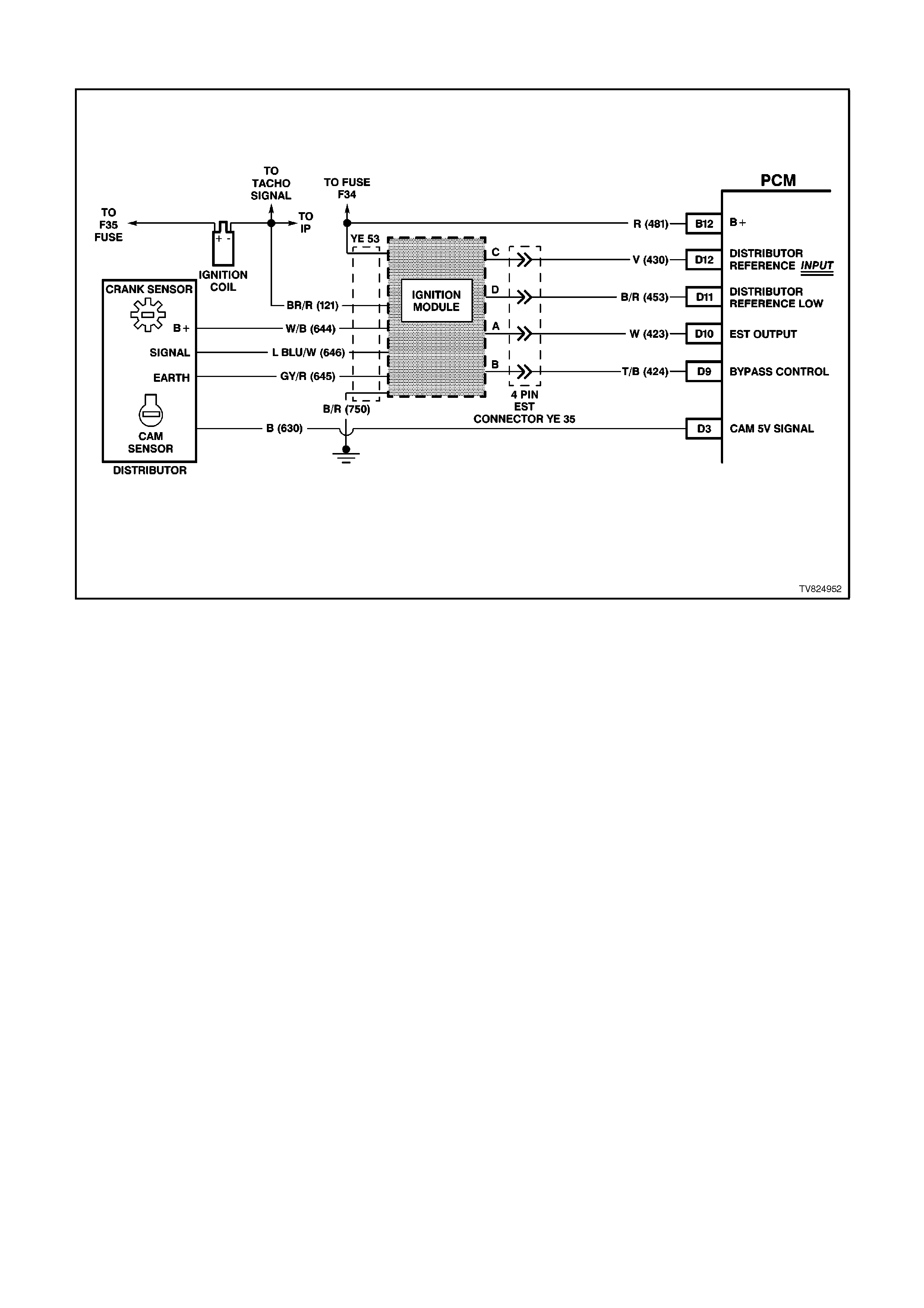
DTC 46 - NO REFERENCE PULSES WHILE CRANKING
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
This DTC is intended to help in diagnosing a no-start condition. Any time the distributor is turning, the ignition
module should generate the crankshaft reference pulses that the PCM should be receiving. Fuel injection pulses
are timed from the crankshaft pulses, and without them no injection pulses will occur. The PCM can determine
when these crankshaft pulses should be present.
DTC 46 WILL SET IF:
• A DTC 32 is not set.
• The MAF sensor is greater than 2000 HZ.
• The battery voltage is less than 11 volts.
• The PCM does not receive any distributor reference input pulse signals.
• The above conditions are present for 2 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to the step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. If fuse F34 has an open find the short to earth in the faulty circuit before replacing the fuse.
4. Leave the module electrical harness connected when performing this procedure. If the circuit reads greater
than 10V the circuit is either shorted to earth or open.
7. If circuit 646 is open the voltage reading would be near 5.0V.
9. The ignition module sends a signal to the PCM based on crankshaft pulses. The normal voltage should range
from less than 1 to about 4.5 volts.
13. Circuit 479 is located between the EFI relay and the number F34 fuse. A fault in this circuit may also set a DTC
46.
19. At this point all the circuits are functioning properly. Replace the ignition module.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Inspect all the circuitry wiring to and from the ignition module and the distributor. Inspect for cuts, abrasions, opens
or any other faults.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Attempt to start the
engine.
Did the engine start and
continue to run?
DTC 46 is
intermittent. If
additional DTC's
were stored, refer
to "Intermittents"
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
Go to Step 3
3Inspect fuse F34 for an
open.
Was an open fuse F34
found?
Go to Step 23 Go to Step 4
41. Remove the ignition
control module.
2. With a DVM connected
to earth, backprobe
circuit W/B (644) on
the ignition module
harness.
3. Ignition ON.
Is the voltage greater than
the specified value?
10.0V Go to Step 15 Go to Step 5
51. Ignition OFF.
2. With a test light
connect to earth,
backprobe circuit
R (481).
3. Ignition ON.
Did the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 13
61. Ignition OFF.
2. With a test light
connected to B+,
backprobe circuit B/R
(750).
3. Ignition ON.
Did the test light
illuminate?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 16
71. Ignition OFF.
2. With a DVM connected
to earth, probe circuit L
BLU/W (646).
3. Crank the engine.
Is the voltage within the
specified value?
2-3V DC Go to Step 8 Go to Step 12
81. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the ignition
module harness six (6)
pin connector.
3. Using a DVM measure
the resistance by
probing circuit GY/R
645 and W/B 644 of
the ignition module
harness.
Is the resistance at the
specified value?
Infinity
(open
loop)
Go to Step 14 Go to Step 9
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
91. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
electrical connector.
3. Backprobe PCM
harness connector
terminal "D12" to earth
with a digital voltmeter
set to read "DC Volts".
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Is the voltage within the
specified value?
Less
than 1
volt or
approx.
4.5 volts
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 17
10 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
electrical connector.
3. Backprobe PCM
harness connector
terminal "D12" to earth
with a digital voltmeter
set to read DC Volts.
4. Ignition ON.
5. While observing digital
voltmeter, crank the
engine.
Is the voltage at the
approximate specified
value?
2 volts Go to Step 11 Go to Step 17
11 1. Check the Crankshaft
Reference Input
terminal in the PCM
connector for a loose
connection.
2. Repair as necessary.
Was a fault found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 18
12 Inspect circuit L BLU/W
(646) for an open or a
short to ground.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 22 Go to Step 24
13 Repair the open in circuit
R (481) or circuit O/Y
(479).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
14 Inspect circuit GY/R (645)
for an open.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 21 Go to Step 24
15 Inspect circuit W/B (644)
for an open or a short to
earth.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 20 Go to Step 24
16 Repair the open in circuit
B/R (750).
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair
17 Check the Crankshaft
Reference Input circuit
(circuit 430) for a faulty
connection or an open or
short to earth.
Was a fault found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 19
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
18 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
19 Replace the Ignition
Module.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
20 Repair the open in circuit
W/B (644).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
21 Repair the open in circuit
GY/R (645).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
22 Repair the open in circuit
L BLU/W (646).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
23 1. Inspect circuit R (481)
for a short to ground.
2. Repair circuit R (481) if
necessary.
3. Replace the fuse F34.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
24 Replace the Crankshaft
Position Sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

DTC 48 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR SIGNAL MI SSING
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
During cranking, the ignition module monitors the crankshaft position sensor signal. The crankshaft position sensor
signal is used to determine the correct cylinder pair to fire. After the crankshaft position sensor signal has been
processed by the ignition module, the ignition module sends a crankshaft reference pulse to the PCM. When the
PCM receives this pulse the PCM will command all eight injectors to open for one priming shot of fuel in all
cylinders. After the priming, all eight of the injectors are left OFF until the next crankshaft reference pulses from the
ignition module (two crankshaft revolutions). This allows each cylinder a chance to use the fuel from the priming
shot. During this waiting period, a cam signal will have been received by the PCM. Now the PCM begins to operate
the injectors in sequential fuelling mode by energising each injector based on true camshaft position. However, if
the camshaft position signal is not present at startup, a DTC 48 will set and the PCM will energise all eight injectors
at the same time and continue to operate like this until the fault is corrected.
DTC 48 WILL SET IF:
• The engine is running.
• The Camshaft position sensor signal is not received by the PCM for at least 5 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. The normal operating voltage of the cam sensor 5V reference circuit should be between 0.8 and 1.5V.
5. A short to voltage in the 5V reference circuit may also set a DTC 49.
7. The Cam/Crank sensor is to replaced as an assembly.
8. Whenever replacing the PCM perform the Security Link procedure found in Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside the
insulation.
CHECK FOR:
• Poor Connection or Damage Harness - Inspect PCM harness connectors for backed out terminal "D3", improper
mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminal, poor terminal to wire connection and damaged
harness.
Intermittent Test - If connections and harness check OK, monitor a digital voltmeter connected from PCM terminal
"D3" to earth while moving related connectors and wiring harness. If the failure is induced, the voltage reading will
change. This may help to isolate the location of the malfunction.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 Scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
3. Record, then clear the
DTCs.
4. Start the engine, idle
for 1 minute.
Does the Tech 2 Scan
tool display Cam Signal as
Missing?
Go to Step 3 DTC 48 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored, refer
to "Diagnostic
Aids" above.
31. Use a DVM connected
to earth to backprobe
the PCM connector
D3.
2. Start the engine and
allow to idle.
Does the voltage vary
between the specified
values?
0.8V to
1.5V Go to Step 8 Go to Step 4
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
C-D connector.
3. Ignition ON Engine
OFF.
4. Use a DVM connected
to earth to probe the
PCM harness
connector D3.
Is the voltage less than
the specified value?
0.1V Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the short to voltage
in the Cam signal 5V ref
circuit (circuit 630).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
6Check for an open or a
short to earth in the Cam
signal 5V ref circuit (circuit
630).
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair Go to Step 7
7Replace the Cam/Crank
sensor assembly.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
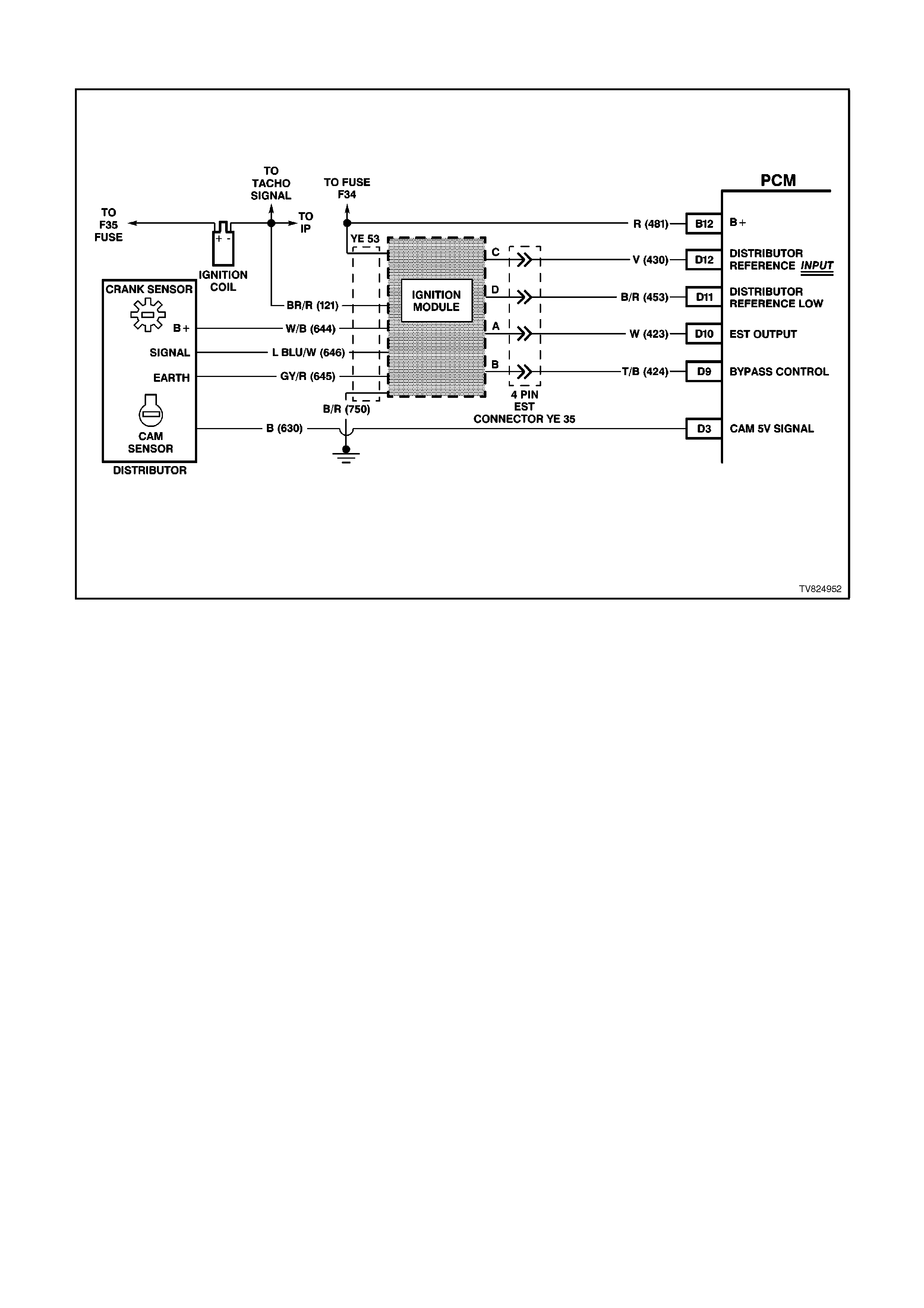
DTC 49 - CAM/ CRANK SENSOR SIGNAL INTERMITTENT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
During cranking, the ignition module monitors the crank sensor signal. The crank sensor signal is used to determine
the correct cylinder pair to spark first. After the crank sensor signal has been processed by the ignition module, it
sends a crankshaft reference pulse to the PCM. When the PCM receives this pulse it will command all eight
injectors to open for one priming shot of fuel in all cylinders. After the priming, the injectors are left OFF for the next
eight crankshaft reference pulses from the ignition module (two crankshaft revolutions). This allows each cylinder a
chance to use the fuel from the priming shot. During this waiting period, a cam signal will have been received by the
PCM. Now the PCM begins to operate the injectors by energising each injector based on true camshaft position.
With the engine running, the PCM monitors the cam and the crank sensor signal pulses it receives and expects to
see eight crankshaft sensor reference pulses for each cam pulse. If the sequence of pulses is not correct for 15
occurrences, a DTC 49 will set, indicating an intermittent problem with the cam signal or crankshaft sensor
reference signal.
DTC 49 WILL SET IF:
• The engine is running.
• The PCM does not receive 8 out of 10 cam sensor signals.
TEST DESCRIPTION
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. Determines if conditions necessary to set DTC 49 exist on this ignition cycle.
6. Move the wiring harness around to try to induce the fault. If the fault is induced while moving the wires inspect
for a loose connection.
NOTE:
If a DTC 48 is set along with a DTC 49, use DTC 48 chart for diagnosis first.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
A DTC 49 indicates an intermittent fault and may not set immediately or under all conditions. Customer comments
of symptoms experienced may help isolate the cause of the condition. A poor connection or fault in the cam sensor
circuits 630, 633, 644, or 645 or a faulty cam sensor may cause the PCM to re-initialise injector sequence when the
fault occurs, causing a possible stumble or miss.
Inspect circuit 630 for a short to voltage.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 Scan
tool.
2. Start and idle the
engine.
3. Using a Tech 2 Scan
tool, look at IGN
Cycles in DTC history.
Is DTC 49 current?
Go to Step 3 DTC 49 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTC's
are set, refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Connect a DVM
between the PCM
harness connector
terminal "D3" and
earth.
4. Ignition ON.
Is the voltage at the
specified value?
Approx.
5 volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4Bump the engine with the
starter.
Is the voltage at the
specified value?
Approx.
5 volts Go to Step 5 Go to DTC 48 in
this Section
5Monitor the voltage at
"D3" while moving the
powertrain wiring harness
to the PCM connector.
Does the voltage remain
steady as the wi ring
harness is being moved?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6Check for:
• Poor connections at
the PCM.
• Faulty crank/cam
sensor (malfunctioning
hot/cold).
Are all the above OK?
Go to Step 7 Verify Repair
7Check for a poor
connection at the
crankshaft position sensor
or the ignition control
module. Repair as
necessary.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Check for a poor
connection between the
distributor 4 wire
connector and the PCM.
Was a fault found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 9
9Repair the intermittent
open/short to earth in
circuit 630.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
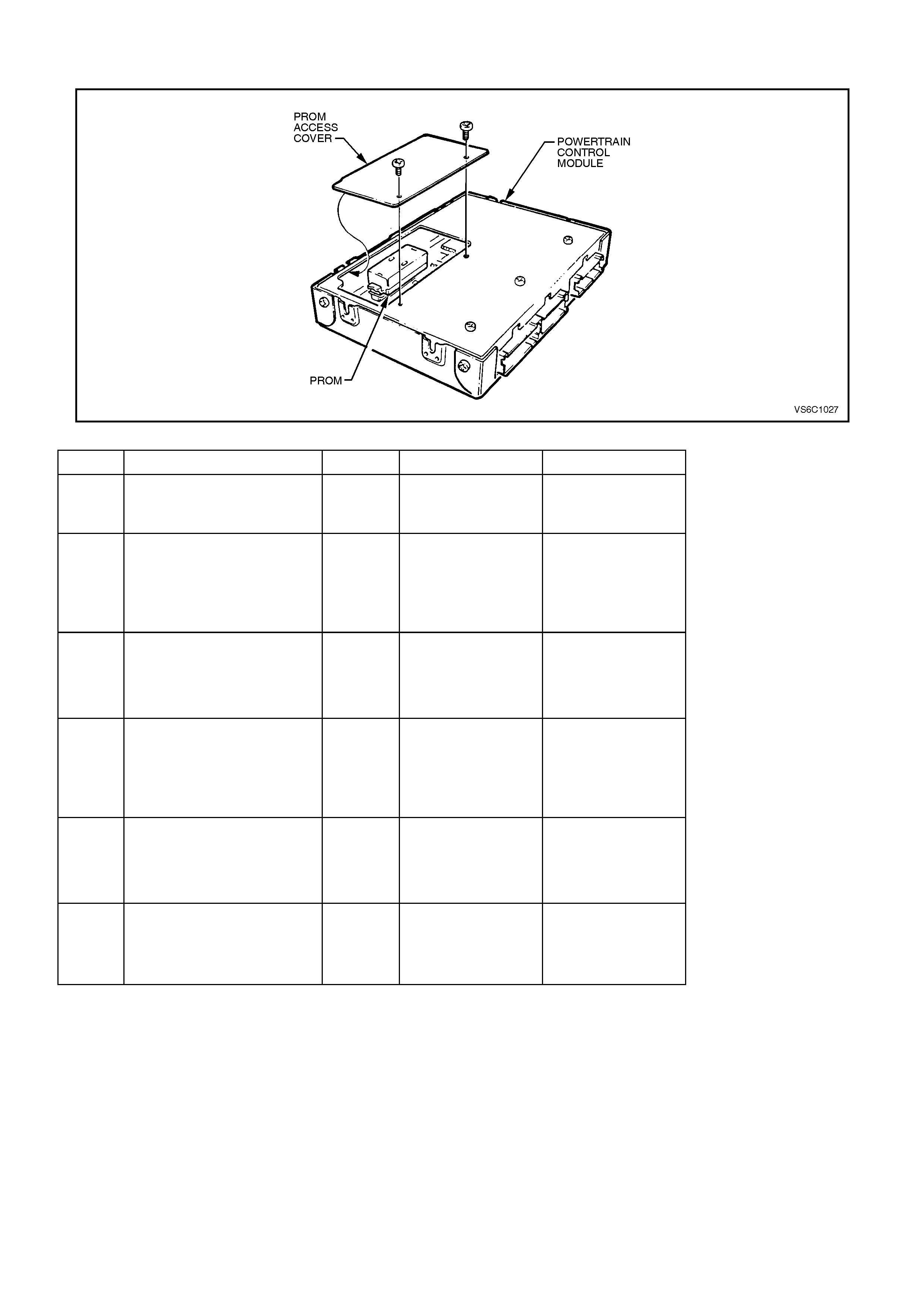
DTC 51 - PROM ERROR
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Check that the PROM is
properly seated into the
PCM.
Is the PROM properly
seated?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 5
3Replace the PROM.
Clear the DTCs and
recheck for a DTC 51.
Does a DTC 51 reset?
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
5Fully insert the PROM.
Clear the DTCs and
recheck for DTC 51.
Does a DTC 51 reset?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
6Clear the DTC’s and
confirm no Check
Powertrain Lamp.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
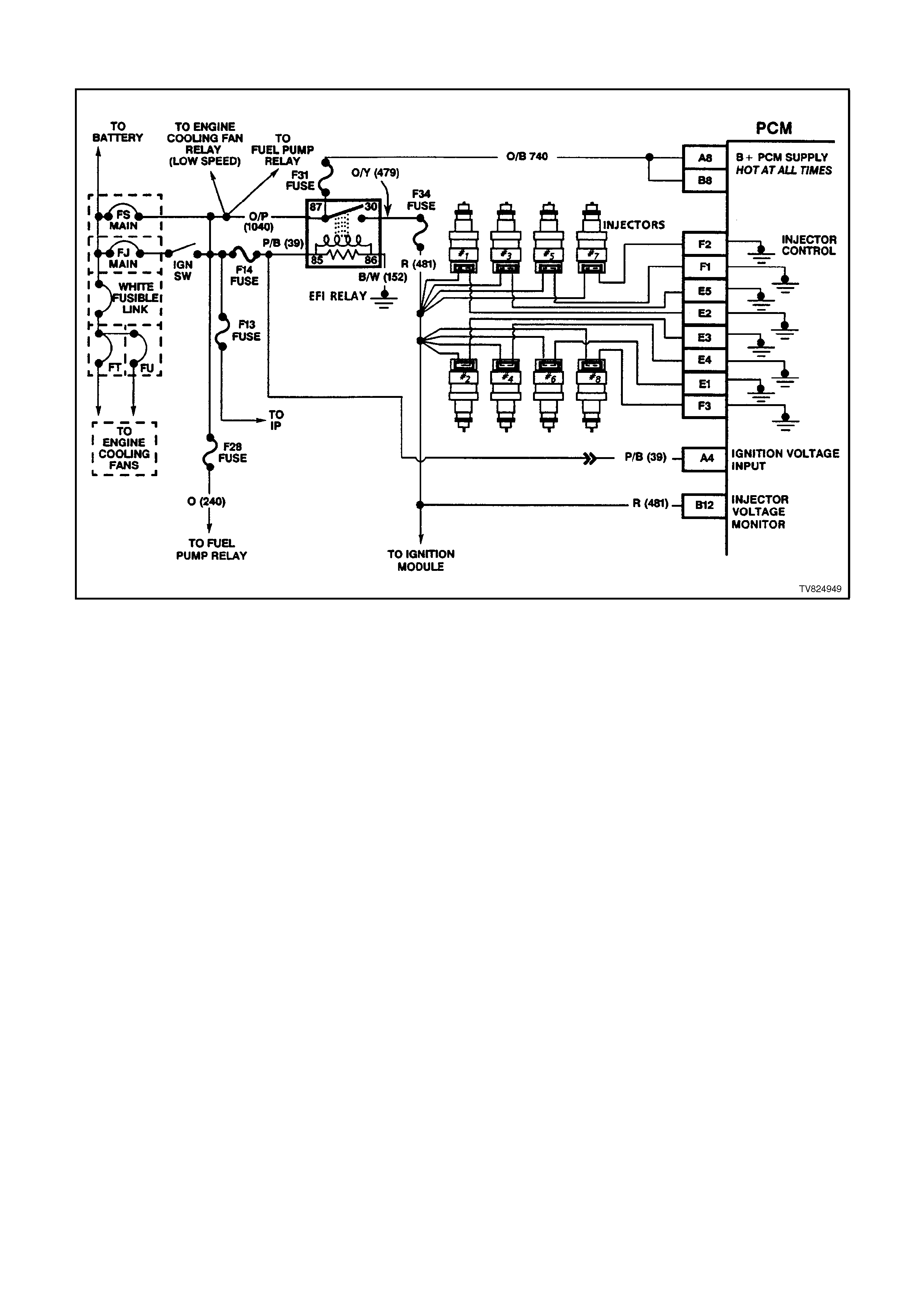
DTC 52 - SYSTEM VOLTAGE TOO HIGH - LONG TIME
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Circuit 39 is the ignition voltage feed circuit to terminal A4 for the PCM. Circuit 740 is the battery voltage feed circuit
to terminals A8 and B8 for the PCM. When the PCM detects a high voltage for a long time, then DTC 52 sets.
DTC 52 WILL SET IF:
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 52 will set when the engine is running and the PCM terminal "A4" voltage is greater
than 16 volts for more than 109 minutes.
During the time the fault is present, the pressure control solenoid will be OFF. The transmission will default
immediately to 3rd gear and the TCC operation will be inhibited. Additional codes may also set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
4. This tests the charging system voltage.
5. This tests the PCM battery voltage.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Look for the following conditions:
A backed out terminal
A damaged terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• Charging the battery with a battery charger may set DTCs. Jump starting an engine may set DTCs.
• If DTCs set when you operate an accessory, inspect the applicable wiring for faulty connections. Inspect the
wiring for excessive current draw.
• Inspect the following items for faulty connections:
The starter solenoid
The fusible link
The generator terminals
The battery cables
• Inspect the belts for excessive wear. Inspect the belts for proper tension.
When a DTC 52 sets, the PCM turns all the transmission output devices OFF and freezes the shift adapts from
being updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
— Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history.
The Clear Info function
will erase the data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Using the J 39200
DVM, measure the
battery voltage across
the battery terminals.
Record the
measurement for
future reference.
Is the voltage higher than
the specified value?
10 volts Go to Step 3 Go to Battery
Diagnosis
31. Start the engine.
2. Warm the engine to
the operating
temperature.
Is the generator/check
engine light ON?
85°C Go to Charging
System Diagnosis Go to Step 4
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Increase the engine
speed to 2000 RPM for
15 seconds.
2. Observe the DVM
battery voltage.
Is the DVM battery voltage
greater than the specified
value?
15 volts Go to Charging
System Diagnosis Go to Step 5
51. Increase the engine
speed to 2000 RPM.
2. Observe the scan tool
Battery Voltage.
Is the scan tool Battery
Voltage greater than the
specified value?
15.5
volts Go to Step 6 System Checks
OK, Go to
“Diagnostic Aids”
above
6Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
— Go to Step 7 —
7In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• Start the vehicle.
• Warm the engine to
the normal operating
temperature.
Is the scan tool Battery
Voltage within the
specified range?
13-15.5
volts System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
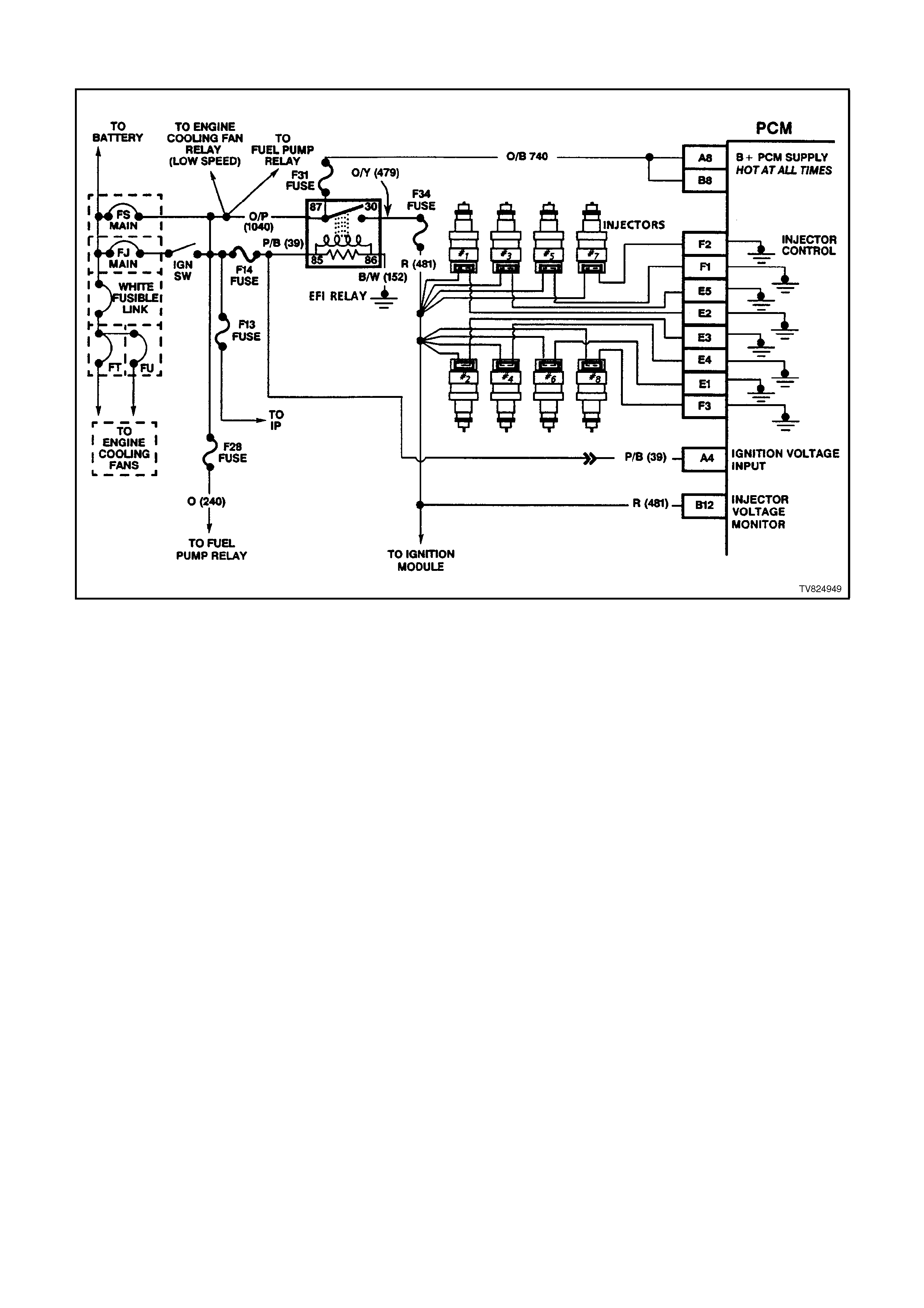
DTC 53 - SYSTEM VOLTAGE TOO HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Circuit 39 is the ignition voltage feed circuit to terminal A4 for the PCM. Circuit 740 is the battery voltage feed circuit
to terminals A8 and B8 for the PCM. When the PCM detects a high voltage, for a short period of time, then DTC 53
sets.
DTC 53 WILL SET IF:
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 53 will set when the ignition is ON and PCM terminal "A4" voltage is greater than
19.5 volts for greater than 2 seconds.
During the time fault is present, the pressure control solenoid is turned OFF, the transmission shifts immediately to
3rd gear and the TCC operation is inhibited. Additional codes may also set.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
4. This tests the charging system voltage.
4. This checks the battery voltage of the PCM, using the scan tool.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Look for the following conditions.
A bent terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
Corrosion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• Charging the battery with a battery charger may set DTCs. Jump starting an engine may set DTCs.
• If DTCs set when you operate an accessory, inspect the applicable wiring for faulty connections. Inspect the
wiring for excessive current draw.
• Inspect the following items for faulty connections:
The starter solenoid
The fusible link
The generator terminals
Battery cables to earth
• Inspect the belts for excessive wear and proper tension.
When a DTC 53 sets, the PCM will turn all transmission output devices are OFF and freeze shift adapts from being
updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
— Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history.
The Clear Info function
will erase the data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Using the J 39200
DVM, measure the
battery voltage across
the battery terminals.
Record the
measurement for
future reference.
Is the voltage higher than
the specified value?
10 volts Go to Step 3 Go to Battery
Diagnosis
31. Start the engine.
2. Warm the engine to
the operating
temperature.
Is the generator/check
engine light ON?
85°C Go to Charging
System Diagnosis
in Section 6D2-1
CHARGING
SYSTEMS - V8
Go to Step 4
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Increase the engine
speed to 2000 RPM for
15 seconds.
2. Observe the DVM
battery voltage and
record your reading.
Did the DVM battery
voltage exceed the
specified value?
16.0
volts Go to Charging
System Diagnosis
in Section 6D2-1
CHARGING
SYSTEMS - V8
Go to Step 5
51. Increase the engine
speed to 2000 RPM.
2. Observe the scan tool
Battery Voltage.
Is the scan tool Battery
Voltage within 0.5 volts of
your recorded voltage in
step 4?
— System Checks
OK, Go to
“Diagnostic Aids”
above
Go to Step 6
6Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure .
Is the action complete?
— Go to Step 7 —
7In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• Start the vehicle.
• Warm the engine to
normal operating
temperature.
Is the scan tool Battery
Voltage within the
specified range?
13-15.5
volts System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
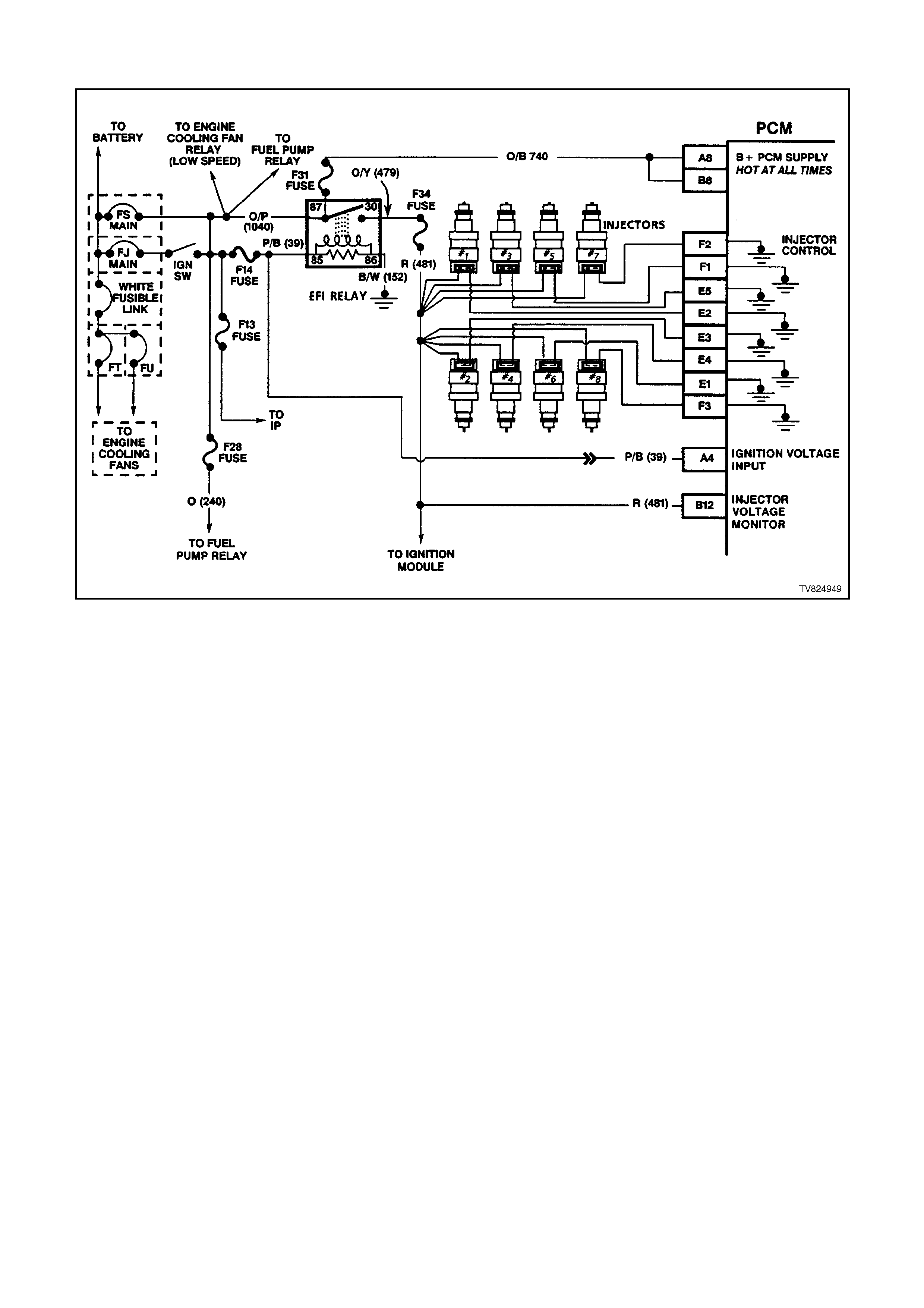
DTC 54 - SYSTEM VOLTAGE UNSTABLE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 54 will set when the ignition is ON and PCM terminal C1 voltage changed more
than 3 .5 volts in 100 milliseconds.
DTC 54 WILL SET IF:
• The system voltage changes more than 3.5V in 2 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to the step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
When diagnosing an intermittent problem, use the snapshot mode on the Tech 2 Scan tool, to review diagnostic
information.

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
3. Wiggle the PCM
connector.
Does the "System
Voltage" reading change
sharply as the connector
is wiggled?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 3
3Wiggle and tug the
harness at the PCM.
Does the "System
Voltage" reading change
sharply as the harness is
wiggled?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4Lightly tap on the PCM.
Does the "System
Voltage" reading change
sharply as the PCM is
being tapped?
Go to Step 8 DTC 54 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTC's
were stored, refer
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
5Check the PCM connector
for corrosi on.
Is there corrosion present
at the connector?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
6Check the tension of the
female terminal grip with a
spare male terminal.
Are the terminals tight?
Go to Step 7 Verify Repair
7Remove the PCM strain
relief connector and
remove the terminal from
the connector to check for
broken or bent locking
tang.
Is the locking tang OK?
Find intermittent
open in
powertrain wiring
harness.
Go to Step 11
8Verify that the PCM is
securely mounted to the
vehicle.
Is the PCM securely
mounted?
Go to Step 9 Verify Repair
9Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Clean the corroded
terminals with electronic
part cleaner.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Replace the terminal.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
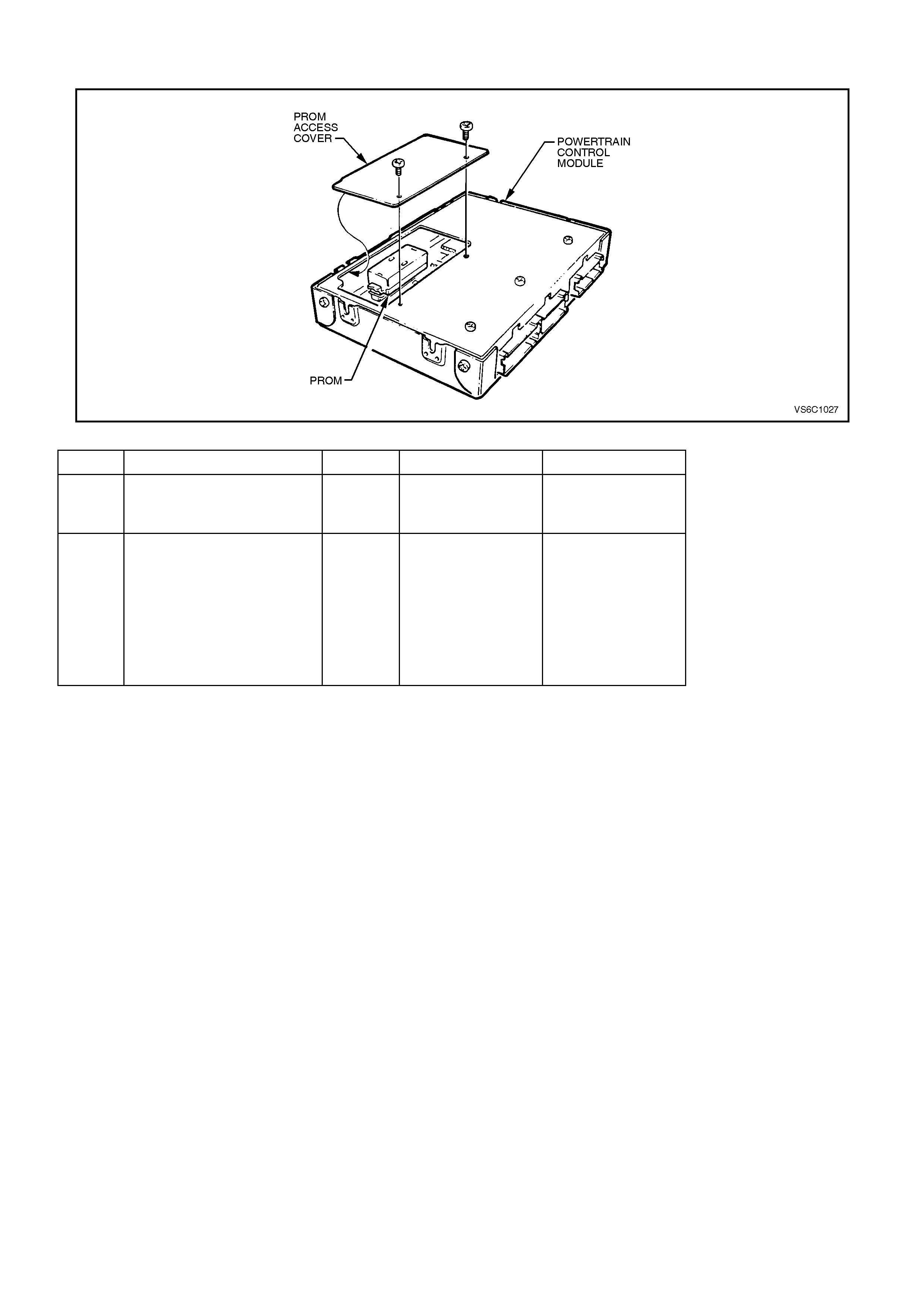
DTC 55 - PCM - ANALOG TO DIGITAL (A/D) CONVERSION ERROR
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Replace the PCM.
Perform the Security Link
procedure. whenever
replacing the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair

DTC 57 - INJECTOR VOLTAGE M O NI TOR CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The injector voltage monitor line is used so that the PCM will know the exact voltage the fuel injectors are operating
at. This voltage is used to control the pulse width modulation of the fuel injectors. If the injector voltage monitor line
drops more than 2.2 volts for more than 3 seconds, Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 57 will set. This DTC will not
turn ON the "Check Powertrain" lamp, but will have a DTC set in the PCM memory that can be read with the Tech 2
"Scan" tool and can be displayed by flashing codes.
DTC 57 WILL SET IF:
• A DTC 54 is not set.
The Injector voltage monitor line voltage is 2.5 volts less than the system voltage for greater than 5 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to the step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
When the injector voltage monitor line voltage drops more than 2.2 volts, the PCM will operate on an incorrect value
for 3 seconds until the DTC 57 is set. After the DTC 57 is set, the PCM will use the battery feed as the voltage value
to control the fuel injectors base pulse width. Check PCM terminal connections for proper mating.
If DTC 16, 53 and 57 are set, check for short to voltage on "Diagnostic Test" line, circuit 451.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. This chart assumes
that a DTC 53 is not
set and that the battery
and the charging
systems are operating
properly.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Using the scan tool,
monitor the fuel
Injector Voltage and
the B+ voltage.
Are they within the
specified value of each
other?
2.4 volts DTC 57 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored.
Refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
Go to Step 3
3Using a DVM, backprobe
PCM terminal "D7" with
the red lead and connect
the black lead to PCM
terminal "D3".
Is the voltage measured
within the specified value
of the "Battery Voltage"
reading on the Scan tool?
2.4 volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4Repair the open in circuit
481 between the splice
and the PCM terminal
"D7".
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
5Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
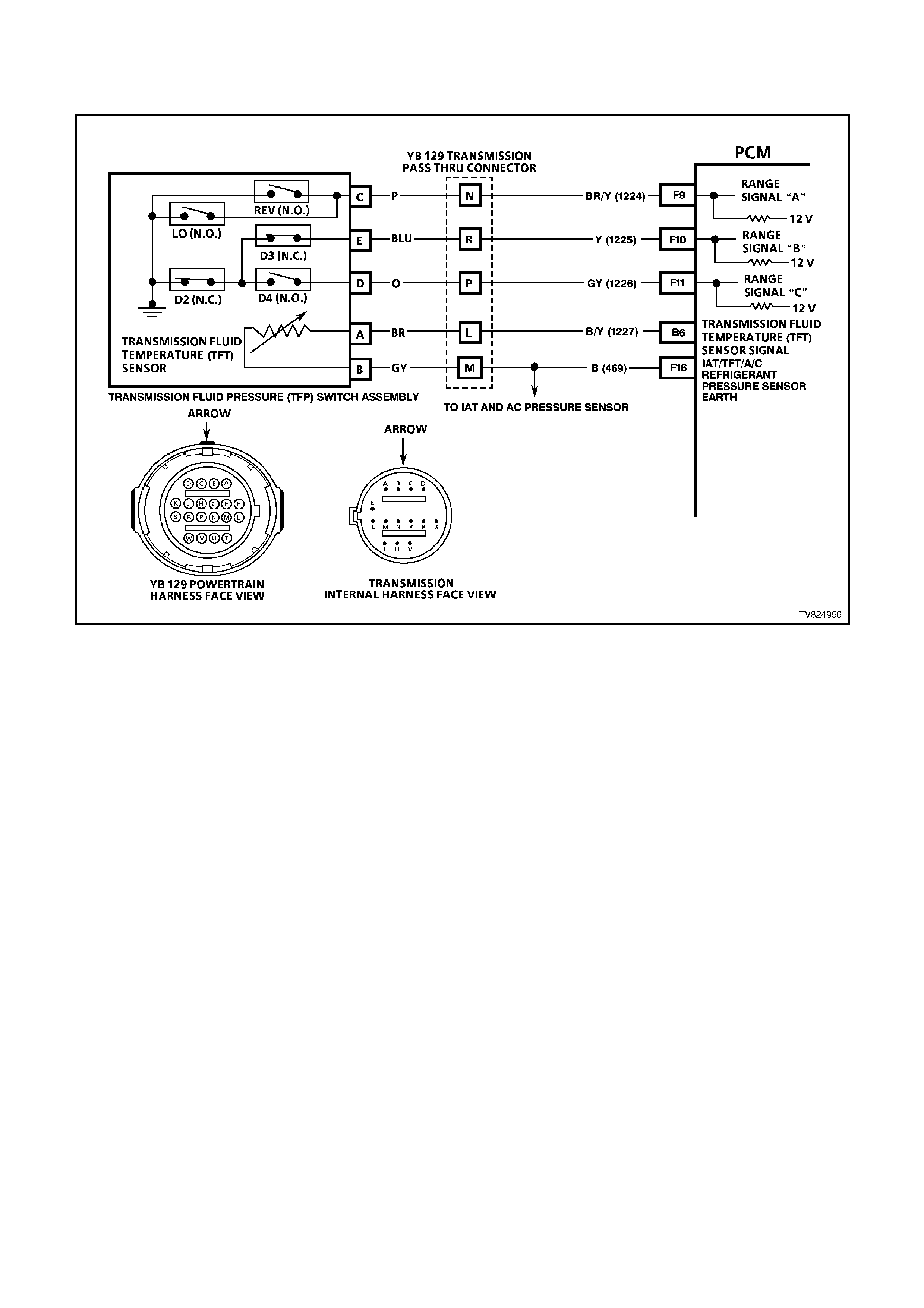
DTC 58 - TRANSMISSION FLUID TEM PERATURE (TFT) SENSOR CIRCUIT -
LOW INPUT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Automatic Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor is a thermistor within the Automatic Transmission
Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch (TFP Val. Position Switch.). The TFT sensor controls the signal
voltage to the PCM. The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference signal to the sensor on circuit 1227. When the
transmission fluid is cold, the sensor resistance will be high. The PCM will then detect a high signal voltage. As the
transmission fluid temperature increases to the normal operating temperature, the sensor resistance becomes less
and the voltage decreases.
When the PCM detects a continuous short to earth in the TFT signal circuit or in the TFT sensor, then a will DTC 58
set.
DTC 58 WILL SET IF:
• The TFT Sensor voltage is less than 0.33 volts for 10 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. This tests for a short to earth or a skewed sensor.
4. This creates an open within the transmission in order to test for an internal fault.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Check for the following conditions.
A backed out terminal
A damaged terminal
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Corrosion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• Use the Temperature vs Resistance table when testing the TFT sensor at various temperature levels. Test the
TFT sensor in order to evaluate the possibility of a skewed (mis-scaled) sensor. A skewed sensor can result in
delayed garage shifts or TCC complaints.
• The scan tool can display the transmission fluid temperature in degrees. After the transmission is operating, the
fluid temperature should rise steadily to a normal operating temperature, then stabilize.
TE MPERATURE TFT RESISTANCE SIGNAL
Degrees °C Minimum W Normal W Maximum W Volts
-40 90636 100707 110778 5.0
-30 47416 52684 57952 4.78
-20 25809 28677 31545 4.34
-10 14558 16176 17784 3.89
0 8481 9423 10365 3.45
10 5104 5671 6238 3.01
20 3164 3515 3867 2.56
30 2013 2237 2461 1.8
40 1313 1459 1605 1.1
50 876 973 1070 3.25
60 600 667 734 2.88
70 420 467 514 2.56
80 299 332 365 2.24
90 217 241 265 1.7
100 159 177 195 1.42
110 119 132 145 1.15
120 89.9 99.9 109.9 0.87
130 69.1 76.8 84.5 0.6
140 53.8 59.8 65.8 0.32
150 42.5 47.2 51.9 0
A shunt in the PCM becomes active as the transmission temperature
increases beyond 50 °C. As the temperature decreases, the internal
shunt deactivates at 40 °C.
When a DTC 58 sets, the PCM uses a default Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) of 135°C. The PCM also
freezes shift adapts from being updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
2Perform the transmission
fluid checking procedure.
Have you performed the
fluid checking procedure?
Go to Step 3 Go to
Transmission Fluid
Checking
Procedure
31. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history.
The Clear Info function will
erase the data.
3. Record the DTC history.
Does the scan tool display
the TFT voltage less than
the specified value?
0.33 volts Go to Step 4 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector.
3. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
Does the scan tool display
a TFT voltage greater than
the specified value?
4.92 volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 9
51. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on the
transmission side of the
pass-through connector.
2. Using the J 39200 DVM
and J 35616 Connector
Test Adapter Kit,
measure the resistance
between terminal L and
terminal M.
Is the resistance within
specifications?
3088-
3942 ohm
@ 20° C
159-
198 ohm
@ 100° C
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 6
61. Check the internal
Automatic Transmission
Wiring Harness
Assembly for a short to
earth.
2. Replace the harness if
necessary.
Did you find and correct the
problem?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 7
71. Disconnect the internal
Automatic Transmission
Wiring Harness
Assembly at the TFT
sensor.
2. Measure the resistance
of the TFT sensor.
Is the resistance within the
3088-
3942 ohm
@ 20° C
159-
198 ohm
@ 100° C
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
specifications?
8Replace the TFT Sensor
(this is part of the TFP Val.
Position Switch.). Refer to
Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 11
91. Check circuit 1227 for a
short to earth.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find a problem?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
10 Replace the PCM. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 11
11 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
Does the scan tool indicate
a TFT voltage greater than
the specified value?
0.33 volts System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
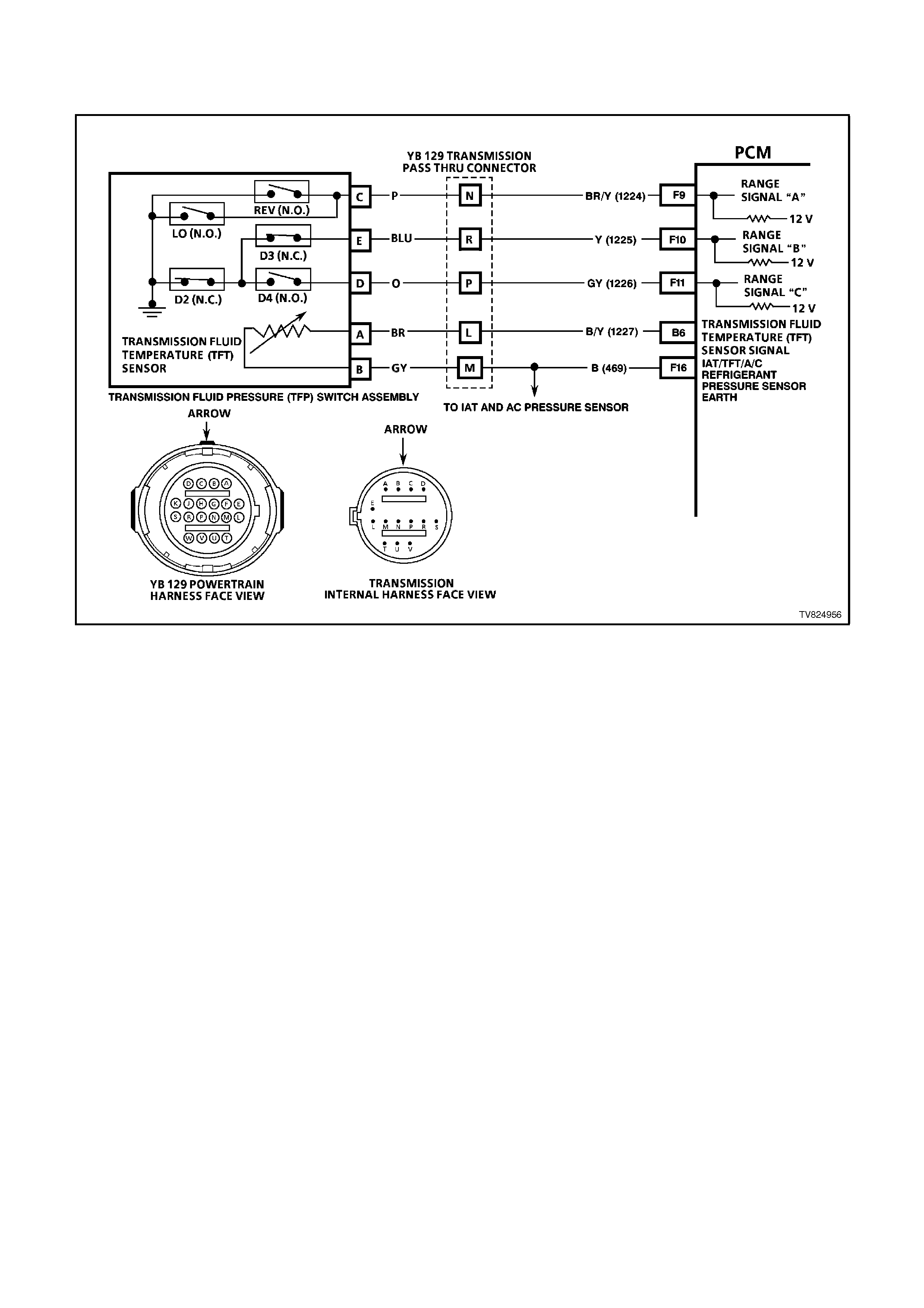
DTC 59 - TRANSMISSION FLUID TEM PERATURE (TFT) SENSOR CIRCUIT -
HIGH INPUT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Automatic Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) sensor is a thermistor within the Automatic Transmission
Fluid Pressure Manual Valve Position Switch (TFP Val. Position Switch.). The TFT sensor controls the signal
voltage to the PCM. The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference signal to the sensor on circuit 1227. When the
transmission fluid is cold, the sensor resistance is high. The PCM detects high signal voltage. As the transmission
fluid temperature increases to a normal operating temperature, the sensor resistance becomes less and the voltage
decreases.
When the PCM detects a continuous open a or short to power in the TFT signal circuit or the TFT sensor, then DTC
59 sets.
DTC 59 WILL SET IF:
• The TFT Sensor voltage is equal to or greater than 4.92 volts for 10 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. This step verifies that a problem exists in the TFT sensor circuit.
4. This step simulates a TFT sensor DTC 58. If the PCM recognises high temperature, the PCM and wiring are
functioning normally.
5. This step tests the TFT sensor and Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• Use the Temperature vs Resistance table when testing the TFT sensor at various temperature levels. Test the
TFT sensor in order to evaluate the possibility of a skewed (mis-scaled) sensor. A skewed sensor can result in
delayed garage shifts or TCC complaints.
• The scan tool can display the transmission fluid temperature in degrees. After the transmission is operating, the
fluid temperature should rise steadily to a normal operating temperature, then stabilize.
TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE (TFT) SENSOR TEMPERATURE TO RESISTANCE TABLE
TE MPERATURE TFT RESISTANCE SIGNAL
Degrees °C Minimum
WNormal W Maximum W Volts
-40 90636 100707 110778 5.0
-30 47416 52684 57952 4.78
-20 25809 28677 31545 4.34
-10 14558 16176 17784 3.89
0 8481 9423 10365 3.45
10 5104 5671 6238 3.01
20 3164 3515 3867 2.56
30 2013 2237 2461 1.8
40 1313 1459 1605 1.1
50 876 973 1070 3.25
60 600 667 734 2.88
70 420 467 514 2.56
80 299 332 365 2.24
90 217 241 265 1.7
100 159 177 195 1.42
110 119 132 145 1.15
120 89.9 99.9 109.9 0.87
130 69.1 76.8 84.5 0.6
140 53.8 59.8 65.8 0.32
150 42.5 47.2 51.9 0
A shunt in the PCM becomes active as the transmission temperature
increases beyond 50 °C. As the temperature decreases, the internal
shunt deactivates at 40 °C.
When a DTC 59 sets, the PCM uses a default Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) of 135°C and freezes shift
adapts from being updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
2Perform the transmission
fluid checking procedure.
Have you performed the
fluid checking procedure?
Go to Step 3 Go to
Transmission
Fluid Checking
Procedure
31. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
Does the scan tool display
a TFT Sensor voltage
greater than the specified
value?
4.92
Volts Go to Step 4 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector.
3. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the engine side of the
pass-through
connector.
4. Install a fused jumper
wire from terminal L to
terminal M on the
engine connector.
5. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
Does the TFT Sensor
voltage drop to less than
the specified value?
0.2 Volts Go to Step 5 Go to Step 9
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the transmission side
of the pass-through
connector.
3. Using the J 39200
DVM and J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance between
terminal L and terminal
M.
Is the resistance within
specification?
3088-
3942 ohm
at 20°C
159-
198 ohm
at 100°C
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 6
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
61. Check the internal
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a open condition.
2. Replace the harness if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 7
71. Disconnect the internal
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly at
the TFT sensor.
2. Measure the
resistance of the TFT
sensor.
Is the resistance within
specifications?
3088-
3942 ohm
at 20° C
159-198
ohm at
100° C
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 8
8Replace the TFT Sensor
(this is part of the TFP
Val. Position Switch.).
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations.
Is the replacement
complete?
Go to Step 12
91. Check circuit 1227 for
an open or short to B+.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find a problem?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 10
10 1. Check circuit 469 for
an open.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find a problem?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 12
12 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
Does the scan tool
indicate a TFT voltage
less than the specified
value?
4.92
volts System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
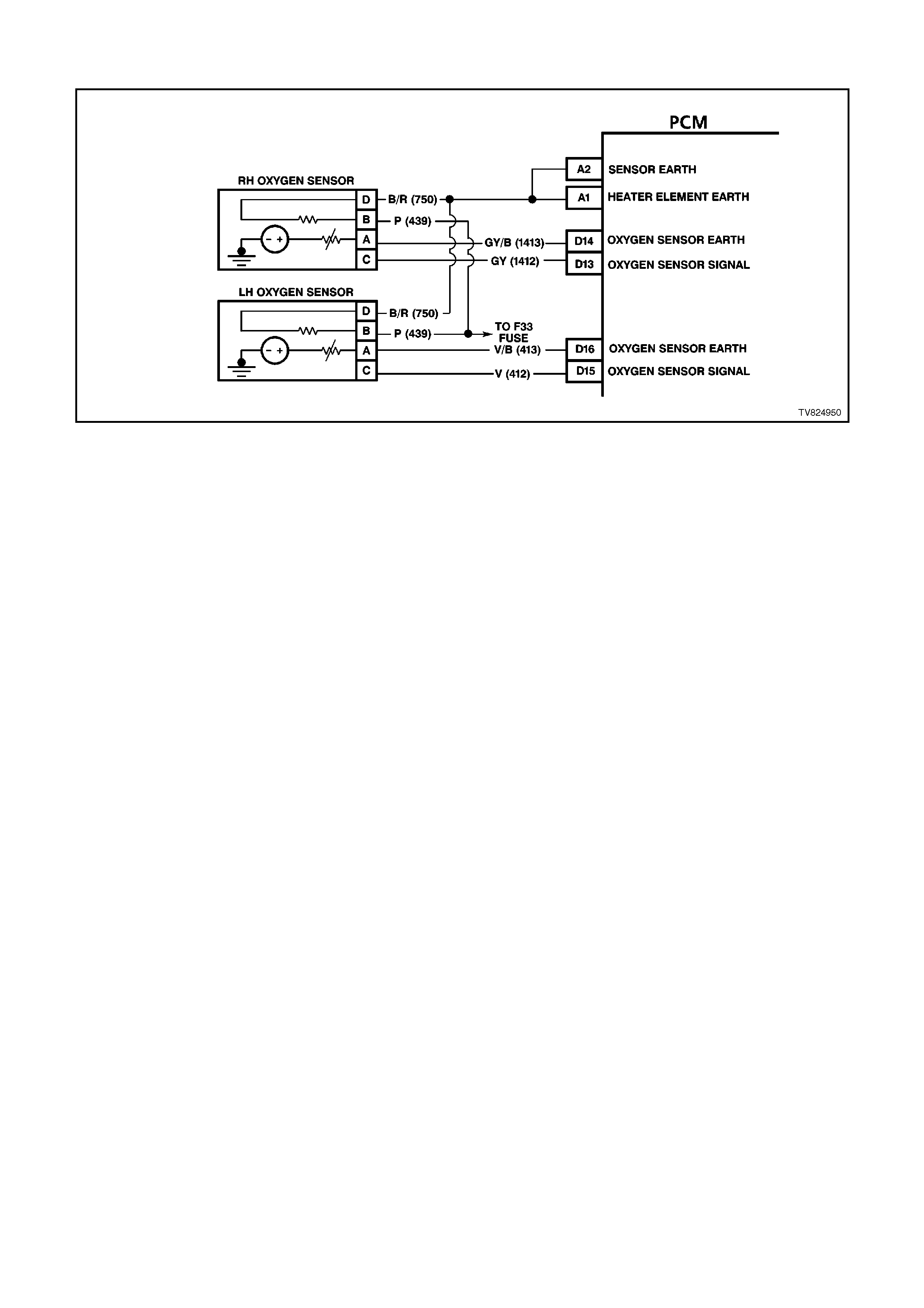
DTC 63 - LEFT HAND (LH) NO OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The LH O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the exhaust gas in the exhaust stream then sends a voltage to
the PCM relative to the oxygen content. This voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean
mixture) to greater than 900 mV(low O2 exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM provides the O2 sensor with a constant 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins heating up its
internal resistance begins to decrease. The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing voltage that differs
from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2 sensor the PCM
knows the LH O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
When the ignition is turned ON, B+ is applied to the O2 sensor’s heater element. Approximately 30 seconds after
the B+ is applied to the heater portion of the O2 sensor, the O2 sensor should reach a temperature greater than
500°C. The heated O2 sensor becomes active much quicker than a non-heated O2 sensor. This allows the PCM to
control the air/fuel ratio more consistent over a wider range of operating conditions.
DTC 63 WILL SET IF:
• One or both of the following DTC's are not set. DTC21, or DTC 22.
• The engine run time is greater than 120 seconds.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 85°C.
• The Throttle Position (TP) sensor angle is greater than 6.25%.
• The LH O2 sensor voltage stays between 347 - 551 mV.
• The above conditions have been present for 20 seconds.
When a DTC 63 is set, the PCM will operate the fuel system in the open-loop mode.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to circled number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This simulates a lean exhaust to the PCM. If the PCM and wiring are OK, the PCM will see the lean indication
and the Scan tool should display the O2 sensor voltage below 200 mV.
8. Use only a high impedance digital volt-ohm meter. This checks the continuity of circuits 412 and 750. If circuit
750 is open, the PCM voltage on circuit 412 will be over 0.6 volts.
9. The earth circuit is a separate wire from the PCM to the engine. The PCM uses this circuit to compare it with
the voltage on circuit 412. It completes the earth path for the PCM's oxygen sensor circuitry. This must be
complete, clean, and tight connection to the engine.

DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Normal Tech 2 Scan tool voltage varies between 100 mV and 999 mV when in Closed Loop.
Carbon deposits caused by a rich running of the engine can cause a temporary poisoning of the sensor. This will
result in a slow or sluggish O2 sensor. The sensor can be cleaned by running the vehicle for several minutes at
operating temperature while not in the rich condition. If a rich condition is present find the problem causing the rich
condition before attempting to clean the O2 sensor.
• Check for other forms of contamination.
• Silica from gasket forming material.
• Lead from the use of leaded gasoline.
• Metallic compounds from the use of inferior or low grades of petrol or engine oil.
Some of these contaminants will clean themselves from continuous running of the engine. Do not attempt to clean
the O2 sensor with any form of cleaner solvent this may cause permanent damage.
Check the O2 sensor pigtail wire for proper routing. If the O2 sensor pigtail wire contacts the exhaust manifold the
wire insulation can burn and short itself to the exhaust manifold.
Also, check the O2 sensor for any leaks around its sealing surface or any exhaust leaks. Refer to "Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS. To diagnose the oxygen sensor, refer CHART A-6.3 in this Section.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Run the engine until
the engine coolant
temperature reaches
85°C.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Monitor the LH O2
sensor voltage on the
scan tool.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage between the
specified values?
347-551
mV Go to Step 3 If no additional
DTCs were
stored, refer to
"Intermittents" in
Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS
31. Turn the engine OFF.
2. Disconnect the LH O2
sensor electrical
connector.
3. Jumper the harness
circuit (PCM side) to
earth.
4. Start the engine and
allow the engine to
idle.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage below the
specified value?
0.2 volt
(200 mV) Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4Check for a faulty
connection at the oxygen
sensor pigtail wire
connector.
Was a poor connection
found?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
51. Turn the engine OFF.
2. Remove the jumper.
3. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
4. Use a DVM to check
the voltage in the LH
O2 sensor signal circuit
(PCM side) at the LH
O2 sensor harness
connector.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage between the
specified values?
0.3 - 0.6
volts
(300-600
mV)
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
61. Turn the engine OFF.
2. Remove the jumper
wire.
3. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
4. Use a DVM to check
the voltage in the LH
O2 sensor signal circuit
(PCM side) at the LH
O2 sensor harness
connector.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage greater than the
specified value?
0.6 volts
(600 mV) Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7Check for an open or a
faulty connection in the
LH O2 sensor ground
circuit (3 total).
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
8Check for an open or a
faulty connection in the LH
O2 sensor signal circuit.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
9Replace the LH O2
sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
10 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Repair the fault in the LH
O2 sensor pigtail
connector.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
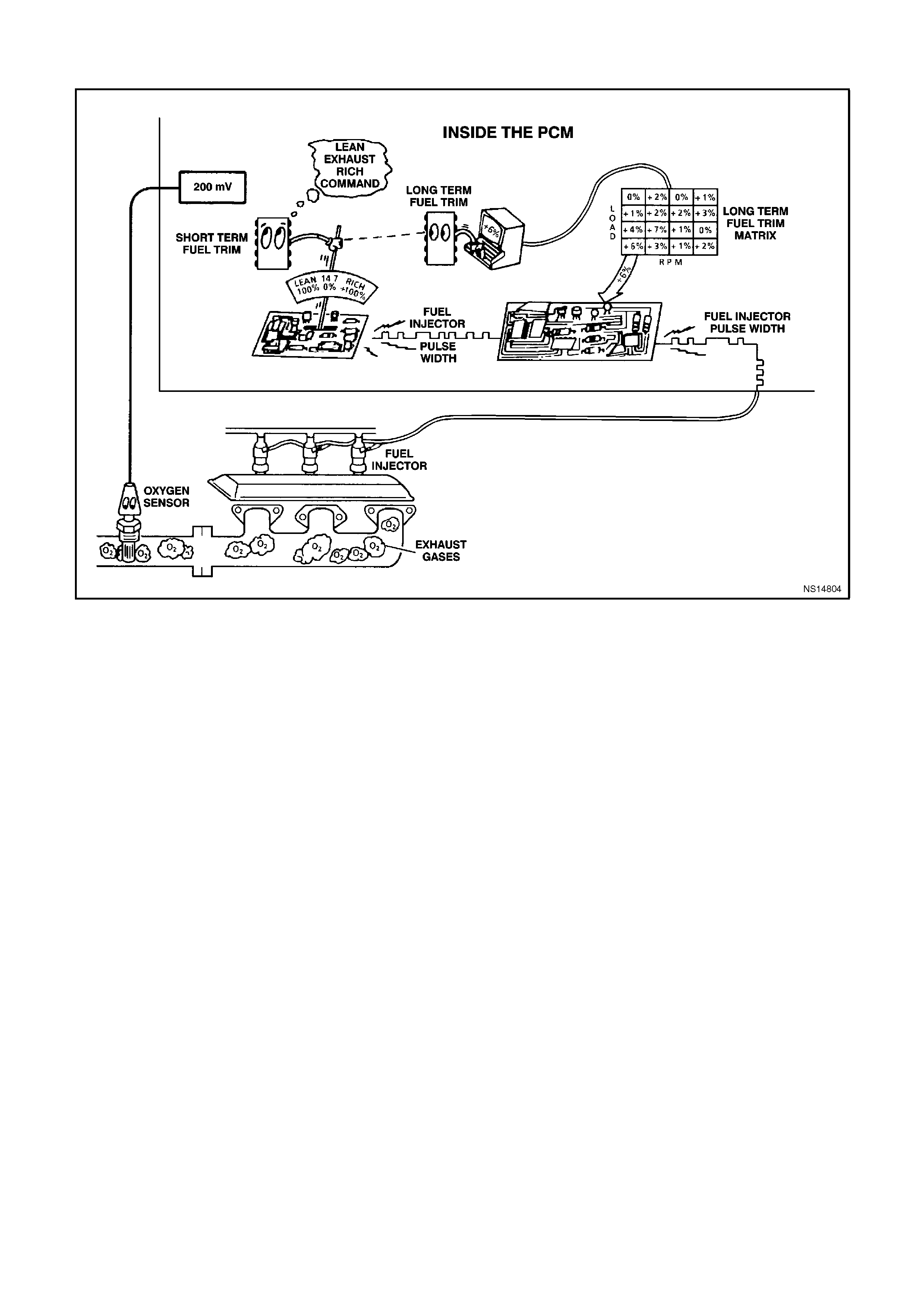
DTC 64 - LEFT HAND (LH) LEAN EXHAUST INDI CATED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The LH O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the exhaust gas in the exhaust stream then sends a voltage to
the PCM relative to the oxygen content. This voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust content-lean
mixture) to greater than 900 mV (low O2 exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM provides the O2 sensor with a constant 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins heating up its
internal resistance begins to decrease . The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing voltage that
differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2 sensor the
PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
When the ignition is turned ON, B+ is applied to the O2 sensor’s heater element. Approximately 30 seconds after
the B+ is applied to the heater portion of the O2 sensor, the O2 sensor should reach a temperature greater than
500°C. The heated O2 sensor becomes active much quicker than a non-heated O2 sensor. This allows the PCM to
control the air/fuel ratio more consistent over a wider range of operating conditions.
DTC 64 WILL SET IF:
• One or more of the following DTC's are not set. DTC 23, 25, or DTC 26.
• The fuel control system is operating in Closed Loop.
• The IAT sensor is less than 90 degrees C.
• The LH O2 sensor signal voltage is less than 250 millivolts.
• The above conditions are present for 45 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
4. A DTC 64 or lean exhaust is most likely caused by one of the following conditions.
• An O2 Sensor Wire - A sensor pigtail may be contacting the exhaust manifold. Check for an intermittent earth in
the wire between the connector and the O2 sensor.
• Fuel Contamination - Water, even in small amounts, near the in-tank fuel pump inlet can be delivered to the
injectors. The water causes a lean exhaust and can set a DTC 44.
• Fuel Pressure - System will go lean if pressure is too low. It may be necessary to monitor fuel pressure while
driving the vehicle at various road speeds and/or loads to confirm. Refer CHART A-4.1 in this Section.
• Exhaust Leaks - If there is an exhaust leak, the engine can cause outside air to be pulled into the exhaust and
past the sensor. Vacuum or crankcase leaks can cause a lean condition.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Use the Tech 2 to observe the Long Term Fuel Trim values at different RPMs and air flow conditions. The Tech 2
also displays the Long Term Fuel Trim cells, so the Long Term Fuel Trim values can be checked in each of the
cells to determine when the DTC 64 may have set. If the conditions for a DTC 64 exists, the Long Term Fuel Trim
values will be around +18%.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Start the engine.
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Run the engine until it
reaches normal
operating temperature
(Above 80 degrees C).
4. Continue to run
between 1600 to 1800
RPM for two minutes.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage fixed below the
specified value?
200 mV Go to Step 3 DTC 44 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored, refer
to "Intermittents"
in Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
31. Disconnect the LH O2
sensor connector.
2. Start the engine.
With the engine idling,
does the Tech 2 Scan tool
display LH O2 sensor
voltage between the
specified values?
Between
347 mV
and 551
mV
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Refer to Test
Descriptions above.
2. Perform the checks on
the items as noted.
• MAF sensor operation
• Low fuel pressure
• Contaminated fuel
• Manifold leaks in front
of the LH O2 sensor
• Lean injector (possibly
restricted)
• LH O2 sensor earth
circuit
Are all the items checked,
OK?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
51. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. With the LH O2 sensor
still disconnected,
check the LH O2
sensor signal for a
short to earth.
Is a short to earth
detected?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
6Replace the LH O2
sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify repair
7Repair the LH O2 signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
8Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
9Replace or repair the
faulty condition.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
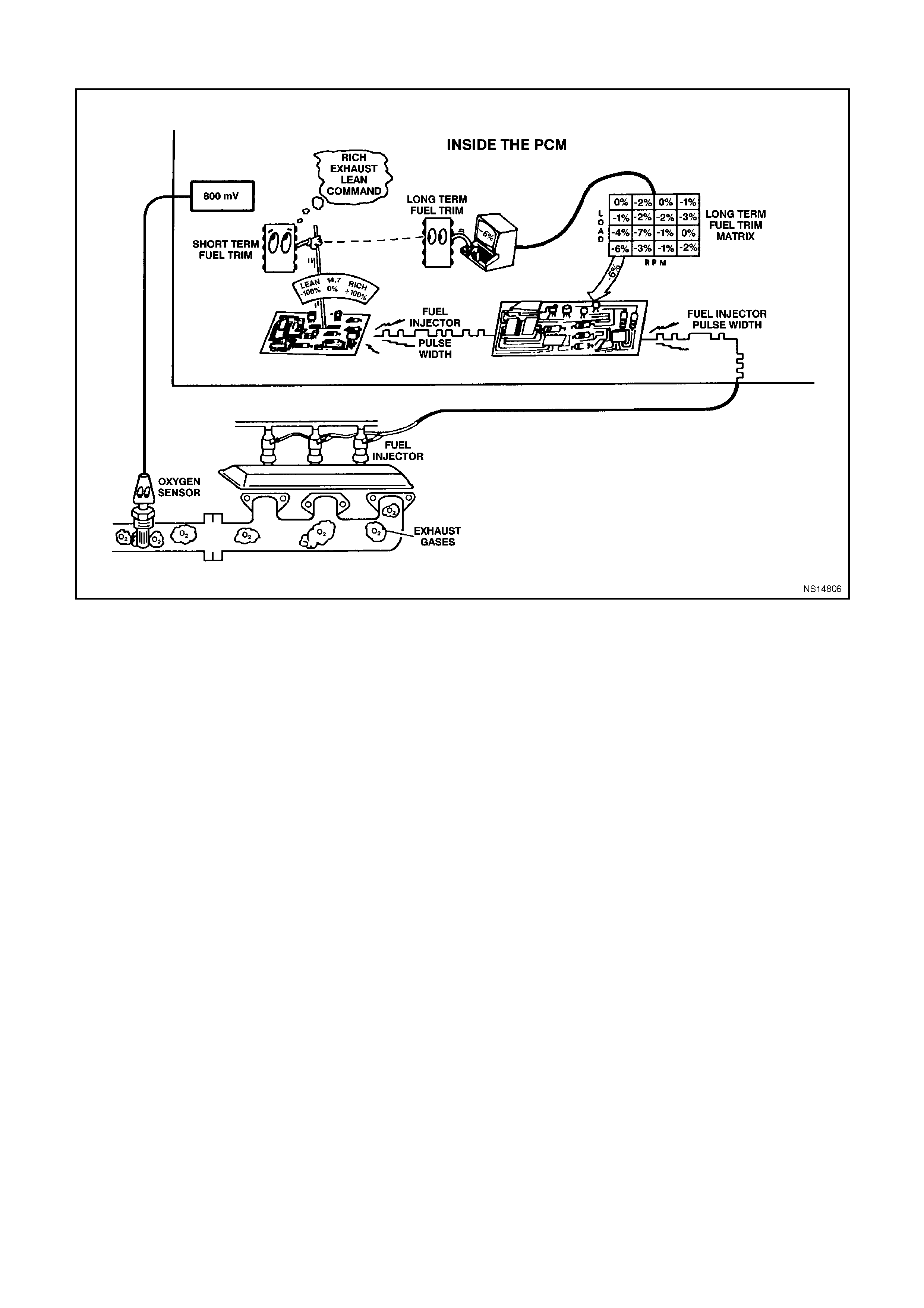
DTC 65 - LEFT HAND (LH) RICH EXHAUST INDICATED
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The LH O2 sensor monitors the oxygen content of the exhaust gases in the exhaust stream then sends an output
voltage to the PCM relative to the oxygen content. This voltage ranges from less than 100 mV (high O2 exhaust
content-lean mixture) to greater than 900 mV(low O2 exhaust content-rich mixture).
The PCM always supplies the O2 sensor with a steady 450 mV bias voltage. As the O2 sensor begins heating up its
internal resistance begins to decrease . The O2 sensor then begins to produce a rapidly changing voltage that
differs from the PCM supplied bias voltage. When the PCM recognises the changing voltage of the O2 sensor the
PCM knows the O2 sensor’s output voltage is ready to be used for fuel control.
DTC 65 WILL SET IF:
• The system is in closed loop.
• The Throttle angle is between 5% and 20%.
• The LH O2 sensor voltage remains greater than 750 millivolts for 30 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The number(s) below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic charts
8. A DTC 65 will most likely not be caused by a faulty LH O2 sensor. A DTC 65 indicates a rich exhaust. Check
the following components or systems.
Fuel Pressure. System will be rich, if pressure is too high. The PCM can compensate for some increase. If the
pressure gets too high, a DTC 65 may set. Refer to CHART A-4.2 in this Section.
• Rich Injector.
• Leaking Injector. Refer CHART A-4.2 in this Section.
• Check for fuel contaminate oil.
• Short to voltage on circuit 412.
• HEI Shielding. An open earth circuit 453 (ignition system) may result in EMI, or induced electrical noise as
reference pulses. The additional pulses result in a higher than actual engine speed signal.
• The PCM than delivers too much fuel, causing system to go rich. Engine tachometer will also show higher than
actual engine speed, which can help in diagnosing this problem.
• Canister Purge. Check for fuel saturation. If full of fuel, check canister control and hoses.
• MAF Sensor. A shifted "High" MAF sensor could cause the fuel system to go rich.
• Check for a leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to the regulator for fuel.
• The TP Sensor. An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system to go rich, due to a false indication of the
engine accelerating.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Use the Tech 2 to observe the Long Term Fuel Trim values at different RPMs and air flow conditions. The Tech 2
also displays the Long Term Fuel Trim cells, so the Long Term Fuel Trim values can be checked in each of the
cells to determine when the DTC 65 may have set. If the conditions for a DTC 65 exists, the Long Term Fuel Trim
values will be around +18%.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to the OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Engine at normal
operating temperature
(above 80 degrees C).
2. Install a Tech 2 scan
tool.
3. Run the engine
between 1600 RPM
and 1800 RPM for two
minutes.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage greater than the
specifiedvalue?
750 mV Go to Step 3 DTC 45 is
intermittent. If no
additional DTCs
were stored, refer
to "Intermittents"
in Section 6C2-2B
SYMPTOMS.
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the LH O2
sensor wiring harness.
3. With an ohmmeter
connected to earth,
probe theLH O2 sensor
signal circuit wiring
harness connector.
4. Ignition ON engine
OFF.
Is the voltage less then
the specified value?
350 mV Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Probe the LH O2
sensor signal circuit
wiring harness
connector.
4. Ignition ON.
Is the voltage less than
the specified value?
350 mV Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the short to voltage
in the LH O2 sensor signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
6Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
71. Disconnect the LH O2
sensor wiring harness
connector.
2. Jumper the LH O2
sensor signal circuit
harness connector to
earth.
3. Install a scan tool.
4. Start the engine.
Is the LH O2 sensor
voltage below the
specified value?
350 mV Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
8Refer to Test Descriptions
step 8 to perform
additional checks for:
• High Fuel Pressure
• MAF Sensor Operation
• Leaking Injectors
• Ignition Earth Circuit
• Canister Purge
• Engine Coolant
Temperature Sensor
Circuit
• Intake Air Temperature
Sensor Circuit
• Throttle Position
Sensor Operation
Do all the additional
checks from Test
Descriptions step 8
test OK?
Refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
Verify Repair
91. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Check the LH O2
sensor earth circuit for
continuity between the
PCM connector
terminal D16 and the
engine earth.
Was an OPEN circuit
found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
10. Check the PCM earth wire
connection at the engine.
This must be a clean and
tight connection.
Is the connection good?
Go to Step 11 Verify Repair
11 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 3 for Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
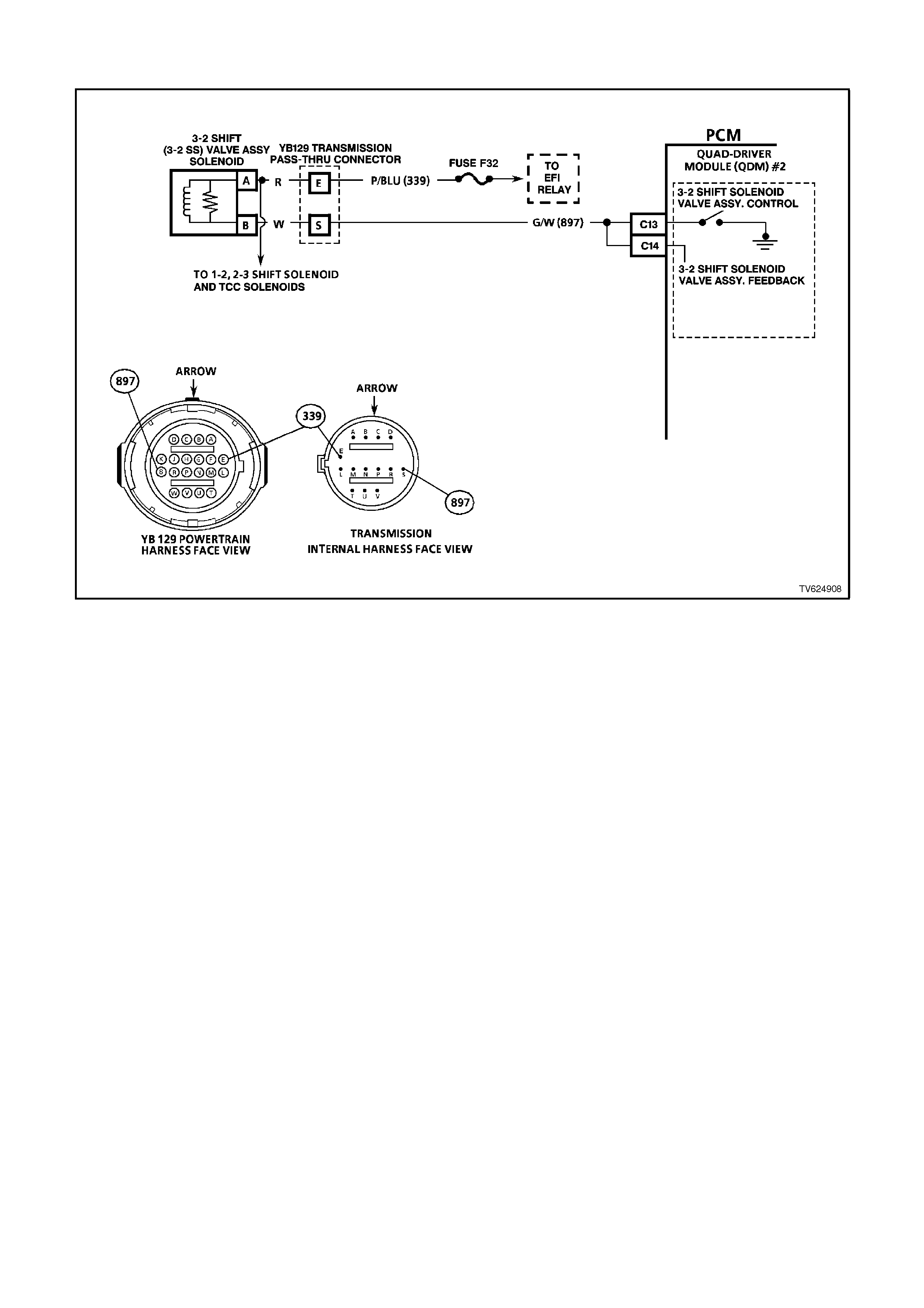
DTC 66 - 3-2 DOWNSHIFT SOLENOID CI RCUI T
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The 3-2 Shift Solenoid Valve Assembly (3-2 SS Valve Assembly) is a normally-closed, 3-port, on/off device that
controls the 3-2 downshift. The solenoid attaches to the control valve body within the transmission. The solenoid
receives ignition voltage through circuit 339. The PCM controls the solenoid by providing an earth path on circuit
687. During a 3-2 downshift, the 2-4 band applies as the 3-4 clutch releases. The PCM varies the timing between
the 3-4 clutch release and the 2-4 band apply depending on the vehicle speed and the throttle position.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or short to earth in the 3-2 SS Valve Assembly circuit or the 3-2 SS
Valve Assembly, then DTC 66 sets.
DTC 66 WILL SET IF:
Either one of the following conditions occurs for 4 seconds.
• The PCM commands the solenoid ON and the voltage remains high (B+).
• The PCM commands the solenoid OFF and the voltage remains low (0 volts).
If the 3-2 shift solenoid is OFF, the voltage on the circuit should remain high whenever the voltage drops
(approximately to 0 volts) for 4 seconds, then a DTC 66 will set. The 3-2 shift solenoid feedback line must detect an
inappropriate voltage status on the line for 4 seconds to set a DTC 66.

TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. An open fuse indicates a short in circuit 339. A short in any of the five solenoids fed by circuit 339 may cause
an open fuse.
4. This tests the ability of the PCM to control the solenoid.
6. This tests for power to the 3-2 SS Valve Assembly.
9-10. This tests the resistance of the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly and the 3-2 SS Valve
Assembly.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
Corrosion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
When a DTC 66 sets, the PCM will command maximum line pressure.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. If DTCs 67, 81, 82, or
83 are also set, inspect
the F32 fuse for an
open.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Check circuit 339 for a
short to earth.
2. Check each of the five
solenoids for being
internally shorted or
shorted to earth.
3. Check the A/T Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a short to earth on
each of the five
solenoid circuits.
4. Make the repair/
replacement
ifnecessary.
Did you find and correct a
problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above.
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector
(additional DTCs will
be set).
3. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the engine harness
connector.
4. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
5. Connect a test lamp
from the J 39775
Jumper Harness cavity
E to earth.
Is the test lamp ON?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the open in the
ignition feed circuit 339 to
the transmission pass-
through connector.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
61. With the ignition switch
in the OFF position,
disconnect the PCM
connector 1.
2. Install a test lamp from
cavity E to cavity S of
the J 39775 Jumper
Harness.
3. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
4. Using a fused jumper
test wire connected to
earth, probe PCM
terminals C13 and
C14.
Is the test lamp ON when
each terminal is
connected to earth, and
then OFF when not
connected to earth?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 11
71. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the transmission pass-
through connector.
2. Using the J 39200
DVM and J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance between
terminal E and
terminal S.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
20-32 ohm Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Measure the resistance
between terminal S and
earth, and between
terminal E and earth.
Are both measurements
greater than the specified
value?
250K ohm Go to Step 12 Go to Step 10
91. Disconnect the
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly
from the 3-2 SS Valve
Assembly.
2. Measure the
resistance of the 3-2
SS Valve Assembly.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
20-32 ohm Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
10 1. Disconnect the
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly
from the 3-2 SS Valve
Assembly.
2. Measure the
resistance from the
components’ terminals
to earth.
Are both measurements
greater than the specified
value?
250K ohm Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
11 1. Check circuit 897 for
an open.
2. Check circuit 897 for a
short to B+.
3. Check circuit 897 for a
short to earth.
4. Repair the circuit as
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
12 Replace the PCM. Refer
to section 3 for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
13 Replace the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly. Refer
to Service Operations in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Is the replacement
complete?
Go to Step 15
14 Replace the 3-2 SS Valve
Assembly. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 SERVICE
OPERATIONS.
Is the replacement
complete?
Go to Step 15
15 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear info.
3. Drive the vehicle in D3.
Perform several 3-2
downshifts for at least
5 seconds at a time.
Does the 3-2 shift
solenoid change states
during a 3-2 downshift?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
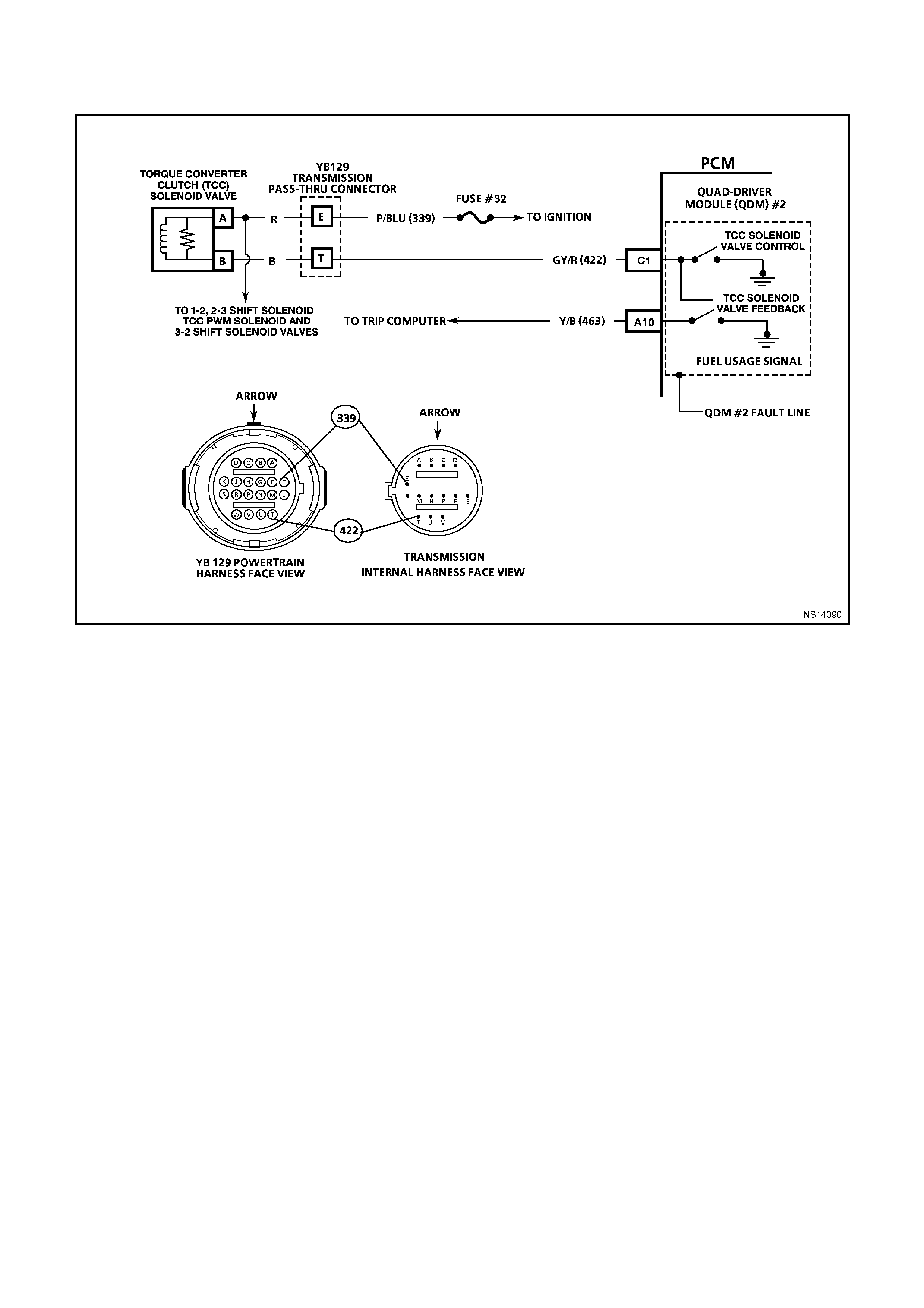
DTC 67 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) ENABLE SOLENOID
CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve (TCC Sol. Valve) is an electrical device used with the TCC PWM Sol.
Valve in order to control the fluid acting on the TCC valve. The TCC valve controls TCC application and release.
The solenoid is a normally-open, ON/OFF device. The TCC Sol. Valve attaches to the transmission case assembly
extending into the pump cover. The PCM monitors the TP voltage, the vehicle speed and other inputs in order to
determine when to energise the TCC Sol. Valve. The TCC Sol. Valve receives ignition voltage through circuit 339.
The PCM controls the solenoid by providing the ground path on circuit 422.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or a continuous short to earth in the TCC Sol. Valve circuit or in the TCC
Sol. Valve, then DTC 67 sets.
DTC 67 WILL SET IF:
• The system voltage is 10-16 volts.
• The above condition is met for 5 seconds and either of the following fail conditions occurs for 4 seconds.
• The PCM commands the solenoid ON and the voltage remains high (B+).
• The PCM commands the solenoid OFF and the voltage remains low (0 volt).
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) 67 will set if there is a fault detected on the TCC solenoid circuit
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. An open fuse indicates a short in circuit 339. A short in any of the five solenoids fed by circuit 339 may cause
an open fuse.
6. This step tests the ability of the PCM and wiring to control the earth circuit.
8. This tests the resistance of the TCC Sol. Valve and the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions:
A backed out terminal
A damaged terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Corrosion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• With the TCC engaged, the TCC slip speed should be -20 to +20 RPM.
• A short to earth in the TCC Sol. Valve circuit may also set a TCC Stuck On DTC 69.
When DTC 67 sets, the PCM inhibits TCC engagement, inhibits 4th gear if the transmission is in hot mode.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. If DTCs 66, 81, 82 or
83 are also set, inspect
the F32 fuse for an
open.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Check circuit 339 for a
short to earth.
2. Check each of the five
solenoids for being
internally shorted or
shorted to earth.
3. Check the A/T Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a short to earth on
each of the five
solenoid circuits.
4. Make the
repair/replacement if
necessary.
Did you find and correct a
problem?
Go to Step 12 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Turn the ignition switch
OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector
(additional DTCs may
set).
3. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the engine harness
connector.
4. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
5. Connect a test tamp
from cavity E of the J
39775 Jumper
Harness to a known
good earth.
Is the test lamp ON?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the open in the
ignition feed circuit 339 to
the transmission pass-
through connector.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 12
61. Install the test lamp
from cavities E to T of
the J 39775 Jumper
Harness.
2. Using the device
control function on the
scan tool, command
the TCC Sol. Valve ON
and OFF three times.
Does the test lamp turn
ON when the TCC Sol.
Valve is commanded ON,
and OFF when
commanded OFF?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
71. Check circuit 422 for
an open.
2. Check circuit 422 for a
short to B+.
3. Check circuit 422 for a
short to earth.
4. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 9
81. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the transmission pass-
through connector.
2. Using the J 39200
DVM and the J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance between
terminals T and E.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
21-33 ohm Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
9Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
the Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 12
10 Measure the resistance
between terminal E and
earth then terminal T and
earth.
Are both readings greater
than the specified value?
250 K ohm Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 11
11 Replace the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness
Assembly (this includes
the TCC Sol. Valve).
Refer to Service
Operations in Section 7C-
5 AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 12
12 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• The PCM commands
the TCC Sol. Valve
ON, and the TCC
Feedback is ON.
• The PCM commands
the TCC Sol. Valve
OFF, and the TCC
Feedback is OFF.
Are both conditions met
for 4 seconds?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
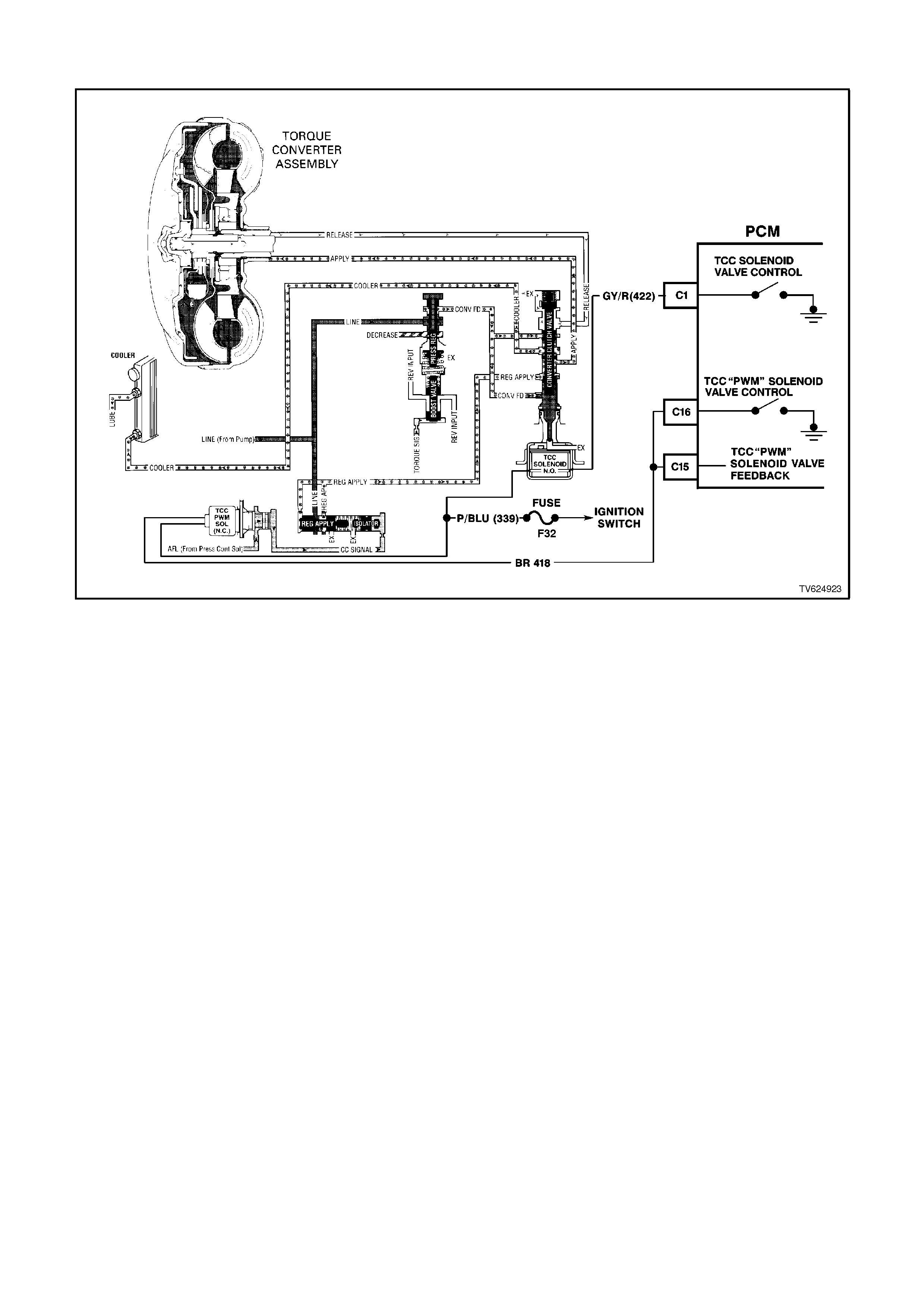
DTC 69 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) - STUCK ON
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM energises the Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve (TCC Solenoid Valve) by creating an earth path on
circuit 422. When circuit 422 is earthed (energised) by the PCM, the TCC Solenoid Valve stops converter signal oil
from exhausting. This causes converter signal oil pressure to increase and move the TCC valve. The TCC Solenoid
Valve de-energises when the PCM no longer provides a path to earth. When the TCC Solenoid Valve de-energises,
the valve exhausts fluid and releases the TCC.
When the PCM detects low torque converter slip when the PCM commands the TCC OFF, then a DTC 69 sets.
DTC 69 WILL SET IF:
The following conditions occur once per TCC cycle, two consecutive times.
• No TP DTCs 19, 21 or 22.
• No VSS Assembly DTC 24.
• No TFP Valve Position Switch DTC 28.
• No TCC Solenoid Valve DTC 67.
• No TCC PWM Solenoid Valve DTC 83.
• The TP angle is greater than 25%.
• The engine speed is greater than 450 RPM for 8 seconds.
• The commanded gear is not 1st.
• The gear range is D4 or D3.
• The PCM commands the TCC OFF.
• The Trans Slip Speed is -20 to +20 RPM.
• All the above conditions are met for 4 seconds.
Diagnostic Trouble Code 69 is for determining a mechanical fault which will cause the Torque Converter Clutch to
be stuck ON. An electrical fault in the torque converter clutch solenoid circuit which could cause the torque
converter clutch to be "Stuck ON" is diagnosed in DTC 67.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3 This step inspects the mechanical state of the TCC. When the PCM commands the TCC Solenoid Valve OFF,
the slip speed should increase to greater than +50 RPM.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• The TCC fluid will mechanically apply the TCC, possibly causing an engine stall, under the following conditions:
The TCC is mechanically stuck ON
The parking brake is applied
Any gear range is selected
A stuck TP sensor may set DTC 69.
When DTC 69 sets, the PCM freezes shift adapts from being updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Using the scan tool,
verify the TP Sensor
operation.
Are the TP Sensor values
within the normal range
(shown in the value
column)?
0.6 to
5.0 volts Go to Step 3 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
3Drive the vehicle in the D4
drive range in fourth gear
under steady acceleration,
with a TP angle greater
than 25%.
While the displayed TCC
Solenoid status is No,
does the scan tool display
a Trans Slip Speed within
the specified range?
-20 to
+20
RPM
Go to Step 4 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
4The TCC is mechanically
stuck ON. Inspect for the
following conditions:
• A clogged exhaust
orifice in the TCC Sol.
Valve.
• The converter clutch
apply valve is stuck in
the apply position.
• A misaligned or
damaged valve body
gasket.
• A restricted release
passage.
Did you find and correct a
problem?
Go to Step 5 Go to Symptoms-
No TCC Release
5In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• Hold the throttle at
25% and accelerate to
55 mph. Ensure that
the Trans Slip Speed
is -50 to +2500 RPM
for 5 seconds, with the
TCC commanded
OFF.
Was the slip speed
greater than 50 RPM in
2nd, 3rd and 4th gears
when the TCC was
commanded OFF?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
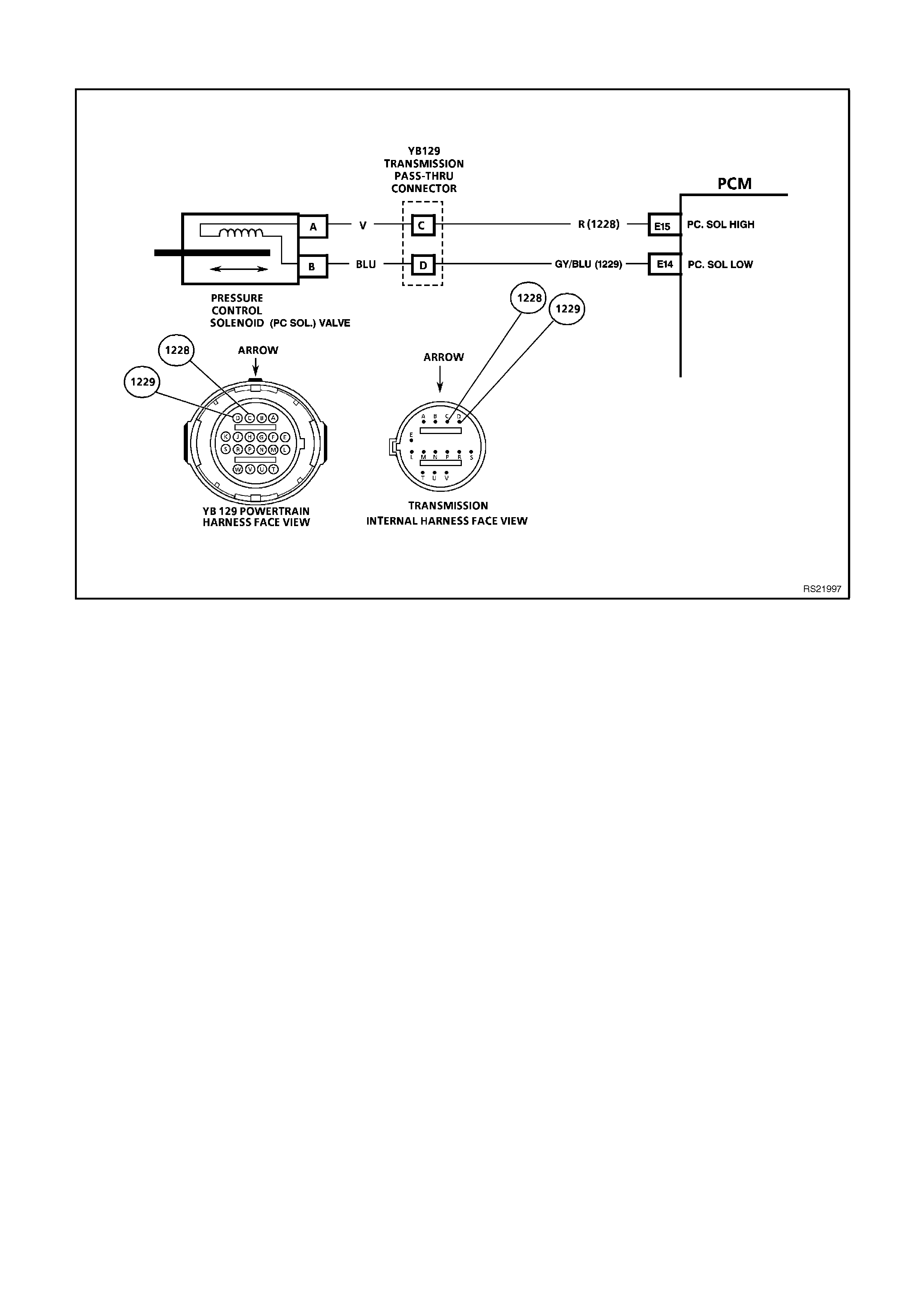
DTC 73 - PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUI T
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Pressure Control Solenoid Valve (PC Sol. Valve) is a PCM controlled device which regulates the transmission
line pressure. The PCM compares the TP voltage, the engine speed and other inputs in order to determine the
appropriate line pressure for a given load. The PCM applies a varying amperage to the PC Sol. Valve in order to
regulate the pressure. The applied amperage can vary from 0.1 to 1.1 amps. The PCM monitors the amperage.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or short to earth in the PC Sol. Valve circuit or the PC Sol. Valve, then a
DTC 73 sets.
DTC 73 WILL SET IF:
• DTC 75 is not set.
• The system voltage is between 10 and 16 volts.
• The engine is running.
• The difference between the PC Sol. Valve actual return amperage and the desired amperage is 0.16 amp or
greater.
Once a DTC 73 is set, the pressure control solenoid is disabled and full line pressure will be applied until the next
time the ignition key is cycled. If upon restart, the current error does not exist, a DTC 73 will remain stored. The
pressure control solenoid will then resume normal function.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
2. This step tests the ability of the PCM to command the PC Sol. Valve.
3. This step tests the PC Sol. Valve and Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly for correct
resistance.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
Corrosion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
When a DTC 73 sets, the PCM will command the PC Sol. Valve OFF, producing maximum line pressure. The PCM
will also freeze shift adapts from being updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. While the engine is
operating, put the
transmission in Park
position.
5. Using the transmission
output control function
on the scan tool, apply
0.1 amp through 1.0
amp while observing
the Commanded PCS
the Actual PCS
amperage.
Is the Actual PCS
amperage always within
the specified value of the
Commanded PCS
amperage?
0.16
amp Go to
“Diagnostic Aids”
above
Go to Step 3
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector.
3. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the transmission side
of the pass-through
connector.
4. Using the J 39200
DVM and J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance between
terminal C and
terminal D.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
3-7 ohm Go to Step 8 Go to Step 4
4Is the resistance greater
than the specified value? 7 ohm Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
51. Check the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly for
an open.
2. Replace the harness if
necessary. Refer to
Service Operations in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 10
6Is the resistance less than
the specified value? 3 ohm Go to Step 7
71. Check the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a shorted together
condition.
2. Replace the harness if
necessary. Refer to
Service Operations.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 10
8Using the J 39200 DVM
and J 35616 Connector
Test Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance from
terminal C to the
transmission case .
Is the resistance less than
the specified value?
9 ohm Go to Step 9 Go to Step 11
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
91. Check the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a short to earth.
2. Replace the harness if
necessary. Refer to
Service Operations in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 10
10 Replace the PC Sol.
Valve.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
11 1. Disconnect the J
39775 Jumper
Harness from the
transmission side of
the pass-through
connector.
2. Reconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector.
3. Disconnect the PCM
connector 3 (BLU 32
pin).
4. Using the J 39200
DVM and the J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance from
terminal E15 to earth.
Is the resistance greater
than the specified value?
9 ohm Go to Step 12 Go to Step 13
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
12 1. Inspect circuit 1228
and circuit 1229 for an
open.
2. Repair the circuits if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
13 1. Check circuit 1228 and
circuit 1229 for a short
to earth.
2. Repair the circuits if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15
14 Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
the Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
15 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• The engine is running.
• Observe the Actual
PCS amperage and
the Commanded PCS
amperage.
Is the difference between
the Actual PCS amperage
and the Commanded PCS
amperage less than the
specified value?
0.16
amp System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1

DTC 75 - SYSTEM VOLTAGE LOW
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Circuit 39 is the ignition voltage feed circuit to terminal A4 for the PCM. Circuit 740 is the battery voltage feed circuit
to terminals A8 and B8 for the PCM. When the PCM detects a low voltage for a short period of time, then DTC 75
sets.
DTC 75 WILL SET IF:
• The system voltage is less than 7.3 volts with the TFT at -40°C.
- OR -
• The system voltage is less than 10 volts with the TFT at 151°C.
One of the above conditions is met for 4 seconds.
Minimum voltage allowed for Diagnostic Trouble Code 75 to set is on a graduated scale and will change with
temperature. The minimum voltage at - 40 degrees C is 7.3 volts. The minimum voltage at 151 degrees C is 10.0
volts. The minimum voltage at 90 degrees C is 8.6 volts.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
4. This tests the charging system voltage.
6. This tests for proper voltage to the PCM on circuits 39 and 740.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• Charging the battery with a battery charger may set DTCs. Jump starting an engine may set DTCs.
• If DTCs set when an accessory is switched ON, inspect the applicable wiring for faulty connections. Inspect the
wiring for excessive current draw.
• Inspect the following items for faulty connections:
The starter solenoid
The fusible link
The generator terminals
Battery cables to earth
• Inspect the belts for excessive wear. Inspect the belts for proper tension.
When DTC 75 sets, the PCM will turn off all transmission output devices and freezes shift adapts from being
updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Using the J 39200
DVM, measure the
battery voltage across
the battery terminals.
Is the voltage higher than
the specified value?
10 volts Go to Step 3 Go to Battery
Diagnosis.
31. Start the engine.
2. Warm the engine to
the normal operating
temperature.
Is the generator/check
engine light ON?
Go to Charging
System Diagnosis Go to Step 4
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Turn on the headlights
and the heater blower
motor.
2. Increase the engine
speed to 1500 RPM.
3. Observe the DVM
battery voltage and
record your reading for
reference.
Is the DVM voltage within
the specified range?
13-15
volts Go to Step 5 Go to Charging
System Diagnosis
51. Increase the engine
speed to 1500 RPM.
2. Observe the scan tool
battery voltage.
Is the scan tool Battery
Voltage within the
specified range?
13-15
volts System Checks
OK, Go to
“Diagnostic Aids”
above
Go to Step 6
61. Turn the ignition switch
to OFF position.
2. Locate terminals A4,
A8 and B8 in the PCM
connector 2 (24 pin).
Do not disconnect the
PCM connector.
3. Connect the DVM
black lead to earth.
4. Start the engine.
5. Run the engine at
1500 RPM with the
headlights and the
blower motor on.
6. Using the J 39200
DVM and J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, backprobe
terminals A4, A8 and
B8 to measure the
battery voltage input at
the PCM connector.
Is there a voltage variance
between the voltage
measured at the battery
(taken in Step 4) and at
terminals A4, A8 and B8
that is greater than the
specified value?
0.5 volts Go to Step 7 Go to Step 10
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Does terminal A4 (circuit
39) have the voltage
variance?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8Repair the high resistance
condition in circuit 39.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 11
9Repair the high resistance
condition in circuit 740.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 11
10 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 11
11 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure.
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• Start the vehicle.
• Warm the engine to
normal operating
temperature.
Is the scan tool Battery
Voltage within the
specified range?
13-15.5
volts System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
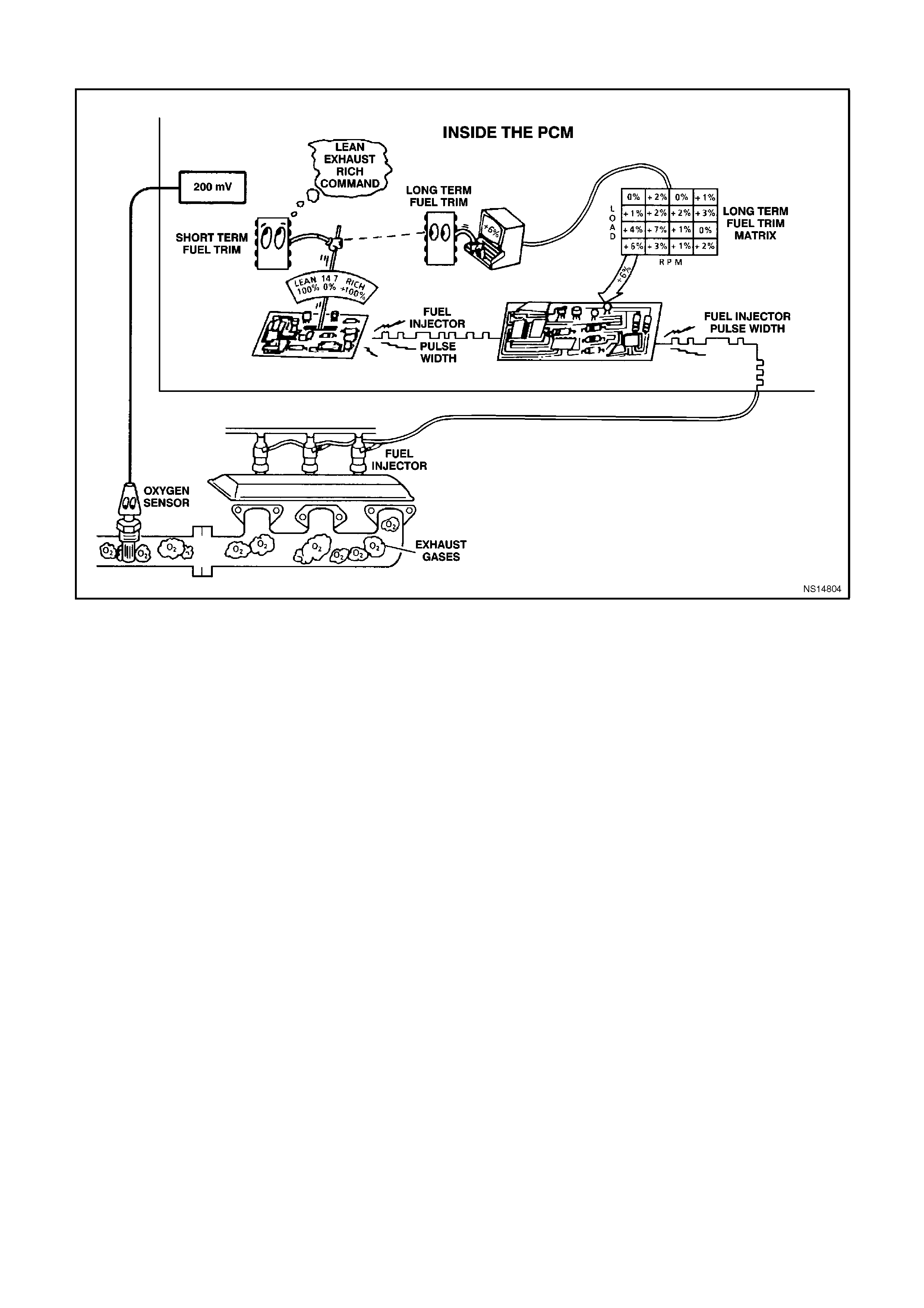
DTC 76 - SHORT TERM FUEL TRIM (STFT) DELTA HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM controls left to right cylinder bank fuel delivery separately based on their respective oxygen sensor
signals. If the PCM detects too great a difference between the left to right cylinder bank Short Term (ST) Fuel Trim
values, a DTC 76 will set.
A DTC 76 will set when the left bank Short Term Fuel Trim value differs from the right bank Short Term Fuel Trim
by more than 63% for 32 seconds while in closed loop.
With a current DTC 76 set, the PCM will not illuminate the MIL (Check Powertrain Lamp). A DTC 76 will clear when
the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is cycled OFF and ON.
DTC 76 WILL SET IF:
• The fuel system is operating in closed loop.
• The above condition is present for 32 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
2. Check and repair other DTC(s) first.
3. Check for other mechanical problems causing the DTC to set.
4. The bank that is the farthest from the neutral value of 0% is the bank which is out of fuel control.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• •Lean or faulty injector(s) on one side of the engine
• Cracked or fouled spark plug(s)
• Exhaust or inlet manifold leak
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Are any other PCM
DTC(s) set? Diagnose other
DTC(s) first Go to Step 3
3Is there a Driveability
complaint associated with
this DTC such as an
Engine Miss, Lack of
Power, or Poor Fuel
Economy?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
41. Start Engine and allow
to warm up (Coolant
Temperature above 85
degrees C).
2. Install Tech 2 "Scan"
tool and note left and
right bank Short Term
Fuel Trim values.
Is the left bank Short
Term Fuel Trim values
further from 0% then the
right bank?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Perform Oxygen Sensor
(O2S) Diagnosis, Chart A-
6.3 in this Section.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
61. Start the engine and
allow it to warm up
(Coolant Temperature
above 85 degrees C).
2. Install a Tech 2 "Scan"
tool and note the left
and right bank Short
Term Fuel Trim
values.
Is the right bank Short
Term Fuel Trim values
further from 0% then the
left bank?
Go to Step 5 DTC 76 is
intermittent. Refer
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
7Perform the following
tests in the order given
until the problem is
corrected.
1. Fuel system check,
(refer Chart A- 4.2 in
this Section).
2. Oscilloscope the
Engine, note and
repair any Ignition
System problems
found.
3. Compression test each
cylinder.
Is the action complete ?
Verify Repair
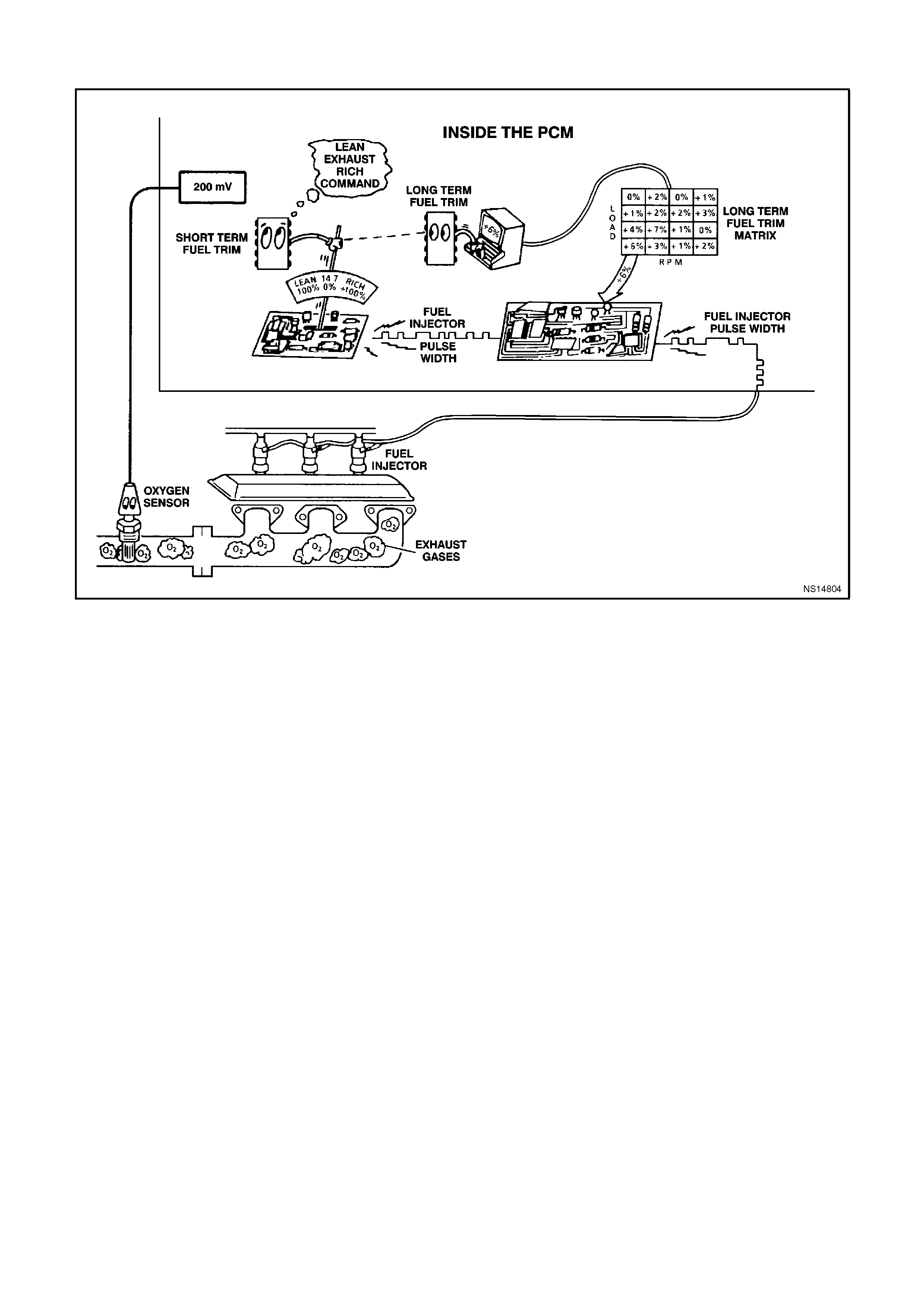
DTC 78 - LONG TERM FUEL TRIM (LTFT) DELTA HIGH
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM controls left to right cylinder bank fuel delivery separately based on their respective oxygen sensor
signals. If the PCM detects too great a difference between the left to right cylinder bank Long Term Fuel Trim
values, it will set a DTC 78.
A DTC 78 will set when the left bank Long Term Fuel Trim value differs from the right bank Long Term Fuel Trim by
more than 59% for 32 seconds while in closed loop.
With a DTC 78 set, the PCM will not illuminate the MIL (Check Powertrain Lamp). A DTC 78 will clear when the fault
no longer exists and the ignition switch is cycled OFF and ON.
DTC 78 WILL SET IF:
• The engine is idling.
• The Left to Right Short Term Fuel Trim values differs by more than 59% for 32 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
2. Check and repair other DTC(s) first.
3. Check for other mechanical problems causing DTC to set.
4. The bank that is the farthest from the neutral value of 0% is the bank which is out of fuel control.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Lean or faulty injector(s) on one side of the engine.
• Cracked or fouled spark plug(s).
• Exhaust or inlet manifold leak.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
2Are any other PCM
DTC(s) set? Diagnose other
DTC(s) first Go to Step 3
3Is there a Driveability
complaint associated with
this DTC such as an
Engine Miss, Lack of
Power, or Poor Fuel
Economy?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
41. Start the Engine and
allow to warm up
(Coolant Temperature
above 85 degrees C).
2. Install Tech 2 "Scan"
tool and note left and
right bank Long Term
Fuel Trim values.
Is the left bank Long Term
Fuel Trim values
furtherfrom 0% then the
right bank?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5Perform Oxygen Sensor
(O2S) Diagnosis, Chart A-
6.3 in this Section.
Is action complete?
Verify Repair
61. Start Engine and allow
to warm up (Coolant
Temperature above 85
degrees C).
2. Install Tech 2 "Scan"
tool and note left and
right bank Long Term
Fuel Trim values.
Is the right bank Long
Term Fuel Trim values
furtherfrom 0% then the
left bank?
Go to Step 5 DTC 78 is
intermittent. Refer
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
7Perform the following
tests in the order given
until the problem is
corrected :
• Fuel System check,
(refer Chart A-4.2 in
this Section).
• Oscilloscope the
Engine, note and
repair any Ignition
System problem found.
• Compression test each
cylinder.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
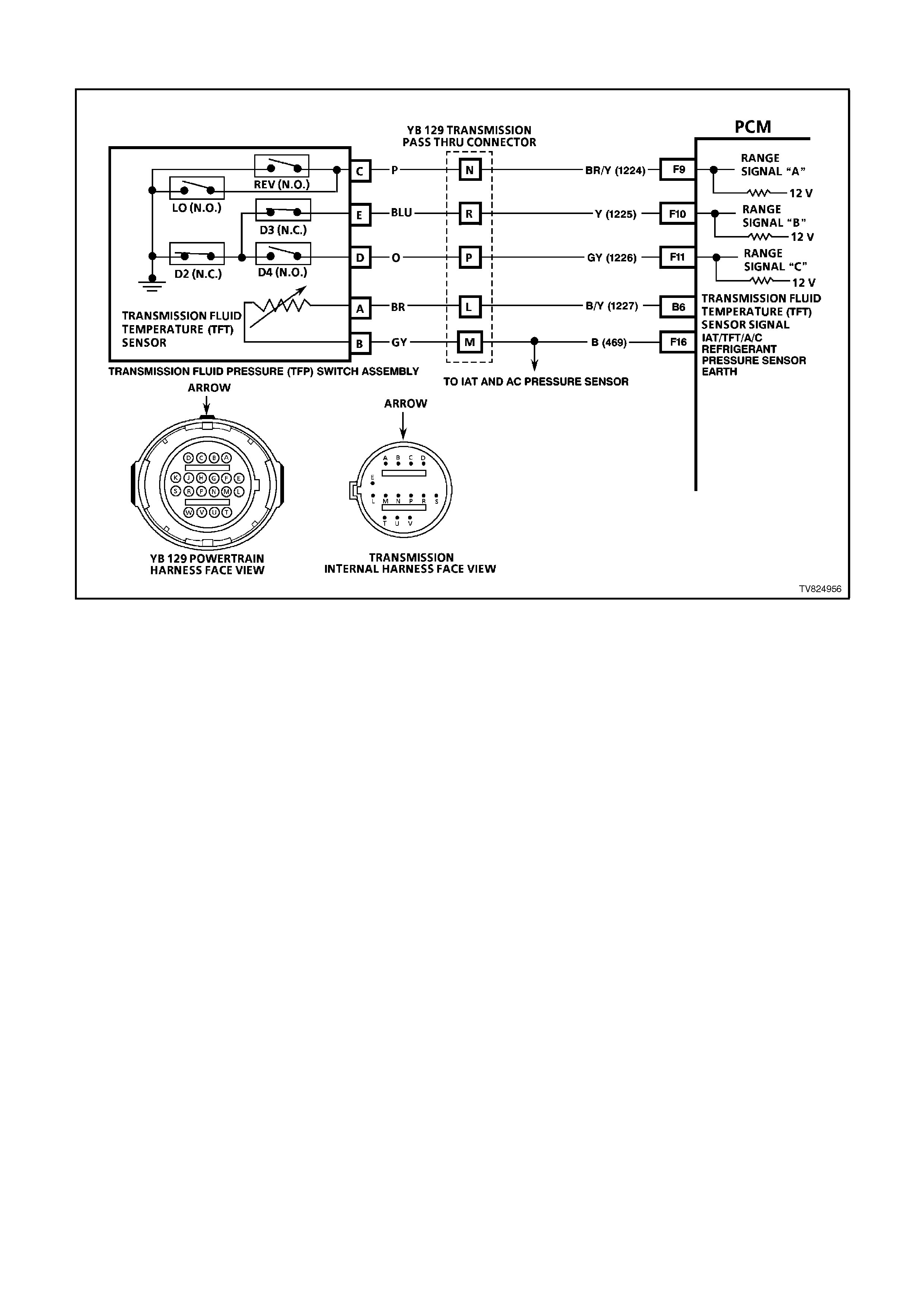
DTC 79 - TRANSMISSION FLUID OVER-TEM PERATURE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The flow of transmission fluid starts in the bottom of the pan and is drawn through the filter, control valve body
assembly, transmission case and into the oil pump assembly. The oil pump assembly pressurises the fluid and
directs it to the pressure regulator valve where it becomes the main supply of fluid to the various components and
hydraulic circuits in the transmission. Hot fluid exiting the torque converter flows through the converter clutch apply
valve and into the transmission cooler lines to the oil cooler located in the radiator (and auxiliary cooler if equipped).
From the cooler, fluid returns to cool and lubricate the front of the transmission. In forward drive ranges, D4 fluid
from the manual valve is routed through an orifice cup plug in the rear of the transmission case to feed the rear lube
fluid circuit.
When the PCM detects a high transmission fluid temperature (TFT) for a long period of time, then DTC 79 sets.
DTC 79 WILL SET IF:
• No TFT sensor DTC 58.
• The TFT is greater than 146°C. Then the TFT is greater than 137°C for 30 minutes.
As the transmission fluid temperature warms (normal transmission operating temperature ranges from 82 degrees
C to 94 degrees C). The sensor's resistance becomes less and the voltage will measure between 1.5 to 2.0 volts. If
the fluid temperature becomes greater than 146 degrees C and does not drop below 137 degrees C for 30 minutes,
a DTC 79 will set.
When a DTC 79 sets the transmission fluid may beseverely degraded.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. DTC 58 may also set a DTC 79. Go to the DTC 58 table for diagnosis.
4. This step inspects for air restrictions and loss of transmission fluid flow, causing an extremely high TFT.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the cooling system fluid level and condition.
• A DTC 79 may set approximately 30 minutes after a DTC 58 has set. Follow the diagnostic charts for a DTC 58
before proceeding to the diagnostic table for a DTC 79. Repairing the condition that set a DTC 58 will likely
eliminate a DTC 79.
• The TFT temperature displayed on the scan tool should rise steadily to a normal operating temperature, then
stabilize.
• Inspect the torque converter stator for a possible problem.
• Ask about the customer's driving habits, trailer towing, etc.
When a DTC 79 sets, the PCM freezes shift adapts from being updated.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Perform the
transmission fluid
checking procedure.
Refer to Transmission
Fluid Checking
Procedure.
Was the fluid checking
procedure performed?
Go to Step 3 Go to
Transmission
Fluid Checking
Procedure
3Is DTC 58 also set? Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 4
41. Inspect the cooling
system for the
following conditions:
Air flow restrictions
Air flow blockage
Debris
2. Inspect the
transmission cooling
system for the
following conditions:
Air flow restrictions
Air flow blockage
Debris
Damaged cooler lines
3. Repair restrictions if
necessary.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
51. Drive the vehicle in D4
with the TCC
commanded On.
2. Observer the TCC slip
speed on the scan
tool.
Is the TCC slip speed
within the specified value?
-20 to
+20
RPM
Go to Step 6 Refer to Torque
Converter Clutch
Diagnosis
Symptoms
6Perform the Line Pressure
Check Procedure. Refer
to Section 7C-3.
Was a problem found?
Go to Step 7 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
7In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Drive the vehicle to
normal operating
engine and
transmission
temperature.
4. Observe the TFT
during the entire drive.
Is the TFT less than the
specified value during the
entire drive?
137°C System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
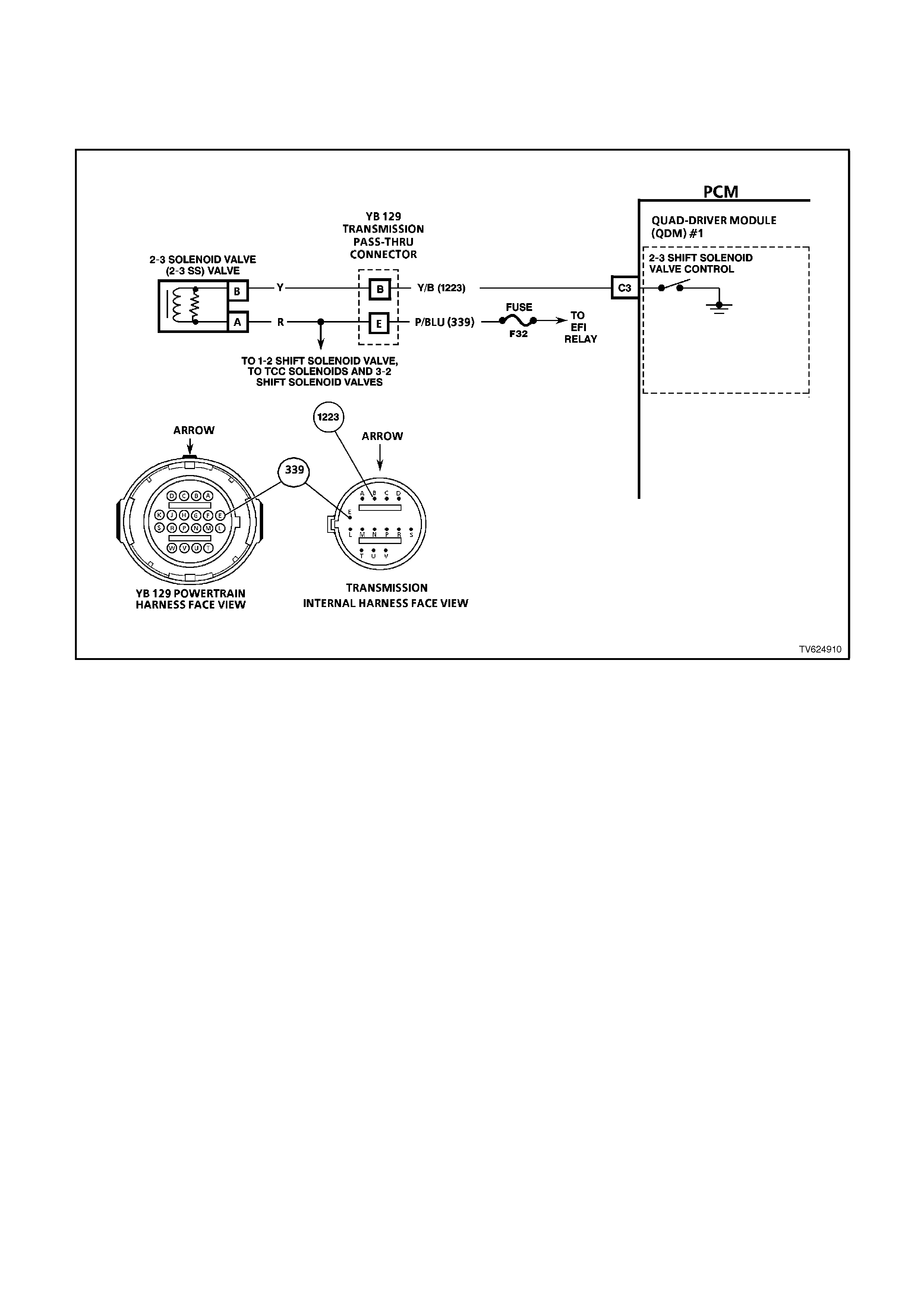
DTC 81 - 2-3 SHIFT SOLENOID CI RCUI T FAULT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The 2-3 Shift Solenoid Valve (2-3 SS Valve) controls the fluid flow acting on the 2-3 shift valves. The 2-3 SS Valve
is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the 1-2 Shift Solenoid Valve in order to allow four different shifting
combinations. The solenoid attaches to the control valve body within the transmission. The 2-3 SS Valve receives
ignition voltage through circuit 339. The PCM controls the solenoid by providing a path to earth on circuit 1223.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or short to earth in the 2-3 SS Valve circuit or the 2-3 SS Valve, then
DTC 81 sets.
DTC 81 WILL SET IF:
Either of the following conditions occurs for 4 seconds.
• The PCM commands the solenoid ON and the voltage remains high (B+).
• The PCM commands the solenoid OFF and the voltage remains low (0 volts).
The PCM continually monitors the voltage on each circuit connected to the "quad driver" module. The PCM looks
for either a low or a high voltage depending on the commanded state of the devices connected to the PCM.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. An open fuse indicates a short circuit or a short to earth on circuit 339. A short in any of the five solenoids fed
by circuit 339 may cause an open fuse.
4. This tests the function of the 2-3 SS Valve and the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly.
5. This tests for power to the transmission pass-through connector from the ignition through the fuse.
6. This tests the ability of the PCM and the wiring to control the earth circuit.
13. This step measures the resistance of the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly and the 2-3 SS
Valve.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
Refer to the following chart for the correct On and Off states of the shift solenoids.
GEAR 1-2 SHIFT
SOLENOID 2-3 SHIFT
SOLENOID
1ON ON
2OFF ON
3OFF OFF
4ON OFF
When DTC 81 sets, the PCM commands third gear only, maximum line pressure, freezes shift adapts from being
updated and inhibits TCC engagement.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. If DTCs 66, 67, 82, or
83 are also set, inspect
the F32 fuse for an
open.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
31. Check circuit 339 for a
short to earth.
2. Check each of the five
solenoids for being
internally shorted or
shorted to earth.
3. Check the A/T Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a short to earth on
each of the five
solenoid circuits.
4. Make the
repair/replacement if
necessary.
Did you find and correct a
problem?
Go to Step 19 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
4Using the device control
function, command the 2-
3 SS Valve ON and OFF
three times while listening
to the bottom of the
transmission pan (a
stethoscope may be
necessary).
Does the solenoid click
when commanded?
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 5
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector
(additional DTCs will
set).
3. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the engine side of the
pass-through
connector.
4. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
5. Connect a test lamp
from J 39775 Jumper
Harness cavity E to
earth.
Is the test light ON?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
61. Install a test lamp from
cavity E to cavity B of J
39775 Jumper
Harness.
2. Using the device
control function,
command the 2-3 SS
Valve ON and OFF
three times.
Is the test lamp ON when
the 2-3 SS Valve is
commanded ON and OFF
when commanded OFF?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 8
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
7Repair the open in the
ignition feed circuit 339 to
the 2-3 SS Valve.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
8Monitor the test lamp
status.
Was the test lamp OFF at
all times?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
91. Check circuit 1223 for
an open.
2. Check circuit 1223 for
a short to B+.
3. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 12
10 Was the test lamp ON at
all times? Go to Step 11
11 1. Check circuit 1223 for
a short to earth.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 12
12 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 3 for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
13 1. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the transmission pass-
through connector.
3. With J 39200 DVM and
J 35616 Connector
Test Adapter Kit,
measure the
resistance between
terminals B and E.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
19-31 ohm Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
14 1. Disconnect the
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly
from the 2-3 SS Valve.
2. Measure the
resistance of the 2-3
SS Valve.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
19-31 ohm Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
15. Using J 39200 DVM,
measure the resistance
between terminals B and
E and earth.
Are both readings greater
than the specified value?
250 ohm Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 16
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
16 1. Disconnect the
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly
from the 2-3 SS Valve.
2. Using J 39200 DVM,
measure the
resistance from the
component's terminals
to earth.
Are both readings greater
than the value shown?
250 ohm Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
17 Replace the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly. Refer
to Service Operations, in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
18 Replace the 2-3 SS Valve.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
19 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions while
observing the 2-3 Shift
Sol. and 2-3 Shift Sol.
Feedback:
• The PCM
commands the 2-3
SS Valve ON and
the 2-3 Shift Sol.
Feedback is ON.
• The PCM
commands the 2-3
SS Valve OFF and
the 2-3 Shift Sol.
Feedback is OFF.
Have both conditions
been met for 4 seconds?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again
Go to Step 1
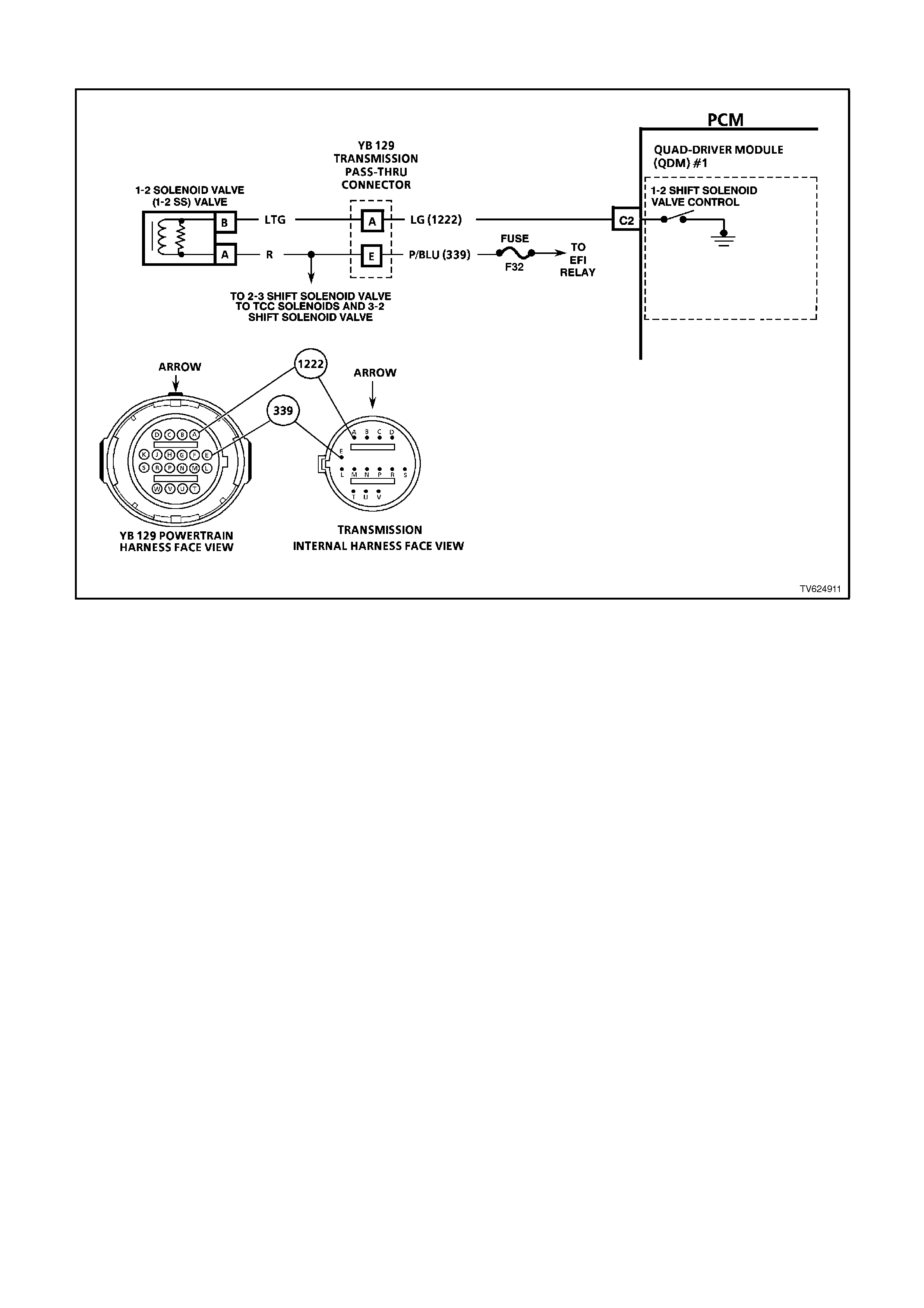
DTC 82 - 1- 2 SHIFT SOLENOID CI RCUI T FAULT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The 1-2 Shift Solenoid Valve (1-2 SS Valve) controls the fluid flow acting on the 1-2 and 3-4 shift valves. The 1-2 SS
Valve is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the 2-3 Shift Solenoid Valve in order to allow four different
shifting combinations. The solenoid attaches to the control valve body within the transmission. The 1-2 SS Valve
receives voltage through circuit 339. The PCM controls the solenoid by providing the ground path on circuit 1222.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or a short to earth in the 1-2 SS Valve circuit or the 1-2 SS Valve, then
DTC 82 sets.
DTC 82 WILL SET IF:
Either of the following fail conditions occurs for 4 seconds.
• The PCM commands the solenoid ON and the voltage remains high (B+).
• The PCM commands the solenoid OFF and the voltage remains low (0 volts).
When a DTC 82 sets, the PCM commands the maximum line pressure and freezes the shift adapts from being
updated.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. An open fuse indicates a short circuit in circuit 339. A short in any of the five solenoids fed by circuit 339 may
cause an open fuse.
4. This tests the function of the 1-2 SS Valve and the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly.
5. This tests for power to the 1-2 SS Valve from the F32 fuse.
6. This tests the ability of the PCM and the wiring to control the earth circuit.
13. This measures the resistance of the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly and the 1-2 SS Valve.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM and at the transmission pass-through connector.
Look for the following conditions:
A backed out terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
• An open ignition feed circuit can cause multiple DTCs to set.
Refer to the following chart for the correct On and Off states of the shift solenoids.
GEAR 1-2 SHIFT
SOLENOID 2-3 SHIFT
SOLENOID
1ON ON
2OFF ON
3OFF OFF
4ON OFF
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. If DTCs 66, 67, 81, or
83 are also set, inspect
the F32 fuse for an
open.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Check circuit 339 for a
short to earth.
2. Check each of the five
solenoids for being
internally shorted or
shorted to earth.
3. Check the A/T Wiring
Harness Assembly for
a short to earth on
each of the five
solenoid circuits.
4. Make the
repair/replacement if
necessary.
Did you find and correct a
problem?
Go to Step 19 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
4Use the scan tool device
control function to
command the 1-2 SS
Valve ON and OFF three
times while listening to the
bottom of the
transmission pan (a
stethoscope may be
necessary).
Does the solenoid click
when commanded?
Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 5
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector
(additional DTCs will
set).
3. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the engine harness
connector.
4. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
5. Connect a test lamp
from J 39775 Jumper
Harness cavity E to
earth.
Is the test lamp ON?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
61. Install a test lamp from
J 39775 Jumper
Harness cavity E to
cavity A.
2. Using the
Transmission Output
Control function on the
scan tool, command
the 1-2 SS Valve ON
and OFF three times.
Is the test lamp ON when
the 1-2 SS Valve is
commanded ON and OFF
when commanded OFF?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 8
7Repair the open in the
ignition feed circuit 339 to
the 1-2 SS Valve.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
8Monitor the test lamp
status.
Was the test lamp OFF at
all times?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
91. Check circuit 1222 for
an open.
2. Check circuit 1222 for
a short to B+.
3. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find and repair the
problem?
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 12
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
10 Was the test lamp ON at
all times? Go to Step 11
11 1. Check circuit 1222 for
a short to earth.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 19 Go to Step 12
12 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
13 1. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Install the J 39775
Jumper Harness on
the transmission pass-
through connector.
3. With the J 39200 DVM
and J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance between
terminals A and E.
Is the resistance within
the range shown?
19-31 ohm Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
14 1. Disconnect the internal
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly
from the 1-2 SS Valve.
2. Measure the
resistance of the 1-2
SS Valve.
Is the resistance within
the range shown?
19-31 ohm Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
15 Using J 39200 DVM,
measure the resistance
between terminals A and
E and earth.
Are both readings greater
than the specified value?
250K W Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 16
16 1. Disconnect the internal
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly
from the 1-2 SS Valve.
2. Using the J 39200
DVM, measure the
resistance from the
component's terminals
to earth.
Are both readings greater
than the specified value
250K ohm Go to Step 17 Go to Step 18
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
17 Replace the internal
Automatic Transmission
Wiring Harness
Assembly. Refer to
Service Operations in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
18 Replace the 1-2 SS Valve.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 19
19 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions while
observing the 1-2 shift
solenoid feedback on
the scan tool.
4. The PCM 1-2
commands the SS
Valve ON and the 1-2
shift solenoid feedback
displays ON.
5. The PCM commands
the 1-2 SS Valve OFF
and the 1-2 shift
solenoid feedback
displays OFF.
6. All conditions are met
for 4 seconds.
Did the scan tool display
ON when the solenoid
was commanded On and
then OFF when
commanded OFF?.
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
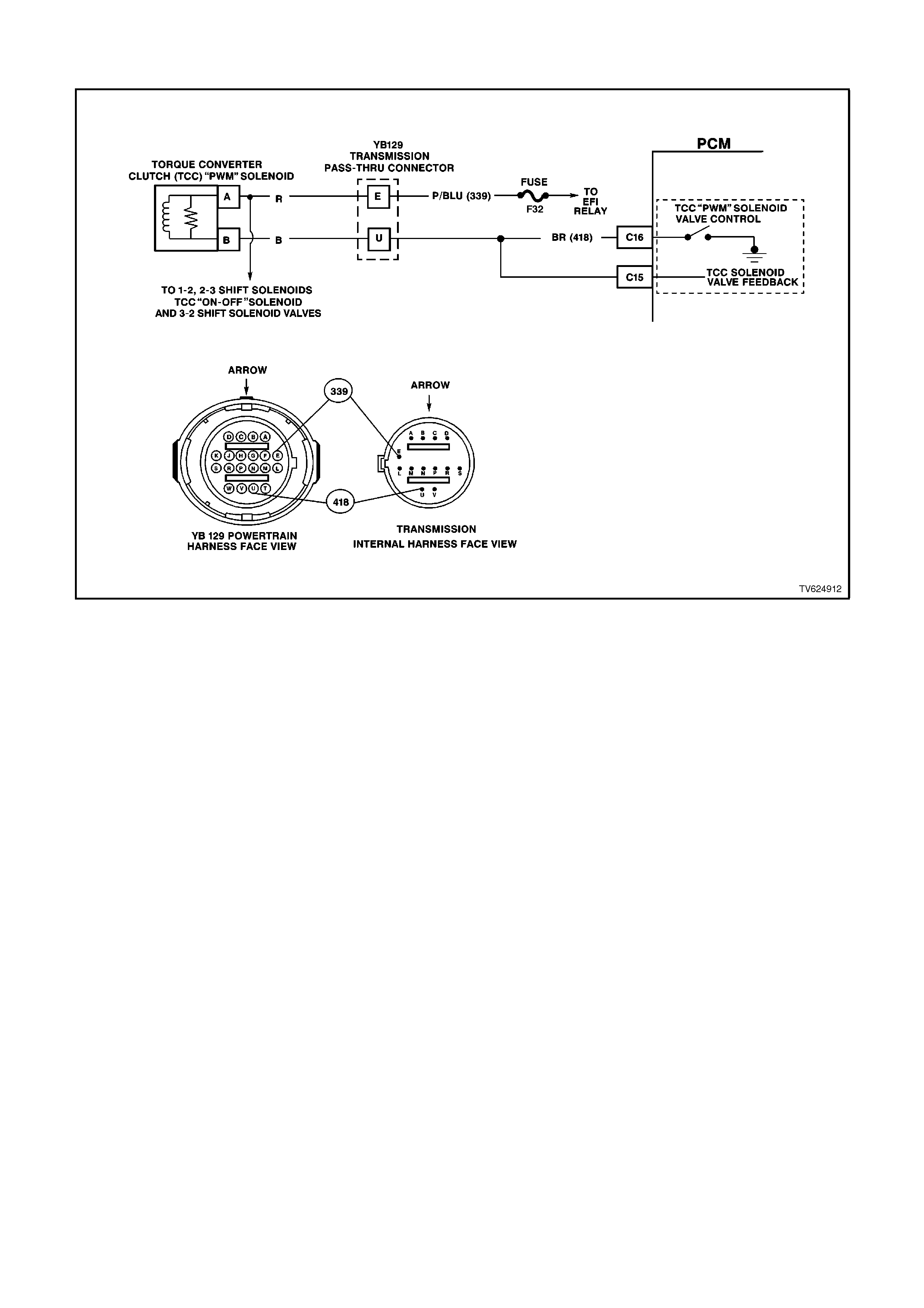
DTC 83 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC) SOLENOID CIRCUI T
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Torque Converter Clutch Pulse Width Modulation Solenoid Valve (TCC PWM Sol. Valve) controls the fluid
acting on the converter clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The
solenoid attaches to the control valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives ignition voltage through
circuit 339. The PCM controls the solenoid by providing a earth path on circuit 418. Current flows through the
solenoid coil according to the duty cycle (percentage of ON and OFF time). The TCC PWM Sol. Valve provides a
smooth engagement of the torque converter clutch by operating during a duty cycle percent of ON time.
When the PCM detects a continuous open or short to earth in the TCC PWM Sol. Valve circuit or the TCC PWM
Sol. Valve, then DTC 83 sets.
DTC 83 WILL SET IF:
Either of the following fail conditions occurs for 4 seconds.
• The PCM commands the solenoid ON (90%) and the voltage remains high (B+).
• The PCM commands the solenoid OFF (0%) and the voltage remains low (0 volt).
The TCC" PWM" solenoid is used in combination with the TCC Enable solenoid to regulate fluid to the torque
converter, and is attached to the control valve body within the transmission. The use of the Torque Converter Clutch
Pulse Width Modulated, (TCC PWM) solenoid provides the ability of being able to control more precisely, the rate of
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) apply and release.

TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. An open fuse indicates a short circuit in circuit 339. A short in any of the five solenoids fed by circuit 339 may
cause an open fuse.
4. This tests for voltage to the solenoid.
6. This tests the ability of the PCM and wiring to control the earth circuit.
This tests the resistance of the TCC PWM Sol. Valve and the Automatic Transmission Wiring Harness Assembly.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at
the transmission pass-through connector. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
A damaged terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
• When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
When DTC 83 Sets, the PCM inhibits TCC engagement and inhibit 4th gear.

STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. If DTCs 66, 67, 81, or
82 are also set, inspect
the F32 fuse for an
open.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
31. Check circuit 339 for a
short to earth.
2. Check each of the five
solenoids for being
internally shorted or
shorted to earth.
3. Check the A/T Wiring
Harness Assy. for a
short to earth on each
of the five solenoid
circuits.
4. Make the
repair/replacement if
necessary.
Did you find and correct a
problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
41. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the
transmission pass-
through connector
(additional DTCs may
set).
3. Install J 39775 Jumper
Harness on the engine
harness connector.
4. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
5. Connect a lest lamp
from J 39775 Jumper
Harness cavity E to
earth.
Is the test lamp on?
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5Repair the open in the
ignition feed circuit 339 to
the TCC PWM Sol. Valve.
Is the repair complete?
Go to Step 15
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
61. Install the test lamp
from cavity E to cavity
U of the J 39775
Jumper Harness.
2. Command the TCC
PWM Sol. Valve ON
and OFF three times.
Does the test lamp turn
ON when the TCC PWM
Sol. Valve is commanded
ON, and OFF when
commanded OFF?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
71. Check circuit 418 for
an open.
2. Check circuit 418 for a
short to B+.
3. Check circuit 418 for a
short to earth.
4. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 9
81. Install J 39775 Jumper
Harness on the
transmission pass-
through connector.
2. Using the J 39200
DVM and the J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, measure
the resistance between
terminals E and U.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
10-15 W Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
10 1. Disconnect the
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
harness Assembly at
the TCC PWM
Solenoid. Valve.
2. Measure the
resistance of the TCC
PWM Solenoid Valve.
Is the resistance within
the specified range?
10-15 W Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
11 Measure the resistance
between terminal E and
earth, and between
terminal U and earth.
Are both readings greater
than the specified value?
250 K W Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 12
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
12 1. Disconnect the
Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly at
the TCC PWM Sol.
Valve.
2. Measure the
resistance between
each of the component
terminals and a known
good earth.
Are both readings greater
than the specified value?
250 K W Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
13 Replace the Automatic
Transmission Wiring
Harness Assembly. Refer
to Service Operations in
Section 7C-5
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
14 Replace the TCC PWM
Sol. Valve. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations.
Is the action complete?
Go to Step 15
15 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions while
observing the TCC
PWM Sol. and TCC
Slip Speed:
• The PCM commands
the TCC PWM Sol.
Valve ON, and the
TCC Slip Speed is -20
to +20 rpm.
• The PCM commands
the TCC PWM Sol.
Valve OFF, and the
TCC Slip Speed is
greater than rpm 50.
Are both of the TCC Slip
conditions met for at least
4 seconds?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again
Go to Step 1
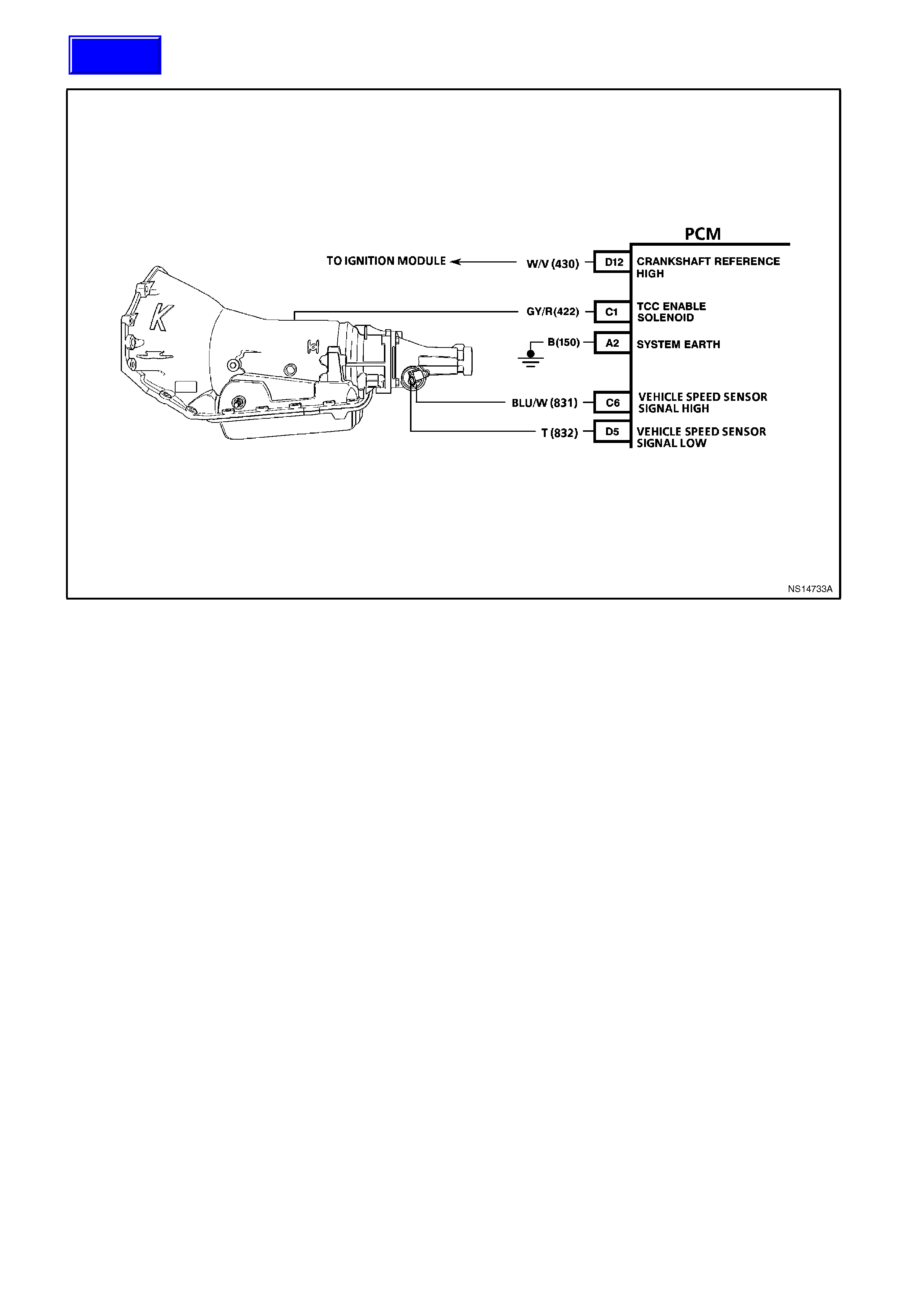
DTC 85 - TRANSMISSION SLIPPING
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM monitors the difference between the engine speed and the transmission output speed. In D3 drive range
with the TCC engaged, the engine speed should closely match the transmission output speed. In D4 drive range,
with the TCC engaged, the Trans Slip Speed should be -20 to +20 RPM.
When the PCM detects an excessive transmission slip speed when the TCC should be engaged, then DTC 85 will
set.
DTC 85 WILL SET IF:
• No DTC 28.
• The throttle angle is between 20% and 100%.
• The TCC is commanded ON.
• The TFT is between 60 and 150°C.
• The engine speed is greater than 450 RPM for 8
• seconds.
• The gear range is D3 or D4.
• The Trans Slip Speed is greater than 400 RPM for 30 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic chart.
3. This step tests the torque converter for slippage while in a commanded lock-up state.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• An internal transmission fault could set DTC 85.
When a DTC 85 sets, the PCM will inhibit the TCC engagement and 4th gear.
Techline
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check
2Perform the transmission
fluid checking procedure.
Have you performed the
transmission fluid
checking procedure?
Go to Step 3 Go to
Transmission
Fluid Checking
Procedure
31. Install a scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
3. Drive the vehicle in 4th
gear with the TCC
engaged.
Is the TCC Slip Speed
between the specified
values for 7 seconds?
300 to
1000
RPM
Go to Step 4 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
4Inspect the Torque
Converter Clutch Solenoid
Valve (TCC Sol. Valve) for
the following conditions:
• Internal malfunction
(such as sediment or
damage)
• Damaged seals
Inspect the Torque
Converter Clutch Pulse
Width Modulation
Solenoid Valve (TCC
PWM Sol. Valve) for the
following conditions:
• Internal malfunction
(such as sediment or
damage)
• Damaged seals
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 5
5Inspect the 1-2 Shift
Solenoid Valve (1-2 SS
Valve) for the following
conditions:
• Internal malfunction
(such as sediment or
damage)
• Damaged seals
Inspect the 2-3 Shift
Solenoid Valve (2-3 SS
Valve) for the following
conditions:
• Internal malfunction
(such as sediment or
damage)
• Damaged seals
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 6
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
6Inspect the valve body
assembly for a stuck TCC
signal valve. Refer to Unit
Repair.
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 7
7Inspect the torque
converter assembly for
the following conditions:
• Stator roller clutch not
holding
• Internal damage
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 8
8Inspect the oil pump
assembly for the following
conditions:
• Stuck converter clutch
valve
• Converter clutch valve
assembled backward
• Mispositioned
converter clutch valve
retaining ring
• Mispositioned pump to
case gasket
• Restricted orifice cup
plugs
• Damaged orifice cup
plugs
• Over-tightened, or
unevenly tightened
pump body to cover
bolts
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 9
9Inspect the input housing
and shaft assembly for the
following conditions:
• Cut turbine shaft o-ring
seal
• Damaged turbine shaft
o-ring seal
• Restricted turbine shaft
retainer and ball
assembly
• Damaged turbine shaft
retainer and ball
assembly
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 10
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
10 Inspect the 2-4 band
assembly for the following
conditions:
• Worn 2-4 band
• Damaged 2-4 band
• Mispositioned 2-4 band
• Misassembled 2-4
band
• The band anchor pin is
not engaged
• Restricted apply
passages in the 2-4
servo assembly
• Blocked apply
passages in the 2-4
servo assembly
• Nicks or burrs on the
servo pin
• Nicks or burrs on the
pin bore in the case
• Damaged fourth servo
piston
• Misassembled fourth
servo piston
• Damaged band apply
pin
• Incorrect band apply
pin
• Damaged servo bore
in the case
• Missing piston seals
• Cut piston seals
• Damaged piston seals
• Porosity in the pistons
• Porosity in the cover
• Poro sity in the ca se
• Damaged piston seal
grooves
• Plugged orifice cup
plug
• Missing orifice cup
plug
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 11
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
11 Inspect the forward clutch
assembly for the following
conditions:
• Worn clutch plates
• Porosity in the forward
clutch piston
• Damaged forward
clutch piston
• Missing forward clutch
piston inner and outer
seals
• Cut forward clutch
piston inner and outer
seals
• Damaged forward
clutch piston inner and
outer seals
• Missing input housing
to forward clutch
housing o-ring seal
• Cut input housing to
forward clutch housing
o-ring seal
• Damaged input
housing to forward
clutch housing o-ring
seal
• Damaged forward
clutch housing
• Damaged forward
clutch housing retainer
and ball assembly
• Forward clutch
housing retainer and
ball assembly is not
sealing
Did you find and correct
problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
12 Inspect the 3-4 clutch
assembly for the following
conditions:
• Worn clutch plates
• Porosity in the 3-4
clutch piston
• Damaged 3-4 clutch
piston
• Missing 3-4 clutch
inner and outer seals
• Cut 3-4 clutch inner
and outer seals
• Damaged 3-4 clutch
inner and outer seals
• Damaged 3-4 clutch
sprin g assembly
• Damaged 3-4 clutch
apply ring
• Damaged piston seal
grooves
• Plugged orifice cup
plug
• Missing orifice cup
plug
Did you find and correct
the problem?
Go to Step 13 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
13 In order to verify your
repair, operate the vehicle
under the following
conditions:
• Drive the vehicle in D4
with the TCC ON and
a throttle position of
16-50%.
Did the vehicle obtain a
Trans Slip Speed of -20 to
+40 RPM?
System OK Begin the
diagnosis again.
Go to Step 1
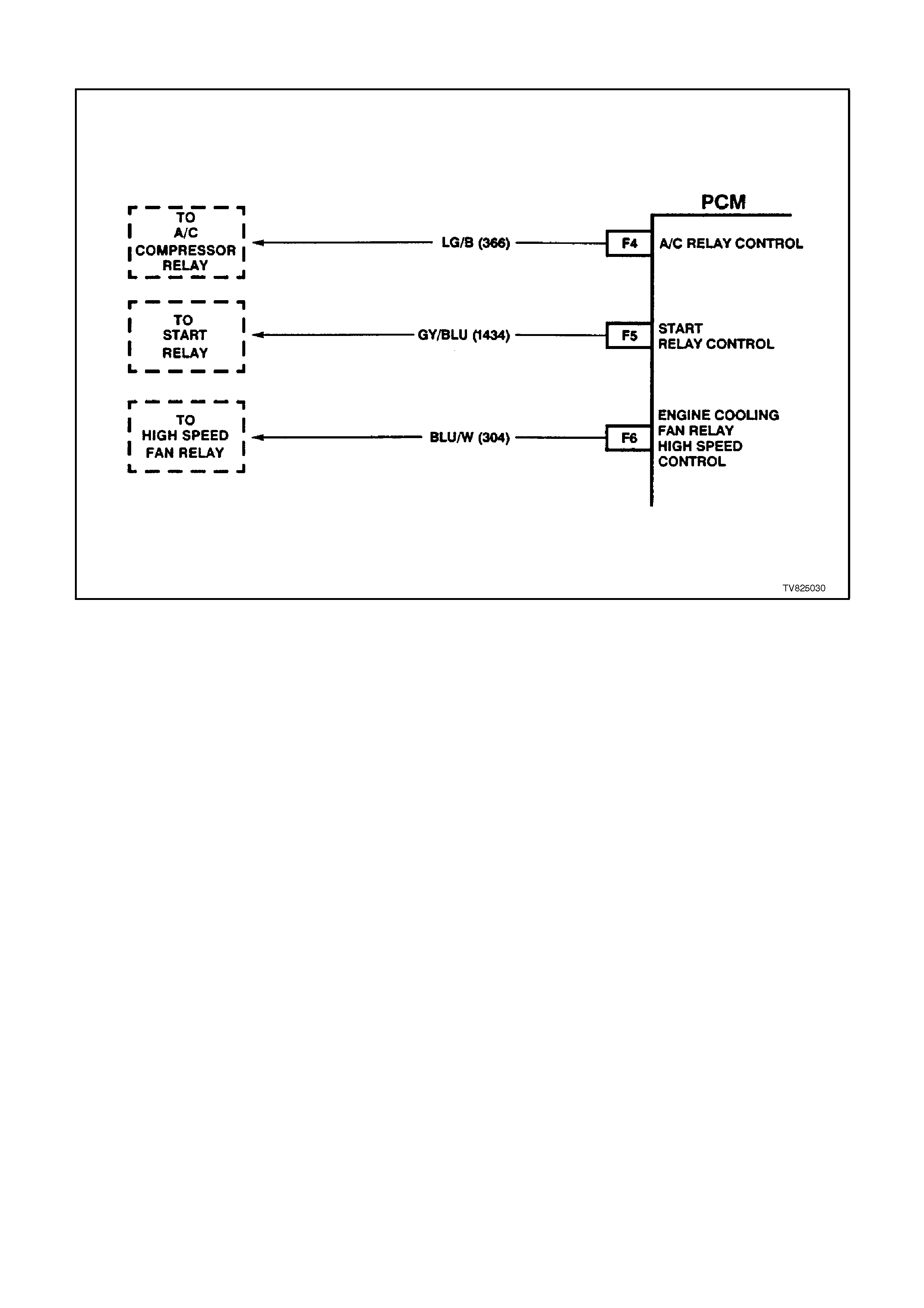
DTC 91 - QUAD DRIVER SURFACE MODULE (QDSM) CI RCUI T
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Quad Driver Surface Modules (QDSM) are used by the PCM to turn ON many of the current-driven devices that are
needed to control various engine functions. A QDSM is capable of controlling up to 4 separate outputs by applying
earth or voltage to the device which the PCM is commanding "ON."
QDSM do not have the capability of diagnosing each output circuit individually. A DTC indicates an improper voltage
level has been detected on one of the QDSM circuits. The QDSM controls the A/C compressor relay, the Start
Inhibit Relay, and the High Speed fan relay.
When a DTC 91 is set, the low speed fan will be turned ON and will remain ON until the DTC 91 has been cleared.
DTC 91 WILL SET IF:
• The ignition has been ON, and the engine has been running longer than 5 seconds.
• An improper voltage level has been detected on a QDSM circuit.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This step checks to see if the A/C compressor relay can be controlled using a scan tool. If the scan tool can
control the A/C relay, the A/C circuit is not causing DTC 91 to set.
8. This step checks to see if the Start relay can be controlled using a scan tool. If the scan tool can control the
Start Inhibit relay, the Start relay circuit is not causing DTC 91 to set.
13. This step checks to see if the High Speed relay can be controlled using a scan tool. If the scan tool can control
the High Speed relay, the High Speed Relay circuit is not causing DTC 91 to set.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Dirty, Damaged, or Loose Connections or Damaged Harness - Check for any damage to the harness which could
cause an intermittent open or short to earth or backed out terminals at the PCM and BCM module connectors,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Using the scan tool,
command the A/C
compressor rel ay ON
and OFF while
listening to the relay.
Did the A/C compressor
relay click ON and OFF
when commanded?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 3
31. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Using DVM, probe
PCM harness
connector terminal
"F4" with negative lead
to earth.
Is the voltage at the
specified value?
B+ Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4Check for a poor
connection at the PCM
harness connectors.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 5
5Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
6Check for an open or a
short to earth between the
PCM harness connector
terminal "F4", and the A/C
compressor relay
terminal "1".
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 7
7Replace the A/C
Compressor Relay.
Is action complete?
Verify Repair
81. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Using the scan tool,
command the Start
relay ON, and OFF
while listening to the
relay.
Did the Start relay click
ON, and OFF?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 9
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
91. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connectors.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Using the DVM, probe
PCM harness
connector terminal
"F5" with negative lead
to earth.
Is the voltage at the
specified value?
B+ Go to Step 10 Go to Step 11
10. Check for poor connection
at PCM harness
connectors.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 5
11 Check for an open or a
short to earth between the
PCM harness connector
terminal "F5", and the
Start relay terminal "2".
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 12
12 Replace the Start Relay.
Is the action complete? Verify Repair
13 1. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Using scan tool,
command High Speed
fan relay ON, and
OFF while listening to
relay.
Did the High Speed relay
click ON and OFF when
commanded?
Go to Step 17 Go to Step 14
14 1. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect PCM
harness connectors.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Using DVM, probe
PCM harness
connector terminal
"F6", with negative
lead to earth.
Is the voltage at the
specified value?
B+ Go to Step 15 Go to Step 16
15 Check for poor connection
at PCM harness
connectors.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 5
16 Check for an open or a
short to earth between the
PCM harness connector
terminal "F6", and the
High Speed fan relay
terminal "86".
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Refer to
Chart A-12.2
for testing of the
High Speed Fan
Relay
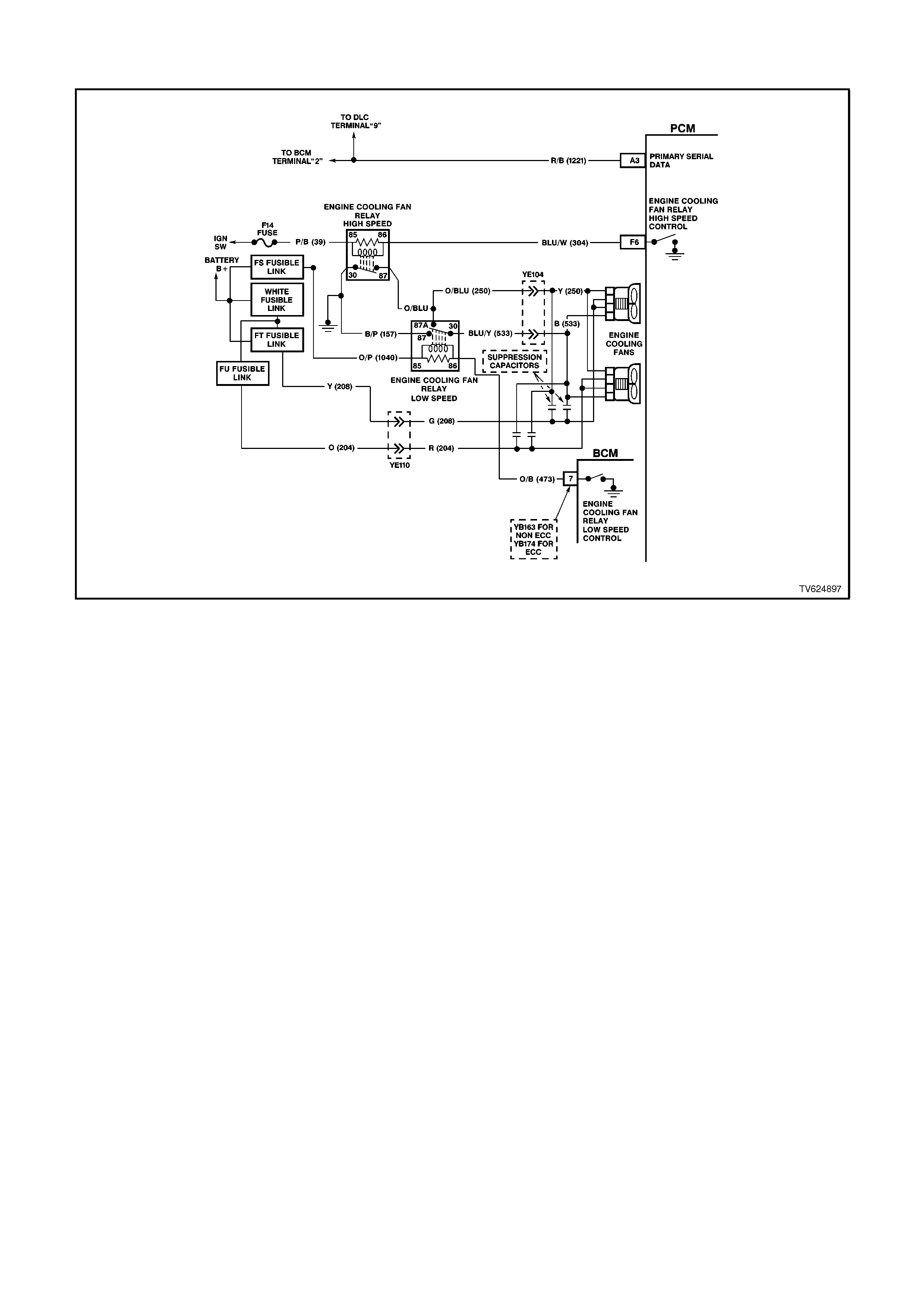
DTC 92 - LOW SPEED FAN-NO BCM RESPONSE
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The PCM determines operation of the two speed engine cooling fan based on A/C request signal input, engine
coolant temperature and vehicle speed.
The engine cooling fan low speed relay (labelled LO FAN in relay housing) is energised by the BCM. When the
PCM determines that the engine cooling fan low speed relay should be turned ON, the PCM will send a message on
circuit 1221 to the BCM. This message will ask the BCM to earth circuit 473 and energise the engine cooling fan low
speed relay. After the BCM provides the earth for circuit 473, the BCM will send a message back to the PCM saying
that the earth circuit was commanded. The DTC 92 will set if the PCM sends out the message to the BCM to turn
ON the engine cooling fan low speed relay and the BCM does NOT send a message back to the PCM.
DTC 92 WILL SET IF:
• The engine is idling.
• The PCM sends 20 low speed fan requests signals to the BCM for fan operation with no response back from the
BCM.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. An open or short to earth on circuit 1221 will disable any communication of the serial data between the PCM
and BCM.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• Dirty, Damaged, or Loose Connections or Damaged Harness - Check for any damage to the harness which
could cause an intermittent open or short to earth or backed out terminals at the BCM module connectors,
broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals.
• The engine will not start if circuit 1221 is open or earthed. Therefore if DTC 92 is set and the engine will start,
then DTC 92 is intermittent. Review DTC history data to determine when DTC 92 set.
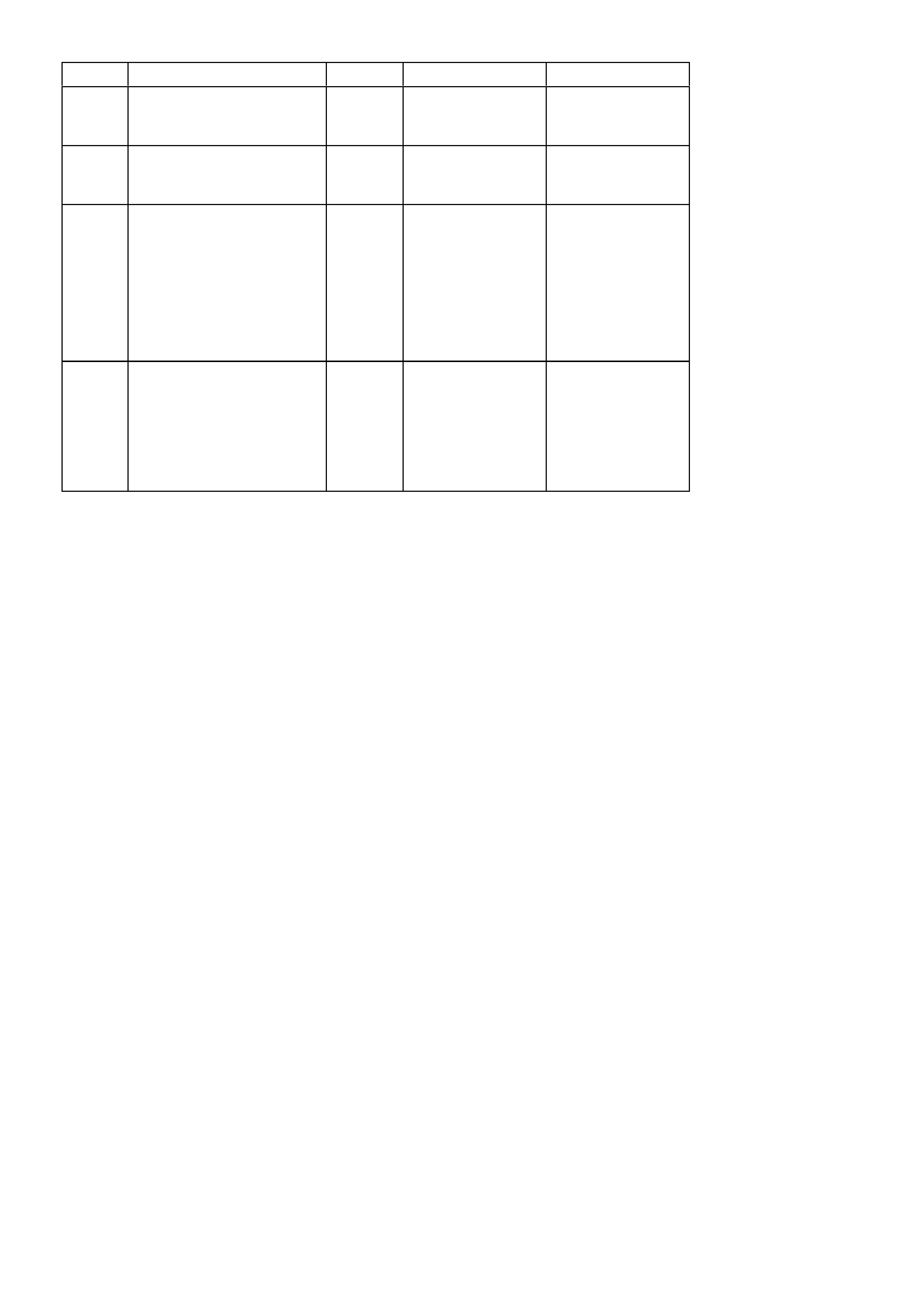
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD System
Check in this
Section
2Is DTC 31 set? Go to DTC 31
Diagnostic Chart in
this Section
Go to Step 3
31. Engine at idle speed.
2. Using a Tech 2 scan
tool, select "LOW FAN"
Does the Tech 2 scan tool
"BCM Response" display
change from "FAN OFF" to
"FAN ON" when the test is
enabled?
104 - 108
degrees
C
Go to Step 4 Go to
Chart A-12.1
in this Section
4Does Tech 2 scan tool
"BCM Response" display
change from "FAN OFF" to
"FAN ON" when test is
enabled?
DTC 92 is
intermittent.
Refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
Refer
Section 12J-1
LOW SERIES
BCM or
Section 12J-2
HIGH SERIES
BCM.
DTC 93 - SNEF CIRCUIT FAULT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Knock sensor is used to detect engine detonation, and the PCM will retard the Electronic Spark Timing (EST)
based on the signal being received The Knock sensor produces an AC signal which varies in amplitude and
frequency depending upon the amount of Knock present.
The PCM monitors the output of the SNEF (Signal To Noise Enhancement Filter) circuit. The PCM determines
whether Knock is occurring by comparing the Knock sensor signal level with the voltage level on the SNEF circuit.
The SNEF circuit allows the PCM to filter out only false Knock signals by indicating the amount of normal engine
mechanical noise present. Normal engine noise varies depending on engine speed and load. A normal Knock
condition could result in a Knock sensor signal from a few milliseconds to possibly as high as 100 milliseconds in
length.
When the SNEF circuit output is significantly longer than the longest expected "Normal" output it is assumed the
SNEF circuitry has failed and DTC 93 will set.
DTC 93 WILL SET IF:
• The engine has been running longer than 10 seconds.
• The SNEF circuit indicates a knocking condition for greater than 10 seconds.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
2. This step checks to see if the Tech 2 "Scan" tool is displaying Knock signal at all times.
3. This step checks to see if a audible knock is being caused by the engine or the transmission.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Install a Tech 2 Scan
tool.
2. Ignition ON, engine
Idling.
3. Using Tech 2 Scan
tool, select "Knock
Signal" and "Knock
Retard".
Is "Knock Signal"
indication "Knock"?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3With engine running, is a
audible "Knock" condition
heard?
Refer to Engine
Mechanical or
Transmission
Sections to repair
audible Knock
Go to Step 4
4Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
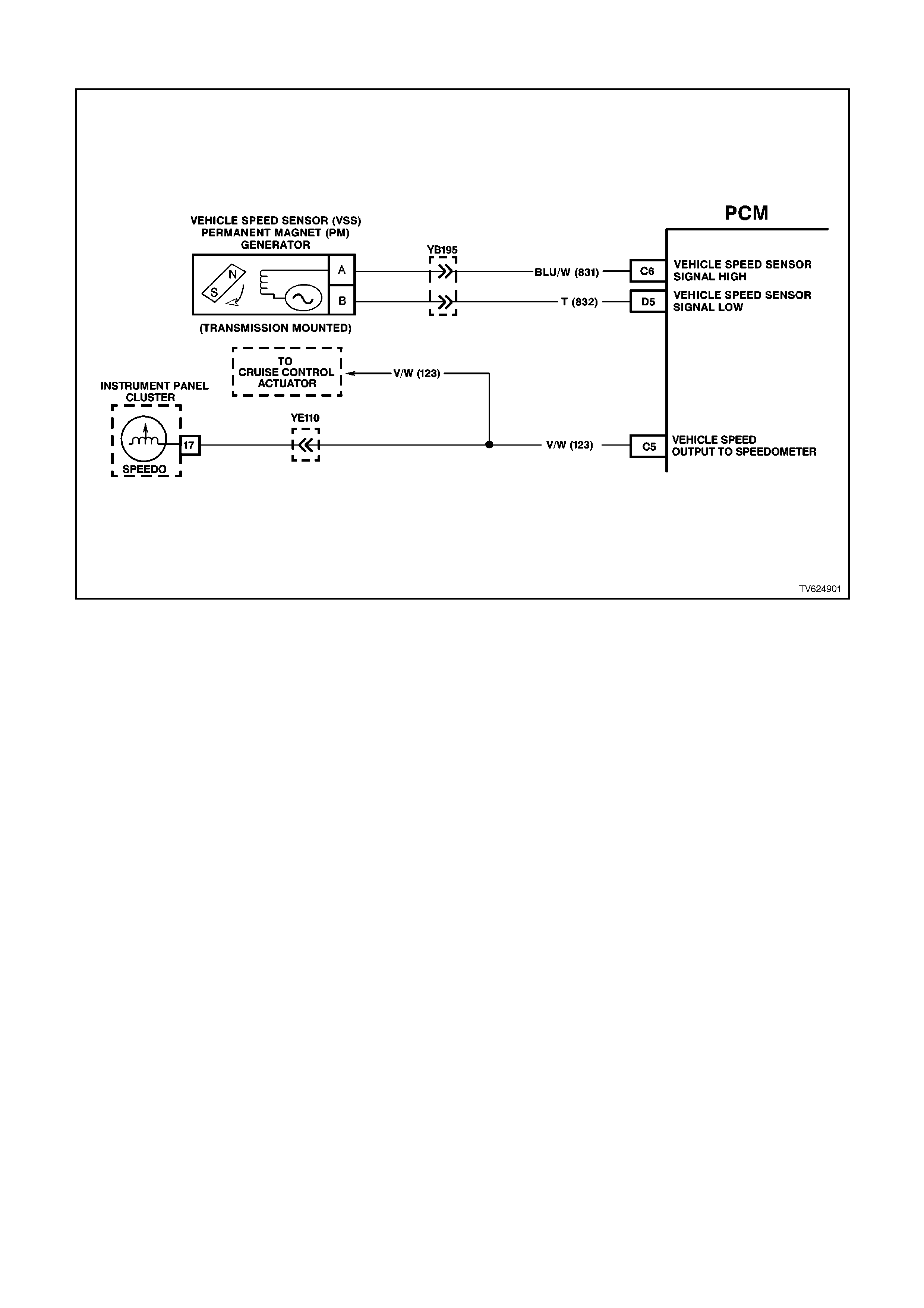
DTC 94 - NO VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL (MANUAL TRANSMISSION)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The Vehicle Speed Sensor Assembly (VSS Assembly) provides vehicle speed information to the PCM. The VSS
Assembly is a Permanent Magnet (PM) generator. The PM generator produces a pulsing AC voltage. The AC
voltage level and the number of pulses increase with the speed of the vehicle. The PCM then converts the pulsing
voltage to vehicle speed. The PCM uses this information for calculations. A scan tool can display the vehicle speed.
When the PCM detects a low or no vehicle speed, when there is high engine speed and low Throttle Position (TP)
%, then DTC 94 sets.
DTC 94 WILL SET IF:
• No DTC 19, 21, 22, or 32 is active, and the following conditions are met for at least 4 seconds:
• Circuit 123 voltage is constant - that is,
NOT pulsing, and
• Engine RPM between 1400 and 3000 RPM, and
• Throttle is closed < 1% (TP Sensor), and
• Engine load very low (MAF sensor) 95 mg/cyl.*
For these conditions to happen during the 4 second period of time, the vehicle must be in-gear, closed-throttle, and
deceleration from road speed must occur.

TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This step tests the integrity of the VSS Assembly.
6. This step tests the VSS Assembly circuit.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Inspect the wiring for poor electrical connections at the PCM. Look for the following conditions:
A bent terminal
A backed out terminal
A damaged terminal
Poor terminal tension
A chafed wire
A broken wire inside the insulation
Moisture intrusion
Corrosion
When diagnosing for an intermittent short or open condition, massage the wiring harness while watching the test
equipment for a change.
Check circuits 831 and 832 for the proper connections to be sure they are clean and tight and the harness is routed
correctly.
The scan tool should indicate vehicle speed whenever the drive wheels are turning greater than 3 km/h.
The vehicle speed sensor resistance should be between 1470-2140 Ohms at 20°C, and 2270-2820 Ohms at 100°C.
Refer to “intermittents” in Section 6C2-2B SYMPTOMS.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check performed?
_ Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check.
21. Install the scan tool.
2. With the engine OFF,
turn the ignition switch
to the RUN position.
IMPORTANT:
Before clearing the DTCs,
use the scan tool in order
to record the DTC history
for reference. The Clear
Info function will erase the
data.
3. Record the DTC
history.
4. Clear the DTC.
5. Raise the drive
wheels.
NOTE:
Do not perform this test
without supporting the
rear axle assembly or the
lower control arms on
vehicles with independent
rear suspension so that
the drive shafts are in a
normal horizontal position.
6. Start the engine.
7. Place the transmission
in any drive gear.
With the rear wheels
rotating, does the scan
tool Vehicle Speed
increase with the drive
wheel speed?
_ Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch
to the OFF position.
2. Disconnect the VSS
connector from the
VSS assembly.
3. Using the J 35616
Connector Test
Adapter Kit, connect
the J 39200 DVM to
the VSS terminals.
4. Select AC volts.
5. Place the transmission
selector in the neutral
position.
6. Rotate the drive
wheels by hand,
ensuring that the
driveshaft is turning.
With rear wheels rotating,
is the DVM voltage
greater than the specified
value?
0.5 volts
AC Go to Step 4 Go to Step 11
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
41. Turn the ignition switch
to the OFF position.
2. Reconnect the VSS
connector to the VSS
Assy.
3. Disconnect the PCM
connector 1 (Pink-32
pin) from the PCM.
4. Connect the DVM test
leads to the connector
terminals D5 (T) and
C6 (Blu/W).
5. Place the transmission
selector in the neutral
position.
6. Rotate the drive
wheels by hand,
ensuring that the
driveshaft is turning.
With rear wheels rotating,
is the DVM voltage
greater than the specified
value?
0.5 volts
AC Go to Step 13 Go to Step 5
51. Select Ω (Ohms), on
the DVM.
2. Measure the
resistance between the
connector terminals D5
(T) and C6 (Blu/W).
Is the circuit resistance
within the specified
range?
1470-
2820 ΩGo to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6Connect the DVM
between the connector
terminal C-6 and earth.
Is the circuit resistance
less than the specified
value?
250k ΩGo to Step 7 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
71. Check circuit 831 and
circuit 832 for a short
to earth.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Was the short to earth
condition found and
corrected?
_ Go to Step 14 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
8Is the resistance reading
in step 6 greater than the
specified value?
2820 ΩGo to Step 10 Go to Step 9
91. Check circuit 831 and
circuit 832 for a
shorted together
condition.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Was a shorted together
condition found and
corrected ?
_ Go to Step 14 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
10 1. Check circuit 831 and
circuit 832 for an open
condition.
2. Repair the circuit if
necessary.
Was an open condition
found and corrected ?
_ Go to Step 14 Go to “Diagnostic
Aids” above
11 1. Remove the VSS
Assembly.
2. Inspect the VSS
Output Sensor Rotor
for damage or
misalignment.
Did you find a condition?
_ Refer to
appropriate
Section for repair
information
Go to Step 12
12 Replace the VSS Assy.
Refer to Service
Operations.
Is the action complete?
_ Go to Step 14 _
13 Replace the PCM. Refer
to Section 3 for the
Security Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
_ Go to Step 14 _
14 In order to verify your
repair, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select DTC.
2. Select Clear Info.
3. Operate the vehicle
ensuring that the
vehicle speed is
greater than 3 km/h
and observe the scan
tool Vehicle Speed.
Is the scan tool Vehicle
Speed greater than the
specified value?
10 km/h System OK Begin the
Diagnosis Again
Go to Step 1
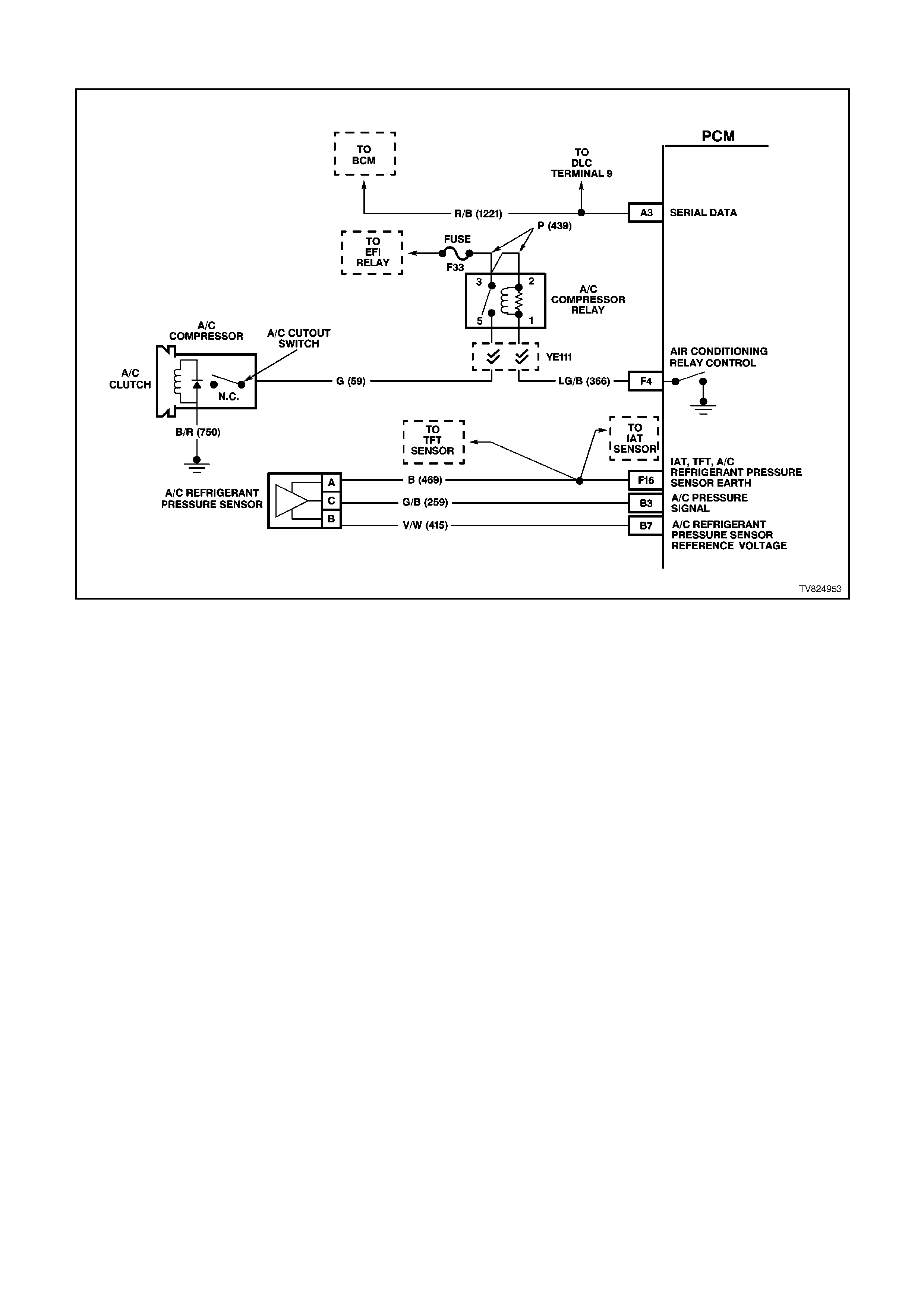
DTC 96 - A/C PRESSURE SENSOR CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor responds to changes in the A/C refrigerant high side pressure. This input to the
PCM indicates how much load the A/C compressor is putting on the engine and is one of the factors used by the
PCM to determine the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve position for idle speed. The circuits consist of a 5 volt reference
and a earth circuit, both provided by the PCM, and a signal circuit from the sensor to the PCM. The signal is a
voltage which is proportional to A/C pressure.
DTC 96 WILL SET IF:
• The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is less than 120°C.
• The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) is less than 90°C.
• The engine speed is less than 2000 RPM.
• The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor signal voltage is less than 0.2 volt.
- OR -
• The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor signal voltage is greater than 4.9 volts.
• The above conditions have been present for 10 seconds.
• The DTC will not set if the engine run time is greater than 10 minutes.
When a DTC 96 is set, the low speed cooling fan will operate for 5 seconds, then the high speed fan will turn ON,
and remain ON until the fault is removed.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to the step(s) on the diagnostic chart.
3. This checks if the low voltage signal was due to an open in the signal circuit, the 5 volt reference circuit or if the
PCM is faulty.
4. An open in a shared earth circuit can cause other DTC's to be set. If no other DTC's were set, the circuit must
be open between the sensor and the circuit splice.
8. Determines if the low voltage signal was from the sensor or the signal circuit. Jumping the signal circuit to the 5
volt reference checks the circuits, connections and the PCM.
9. An open in a shared 5 volt reference circuit can cause other DTC's to be set. If no other DTC's were set, the
circuit must have an open between the sensor and the circuits wiring harness splice.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
• A DTC 96 will only set wi th a short to voltage or a open circuit. A short to earth will not set the DTC, but the A/C
system will be inoperable.
• A DTC 96 sets when the signal voltage falls outside the normal possible range of the sensor. Repair any A/C
pressure problems before using this table.
• Any circuit, that is suspected of causing the intermittent, should be checked for proper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, or physical damage to the wiring harness.
• The sensors operating range is between 0 and 3160 kPa ( 0-468 psi). At 0 kpa, the signal voltage will be about
0.1 volts, varying to about 5.0 volts at 3160 kPa.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD
System Check in
this Section
21. Ignition ON, engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Monitor the A/C
pressure sensor
voltage.
Is the A/C pressure
sensor voltage at or
above the specified
value?
4.0V Go to Step 3 Go to Step 7
3Disconnect the A/C
pressure sensor electrical
connector.
Does scan tool display
A/C pressure sensor
voltage at or below the
specified value?
0.2 V Go to Step 4 Go to Step 11
41. Ignition OFF.
2. Using test light
connected to B+,
probe A/C pressure
sensor earth circuit at
harness electrical
connector.
Does test light illuminate?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 12
5Check for a poor
connection at A/C
pressure sensor.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 6
6Replace the A/C pressure
sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
7Is the A/C pressure
sensor voltage at or below
the specified value?
0.2 V Go to Step 8 Go to Step 15
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
81. Disconnect the A/C
pressure sensor
electrical connector.
2. Using a fused jumper
wire, jumper the A/C
pressure sensor 5 volt
reference circuit and
signal circuits together
at harness connector.
Does scan tool indicate
A/C pressure sensor
voltage at or above the
specified value?
4.0 V Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
91. Remove the jumper
wire.
2. Connect a DVM
between the A/C
pressure sensor 5 volt
reference circuit and
earth circuit at the
harness connector.
Does the DVM read at or
between the specified
value?
4.0 -
5.0 V Go to Step 10 Go to Step 13
10 Repair the open or the
short to earth in the A/C
pressure sensor signal
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
11 Check the A/C pressure
sensor signal; circuit for a
short to voltage.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 14
12 Repair the open in the
earth circuit to the A/C
pressure sensor.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
13 Repair the open in the 5
volt reference circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
14 Replace the PCM.
Refer to Section 6C2-3
Service Operations, for
PCM Security Link
procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 1. Using a scan tool,
clear the DTC.
2. Start the engine and
idle at normal
operating temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle
A/C system and note
the A/C pressure
sensor voltage on scan
tool.
Is the voltage displayed at
or between the specified
value?
0.2 -
4.6 V System OK,
refer to
Diagnostic Aids
Go to Step 2
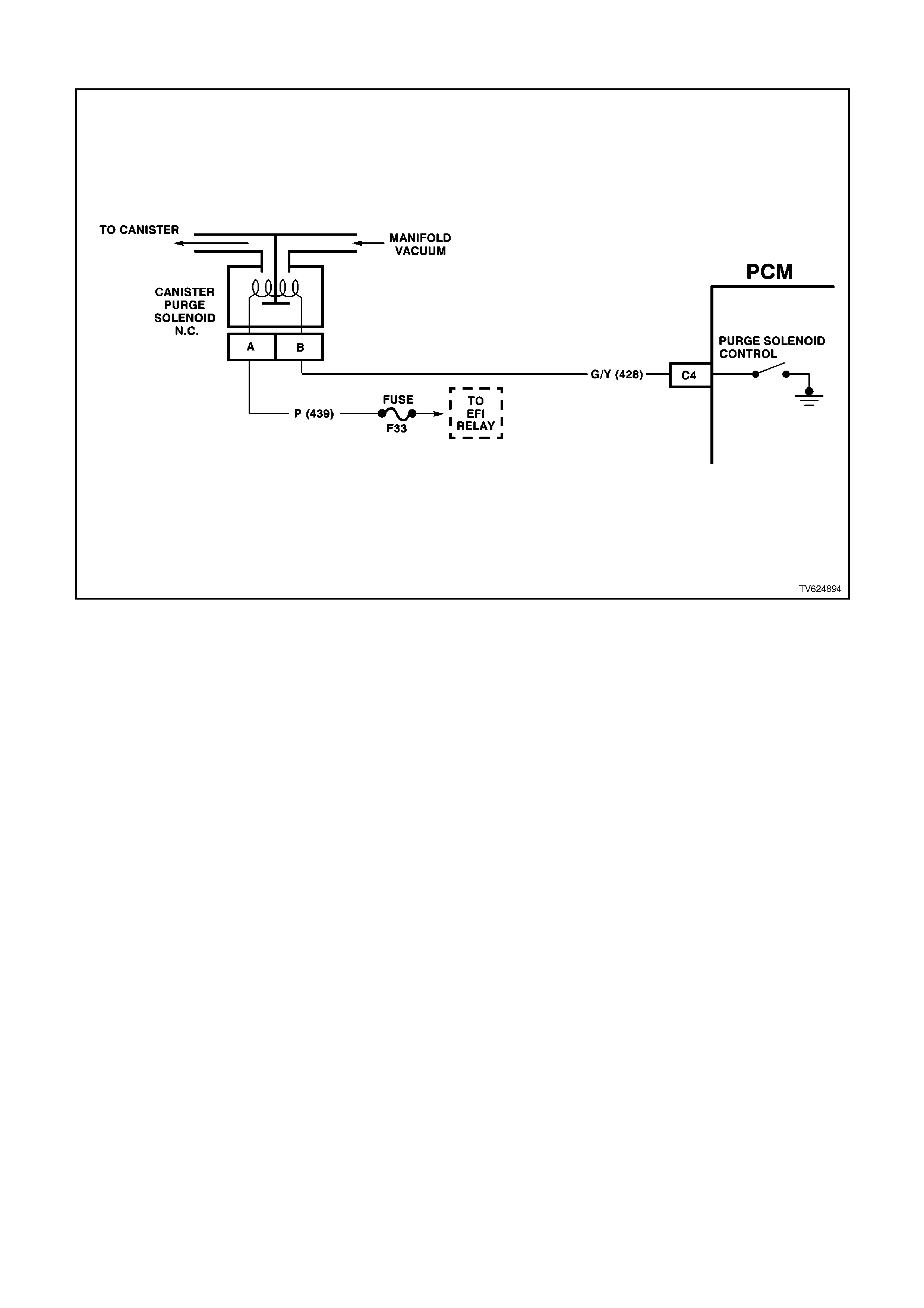
DTC 97 - CANISTER PURGE CIRCUIT
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION:
Quad Driver Modules (QDMs) are used by the PCM to turn ON many of the current-driven devices that are needed
to control various engine and transmission functions. Each QDM is capable of controlling up to 4 separate outputs
by applying earth to the device which the PCM is commanding ON.
The Quad Driver Modules (QDMs) used has the capability of diagnosing each output circuit individually. DTC 97 set
indicates an improper voltage level has been detected on the QDM fault line, which controls the Canister Purge
Solenoid.
DTC 97 WILL SET IF:
• The Ignition is ON.
• The QDM fault line has detected an improper voltage on the Canister Purge Solenoid driver.
When a DTC 97 sets, the PCM will not illuminate the MIL (Check Powertrain Lamp) the first time the fault is
detected and the PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set in DTC History Data.
TEST DESCRIPTION:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the diagnostic chart:
2. Normally, ignition feed voltage is present on the output driver circuit with the PCM disconnected and the ignition
ON.
3. Checks for a shorted component or a short to B+ or the Quad driver circuit. Either condition would result in a
measured current of over 1.5 amps. Also checks for a component that is open while being operated, resulting
in a measured current of 0 amps.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS:
Check for the following conditions.
• A poor connection at PCM. Inspect harness connections for backed out terminals, improper mating , broken
locks, improper formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection.
• A damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect the
PCM, turn the ignition ON and observe a voltmeter connected to the Canister Purge Solenoid driver circuit at the
PCM harness connector while moving connectors and wiring harness related to the Canister Purge Solenoid. A
change in voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC 97 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the DTC History can be useful in determining how many
ignition cycles have passed since the DTC was last set.
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
1Was the "On-Board
Diagnostic" (OBD) System
Check performed?
Go to Step 2 Go to OBD System
Check
21. Ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the PCM
connector.
3. Ignition ON.
4. Using a voltmeter,
measure the voltage
between the Canister
Purge Solenoid driver
circuit at the PCM
harness connector and
earth.
Is the voltage near the
specified value?
B+ Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
31. Digital volt/ohmmeter
set to 10 amp scale,
install digital
volt/ohmmeter to
measure the current
between the Canister
Purge Solenoid driver
and earth.
2. Monitor the current
reading on the digital
volt/ohmmeter for at
least 2 minutes.
Does the current reading
between the specified
values?
0.1 amp
to
1.5 amps
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 4
41. Disconnect the Canister
Purge Solenoid (leave
the PCM disconnected).
2. Using the digital
volt/ohmmeter, measure
the voltage between the
Canister Purge Solenoid
driver circuit and the
earth.
Is the voltage less than the
specified value?
0.5 volts Go to Step 14 Go to Step 5
5Locate and repair the short
to voltage in the Canister
Purge Solenoid driver
circuit.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
6Check the ignition feed
fuse for the Canister Purge
Solenoid.
Is the fuse open?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
71. Locate and repair the
short to earth in the
ignition feed circuit for
the Canister Purge
Solenoid.
2. Replace the fuse.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
STEP ACTION VALUE YES NO
81. Disconnect the Canister
Purge Solenoid.
2. Ignition ON.
3. Measure the voltage
between the ignition
feed circuit for the
Canister Purge Solenoid
and earth.
Is the voltage at the
specified value?
B+ Go to Step 9 Go to Step 13
9Check the Canister Purge
Solenoid driver circuit for
an open or a short to earth.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 10
10 Check the Canister Purge
Solenoid driver circuit and
the ignition feed circuit for a
poor connection at the
Canister Purge Solenoid
and the PCM.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 14
11 1. Ignition OFF, reconnect
the PCM and
disconnect the Canister
Purge Solenoid.
2. Ignition ON, connect a
test light between the
Canister Purge Solenoid
driver circuit and the
ignition feed circuit at
the Canister Purge
Solenoid connector.
3. Using the Tech 2 Scan
tool, cycle the Canister
Purge Solenoid ON and
OFF.
Does the test light flash ON
and OFF?
Refer to
"Diagnostic Aids"
above.
Go to Step 12
12 Check the Canister Purge
Solenoid driver for a poor
connection at the PCM.
Was a problem found?
Verify Repair Go to Step 15
13 Locate and repair the open
ignition feed circuit to the
Canister Purge Solenoid.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
14 Replace the Canister
Purge Solenoid.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair
15 Replace the PCM. Refer to
Section 6C2-3 Service
Operations, for the Security
Link procedure.
Is the action complete?
Verify Repair