Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–1
Page 6C1-2–1
Section 6C1-2
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to Section 00
Warnings, Cautions and Notes for correct w orkshop practices wi th regard to safety and/or property damage.
1 General Information.............................................................................................................................16
1.1 Diagnostic System Check................................................................................................................................... 16
1.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables........................................................................................................................ 17
Multiple DTC Fault Conditions............................................................................................................................ 17
1.3 Symptoms Diagnostics ....................................................................................................................................... 18
1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes .................................................................................................................................. 19
Type A – Emission Related DTCs....................................................................................................................... 19
Type B – Emission Related DTCs....................................................................................................................... 19
Conditions for Clearing Type A or Type B DTCs .............................................................................................. 19
Type C – Non-Emission Related DTCs............................................................................................................... 20
Conditions for Clearing Type C DTCs .............................................................................................................. 20
Current DTCs........................................................................................................................................................ 20
History DTCs........................................................................................................................................................ 20
2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts............................................................................................21
2.1 Wiring Diagrams .................................................................................................................................................. 21
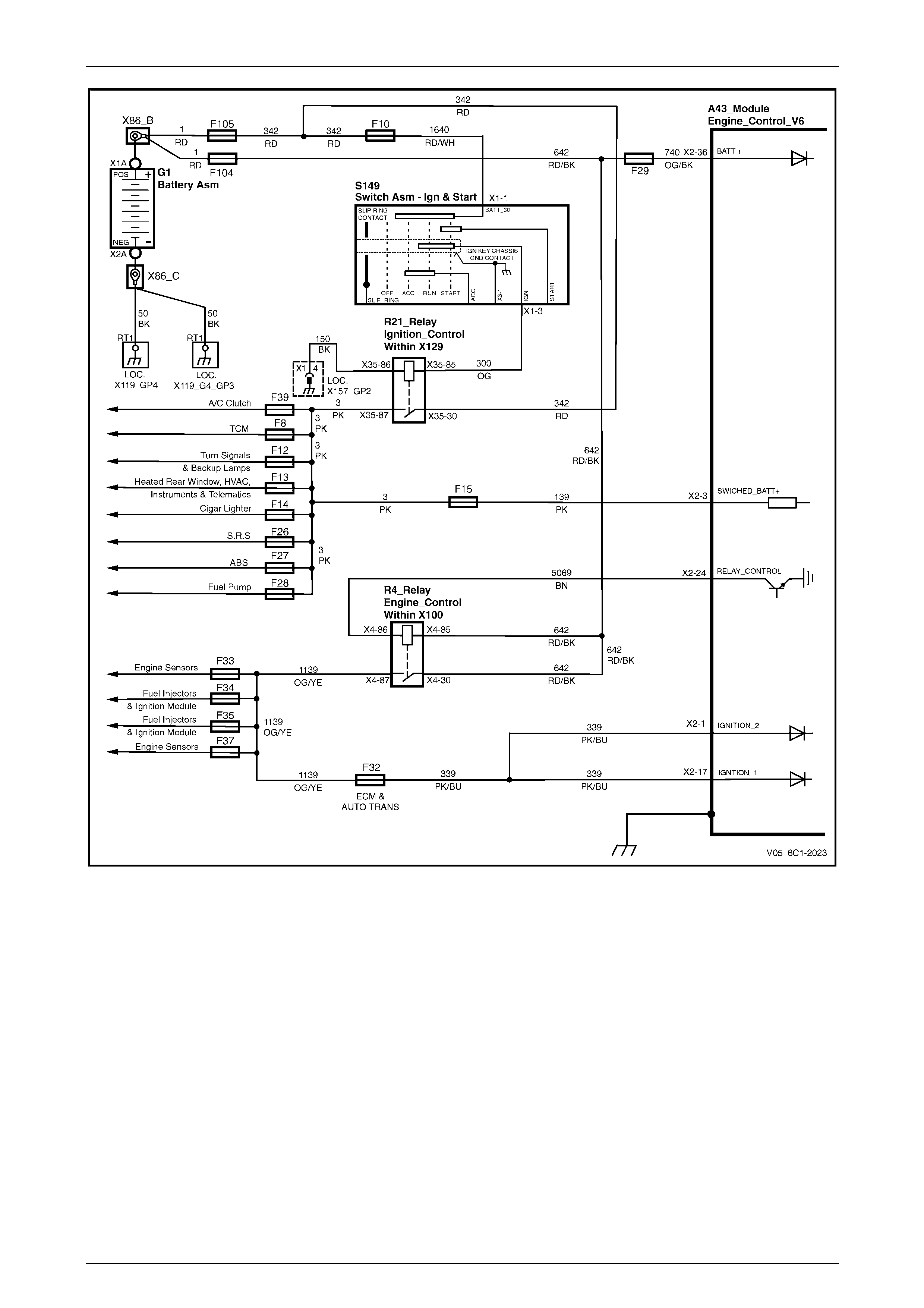
Power Distribution............................................................................................................................................... 21
Generator, Cooling Fans and A/C....................................................................................................................... 22
Sensors................................................................................................................................................................. 23
Sensors and Throttle Control ............................................................................................................................. 24
Camshaft Control – Alloytec190......................................................................................................................... 25
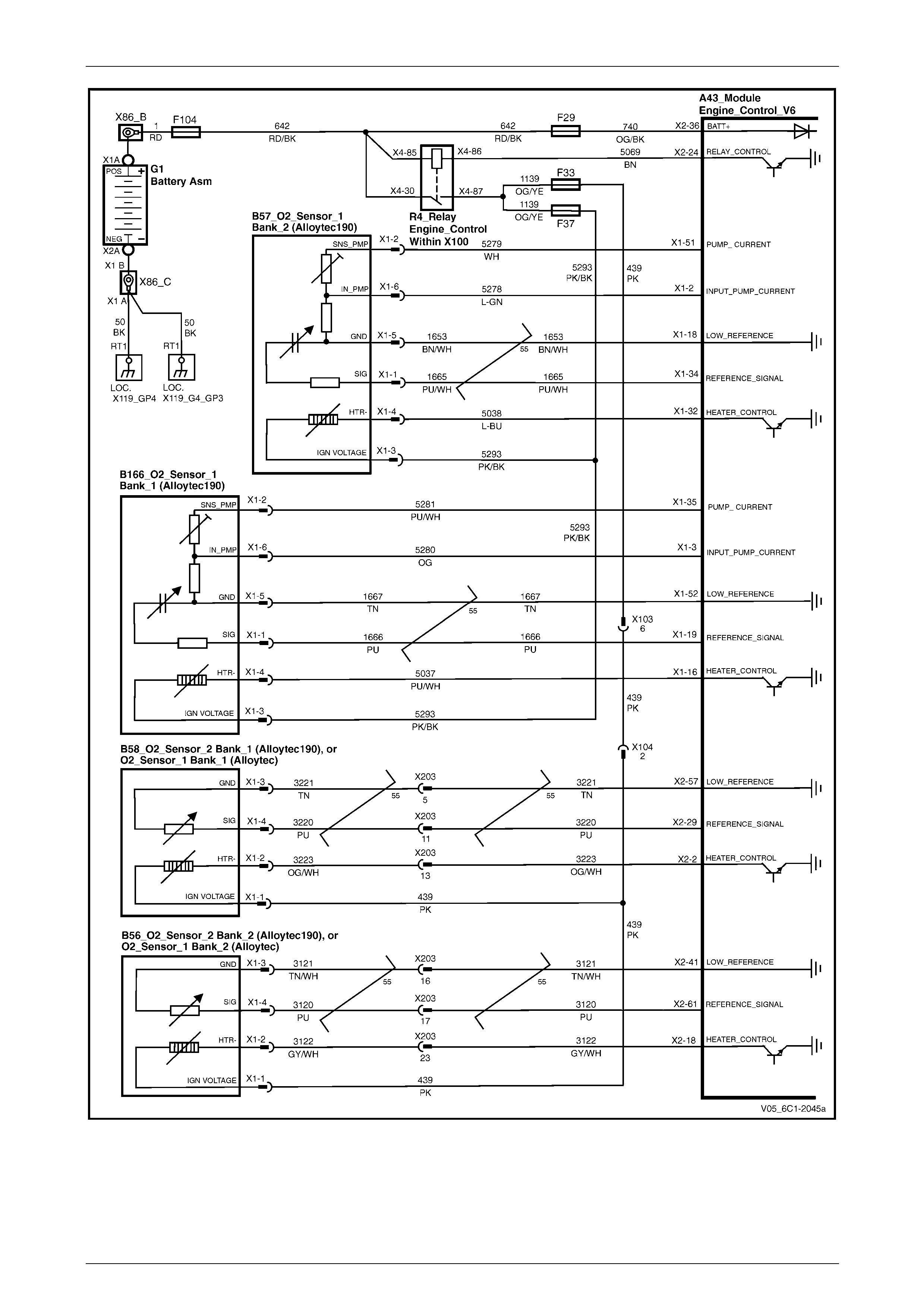
Camshaft Control and HO2S – Alloytec............................................................................................................. 26
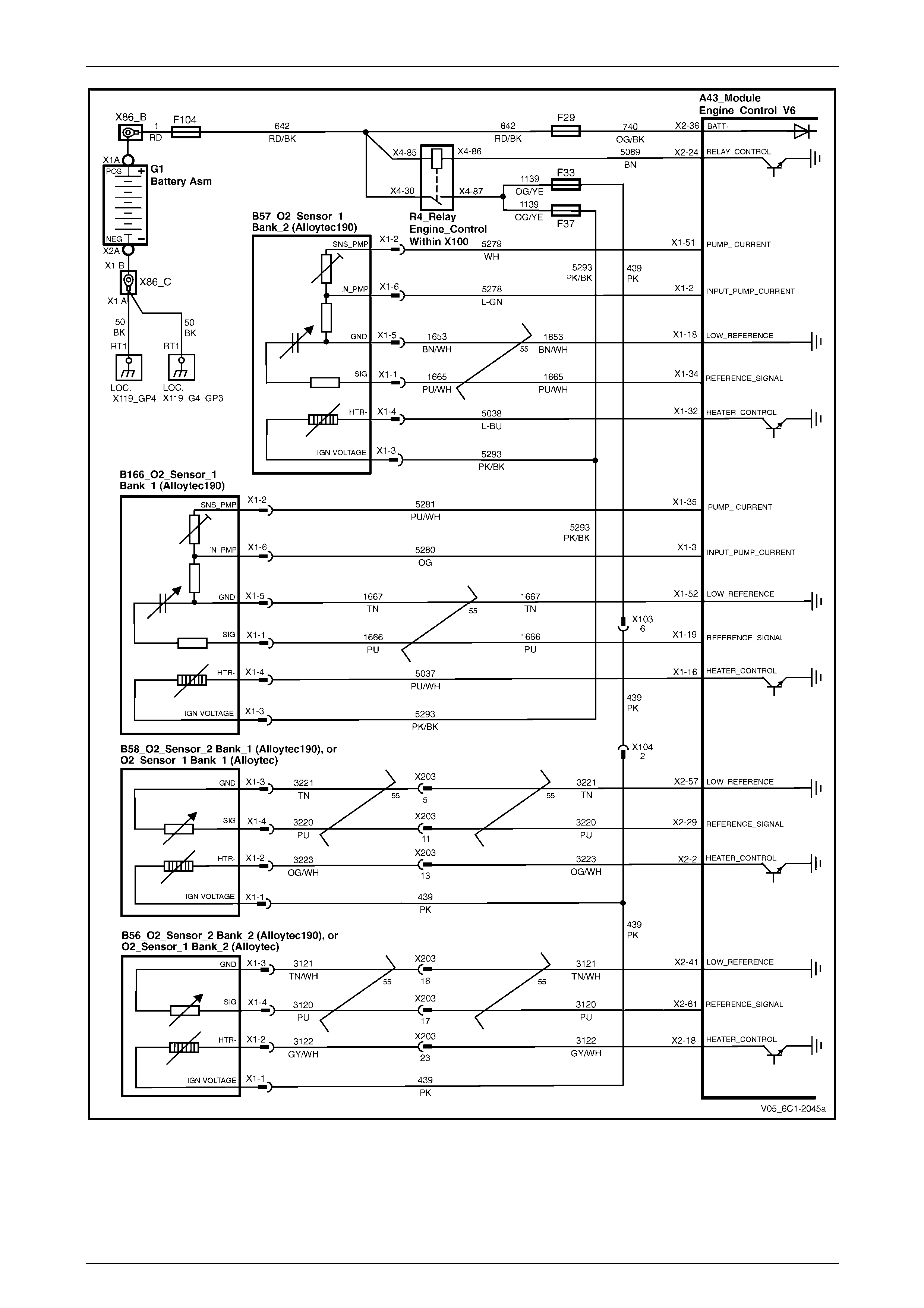
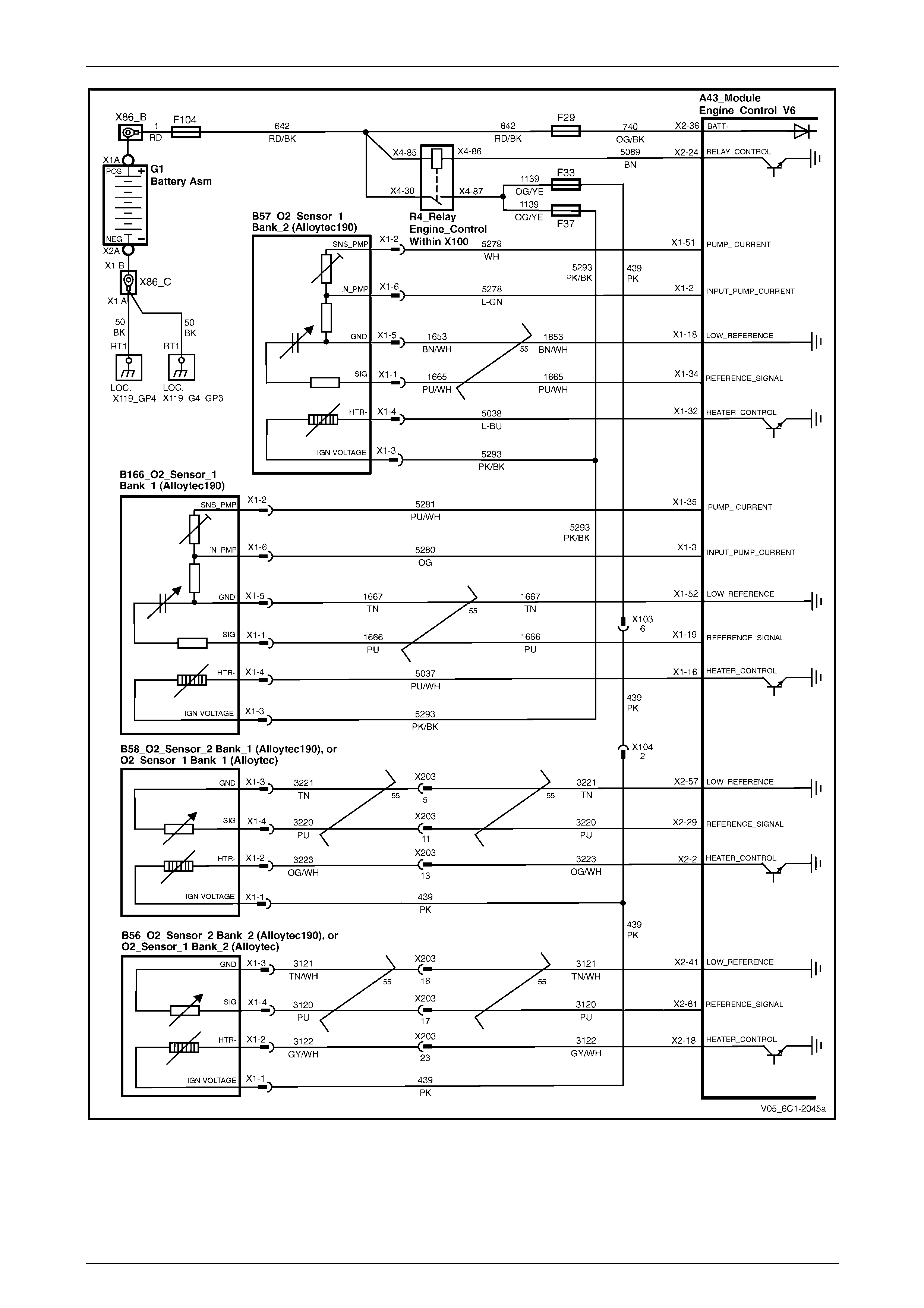
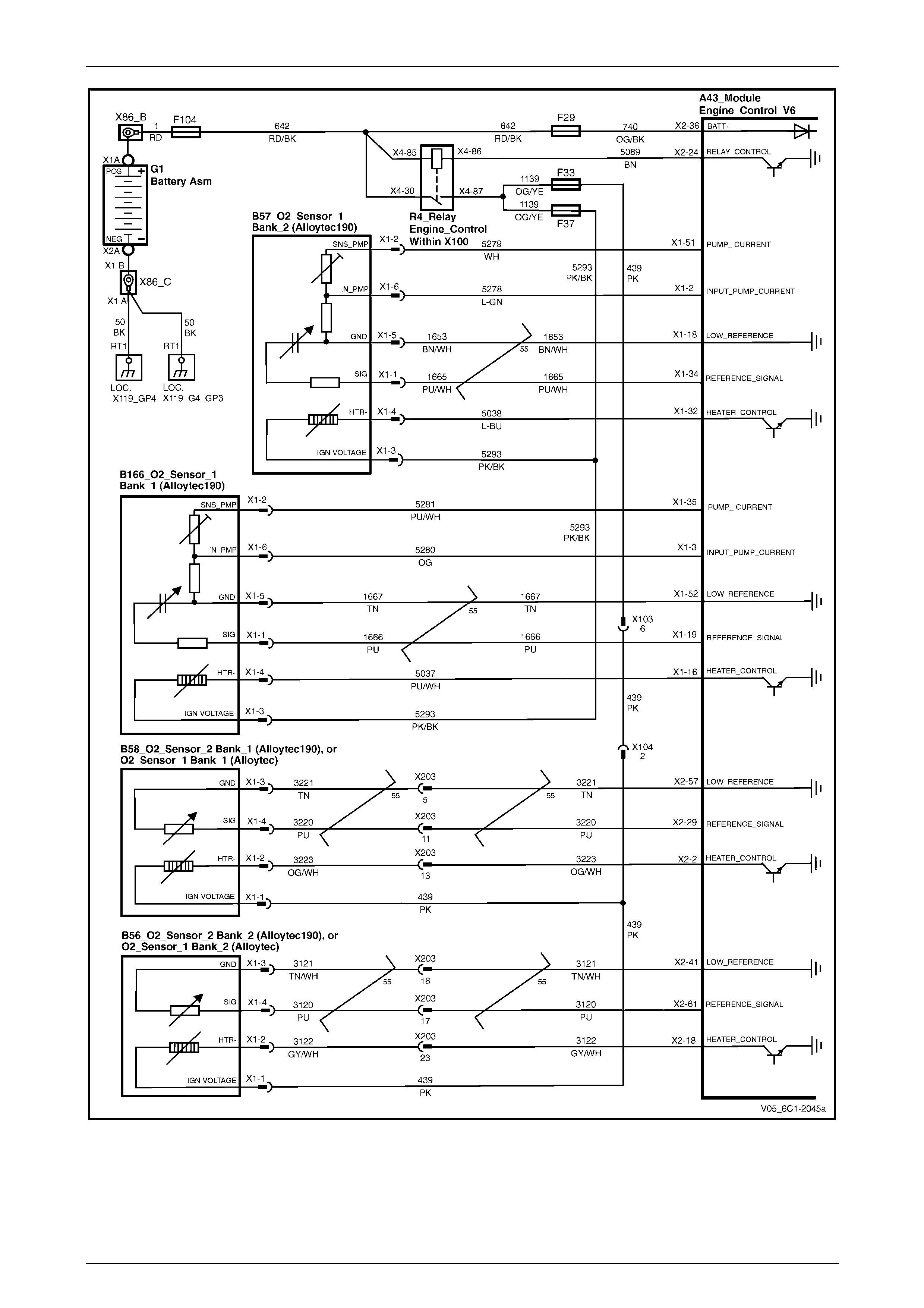
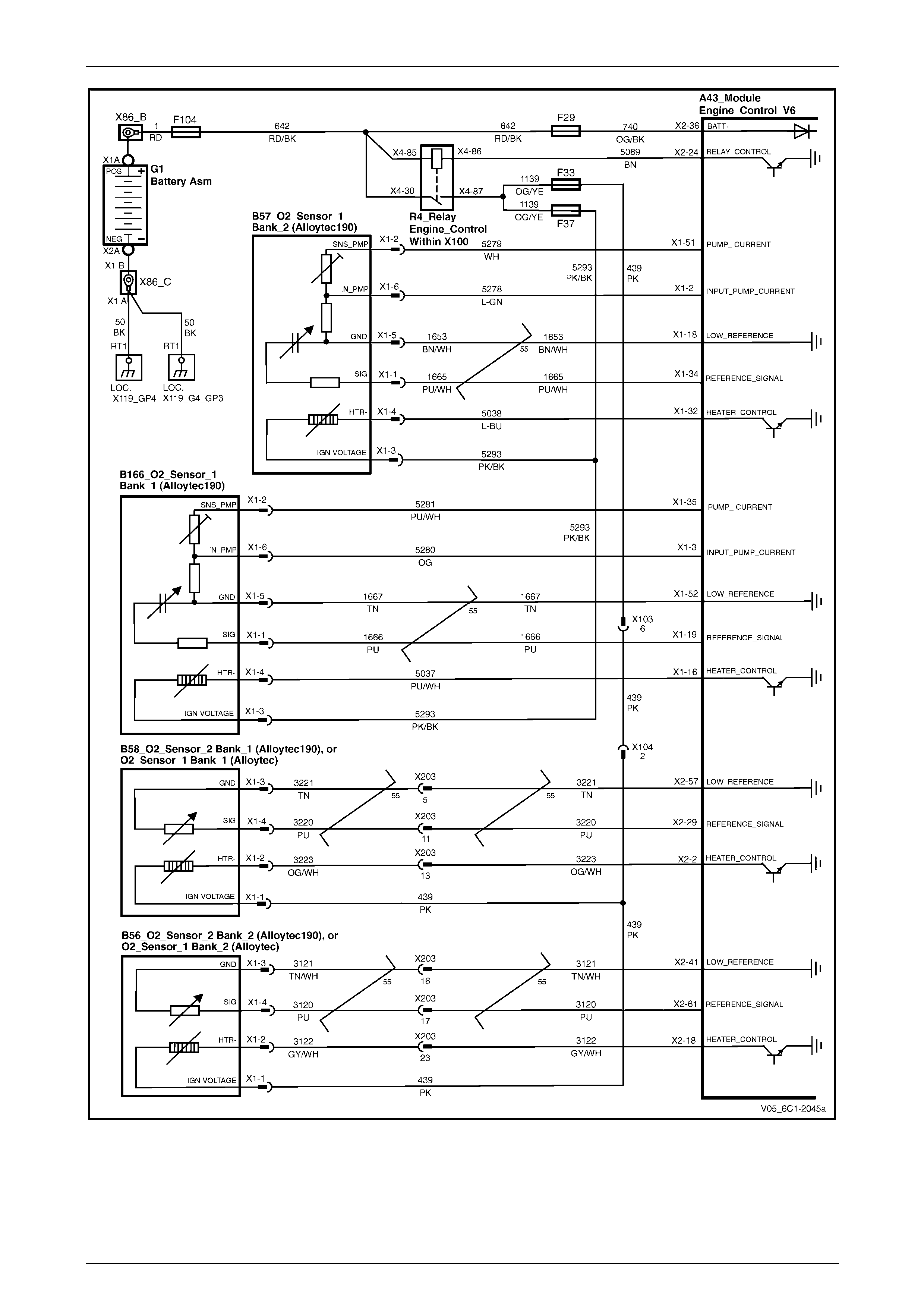
HO2S – Alloytec190 ............................................................................................................................................. 27
Fuel Injectors........................................................................................................................................................ 28
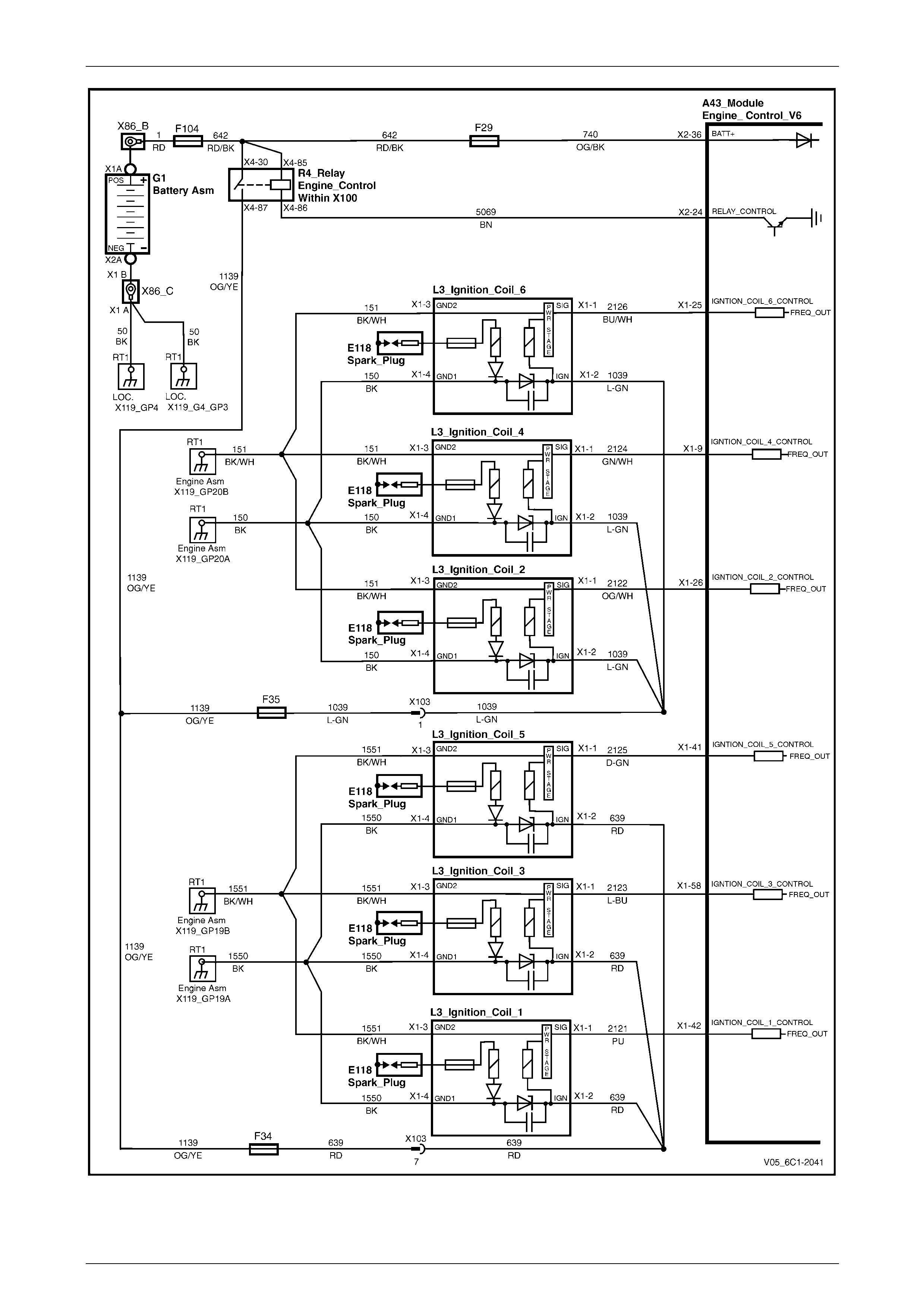
Ignition.................................................................................................................................................................. 29
2.2 Connector Chart................................................................................................................................................... 30
3 Diagnostics Starting Point ..................................................................................................................32
3.1 Basic Requirements ............................................................................................................................................ 32
Basic Know ledge Required................................................................................................................................. 32
Basic Tools Required .......................................................................................................................................... 32
3.2 Diagnostic Precautions....................................................................................................................................... 33
3.3 Preliminary Checks.............................................................................................................................................. 34
3.4 Diagnostic System Check................................................................................................................................... 35
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 35
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 35
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline
Techline

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–2
Page 6C1-2–2
4 Symptoms Diagnostics........................................................................................................................37
4.1 Symptoms Diagnosis Table................................................................................................................................ 37
4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.............................................................................................................................. 38
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 38
Diagnostic Table.................................................................................................................................................. 38
4.3 Backfire................................................................................................................................................................. 40
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 40
4.4 Cranks But Does Not Run................................................................................................................................... 42
Definition .............................................................................................................................................................. 42
4.5 Cuts Out, Misses.................................................................................................................................................. 43
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 43
4.6 Detonation/Spark Knock ..................................................................................................................................... 44
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 44
4.7 Dieseling, Run-on ................................................................................................................................................ 45
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 45
4.8 Hard Start.............................................................................................................................................................. 46
Definition .............................................................................................................................................................. 46
4.9 Hesitation, Sag and Stumble .............................................................................................................................. 47
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 47
4.10 Lack of Pow er, Sluggishness or Sponginess ................................................................................................... 48
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 48
4.11 Poor Fuel Economy............................................................................................................................................. 49
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 49
4.12 Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or Stalling ....................................................................................................... 51
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 51
4.13 Surges / Chuggles ............................................................................................................................................... 52
Description........................................................................................................................................................... 52
5 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables........................................................................................................53
5.1 DTC List................................................................................................................................................................ 53
5.2 DTC P0219 Engine Overspeed Condition.......................................................................................................... 68
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 68
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 68
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 68
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 68
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 68
Conditions for Clearing the DTC........................................................................................................................ 68
DTC P0219 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................... 69
5.3 DTC P0645 to P0647 – A/C Relay Control Circuit.............................................................................................. 70
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 70
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 70
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 71
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 71
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 71
Conditions for Setting DTC P0645 ................................................................................................................... 71
Conditions for Setting DTC P0646 ................................................................................................................... 71
Conditions for Setting DTC P0647 ................................................................................................................... 71
Conditions for Clearing the DTC........................................................................................................................ 71
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 71
DTC P0645 to P0647 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................... 72

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–3
Page 6C1-2–3
5.4 DTC P0532 and P0533 – A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit.................................................................. 73
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 73
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 73
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 73
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 74
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 74
DTC P0532 ...................................................................................................................................................... 74
DTC P0533 ...................................................................................................................................................... 74
Conditions for Clearing the DTC........................................................................................................................ 74
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 74
DTC P0532 and P0533 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................ 74
5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit................................................................ 76
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 76
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 76
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 77
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 77
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 77
DTC P2122 ...................................................................................................................................................... 77
DTC P2123 ...................................................................................................................................................... 77
DTC P2127 ...................................................................................................................................................... 77
DTC P2128 ...................................................................................................................................................... 77
DTC P2138 ...................................................................................................................................................... 77
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................... 77
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 77
DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and P2138 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................78
5.6 DTC P2227 to P2229 – Barometric Pressure Sensor Circuit............................................................................ 80
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 80
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 80
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 80
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 80
DTC P2227 ...................................................................................................................................................... 80
DTC P2228 and P2229 .................................................................................................................................... 80
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 81
DTC P2227 ...................................................................................................................................................... 81
DTC P2228 ...................................................................................................................................................... 81
DTC P2229 ...................................................................................................................................................... 81
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................... 81
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 81
DTC P2227 to P2229 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................... 81
5.7 DTC P0504 Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction ................................................................................................... 83
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 83
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 83
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 84
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 84
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 84
Conditions for Clearing the DTC........................................................................................................................ 84
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 84
DTC P0504 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................... 85

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–4
Page 6C1-2–4
5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP / CMP Position Correlation .......................................................... 87
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 87
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 87
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 88
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 88
DTC P0008 or P0009 ....................................................................................................................................... 88
DTC P0016, P0017, P0018 or P0019 .............................................................................................................. 88
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 88
DTC P0008 ...................................................................................................................................................... 88
DTC P0009 ...................................................................................................................................................... 88
DTC P0016, P0017, P0018 or P0019 .............................................................................................................. 88
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................... 88
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 89
DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 Diagnostic Table ...................................................................................... 89
5.9 DTC P0335 to P0338 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit ............................................................................. 90
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 90
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 90
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 90
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 91
DTC P0335 ...................................................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0336 ...................................................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0337 and P0338 .................................................................................................................................... 91
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0335 ...................................................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0336 ...................................................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0337 ...................................................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0338 ...................................................................................................................................................... 91
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................... 91
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 91
DTC P0335 to P0338 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................... 92
5.10 DTC P0704 – Clutch Sw itch Circuit.................................................................................................................... 93
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 93
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 93
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 93
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 94
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 94
Conditions for Clearing the DTC........................................................................................................................ 94
DTC P0704 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................... 94
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088 to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator Solenoid Control Circuit96
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................... 96
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................... 96
Additional Information......................................................................................................................................... 97
Conditions for Running the DTC........................................................................................................................ 97
DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088, P2090, P2092 or P2094 ............................................................. 97
DTC P2089, P2091, P2093, or P2095 ............................................................................................................. 97
Conditions for Setting the DTC .......................................................................................................................... 98
DTC P0010, P0013, P0020 or P0023 .............................................................................................................. 98
DTC P2088, P2090, P2092 or P2094 .............................................................................................................. 98
DTC P2089, P2091, P2093 or P2095 .............................................................................................................. 98
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................... 98
Test Description................................................................................................................................................... 98
DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088 to P2095 Diagnostic Table.............................................................. 98

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–5
Page 6C1-2–5
5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348, P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 – Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit100
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 100
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 100
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 101
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 102
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 102
DTC P0342 or P0347 ..................................................................................................................................... 102
DTC P0367 or P0392 ..................................................................................................................................... 102
DTC P0341, P0346, P0366 or P0391 ............................................................................................................ 102
DTC P0343 or P0348 ..................................................................................................................................... 102
DTC P0368 or P0393 ..................................................................................................................................... 102
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 102
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 102
DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348, P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 Diagnostic Table......................... 103
5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011 to P1014 – Camshaft Position System Performance or Park
Position............................................................................................................................................................... 105
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 105
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 105
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 106
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 106
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021 and P0024.......................................................................................................... 106
DTC P1011, P1012, P1013 and P1014.......................................................................................................... 106
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 106
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021 or P0024 ............................................................................................................ 106
DTC P1011, P1012, P1013 and P1014.......................................................................................................... 106
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 107
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021 and P0024.......................................................................................................... 107
DTC P1011, P1012, P1013 and P1014.......................................................................................................... 107
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 107
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011 to P1014 Diagnostic Table............................................................ 107
5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 – Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit..................................................... 108
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 108
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 108
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 109
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 109
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 109
DTC P0480 .................................................................................................................................................... 109
DTC P0481 .................................................................................................................................................... 109
DTC P0691 .................................................................................................................................................... 109
DTC P0692 .................................................................................................................................................... 109
DTC P0693 .................................................................................................................................................... 109
DTC P0694 .................................................................................................................................................... 109
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 109
DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 Diagnostic Table .................................................................................... 110

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–6
Page 6C1-2–6
5.15 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 – ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or Memory Fault................... 111
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 111
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 111
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 111
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 111
DTC P0601 .................................................................................................................................................... 111
DTC P0602 and P0606 .................................................................................................................................. 111
DTC P0604 .................................................................................................................................................... 111
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 111
DTC P0601 .................................................................................................................................................... 111
DTC P0602 .................................................................................................................................................... 111
DTC P0604 .................................................................................................................................................... 111
DTC P0606 .................................................................................................................................................... 111
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 111
DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 Diagnostic Table ................................................................................. 112
5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit .................... 113
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 113
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 113
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 113
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P0116 .................................................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P0117, P0118 and P1258 ...................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P00125................................................................................................................................................... 114
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 114
DTC P0116 .................................................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P0117 .................................................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P0118 .................................................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P0125 .................................................................................................................................................... 114
DTC P1258 .................................................................................................................................................... 114
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 114
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 114
DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and P1258 Diagnostic Table..................................................................... 115
5.17 DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Engine Control Module System Voltage ....................................................... 117
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 117
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 117
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 119
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 119
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 119
DTC P0560 .................................................................................................................................................... 119
DTC P0562 .................................................................................................................................................... 119
DTC P0563 .................................................................................................................................................... 119
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 119
DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Diagnostic Table.............................................................................................. 120
5.18 DTC P0685 to P0687 – Engine Control Relay Circuit...................................................................................... 121
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 121
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 121
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 121
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 122
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 122
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 122
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 122
DTC P0685 to P0687 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................. 122

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–7
Page 6C1-2–7
5.19 DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction...................................................................................... 124
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 124
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 124
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 124
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 124
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 124
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 124
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 124
DTC P1845 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 125
5.20 P0521 to P0523 – Engine Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit ................................................................................... 126
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 126
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 126
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 126
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 126
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 127
P0521............................................................................................................................................................. 127
P0522............................................................................................................................................................. 127
P0523............................................................................................................................................................. 127
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 127
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 127
P0521 to P0523 Diagnostic Table..................................................................................................................... 127
5.21 DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 – Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit...................................................... 129
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 129
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 129
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 129
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 129
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 130
DTC P0196 .................................................................................................................................................... 130
DTC P0197 .................................................................................................................................................... 130
DTC P0198 .................................................................................................................................................... 130
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 130
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 130
DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 Diagnostic Table.............................................................................................. 130
5.22 DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 – Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid Valve Control Circuit................... 132
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 132
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 132
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 132
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 133
DTC P0443 and P0458 .................................................................................................................................. 133
DTC P0459 .................................................................................................................................................... 133
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 133
DTC P0443 .................................................................................................................................................... 133
DTC P0458 .................................................................................................................................................... 133
DTC P0459 .................................................................................................................................................... 133
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 133
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 133
DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 Diagnostic Table.............................................................................................. 134

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–8
Page 6C1-2–8
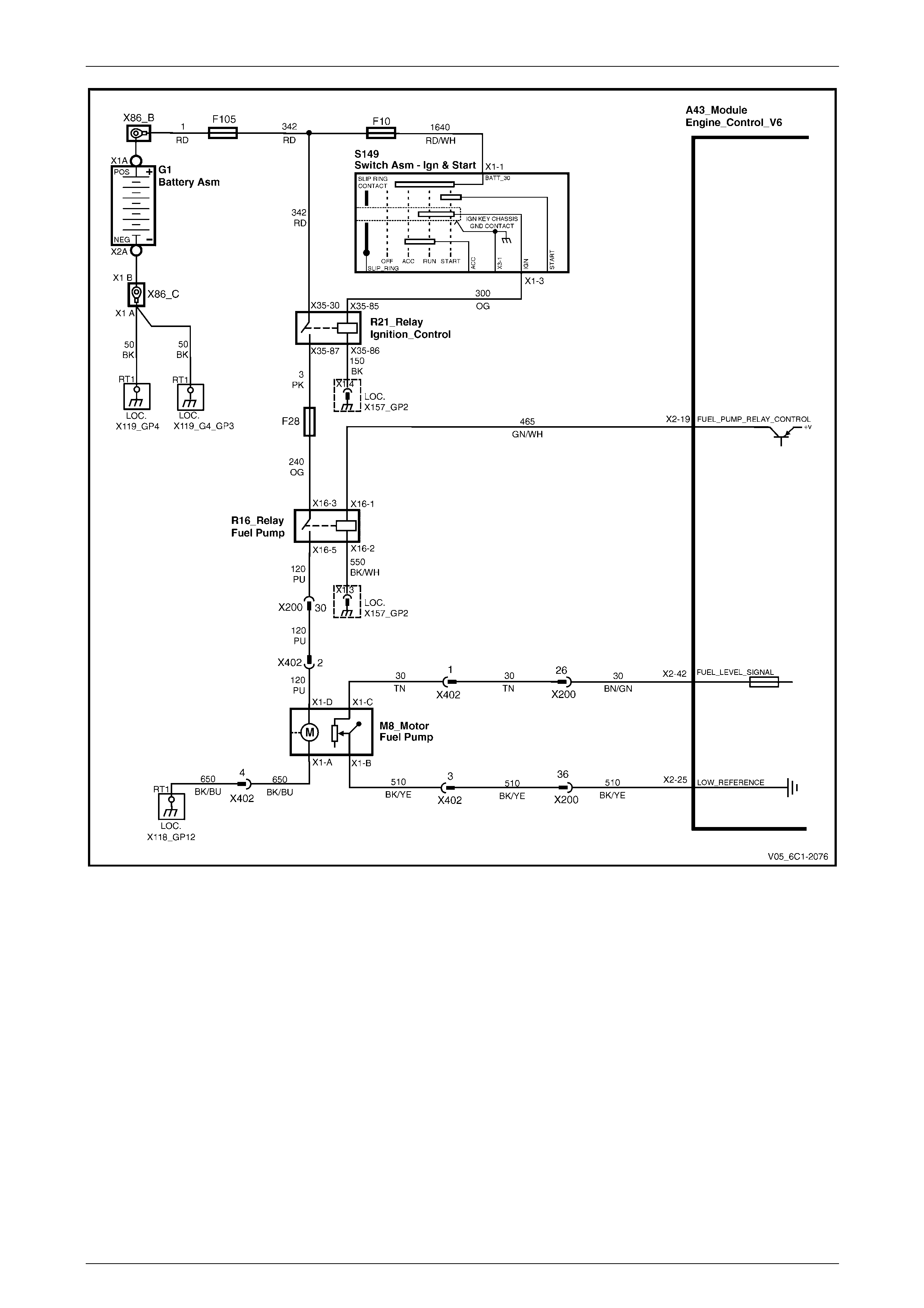
5.23 DTC P0627 to P0629 – Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit................................................................................ 135
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 135
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 135
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 137
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 137
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 137
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 137
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 137
DTC P0627 to P0629 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................. 137
5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and
P0277 – Fuel Injector Control Circuit............................................................................................................... 139
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 139
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 139
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 140
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 141
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 141
DTC P0201,P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205 or P0206..................................................................................... 141
DTC P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270, P0273 and P0276 ................................................................................. 141
DTC P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271, P0274 and P0277 ................................................................................. 141
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 141
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 141
DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and
P0277 Diagnostic Table ............................................................................................................................... 141
5.25 DTC P0625 and P0626 – Generator F-Terminal Circuit................................................................................... 143
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 143
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 143
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 143
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 144
DTC P0625 .................................................................................................................................................... 144
DTC P0626 .................................................................................................................................................... 144
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 144
DTC P0625 .................................................................................................................................................... 144
DTC P0626 .................................................................................................................................................... 144
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 144
DTC P0625 and P0626 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 144
5.26 DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 – Generator L Terminal Circuit....................................................................... 145
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 145
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 145
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 145
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 146
DTC P1668 .................................................................................................................................................... 146
DTC P2500 .................................................................................................................................................... 146
DTC P2501 .................................................................................................................................................... 146
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 146
DTC P1668 .................................................................................................................................................... 146
DTC P2500 .................................................................................................................................................... 146
DTC P2501 .................................................................................................................................................... 146
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 146
DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 Diagnostic Table.............................................................................................. 147

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–9
Page 6C1-2–9
5.27 DTC P0112 and P0113 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit ................................................................... 148
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 148
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 148
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 149
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 149
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 149
DTC P0112 .................................................................................................................................................... 149
DTC P0113 .................................................................................................................................................... 149
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 149
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 149
DTC P0112 and P0113 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 150
5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and
P2316 – Ignition Coil Control Circuit................................................................................................................ 151
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 151
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 151
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 153
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 153
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 153
DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354, P0355 or P0356.................................................................................... 153
DTC P2300, P2303, P2306, P2309, P2312 or P2315.................................................................................... 153
DTC P2301, P2304, P2307, P2310, P2313 and P2316 ................................................................................. 153
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 153
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 153
DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and
P2316 Diagnostic Table ............................................................................................................................... 154
5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632, P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser Signal ...................................... 156
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 156
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 156
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 156
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 157
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 157
P0513............................................................................................................................................................. 157
P0633............................................................................................................................................................. 157
P1629............................................................................................................................................................. 157
P1632............................................................................................................................................................. 157
P1677............................................................................................................................................................. 157
P1678............................................................................................................................................................. 157
P1679............................................................................................................................................................. 157
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 157
DTC P0513, P1629, P1632, P0633, P1677, P1678, P1679 Diagnostic Table................................................... 158
5.30 DTC P1648 – Wrong Security Code Entered.................................................................................................... 159
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 159
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 159
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 159
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 159
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 159
Action Taken When the DTC Sets .................................................................................................................... 159
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 159
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 159
DTC P1648 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 160

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–10
Page 6C1-2–10
5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 – Knock Sensor Circuit....................................................................... 161
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 161
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 161
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 161
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 162
DTC P0327 and P0332 .................................................................................................................................. 162
DTC P0328 or P0333 ..................................................................................................................................... 162
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 162
DTC P0327 and P0332 .................................................................................................................................. 162
DTC P0328 and P0333 .................................................................................................................................. 162
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 162
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 162
DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 Diagnostic Table ................................................................................. 163
5.32 DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor Module Performance.......................................................................................... 164
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 164
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 164
Test One ........................................................................................................................................................ 164
Test Two ........................................................................................................................................................ 164
Test Three...................................................................................................................................................... 164
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 165
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 165
Condition One ................................................................................................................................................ 165
Condition Two ................................................................................................................................................ 165
Condition Three.............................................................................................................................................. 165
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 165
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 165
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 165
DTC P0324 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 166
5.33 DTC P0101 to P0103 – MAF Sensor Circuit ..................................................................................................... 167
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 167
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 167
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 168
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 168
DTC P0101 .................................................................................................................................................... 168
DTC P0102 .................................................................................................................................................... 168
DTC P0103 .................................................................................................................................................... 168
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 169
DTC P0101 .................................................................................................................................................... 169
DTC P0102 .................................................................................................................................................... 169
DTC P0103 .................................................................................................................................................... 169
DTC P0101 to P0103 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................. 169
5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038, P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2 Sensor Heater Control
Circuit ................................................................................................................................................................. 171
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 171
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 171
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 173
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 173
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 173
DTC P0030, P0036, P0050 or P0056 ............................................................................................................ 173
DTC P0031, P0037, P0051 or P0057 ............................................................................................................ 173
DTC P0032, P0038, P0052 or P0058 ............................................................................................................ 173
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 173
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 173
DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038, P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 Diagnostic Table ................... 174

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–11
Page 6C1-2–11
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160,
P0161, P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit................................. 175
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 175
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 176
Alloytec Engine O2 Sensor 1 or Alloytec190 Engine O2 Sensor 2 ................................................................. 176
Alloytec190 Engine O2 Sensor 1.................................................................................................................... 176
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 178
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 178
DTC P0130, P0131, P0132, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0150, P0151 or P0152 ............................................... 178
DTC P0135 and P0155 .................................................................................................................................. 178
DTC P0137 and P0157 .................................................................................................................................. 178
DTC P0138 and P0158 .................................................................................................................................. 179
DTC P0140 and P0160 .................................................................................................................................. 179
DTC P0141 and P0161 .................................................................................................................................. 179
DTC P2243 and P2247 .................................................................................................................................. 179
DTC P2270 and P2272 .................................................................................................................................. 179
DTC P2297 and P2298 .................................................................................................................................. 179
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 180
DTC P0130 and P0150 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0131 and P0151 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0132 and P0152 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0135 and P0155 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0137 and P0157 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0138 and P0158 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0140 and P0160 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P0141 and P0161 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P2243 and P2247 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P2270 and P2272 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P2271 and P2273 .................................................................................................................................. 180
DTC P2297 and P2298 .................................................................................................................................. 180
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 180
DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135 to P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 Diagnostic Table .............................................................. 181
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 – O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control Circuit, Alloytec190........ 182
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 182
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 182
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 183
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 184
DTC P2237, P2238, P2239, P2240, P2241 and P2242 ................................................................................. 184
DTC P2626 and P2629 .................................................................................................................................. 184
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 185
DTC P2237, P2238, P2239, P2240, P2241 or P2242.................................................................................... 185
DTC P2626 or P2629 ..................................................................................................................................... 185
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 185
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 185
DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 Diagnostic Table.............................................................................. 186
5.37 DTC P0053 and P0059 – O2 Sensor Internal Heater Resistance Range / Performance, Alloytec190 ......... 188
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 188
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 188
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 190
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 190
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 190
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 190
DTC P0053 and P0059 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 190

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–12
Page 6C1-2–12
5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235, P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit Shorted to Heater Cont ro l
Circuit, Alloytec 190........................................................................................................................................... 191
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 191
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 191
O2 Sensor 1 ................................................................................................................................................... 191
O2 Sensor 2 ................................................................................................................................................... 191
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 193
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 193
DTC P2231 or P2234 ..................................................................................................................................... 193
DTC P2232 and P2235 .................................................................................................................................. 193
DTC P2251 and P2254 .................................................................................................................................. 193
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 194
DTC P2231 or P2234 ..................................................................................................................................... 194
DTC P2232 or P2235 ..................................................................................................................................... 194
DTC P2251 or P2254 ..................................................................................................................................... 194
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 194
DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235, P2251, P2254 Diagnostic Table............................................................... 194
5.39 DTC P0040 and P0041 – O2 Sensor Signal Not Plausible Bank 1 / Bank 2................................................... 196
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 196
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 196
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 198
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 198
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 198
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 198
DTC P0040 and P0041 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 198
5.40 DTC P0850 – Park / Neutral Signal Circuit Incorrect Signal........................................................................... 199
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 199
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 199
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 199
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 199
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 199
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 199
DTC P0850 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 200
5.41 DTC U0001 – No Communication w ith CAN Bus (High Speed)...................................................................... 201
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 201
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 201
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 201
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 201
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 201
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 201
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 201
DTC U0001 Diagnostic Table ............................................................................................................................ 202
5.42 DTC U0155 and U0423 – Serial Data Communication Circuit, PIM................................................................ 203
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 203
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 203
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 203
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 203
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 203
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 203
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 203
DTC U0155 and U0423 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 204

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–13
Page 6C1-2–13
5.43 DTC P0864 and U0101 – Serial Data Communication Circuit, TCM............................................................... 205
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 205
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 205
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 205
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 205
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 205
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 205
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 205
DTC P0864 and U0101 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 206
5.44 DTC U0121 and U0415 Serial Data Communication Circuit, ABS / TC / ESP................................................ 207
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 207
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 207
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 207
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 207
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 207
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 207
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 207
DTC U0121 and U0415 Diagnostic Table.......................................................................................................... 208
5.45 DTC P0615 to P0617 – Starter Relay Control Circuit....................................................................................... 209
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 209
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 209
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 209
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 210
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 210
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 210
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 210
DTC P0615 to P0617 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................. 210
5.46 DTC P2107 – Throttle Control Malfunction...................................................................................................... 212
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 212
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 212
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 213
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 213
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 213
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 213
DTC P2107 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 213
5.47 DTC P2105 – Throttle Control Forced Engine Shutdown............................................................................... 214
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 214
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 214
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 215
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 215
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 215
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 215
DTC P2105 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 216

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–14
Page 6C1-2–14
5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle Actuator Control Motor Control
Circuit ................................................................................................................................................................. 217
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 217
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 217
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 218
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 218
DTC P0506 and P0507 .................................................................................................................................. 218
DTC P0638 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P2100 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P2101 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P1551, P2119 and P2176 ...................................................................................................................... 219
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 219
DTC P0506 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P0507 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P0638 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P1551 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC 2100....................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P2101 .................................................................................................................................................... 219
DTC P2119 .................................................................................................................................................... 220
DTC P2176 .................................................................................................................................................... 220
Conditions for Clearing DTC............................................................................................................................. 220
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 220
P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2119 and P2176 Diagnostic Table......................................... 221
5.49 DTC P0700 – Malfunction Indicator Request from Transmission Control Module....................................... 223
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 223
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 223
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 223
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 223
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 223
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 223
DTC P0700 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 223
5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 – Throttle Position Sensor Circuit..................................................... 224
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 224
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 224
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 225
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 225
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 225
DTC P0121 .................................................................................................................................................... 225
DTC P0122 .................................................................................................................................................... 225
DTC P0123 .................................................................................................................................................... 225
DTC P0221 .................................................................................................................................................... 225
DTC P0222 .................................................................................................................................................... 225
DTC P0223 .................................................................................................................................................... 225
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 226
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 226
DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 Diagnostic Table................................................................................. 226
5.51 DTC P0500 – Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction, Manual Transmission......................................... 228
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 228
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 228
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 228
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 229
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 229
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 229
DTC P0500 Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................. 229

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–15
Page 6C1-2–15
5.52 DTC P0461 to P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor Circuit............................................................................................ 231
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 231
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 231
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 231
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 231
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 232
DTC P0461 .................................................................................................................................................... 232
DTC P0462 .................................................................................................................................................... 232
DTC P0463 .................................................................................................................................................... 232
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 232
DTC P0461, P0462 or P0463 Diagnostic Table ................................................................................................ 232
5.53 DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 – Intake Manifold Runner Control Valve Control Circuit.............................. 234
DTC Description................................................................................................................................................. 234
Circuit Description............................................................................................................................................. 234
Additional Information....................................................................................................................................... 234
Conditions for Running the DTC...................................................................................................................... 235
DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 ...................................................................................................................... 235
Conditions for Setting the DTC ........................................................................................................................ 235
DTC P2008 .................................................................................................................................................... 235
DTC P2009 .................................................................................................................................................... 235
DTC P2010 .................................................................................................................................................... 235
Conditions for Clearing the DTC...................................................................................................................... 235
Test Description................................................................................................................................................. 235
DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 Diagnostic Table.............................................................................................. 235
6 Tech 2 Data Lists................................................................................................................................237
6.1 Data Display ....................................................................................................................................................... 237
6.2 Actuator Tests List............................................................................................................................................. 241

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–16
Page 6C1-2–16
1 General Information
1.1 Diagnostic System Check
The engine management diagnostic procedure is organised in a logical structure that begins with the Diagnostic System
Check. The Diagnostic System Check directs the diagnostic procedure to the logical steps necessary to diagnose an
engine driveability fault condition.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–17
Page 6C1-2–17
1.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables
The Diagnostic System Check directs the diagnostic procedure to the appropriate diagnostic trouble code (DTC) tables if
there is a DTC currently stored in the engine control module (ECM).
The diagnostic tables locate a faulty circuit or component through a logic based on the process of elimination. These
diagnostic tables are developed with the following assumptions:
• the vehicle functioned correctly at the time of assembly,
• there are no multiple faults, and
• the problem currently exists.
Understanding and the correct use of the diagnostic tables are essential to reduce diagnostic time and to prevent
misdiagnosis.
Multiple DTC Fault Conditions
Some fault conditions trigger multiple component DTCs even if the fault condition exists only on a single component. If
there are multiple DTCs stored in the ECM, the service technician must view and record all DTCs logged.
The relationship between the logged DTCs can then be analysed to determine the source of the fault condition. Always
begin the diagnostic process with the DTC table of the fault condition that may trigger other DTCs to set.
The following fault conditions may trigger multiple DTCs:
• a fault in the serial data communication circuit,
• a system voltage that is too low may cause incorrect engine management system operation or engine management
component malfunction,
• a system voltage that is too high may damage the ECM and/or other engine management components,
• fault condition in the ECM read only memory (ROM) or random access memory (RAM),
• fault condition in the ECM internal circuitry or programming,
• improperly connected sensor or component wiring connector, or
• an electrical fault condition in the following shared ECM electrical circuits trigger DTCs on components or sensors
that share in the faulty shared circuit. Test the electrical circuit of the appropriate sensors or components to isolate
the fault condition. Refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts.
• 5 V Reference Circuit,
• Low Reference Circuit, or
• Ignition Control Voltage Circuit.
If there are no obvious faults to begin a multiple DTC fault condition diagnostic procedure, diagnose the DTCs in the
following order unless directed otherwise:
1 Always start with the lowest numbered component level DTCs such as:
• sensor DTCs,
• solenoid DTCs, or
• relay DTCs.
2 Then follow with system level DTCs such as:
• misfire DTCs,
• fuel trim DTCs, or
• catalyst DTCs.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–18
Page 6C1-2–18
1.3 Symptoms Diagnostics
The Diagnostic System Check directs the service technician to the symptoms diagnostics if the following conditions exist:
• a vehicle driveability fault condition exists,
• there is no current diagnostic trouble code presently stored in the ECM, and
• all Tech 2 engine data parameters are within normal operating range.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–19
Page 6C1-2–19
1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The ECM constantly performs self-diagnostic tests on the engine management system. When the ECM detects a fault
condition in the engine operating parameters, the ECM sets a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) to represent that fault
condition. The following are the types of DTCs programmed in the ECM. In addition, DTCs are classified as either a
current or history DTC.
• Type A – emission related DTCs,
• Type B – emission related DTCs, and
• Type C – non-emission related DTCs.
NOTE
Depending on the type of DTC set, the ECM may
command the check engine warning display to
illuminate and warn the driver there is a fault in
the engine management system. Refer to
Section 12C Instrumentation for further
information on the Check Engine warning display.
Type A – Emission Related DTCs
The ECM takes the following action when a Type A DTC runs and fails:
• sets a current Type A DTC that represents the fault condition,
• illuminates the instrument cluster MFD Check Engine icon, and
• records the operating condition at the time the diagnostic fails and stores this information in the freeze frame/ failure
record.
Type B – Emission Related DTCs
The ECM takes the following action when a Type B DTC runs and fails:
• On the first time a Type B DTC fails, the ECM takes the following actions:
• sets a current Type B DTC that represents the fault condition, and
• records the operating conditions at the time the fault sets and stores this information in the failure records.
• On the second consecutive ignition cycle that a Type B DTC fails, the ECM takes the following actions:
• illuminates the instrument cluster MFD Check Engine icon, and
• records the operating condition at the time the diagnostic fails and stores this information in the freeze frame/
failure record.
Conditions for Clearing Type A or Type B DTCs
• The current DTC clears when there is no fault condition in the current ECM self-diagnostics.
• If there are no DTCs logged after three or four consecutive ignition cycles, the ECM deactivates the MFD Check
Engine icon.
• Type A or Type B History DTC clears when there is no fault condition after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles.
• Use of Tech 2 to clear DTCs.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–20
Page 6C1-2–20
Type C – Non-Emission Related DTCs
The ECM takes the following action when a Type A DTC runs and fails:
• sets a current Type C DTC that represents the fault condition,
• records the operating conditions at the time the DTC is logged and stores this information in the Failure Record,
and
• the instrument cluster MFD may display a message.
NOTE
The instrument cluster MFD check engine icon
does not illuminate when a Type C DTC sets.
Conditions for Clearing Type C DTCs
• The current DTC clears when there is no fault condition in the current ECM self-diagnostics.
• Type C History DTC clears when there is no fault condition after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles.
• Use of Tech 2 to clear DTCs.
Current DTCs
A DTC is a Current DTC if the fault condition that triggers that DTC is present during the last ECM self-diagnostics.
History DTCs
A DTC is a History DTC if the fault condition that triggers that DTC is not present during the last ECM self-diagnostics.
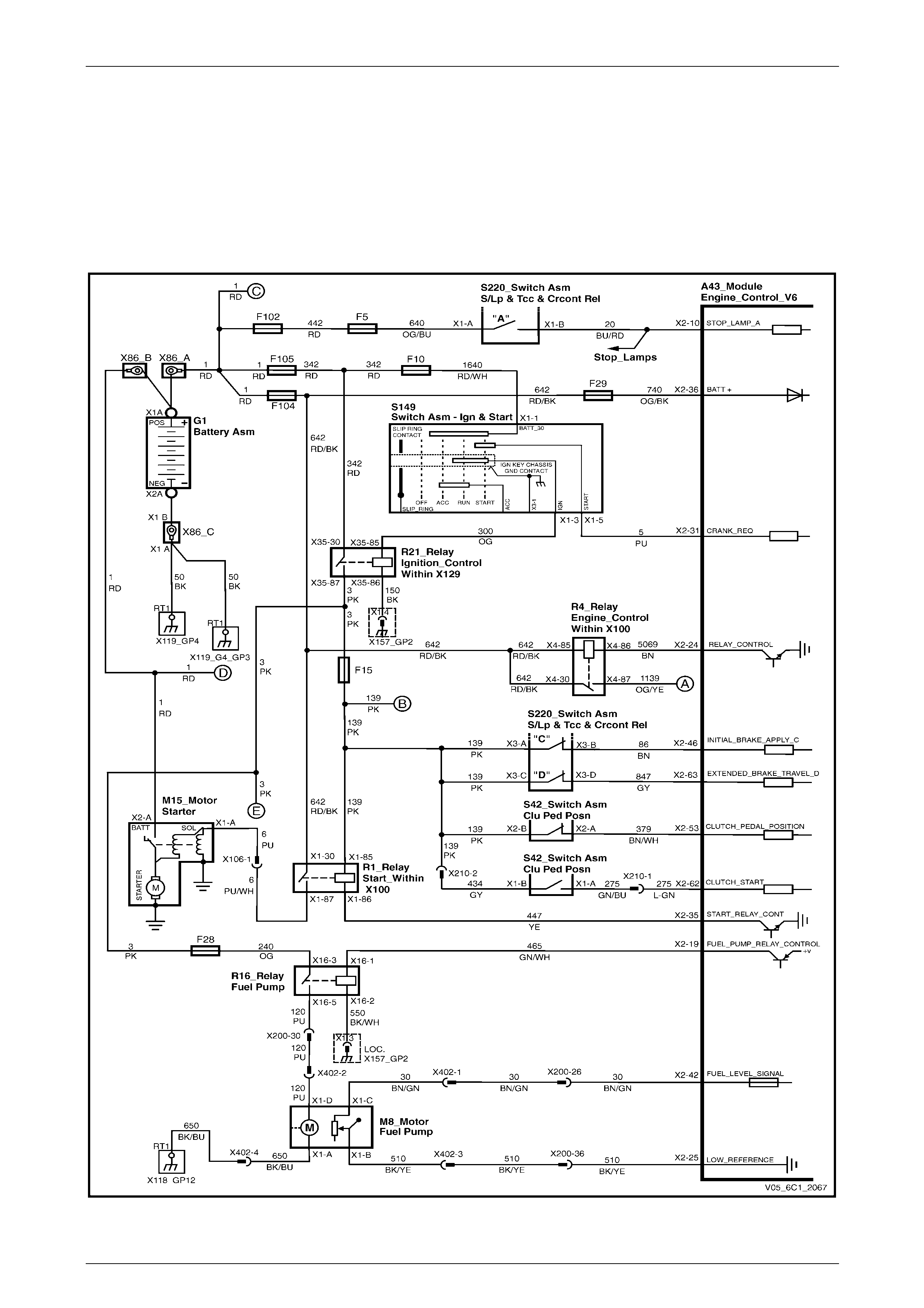
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–21
Page 6C1-2–21
2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector
Charts
2.1 Wiring Diagrams
Power Distribution
Figure 6C1-2 – 1
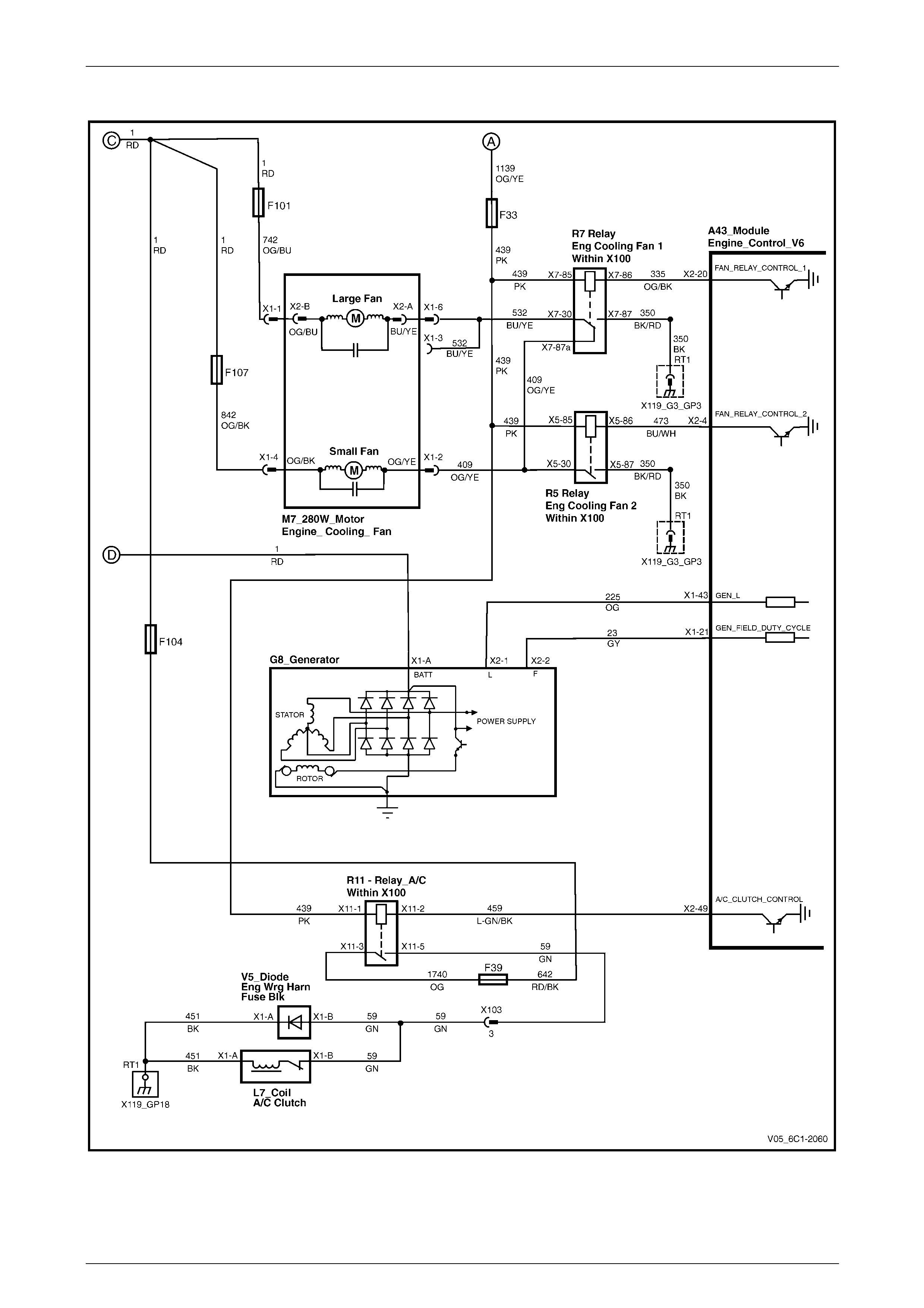
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–22
Page 6C1-2–22
Generator, Cooling Fans and A/C
Figure 6C1-2 – 2

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–23
Page 6C1-2–23
Sensors
Figure 6C1-2 – 3

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–24
Page 6C1-2–24
Sensors and Throttle Control
Figure 6C1-2 – 4
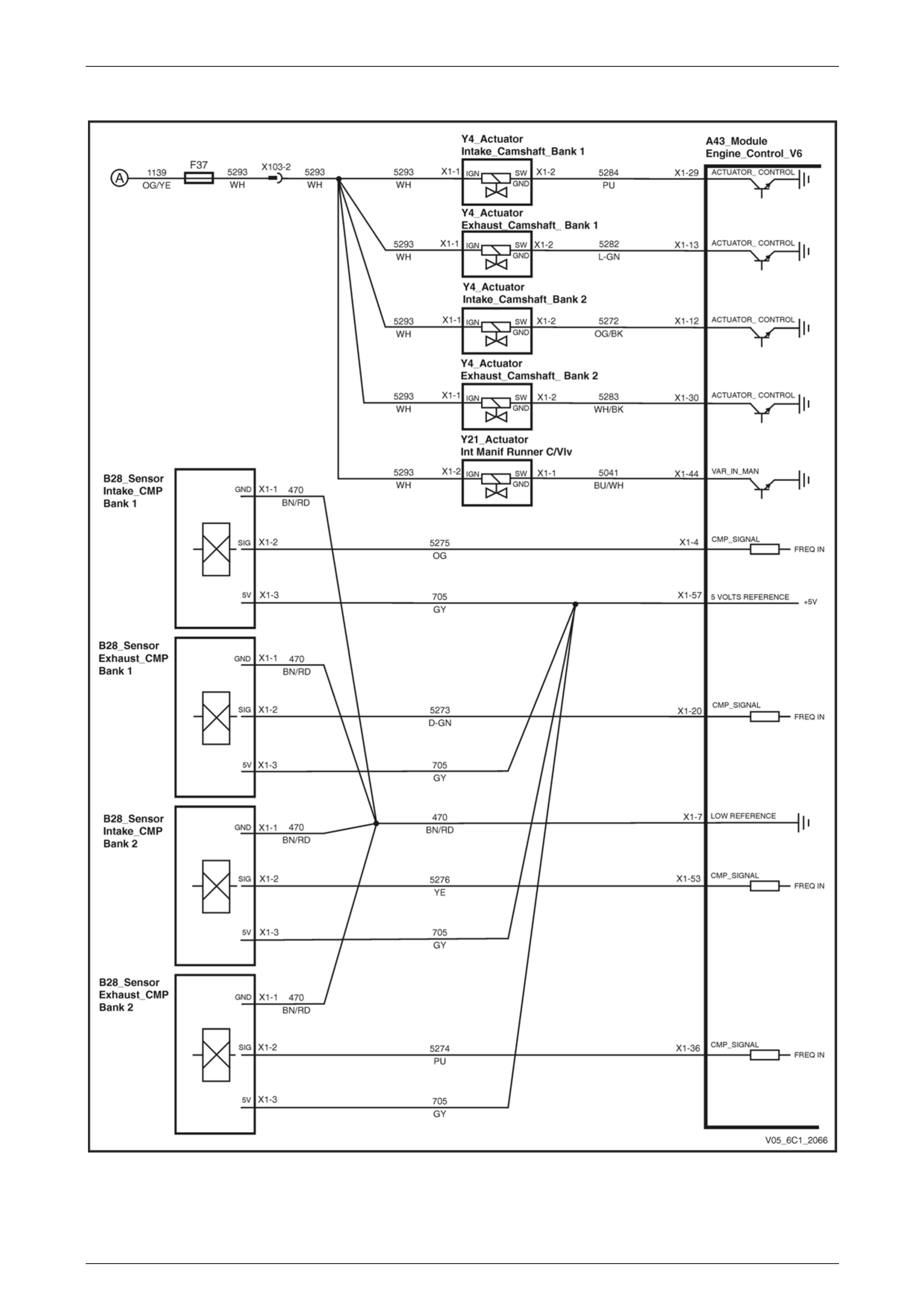
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–25
Page 6C1-2–25
Camshaft Control – Alloytec190
Figure 6C1-2 – 5
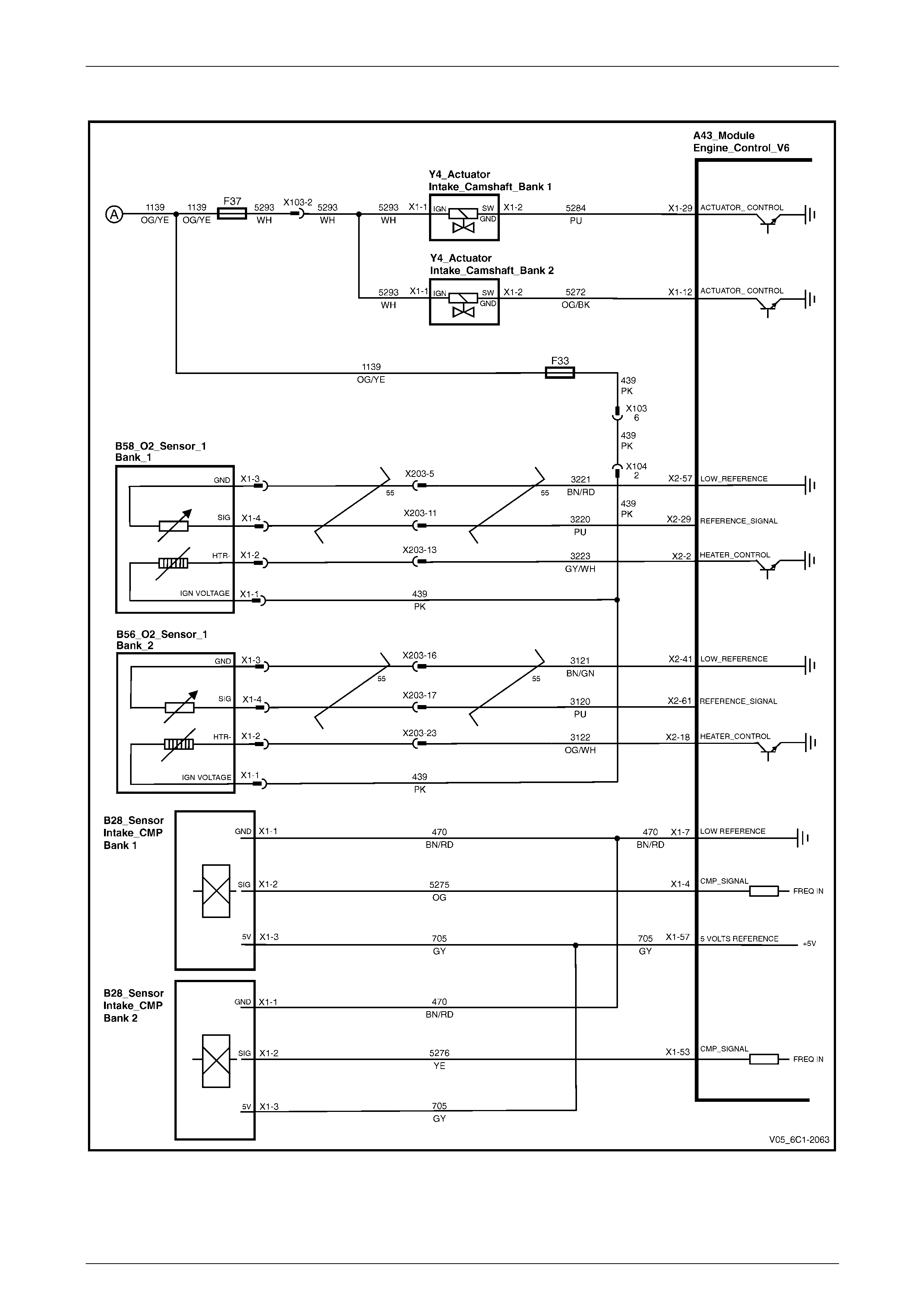
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–26
Page 6C1-2–26
Camshaft Control and HO2S – Alloytec
Figure 6C1-2 – 6
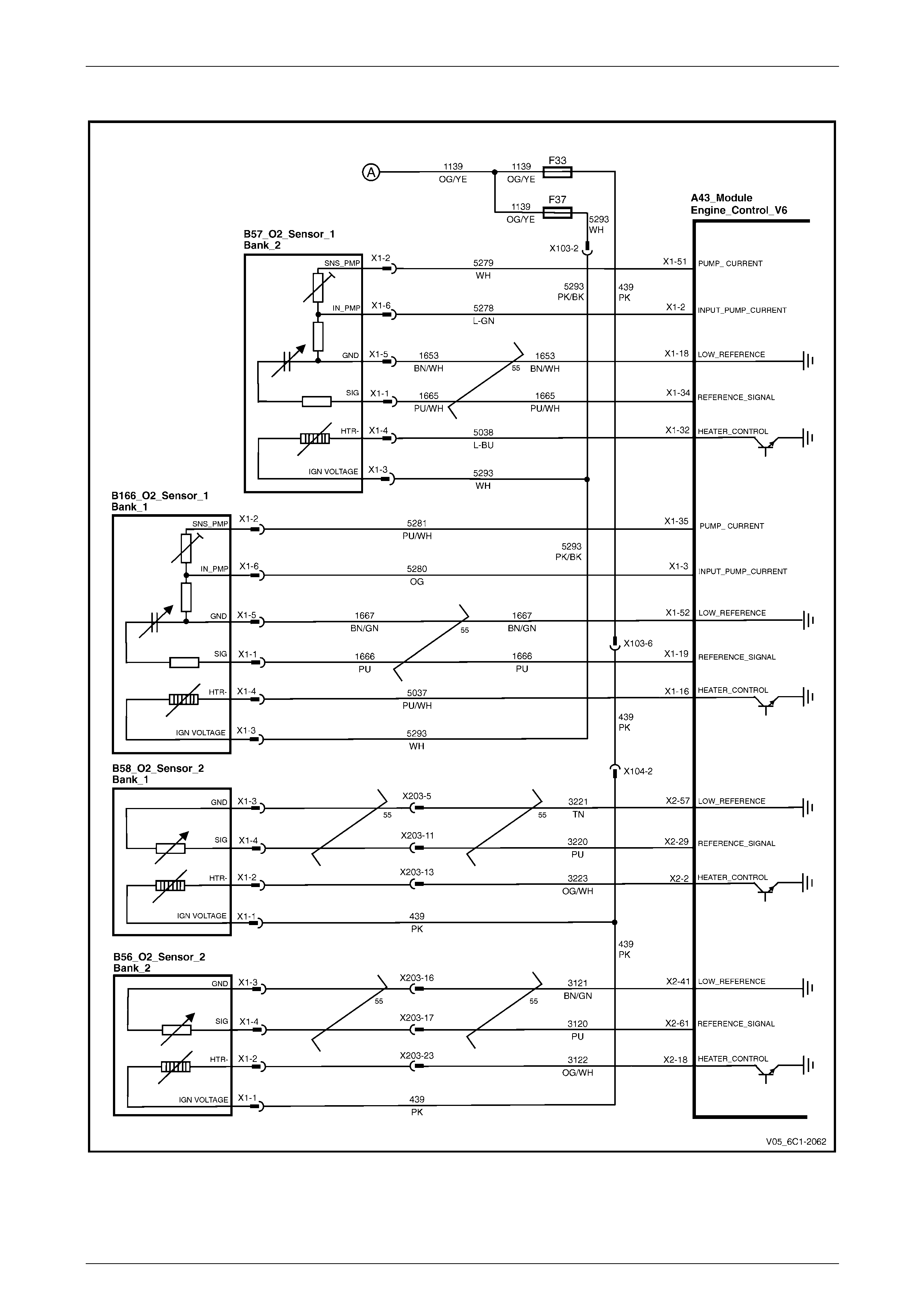
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–27
Page 6C1-2–27
HO2S – Alloytec190
Figure 6C1-2 – 7
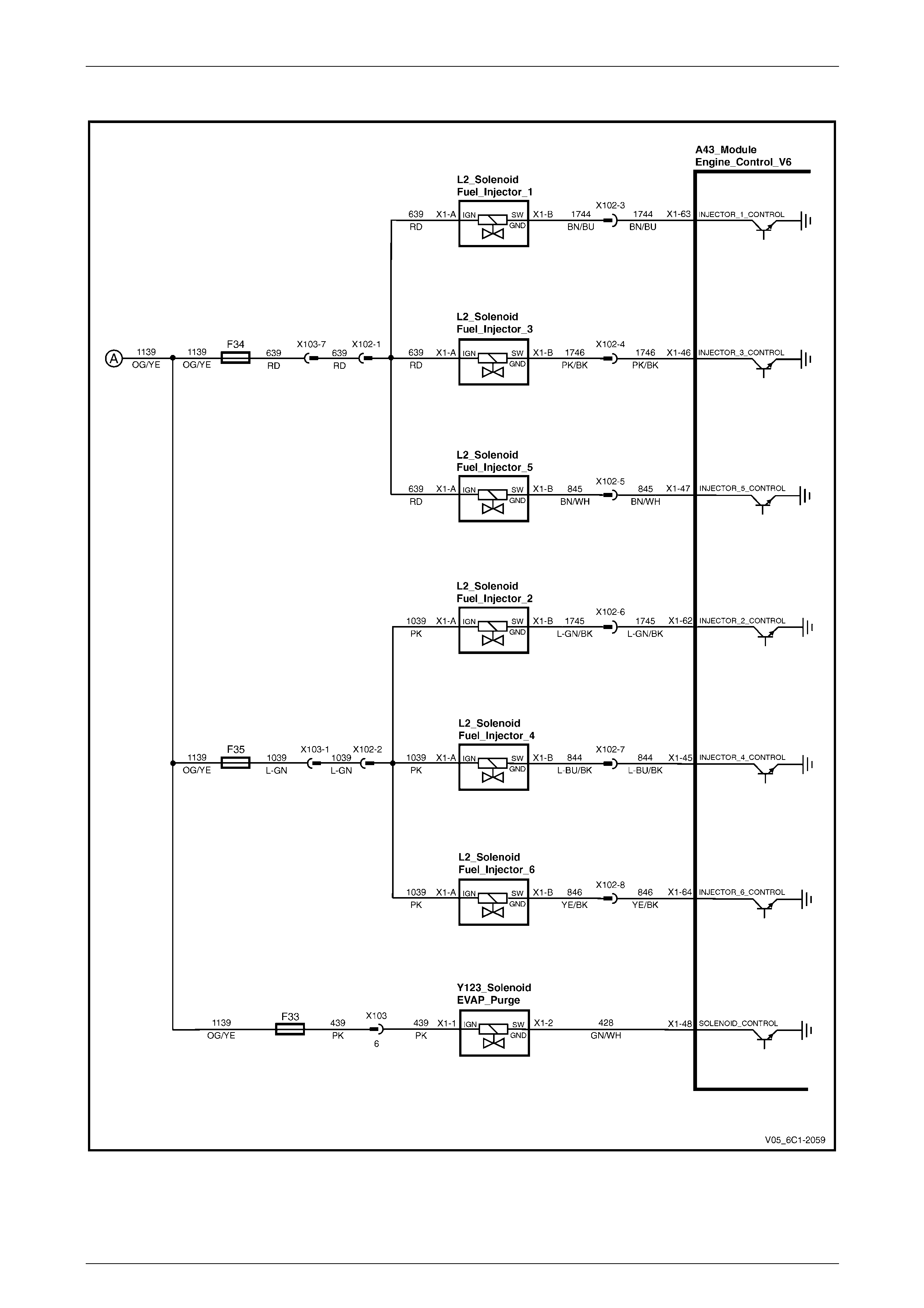
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–28
Page 6C1-2–28
Fuel Injectors
Figure 6C1-2 – 8
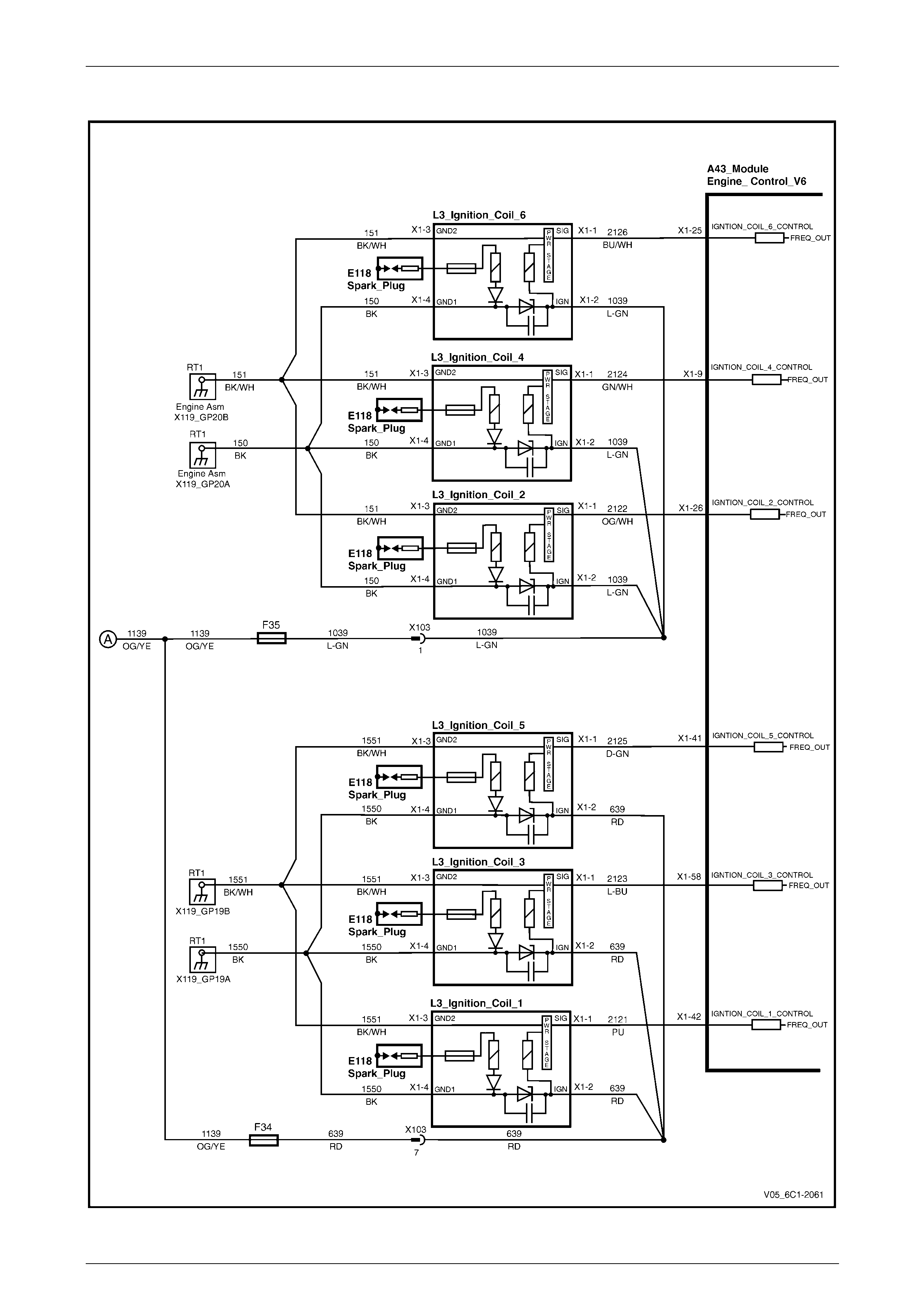
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–29
Page 6C1-2–29
Ignition
Figure 6C1-2 – 9
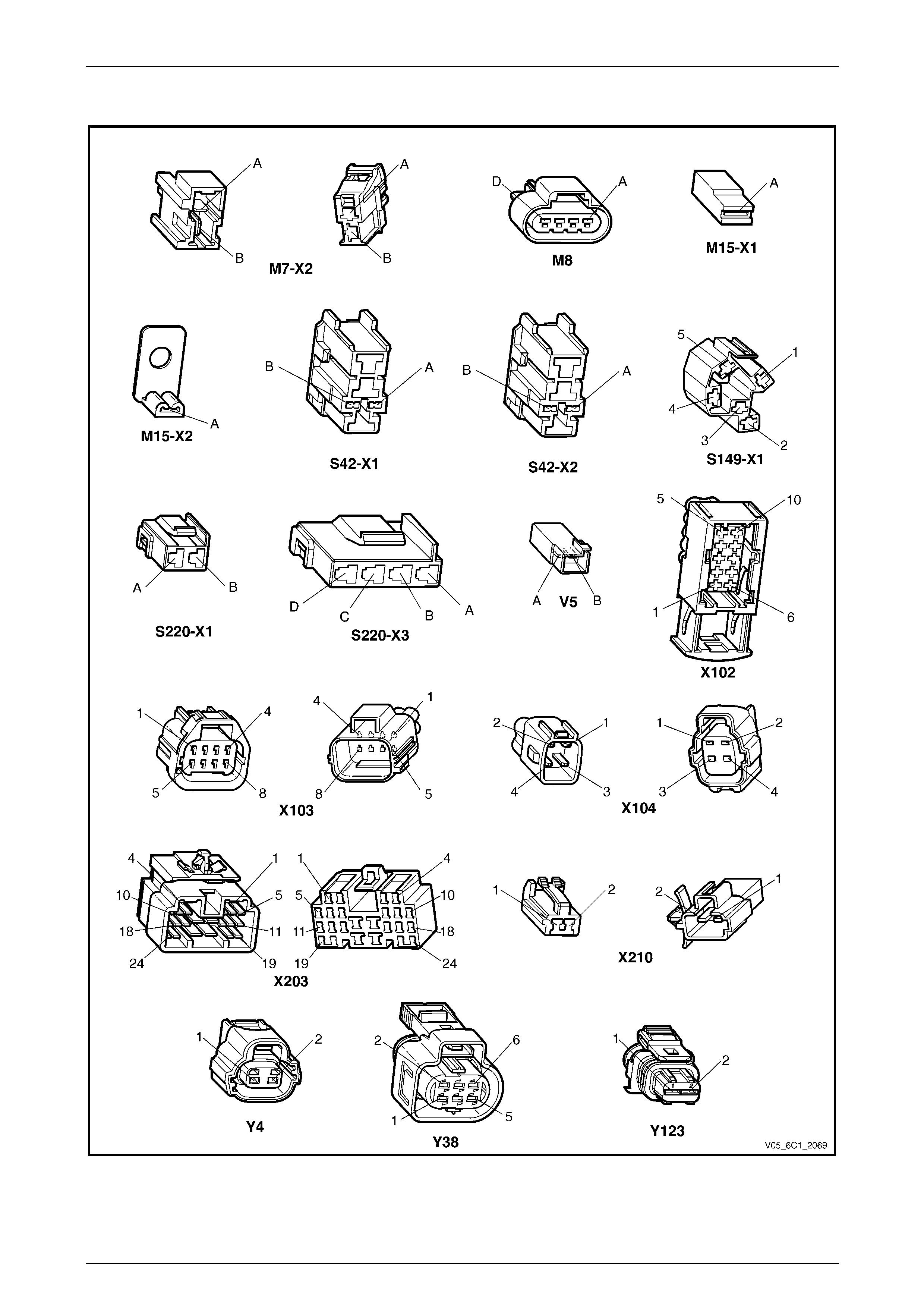
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–30
Page 6C1-2–30
2.2 Connector Chart
Figure 6C1-2 – 10
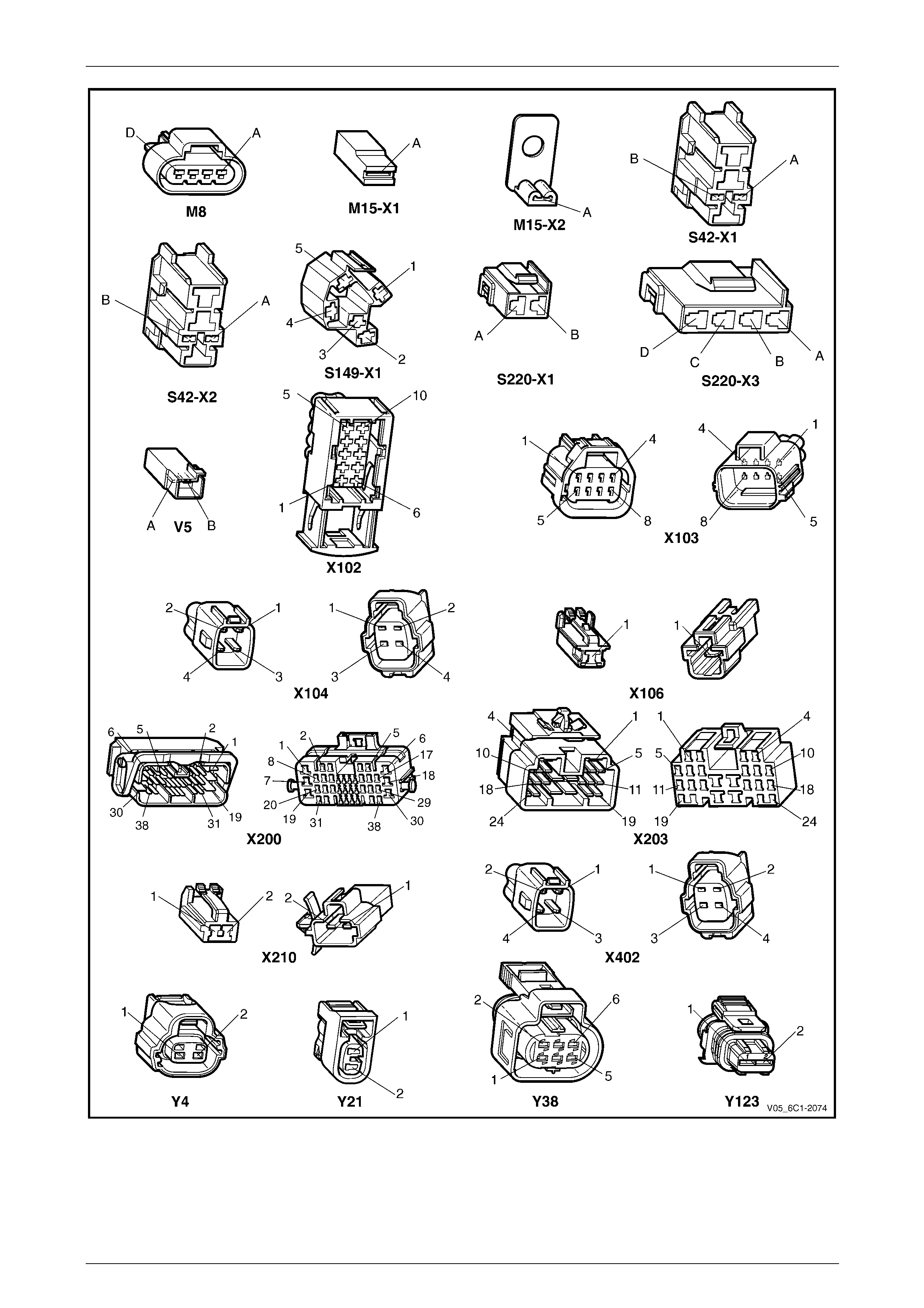
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–31
Page 6C1-2–31
Figure 6C1-2 – 11

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–32
Page 6C1-2–32
3 Diagnostics Starting Point
3.1 Basic Requirements
Basic Knowledge Required
A lack of basic understanding regarding
electronics, electrical wiring circuits and use
of electrical circuit testing tools when
performing an engine management system
diagnostic procedure could result in incorrect
diagnostic results or damage to engine
management system components.
Understanding of the following is required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams and to Basic Tools Required.
• basic electronics,
• electrical wiring circuits,
• electrical circuits testing, and
• correct use of the basic engine management system diagnostic tools.
In addition, understanding of the engine management system is essential to prevent misdiagnosis and component
damage. Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information.
Basic Tools Required
Use of incorrect electrical circuit diagnostic
tools when performing the Engine
Management diagnostic procedures could
result in incorrect diagnostic results or
damage to engine management system
components.
The following electrical circuit testing tools are required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section.
• Tech 2, refer to Section 0C Tech 2,
• test lamp, refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams, and
• digital multimeter with 10 MΩ impedance, refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–33
Page 6C1-2–33
3.2 Diagnostic Precautions
The following precautions must be observed when performing the powertrain diagnostic procedure, otherwise incorrect
diagnostic results or damage to engine management system components will occur:
• Disconnection of the battery affects certain vehicle electronic systems.
Refer to Section 00 Warnings, Cautions and Notes before disconnecting the battery.
• Disconnect the battery negative lead when performing the following procedures:
• disconnecting the ECM connectors, or
• charging the battery.
• Disconnect the battery terminal lead and the ECM connectors before attempting any electric arc welding on the
vehicle.
• Do not start the engine if the battery terminal is not properly secured to the battery.
• Do not disconnect or reconnect the following while the ignition is switched on or when the engine is running:
• any engine management system component electrical wiring connector, or
• battery terminal leads.
• Ensure the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting engine management system electrical wiring
connectors is always followed. For information on the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting specific
wiring connectors, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are fitted correctly.
• When steam or pressure cleaning engines, do not direct the cleaning nozzle at engine management system
components.
• Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
• The fault must be present when using the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) diagnostic tables. Otherwise, misdiagnosis
or replacement of good parts may occur.
• Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered components on the ECM circuit board to prevent ECM
Electrostatic Discharge damage. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on Electrostatic Discharge.
• Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables as other test equipment may give incorrect results or
damage good components.
• The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draw associated with vehicle operations. However, the following
fault conditions or incorrect test procedure may overload the ECM internal circuit and damage the ECM:
• A short to voltage fault condition in any of the ECM low reference circuits may cause internal ECM and/or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to voltage fault condition in the ECM low reference circuits must be
rectified before replacing a faulty component.
• A short to ground fault condition in any of the ECM 5 V reference circuits may cause internal ECM and/or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to ground fault condition in the ECM 5 V reference circuits must be
rectified before replacing a faulty component.
• When using a test lamp to test an electrical circuit, do not use any of the ECM low reference circuits or 5 V
reference circuits as a reference point. Otherwise, excessive current draw from the test lamp may damage the
ECM.
• Disregard DTCs that set while performing the following diagnostic Steps:
• using Tech 2 actuator tests, or
• disconnecting an engine management system sensor connector then switching on the ignition.
• After completing the required diagnostics and service operations, road test the vehicle to ensure correct engine
management system operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–34
Page 6C1-2–34
3.3 Preliminary Checks
The preliminary checks is a set of visual and physical checks or inspections that may quickly identify engine management
system fault condition.
• Refer to the appropriate Service Techlines for relevant information regarding the fault condition.
• Ensure the battery is fully charged.
• Inspect the battery connections for corrosion or a loose terminal.
• Ensure that all engine management system related fuses are serviceable.
• Inspect for incorrect aftermarket theft deterrent devices, lights or mobile phone installation.
• Ensure there is no speaker magnet positioned too close to any electronic module that contains relays.
• Inspect the engine wiring harness for proper connections, pinches or cuts.
• Ensure that all engine management related electrical wiring connectors are fitted correctly.
• Inspect the ECM ground connections for corrosion, loose terminal or incorrect position.
• Ensure the resistance between the ECM housing and the battery negative cable is less than 0.5 Ω.
• Check the ECM bracket fasteners for correct torque value.
• Check all engine management related components for correct installation.
• Inspect the vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, oil contamination and proper connections, refer to the vehicle emission
control information label. Check the hoses thoroughly for any type of leak or restriction.
• Inspect the air intake ducts for being collapsed, split or for having damaged areas.
• Inspect for air leaks at the throttle body mounting area, mass air flow (MAF) sensor, intake manifold and intake
manifold sealing surfaces.
• Check for wiring harness routing that may be positioned too close to a high voltage or high current device such as
the following:
• secondary ignition components, and
• motors and generators.
NOTE
High voltage or high current devices may induce
electrical noise on a circuit, which can interfere
with normal circuit operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–35
Page 6C1-2–35
3.4 Diagnostic System Check
Description
The engine management diagnostic procedure is organised in a logical structure that begins with the Diagnostic System
Check. The Diagnostic System Check directs the diagnostic procedure to the logical steps necessary to diagnose an
engine driveability fault condition.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 Tests the operation of Tech 2.
6 Tests the integrity of the GM LAN serial data communication circuit. A PIM DTC sets if the PIM detects a fault
condition in the communication circuit. A fault condition on the serial data communication circuit may trigger multiple
DTCs on other sensors and components.
7 Tests for fault conditions on the vehicle theft deterrent system. The BCM is an integral part of the theft deterrent
system. Any fault condition on the BCM that may affect the operation of the theft deterrent system must be rectified
before proceeding with this diagnostic table.
Step Action Yes No
1 Have you read the basic requirements?
Go to Step 2
Refer to 3.1 Basic
Requirements
2 Have you read the diagnostic precautions?
Go to Step 3
Refer to
3.2 Diagnostic
Precautions
3 Have you performed the preliminary checks?
Go to Step 4
Refer to
3.3 Preliminary
Checks
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Connect Tech 2 to the diagnostic link connector (DLC).
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Push Tech 2 power button on.
Does Tech 2 screen illuminate and display Tech 2? Go to Step 5
Refer to Section 0C
Tech 2
5 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM and the BCM.
Does the PIM or the BCM fail to communicate?
Refer to Section
6E1 Powertrain
Interface Module –
V6 Go to Step 6
6 Does DTC U1064, U2100, U2105, U2106, U2108, B1009, B1013,
B1014, B1000, B1019, B3057, B3924, P0633, P1611 or P1678 also
set in the PIM?
Refer to Section
6E1 Powertrain
Interface Module –
V6 Go to Step 7
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–36
Page 6C1-2–36
Step Action Yes No
7 Does DTC 2, DTC 17, DTC 19, DTC 20, DTC 24 DTC 25 also set in
the BCM?
Refer to Section 12J
Body Control
Module Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, view and record DTCs set at the ECM and TCM.
Does Tech 2 display any DTC? Go to Step 9
Refer to
4.1 Symptoms
Diagnosis Table
9 Does Tech 2 display multiple DTCs?
Go to Step 10
Go to the diagnostic
table of the DTC
displayed. Refer to
5.1 DTC List
10 Does Tech 2 display any serial data communication circuit DTC? Go to the
appropriate serial
data communication
circuit DTC table.
Refer to 5.1 DTC
List Go to Step 11
11 Does Tech 2 display any immobiliser circuit DTC? Go to the
appropriate
immobiliser circuit
DTC table. Refer to
5.1 DTC List Go to Step 12
12 Refer to the DTC Table of the fault condition that is most likely to
trigger multiple DTCs. Refer to 1.2 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables. — —
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–37
Page 6C1-2–37
4 Symptoms Diagnostics
4.1 Symptoms Diagnosis Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 Is the fault intermittent? Refer to
4.2 Intermittent
Fault Conditions
Go to Step 3
3 Does the engine backfire? Refer to
4.3 Backfire
Go to Step 4
4 Does the engine crank but does not run? Refer to
4.4 Cranks But
Does Not Run
Go to Step 5
5 Does the engine cut-out or miss? Refer to
4.5 Cuts Out,
Misses
Go to Step 6
6 Is there a detonation or spark knock noise coming from the engine? Refer to
4.6
Detonation/Spark
Knock
Go to Step 7
7 Is there an engine dieseling or run-on condition? Refer to
4.7 Dieseling, Run-
on
Go to Step 8
8 Is there an engine hard starting condition? Refer to
4.8 Hard Start
Go to Step 9
9 Is there an engine hesitation, sag or stumble condition? Refer to
4.9 Hesitation, Sag
and Stumble
Go to Step 10
10 Does the engine suffer from lack of power, sluggishness or
sponginess?
Refer to
4.10 Lack of Power,
Sluggishness or
Sponginess
Go to Step 11
11 Does the engine suffer from poor fuel economy? Refer to
4.11 Poor Fuel
Economy
Go to Step 12
12 Does the engine suffer from rough, unstable or incorrect idle and
engine stalling?
Refer to
4.12 Rough,
Unstable, Incorrect
Idle or Stalling
Go to Step 13
13 Does the engine surge or chuggle? Refer to
4.13 Surges /
Chuggles
Go to Step 14
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–38
Page 6C1-2–38
4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions
Description
A fault condition is intermittent if one of the following conditions exists:
• the fault condition is not always present,
• the fault condition cannot be presently duplicated, or
• there is no Current DTC but a History DTC is stored.
Diagnostic Table
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Gather information from the customer regarding the conditions that trigger the
intermittent fault such as:
• At what engine or ambient temperature range does the fault occur?
• Does the fault occur when operating aftermarket electrical equipment inside
the vehicle?
• Does the fault occur on rough roads or in wet road conditions?
• If the intermittent fault is a start and then stall condition, check theft deterrent
system. Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module.
Tech 2 Tests The following are lists of Tech 2 diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose
intermittent faults:
• Wriggle test the suspected wiring harness and connectors while observing Tech 2
operating parameters. If Tech 2 read-out fluctuates during this procedure, check
the tested wiring harness circuit for a loose connection.
• Observe the freeze frame / failure records for the suspected history DTC and then
operate the vehicle in the conditions that triggers the intermittent fault while an
assistant observes the suspected Tech 2 operating parameter data.
• Capture and store data in the snapshot mode when the fault occurs. The stored
data may be played back at a slower rate to aid diagnostics. Refer to Tech 2 User
Instructions for further information on the Snapshot function.
• Compare the engine operating parameters of the engine being diagnosed to the
engine operating parameters of a known good engine.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp The following conditions may cause an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp fault with
no DTC listed:
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid, switch or other external source.
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• ECM grounds are loose.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–39
Page 6C1-2–39
Checks Actions
Temperature Related Temperature related intermittent fault condition occurs only when the engine or ambient
temperature is hot, or only when it is cold.
• If the intermittent fault is heat related, review Tech 2 data in relationship to the
following:
• high ambient temperature,
• engine generated heat,
• circuit generated heat due to a poor electrical connection or high electrical
load, and
• higher than normal load conditions (towing, etc.).
• If the intermittent fault is related to cold ambient or engine temperature, review
Tech 2 data in relationship to the following:
• low ambient temperature, and
• the fault condition that occurs only on a cold start situation.
Additional Tests • Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid or switch. The fault is triggered when the relay or solenoid is activated.
• Test the A/C compressor clutch and some relays that contain a clamping diode or
resistor for an open circuit.
• Test the generator for a faulty rectifier bridge that may allow the A/C noise into the
ECM electrical circuit.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–40
Page 6C1-2–40
4.3 Backfire
Description
The air/fuel mixture in the intake manifold or in the exhaust system ignites which produces a loud popping noise.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the Preliminary Checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
Sensor/System • Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard activity.
Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the items that can cause an engine to run lean.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System • Check for an intermittent ignition circuit malfunction.
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–41
Page 6C1-2–41
Checks Actions
Engine Cooling System Check the engine for over-heating. Refer to Section 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks • Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to Section 8B Exhaust
System.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the
engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
Wiring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or
high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
Dirty starter motor commutator or brushes can mask the crankshaft position
sensor signal.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to
Section 7C1 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information or
Section 7E1 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – General Information.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–42
Page 6C1-2–42
4.4 Cranks But Does Not Run
Definition
The engine cranks normally but does not start.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the theft deterrent system for correct operation. Refer to Section 12J Body
Control Module.
Sensor/System • Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for
details of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the MAF
sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check for a dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the
crankshaft position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure,
• contaminated fuel, and
• incorrect fuel pump relay operation.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical • Check for excessive oil in combustion chamber. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Techline
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–43
Page 6C1-2–43
4.5 Cuts Out, Misses
Description
Steady pulsation or jerking that is usually more severe as the engine load increases. This condition is not normally felt
greater than 1500 r.p.m. or 48 km/h. The exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle or low speed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
• Check for intake manifold vacuum leak.
Sensor/System • Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters. The
HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard activity.
Check for items that cause spark retard activity. Refer to
5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 – Knock Sensor Circuit.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check for fault conditions that cause an engine to run rich or to run lean.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil grounds.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks • Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to Section 8B Exhaust
System.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the
engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
electromagnetic interference fault may be present.
• Wiring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or
high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–44
Page 6C1-2–44
4.6 Detonation/Spark Knock
Description
The engine produces sharp rapid metallic knocks that are more audible during acceleration.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
Sensor System Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Ensure the fuel tank is filled with petrol that has a minimum octane reading of 92.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause an engine to run lean.
Ignition System Check the spark plugs for proper heat range. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Engine Mechanical • Check the combustion chambers for excessive carbon build-up. Refer to Section
6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• Check the camshaft timing. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
Additional Checks • Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. The TCC applying too soon
can cause the engine to spark knock. Refer to Section 7C2 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis or Section 7E2 Automatic
Transmission – 5L40E – Electrical Diagnosis.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–45
Page 6C1-2–45
4.7 Dieseling, Run-on
Description
The engine continues to run after the ignition is switched off but runs very roughly and then stalls.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
Fuel System Inspect the injectors for leaking condition. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
Engine Cooling System • Check for engine overheating. Refer to Section 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
• Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
Section 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical • Check for build up of carbon deposit in the combustion chamber, which may cause
hot spots and increased compression ratio. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Using Tech 2, check for incorrect engine idle speed.
Additional • If the engine continues to run after the ignition is switched off but the engine runs
normally, check the following:
• ignition switch operation,
• voltage feedback from alternator L terminal to ignition switch, and
• sticking ignition control relay.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–46
Page 6C1-2–46
4.8 Hard Start
Definition
The engine cranks normally but takes longer to start than usual. As soon as the engine runs, the engine may stall
immediately.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the theft deterrent system for correct operation. Refer to Section 12J Body
Control Module.
Sensor/System • Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for
details of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the MAF
sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Test the resistance of the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor
resistance must be within 700 – 1,200 Ω at all temperatures.
• Check for dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the crankshaft
position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical • Check for excessive oil in combustion chamber. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–47
Page 6C1-2–47
4.9 Hesitation, Sag and Stumble
Description
Momentary lack of response or hesitation as the accelerator is depressed. This condition is usually more severe when
first trying to make the vehicle move from a standing start but can occur at any vehicle speed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor/System • Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters. The
HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Inspect the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor harness connector for correct
connection. Poor connection of this connector will not set a DTC.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel System.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check for fault conditions that cause an engine to run rich or to run lean.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine thermostat for correct operation and heat range. Refer to Section 6B1
Engine Cooling – V6.
Additional Checks • If fitted, check for the correct operation of the intake manifold runner control
system. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the generator output voltage. Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging System –
V6 – V6.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–48
Page 6C1-2–48
4.10 Lack of Power, Sluggishness or
Sponginess
Description
The engine delivers less than normal power. There is little or no increase in vehicle speed when the accelerator pedal is
partially depressed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor/System • Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard activity.
Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Inspect the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor harness connector for correct
connection. Poor connection of this connector will not set a DTC.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause the engine to run rich or run lean.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical • Check for the following engine mechanical fault condition. Refer to Section 6A1
Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low engine compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks • Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to Section 8B Exhaust
System.
• Test for other TCM related faults that may cause the transmission to operate in the
default mode.
• Check for transmission mechanical faults that may produce similar symptoms such
as slipping clutch.
• If fitted, check for the correct operation of the intake manifold runner control
system. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–49
Page 6C1-2–49
4.11 Poor Fuel Economy
Description
As confirmed by an actual road test, the fuel economy as compared to the previous fuel consumption of the same vehicle
is noticeably lower.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
• Check for correct tyre pressure. Refer to Section 10 Wheels and Tyres.
• Check the recent driving conditions are the same compared to the previous when
the fuel consumption is normal. The following are list of driving conditions that may
affect fuel consumption:
• vehicle load,
• acceleration rate,
• A/C or other electrical equipment use, and
• vehicle used for towing.
Sensor/System • Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Check for the correct calibration of the speedometer. Refer to Section 12C
Instrumentation.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard activity.
Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters. The
HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
• Check for foreign material accumulation in the throttle bore, carbon build-up on the
throttle valve or on the throttle shaft.
• Check the throttle body for tampering.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–50
Page 6C1-2–50
Checks Actions
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System • Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
Section 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks • Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to Section 8B Exhaust
System.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the
engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
Wiring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or
high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, and
• motors and generators.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to
Section 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosisor Section
7E2 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – Electrical Diagnosis.
• Test for other TCM related faults that may cause the transmission to operate in the
default mode. Refer to Section 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical
Diagnosisor Section 7E2 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – Electrical Diagnosis.
• Check for transmission mechanical faults such as slipping clutch. Refer to
Section 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical
Diagnosis or Section 7E3 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – Hydraulic and
Mechanical Diagnosis.
• Check the brake system including the parking brake for sticking or incorrect
operation. Refer to 5A Service and Park Braking System.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–51
Page 6C1-2–51
4.12 Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or
Stalling
Description
Engine idle speed fluctuates causing the engine to run unevenly. If the engine idle speed drops too low, the engine may
stall.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor/System • Check the throttle actuator control (TAC) system. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks. Refer to Section 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard activity.
Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters. The
HO2s sensor should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug and ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil grounds.
Engine Mechanical • Parasitic load on the engine such as the following:
• automatic transmission fault condition, or
• a belt driven accessory fault condition.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, or
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–52
Page 6C1-2–52
4.13 Surges / Chuggles
Description
With the accelerator pedal in a steady position, the vehicle speeds up and slows down or the engine power fluctuates.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 3.3 Preliminary Checks.
Sensor/System • Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters. The
HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Test the resistance of the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor
resistance must be 700 – 1,200 Ω at all temperatures.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel
System.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause an engine to run lean.
Ignition System • Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug/ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Additional Checks • Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to
Section 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosisor Section
7E2 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – Electrical Diagnosis.
• Test the A/C clutch for correct operation. Refer to Section 2B HVAC Climate
Control – Servicing and Diagnosis.
• Check the evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge solenoid for the following
conditions: Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
• stuck open condition, and
• charcoal contamination.
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to Section 8B Exhaust
System.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the
engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
Wiring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or
high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–53
Page 6C1-2–53
5 Diagnostic Trouble Code Tables
5.1 DTC List
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0008 Engine Position System Performance (Bank 1) 5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP
/ CMP Position Correlation
P0009 Engine Position System Performance (Bank 2) 5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP
/ CMP Position Correlation
P0010 Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit
Malfunction (Bank 1)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator Solenoid
Control Circuit
P0011 Intake Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 1) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P0013 Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit
Malfunction (Bank 1)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator Solenoid
Control Circuit
P0014 Exhaust Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 1) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P0016 Crankshaft / Intake Camshaft Position not Plausible
(Bank 1)
5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP
/ CMP Position Correlation
P0017 Crankshaft / Exhaust Camshaft Position not Plausible
(Bank 1)
5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP
/ CMP Position Correlation
P0018 Crankshaft / Intake Camshaft Position not Plausible
(Bank 2)
5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP
/ CMP Position Correlation
P0019 Crankshaft / Exhaust Camshaft Position not Plausible
(Bank 2)
5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 – CKP
/ CMP Position Correlation
P0020 Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit
Malfunction (Bank 2)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator Solenoid
Control Circuit
P0021 Intake Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 2) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P0023 Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit
Malfunction (Bank 2)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator Solenoid
Control Circuit
P0024 Exhaust Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 2) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P0030 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0031 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–54
Page 6C1-2–54
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0032 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0036 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0037 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0038 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0040 O2 Sensor Signals Not Plausible (Bank 1, Sensor 1 &
Bank 2, Sensor 1)
5.39 DTC P0040 and P0041 – O2 Sensor
Signal Not Plausible Bank 1 / Bank 2
P0041 O2 Sensor Signals Not Plausible (Bank 1, Sensor 2 &
Bank 2, Sensor 2)
5.39 DTC P0040 and P0041 – O2 Sensor
Signal Not Plausible Bank 1 / Bank 2
P0050 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0051 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0052 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0053 O2 Sensor Heater Resistance Range / Performance
(Bank 1, Sensor 1)
5.37 DTC P0053 and P0059 – O2 Sensor
Internal Heater Resistance Range /
Performance, Alloytec190
P0056 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 2) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0057 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0058 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2) 5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
P0059 O2 Sensor Heater Resistance Range / Performance (Bank
2, Sensor 1)
5.37 DTC P0053 and P0059 – O2 Sensor
Internal Heater Resistance Range /
Performance, Alloytec190
P0101 Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Range / Performance 5.33 DTC P0101 to P0103 – MAF Sensor
Circuit
P0102 Mass Air Flow Sensor Voltage Low 5.33 DTC P0101 to P0103 – MAF Sensor
Circuit
P0103 Mass Air Flow Sensor Voltage High 5.33 DTC P0101 to P0103 – MAF Sensor
Circuit
P0112 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 5.27 DTC P0112 and P0113 – Intake Air
Temperature Sensor Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–55
Page 6C1-2–55
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0113 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Voltage 5.27 DTC P0112 and P0113 – Intake Air
Temperature Sensor Circuit
P0116 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Range /
Performance
5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and
P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Circuit
P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Voltage 5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and
P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Circuit
P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High Voltage 5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and
P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Circuit
P0121 Throttle Position Sensor 1 Circuit Range / Performance 5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
P0122 Throttle Position Sensor 1 Circuit Low Voltage 5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
P0123 Throttle Position Sensor 1 Circuit High Voltage 5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
P0125 Insufficient Engine Coolant Temperature For Closed Loop
Fuel Control
5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and
P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Circuit
P0130 O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0131 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0132 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0135 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0137 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0138 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–56
Page 6C1-2–56
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0140 O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0141 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 1,
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0150 O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0151 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0152 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0155 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0157 O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0158 O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0160 O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2, Sensor 2) 5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0161 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 2,
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155,
P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit
P0196 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Range / Performance 5.21 DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 – Engine
Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–57
Page 6C1-2–57
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0197 Engine Oil Temperature Voltage Low 5.21 DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 – Engine
Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit
P0198 Engine Oil Temperature Voltage High 5.21 DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 – Engine
Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit
P0201 Injector 1 Control Circuit Malfunction 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0202 Injector 2 Control Circuit Malfunction 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0203 Injector 3 Control Circuit Malfunction 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0204 Injector 4 Control Circuit Malfunction 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0205 Injector 5 Control Circuit Malfunction 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0206 Injector 6 Control Circuit Malfunction 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0219 Engine Overspeed Condition 5.2 DTC P0219 Engine Overspeed Condition
P0221 Throttle Position Sensor 2 Circuit Range / Performance 5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
P0222 Throttle Position Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage 5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
P0223 Throttle Position Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage 5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
P0261 Injector 1 Control Circuit Low Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0262 Injector 1 Control Circuit High Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0264 Injector 2 Control Circuit Low Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0265 Injector 2 Control Circuit High Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–58
Page 6C1-2–58
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0267 Injector 3 Control Circuit Low Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271,
P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 – Fuel Injector
Control Circuit
P0268 Injector 3 Control Circuit High Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0270 Injector 4 Control Circuit Low Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0271 Injector 4 Control Circuit High Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0273 Injector 5 Control Circuit Low Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0274 Injector 5 Control Circuit High Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0276 Injector 6 Control Circuit Low Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0277 Injector 6 Control Circuit High Voltage 5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
P0324 Knock Sensor Module Performance 5.32 DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor
P0327 Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 1) 5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 –
Knock Sensor Circuit
P0328 Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 1) 5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 –
Knock Sensor Circuit
P0332 Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 2) 5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 –
Knock Sensor Circuit
P0333 Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 2) 5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 –
Knock Sensor Circuit
P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction 5.9 DTC P0335 to P0338 – Crankshaft Position
Sensor Circuit
P0336 Crankshaft Position Sensor Signal Range / Performance 5.9 DTC P0335 to P0338 – Crankshaft Position
Sensor Circuit
P0337 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Duty Cycle 5.9 DTC P0335 to P0338 – Crankshaft Position
Sensor Circuit
P0338 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit High Duty Cycle 5.9 DTC P0335 to P0338 – Crankshaft Position
Sensor Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–59
Page 6C1-2–59
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0341 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance
(Bank 1)
5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0342 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 1) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0343 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 1) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0346 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance
(Bank 2)
5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0347 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 2) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0348 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 2) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0351 Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit Malfunction 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P0352 Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit Malfunction 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P0353 Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit Malfunction 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P0354 Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit Malfunction 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P0355 Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit Malfunction 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P0356 Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit Malfunction 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P0366 Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance
(Bank 1)
5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0367 Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 1) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0368 Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 1) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–60
Page 6C1-2–60
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0391 Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance
(Bank 2)
5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0392 Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 2) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0393 Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 2) 5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
P0443 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid
Circuit Malfunction
5.22 DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 –
Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid
Valve Control Circuit
P0458 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid
Circuit Low Voltage
5.22 DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 –
Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid
Valve Control Circuit
P0459 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid
Circuit High Voltage
5.22 DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 –
Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid
Valve Control Circuit
P0461 Fuel Level Sensor Range / Performance 5.52 DTC P0461 to P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor
Circuit
P0462 Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage 5.52 DTC P0461 to P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor
Circuit
P0463 Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage 5.52 DTC P0461 to P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor
Circuit
P0480 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Malfunction 5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
P0481 Cooling Fan Relay 2 and 3 Circuit Malfunction 5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction 5.51 DTC P0500 – Vehicle Speed Sensor
Circuit Malfunction
P0504 Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction 5.7 DTC P0504 Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction
P0506 Idle Speed Control r.p.m. Too Low 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P0507 Idle Speed Control r.p.m. Too High 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P0513 Wrong Transponder Key 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser
Signal
P0521 Oil Pressure Sensor Range / Performance 5.20 P0521 to P0523 – Engine Oil Pressure
Sensor Circuit
P0522 Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 5.20 P0521 to P0523 – Engine Oil Pressure
Sensor Circuit
P0523 Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage High 5.20 P0521 to P0523 – Engine Oil Pressure
Sensor Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–61
Page 6C1-2–61
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0532 A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 5.4 DTC P0532 and P0533 – A/C Refrigerant
Pressure Sensor Circuit
P0533 A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage High 5.4 DTC P0532 and P0533 – A/C Refrigerant
Pressure Sensor Circuit
P0560 System Voltage Malfunction 5.17 DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Engine
Control Module System Voltage
P0562 System Voltage Low Voltage 5.17 DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Engine
Control Module System Voltage
P0563 System Voltage High Voltage 5.17 DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Engine
Control Module System Voltage
P0601 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 5.15 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 –
ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or
Memory Fault
P0602 Program Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 5.15 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 –
ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or
Memory Fault
P0604 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 5.15 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 –
ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or
Memory Fault
P0606 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 5.15 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 –
ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or
Memory Fault
P0615 Starter Relay Circuit Malfunction 5.45 DTC P0615 to P0617 – Starter Relay
Control Circuit
P0616 Starter Relay Circuit Low Voltage 5.45 DTC P0615 to P0617 – Starter Relay
Control Circuit
P0617 Starter Relay Circuit High Voltage 5.45 DTC P0615 to P0617 – Starter Relay
Control Circuit
P0625 Alternator F Terminal Low Voltage 5.25 DTC P0625 and P0626 – Generator F-
Terminal Circuit
P0626 Alternator F Terminal High Voltage 5.25 DTC P0625 and P0626 – Generator F-
Terminal Circuit
P0627 Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Malfunction 5.23 DTC P0627 to P0629 – Fuel Pump Relay
Control Circuit
P0628 Fuel Pump Relay Voltage Low 5.23 DTC P0627 to P0629 – Fuel Pump Relay
Control Circuit
P0629 Fuel Pump Relay Voltage High 5.23 DTC P0627 to P0629 – Fuel Pump Relay
Control Circuit
P0633 Immobiliser Function Not Programmed 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser
Signal
P0638 Commanded Versus Actual Throttle Position Correlation 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P0645 A/C Relay Circuit Malfunction 5.3 DTC P0645 to P0647 – A/C Relay Control
Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–62
Page 6C1-2–62
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0646 A/C Relay Voltage Low 5.3 DTC P0645 to P0647 – A/C Relay Control
Circuit
P0647 A/C Relay Voltage High 5.3 DTC P0645 to P0647 – A/C Relay Control
Circuit
P0685 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Malfunction 5.18 DTC P0685 to P0687 – Engine Control
Relay Circuit
P0686 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Low Voltage 5.18 DTC P0685 to P0687 – Engine Control
Relay Circuit
P0687 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit High Voltage 5.18 DTC P0685 to P0687 – Engine Control
Relay Circuit
P0691 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Low Voltage 5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
P0692 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit High Voltage 5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
P0693 Cooling Fan Relay 2 and 3 Circuit Low Voltage 5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
P0694 Cooling Fan Relay 2 and 3 Circuit High Voltage 5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
P0700 Malfunction Indicator (MI) Request from Transmission
Control Module (TCM)
5.49 DTC P0700 – Malfunction Indicator
Request from Transmission Control
Module
P0704 Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction 5.10 DTC P0704 – Clutch Switch Circuit
P0850 Park / Neutral Signal Circuit Incorrect Signal 5.40 DTC P0850 – Park / Neutral Signal Circuit
Incorrect Signal
P0864 CAN-Bus Invalid Data From TCM (Transmission Control
Module)
5.43 DTC P0864 and U0101 – Serial Data
Communication Circuit, TCM
P1011 Intake Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 1) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P1012 Exhaust Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 1) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P1013 Intake Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 2) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P1014 Exhaust Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 2) 5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
P1258 Engine Coolant Over Temperature - Protection Mode Active 5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and
P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor Circuit
P1551 Throttle Control Lower Position Not Reached during
Learning Mode
5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P1629 Immobiliser Fuel Enable Signal Not Received 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser
Signal
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–63
Page 6C1-2–63
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P1632 Immobiliser Fuel Disable Signal Received 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser Signal
P1648 Wrong Security Code Entered 5.30 DTC P1648 – Wrong Security Code
Entered
P1668 Alternator L Terminal Circuit Malfunction 5.26 DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 –
Generator L Terminal Circuit
P1677 Immobiliser Function not Enabled 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser
Signal
P1678 Engine Control Module Identification Failed 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser
Signal
P1679 Immobiliser Environment Identification Failed 5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser
Signal
P1845 Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction 5.19 DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction
Malfunction
P2008 Intake Manifold Runner Control Solenoid Circuit Malfunction 5.53 DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 – Intake
Manifold Runner Control Valve Control
Circuit
P2009 Intake Manifold Runner Control Solenoid Circuit Low
Voltage
5.53 DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 – Intake
Manifold Runner Control Valve Control
Circuit
P2010 Intake Manifold Runner Control Solenoid Circuit High
Voltage
5.53 DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 – Intake
Manifold Runner Control Valve Control
Circuit
P2088 Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low
Voltage (Bank 1)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
P2089 Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High
Voltage (Bank 1)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
P2090 Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low
Voltage (Bank 1)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
P2091 Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High
Voltage (Bank 1)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
P2092 Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low
Voltage (Bank 2)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
P2093 Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High
Voltage (Bank 2)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
P2094 Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Low Voltage
(Bank 2)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–64
Page 6C1-2–64
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P2095 Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High
Voltage (Bank 2)
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator Solenoid
Control Circuit
P2100 Throttle Control Motor Malfunction 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P2101 Throttle Control Position Range / Performance 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P2105 Throttle Control Forced Engine Shutdown 5.47 DTC P2105 – Throttle Control Forced
Engine Shutdown
P2107 Throttle Control Malfunction 5.46 DTC P2107 – Throttle Control Malfunction
P2119 Closed Throttle Position Range / Performance 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P2122 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1 Voltage Low 5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and
P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit
P2123 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1 Voltage High 5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and
P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit
P2127 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2 Voltage Low 5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and
P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit
P2128 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2 Voltage High 5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and
P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit
P2138 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1-2 Correlation 5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and
P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit
P2176 Throttle Control Lower Position not Learned 5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
P2227 Barometric Pressure Sensor Range / Performance 5.6 DTC P2227 to P2229 – Barometric Pressure
Sensor Circuit
P2228 Barometric Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 5.6 DTC P2227 to P2229 – Barometric Pressure
Sensor Circuit
P2229 Barometric Pressure Sensor Voltage High 5.6 DTC P2227 to P2229 – Barometric Pressure
Sensor Circuit
P2231 O2 Sensor Signal Interference by Heater Circuit (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235,
P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit
P2232 O2 Sensor Signal Short to Heater Circuit (Bank 1
Sensor 2)
5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235,
P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit
P2234 O2 Sensor Signal Interference by Heater Circuit (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235,
P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit
P2235 O2 Sensor Signal Short to Heater Circuit (Bank 2
Sensor 2)
5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235,
P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–65
Page 6C1-2–65
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P2237 O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control Circuit,
Alloytec190
P2238 O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
P2239 O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
P2240 O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
P2241 O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
P2242 O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
P2243 O2 Sensor Voltage Signal Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2247 O2 Sensor Voltage Signal Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2251 O2 Sensor Ground Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1) 5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235,
P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit
P2254 O2 Sensor Ground Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1) 5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235,
P2251, P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit
P2270 O2 Sensor Lean / Rich Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 1,
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2271 O2 Sensor Rich / Lean Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 1,
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2272 O2 Sensor Lean / Rich Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 2,
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2273 O2 Sensor Rich / Lean Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 2,
Sensor 2)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–66
Page 6C1-2–66
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P2297 O2 Sensor Range / Performance During Deceleration Fuel
Cutoff (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2298 O2 Sensor Range / Performance During Deceleration Fuel
Cutoff (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
P2300 Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit Low Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2301 Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit High Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2303 Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit Low Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2304 Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit High Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2306 Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit Low Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2307 Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit High Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2309 Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit Low Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2310 Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit High Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2312 Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit Low Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2313 Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit High Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
P2315 Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit Low Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–67
Page 6C1-2–67
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P2316 Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit High Voltage 5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 – Ignition Coil
Control Circuit
P2500 Alternator L Terminal Low Voltage 5.26 DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 –
Generator L Terminal Circuit
P2501 Alternator L Terminal High Voltage 5.26 DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 –
Generator L Terminal Circuit
P2626 O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
P2629 O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2,
Sensor 1)
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
U0001 No Communication with CAN-Bus (High Speed) 5.41 DTC U0001 – No Communication with
CAN Bus (High Speed)
U0101 CAN-Bus No Communication With TCM (Transmission
Control Module)
5.43 DTC P0864 and U0101 – Serial Data
Communication Circuit, TCM
U0121 CAN-Bus No Communication With ABS / TC / ESP 5.44 DTC U0121 and U0415 Serial Data
Communication Circuit, ABS / TC / ESP
U0155 CAN-Bus No Communication With Gateway 5.42 DTC U0155 and U0423 – Serial Data
Communication Circuit, PIM
U0415 CAN-Bus Invalid Data ABS / TC / ESP 5.44 DTC U0121 and U0415 Serial Data
Communication Circuit, ABS / TC / ESP
U0423 CAN-Bus Invalid Data From Gateway 5.42 DTC U0155 and U0423 – Serial Data
Communication Circuit, PIM

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–68
Page 6C1-2–68
5.2 DTC P0219 Engine Overspeed Condition
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0219 – Engine Overspeed Condition
Circuit Description
The ECM continually monitors the engines operating environment. A engine over-speed condition DTC sets if the ECM
detects an engine speed in excess of 7200 RPM.
NOTE
An over-speed condition will occur when a low
gear on a manual transmission vehicle has been
selected whilst the vehicle is travelling at high
road speed. This DTC will not set if the engine is
free-revved as the ECM will limit engine speed.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0219 runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• The vehicle is fitted with a manual transmission
• The engine is running.
• The ignition voltage is between 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects an engine speed in excess of 7200 RPM for 1 second or longer.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The engine over-speed DTC is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type C
DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–69
Page 6C1-2–69
DTC P0219 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the diagnostic system check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0219 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0219 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
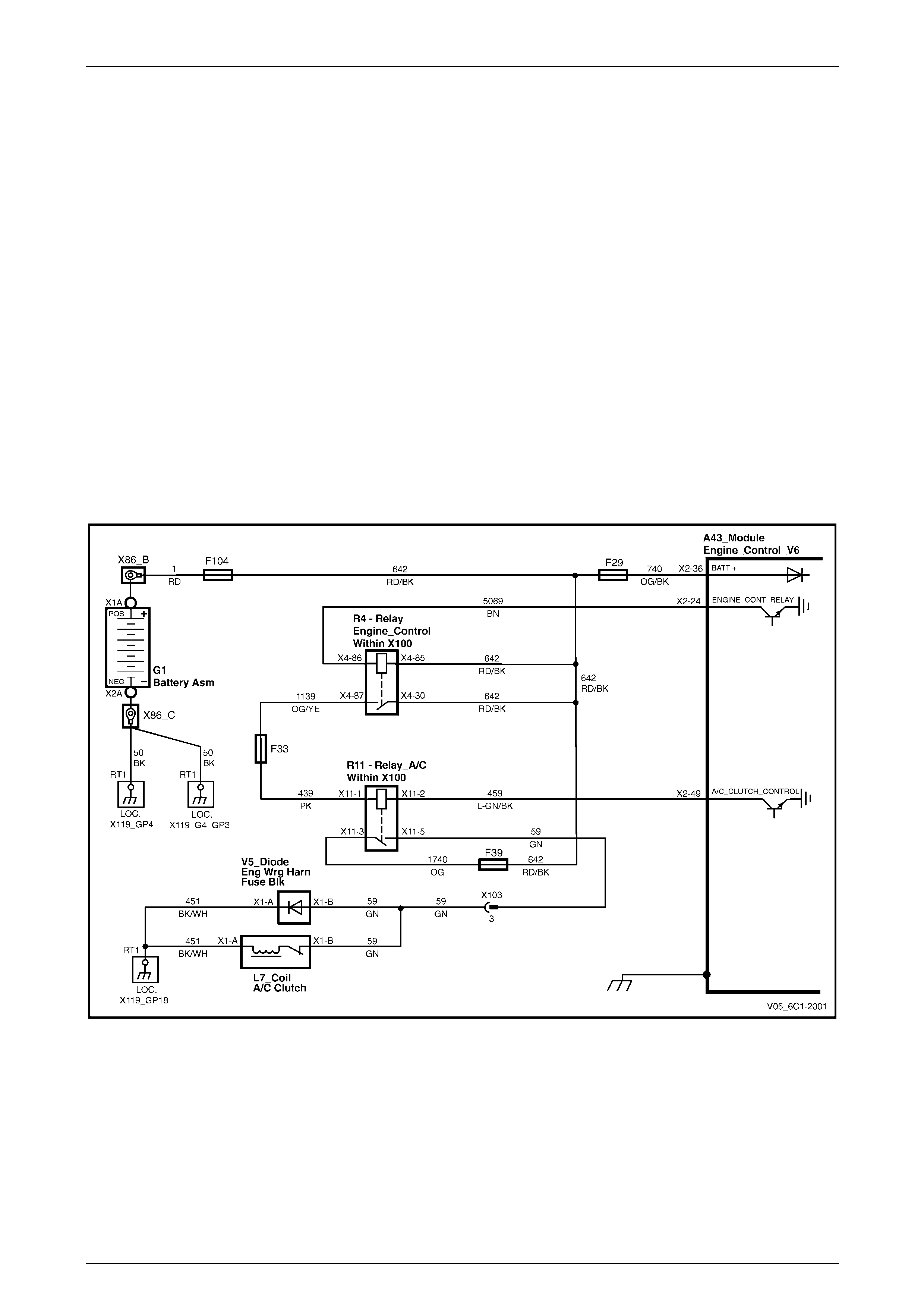
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–70
Page 6C1-2–70
5.3 DTC P0645 to P0647 – A/C Relay Control
Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0645 – A/C Relay Circuit Malfunction.
• DTC P0646 – A/C Relay Voltage Low.
• DTC P0647 – A/C Relay Voltage High.
Circuit Description
The Engine control relay applies battery voltage to the coil circuit of the air-conditioning (A/C) clutch relay through the
ignition circuit. Using a device called a driver, the ECM grounds control circuit of the A/C relay to activate the A/C clutch
and operate the A/C compressor. Refer to Section 2A HVAC Climate Control – Description and Operation for details of
the A/C compressor operation.
The Driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up to a voltage. The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to
determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
An A/C relay control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the A/C relay control circuit.
Figure 6C1-2 – 12
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–71
Page 6C1-2–71
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 2A HVAC Climate Control – Description and Operation for details of the A/C system operation.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0645 P0646 or P0647 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is 10–16 V.
• The engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Conditions for Setting DTC P0645
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in the A/C relay control circuit.
Conditions for Setting DTC P0646
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the A/C relay control circuit.
Conditions for Setting DTC P0647
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the A/C relay control circuit.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The A/C relay control circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type
C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in the HVAC system may trigger this DTC.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–72
Page 6C1-2–72
DTC P0645 to P0647 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Switch on the A/C system or operate the vehicle within the
conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0645 P0646 or P0647 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Check for a fault condition in the HVAC system, which can disable the
AC compressor clutch. Refer to Section 2A HVAC Climate Control –
Description and Operation for details of the A/C compressor operation.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 4
4 1 Remove the A/C relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses, Relays and
Wiring Harnesses.
2 Connect a test lamp between the ignition circuit of the A/C relay
coil and the ECM housing.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1 Connect a test lamp between the control circuit of the A/C relay
and a 12 V.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using Tech 2, command the A/C relay on and then off.
Does the test lamp turn on and off when the A/C relay is commanded
on and off? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
6 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the ignition
voltage circuit of the A/C relay. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams
for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
7 Test the control circuit of the A/C relay for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Replace the A/C relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses, Relays and
Wiring Harnesses.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the A/C relay control circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–73
Page 6C1-2–73
5.4 DTC P0532 and P0533 – A/C Refrigerant
Pressure Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0532 – A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage Low
• DTC P0533 – A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ECM supplies a positive 5 V reference voltage to the air-conditioning (A/C) refrigerant pressure sensor through
reference circuit and the ground through the low reference circuit.
The A/C pressure sensor provides signal voltage to the ECM through the signal circuit that is proportional to the A/C
refrigerant pressure. The ECM monitors the signal voltage of the A/C pressure sensor to determine the refrigerant
pressure.
• The A/C pressure sensor voltage increases as the refrigerant pressure increases.
• When the ECM detects the refrigerant pressure exceeds a predetermined value, the ECM activates the cooling
fans to reduce the refrigerant pressure.
• When the ECM detects the refrigerant pressure is too high or too low, the ECM disables the A/C clutch to protect
the A/C compressor from damage.
An A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the A/C pressure sensor signal is not within the
specified range for 3 seconds.
Figure 6C1-2 – 13
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the A/C Refrigerant Pressure
Sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit diagnostic table is developed with the assumption the A/C refrigerant
system is functioning correctly. Therefore, rectify any A/C refrigerant system fault conditions before proceeding with
this diagnostic procedure.
• An A/C refrigerant low-pressure fault condition may cause DTC P0532 to set.
• An A/C refrigerant high-pressure fault condition may cause DTC P0533 to set.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–74
Page 6C1-2–74
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0532 and P0533 run continuously when the engine is running or when the A/C is switched on.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0532
The A/C refrigerant pressure signal voltage is less than 0.2 V for longer than 3 seconds.
DTC P0533
The A/C refrigerant pressure signal voltage is greater than 4.9 V for longer than 3 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action
taken when Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Determines if there is an A/C refrigerant system fault condition.
6 Measures the integrity of the A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29
enables the ECM to power down completely prior to the test procedure.
DTC P0532 and P0533 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 Test the A/C refrigerant system. Refer to Section 2B HVAC Climate
Control – Servicing and Diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 3
3 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0532 or P0533 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 4
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the A/C pressure sensor connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the A/C
pressure sensor 5 V reference circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the A/C pressure
sensor 5 V reference circuit and signal circuit.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using Tech 2, observe the ECM A/C pressure voltage
parameter.
Does Tech 2 display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–75
Page 6C1-2–75
Step Action Yes No
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
A/C refrigerant pressure low reference circuit and the ECM
housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing the test.
Does the multimeter display 5Ω? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
7 Test the A/C pressure sensor 5 V reference circuit for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground, or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
8 Test the A/C pressure sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground, or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
9 Test the A/C pressure sensor low reference circuit for a high
resistance or open circuit condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
10 Replace the A/C pressure sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
11 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
12 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the A/C refrigerant pressure sensor circuit DTCs fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 13
13 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
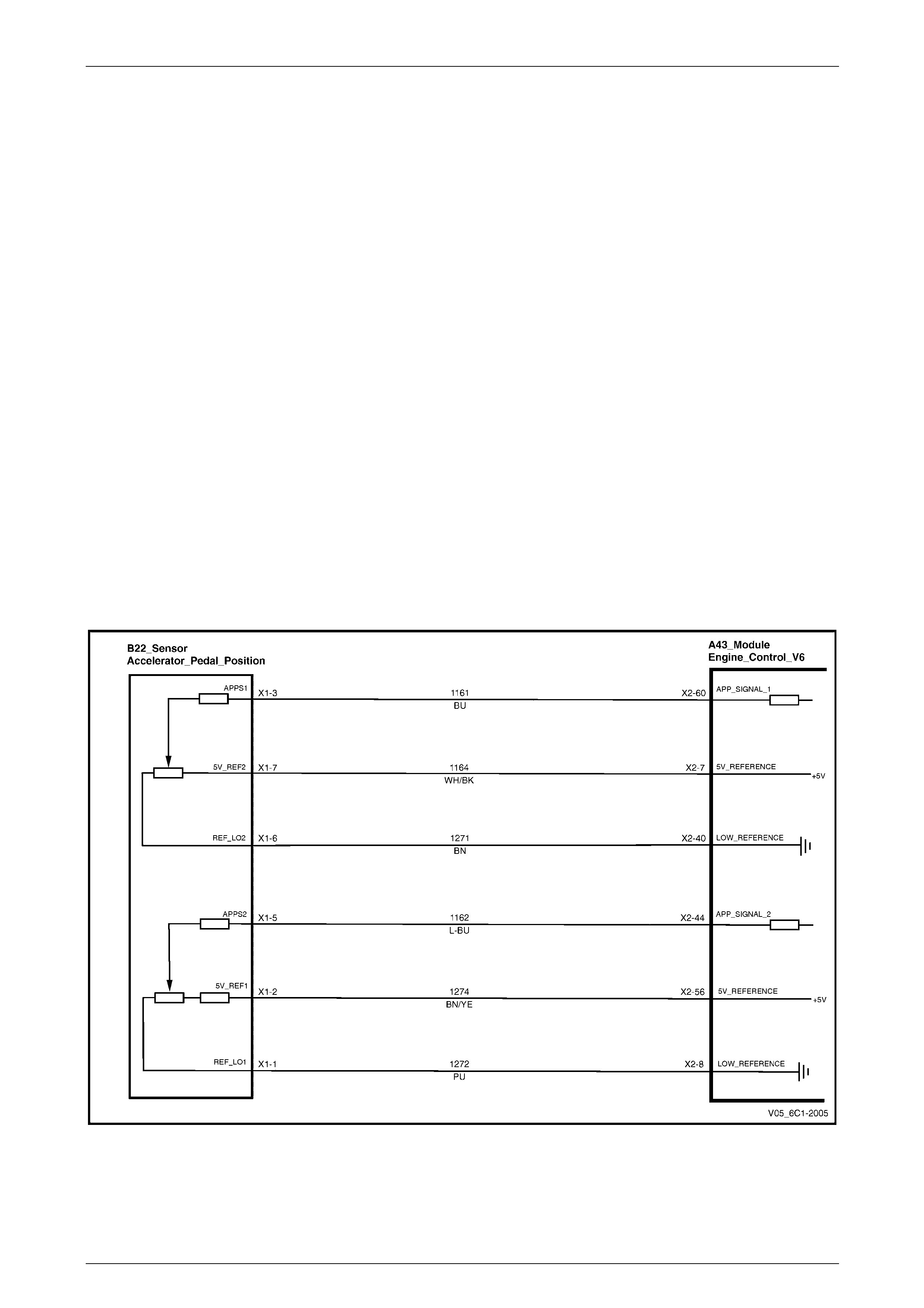
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–76
Page 6C1-2–76
5.5 DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and
P2138 – APP Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2122 – Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1 Voltage Low
• DTC P2123 – Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1 Voltage High
• DTC P2127 – Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2 Voltage Low
• DTC P2128 – Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2 Voltage High
• DTC P2138 – Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1 – 2 Correlation
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a separate 5 V reference circuit and low reference circuit to the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
1 and sensor 2. The APP sensors produce a signal voltage that represents the accelerator pedal position.
• The APP sensor 1 signal voltage increases from 1 V at rest position to greater than 4 V when the accelerator pedal
is fully depressed.
• The APP sensor 2 signal voltage increases from 0.5 V at rest position to greater than 2 V when the accelerator
pedal is fully depressed.
The ECM monitors and evaluates the APP sensors signal voltage along with other sensor inputs to determine the desired
throttle opening. An APP sensor circuit DTC sets if the signal voltage of the APP sensor is outside the predetermined
range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 14
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–77
Page 6C1-2–77
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the APP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and P2138 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 7 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2122
The ECM determines the APP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 0.84 V.
DTC P2123
The ECM determines the APP sensor 1 signal voltage is greater than 4.82 V.
DTC P2127
The ECM determines the APP sensor 2 signal voltage is less than 0.66 V.
DTC P2128
The ECM determines the APP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4.82 V.
DTC P2138
The ECM detects the difference between the APP sensor 1 and sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than the
predetermined value.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The APP sensor circuit DTCs are Type A DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type A
DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type A DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Tests the APP sensor internal circuits throughout its range of motion. If the DTC fails while performing this test,
there is an internal fault condition in the APP sensor internal circuitry.
5 Measures the integrity of the TP sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to
power down completely prior to the test procedure.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–78
Page 6C1-2–78
DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 and P2138 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Quickly depress the accelerator pedal to wide-open throttle then
release pedal. Repeat this procedure several times or operate
the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
4 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2122, P2123, P2127, P2128 or P2138 fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the APP sensor wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the 5 V
reference circuit of the appropriate APP sensor and the ECM
housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the 5 V reference
circuit and the signal circuit of the appropriate APP sensor.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using Tech 2, observe the voltage parameter appropriate APP
sensor.
Does Tech 2 display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM/TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
appropriate TP sensor low reference circuit and the ECM
housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Test the 5 V reference circuit of the appropriate APP sensor for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–79
Page 6C1-2–79
Step Action Yes No
7 Test the signal circuit of the appropriate APP sensor for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 Test the low reference circuit of the appropriate APP sensor for a high
resistance or an open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9 Replace the accelerator pedal assembly. Refer to Section 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the APP Sensor Circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
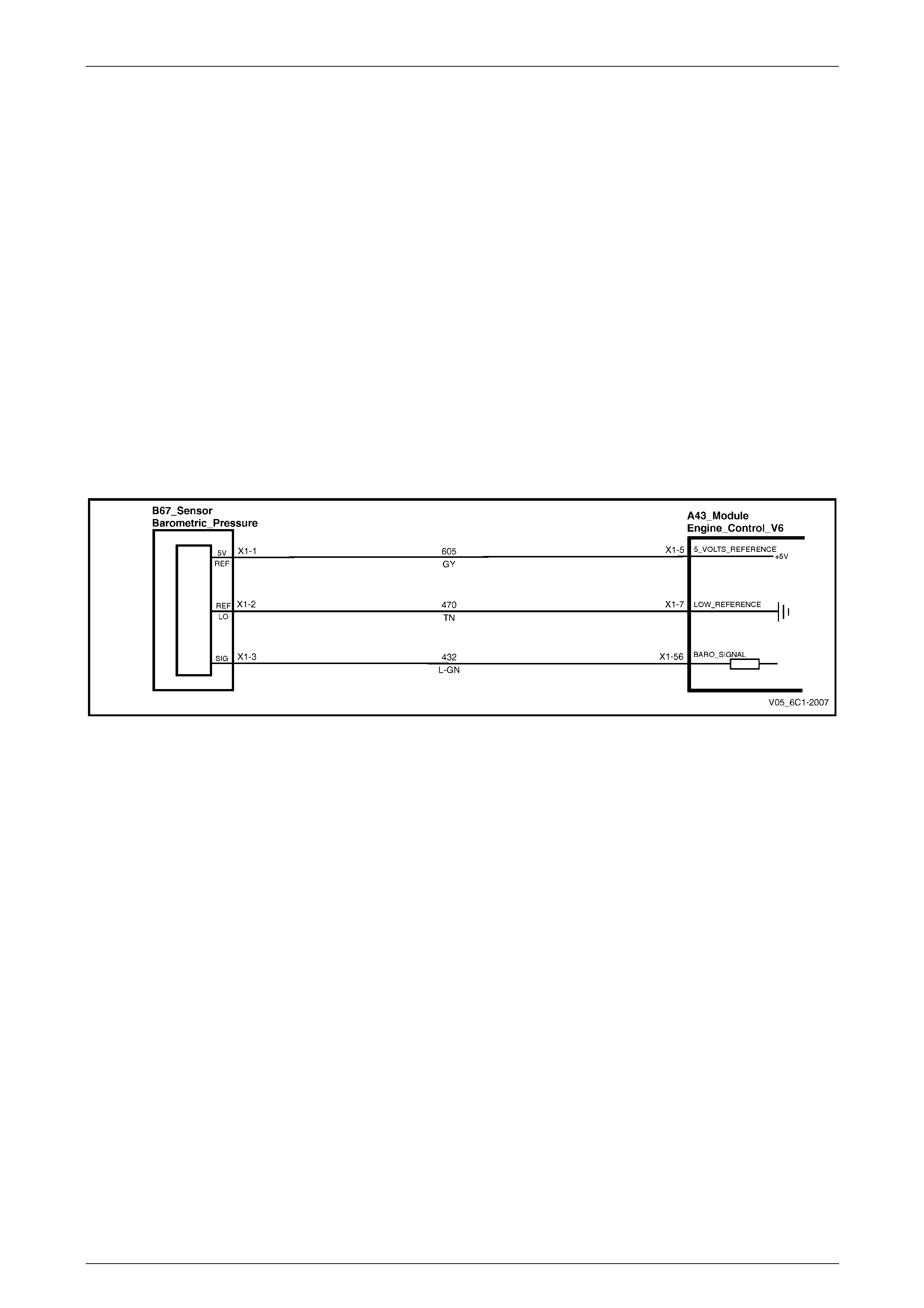
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–80
Page 6C1-2–80
5.6 DTC P2227 to P2229 – Barometric
Pressure Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2227 – Barometric Pressure Sensor Circuit Range / Performance
• DTC P2228 – Barometric Pressure Sensor Voltage Low
• DTC P2229 – Barometric Pressure Sensor Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a positive 5 V reference voltage to the barometric pressure (BARO) sensor through the 5 V reference
circuit and the ground through the low reference circuit.
The BARO sensor provides signal voltage to the ECM that is proportional to the atmospheric pressure changes through
the signal circuit. The ECM uses the BARO signal voltage to maintain the correct fuel delivery at different altitudes.
The ECM monitors and compares the BARO sensor signal voltage against a specified range. A BARO pressure sensor
circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the BARO sensor signal voltage is outside the specified range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 15
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the BARO Sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2227
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met for 3 seconds:
• DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0122, P0123 are not set.
• The engine is running.
DTC P2228 and P2229
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met for 3 seconds:
• DTCs P0101, P0102 or P0103 are not set.
• The engine is running.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–81
Page 6C1-2–81
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2227
The ECM detects the BARO pressure changed greater than 5 kPa within 20 seconds or the BARO pressure changed
greater than 30 kPa since the last ignition cycle.
DTC P2228
The ECM detects the BARO sensor signal voltage is less than 0.20 V.
DTC P2229
The ECM detects the BARO sensor signal voltage is greater than 4.8 V for longer than 2.0 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The BARO pressure sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 Test signal circuit of the BARO sensor. This circuit should display a voltage within the specified range.
5 Measures the integrity of the TP sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to
power down completely prior to the test procedure.
DTC P2227 to P2229 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to 3.4
Diagnostic System
Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2227, P2228 or P2229 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the BARO sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
BARO sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.5 – 5.5 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
BARO sensor 5 V reference circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–82
Page 6C1-2–82
Step Action Yes No
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM/TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
BARO sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Test BARO sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
7 Test the BARO sensor 5 V reference circuit for an open, short to
ground or high resistance fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
NOTE
The BARO sensor shares the 5 V reference circuit with
other sensors. A fault condition in the 5 V reference circuit
may trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit. Refer
to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts to aid
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 1 Disconnect the ECM wiring connector.
2 Test the BARO sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance
and open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9 Replace the BARO sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the BARO pressure sensor circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
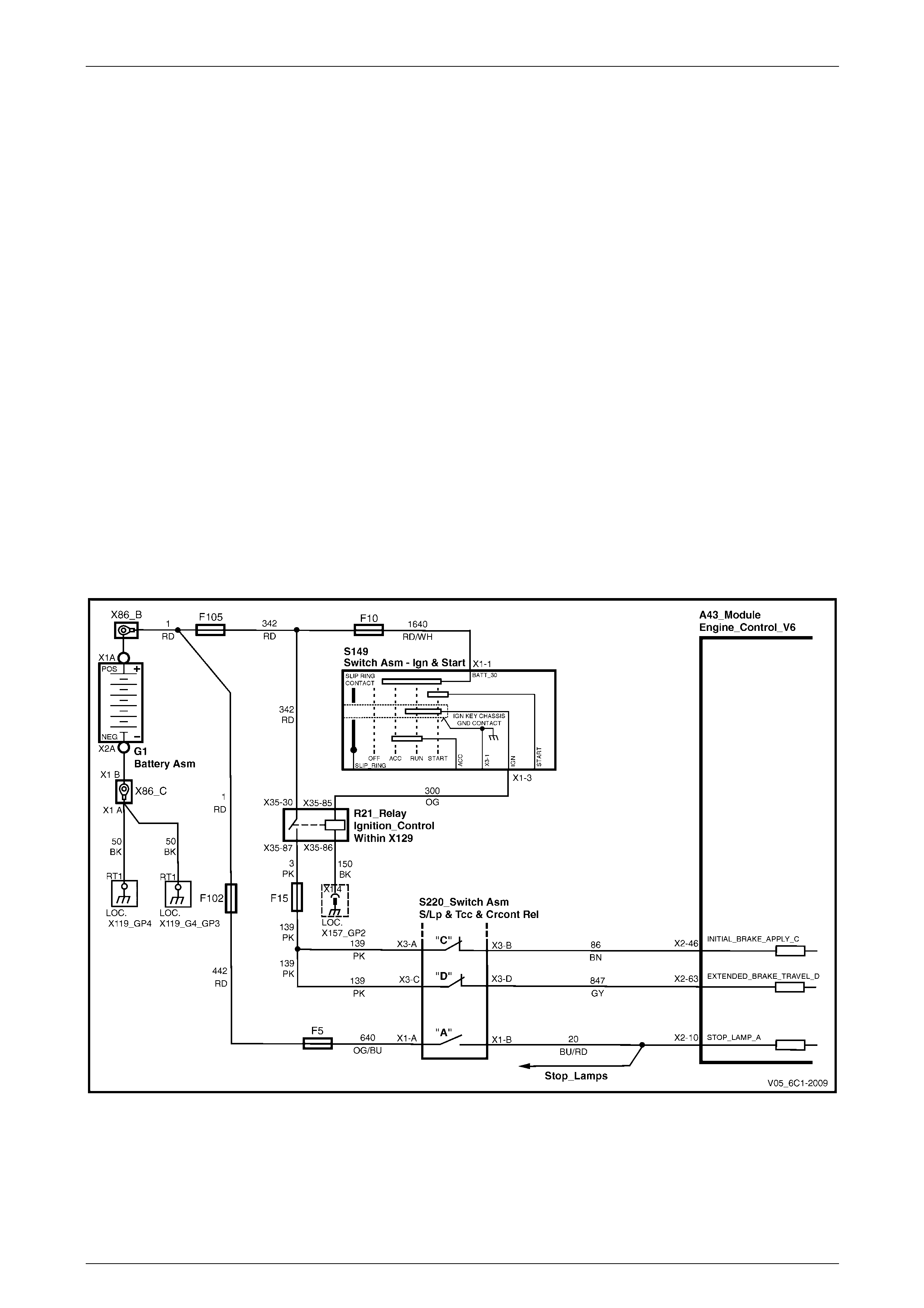
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–83
Page 6C1-2–83
5.7 DTC P0504 Brake Switch Circuit
Malfunction
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0504 – Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction.
Circuit Description
There are two stop lamp switch assemblies which comprise of two individual switches within each assembly. The ECM
uses inputs from stop lamp switch A and C.
NOTE
Stop lamp switch A is the stop lamp switch, stop
lamp switch C is the cruise control cancel switch,
and switch D is the extended brake travel switch.
DTC P0504 will not set if there is a fault with
switch D.
Switch A is a normally open switch that closes when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake pedal is depressed,
the stop lamp switch supplies signal voltage to the stop lamp signal circuit.
Switch C is a normally closed switch that opens when the brake pedal is depressed. For further information on the brake
switch assemblies, refer to Section 6C1–1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information.
The ECM monitors brake pedal A and C stop lamp switch signals, and if the signals do not correlate, DTC P0504 will set.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Figure 6C1-2 – 16

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–84
Page 6C1-2–84
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the brake switch operation.
• Refer to Section 12E Cruise Control for brake pedal switch operation and testing.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects one of the following conditions:
• Only one switch signal is present when the vehicle accelerates or decelerates rapidly ten times.
NOTE
The ECM will count over several drive cycles.
• A signal is seen from stop lamp switches A and C when the vehicle accelerates rapidly.
• The ECM does not detect a signal from the switches during braking.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The brake switch circuit DTC is a Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type B
DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in stop lamp switches A and C may trigger this DTC.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–85
Page 6C1-2–85
DTC P0504 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the diagnostic system check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0504 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display /
Cruise/Traction Data.
3 Observe the status of the brake lamp switch, initial brake apply
signal and the extended travel brake pedal switch.
4 Fully depress the brake pedal.
NOTE
Full brake pedal travel must be achieved in order to test
the activation of the extended brake travel switch
assembly.
Does Tech 2 display change from Inactive to Active in all switches
when the pedal is pressed?
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section Go to Step 4
4 Did the brake lamp switch Tech 2 status fail to change? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 9
5 1 Disconnect the wiring connector from stop lamp switch A. Refer
to Section 12E Cruise Control.
2 Switch on the ignition.
3 Connect a test lamp between the voltage circuit of stop lamp
switch A and a ground.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the voltage
circuit of stop lamp switch A . Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams
for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 —
7 Test stop lamp switch A. Refer to Section 12E Cruise Control.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 8
8 Test the control circuit of the stop lamp switch A for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 13
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–86
Page 6C1-2–86
Step Action Yes No
9 1 Disconnect the wiring connector from stop lamp switch C / stop
lamp switch D. Refer to Section 12E Cruise Control.
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
10 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the voltage
circuit of stop lamp switch C / stop lamp switch D . Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair
procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 —
11 Test stop lamp switch C / stop lamp switch D assembly. Refer to
Section 12E Cruise Control.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 12
12 Test the control circuit of the stop lamp switch C / stop lamp switch D
for a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage
fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information
on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 13
13 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 —
14 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0504 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 2
15 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
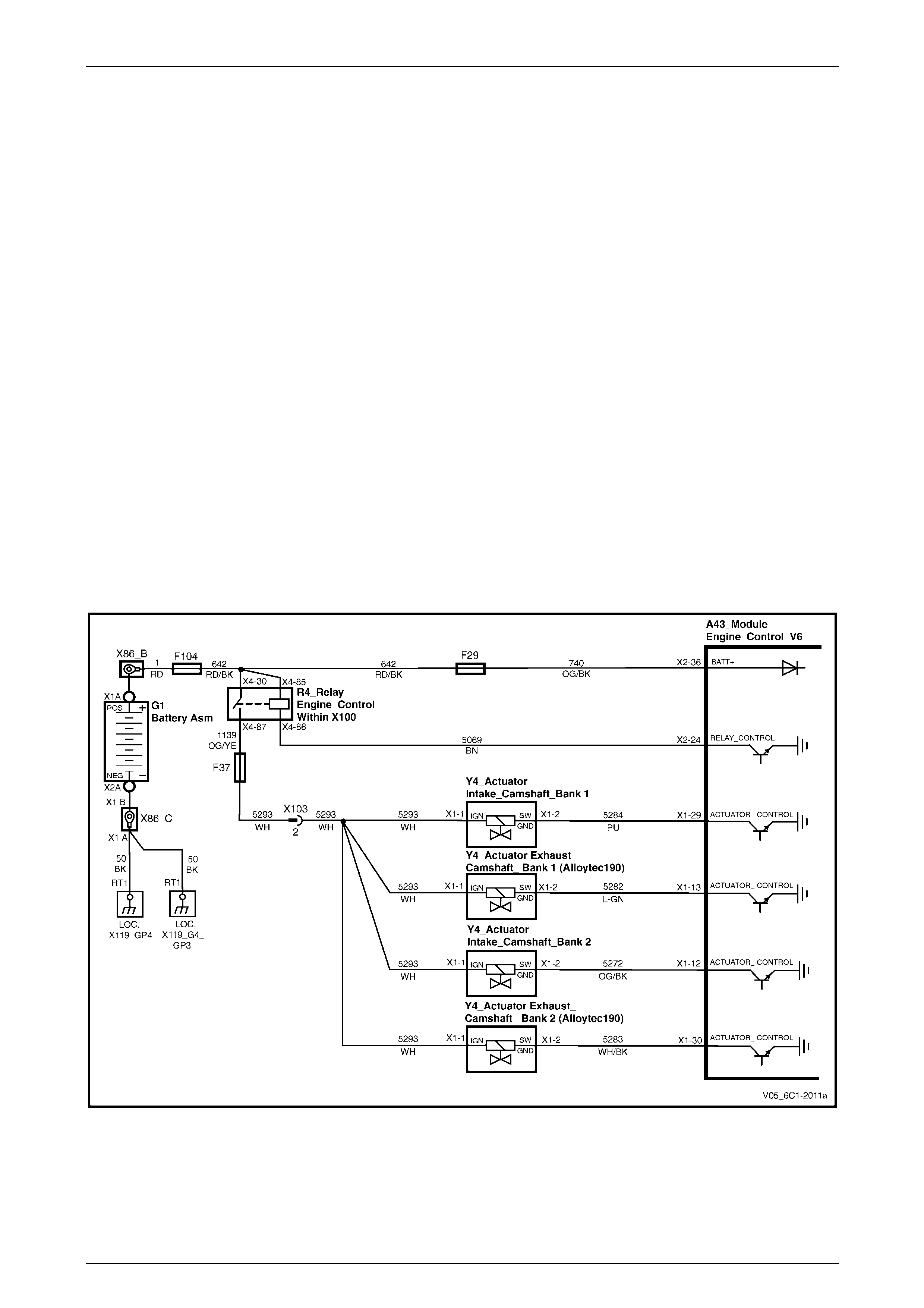
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–87
Page 6C1-2–87
5.8 DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 –
CKP / CMP Position Correlation
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0008 – Engine Position System Performance (Bank 1)
• DTC P0009 – Engine Position System Performance (Bank 2)
• DTC P0016 – Crankshaft / Intake Camshaft Position Not Plausible (Bank 1)
• DTC P0017 – Crankshaft / Exhaust Camshaft Position Not Plausible (Bank 1)
• DTC P0018 – Crankshaft / Intake Camshaft Position Not Plausible (Bank 2)
• DTC P0019 – Crankshaft / Exhaust Camshaft Position Not Plausible (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The Engine control relay applies ignition positive battery voltage to the camshaft position (CMP) actuator solenoids
through the ignition voltage circuit.
Using a device called a Driver, the ECM applies a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the individual CMP solenoid
control circuit. This controls the oil pressure that advances or retards each camshaft position.
The ECM compares the camshaft position to the crankshaft position to detect CMP system malfunction. A CKP / CMP
sensor correlation DTC sets if the ECM detects a deviation between the target position of the camshaft and the
crankshaft position.
Figure 6C1-2 – 17
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–88
Page 6C1-2–88
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CMP system operation.
• Inspect the engine for recent engine mechanical repairs. Incorrect camshaft, camshaft actuator or timing chain
installation will trigger these DTCs.
• The engine oil condition has a major impact on the operation of the camshaft actuator.
• A low oil level may set these DTCs.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0008 or P0009
Run continuously once the following conditions are met.
• DTCs P0010, P0011, P0013, P0014, P0020, P0021, P0023, P0024, P0341, P0342, P0343, P0346, P0347, P0348,
P0366, P0367, P0368, P0391, P0392, P0393, P2088, P2089, P2090, P2091, P2092, P2093, P2094 and P2095 ran
and passed:
• The engine is running.
• The ECM has learned the camshafts position.
DTC P0016, P0017, P0018 or P0019
Run continuously once the following conditions are met.
• DTCs P0010, P0011, P0013, P0014, P0020, P0021, P0023, P0024, P0335, P0336, P0338, P0341, P0342, P0343,
P0346, P0347, P0348, P0366, P0367, P0368, P0391, P0392, P0393, P2088, P2089, P2090, P2091, P2092,
P2093, P2094 and P2095 ran and passed:
• The calculated engine oil temperature is less than 95°C.
• The engine coolant temperature is 20 – 90°C.
• The engine is running for greater than 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0008
The ECM detects that both camshafts on bank 1 of the engine are misaligned with the crankshaft.
DTC P0009
The ECM detects that both camshafts on bank 2 of the engine are misaligned with the crankshaft.
DTC P0016, P0017, P0018 or P0019
The ECM detects the following deviation in the correlation between the camshaft position and the crankshaft position for
greater than 10 minutes:
• a camshaft position is too advanced in relationship to the crankshaft, or
• a camshaft position is too retarded in relationship to the crankshaft.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The CKP / CMP sensor correlation DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when Type B DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–89
Page 6C1-2–89
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in any of the listed sensors will trigger these DTCs.
5 Incorrect camshaft, camshaft actuator or timing chain installation will trigger these DTCs.
DTC P0008, P0009, P0016 to P0019 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0008, P0009, P0016, P0017, P0018 or P0019 fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs relating to the following DTCs also set:
• Camshaft actuator circuit
• CMP sensor circuit
• CKP sensor circuit
Refer to the
appropriate DTC
table Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the engine for the following fault conditions. Refer to Section
6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6:
• incorrect installation of the CMP sensor,
• incorrect installation of the CKP sensor,
• timing chain tensioner fault condition,
• incorrectly installed timing chain,
• excessive play in the timing chain, and
• timing chain that jumped teeth.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 5
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the crankshaft / camshaft position correlation DTCs fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
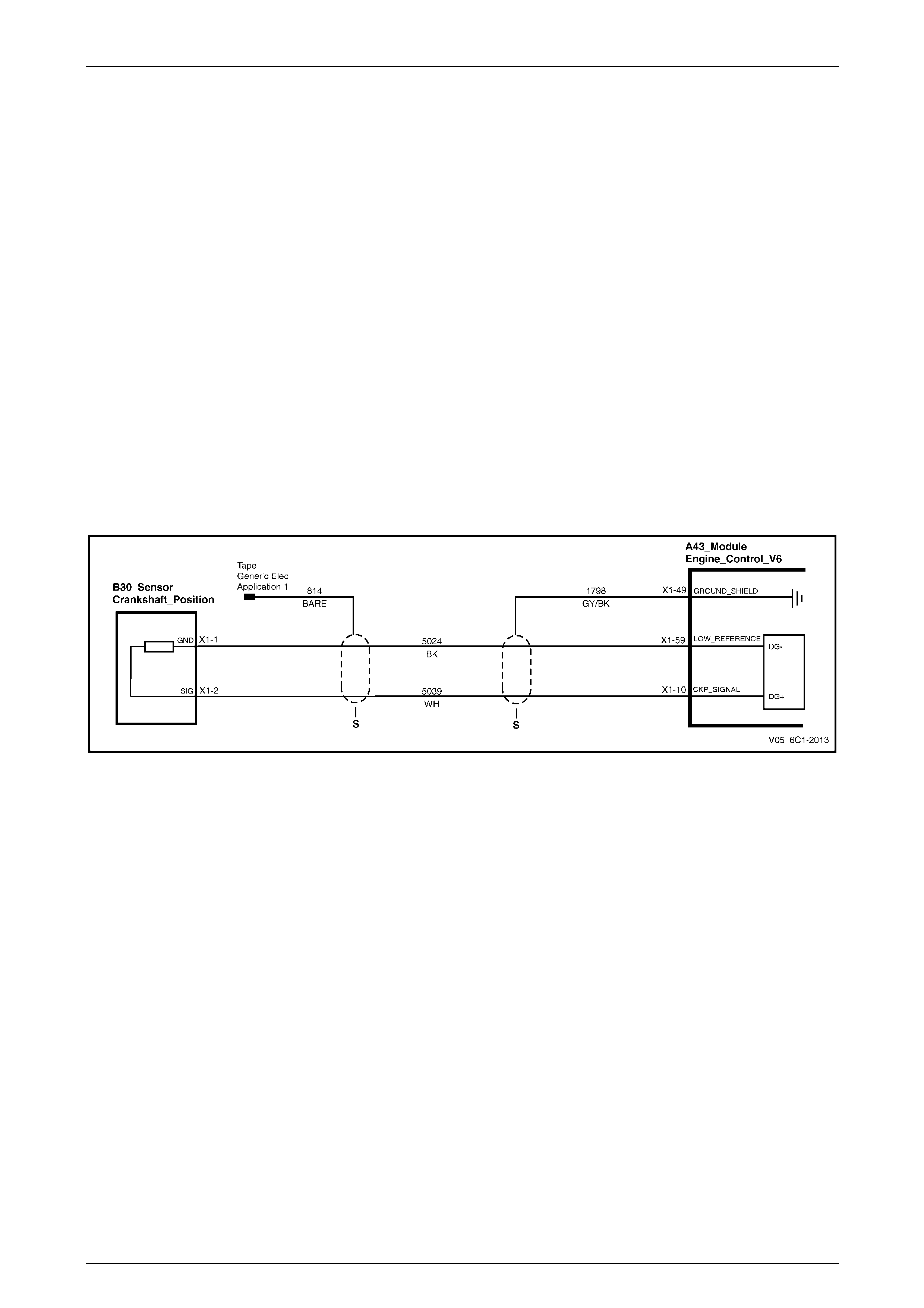
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–90
Page 6C1-2–90
5.9 DTC P0335 to P0338 – Crankshaft
Position Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0335 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0336 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Signal Range / Performance
• DTC P0337 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Low Duty Cycle
• DTC P0338 – Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit High Duty Cycle
Circuit Description
The ECM applies the ground to the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor low reference circuit.
The CKP sensor in conjunction with the 58X reluctor wheel generates an AC signal voltage. The amplitude and frequency
of the signal generated is proportional to the engine speed. The ECM uses this signal from the CKP sensor signal circuit
to determine the engine r.p.m.
In addition, the CKP sensor sends a signal to the ECM when piston No. 1 and piston No. 4 are at the top dead centre
position. The ECM monitors both the CKP signal and the camshaft position (CMP) sensor signal to determine the
compression stroke of piston No. 1.
A CKP sensor DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the CKP sensor signal circuit.
Figure 6C1-2 – 18
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CKP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• If the ECM has stored and learned the camshafts reference position, the ECM will utilise the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor signal in place of the CKP signal when there is fault condition in the CKP circuit. This will enable the
engine to operate in a limp mode when there is a CKP circuit fault condition.
• During a limp mode, the following DTCs may set and should be ignored.
• DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor Module Performance
• DTC P01011 – Intake Camshaft Position Actuator Park Position Bank 1
• The following fault condition may trigger DTC P0338:
• Fault condition in the CMP sensor circuits.
• Misaligned CKP sensor reluctor wheel or incorrect reluctor wheel installation.
• Excessive crankshaft end play that alters the alignment of the reluctor wheel.
• Obstruction between the CKP sensor and the reluctor wheel.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–91
Page 6C1-2–91
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0335
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is cranking or running.
• The ECM detects greater than 8 CMP sensor pulses.
DTC P0336
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0341, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed.
• The engine is cranking or running.
• The ECM detects a valid CMP signal.
DTC P0337 and P0338
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0341, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed.
• The engine is cranking or running.
• The ECM detects a valid CMP signal.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0335
The ECM does not detect a signal from the CKP sensor for 5 seconds.
DTC P0336
The ECM loses the crankshaft reference position and has to re-synchronise the crankshaft to camshaft one or more
times during six consecutive crankshaft revolutions.
DTC P0337
The ECM detects less than 58 reference signal pulses from the CKP sensor in the last eight consecutive crankshaft
revolutions.
DTC P0338
The ECM detects more than 58 reference signal pulses from the CKP sensor in the last eight consecutive crankshaft
revolutions.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The CKP sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type B
DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 The ECM supplies 2.5 V to signal circuit of the CKP sensor circuit to reduce the electro-magnetic interference
(EMI). If the voltage is not within range, this indicates there is an ECM or an ECM circuit fault condition.
4 The ECM supplies 2.5 V to low reference circuit of the CKP sensor circuit to reduce the electro-magnetic
interference (EMI). If the voltage is not within range, this indicates there is an ECM or an ECM circuit fault condition.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–92
Page 6C1-2–92
DTC P0335 to P0338 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Increase the engine speed to 1000 r.p.m. for 30 seconds.
4 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0335, P0336, P0337 or P0338 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the CKP sensor connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
signal circuit of the sensor connector and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 2 – 3 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the CKP
sensor low reference circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 2 – 3 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
ground shield circuit of the CKP sensor at the ECM connector and the
ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6 Perform the following CKP sensor inspection:
• Inspect the sensor wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault
Conditions.
• Inspect the sensor for incorrect sensor installation or incorrect
attaching bolt torque value. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
7 Test the CKP sensor signal circuit and low reference circuit for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground, short to voltage or shorted
together fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 Repair the open or high resistance fault condition in the CKP sensor
ground shield circuit. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
9 Replace CKP sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the CKP sensor circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
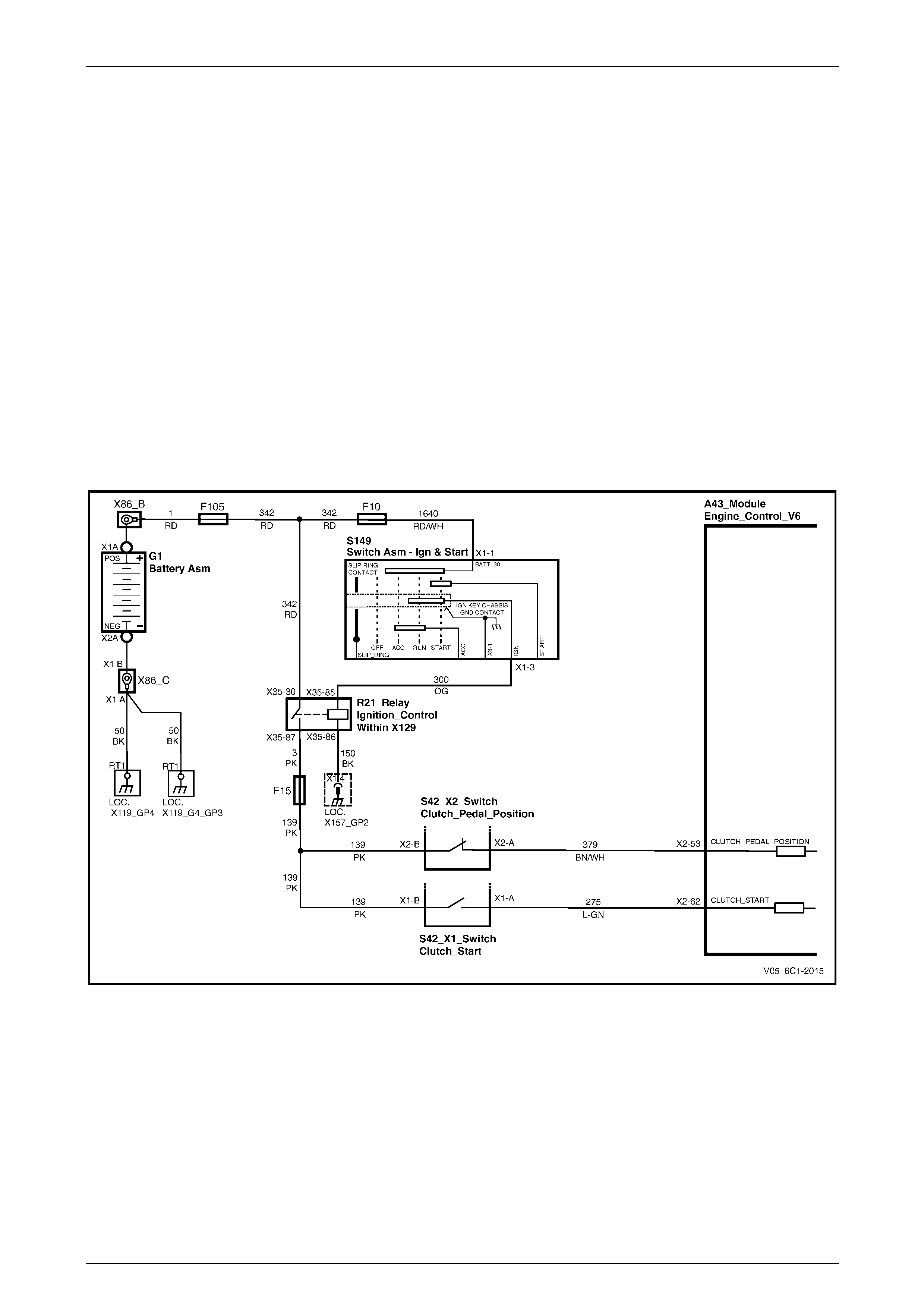
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–93
Page 6C1-2–93
5.10 DTC P0704 – Clutch Switch Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0704 – Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction.
Circuit Description
NOTE
There are two clutch pedal switch assemblies.
The one switch ensures the engine can only be
cranked with the clutch pedal fully depressed,
whilst the other disengages the cruise control
when the clutch is depressed. The switch
mounted away from the firewall is the cruise
control cancel switch.
The cruise control cancel switch is normally closed when the clutch pedal is at rest, opening when the pedal is pressed.
Activation of this switch removes the signal to the ECM which will then deactivate the cruise control.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Figure 6C1-2 – 19
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the clutch switch operation.
• Refer to Section 12E Cruise Control for clutch pedal switch operation and testing.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–94
Page 6C1-2–94
Conditions for Running the DTC
Runs continuously when the ignition is switched and the engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects 15 gear changes with less than three clutch switch inputs.
NOTE
The ECM determines that a gear change has
been performed by the engine speed/vehicle
speed ratio.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The clutch switch circuit DTC is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type C
DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
DTC P0704 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0704 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Engine
Data 1.
3 Observe the status of the cruise control cancel switch.
4 Depress the clutch pedal.
Does Tech 2 display change from Inactive to Active when the pedal
is pressed?
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section Go to Step 4
4 1 Disconnect the wiring connector from the cruise control cancel
switch. Refer to Section 12E Cruise Control.
2 Switch on the ignition.
3 Connect a test lamp between the voltage circuit of cruise control
cancel clutch switch and a ground.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–95
Page 6C1-2–95
Step Action Yes No
5 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the voltage
circuit of the clutch switch. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the cruise control cancel clutch switch. Refer to Section 12E
Cruise Control.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 7
7 Test the control circuit of the cruise control clutch switch, which failed
for a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage
fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information
on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0704 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–96
Page 6C1-2–96
5.11 DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088
to P2095 – Camshaft Position Actuator
Solenoid Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0010 – Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1)
• DTC P0013 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1)
• DTC P0020 – Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
• DTC P0023 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2)
• DTC P2088 – Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P2089 – Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P2090 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P2091 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P2092 – Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2)
• DTC P2093 – Intake Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2)
• DTC P2094 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2)
• DTC P2095 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Control Solenoid Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The Engine control relay applies ignition positive battery voltage to the camshaft position (CMP) actuator solenoids
through the ignition voltage circuit.
Using a device called a driver, the ECM applies pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the individual CMP solenoid
control circuit to control the oil pressure that advances or retards each camshaft position.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up to a voltage. The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to
determine an open, short to ground or short to a positive voltage fault condition in the control circuit.
A CMP actuator solenoid control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in a CMP solenoid
control circuit when the solenoid is commanded off.
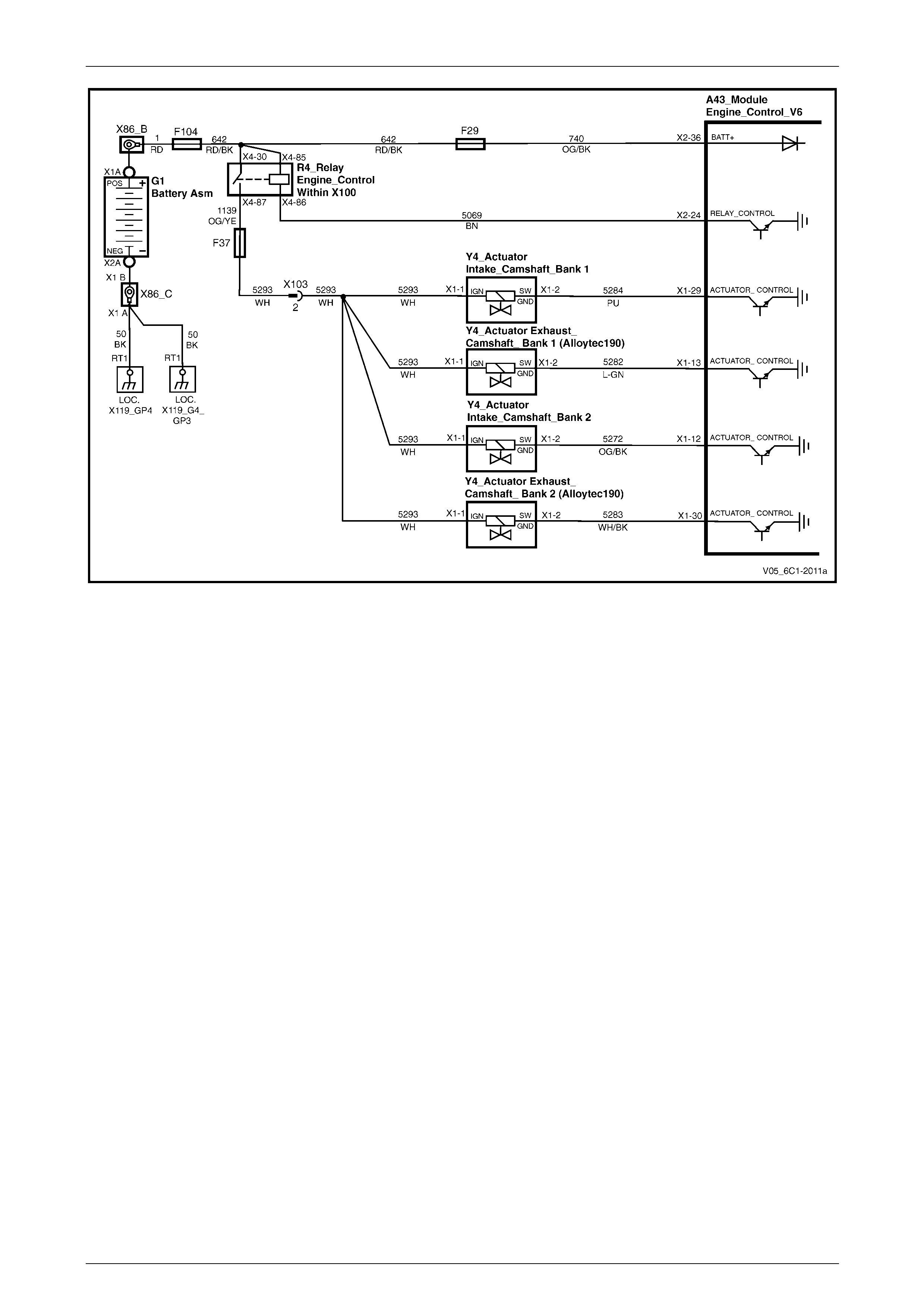
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–97
Page 6C1-2–97
Figure 6C1-2 – 20
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the intake CMP actuator
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088, P2090, P2092 or P2094
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The ECM has commanded the CMP actuator on and off at least once during the ignition cycle.
DTC P2089, P2091, P2093, or P2095
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–98
Page 6C1-2–98
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0010, P0013, P0020 or P0023
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in a CMP solenoid control circuit when the solenoid is commanded off.
DTC P2088, P2090, P2092 or P2094
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in a CMP solenoid control circuit.
DTC P2089, P2091, P2093 or P2095
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in a CMP solenoid control circuit.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The CMP actuator solenoid control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action
taken when Type B DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to determine if the CMP actuator control circuit is open, shorted to
ground or shorted to a positive voltage. If the voltage is outside the specified range, there is a fault condition with
the control circuit.
DTC P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088 to P2095 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds or
operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088, P2089, P2090, P2091,
P2092, P2093, P2094 or P2095 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the appropriate CMP actuator wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the CMP actuator ignition voltage
circuit and a good ground.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–99
Page 6C1-2–99
Step Action Yes No
4 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the open circuit fault condition at the CMP solenoid ignition
voltage circuit. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information
on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the appropriate CMP control circuit for a high resistance or open
circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the appropriate CMP solenoid. Refer to Section 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the CMP actuator solenoid control circuit DTCs fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–100
Page 6C1-2–100
5.12 DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348,
P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 –
Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0341 – Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance (Bank 1)
• DTC P0342 – Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P0343 – Intake Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P0346 – Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance (Bank 2)
• DTC P0347 – Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 2)
• DTC P0348 – Intake Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 2)
• DTC P0366 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance (Bank 1)
• DTC P0367 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P0368 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 1)
• DTC P0391 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance (Bank 2)
• DTC P0392 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 2)
• DTC P0393 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The ECM applies 5 V to the camshaft position (CMP) sensors through the 5 V reference and ground through the low
reference circuit.
The CMP sensor is a Hall effect switch. In conjunction with a 4X reluctor wheel, the CMP sensors provide a signal
voltage to the ECM. The ECM uses this signal voltage to determine the position of the camshafts.
The ECM compares the CMP signal voltage to the number of crankshaft revolutions. A CMP sensor DTC sets if the ECM
detects a fault condition in the CMP sensor circuits.
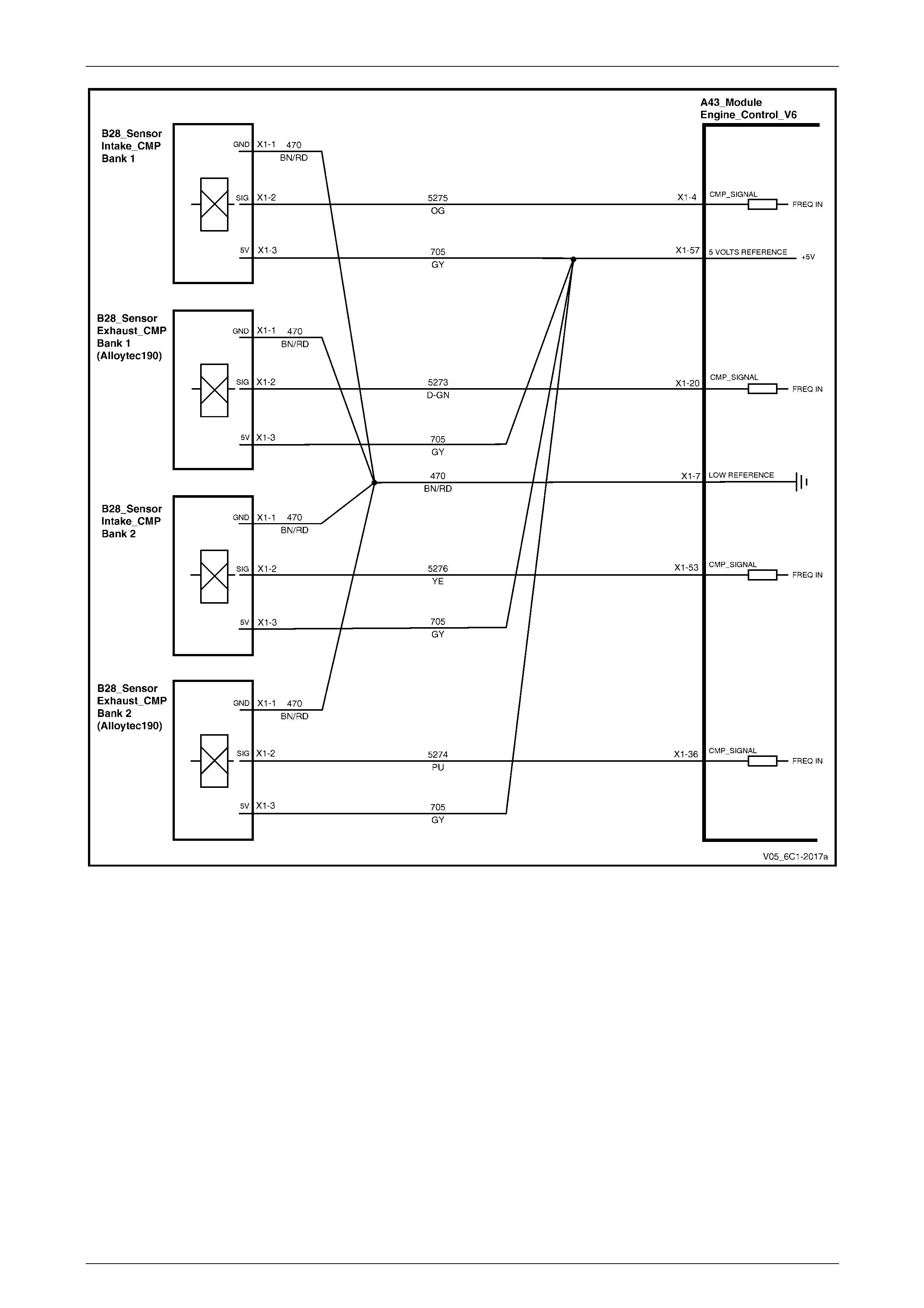
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–101
Page 6C1-2–101
Figure 6C1-2 – 21
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CMP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–102
Page 6C1-2–102
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0342 or P0347
The ECM detects no pulses from the CMP sensor signal circuit and the CMP sensor signal voltage is low in correlation
with the number of crankshaft revolutions.
DTC P0367 or P0392
The ECM detects no pulses from the CMP sensor signal circuit and the CMP sensor signal voltage is low in correlation
with the number of crankshaft revolutions.
DTC P0341, P0346, P0366 or P0391
The ECM detects a signal from the CMP sensor signal circuit and the sensor signal range is not within the predetermined
parameter or the when the CMP sensor does not correlate with the crankshaft position.
DTC P0343 or P0348
The ECM detects no pulses from the CMP sensor signal circuit and the CMP sensor signal voltage is always high.
DTC P0368 or P0393
The ECM detects no pulses from the CMP sensor signal circuit and the CMP sensor signal voltage is always high.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The CMP sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type B
DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Tests the signal circuit of the CMP sensor. This circuit is pulled-up to about 5 V.
4 Measures the integrity of the CMP sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to
power down completely prior to the test procedure.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–103
Page 6C1-2–103
DTC P0341 to P0343, P0346 to P0348, P0366 to P0368, P0391 to P0393 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Increase the engine speed to 1000 r.p.m. for 30 seconds.
4 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does P0341, P0342, P0343, P0346, P0347, P0348, P0366, P0367,
P0368, P0391, P0392 or P0393 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the appropriate CMP sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
signal circuit of the appropriate CMP sensor and the ECM
housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
CMP sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
5 Test the signal circuit of the CMP sensor for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 6
6 Perform the following CMP sensor inspection:
• Inspect the sensor wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault
Conditions.
• Inspect the sensor for incorrect sensor installation or incorrect
attaching bolt torque value. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Inspect the CMP sensor reluctor wheel for damage or conditions
that causes misalignment.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–104
Page 6C1-2–104
Step Action Yes No
7 Test the CMP sensor 5 V reference circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to voltage or short to ground fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
NOTE
Each CMP sensor shares a common 5 V reference circuit.
A fault condition in the 5 V reference circuit may trigger
DTCs on all CMP sensors. Refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams
and Connector Charts to aid diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 Test the CMP sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance or an
open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
NOTE
The CMP sensor shares the low reference circuit with
other sensors. A fault condition in the low reference circuit
may trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit. Refer
to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts to aid
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9 Replace the appropriate CMP sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the CMP Sensor Circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
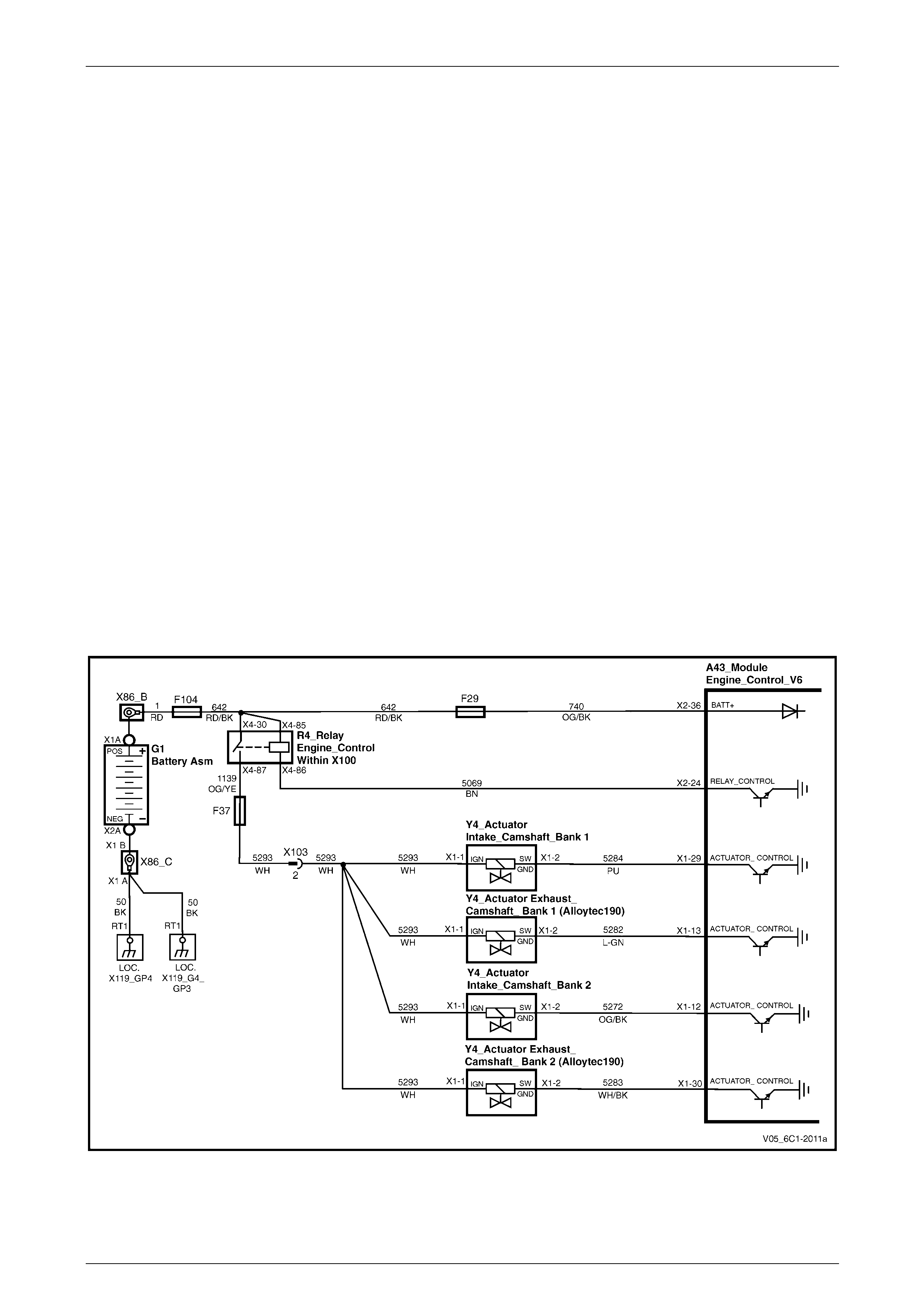
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–105
Page 6C1-2–105
5.13 DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011
to P1014 – Camshaft Position System
Performance or Park Position
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0011 – Intake Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 1)
• DTC P0014 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 1)
• DTC P0021 – Intake Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 2)
• DTC P0024 – Exhaust Camshaft Position Range / Performance (Bank 2)
• DTC P1011 – Intake Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 1)
• DTC P1012 – Exhaust Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 1)
• DTC P1013 – Intake Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 2)
• DTC P1014 – Exhaust Camshaft Actuator Park Position (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies ignition positive battery voltage to the camshaft position (CMP) actuator solenoids
through the ignition voltage circuit.
Using a device called a driver, the ECM applies a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the individual CMP solenoid
control circuit. This controls the oil pressure that advances or retards each camshaft position.
The ECM compares the camshaft position to the crankshaft position to detect CMP system malfunction. A CMP system
performance or park position DTC sets if the ECM detects a deviation between the camshafts actual position and the
ECM's calculated camshaft position.
Figure 6C1-2 – 22
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–106
Page 6C1-2–106
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CMP system operation.
• The following conditions may trigger the camshaft position system performance or park position DTCs:
• Mechanical fault condition in the CMP actuator assembly. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• Switching off the engine while the accelerator pedal is depressed.
• Switching off the engine while driving.
• Pressing the accelerator pedal while cranking the engine.
• An engine idle flare during start-up.
• The engine oil condition has a major impact on the operation of the camshaft actuator.
• A low oil level may set these DTCs.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021 and P0024
Run continuously once the following conditions are met.
• DTCs P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P0342, P0343, P0347, P0348, P0367, P0368, P0392, P0393, P2088, P2089,
P2090, P2091, P2092, P2093, P2094 and P2095 ran and passed:
• The ECM has commanded the CMP actuator from the park position to the phased position 5 times in 10 seconds.
• The engine speed is greater than 1,000 r.p.m.
• The engine is operating for approximately 5 minutes.
DTC P1011, P1012, P1013 and P1014
Run continuously once the following conditions are met.
• DTCs P0010, P0013, P0020, P0023, P2088, P2089, P2090, P2091, P2092, P2093, P2094 and P2095 ran and
passed:
• The ECM has completed the CMP actuator solenoid output driver test.
• The engine speed is greater than 1,000 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021 or P0024
The ECM detects the following conditions:
• The target position (ECM's calculated position of the camshaft) and the actual position of the camshaft deviates by
greater than 5 degrees.
• The difference between the actual camshaft angle and the locked position angle deviates by greater than
1 degree.
• The above conditions exists for 7 seconds.
DTC P1011, P1012, P1013 and P1014
The ECM detects that a CMP actuator is not in the parked position on engine start-up.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–107
Page 6C1-2–107
Conditions for Clearing DTC
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021 and P0024
The CMP system performance DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type B DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
DTC P1011, P1012, P1013 and P1014
The CMP system park position DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in any of the listed sensors will trigger these DTCs.
5 Isolates the fault condition. The CMP actuator is faulty if the DTC moves with the suspected sensor.
DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011 to P1014 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0011, P0014, P0021, P0024, P1011, P1012, P1013 or
P1014 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs relating to the following sensors also set:
• CMP sensor circuit or performance
• CMP actuator circuit or performance
• CKP sensor circuit or performance
• Oil pressure sensor
Refer to the
appropriate DTC
table Go to Step 4
4 Remove and inspect the CMP actuator solenoid. Refer to Section
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1 Swap the suspected the CMP actuator solenoid with the CMP
actuator solenoid that is operating correctly.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does the suspected CMP actuator solenoid trigger a DTC in its new
location? Go to Step 6
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
6 Replace the suspected CMP solenoid. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the camshaft position system performance or park DTCs
position fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
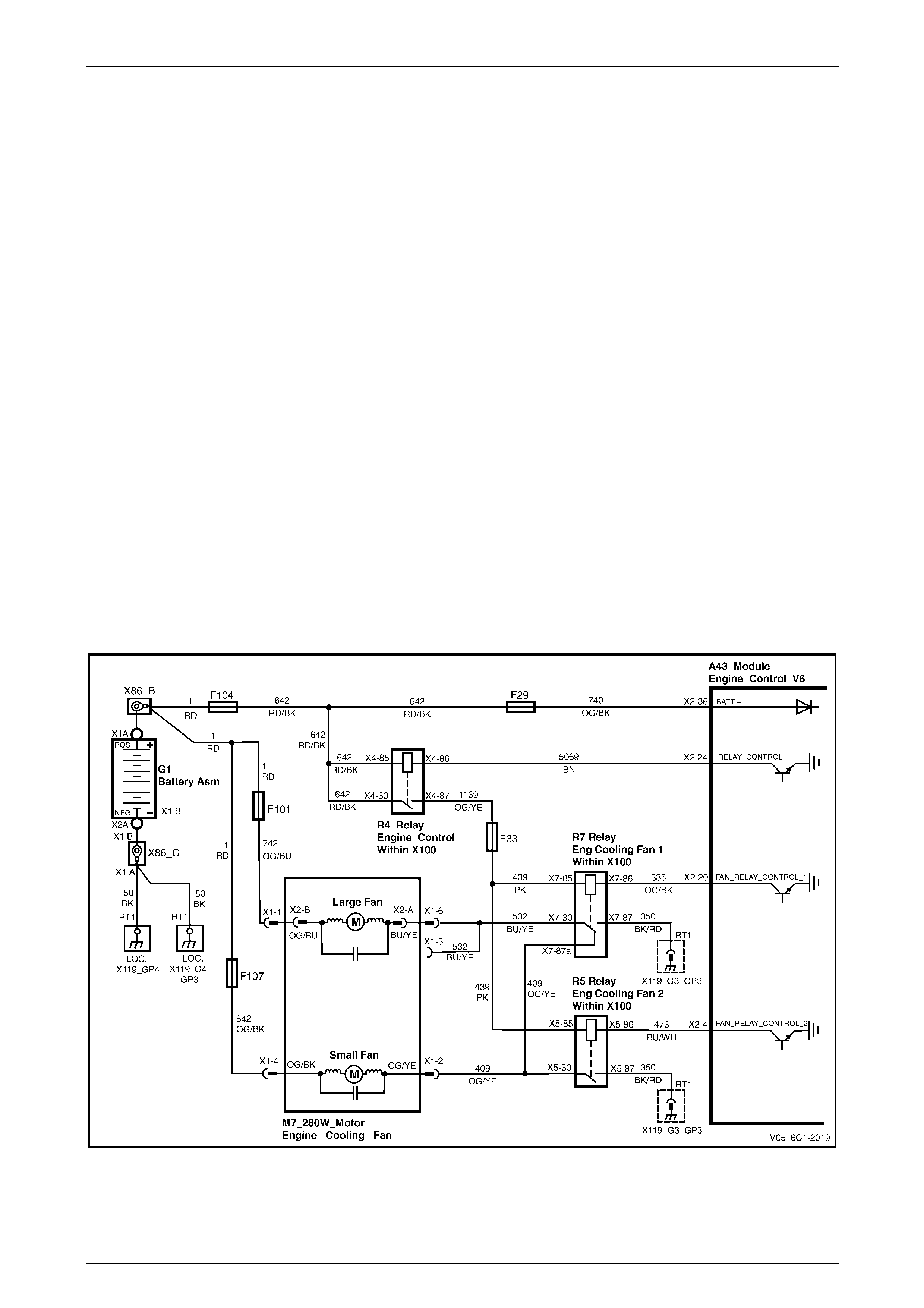
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–108
Page 6C1-2–108
5.14 DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 –
Cooling Fan Relay Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0480 – Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0481 – Cooling Fan Relay 2 and 3 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0691 – Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0692 – Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0693 – Cooling Fan Relay 2 and 3 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0694 – Cooling Fan Relay 2 and 3 Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies ignition positive battery voltage to the ignition circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 1 and
relay 2. Using a device called a driver, the ECM performs the following tasks:
• grounds the engine cooling fan relay 1 control signal circuit to operate the small engine cooling fan, or
• grounds the engine cooling fan relay 2 control signal circuit to operate both the small engine cooling fan and the
large engine cooling fan.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up to a voltage. The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to
determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
A cooling fan relay control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the engine cooling fan relay control
circuit.
Figure 6C1-2 – 23
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–109
Page 6C1-2–109
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6B1 – Engine Cooling – V6 for details of the engine cooling fan operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• the ignition voltage is 10 – 16 V,
• the engine speed is greater than 40 r.p.m., and
• the ECM driver transitions from on to off or from off to on.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0480
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in the control circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 1.
DTC P0481
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in the control circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 2.
DTC P0691
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the control circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 1.
DTC P0692
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the control circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 1.
DTC P0693
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the control circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 2.
DTC P0694
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the control circuit of the engine cooling fan relay 2.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The cooling fan relay control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when Type B DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–110
Page 6C1-2–110
DTC P0480, P0481, P0691 to P0694 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds or
operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0480, P0481, P0691, P0692, P0693 or P0694 fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information
3 1 Remove the appropriate engine cooling fan relay. Refer to
Section 12O Fuses, Relays and Wiring Harnesses.
2 Connect a test lamp between the ignition voltage circuit of the
engine cooling fan relay and the ECM housing.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Connect a test lamp between the control circuit of the
appropriate engine cooling fan relay and a 12 V.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using Tech 2, command the appropriate engine cooling fan relay
on and then off.
Does the test lamp turn on and off when the engine cooling fan relay is
commanded on and off? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the ignition
voltage circuit of the engine cooling fan relay. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the engine cooling fan relay control circuit for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the faulty engine cooling fan relay. Refer to Section 12O
Fuses, Relays and Wiring Harnesses.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the cooling fan relay control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–111
Page 6C1-2–111
5.15 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 –
ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or
Memory Fault
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0601 – Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
• DTC P0602 – Program Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
• DTC P0604 – Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
• DTC P0606 – Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) is the control centre of the engine management system. The programming and
calibration needed by the ECM to control the functionality of the engine management system are stored in the ECM read
only memory (ROM).
An ECM internal circuit, programming or memory fault DTC sets if there is an internal microprocessor integrity fault
condition with the ECM or if the ECM is not programmed.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0601
Runs once when the checksum calculation at power down is completed in the last ignition cycle.
DTC P0602 and P0606
Runs continuously when the ignition is switched on with the engine not running.
DTC P0604
Runs once when the read / write test at power-down is completed in the last ignition cycle.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0601
The ECM detects an incorrect ROM checksum for greater than 30 seconds.
DTC P0602
The ECM programming is incomplete.
DTC P0604
The ECM detects an error in the RAM for 6 seconds.
DTC P0606
There is an internal ECM circuit fault condition for 6 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The ECM Internal Circuit, Programming or Memory Fault DTCs are Type A DTCs.
Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type A DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type A
DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–112
Page 6C1-2–112
DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 and P0606 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Test all ECM fuses and ground connections. Refer to Section 12O
Relays, Fuses and Wiring Harnesses.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4 Attempt to program the ECM. Refer to Section 0C Tech 2.
Was the programming successful? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the ECM internal circuit, programming or memory fault
DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
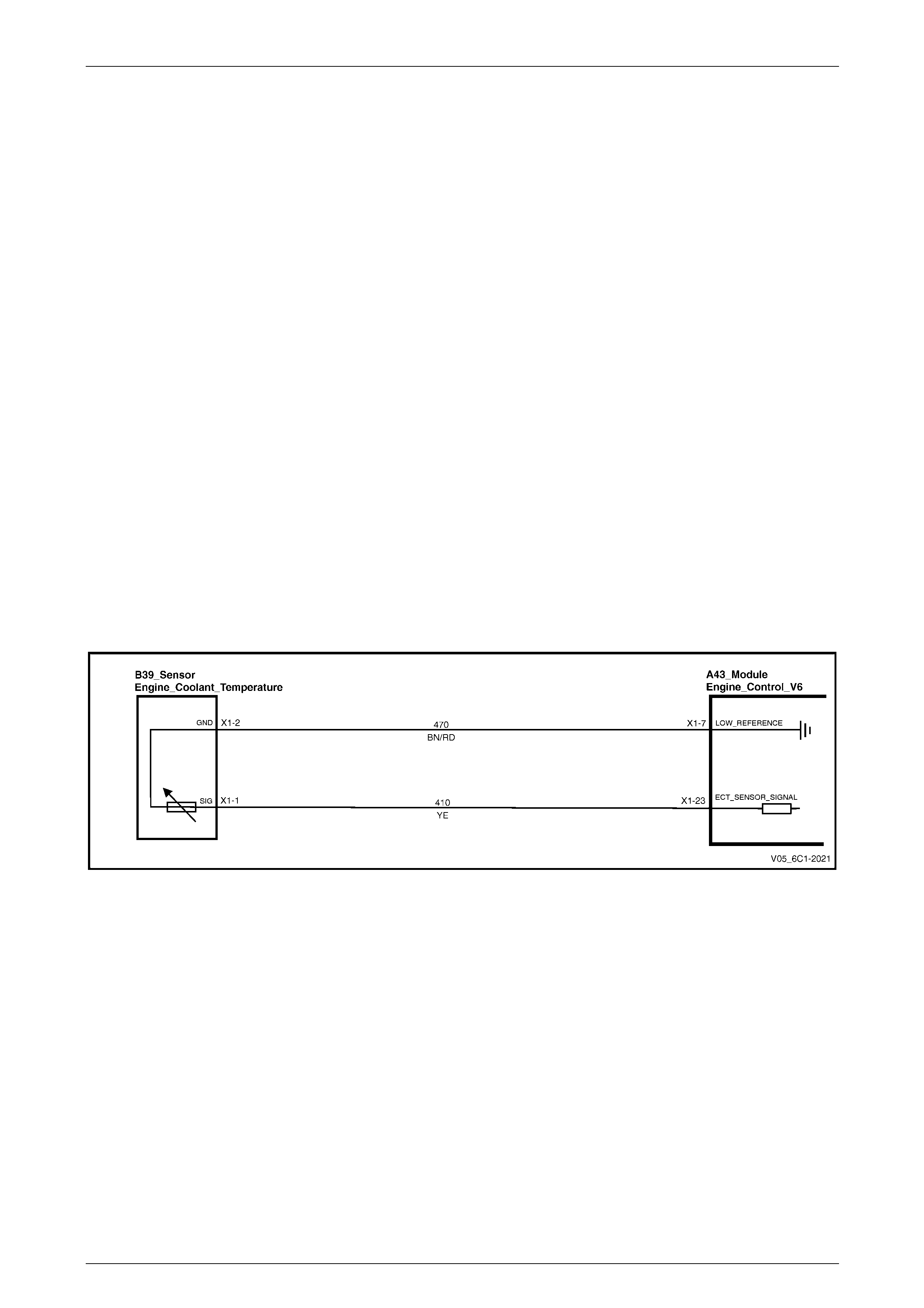
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–113
Page 6C1-2–113
5.16 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and
P1258 – Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0116 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Range / Performance
• DTC P0117 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0118 – Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0125 – Insufficient Engine Coolant Temperature For Closed Loop Fuel Control
• DTC P1258 – Engine Coolant Over Temperature - Protection Mode Active
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a reference 5 V to the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor signal circuit and ground through the
low reference circuit. The ECT sensor is a variable resistor that measures the temperature of the engine coolant.
• Increased temperature in the engine coolant decreases the resistance value of the ECT sensor. This increases the
ECT sensor pull-down rate to ground. Therefore, the higher the engine coolant, the lower the signal voltage output
of the ECT sensor.
• Decreased temperature in the engine coolant increases the resistance value of the ECT sensor. This reduces the
ECT sensor pull-down rate to ground. Therefore, the lower the engine coolant temperature, the higher the signal
voltage output of the ECT sensor.
An ECT sensor DTC sets if the ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is outside the predetermined range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 24
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECT sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• DTCs P0116, P0117, P0118 and P0125 diagnostic table is developed with the assumption the engine cooling
system is functioning correctly. Therefore, rectify any engine cooling system fault conditions before proceeding with
this diagnostic table.
• Test the ECT sensor using the ECT Temperature vs. Resistance in
Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations. If the engine has sat overnight, the ECT sensor
should display within 3°C of the IAT sensor values. When the engine is first started, the ECT should rise steadily to
about 90°C then stabilise when thermostat opens.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–114
Page 6C1-2–114
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0116
Runs continuously when the engine is running.
DTC P0117, P0118 and P1258
Runs continuously when the ignition is switched on.
DTC P00125
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0480, P0481, P0691, P0692, P0693, and P0694 are not set.
• The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0116
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature sensor value is 10°C less than the minimum calculated engine
temperature.
DTC P0117
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is greater than 140°C for longer than 3 seconds.
DTC P0118
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is less than -39°C for longer than 3 seconds.
DTC P0125
The ECM determines the calculated engine temperature by measuring the amount of airflow into the engine. This DTC
sets if the ECM detects the actual ECT sensor is not within 10ºC of the calculated engine temperature for approximately
2 – 5 minutes.
DTC P1258
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is greater than 131°C for longer than 2 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The ECT sensor DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type B DTC
sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 A fault condition in the engine cooling system may trigger these DTCs.
7 The ECT sensor low reference circuit is shared with other components. DTC P0118 may set if the shared low
reference circuit is shorted to voltage. Test the low reference circuit of all components that share this circuit to find
the source of the fault condition.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–115
Page 6C1-2–115
DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and P1258 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 Test the engine cooling system for correct operation. Refer to Section
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 3
3 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 or P1258 fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 4
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the ECT sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
ECT sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
ECT sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
6 Test the IAT sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–116
Page 6C1-2–116
Step Action Yes No
7 Test the ECT sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Replace the ECT sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the ECT sensor DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–117
Page 6C1-2–117
5.17 DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Engine
Control Module System Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0560 – System Voltage Malfunction
• DTC P0562 – System Voltage Low Voltage
• DTC P0563 – System Voltage High Voltage
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied continuously to the engine control module (ECM) through the continuous battery supply circuit
and the ground through the ground connection of the ECM housing to the engine.
Turning the ignition switch on activates the ignition control relay, which directs ignition positive voltage from the battery to
the ECM switched battery supply circuit which activates the ECM. The ECM then applies control voltage to the control
circuit of the Engine control relay to activate the Engine control relay. The Engine control relay supplies ignition voltage to
the various engine management system components.
The ECM monitors the battery voltage circuits to ensure the voltage available to the engine management system stays
within the specified range. Incorrect system voltage may cause incorrect engine management system operation or
component malfunction.
An ECM system voltage DTC sets if the ECM detects the voltage available to any of the ECM voltage supply circuit is
outside the specified range.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–119
Page 6C1-2–119
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0560, P0563 and P0563 runs continuously when the engine is running at speeds greater than 1500 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0560
The ECM detects the ignition 1, ignition 2 or switched battery supply voltage is out of the specified range for 30 seconds.
DTC P0562
The ECM detects the ECM system voltage is less than 11 V for 5 seconds.
DTC P0563
The ECM detects the ECM system voltage is greater than 16 V.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The ECM system voltage DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type
C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–120
Page 6C1-2–120
DTC P0560, P0562 and P0563 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Increase the engine speed to 1500 r.p.m. or operate the vehicle
within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0560, P0562, or P0563 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Test the battery condition. Refer to Section 12A Battery.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 4
4 Test the charging system operation. Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging
System – V6 – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5 Test all the ECM fuses. Refer to Section 12O Relays, Fuses and
Wiring Harnesses.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
6 Check the ECM ground connections for corrosion, loose terminal or
incorrect position. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 7
7 Test the following circuits for a high resistance or open circuit fault
condition.
• Continuous battery supply circuit,
• switched battery supply circuit,
• ignition 1 circuit, and
• ignition 2 circuit.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical
fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the ECM system voltage DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
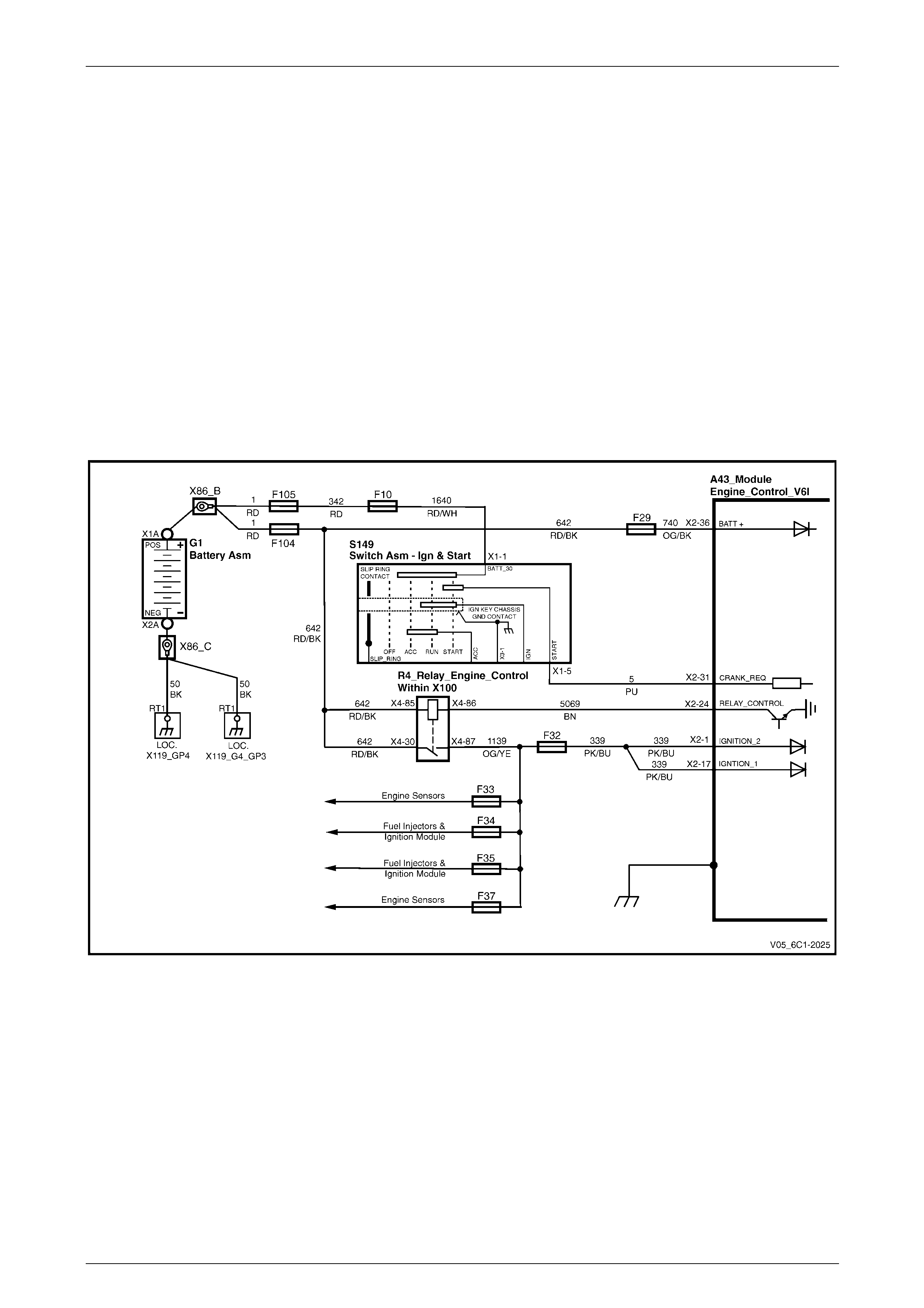
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–121
Page 6C1-2–121
5.18 DTC P0685 to P0687 – Engine Control
Relay Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0685 – Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0686 – Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0687 – Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The supply voltage circuit of the engine control relay is directly connected to battery voltage. When the ignition switch is
turned on, the ECM grounds the relay control circuit to provide ignition voltage to various sensors and components that
controls the engine operation.
The ECM monitors the control circuit of the engine control relay for conditions that are incorrect for the commanded state.
An engine control relay circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in this circuit.
Figure 6C1-2 – 26
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–122
Page 6C1-2–122
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0685, P0686 and P0687 run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects a condition that is incorrect for the engine control relay commanded state.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The engine control relay control circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to power down completely prior to the test procedure.
DTC P0685 to P0687 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Turn the ignition switch to the Start position or operate the
vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0685, P0686 and P0687 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Remove the engine control relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses,
Relays and Wiring Harnesses.
2 Connect a test lamp between the battery voltage circuit of the
engine control relay and a good ground.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove and reinstall the ECM fuse 29 from the engine
compartment fuse and relay panel assembly.
3 Connect a test lamp between the control circuit and the battery
voltage circuit of the engine control relay.
4 Switch on the ignition.
Does the test lamp switches from off to on when the ignition switch is
turned form off to on? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the battery
voltage circuit of the engine control relay. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–123
Page 6C1-2–123
Step Action Yes No
6 Test the control circuit of the engine control relay for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or a short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the engine control relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses, Relays
and Wiring Harnesses.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does the engine control relay control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–124
Page 6C1-2–124
5.19 DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction
Malfunction
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction
Circuit Description
The ECM monitors and compares the engine torque output against the maximum allowable engine torque. Refer to
Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the engine torque limit management
operation.
If the requested torque is higher than the maximum allowable torque, the ECM applies engine torque limitation and DTC
P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction sets.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the Engine Torque Limit
Management operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P1845 runs continuously when the engine is running at speeds greater than 40 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The engine torque output exceeds the maximum allowable torque output for 10 minutes.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P1845 – Engine Torque Reduction Malfunction is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action
taken when a Type C DTC set and conditions for clearing Type C DTC.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 Fault conditions that apply excessive load on the engine may trigger this DTC.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–125
Page 6C1-2–125
DTC P1845 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC or
road test the vehicle under various driving condition.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P1845 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are there any other ECM or TCM DTCs set? Refer to the
appropriate DTC
table. Go to Step 4
4 Inspect for fault conditions in the engine or transmission that applies
excessive load on the engine.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P1845 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
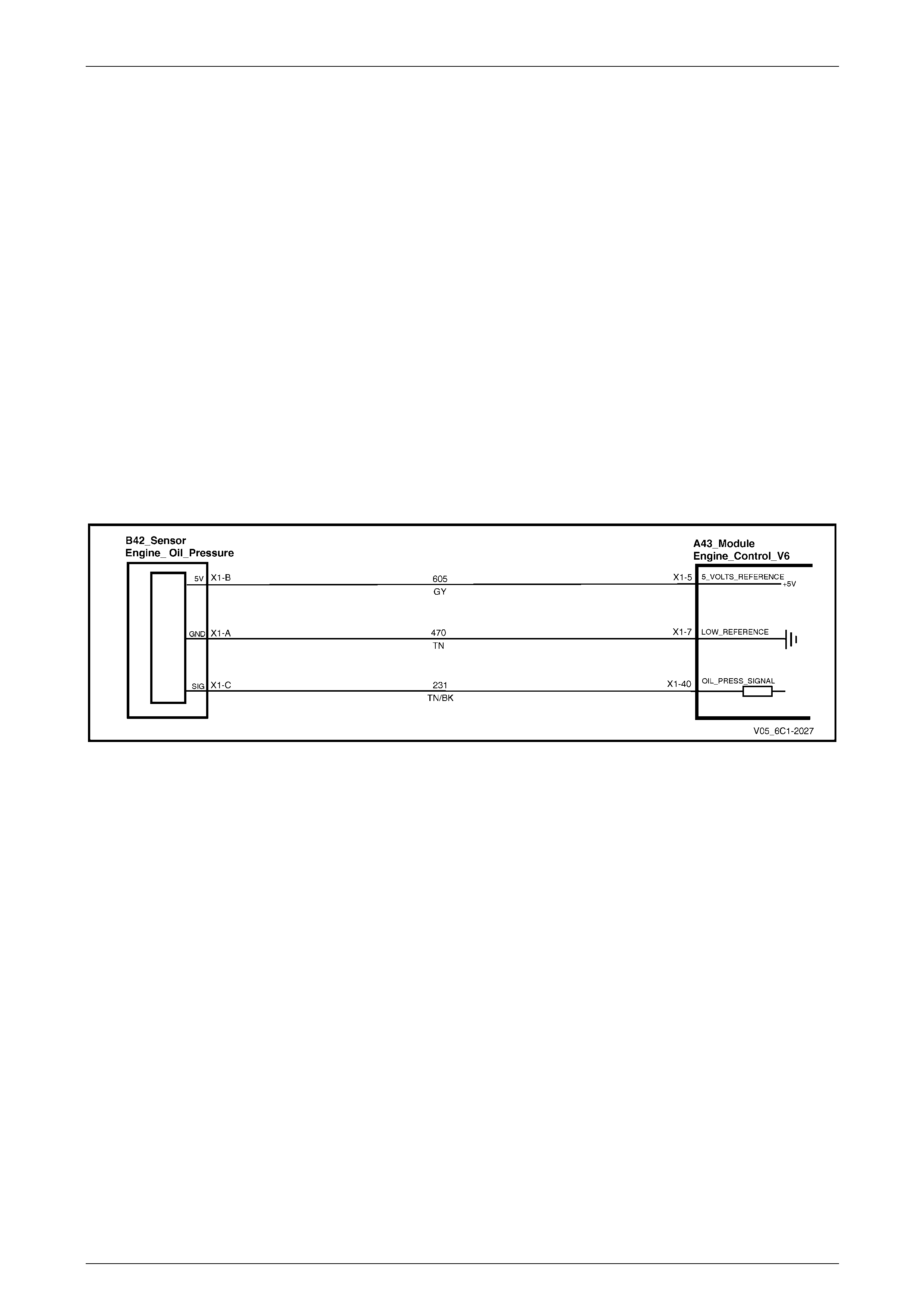
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–126
Page 6C1-2–126
5.20 P0521 to P0523 – Engine Oil Pressure
Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0521 – Oil Pressure Sensor Range / Performance
• DTC P0522 – Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage Low
• DTC P0523 – Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a positive 5 V reference voltage to the engine oil pressure (EOP) sensor through the 5 V reference
circuit and the ground through the low reference circuit.
The EOP sensor provides signal voltage to the ECM that is proportional to the oil pressure generated by the engine oil
pump. The ECM monitors the EOP sensor signal voltage. If the ECM detects a low oil pressure condition, it sends a
serial data communication signal to the instrument cluster to illuminate the check oil warning icon.
The ECM monitors and compares the EOP sensor signal voltage against a specified range. An EOP sensor circuit DTC
sets if the ECM detects the EOP sensor signal voltage is outside the specified range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 27
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the EOP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0521, P0522 and P0523 run continuously when the engine is running.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–127
Page 6C1-2–127
Conditions for Setting the DTC
P0521
The ECM detects engine oil pressure is:
• greater than 800 kPa at idle, or
• engine r.p.m. is greater than 2000 r.p.m and oil pressure is less than 8 kPa.
P0522
The oil pressure sensor signal voltage is less than 0.2 V for more than 10 seconds.
P0523
The oil pressure sensor signal voltage is more than 4.9 V for more than 10 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The EOP sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type B
DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 Test signal circuit of the EOP sensor. This circuit should display a voltage within the specified range.
5 Measures the integrity of the EOP sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to
power down completely prior to the test procedure.
P0521 to P0523 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the EOP sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
EOP sensor 5 V reference circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the EOP sensor 5 V
reference circuit and the EOP sensor signal circuit.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using Tech 2, observe the EOP sensor parameter.
Does Tech 2 display 780 – 980 kPa? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–128
Page 6C1-2–128
Step Action Yes No
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM/TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
EOP sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Test the EOP sensor 5 V reference circuit for an open, short to ground
or high resistance fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
7 Test EOP sensor signal circuit for short to ground fault condition.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical
fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 1 Disconnect the ECM wiring connector.
2 Test the EOP sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance
and open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
NOTE
The EOP sensor shares the low reference circuit with other
sensors. A fault condition in the low reference circuit may
trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit. Refer to 2
Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts to aid diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9 Replace the EOP sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the for the engine oil pressure sensor circuit DTCs s fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
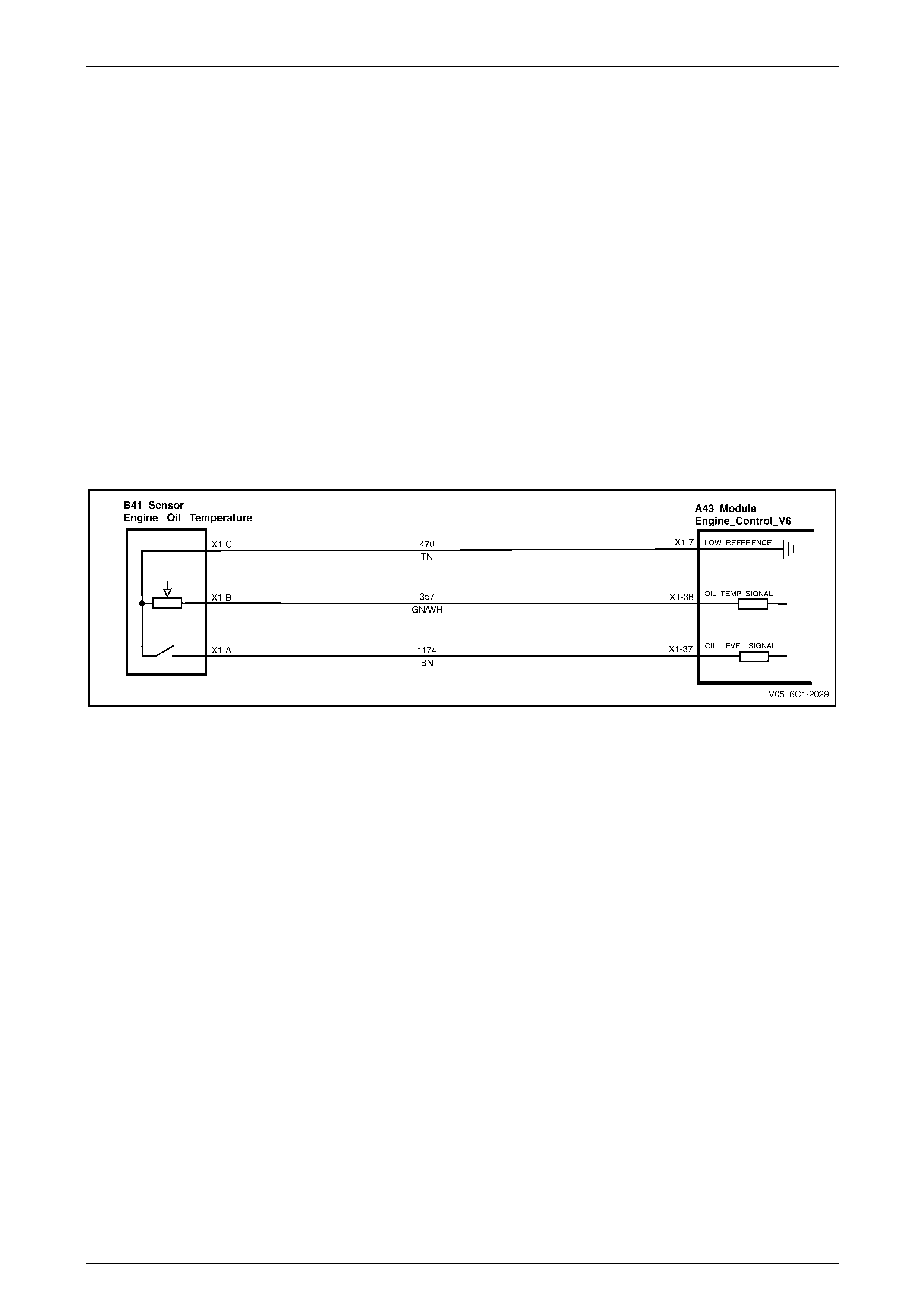
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–129
Page 6C1-2–129
5.21 DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 – Engine
Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0196 – Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Range / Performance
• DTC P0197 – Engine Oil Temperature Voltage Low
• DTC P0198 – Engine Oil Temperature Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a positive 5 V reference voltage to the engine oil temperature (EOT) sensor through the 5 V reference
circuit and the ground through the low reference circuit.
The EOT sensor is a variable resistor that measures the temperature of the engine oil. This sensor provides signal
voltage to the ECM that is proportional to the oil temperature off the engine.
The ECM monitors and compares the EOT sensor signal voltage against a specified range. An EOT sensor circuit DTC
sets if the ECM detects the EOT sensor signal voltage is outside the specified range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 28
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the EOT sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 run continuously when the engine is running.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–130
Page 6C1-2–130
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0196
The ECM detects the engine oil temperature sensor is not within 100°C of the modelled temperature
NOTE
The modelled temperature is the temperature that
the ECM expects to see given current engine
operating conditions.
DTC P0197
The ECM detects the engine oil temperature is less than -35°C for longer than 3 seconds.
DTC P0198
The ECM detects the engine oil temperature is
greater than 170°C for longer than 3 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The EOT sensor circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type C
DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
5 Test signal circuit of the EOT sensor. This circuit should display a voltage within the specified range.
6 Measures the integrity of the EOT sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the Fuse 29 enables the ECM to power
down completely prior to the test procedure.
DTC P0196, P0197 and P0198 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 Test the engine cooling system for correct operation. Refer to Section
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 3
3 Inspect the engine oil condition. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 4
4 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0196, P0197 or P0198 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 5
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–131
Page 6C1-2–131
Step Action Yes No
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the EOT sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
EOT sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM/TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
EOT sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Test EOT sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit, short
to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
8 Test the EOT sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance and
open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
NOTE
The EOT sensor shares the low reference circuit with other
sensors. A fault condition in the low reference circuit may
trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit. Refer to 2
Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts to aid diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9 Replace the EOT sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the for the engine oil pressure sensor circuit DTCs s fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
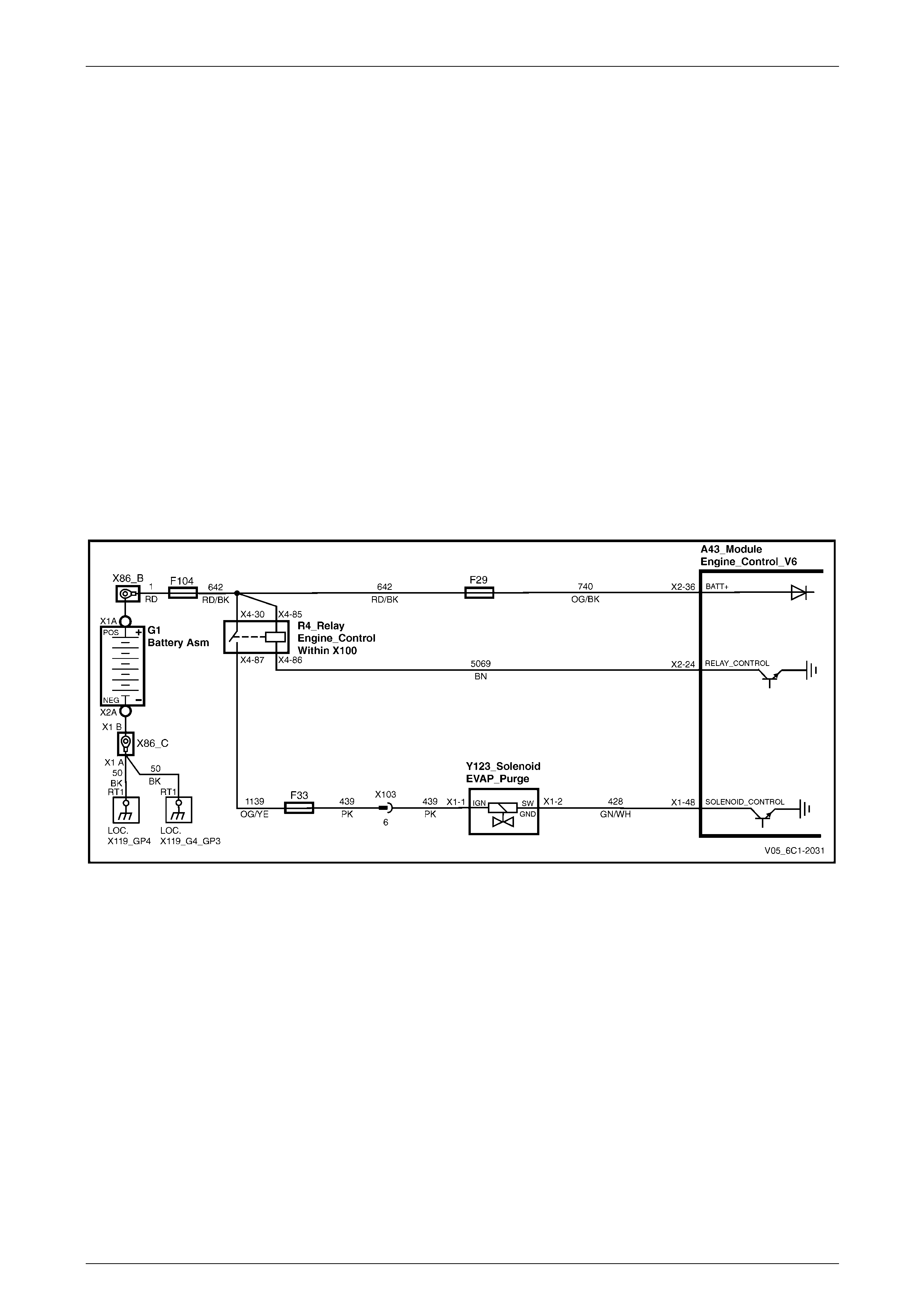
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–132
Page 6C1-2–132
5.22 DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 –
Evaporative Emission Purge Solenoid
Valve Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0443 – Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0458 – Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0459 – Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The Engine control relay applies ignition positive battery voltage to the evaporative emission (EVAP) purge solenoid.
Using a device called a driver, the ECM applies a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the EVAP solenoid control
circuit to purge the fuel vapour from the EVAP canister into the intake manifold.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up to a voltage. The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to
determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
An EVAP purge solenoid valve control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the voltage on the EVAP solenoid control
circuit outside the predetermined range when the solenoid is commanded off.
Figure 6C1-2 – 29
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the EVAP Purge Solenoid
Valve operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–133
Page 6C1-2–133
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0443 and P0458
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The ECM has commanded the EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve on and off at least once during the ignition cycle.
DTC P0459
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The fuel system is in closed loop.
• The engine speed is above idle.
• The engine is at operating temperature.
• The ECM has commanded the EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve on and off with a duty cycle of greater than 2.5%.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0443
The ECM detects the voltage on the EVAP solenoid control circuit is not within the predetermined range when the
solenoid is commanded off.
DTC P0458
The ECM detects the voltage on the EVAP solenoid control circuit is less than 2.6 V when the solenoid is commanded
off.
DTC P0459
The ECM detects the voltage on the EVAP solenoid control circuit is greater than 4.6 V when the solenoid is commanded
on.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The EVAP Purge Solenoid Valve Control Circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for
action taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 Tests the feedback voltage from the ECM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–134
Page 6C1-2–134
DTC P0443, P0458 and P0459 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature or
operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0443, P0458 or P0459 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the EVAP solenoid valve wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the EVAP solenoid valve ignition
voltage circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
EVAP solenoid valve control circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 2.6 – 4.6 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the high resistance, open circuit or short to ground fault
condition at the EVAP solenoid valve ignition voltage circuit. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair
procedures
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the control circuit of the EVAP solenoid valve for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault
condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the EVAP solenoid valve. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the EVAP purge solenoid valve control circuit DTCs fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–135
Page 6C1-2–135
5.23 DTC P0627 to P0629 – Fuel Pump Relay
Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0627 – Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0628 – Fuel Pump Relay Voltage Low
• DTC P0629 – Fuel Pump Relay Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ground circuit of the fuel pump relay coil is directly connected to ground. When the ignition switch is turned on and all
the conditions required to enable fuel pump operation are met, the ECM applies battery voltage to the fuel pump relay
control circuit to operate the fuel pump. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel System for further information.
The ECM monitors the control circuit of the fuel pump relay for conditions that are incorrect for the commanded state. A
fuel pump relay control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in this circuit.
NOTE
The immediate engine immobilisation system, if
activated, disables the operation of the fuel pump
relay. Refer to Section 12K Telematics for further
information.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–137
Page 6C1-2–137
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel System for details of the fuel pump operation.
• Refer to Section 12K Telematics for details of the Immediate Engine Immobilisation System.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• the ignition is switched on, and
• the ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects a condition that are incorrect for the fuel pump relay commanded state.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The fuel pump relay control circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
7 A fault condition in the vehicle Telematics may trigger a fault condition in the fuel pump relay control circuit.
DTC P0627 to P0629 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Turn the ignition switch to the Start position or operate the
vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0627, P0628 and P0629 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Remove the fuel pump relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses,
Relays and Wiring Harnesses.
2 Connect a test lamp between the ground circuit of the fuel pump
relay and a 12 V.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Connect a test lamp between the control circuit and ground
circuit of the fuel pump relay.
2 Using Tech 2, command the fuel pump relay on.
Does the test lamp switch from off to on as Tech 2 commands the fuel
pump relay from off to on? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–138
Page 6C1-2–138
Step Action Yes No
5 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the ground
circuit of the fuel pump relay. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams
for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the control circuit of the fuel pump relay for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or a short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
NOTE
If the vehicle is equipped with an Immediate Engine
Immobilisation System, test this system for a fault condition
that may trigger a fuel pump relay control circuit DTC,
before proceeding to the next step. Refer to Section 12K
Telematics for further information.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the fuel pump relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses, Relays and
Wiring Harnesses.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does the fuel pump relay control circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–139
Page 6C1-2–139
5.24 DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262,
P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270,
P0271, P0273, P0274, P0276 and P0277 –
Fuel Injector Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0201 – Injector 1 Control Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0202 – Injector 2 Control Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0203 – Injector 3 Control Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0204 – Injector 4 Control Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0205 – Injector 5 Control Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0206 – Injector 6 Control Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0261 – Injector 1 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0262 – Injector 1 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0264 – Injector 2 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0265 – Injector 2 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0267 – Injector 3 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0268 – Injector 3 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0270 – Injector 4 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0271 – Injector 4 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0273 – Injector 5 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0274 – Injector 5 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0276 – Injector 6 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0277 – Injector 6 Control Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies ignition positive voltage to the fuel injector ignition circuit. The ECM applies a pulse width
modulated (PWM) ground to the injector control circuit through a device within the ECM called a driver to control each
fuel injector on time.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up when the voltage is approximately 3.3 V. The ECM monitors the Driver
feedback circuit to determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
A fuel injector control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in a fuel injector control circuit.
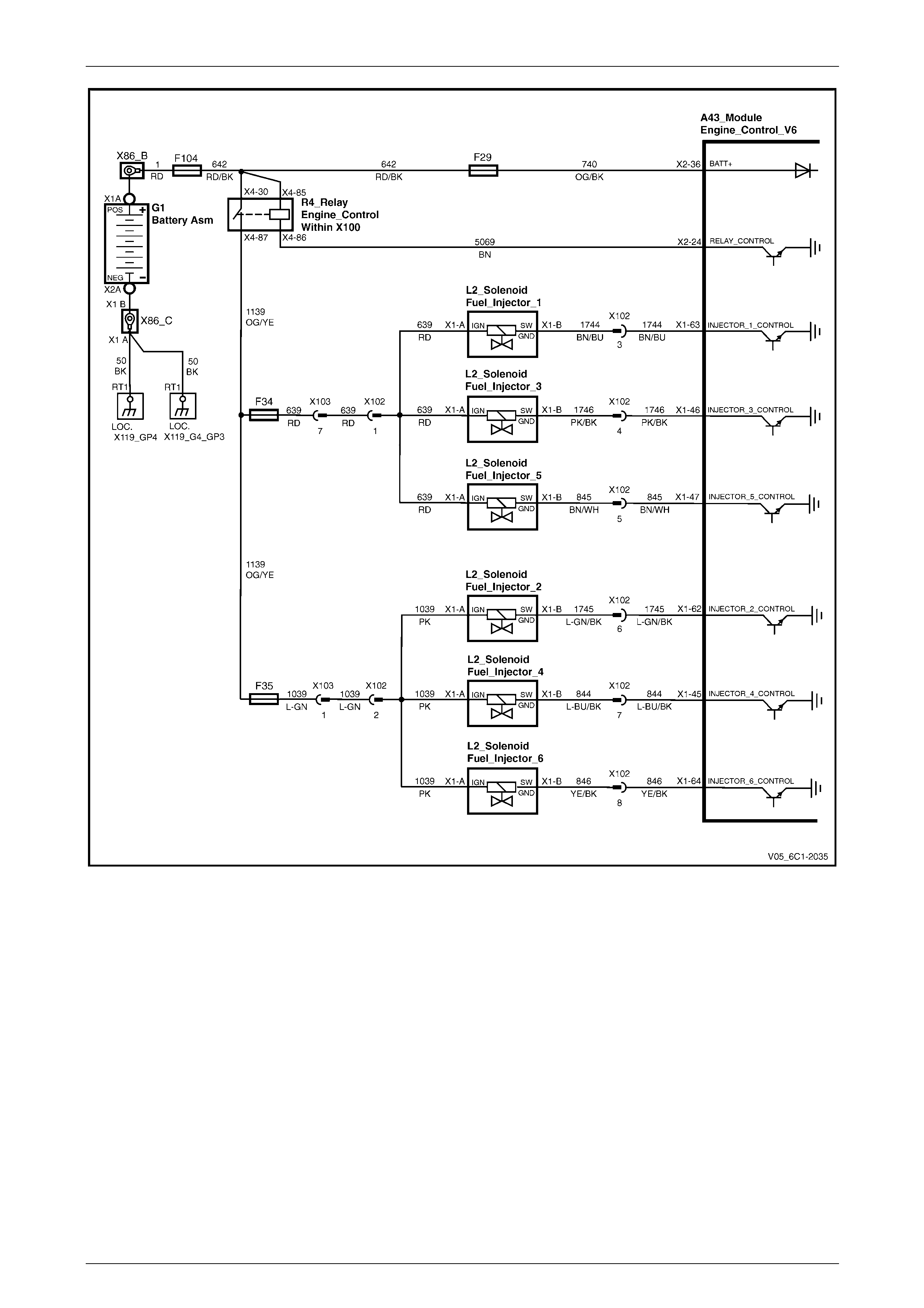
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–140
Page 6C1-2–140
Figure 6C1-2 – 31
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the fuel injector operation.
• Using Tech 2, observe the appropriate fuel injector status parameter while wriggle testing related harness and
connectors. Tech 2 reading will change from Ok to Fault if there is an intermittent fault condition in the harness or
connector being tested.
• Perform the fuel injector coil test to help isolate an intermittent condition.
Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–141
Page 6C1-2–141
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• the battery voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V, and
• engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0201,P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205 or P0206
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in a fuel injector circuit.
DTC P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270, P0273 and P0276
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the control circuit a fuel injector.
DTC P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271, P0274 and P0277
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the control circuit of a fuel injector.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The fuel injector control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Determines if there is a fault condition in the ignition voltage supply circuit. The fuel injectors for each bank of the
engine are fused separately. If all DTCs for a single bank are set, there may be a fault in one of the ignition supply
circuits.
5 Verifies the ECM is sending control voltage to the fuel injector.
6 Tests if the feed back voltage circuit within the ECM is providing the correct voltage.
DTC P0201 to P0206, P0261, P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271, P0273,
P0274, P0276 and P0277 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205, P0206, P0261,
P0262, P0264, P0265, P0267, P0268, P0270, P0271, P0273, P0274,
P0276 or P0277 set? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the fuel injector interconnect harness connector.
Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the ignition voltage circuit of the
appropriate fuel injector, ECM side of the interconnect
connector, and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–142
Page 6C1-2–142
Step Action Yes No
4 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
appropriate fuel injector control circuit, ECM side of the
interconnect connector, and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 2.6 – 4.6 mV? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the open circuit or short to ground fault condition in the ignition
voltage circuit of the appropriate fuel injector. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
6 Test the control circuit of the appropriate fuel injector, between the
interconnect connector and the ECM, for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
7 1 Remove the upper intake manifold. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
2 Test the control circuit and the ignition voltage circuit of the
appropriate fuel injector, between the interconnect connector
and the appropriate fuel injector connector, for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
8 Replace the appropriate fuel injector. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the fuel injector control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
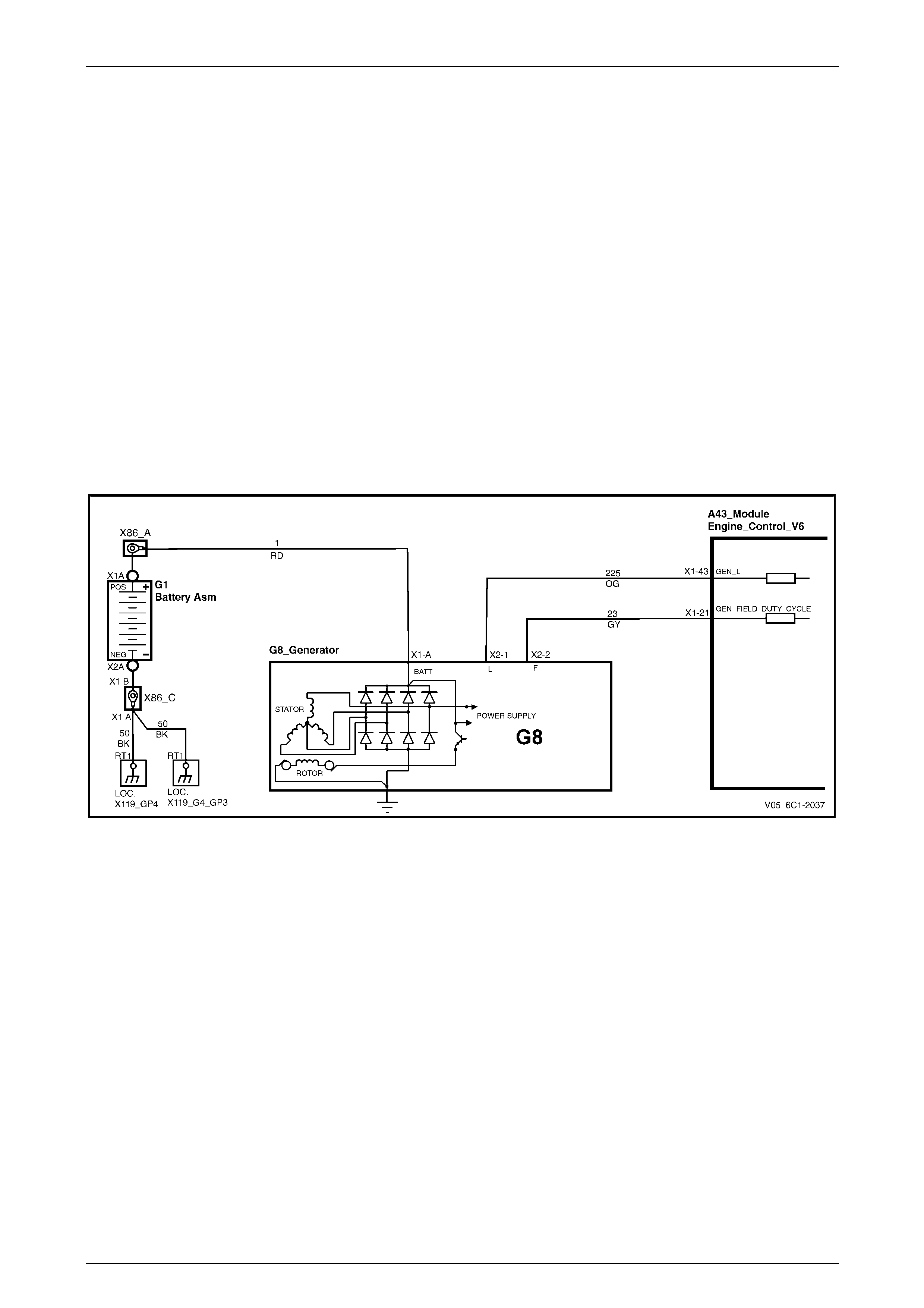
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–143
Page 6C1-2–143
5.25 DTC P0625 and P0626 – Generator F-
Terminal Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0625 – Alternator F Terminal Low Voltage
• DTC P0626 – Alternator F Terminal High Voltage
Circuit Description
The voltage regulator within the generator regulates the generator charge output by increasing or decreasing the
generator on time. The generator field (Gen F) duty cycle output signal represents the generator on time.
Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging System – V6 for details of the charging system operation.
The ECM monitors the Gen F terminal output signal to calculate Gen F duty cycle percentage. This enables the ECM to
provide engine idle compensation based on electrical loads and to detect a fault condition in the generator operation.
A Generator F-terminal circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the Gen F duty cycle is outside the specified range for a
predetermined set of parameters.
Figure 6C1-2 – 32
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging System – V6 for details of the charging system operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–144
Page 6C1-2–144
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0625
Runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• There is no generator, CKP sensor or CMP sensor DTC set.
• The engine speed is less than 3000 r.p.m.
• The generator is not commanded off.
DTC P0626
Runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• There is no generator, CKP sensor or CMP sensor DTC set.
• The ignition is switched on with the engine not running
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0625
The ECM detects the Gen F Terminal Signal parameter is less than 5 percent for 15 seconds.
DTC P0626
The ECM detects the Gen F Terminal Signal parameter is greater than 5 percent for 15 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The Generator F-terminal circuit are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type
C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
DTC P0625 and P0626 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0625 or P0626 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Test the charging system for any fault condition that may cause
incorrect generator operation. Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging
System – V6 – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4 Test the Gen F signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit, short
to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the Generator F-terminal circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
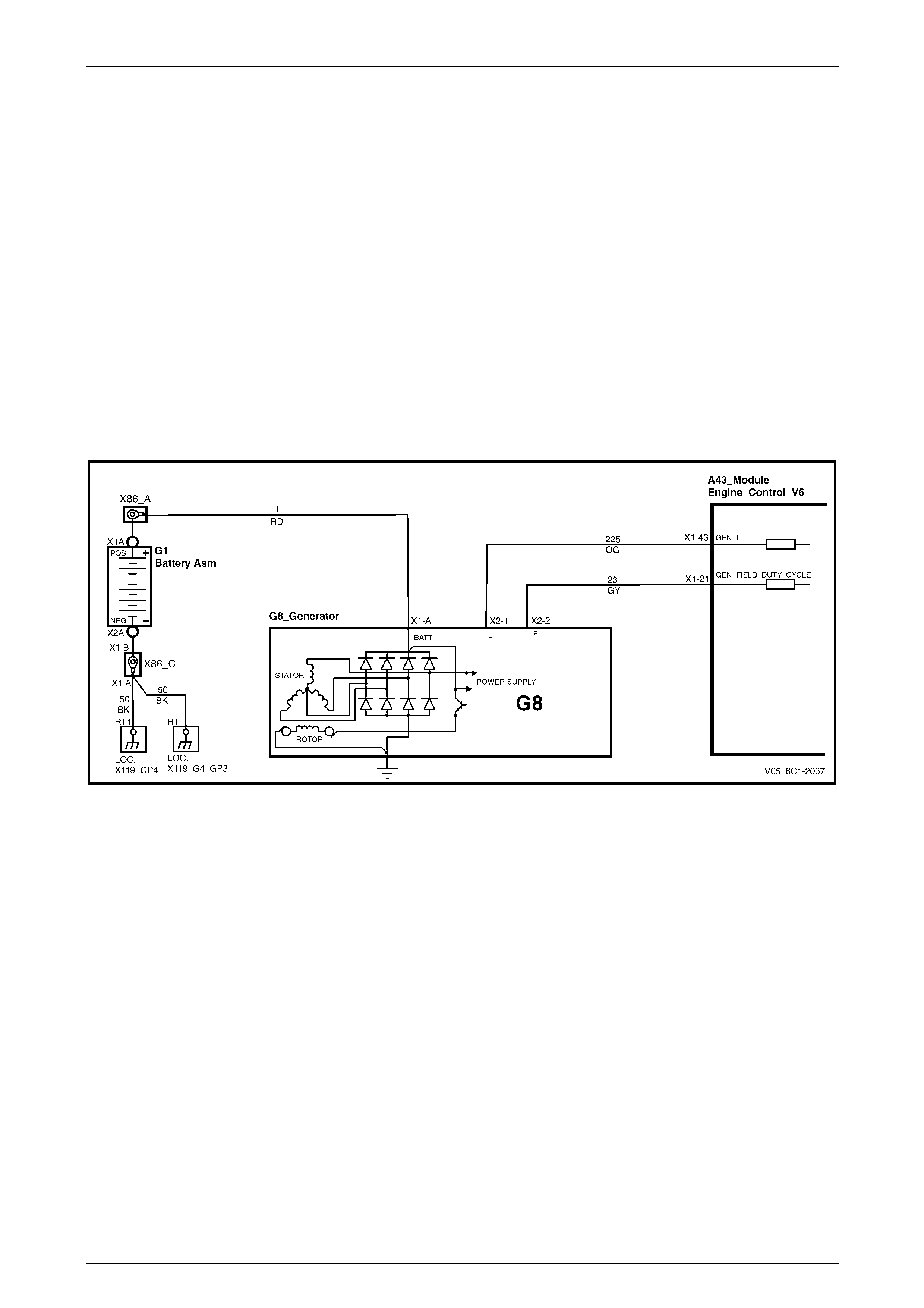
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–145
Page 6C1-2–145
5.26 DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 –
Generator L Terminal Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P1668 – Generator L Terminal Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P2500 – Generator L Terminal Low Voltage
• DTC P2501 – Generator L Terminal High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) applies a signal voltage to the Generator L (GEN L) terminal circuit to control the load
of the generator on the engine. Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging System – V6 for details of the charging system
operation.
A GEN L terminal circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the Gen L circuit voltage is outside the specified range for a
predetermined set of parameters.
Figure 6C1-2 – 33
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging System – V6 for details of the charging system operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–146
Page 6C1-2–146
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P1668
Runs continuously when one of the following conditions are met:
• Ignition on Test – The ignition is switched on with the engine not running for 5 seconds.
• Engine Run Test – The engine is running at speed less than 3,000 r.p.m.
DTC P2500
Runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• There is no generator, CKP sensor or CMP sensor DTC set.
• The engine is running.
• The generator is not commanded off.
DTC P2501
Runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• There is no generator, CKP sensor or CMP sensor DTC set.
• The ignition is switched on with the engine not running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P1668
• Ignition on Test – the ECM detects a high signal voltage on the Gen L for 5 seconds.
• Engine Run Test – the ECM detects a low signal voltage on the Gen L for 5 seconds.
DTC P2500
The ECM detects a low signal voltage on the Gen L for 15 seconds.
DTC P2501
The ECM detects a high signal voltage on the Gen L for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The Generator L-terminal circuit are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type
C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–147
Page 6C1-2–147
DTC P1668, P2500 and P2501 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P1668, P2500 or P2501 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Test the charging system for any fault condition that may cause
incorrect generator operation. Refer to Section 6D1-1 Charging
System – V6 – V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
4 Test the Gen L signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit, short
to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the Generator L terminal circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–148
Page 6C1-2–148
5.27 DTC P0112 and P0113 – Intake Air
Temperature Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0112 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0113 – Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The ECM applies a reference 5 V to the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor signal circuit and ground through the low
reference circuit. The IAT sensor is a variable resistor that measures the engine intake air temperature.
• Increased temperature in the intake air decreases the resistance value of the IAT sensor. This increases the IAT
sensor pull-down rate to ground. Therefore, the higher the intake air temperature, the lower the signal voltage
output of the IAT sensor.
• Decreased temperature in the intake air increases the resistance value of the IAT sensor. This reduces the IAT
sensor pull-down rate to ground. Therefore, the lower the intake air temperature, the higher the signal voltage
output of the IAT sensor.
An IAT sensor circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the intake air temperature is outside the specified range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 34
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–149
Page 6C1-2–149
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the IAT Sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Test the IAT sensor using the IAT Temperature vs. Resistance in Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations. If the engine has sat overnight, the IAT sensor should display within 3°C of the ECT sensor
values.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is running for longer than 3.0 minutes.
• The engine is idling for longer than 10.0 seconds
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0112
The ECM detects the intake air temperature is greater than 132°C for longer than 3.0 seconds.
DTC P0113
The ECM detects the intake air temperature is less than - 38°C for longer than 3.0 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The IAT sensor DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type B DTC
sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Tests the signal circuit of the IAT sensor.
4 Measures the integrity of the IAT sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to
power down completely prior to the test procedure.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–150
Page 6C1-2–150
DTC P0112 and P0113 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0112 or P0113 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the IAT sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the IAT
sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
IAT sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Test the IAT sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Test the IAT sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
NOTE
The IAT sensor shares the low reference circuit with other
sensors. A fault condition in the low reference circuit may
trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit. Refer to
2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts to aid diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the IAT sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the IAT sensor DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–151
Page 6C1-2–151
5.28 DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301,
P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309,
P2310, P2312, P2313, P2315 and P2316 –
Ignition Coil Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0351 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0352 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0353 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0354 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0355 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0356 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P2300 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2301 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P2303 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2304 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P2306 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2307 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P2309 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2310 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P2312 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2313 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P2315 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2316 – Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the ignition voltage circuit of the ignition coil and the ignition coil dual
line ground circuits are directly connected to ground.
The ECM applies control voltage to the control circuit of the ignition coil during the calculated dwell period that allows
current flow to the ignition coil primary winding to generate a magnetic flux field. At the appropriate firing point, the ECM
interrupts the control voltage applied to the ignition coil.
Interruption of voltage applied to the control circuit of the ignition coil primary winding induces the transfer of electrical
energy from the ignition coil primary winding to the ignition coil secondary winding, which triggers the ignition coil to
produce a spark at the spark plug.
An ignition coil control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the control circuit of an ignition coil.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–153
Page 6C1-2–153
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ignition coil operation.
• A short to voltage fault condition damages the ignition coil. Do not replace the ignition until this fault condition is
rectified.
• The ignition coils for each bank of the engine are fused separately. If all DTCs for a single bank are set, there may
be a fault in one of the ignition supply circuits.
• The ignition coils for each bank of the engine have a separate ground connections. If all DTCs for a single bank are
set, there may be a fault in one of the ground circuits.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is running.
• The engine speed is 480 – 5,000 r.p.m.
• The battery voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354, P0355 or P0356
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in the ignition coil control circuit.
DTC P2300, P2303, P2306, P2309, P2312 or P2315
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the ignition coil control circuit.
DTC P2301, P2304, P2307, P2310, P2313 and P2316
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the ignition coil control circuit.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The ignition coil control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Determines if there is a fault condition in the ignition voltage supply circuit.
5 Determines if there is a fault condition in the ground circuits of the ignition coil.
6 Tests if the ECM is commanding the ignition coil on and off.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–154
Page 6C1-2–154
DTC P0351 to P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303, P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310, P2312,
P2313, P2315 and P2316 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354, P0355, P0356, P2300,
P2301, P2303, P2304, P2306, P2037, P2309, P2310, P2312, P2313,
P2315 or P2316 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the wiring connector of the appropriate ignition coil.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the ignition voltage circuit of the
appropriate ignition coil connector and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 6
4 Connect a test lamp between a 12 V and each of the ground circuits of
the ignition coil connector.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 1 Start the engine.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the frequency at the control
circuit of the ignition coil.
Does the multimeter display 3 – 20 Hz? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition at the ignition
voltage circuit of the ignition coil. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
7 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition at the ignition
coil ground circuits. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
8 Test the appropriate ignition coil control circuit for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–155
Page 6C1-2–155
Step Action Yes No
9
A short to voltage fault condition damages the ignition
coil. Do not replace the ignition until this fault
condition is rectified.
Replace the faulty ignition coil. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the ignition coil control circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–156
Page 6C1-2–156
5.29 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632, P1677,
P1678 and P1679 – Immobiliser Signal
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0513 – Wrong Transponder Key
• DTC P0633 – Immobiliser Function Not Programmed
• DTC P1629 – Immobiliser Fuel Enable Signal Not Received
• DTC P1632 – Immobiliser Fuel Disable Signal Received
• DTC P1677 – Immobiliser Function Not Enabled
• DTC P1678 – Engine Control Module Identification Failed
• DTC P1679 – Immobiliser Environment Identification Failed
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM), the powertrain interface module (PIM) and the body control module (BCM) are integral
part of the vehicle theft deterrent system. The theft deterrent system authenticates the security code programmed into
each of these modules to prevent unauthorised vehicle operation. This authentication process includes the following
steps:
1 At predetermined conditions, the BCM sends a security code to the PIM.
2 When the ignition is switched on, the PIM receives and compares this security code from the BCM against the
security code programmed into the PIM.
3 Once the PIM receives the correct security code from the BCM, it sends a security code to the ECM.
4 The ECM receives and compares this security code from the PIM against the security code programmed into the
ECM.
5 The authentication process is complete once the ECM receives the correct security code from the PIM within the
specified time frame.
6 The ECM allows normal vehicle operation.
NOTE
If any of these authentication processes fail, the
vehicle will not start and DTCs will set. For further
information on the theft deterrent system, refer to
Section 12J Body Control Module.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module for the following information:
• BCM link to PIM, and
• Theft Deterrent System.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–157
Page 6C1-2–157
Conditions for Running the DTC
Conditions for running the DTC are:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
P0513
The ECM receives an incorrect response from the PIM during the theft deterrent security authentication process.
P0633
An attempt is made to start the engine before the immobiliser function has been programmed into a new PIM.
P1629
The ECM has not received a fuel enable password from the body control module (BCM).
P1632
The ECM receives an incorrect response from the PIM during the theft deterrent security authentication process.
P1677
An attempt is made to start the vehicle after the ECM was reset.
P1678
The ECM does not receive a valid response from the PIM when an attempt is made to start the engine.
P1679
The ECM receives a message from the PIM stating that it can't authenticate to the BCM.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B
DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–158
Page 6C1-2–158
DTC P0513, P1629, P1632, P0633, P1677, P1678, P1679 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0513, P1629, P1632, P0633, P1677, P1678 or P1679 fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Using Tech 2, perform the BCM Link to ECM / PIM procedure. Refer
to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6.
Has the linking procedure been performed correctly? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4 Test the BCM system. Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1 Test all ground circuits of the PIM for a high resistance or an
open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
2 Test the PIM ignition supply voltage circuit for a high resistance,
open circuit or short to ground fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Replace the PIM. Refer to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module –
V6.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Do any of the immobiliser DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–159
Page 6C1-2–159
5.30 DTC P1648 – Wrong Security Code
Entered
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P1648 – Wrong Security Code Entered.
Circuit Description
Tech 2 is used to program the engine control module (ECM). Before any programming, a security code must be entered
into Tech 2. The ECM will check if the code entered is correct before continuing. If the security code is incorrect, DTC
P1648 sets.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for details on resetting the ECM.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Conditions for running the DTC are:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
An incorrect security code is entered into Tech 2 when attempting to program the ECM.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
When the DTC sets, there is no icon displayed on the instrument cluster multi-function display.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The immobiliser security code is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type B
DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 This step tests the ECM ground circuits and supply voltage.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–160
Page 6C1-2–160
DTC P1648 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
NOTE
Do not attempt to perform any Tech 2 function that
requires the ECM security code to be entered.
Does DTC P1648 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3 Using Tech 2, attempt a programming function that requires the ECM
security code to be entered. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations for details on resetting the
ECM.
Has the programming function been successfully performed? System OK Go to Step 4
4 1 Test all ground circuits of the ECM for a high resistance or an
open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
2 Test the ECM ignition supply voltage circuit for a high resistance,
open circuit or short to ground fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations for details on replacing the ECM.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 6 —
6 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
Does DTC P1648 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
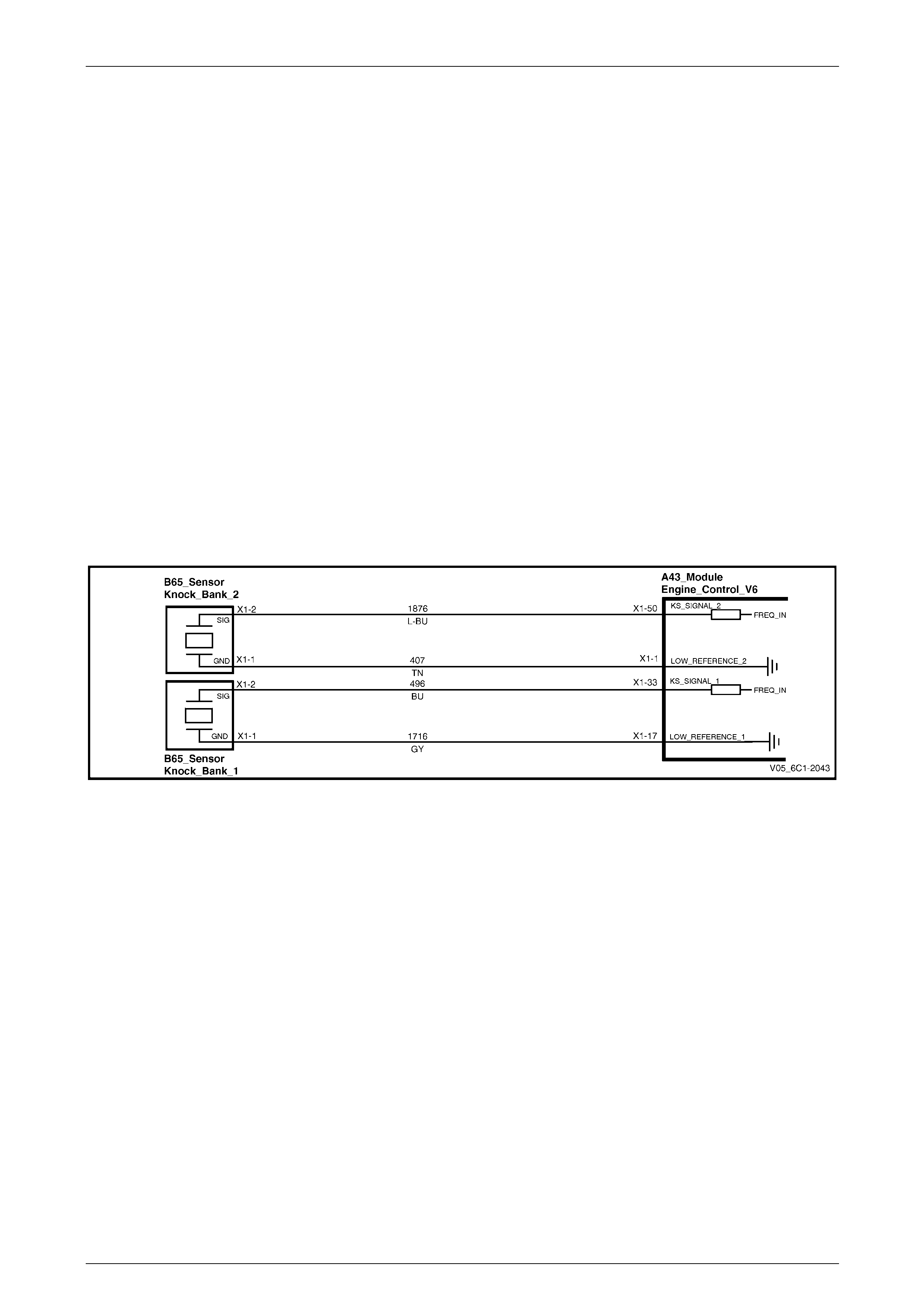
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–161
Page 6C1-2–161
5.31 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 –
Knock Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0327 – Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 1)
• DTC P0328 – Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 1)
• DTC P0332 – Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 2)
• DTC P0333 – Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The ECM supplies the ground to the knock sensor (KS) low reference circuit. The KS produces a signal voltage, which is
proportional to the level of the engine vibration or spark knock.
When the ECM detects an excessive spark knock, it retards the ignition timing until the spark knock stops.
To differentiate between a normal engine vibration and the vibration created by a spark knock, the ECM samples the KS
signal under different engine speeds and load condition. The ECM uses this samples to determine maximum and
minimum KS signal voltage produced when the engine is running under normal conditions.
A knock sensor circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the KS signal voltage is outside the normal range.
Figure 6C1-2 – 36
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the knock sensor (KS)
system operation.
• Preconditions for running knock sensor circuit DTCs requires that DTC P0324 has ran and passed. Therefore, the
diagnostic table for the knock sensor circuit DTCs is developed with the assumption the ECM internal KS circuitry is
functioning correctly.
• Excessive engine mechanical noise or engine knocking condition may trigger knock sensor circuit DTCs.
• The knock sensor must be tightened correctly.
Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• The mounting between the knock sensor and engine must be free of burrs, casting flash and foreign material.
• The knock sensor head must be clear from hoses, brackets and engine wiring.
• If the knock sensor lead is damaged in any way, the sensor must be replaced.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–162
Page 6C1-2–162
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0327 and P0332
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0324, P0335, P0342, P0343, P0347, P0348, P0367, P0368, P0392, and P0393 ran and passed.
• The ECM controls the ignition spark.
• Engine speed is greater than 2000 r.p.m. and steady.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60ºC.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
DTC P0328 or P0333
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM controls the ignition spark.
• Engine speed is greater than 2,000 r.p.m. and steady.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60°C.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0327 and P0332
The ECM detects the KS signal voltage is less than the minimum KS signal normal range for at least 10 seconds.
DTC P0328 and P0333
The ECM detects the KS signal voltage is greater than the maximum KS signal normal range.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The knock sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type B
DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 Identifies engine mechanical fault conditions that may trigger knock sensor circuit DTCs.
4 Identifies KS fault conditions that may trigger knock sensor circuit DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–163
Page 6C1-2–163
DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 or P0333 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Check the engine for excessive mechanical engine noise or engine
knocking fault condition. Refer to Section 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the appropriate KS for the following fault condition. Refer to
Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• incorrect KS attaching bolt torque value,
• burrs, casting flash or foreign material between the knock sensor
and engine,
• hoses, brackets or engine wiring touching the KS, and
• damaged KS wiring harness.
• sensor wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault
Conditions.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 Test the appropriate KS signal circuit and low reference circuit for a
high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage or
shorted together fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams
for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Replace the faulty KS. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the knock sensor circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–164
Page 6C1-2–164
5.32 DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor Module
Performance
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor Module Performance
Circuit Description
The ECM supplies the ground to the knock sensor (KS) low reference circuit. The KS produces a signal voltage, which is
proportional to the level of the engine vibration or spark knock.
When the ECM detects an excessive spark knock, it retards the ignition timing until the spark knock stops.
The KS circuitry within the ECM receives, amplifies, filters and evaluates the KS signal voltage. The ECM performs the
following tests to determine if the ECM internal KS circuitry is functioning correctly.
Test One
The ECM performs the following:
1 Turns off the knock sensor signal circuits.
2 Applies different test signals to the ECM internal KS circuitry.
3 Verifies each test signal output response is within range.
4 If the ECM detects any of the tested signals are not within the normal range, DTC P0324 sets.
Test Two
The ECM performs the following:
1 Turns off the knock sensor signal circuits.
2 Tests for any output response when no test signals are applied.
3 If the ECM detects an output response, DTC P0324 sets.
Test Three
1 Turns off the knock sensor signal circuits.
2 Generates an internal test pulse then monitors the return signal.
3 If the return test pulse is less than a calibrated threshold, DTC P0324 sets.
DTC P0324 sets if the ECM detects an incorrect response to the ECM internal KS circuitry tests.
Figure 6C1-2 – 37
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–165
Page 6C1-2–165
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the knock sensor (KS)
system operation.
• The ECM turns off the KS signal circuits when performing the ECM internal KS circuitry tests. DTC P0324 sets if
there is a fault condition in the internal ECM KS circuitry. Therefore, the KS and the KS signal circuits are not tested
in DTC P0324 Diagnostic Table.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Condition One
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM is controlling the ignition spark.
• The engine speed is less than 2,300 r.p.m. and steady.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Condition Two
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM is controlling the ignition spark.
• The engine speed is 1,000 – 4,000 r.p.m.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60°C.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Condition Three
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM is controlling the ignition spark.
• The engine speed is less than 2,300 r.p.m. and steady.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 40°C.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects an incorrect response to an internal ECM KS circuitry test.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P0324 – Knock Sensor (KS) Module Performance is a Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for
action taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
3 A crankshaft sensor DTC may trigger DTC P0324.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–166
Page 6C1-2–166
DTC P0324 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0324 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs relating to the CKP Sensor Circuit also set? Refer to 5.9 DTC
P0335 to P0338 –
Crankshaft Position
Sensor Circuit Go to Step 4
4 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 5 —
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running DTC
P0324.
Does DTC P0324 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
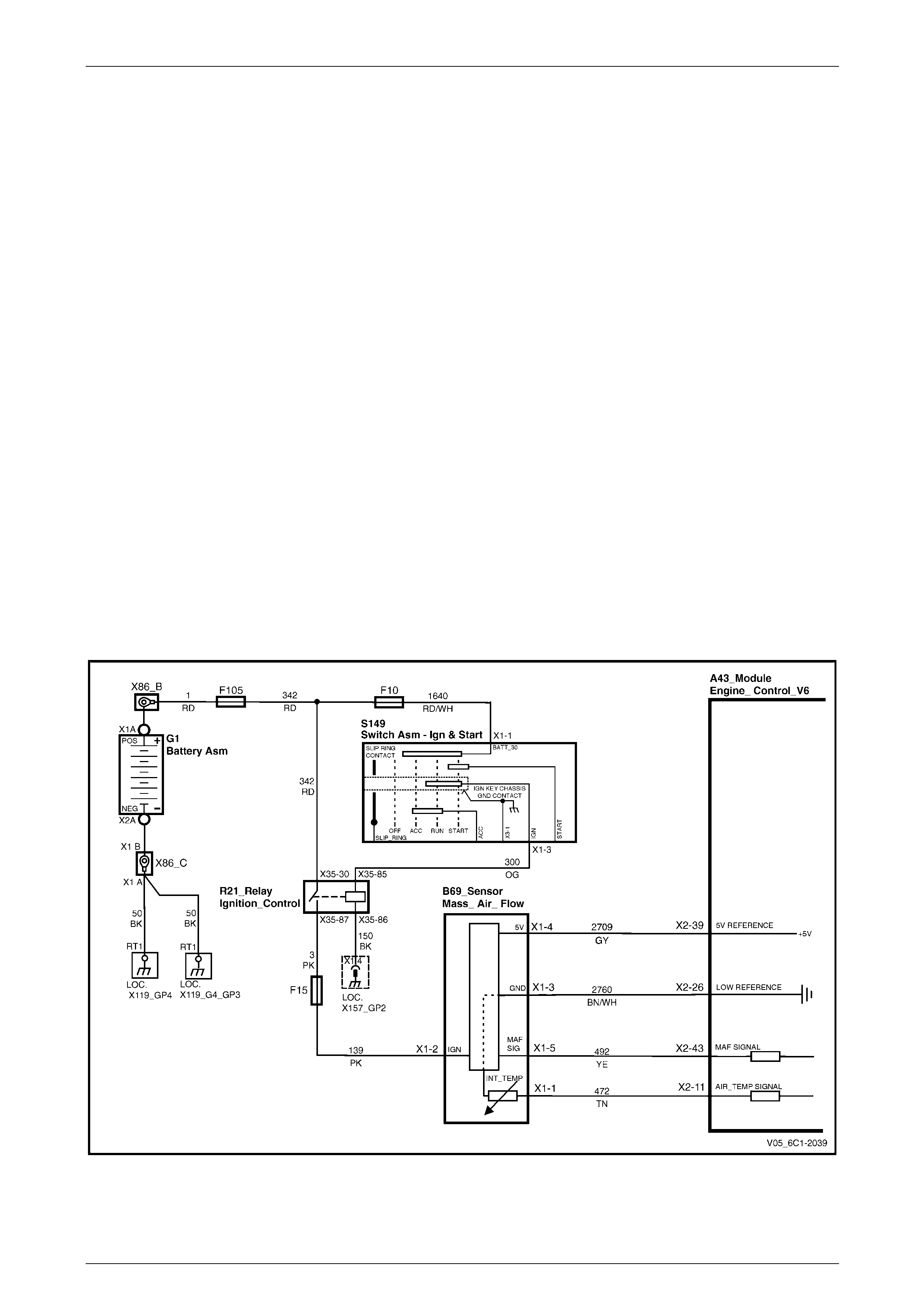
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–167
Page 6C1-2–167
5.33 DTC P0101 to P0103 – MAF Sensor
Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0101 – Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Range / Performance
• DTC P0102 – Mass Air Flow Sensor Voltage Low
• DTC P0103 – Mass Air Flow Sensor Voltage High
Circuit Description
The ignition control relay applies ignition positive voltage to the mass airflow (MAF) sensor. The ECM applies 5 V
reference voltage and ground through the low reference circuit.
A heater resistor on the MAF sensor heats a micro-mechanical sensor diaphragm at a constant temperature. Two
temperature dependent resistors positioned at each side of the heater resistor measure the intake air temperature:
• The first is located at a position before the intake air passes through the heater resistor. This temperature
dependent resistor measures the temperature of the intake air before the air is heated.
• The second is located at a position after the intake air has passed through the heater resistor. This sensor
measures the temperature of the intake air after the air is heated.
The evaluation circuit on the MAF sensor converts the difference in the resistance value of these two temperature
dependent resistors into an analog signal voltage. The ECM monitors this signal voltage through the MAF sensor signal
to calculate the engine intake air mass.
A MAF sensor circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the actual MAF sensor signal is not within the predetermined range of
the calculated MAF sensor value.
Figure 6C1-2 – 38
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–168
Page 6C1-2–168
Additional Information
• The MAF sensor circuit DTCs is a Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a
Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the MAF sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Inspect the MAF sensor for an incorrectly routed harness or if the harness is too close to the following:
• ignition coil,
• solenoids,
• relays, and
• motors.
• A low minimum air rate may cause this DTC to set during deceleration. Inspect for the following conditions:
• a plugged or a collapsed intake air duct, or a dirty air filter element,
• objects that block the MAF sensor air inlet screen, and
• sticking or dirty throttle plate or throttle bore.
• Any un-metered air that enters the engine may cause this DTC to set. Inspect for vacuum leaks in the following:
• intake manifold,
• throttle body,
• barometric pressure (BARO) sensor seal,
• EVAP canister purge valve seal,
• brake booster system,
• air induction system, and
• crankcase ventilation system.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0101
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 and P0223 ran and passed.
• The engine is running.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The MAF sensor signal is -11.6 to +295 grams per second.
• The ECM detects greater than 150 crankshaft revolutions.
DTC P0102
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 and P0223 ran and passed.
• The engine is running.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
DTC P0103
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 and P0223 ran and passed.
• The engine is running at speed greater than 320 r.p.m.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–169
Page 6C1-2–169
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0101
The ECM detects the MAF sensor signal is not within the predetermined range of the calculated MAF value for 2
seconds.
DTC P0102
The ECM detects the MAF sensor signal is less than -11.7 grams per second.
DTC P0103
The ECM detects the MAF sensor signal is greater than 294 grams per second.
DTC P0101 to P0103 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0101, P0102 or P0103 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Inspect for the following fault conditions:
• engine vacuum leak,
• air leak in the intake air duct between the MAF sensor and the
throttle body,
• plugged or collapsed intake air duct,
• objects that block the MAF sensor inlet screen,
• restricted air filter element,
• restricted throttle plate or carbon build-up around the throttle
plate,
• unseated engine oil dipstick,
• loose or missing engine oil cap, and
• over filled crankcase.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 4
4 1 Disconnect the MAF sensor wiring connector.
2 Connect a test lamp between the MAF sensor ignition voltage
circuit and the ECM housing.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 11
5 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
MAF sensor 5 V reference circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the MAF sensor 5 V
reference circuit and signal circuit.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using Tech 2, observe the MAF sensor voltage parameter.
Does Tech 2 display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 9
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–170
Page 6C1-2–170
Step Action Yes No
7 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
MAF sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly after completing the test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 10
8 Test the MAF sensor 5 V reference circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
NOTE
The MAF sensor shares the 5 V reference circuit with other
sensors. A fault condition in the 5 V reference circuit will
trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 13
9 Test the MAF sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 13
10 Test the MAF sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance or an
open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 13
11 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the MAF
sensor circuit ignition voltage. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams
for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 —
12 Replace the MAF sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 —
13 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 14 —
14 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the MAF Sensor Circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 15
15 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–171
Page 6C1-2–171
5.34 DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038,
P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 – O2
Sensor Heater Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0030 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0031 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0032 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0036 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0037 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0038 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0050 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0051 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0052 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0056 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0057 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0058 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the O2 sensor. The ECM applies
a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the heater control circuit of the O2 sensor through a device within the ECM
called a driver, to control the O2 sensor rate of heating.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up when the voltage is approximately 3.3 V. The ECM monitors the Driver
feedback circuit to determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
An O2 sensor heater control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short
to voltage fault condition in the O2 sensor heater control circuit.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–173
Page 6C1-2–173
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the O2 sensor system
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• A faulty O2 sensor heater element may cause an open heater circuit condition. This fault may be intermittent or only
show up after the sensor has operated for a period.
• Inspect the O2 sensor wiring harness for contact with the exhaust system.
• The front and the rear O2 sensors have a separate fuse connection. If both front or both the rear DTCs are set, the
appropriate O2 sensor ignition voltage circuit may be open.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• Engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0030, P0036, P0050 or P0056
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in the O2 sensor heater control circuit when the O2 sensor heater is
commanded off.
DTC P0031, P0037, P0051 or P0057
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the O2 sensor heater control circuit when the O2 sensor heater is
commanded off.
DTC P0032, P0038, P0052 or P0058
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the O2 sensor heater control circuit for five seconds when the O2
sensor heater is commanded on.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The O2 sensor heater control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 The ECM monitors the Driver feedback circuit to determine if the heater control circuit is open, shorted to ground or
shorted to a positive voltage. If the voltage is outside the specified range, there is a fault condition with the heater
control circuit.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–174
Page 6C1-2–174
DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038, P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to 3.4
Diagnostic System
Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to run at idle speed for at least 30 seconds.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037, P0038, P0050,
P0051, P0052, P0056, P0057 or P0058 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the appropriate O2 sensor wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the O2 sensor heater ignition
voltage circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the O2
sensor heater control circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display:
• Alloytec190 O2 sensor 1: 4.6 – 5.2 V?
• Alloytec190 O2 sensor 2: 2.8 – 4.2 V?
• Alloytec O2 sensor 1: 2.8 – 4.2 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 NOTE
The O2 sensor ignition voltage circuit is shared with other
sensors. Ensure that all circuits and components that
share this ignition voltage circuit are tested for a short to
ground.
Repair the high resistance open circuit or short to ground fault
condition in the O2 sensor heater ignition voltage circuit. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair
procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the O2 sensor heater control circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the appropriate O2 sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the O2 sensor heater control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–175
Page 6C1-2–175
5.35 DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135, P0137,
P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor Reference Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0130 – O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0131 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0132 – O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0135 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0137 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0138 – O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0140 – O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0141 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0150 – O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0151 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0152 – O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0155 –O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0157 – O2 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0158 – O2 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0160 – O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0161 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Range / Performance (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2243 – O2 Sensor Voltage Signal Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2247 – O2 Sensor Voltage Signal Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2270 – O2 Sensor Lean / Rich Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2271 – O2 Sensor Rich / Lean Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2272 – O2 Sensor Lean / Rich Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2273 – O2 Sensor Rich / Lean Switch Signal Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2297 – O2 Sensor Range / Performance During Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2298 – O2 Sensor Range / Performance During Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (Bank 2, Sensor 1)

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–176
Page 6C1-2–176
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the O2 sensor. The ECM applies
a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the heater control circuit of the O2 sensor through a device within the ECM
called a driver, to control the O2 sensor rate of heating.
Alloytec Engine O2 Sensor 1 or Alloytec190 Engine O2 Sensor 2
The ECM applies a voltage of approximately 450 mV between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the
O2 sensor while the sensor temperature is less than the operating range.
Once the O2 sensor reaches operating temperature, the sensor varies this reference signal voltage, which constantly
fluctuates between the high voltage output and the low voltage output.
• The low voltage output is 0 – 450 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is lean.
• The high voltage output is 450 – 1,000 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is rich.
The ECM monitors, stores and evaluates the O2 sensor voltage fluctuation information to determine the level of oxygen
concentration in the exhaust.
Alloytec190 Engine O2 Sensor 1
The ECM maintains the voltage between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the O2 sensor 1 to about
450 mV by increasing or decreasing the oxygen content in the O2 sensor diffusion gap. To achieve this, the ECM
controls the current applied to the oxygen pumping cell in the O2 sensor
The pumping current required to maintain the O2 sensor 1 signal circuit voltage to about 450 mV is proportional to the
level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.
• If the air/fuel mixture in the exhaust is balanced (lambda = 1), the oxygen pumping cell current is zero.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is lean, the ECM applies a positive current to the oxygen
pumping cell to discharge oxygen from the diffusion gap.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is rich, the ECM applies a negative current to the oxygen
pumping cell to draw oxygen into the diffusion gap.
The ECM monitors and evaluates the oxygen pumping current to determine the level of oxygen concentration in the
exhaust.
An O2 sensor reference circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltage is outside the predetermined
range for a specified period.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–178
Page 6C1-2–178
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the O2 sensor system
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• The O2 sensor must be tightened correctly. A loose O2 sensor will trigger these DTCs.
• A fault condition in the fuel delivery system, air intake system or exhaust system may trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0130, P0131, P0132, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0150, P0151 or P0152
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The engine is running.
DTC P0135 and P0155
Condition 1
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051, P0052, P0101, P103, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0151,
P0152, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, P0338, P2237, P2240, P2243, P2247, P2251 and P2254 ran and
passed.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance test is enabled.
Condition 2
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051, P0052, P0101, P103, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0151,
P0152, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, P0338, P2237, P2240, P2243, P2247, P2251 and P2254 ran and
passed.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance test is enabled.
• The fuel injectors are not disabled.
• If the engine is operating and the ignition is turned off, the engine must be off for at least 5 minutes for this DTC to
run.
DTC P0137 and P0157
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0117, P0118, P0125 and P0128 ran and passed.
• The engine is operating for longer than two minutes.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250ºC – 800ºC.
• The engine coolant temperature is less than 40ºC at start-up and greater than 60ºC when the ignition was turned off
last ignition cycle.
• The fuel tank level is greater than 25 percent.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–179
Page 6C1-2–179
DTC P0138 and P0158
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is operating for longer than two minutes.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250ºC – 800ºC.
DTC P0140 and P0160
Run continuously once the following conditions are met for longer than 90 seconds:
• The engine is operating.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250ºC – 800ºC.
DTC P0141 and P0161
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0036, P0037, P0038, P0056, P0057, and P0058 ran and passed.
• DTCs P0137, P0138, P0140, P0157, P0158 or P0160 are not set.
• The engine is operating.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance is valid.
• The fuel system is not in decel fuel shut-off.
• The intake air temperature is greater than -7ºC.
• If the engine is operating and the ignition is turned off, the engine must be off for at least 5 minutes for this DTC to
run.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 360ºC – 500ºC.
DTC P2243 and P2247
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051 and P0052 ran and passed.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance is greater than 570 Ω.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature.
DTC P2270 and P2272
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0036, P0037, P0038, P0056, P0057, P0058, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0157, P0158, P0160, P0161,
P0342, P0343, P0366, P0367, P0368, P0443, P0451, P0452, P0453, P0458 and P0459 ran and passed.
• The engine is running.
• The O2 sensor 2 are at operating temperature for longer than 10 seconds.
• The long term fuel control is enabled.
• The MAF sensor is greater than 10 g/s.
DTC P2297 and P2298
Condition 1
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0130 and P0150 ran and passed.
• The O2 sensor 1 are at operating temperature.
• The desired O2 sensor 1 signal is less than 1.6 lambda.
• The internal ECM O2 sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 4.81 V.
• The fuel injectors are enabled.
Condition 2
Run continuously once a decel fuel cut-off has occurred 11 times with successful adjustments

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–180
Page 6C1-2–180
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0130 and P0150
The ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltage is out of range.
DTC P0131 and P0151
The ECM internal O2 sensor voltage is less than the specified threshold.
DTC P0132 and P0152
The ECM internal O2 sensor voltage is less than the specified threshold.
DTC P0135 and P0155
Condition 1
The ECM internal O2 sensor sensing element resistance is less than the specified threshold for longer than 15 seconds.
Condition 2
The ECM detects the calculated O2 sensor temperature is greater than a predetermined threshold.
DTC P0137 and P0157
The ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltage is less than 60 mV.
DTC P0138 and P0158
The ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltage is greater than 1050 mV.
DTC P0140 and P0160
The ECM detects one of the following conditions:
• The O2 sensor signal voltage is 400 – 500 mV for longer than 5 minutes, or
• the internal resistance of the O2 sensor is greater than 40,000 Ω when the calculated exhaust temperature is
greater than 600ºC.
DTC P0141 and P0161
The ECM detects the O2 sensor internal resistance is not within the expected range for longer than 6 seconds.
DTC P2243 and P2247
The ECM detects the internal O2 sensor signal voltage is not 0.2 – 4.7 V.
DTC P2270 and P2272
When the ECM detects the O2 sensor 2 is less than 650 mV for 100 seconds, the ECM enriches the fuel mixture up to 30
percent for 10 seconds. This DTC sets if the ECM detects the O2 sensor 2 is still less than 650 mV.
DTC P2271 and P2273
When the ECM detects the O2 sensor 2 is greater than 650 mV for 100 seconds, the ECM leans the fuel mixture up to -7
percent for 10 seconds. If this signal voltage is still greater than 650 mV, the ECM tests the O2 sensor at the next decel
fuel cut-off. This DTC sets if the ECM detects the O2 sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 200 mV after 4 seconds in
decel fuel cu-off mode.
DTC P2297 and P2298
The ECM detects the internal O2 sensor 1 signal voltage is greater than 3.7 V for longer than 10 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The O2 sensor reference circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–181
Page 6C1-2–181
DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135 to P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297, P2298 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to 3.4
Diagnostic System
Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds or
operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0130, P0131, P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140,
P0141, P0150, P0151, P0152 P0155 P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270, P2271, P2272, P2273, P2297 or P2298 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs relating to the heater circuit of the O2 sensor also set? Go to Step 4
4 1 Disconnect the appropriate O2 sensor wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the O2
sensor reference signal circuit and low reference circuit.
Does the multimeter display 350 – 550 mV? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 Test the reference signal circuit of the O2 sensor for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
6 Test the low reference circuit of the O2 sensor for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
7 Test or inspect for the following conditions that may cause the O2
sensor to detect an incorrect air/fuel mixture:
• lean or rich fuel injector fuel delivery,
• restricted air intake system,
• contaminated fuel,
• low fuel line pressure,
• exhaust leak near the O2 sensor, and
• leak in the crankcase or vacuum line.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
8 Replace the appropriate O2 sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any O2 sensor reference circuit DTC fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–182
Page 6C1-2–182
5.36 DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 –
O2 Sensor Pumping Current Control
Circuit, Alloytec190
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2237 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2238 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2239 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2240 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2241 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2242 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2626 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2629 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the O2 sensor. The ECM applies
a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the heater control circuit of the O2 sensor through a device within the ECM
called a Driver, to control the O2 sensor rate of heating.
The ECM maintains the voltage between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the O2 sensor 1 to about
450 mV by increasing or decreasing the oxygen content in the O2 sensor diffusion gap. To achieve this, the ECM
controls the current applied to the oxygen pumping cell in the O2 sensor
• If the air/fuel mixture in the exhaust is balanced (lambda = 1), the oxygen pumping cell current is zero.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is lean, the ECM applies a positive current to the oxygen
pumping cell to discharge oxygen from the diffusion gap.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is rich, the ECM applies a negative current to the oxygen
pumping cell to draw oxygen into the diffusion gap.
The pumping current required to maintain the O2 sensor 1 signal circuit voltage to about 450 mV is proportional to the
level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The ECM monitors and evaluates the oxygen pumping current to
determine the level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust.
An O2 sensor pumping current control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltage is outside the
predetermined range.
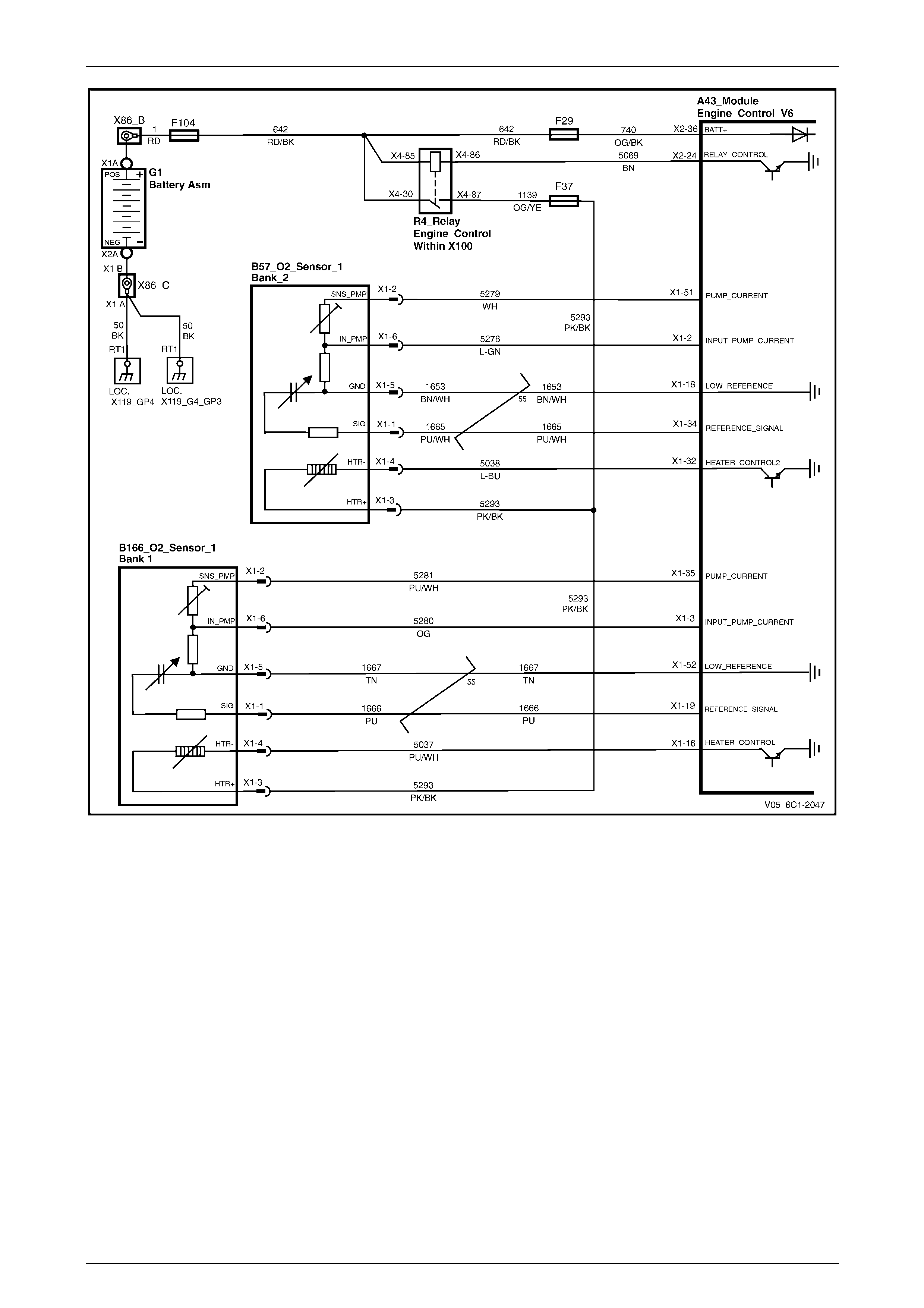
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–183
Page 6C1-2–183
Figure 6C1-2 – 41
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the O2 sensor system
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Inspect the O2 sensor wiring harness for contact with the exhaust system.
• The O2 sensor must be tightened correctly. A loose O2 sensor will trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–184
Page 6C1-2–184
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2237, P2238, P2239, P2240, P2241 and P2242
Condition 1
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0133, P0135, P0153, P0155, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336 and P0338 ran
and passed.
• The ECM is commanding the lambda outside the range of 0.97 – 1.03.
• The engine is operating in closed loop.
• The O2 sensor heater is at operating temperature.
Condition 2
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0133, P0135, P0153, P0155, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336 and P0338 ran
and passed.
• The ECM is commanding the lambda rich and then lean periodically with a change of greater than 2 percent.
• The ECM detects the internal O2 sensor signal voltage is 1.48 – 1.52 V.
• The O2 sensor is 0.97 – 1.03 lambda.
• The engine is operating in closed loop.
• The O2 sensor heater is at operating temperature.
Condition 3
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0133 and P0153 ran and passed.
• The O2 sensor heater is at operating temperature.
DTC P2626 and P2629
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336 and P0338 ran and pass.
• The engine is running.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The fuel system is in fuel shut-off mode.
• The calculated is exhaust temperature is less than 750ºC.
• The O2 sensor heater is at operating temperature.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–185
Page 6C1-2–185
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2237, P2238, P2239, P2240, P2241 or P2242
Condition 1
The ECM detects the following conditions:
• The internal O2 sensor signal voltage change is 1.52 – 1.48 V.
• The above condition exists and 200 grams of exhausts gas has passed.
Condition 2
The ECM stores the fuel trim control values. This DTC sets if the ECM detects a deviation of greater than 10 percent
within 1.5 seconds between the stored value and the current value of the fuel trim.
Condition 3
The ECM detects that 5 seconds after decel fuel shut-off, the internal O2 sensor signal voltage is less than 1.7 V.
DTC P2626 or P2629
The ECM internal O2 sensor voltage is greater than 4.81 V for longer than 4 seconds or 600 seconds if the fuel level is
less than 15 percent.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The O2 sensor pumping current control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action
taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 When performing this test, the O2 sensor should react immediately.
4 Connecting a jumper wire between the O2 sensor reference signal circuit and the low reference circuit causes the
ECM to apply signal voltage to the pumping current and input pumping current.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–186
Page 6C1-2–186
DTC P2237 to P2242, P2626 and P2629 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2237, P2238, P2239, P2240, P2241, P2242, P2626 or
P2629 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs relating to the reference circuit of the O2 sensor also set? Refer to
5.35 DTC P0130 to
P0132, P0135,
P0137, P0138,
P0140, P0141,
P0150 to P0152,
P0155, P0157,
P0158, P0160,
P0161, P2243,
P2247, P2270 to
P2273, P2297,
P2298 – O2 Sensor
Reference Circuit Go to Step 4
4 1 Disconnect the appropriate O2 sensor wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
input pump current circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display greater than 50 mV? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 5
5 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
pump current circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display greater than 50 mV? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 6
6 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the O2 sensor
reference signal circuit and the low reference circuit.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
input pump current circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the O2 sensor
reference signal circuit and the low reference circuit.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
pump current circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–187
Page 6C1-2–187
Step Action Yes No
8 Test the input pump current and the pump current circuit of the O2
sensor for a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground, short to
voltage or shorted together fault condition. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
9 Test or inspect for the following conditions that may cause the O2
sensor to detect an incorrect air/fuel mixture:
• lean or rich fuel injector fuel delivery,
• contaminated fuel,
• low fuel line pressure,
• exhaust leak near the O2 sensor, and
• leak in the crankcase or vacuum line.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 10
10 Replace the appropriate O2 sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
11 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
12 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the O2 sensor pumping current control circuit DTCs fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 13
13 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–188
Page 6C1-2–188
5.37 DTC P0053 and P0059 – O2 Sensor
Internal Heater Resistance Range /
Performance, Alloytec190
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0053 – O2 Sensor Heater Resistance Range / Performance (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0059 – O2 Sensor Heater Resistance Range / Performance (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the O2 sensor. The ECM applies
a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the heater control circuit of the O2 sensor through a device within the ECM
called a Driver, to control the O2 sensor rate of heating.
The ECM maintains the voltage between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the O2 sensor 1 to about
450 mV by increasing or decreasing the oxygen content in the O2 sensor diffusion gap. To achieve this, the ECM
controls the current applied to the oxygen pumping cell in the O2 sensor.
• If the air/fuel mixture in the exhaust is balanced (lambda = 1), the oxygen pumping cell current is zero.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is lean, the ECM applies a positive current to the oxygen
pumping cell to discharge oxygen from the diffusion gap.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is rich, the ECM applies a negative current to the oxygen
pumping cell to draw oxygen into the diffusion gap.
The pumping current required to maintain the O2 sensor 1 signal circuit voltage to about 450 mV is proportional to the
level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The ECM monitors and evaluates the oxygen pumping current to
determine the level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust.
An O2 sensor internal heater resistance performance DTC sets if the ECM detects an internal fault condition in the ECM
O2 sensor heater circuit.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–190
Page 6C1-2–190
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the O2 sensor system
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• The O2 sensor must be tightened correctly. A loose O2 sensor will trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0101, P0121, P012, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336,
P0338, P2237, P2243 and P2626 ran and passed.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is greater than 400ºC.
• The engine does not misfire.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The O2 sensor is commanded on.
• The engine is running at speed greater than 25 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
There is an internal fault condition in the ECM O2 sensor heater circuit.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The O2 sensor internal heater resistance performance DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes
for action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
DTC P0053 and P0059 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does P0053 or P0059 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs relating to other circuits of the O2 sensor also set? Refer to the
appropriate DTC
Table. Go to Step 4
4 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 5 —
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the O2 sensor internal heater resistance performance
DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–191
Page 6C1-2–191
5.38 DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235, P2251,
P2254 – O2 Sensor Signal Circuit
Shorted to Heater Control Circuit,
Alloytec 190
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2231 – O2 Sensor Signal Interference by Heater Circuit (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2232 – O2 Sensor Signal Short to Heater Circuit (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2234 – O2 Sensor Signal Interference by Heater Circuit (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2235 – O2 Sensor Signal Short to Heater Circuit (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P2251 – O2 Sensor Ground Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2254 – O2 Sensor Ground Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
Circuit Description
The Engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the O2 sensor. The ECM applies
a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the heater control circuit of the O2 sensor through a device within the ECM
called a Driver, to control the O2 sensor rate of heating.
O2 Sensor 1
The ECM maintains the voltage between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the O2 sensor 1 to about
450 mV by increasing or decreasing the oxygen content in the O2 sensor diffusion gap. To achieve this, the ECM
controls the current applied to the oxygen pumping cell in the O2 sensor
• If the air/fuel mixture in the exhaust is balanced (lambda = 1), the oxygen pumping cell current is zero.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is lean, the ECM applies a positive current to the oxygen
pumping cell to discharge oxygen from the diffusion gap.
• If the exhaust gas in the O2 sensor 1 diffusion gap is rich, the ECM applies a negative current to the oxygen
pumping cell to draw oxygen into the diffusion gap.
The pumping current required to maintain the O2 sensor 1 signal circuit voltage to about 450 mV is proportional to the
level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The ECM monitors and evaluates the oxygen pumping current to
determine the level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust.
An O2 sensor signal circuit shorted to heater control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltage is
increasing or decreasing at the same rate as the O2 sensor heater control circuit.
O2 Sensor 2
The ECM applies a voltage of approximately 450 mV between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the
O2 sensor while the sensor temperature is less than the operating range.
Once the O2 sensor reaches operating temperature, the sensor varies this reference signal voltage, which constantly
fluctuates between the high voltage output and the low voltage output.
The low voltage output is 0 – 450 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is lean.
The high voltage output is 450 – 1,000 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is rich.
The ECM monitors, stores and evaluates the O2 sensor voltage fluctuation information to determine the level of oxygen
concentration in the exhaust.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–193
Page 6C1-2–193
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the O2 sensor system
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• The O2 sensor must be tightened correctly. A loose O2 sensor will trigger this DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2231 or P2234
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051, P0052, P0053, P0059, P0130, P0135, P0150 or P0155 are not set.
• The O2 sensor heater control is enabled.
• The O2 sensor heater duty cycle is greater than 5 percent.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature for 10 seconds.
• The ECM does not detect an engine misfire fault condition.
• The fuel injectors are enabled.
• The ignition voltage is 10.5 – 18 V.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is less than 800°C.
• The MAF sensor signal output is steady within 3 percent of the airflow into the engine .
DTC P2232 and P2235
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine is running.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature for longer than 90 seconds.
• The fuel injectors are enabled.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 10.5 V.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is 250 – 800°C.
DTC P2251 and P2254
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0050, P0051 and P0052 ran and passed.
• The O2 sensor heater control is enabled.
• The ECM internal sensing element resistance is greater than 570 Ω.
• The ECM detects the internal O2 sensor signal voltage is 1.47 – 1.53 V.
• The O2 sensor is at operating temperature.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–194
Page 6C1-2–194
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2231 or P2234
The ECM detects the following conditions:
• The internal O2 sensor signal voltage changes greater than 100 mV as the heater control switches.
• The above condition occurs 18 times in the last 10 seconds.
DTC P2232 or P2235
The ECM detects the following conditions:
• The internal O2 sensor signal voltage switches at the same rate as the heater circuit.
• The above condition occurs 4 times out of 6 as the heater is turned off.
DTC P2251 or P2254
The ECM detects the following conditions:
• The internal O2 sensor signal voltage changes greater than 10 mV as the heater control switches.
• The above condition occurs 20 times in the last 10 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The O2 sensor signal circuit shorted to heater control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs.
Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235, P2251, P2254 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2231, P2232, P2234, P2235, P2251 or P2254 fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the appropriate O2 sensor connector.
2 From the O2 sensor to the sensor wiring connector, test the
following circuit for a shorted to the sensor heater control circuit
fault condition:
• Reference signal circuit,
• low reference circuit,
• pump current,
• input pump current.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 4
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–195
Page 6C1-2–195
Step Action Yes No
4 1 Disconnect the ECM and the appropriate O2 sensor connector.
2 From the O2 sensor wiring connector to the ECM wiring
connector, test the following circuit for a shorted to the sensor
heater control circuit fault condition:
• Reference signal circuit,
• low reference circuit,
• pump current,
• input pump current.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on
electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
6 Replace the appropriate O2 sensor. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 8 —
7 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 8 —
8 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the O2 Sensor Signal Circuit Shorted to Heater Control
Circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 9
9 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–196
Page 6C1-2–196
5.39 DTC P0040 and P0041 – O2 Sensor
Signal Not Plausible Bank 1 / Bank 2
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0040 – O2 Sensor Signals Not Plausible (Bank 1, Sensor 1 & Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0041 – O2 Sensor Signals Not Plausible (Bank 1, Sensor 2 & Bank 2, Sensor 2)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the O2 sensor. The ECM applies
a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the heater control circuit of the O2 sensor through a device within the ECM
called a Driver, to control the O2 sensor rate of heating.
The ECM applies a voltage of approximately 450 mV between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the
O2 sensor while the sensor temperature is less than the operating range.
Once the O2 sensor reaches operating temperature, the sensor varies this reference signal voltage, which constantly
fluctuates between the high voltage output and the low voltage output.
• The low voltage output is 0 – 450 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is lean.
• The high voltage output is 450 – 1,000 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is rich.
The ECM monitors, stores and evaluates the O2 sensor voltage fluctuation information to determine the level of oxygen
concentration in the exhaust.
An O2 sensor signal not plausible or wire connector swapped DTC sets if the ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltages
are heading in the opposite direction of what was commanded.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–198
Page 6C1-2–198
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the O2 sensor system
operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• The O2 sensor must be tightened correctly. A loose O2 sensor will trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The engine is running.
• The O2 Sensors 2 (Alloytec190 engine) or O2 Sensors 1 (Alloytec engine) are in closed loop.
• The ECM is commanding the O2 sensors fuel trim.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects the O2 sensor signal voltages are heading in the opposite direction of what was commanded.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The O2 sensor signal not plausible DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
DTC P0040 and P0041 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does P0040 or P0041 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Check the O2 sensor 2 (Alloytec190 engine) or O2 sensor 1 (Alloytec
engine) wiring connectors for a swapped connector fault condition.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 Are DTCs relating to other circuits of the O2 sensor also set?
Refer to the
appropriate DTC
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the O2 sensor signal not plausible or wire connector
swapped DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
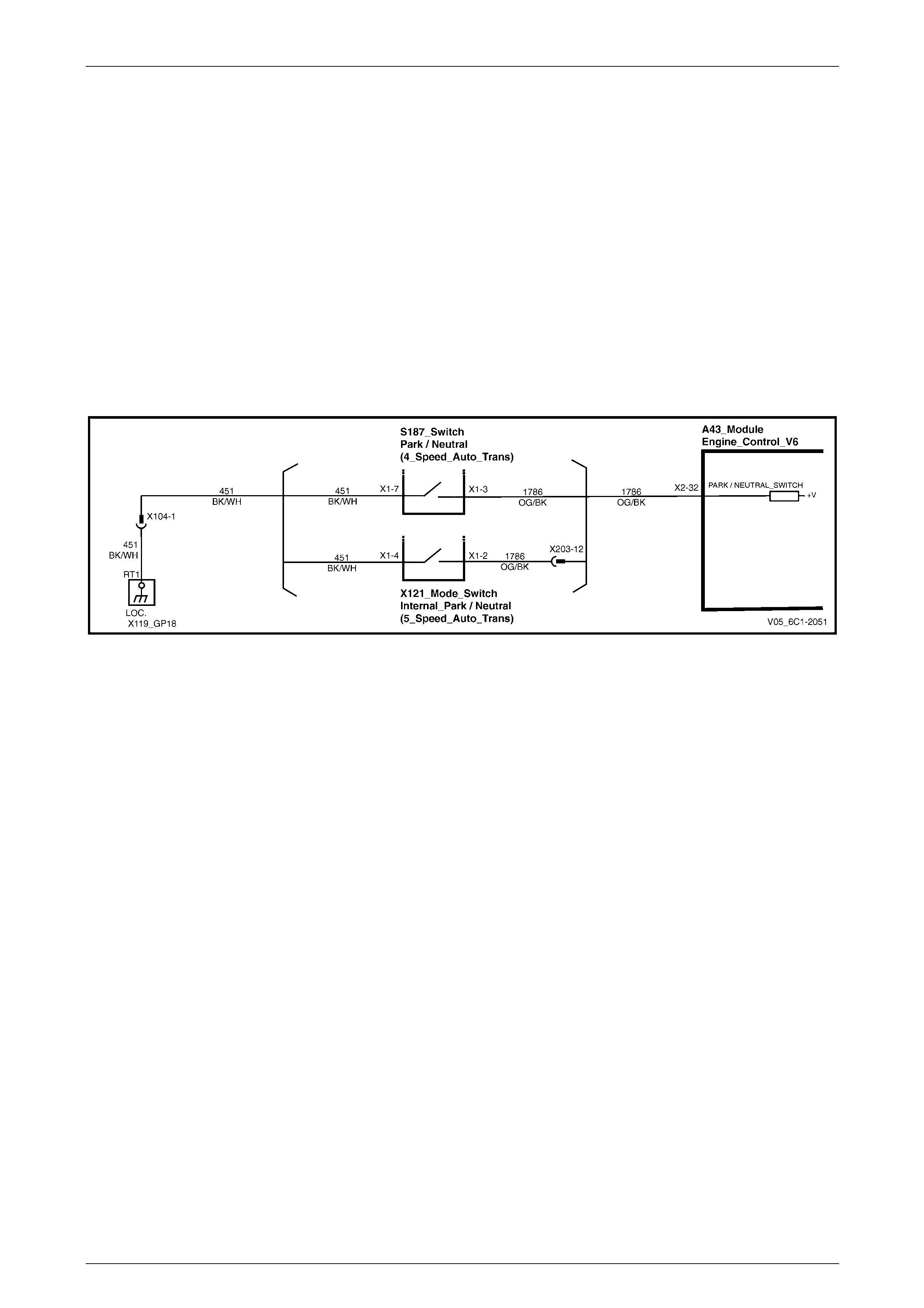
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–199
Page 6C1-2–199
5.40 DTC P0850 – Park / Neutral Signal Circuit
Incorrect Signal
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0850 – Park / Neutral Signal Circuit Incorrect Signal
Circuit Description
The park / neutral (P / N) switch is a part of the automatic transmission gear selector position switch assembly.
Refer to Section 7C1 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information or
Section 7E1 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – General Information for further information on this switch assembly.
The P / N switch is a normally open switch that closes when the transmission is shifted to Park or Neutral position. The
ECM applies reference 12 V to the signal circuit of the P / N switch when it is open. When the transmission is shifted to
the Park or Neutral position, the P / N switch closes and pulls the P/ N switch signal circuit to ground.
DTC P0850 sets when the ECM detects a fault condition in the P / N switch circuit.
Figure 6C1-2 – 45
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• The ECM uses the transmission range data to enable engine cranking when DTC P0850 sets.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the park / neutral switch
operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0850 runs continuously when the ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0850 sets when the ECM detects one of the following fault conditions:
• The P / N switch signal circuit is pulled to ground for 100 seconds while the TCM sends a signal the transmission is
in gear.
• The P / N switch signal circuit is 12 V for 100 seconds while the TCM sends a signal the transmission is in park or
neutral.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P0850 is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type C DTCs set and
conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–200
Page 6C1-2–200
DTC P0850 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch on the ignition.
2 Using Tech 2, observe the status of the automatic transmission
gear position.
3 Shift the transmission lever across all gear levels.
Does Tech 2 display P/N when the transmission is in park or neutral
and In Gear when the transmission lever is in other positions? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Switch on the ignition.
3 Shift the transmission lever across all gear levels.
Does DTC P0850 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 4
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
4 1 Remove the transmission position switch wiring connector. Refer
to Section 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle
Servicing or Section 7E4 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – On-
vehicle Servicing.
2 Connect a test lamp between the ground circuit of the
transmission switch and a 12 V.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1 Connect a 3 A jumper wire between the signal circuit of the
park/neutral signal circuit and a good ground.
2 Using Tech 2, observe the status of the transmission gear.
Does Tech 2 display a change from In Gear to P/N when the jumper
wire is connected? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
6 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the ground
circuit of the transmission position switch. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
7 Test the signal circuit of the park / neutral switch for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Replace the transmission position switch. Refer to Section 7C4
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing or Section
7E4 Automatic Transmission – 5L40E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0850 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–201
Page 6C1-2–201
5.41 DTC U0001 – No Communication with
CAN Bus (High Speed)
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC U0001 – No Communication with CAN-Bus (High Speed).
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) communicates directly with the control modules connected to the GM LAN serial data
communication circuit through the GM LAN protocol.
However, the body control module (BCM) along with control modules connected to the universal asynchronous receive
and transmit (UART) serial data communication circuit communicates with each other using the UART protocol.
Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module for information on the UART serial data communication circuit.
Since the GM LAN and UART protocols are not compatible, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated into serial
data communication system to serve as a gateway. This gateway allows communication between the two protocols.
Refer to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6 for further information on the GM LAN serial data communication
circuit.
DTC U0001 sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the serial data communication circuit.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC U0001 runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
The vehicle power mode requires serial data communication.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects a specified number of transmitted messages are not valid.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The Serial Data Communication Circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 The following tests are included in the Diagnostic System Check.
• Tests the integrity of the GM LAN serial data communication circuit.
• Tests for fault conditions on the vehicle theft deterrent system stored in the BCM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–202
Page 6C1-2–202
DTC U0001 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC U0001 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC U0001 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–203
Page 6C1-2–203
5.42 DTC U0155 and U0423 – Serial Data
Communication Circuit, PIM
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC U0155 – CAN-Bus No Communication With Gateway
• DTC U0423 – CAN-Bus Invalid Data From Gateway
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) communicates directly with the control modules connected to the GM LAN serial data
communication circuit through the GM LAN protocol.
However, the body control module (BCM) along with control modules connected to the universal asynchronous receive
and transmit (UART) serial data communication circuit communicates with each other using the UART protocol.
Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module for information on the UART serial data communication circuit.
Since the GM LAN and UART protocols are not compatible, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated into serial
data communication system to serve as a gateway. This gateway allows communication between the two protocols.
Refer to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6 for further information on the GM LAN serial data communication
circuit.
A PIM serial data communication circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects an invalid signal from the PIM.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs U0155 and U0423 run continuously when the following conditions are met:
• The engine is running.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM did not receive a valid signal from the PIM within the specified time frame.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The PIM serial data communication circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action
taken when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 The following tests are included in the Diagnostic System Check.
• Tests the integrity of the GM LAN serial data communication circuit.
• Tests for fault conditions on the vehicle theft deterrent system stored in the BCM.
Techline
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–204
Page 6C1-2–204
DTC U0155 and U0423 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC U0155, or U0423 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Replace the PIM. Refer to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module –
V6.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the PIM serial data communication circuit DTCs fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–205
Page 6C1-2–205
5.43 DTC P0864 and U0101 – Serial Data
Communication Circuit, TCM
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0864 – CAN-Bus Invalid Data From TCM (Transmission Control Module)
• DTC U0101 – CAN-Bus No Communication With TCM (Transmission Control Module)
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) communicates directly with the transmission control module (TCM) and other control
modules connected to the GM LAN serial data communication circuit through the GM LAN protocol.
However, the body control module (BCM) along with control modules connected to the universal asynchronous receive
and transmit (UART) serial data communication circuit communicates with each other through the UART protocol.
Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module for information on the UART serial data communication circuit.
Since the GM LAN and UART protocols are not compatible, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated into serial
data communication system to serve as a gateway. This gateway allows communication between the two protocols.
Refer to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6 for further information on the GM LAN serial data communication
circuit.
A serial data communication circuit – TCM DTC sets if the ECM detects an invalid signal from the TCM.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0864 and U0101 run continuously when the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is on for longer than 3 seconds.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM did not receive a valid signal from the TCM within the specified time frame.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The Serial Data Communication Circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 The following tests are included in the Diagnostic System Check.
• Tests the integrity of the GM LAN serial data communication circuit.
• Tests for fault conditions on the vehicle theft deterrent system stored in the BCM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–206
Page 6C1-2–206
DTC P0864 and U0101 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC U0864 or U0101 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does the PIM failed to communicate?
Refer to the Section
6E1 Powertrain
Interface Module –
V6 Go to Step 4
4 Are DTCs also set in the PIM? Refer to Section
6E1 Powertrain
Interface Module –
V6 Go to Step 5
5 Are DTCs that may trigger a fault condition in the serial data
communication circuit also set in the TCM?
Refer to Section
7C2 Automatic
Transmission –
4L60E – Electrical
Diagnosisor Section
7E2 Automatic
Transmission –
5L40E – Electrical
Diagnosis Go to Step 6
6 Replace the TCM, refer to Section 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing or Section 7E4 Automatic Transmission
– 5L40E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the serial data communication circuit – TCM DTCs fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–207
Page 6C1-2–207
5.44 DTC U0121 and U0415 Serial Data
Communication Circuit, ABS / TC / ESP
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC U0121 – CAN-Bus No Communication With ABS / TC / ESP
• DTC U0415 – CAN-Bus Invalid Data ABS / TC / ESP
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) communicates directly with the ABS/TCS/ESP electronic control unit (ECU) and other
control modules connected to the GM LAN serial data communication circuit through the GM LAN protocol.
However, the body control module (BCM) along with control modules connected to the universal asynchronous receive
and transmit (UART) serial data communication circuit communicates with each other through the UART protocol.
Refer to Section 12J Body Control Module for information on the UART serial data communication circuit.
Since the GM LAN and UART protocols are not compatible, a powertrain interface module (PIM) is integrated into the
serial data communication system to serve as a gateway. This gateway allows communication between the two protocols.
Refer to Section 6E1 Powertrain Interface Module – V6 for further information on the GM LAN serial data communication
circuit.
DTC U0415 – Controller Area Network Invalid Signal from the TCS sets if the ECM detects an invalid signal from the
ABS /TCS / ESP ECU.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC U0121 and U0415 runs continuously when the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is on for longer than 3 seconds.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM did not receive a valid signal from the ECU of the ABS /TCS / ESP.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The Serial Data Communication Circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken
when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 The following tests are included in the Diagnostic System Check.
• Tests the integrity of the GM LAN serial data communication circuit.
• Tests for fault conditions on the vehicle theft deterrent system stored in the BCM.
Techline
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–208
Page 6C1-2–208
DTC U0121 and U0415 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC U0121 and U0415 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does the PIM fail to communicate?
Refer to the Section
6E1 Powertrain
Interface Module –
V6 Go to Step 4
4 Are DTCs also set in the PIM? Refer to Section
6E1 Powertrain
Interface Module –
V6 Go to Step 5
5 Are DTCs that may trigger a fault condition in the serial data
communication circuit also set in the ABS /TCS / ESP ECU?
Refer to Section 5
ABS /TCS / ESP
General Information Go to Step 6
6 Replace the ABS /TCS / ESP ECU. Refer to Section 5 ABS /TCS /
ESP General Information.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the serial data communication circuit DTCs fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
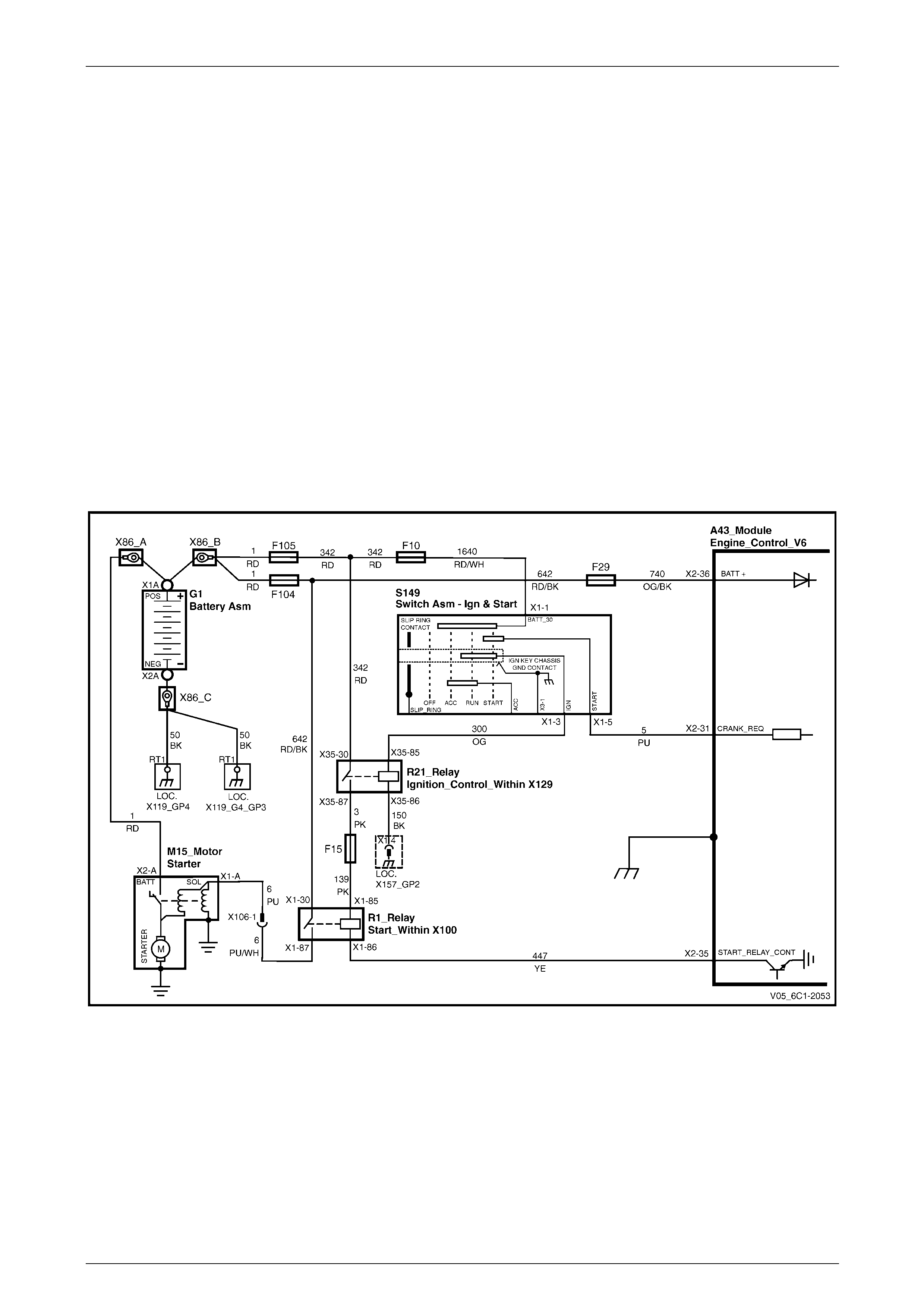
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–209
Page 6C1-2–209
5.45 DTC P0615 to P0617 – Starter Relay
Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0615 – Starter Relay Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P0616 – Starter Relay Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0617 – Starter Relay Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies battery voltage to the coil circuit of the starter relay through the ignition circuit. When the
ignition switched is turned to the Start position and all the conditions required to enable an engine cranking is met, the
ECM grounds the starter relay control circuit to activate the starter relay. When active, the starter relay applies battery
voltage to the starter motor solenoid control circuit to operate the starter motor.
Refer to Section 6D1-2 Starting System – V6 for information on the cranking system operation.
The ECM monitors the control circuit of the starter relay for conditions that are incorrect for the commanded state. A
starter relay control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the starter relay control circuit.
Figure 6C1-2 – 46
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6D1-2 Starting System – V6 for information on the cranking system operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–210
Page 6C1-2–210
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0615, P0616 and P0617 run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects a condition that is incorrect for the starter relay commanded state.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The starter relay control circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in the starting system or theft deterrent system may trigger this DTC.
DTC P0615 to P0617 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Turn the ignition switch to the Start position or operate the
vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0615, P0616 and P0617 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Check for a fault condition in the following systems which can disable
the starting system:
• Starting System, refer to Section 6D1-2 Starting System – V6 .
• Theft Deterrent System, refer to Section 12J Body Control
Module.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 4
4 1 Remove the starter relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses, Relays
and Wiring Harnesses.
2 Connect a test lamp between the ignition circuit of the starter
relay and a good ground.
3 Switch on the ignition.
Does the test lamp illuminate when the ignition switch is turned to the
on position? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1 Connect a test lamp between the control circuit of the starter
relay and a 12 V.
2 Turn the ignition switch to the Start position and then release it
back to the on position.
Does the test lamp turn on when the ignition switch is turned to the
Start position and then turn off when the ignition switch returns to the
on position? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–211
Page 6C1-2–211
Step Action Yes No
6 Repair the ignition voltage circuit of the starter relay for a high
resistance or open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
7 Test the control circuit of the starter relay for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or a short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Replace the starter relay. Refer to Section 12O Fuses, Relays and
Wiring Harnesses.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does the starter relay control circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
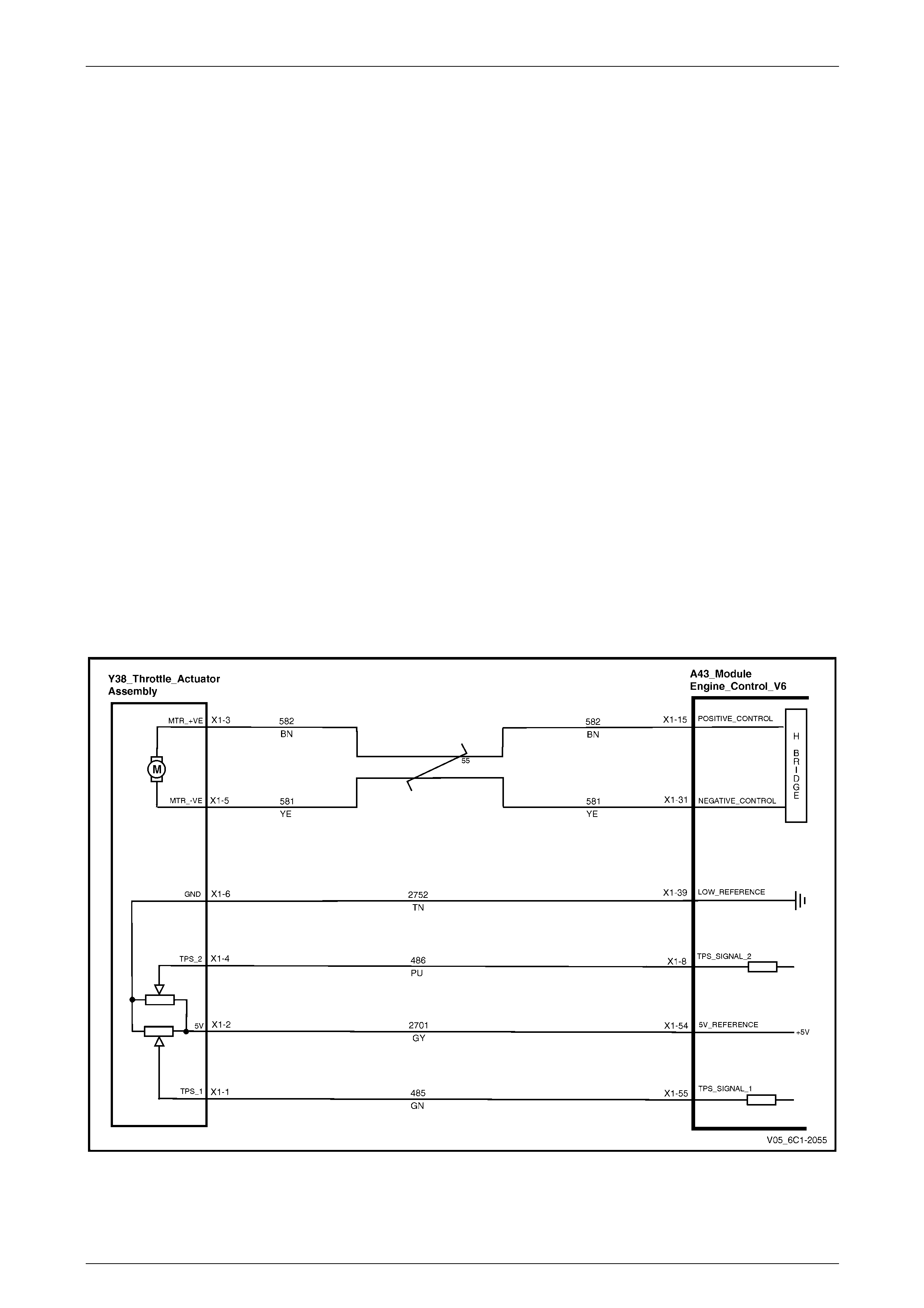
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–212
Page 6C1-2–212
5.46 DTC P2107 – Throttle Control
Malfunction
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2107 – Throttle Control Malfunction.
Circuit Description
The ECM applies 5 V to the throttle position (TP) sensor 1 through the 5 V reference circuit 2701 and the ground through
the low reference circuit 2752. TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 share common 5 V reference circuit and low reference
circuit.
The TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 have individual signal circuits with opposite functionality. These signal circuits provide
the ECM with a signal voltage that is proportional to the throttle plate movement.
• The TP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 1 V when the throttle plate is in closed position, which increases to
greater than 4 V when the throttle plate is moved to wide-open throttle.
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4 V when the throttle plate is in closed position, which decreases to
less than 1 V when the throttle plate is moved to wide-open throttle.
The ECM monitors and evaluates the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensors signal voltage along with other sensor
inputs to determine the desired throttle opening. To control the throttle plate movement, the ECM applies a pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal voltage to the throttle actuator motor through the throttle actuator motor control circuits.
• At engine idle speed or when no current is flowing into the throttle actuator control (TAC) motor, a constant force
return spring holds the throttle plate at a constant 7 percent throttle opening position.
• To control the throttle opening, the ECM applies PWM voltage to the TAC motor. The ECM increases this PWM
voltage duty cycle to increase the throttle opening.
To decrease the throttle opening from the 7 percent rest position, the ECM reverses the polarity of the TAC motor control
circuit then applies a PWM voltage to the TAC motor.
If the ECM detects the TP sensor 1 amplification output does not correlate with the TP sensor 1 signal voltage during a
predetermined sets of conditions, DTC P2107 sets.
Figure 6C1-2 – 47
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–213
Page 6C1-2–213
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the TP sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2107 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine speed is less than 40 r.p.m.
• The engine coolant temperature is 5 – 60°C.
• The intake air temperature is 5 – 60°C.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
• The APP is less than 15 percent.
• The ECM is performing the closed throttle test with the ignition switched on and the engine not running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects that its internal TP sensor 1 amplification output does not correlate with the TP sensor 1 signal voltage.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P2107 – Throttle Actuator Control Module Internal Circuit is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes
for action taken when a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTC.
DTC P2107 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2107 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P2107 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–214
Page 6C1-2–214
5.47 DTC P2105 – Throttle Control Forced
Engine Shutdown
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2105 – Throttle Control Forced Engine Shutdown.
Circuit Description
The ECM monitors and evaluates the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensors signal voltage along with other sensor
inputs to determine the desired throttle opening. To control the throttle plate movement, the ECM applies a pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal voltage to the throttle actuator motor through the throttle actuator motor control circuits.
• At engine idle speed or when no current is flowing into the throttle actuator control (TAC) motor, a constant force
return spring holds the throttle plate at a constant 7 percent throttle opening position.
• To control the throttle opening, the ECM applies PWM voltage to the TAC motor. The ECM increases this PWM
voltage duty cycle to increase the throttle opening.
To decrease the throttle opening from the 7 percent rest position, the ECM reverses the polarity of the TAC motor control
circuit then applies a PWM voltage to the TAC motor.
The ECM monitors the ignition supply voltage to ensure the correct operation of the engine management components
and sensors. DTC P2105 sets if the ECM detects an incorrect ignition voltage.
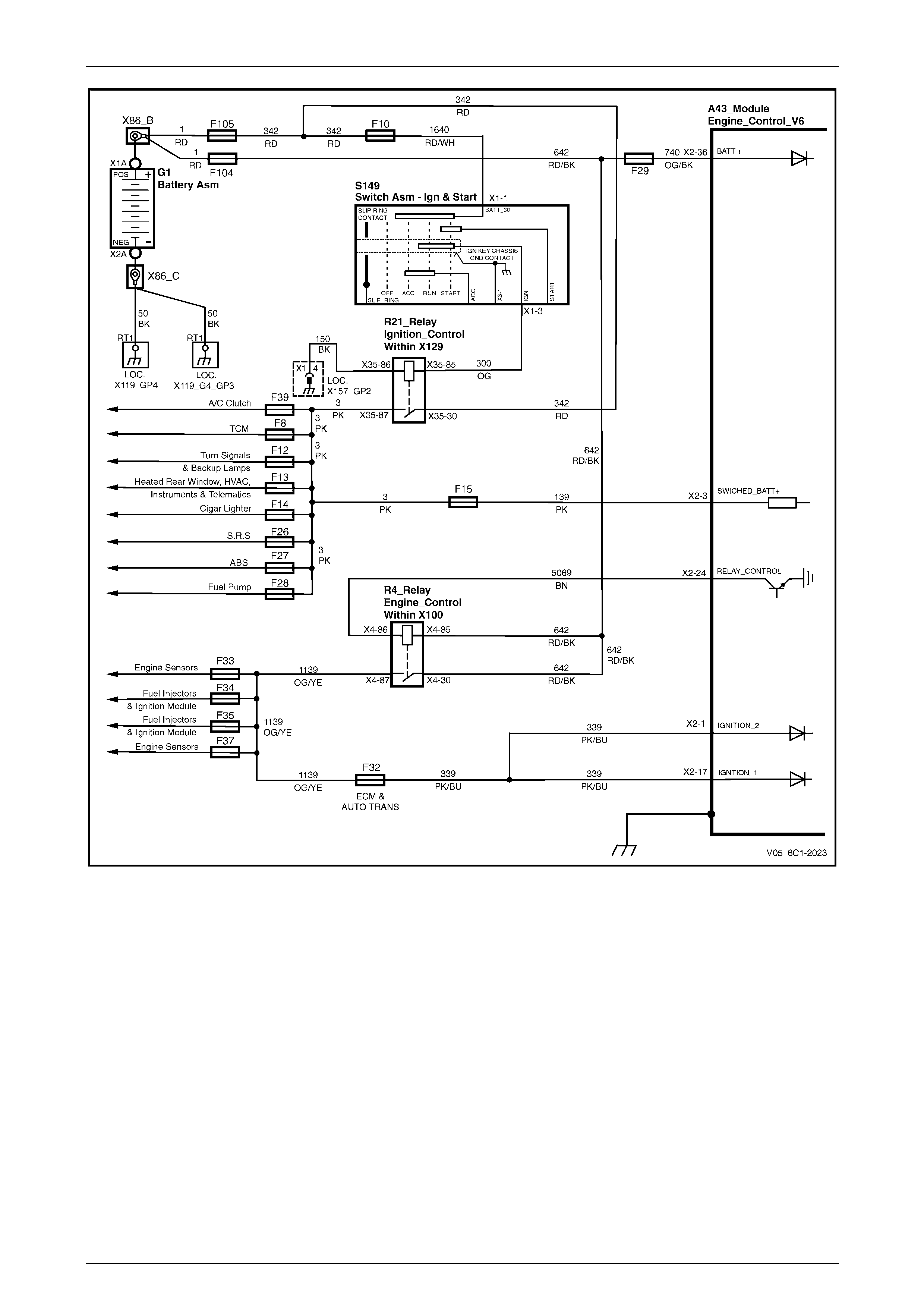
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–215
Page 6C1-2–215
Figure 6C1-2 – 48
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the TP actuator operation.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2105 runs continuously when the ECM completed the power-down process in the last ignition cycle.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects an incorrect voltage level at the ignition supply circuits.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P2105 – Throttle Actuator Control (TAC) Module Internal Circuit is a Type A DTC.
Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a Type A DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type A
DTC.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–216
Page 6C1-2–216
DTC P2105 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2105 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Remove the ECM / TCM Fuse 32 from the engine compartment
relay panel assembly.
NOTE
Voltage may be available at both terminals of Fuse 32
because of normal voltage feed back condition. Therefore,
the fuse must be removed prior to testing.
2 Inspect the ECM / TCM Fuse 32 for an open circuit fault
condition.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4 1 Remove the engine control relay from the engine compartment
relay panel assembly.
2 Test the ignition circuit of the ECM, from the fuse terminal to the
Engine control relay for a high resistance, open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P
Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
NOTE
The engine control relay supplies ignition voltage to other
components and sensors through the ECM ignition circuit.
A fault condition in this ignition circuit may trigger DTCs on
components or sensors connected to this circuit.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 Disconnect the vehicle side wiring connector of the ECM. Refer to
Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Test both ignition circuits of the ECM, from the fuse terminal to the
ECM wiring connector for a high resistance, open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 7 —
7 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P2105 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 8
8 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–217
Page 6C1-2–217
5.48 P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100,
P2101, P2119 and P2176 – Throttle
Actuator Control Motor Control Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0506 – Idle Speed Control r.p.m. Too Low
• DTC P0507 – Idle Speed Control r.p.m. Too High
• DTC P0638 – Commanded Versus Actual Throttle Position Correlation
• DTC P1551 – Throttle Control Lower Position Not Reached During Learning Mode
• DTC P2100 – Throttle Control Motor Malfunction
• DTC P2101 – Throttle Control Position Range / Performance
• DTC P2119 – Closed Throttle Position Range / Performance
• DTC P2176 – Throttle Control Lower Position not Learned
Circuit Description
The ECM monitors and evaluates the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensors signal voltage along with other sensor
inputs to determine the desired throttle opening. To control the throttle plate movement, the ECM applies a pulse width
modulated (PWM) signal voltage to the throttle actuator motor through the throttle actuator motor control circuits.
• At engine idle speed or when no current is flowing into the throttle actuator motor, a constant force return spring
holds the throttle plate at a constant 7 percent throttle opening position.
• To control the throttle opening, the ECM applies PWM voltage to the throttle actuator motor. The ECM increases
this PWM voltage duty cycle to increase the throttle opening.
• To decrease the throttle opening from the 7 percent rest position, the ECM reverses the polarity of the throttle
actuator motor control circuit then applies a PWM voltage to the throttle actuator motor.
In addition, the ECM monitors the signal voltage applied to the throttle actuator motor control circuit. A TAC motor control
circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the TAC circuits or motor performance.
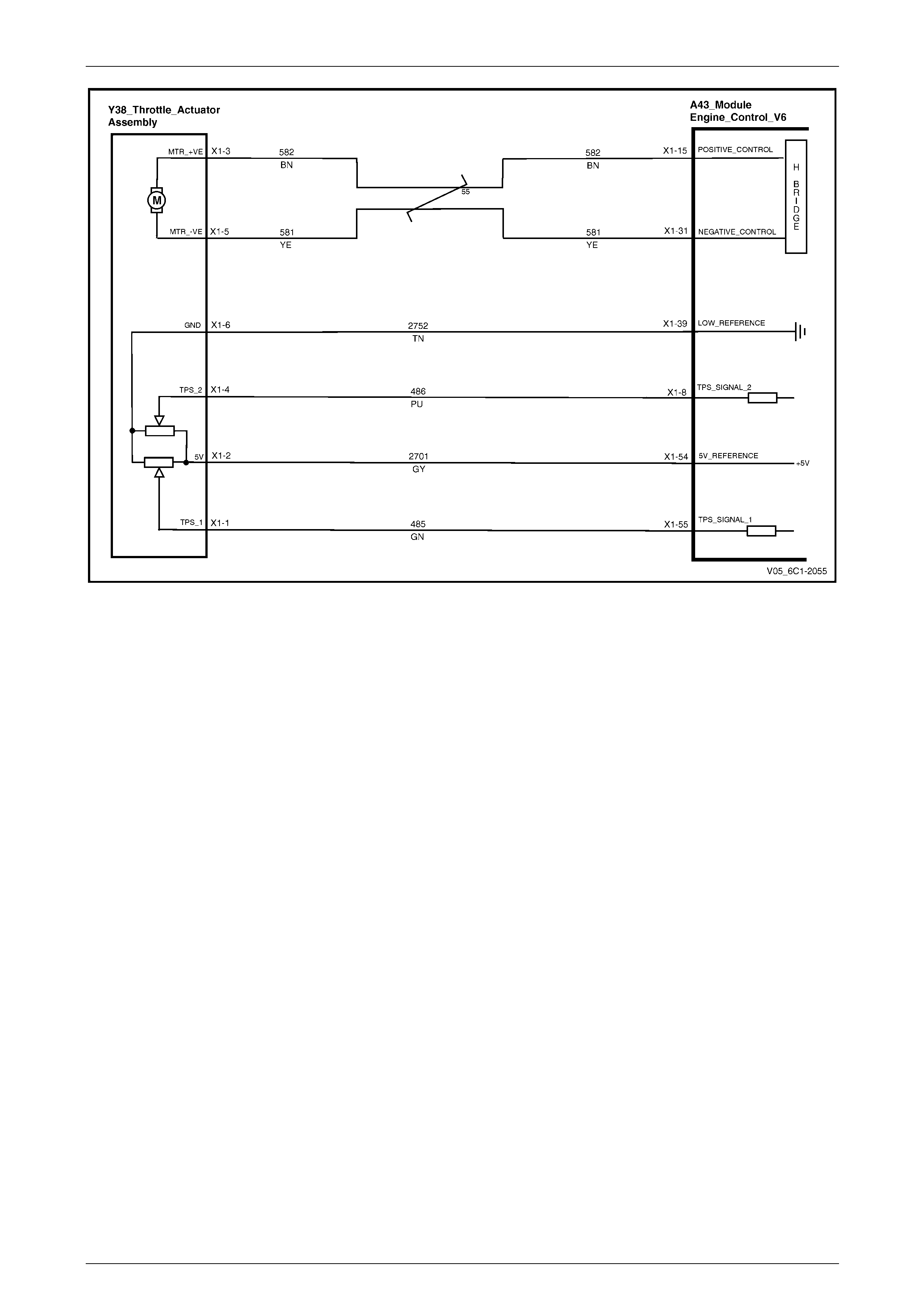
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–218
Page 6C1-2–218
Figure 6C1-2 – 49
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the Throttle Actuator Control
System operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0506 and P0507
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0443, P0446, P0455, P0458
and P0459 are not set.
• The ignition is switched on.
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60°C.
• The intake air temperature is greater than -10.5°C.
• The volumetric efficiency is less than 35 percent.
• The EVAP purge solenoid is off.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–219
Page 6C1-2–219
DTC P0638
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 7 V.
DTC P2100
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTC P2101 ran and passed.
• The ignition is switched on.
DTC P2101
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The battery voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The ignition is switched on.
DTC P1551, P2119 and P2176
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine speed is less than 40 r.p.m.
• The engine coolant temperature is 5 – 60°C.
• The intake air temperature is 5 – 60°C.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
• The APP is less than 15 percent.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0506
The actual engine speed is less than the desired idle speed by at least 100 r.p.m. for 10 seconds.
DTC P0507
The actual engine speed is greater than the desired idle speed by at least 200 r.p.m. for 10 seconds or the ECM detects
3 fuel cut-offs due to an engine over speed condition while the engine is idling.
DTC P0638
• The ECM detects the commanded duty cycle is greater than 80 percent for longer than 0.6 second.
DTC P1551
The ECM detects the TP sensor angle is outside the predetermined range of 1.8 – 13.0 percent when the TAC motor is
deactivated.
DTC 2100
The ECM detects that its internal TAC motor output driver does not deactivate when commanded off.
DTC P2101
The ECM detects the difference between the commanded and the actual throttle opening is greater than 10 percent.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–220
Page 6C1-2–220
DTC P2119
The ECM determines the throttle plate didn't return to the rest position within 720 milliseconds.
DTC P2176
One of the following conditions exist:
• The TP sensor 1 voltage is outside the range of 0.2 – 0.9 V during the throttle learn procedure.
• The TP sensor 2 voltage is outside the range of 4.2 – 4.8 V during the throttle learn procedure.
• The throttle learn procedure is not learned after an ECM replacement.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The TAC motor control circuit DTCs are Type A DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when a
Type A DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type A DTCs.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
4 A constant force return spring holds the throttle plate at a constant 7 percent throttle opening position and should
move in either direction under spring pressure and without binding.
8 When the ignition is switched on, the ECM operates the throttle actuator motor to verify the integrity of the TAC
system prior to start up. This can be seen by the momentary flash of the test lamp as the ignition is switched on.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–221
Page 6C1-2–221
P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2119 and P2176 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Start the engine.
4 Quickly depress the accelerator pedal to wide-open throttle then
release pedal. Repeat this procedure several times.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2119 or
P2176 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Is DTC P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 or P0223 also set? Refer to the
appropriate DTC
table. Go to Step 4
4 1 Disconnect the throttle actuator wiring connector.
Accidental operation of the TAC motor while
performing throttle plate inspection may cause severe
personal injury. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations for additional
precautions on throttle body servi ce procedure.
2 Inspect the throttle plate for the following:
• excessive dirt build-up in the throttle body,
• not in rest position,
• binding open or binding close,
• binding when moving from open to close or close to open
position, and
• free to move open or close without spring pressure.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 5
5 Inspect the engine for fault conditions that causes incorrect idle speed.
Refer to 4.12 Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or Stalling.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 6
6 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
TAC positive circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 2 – 4 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 9
7 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
TAC negative control circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 2 – 4 V? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–222
Page 6C1-2–222
Step Action Yes No
8 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Connect Tool No. J34730-405 injector test lamp between the
positive and negative control circuit of the TAC.
3 Switch on the ignition for about 5 seconds then switch off while
observing the test lamp.
Does the test lamp illuminate briefly each time the ignition cycles? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
9 Test the TAC control circuit that measured outside the specified value
for a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage
fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information
on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
10 Test the positive and negative control circuits of the TAC for a shorted
together fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
11 Replace the throttle body assembly. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 13 —
12 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 13 —
13 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the TAC motor control circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 14
14 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–223
Page 6C1-2–223
5.49 DTC P0700 – Malfunction Indicator
Request from Transmission Control
Module
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0700 – Malfunction Indicator (MI) Request from Transmission Control Module
(TCM).
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) communicates directly with the transmission control module (TCM) and other control
modules connected to the GM LAN serial data communication circuit through the GM LAN protocol.
DTC P0700 – Malfunction Indicator Request from TCM sets if the following condition exists:
• The TCM detects an emission related fault condition and sets a TCM DTC that represent the fault condition.
• The ECM receives a serial data signal from the TCM requesting the illumination of the malfunction indicator.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECM operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0700 runs continuously when the ignition is switched on.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM receives a serial data signal from the TCM requesting the illumination of the malfunction indicator.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P0700 – Malfunction Indicator Request from TCM is a Type A DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for
action taken when a Type A DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type A DTCs.
DTC P0700 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0700 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 Are DTCs other than DTC P0700 also set in the ECM?
Refer to appropriate
DTC table
Refer to Section
7C2 Automatic
Transmission –
4L60E – Electrical
Diagnosisor Section
7E4 Automatic
Transmission –
5L40E – Electrical
Diagnosis
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
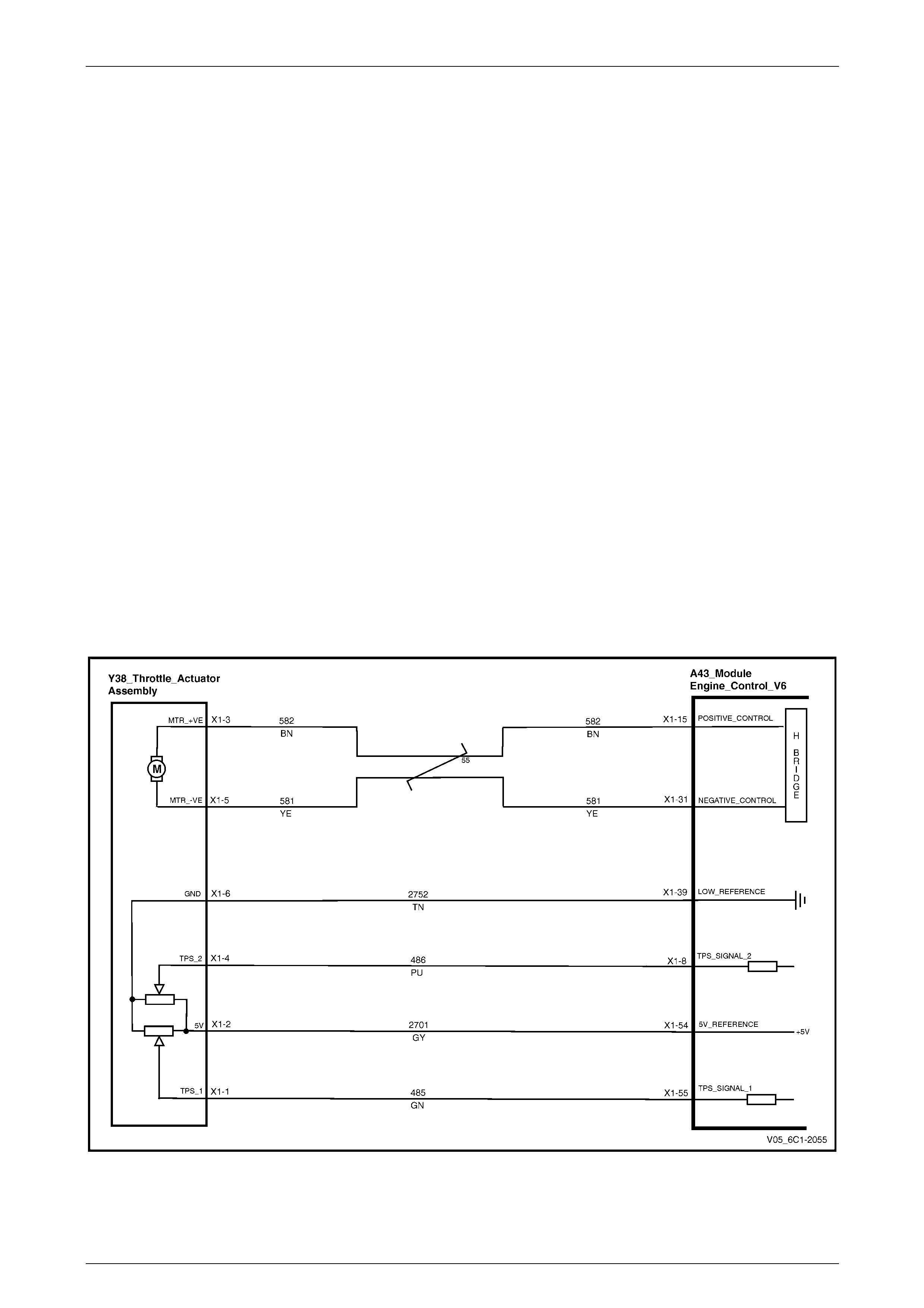
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–224
Page 6C1-2–224
5.50 DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 –
Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0121 – Throttle Position Sensor 1 Circuit Range / Performance
• DTC P0122 – Throttle Position Sensor 1 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0123 – Throttle Position Sensor 1 Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0221 – Throttle Position Sensor 2 Circuit Range / Performance
• DTC P0222 – Throttle Position Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0223 – Throttle Position Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The ECM applies 5 V to the throttle position (TP) sensor 1 through the 5 V reference circuit and the ground through the
low reference circuit. TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 share common 5 V reference circuit and low reference circuit.
The TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 have individual signal circuits with opposite functionality. These signal circuits provide
the ECM with a signal voltage that is proportional to the throttle plate movement.
• The TP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 1 V when the throttle plate is in closed position, which increases to
greater than 4 V when the throttle plate is moved to wide-open throttle.
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4 V when the throttle plate is in closed position, which decreases to
less than 1 V when the throttle plate is moved to wide-open throttle.
The ECM monitors and compares the TP sensor 1 signal voltage to the TP sensor signal voltage 2. In addition, the ECM
compares the TP sensor signal to the MAF sensor signal to determine a calculated TP sensor signal.
A TP sensor DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the TP sensor signal output.
Figure 6C1-2 – 50
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–225
Page 6C1-2–225
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the TP sensor operation.
• The ECM defaults to a reduced power mode if there is a fault condition in the TP sensor circuits for the entire
ignition cycle, even if the fault condition is corrected.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• The TP sensors share a common 5 V reference circuit, test for a fault condition in the 5 V reference circuit if both
DTCs P0122 and P0222 are set.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0121 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The TP sensor 1 signal voltage is 0.17 – 4.6 V.
DTC P0122, P0123, P0222 and P0223 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The ignition is switched on.
DTC P0221 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The battery voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage is 0.15 – 4.8 V.
DTC P0222 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The battery voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The ignition is switched on.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0121
The following conditions exist:
• The TP sensor 1 signal voltage and the TP sensor 2 signal voltage have a difference of greater than 9 percent.
• The TP sensor signal voltage has a difference of greater than 9 percent from the calculated TP sensor signal
voltage.
DTC P0122
The ECM detects the TP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 0.18 volt.
DTC P0123
The ECM detects the TP sensor 1 signal voltage is greater than 4.6 V.
DTC P0221
The following conditions exist:
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage and the TP sensor 1 signal voltage have a difference of greater than 9 percent.
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage has a difference of greater than 9 percent from the calculated TP sensor signal
voltage.
DTC P0222
The ECM detects the TP sensor 2 signal voltage is less than 0.16 volt.
DTC P0223
The ECM detects the TP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4.8 V.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–226
Page 6C1-2–226
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 are P0223 are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for
action taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
6 Measures the integrity of the TP sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the ECM Fuse 29 enables the ECM to
power down completely prior to the test procedure.
DTC P0121 to P0123, P0221 to P0223 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Quickly depress the accelerator pedal to wide-open throttle then
release pedal. Repeat this procedure several times or operate
the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
4 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 or P0223 fail this
ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the throttle actuator wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the TP
sensor 5 V reference circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the TP sensor 5 V
reference circuit and the TP sensor 1 signal circuit.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using Tech 2, observe the TP sensor 1 voltage parameter.
Does Tech 2 display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
5 1 Connect a 3 A fused jumper wire between the TP sensor 5 V
reference circuit and the TP sensor 2 signal circuit.
2 Using Tech 2, observe the TP sensor 2 voltage parameter.
Does Tech 2 display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
TP sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing the test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–227
Page 6C1-2–227
Step Action Yes No
7 NOTE
TP sensor 1 share the 5 V reference circuit with TP sensor
2. A fault condition in the TP sensor 5 V reference circuit
may trigger DTCs on both sensors.
Test the TP sensor 5 V reference circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
8 Test the TP sensor 1 signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
9 Test the TP sensor 2 signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
10 Test the TP sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance or an
open circuit fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 12
11 Replace the throttle body assembly. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 13 —
12 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 13 —
13 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the TP Sensor Circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 14
14 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
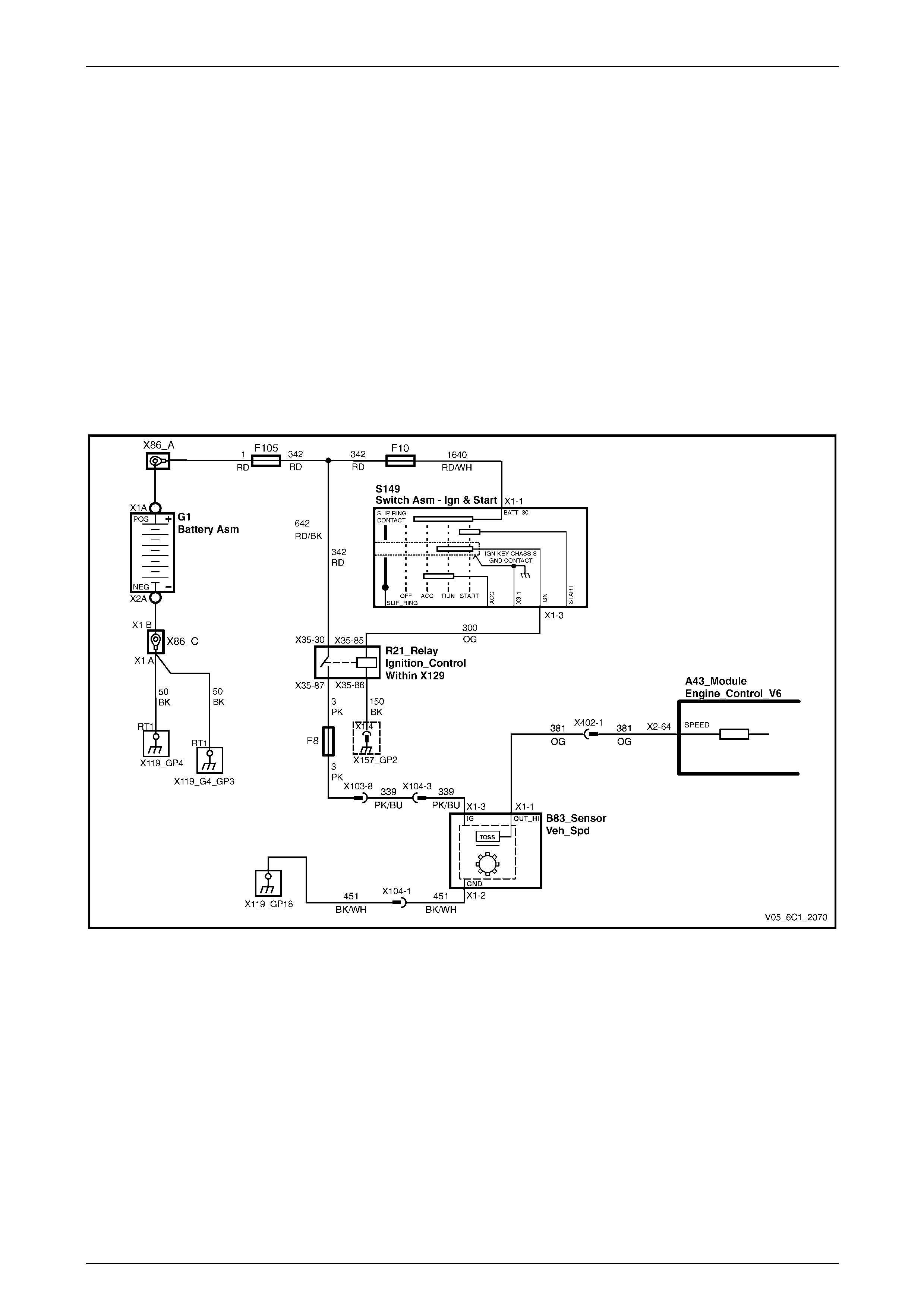
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–228
Page 6C1-2–228
5.51 DTC P0500 – Vehicle Speed Sensor
Circuit Malfunction, Manual
Transmission
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0500 – Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
Circuit Description
Vehicle speed information is provided to the engine control module (ECM) by the vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The
ignition control relay applies ignition positive voltage to the VSS, and the ground circuit of the VSS is directly connected
to ground.
The VSS is a Hall effect switch. In conjunction with a 18 teeth reluctor wheel, the VSS provide a signal voltage to the
ECM. The ECM uses this signal voltage to determine vehicle speed.
If the ECM detects no vehicle speed, while other sensors indicate that the vehicle is moving, then DTC P0500 sets.
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Figure 6C1-2 – 51
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details on:
• VSS operation, and
• fuel shut-off mode.
• Refer to Section 7B1 Manual Transmission for VSS replacement procedures.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–229
Page 6C1-2–229
Conditions for Running the DTC
Runs once the following conditions are met:
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 40ºC,
• the ECM is in fuel shut-off mode, and
• the engine speed is between 1520 and 3520 r.p.m.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects a speed of less than 0 km/h for 8 seconds continuously, or 50 seconds cumulative.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The vehicle speed sensor circuit malfunction DTC is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action
taken when Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
DTC P0500 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the diagnostic system check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0500 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the wiring connector from the VSS.
3 Connect a test lamp between the ignition circuit of the VSS and
ground.
4 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the ignition
circuit of the VSS. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
5 1 Connect a test lamp between the ground circuit and ignition
circuit of the VSS.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Repair the high resistance or open circuit fault condition in the ground
circuit of the VSS. Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for
information on electrical wiring repair procedures.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–230
Page 6C1-2–230
Step Action Yes No
7
To avoid damage to the drive axles, support the low er
control arms in the normal horizontal position. Do not
run the vehicle in gear with the wheels hanging down
at full travel.
1 Raise the vehicle and support the drive axles with safety stands.
Refer to Section 0A General Information for the location of
jacking and support points.
2 Connect a fused jumper wire between the ground circuit of the
connector and the ground circuit of the VSS.
3 Connect a fused jumper wire between the ignition circuit of the
connector and the ignition circuit of the VSS.
4 Using connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A, connect a digital
multimeter between the VSS signal circuit and ground.
5 Place the transmission in neutral.
6 Rotate the rear wheels by hand while observing the multimeter.
Does the multimeter indicate greater than 0.15 V AC? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
8 Perform the following VSS inspection:
• Inspect the VSS wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault
Conditions.
• Inspect the VSS for incorrect installation or incorrect attaching
bolt torque value. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Inspect the VSS sensor reluctor wheel for damage or conditions
that causes misalignment.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 9
9 Replace the VSS. Refer to Section 7B1 Manual Transmission – V6.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
10 Test the VSS signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit, short to
ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to Section 12P Wiring
Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
11 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 12 —
12 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0500 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 13
13 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
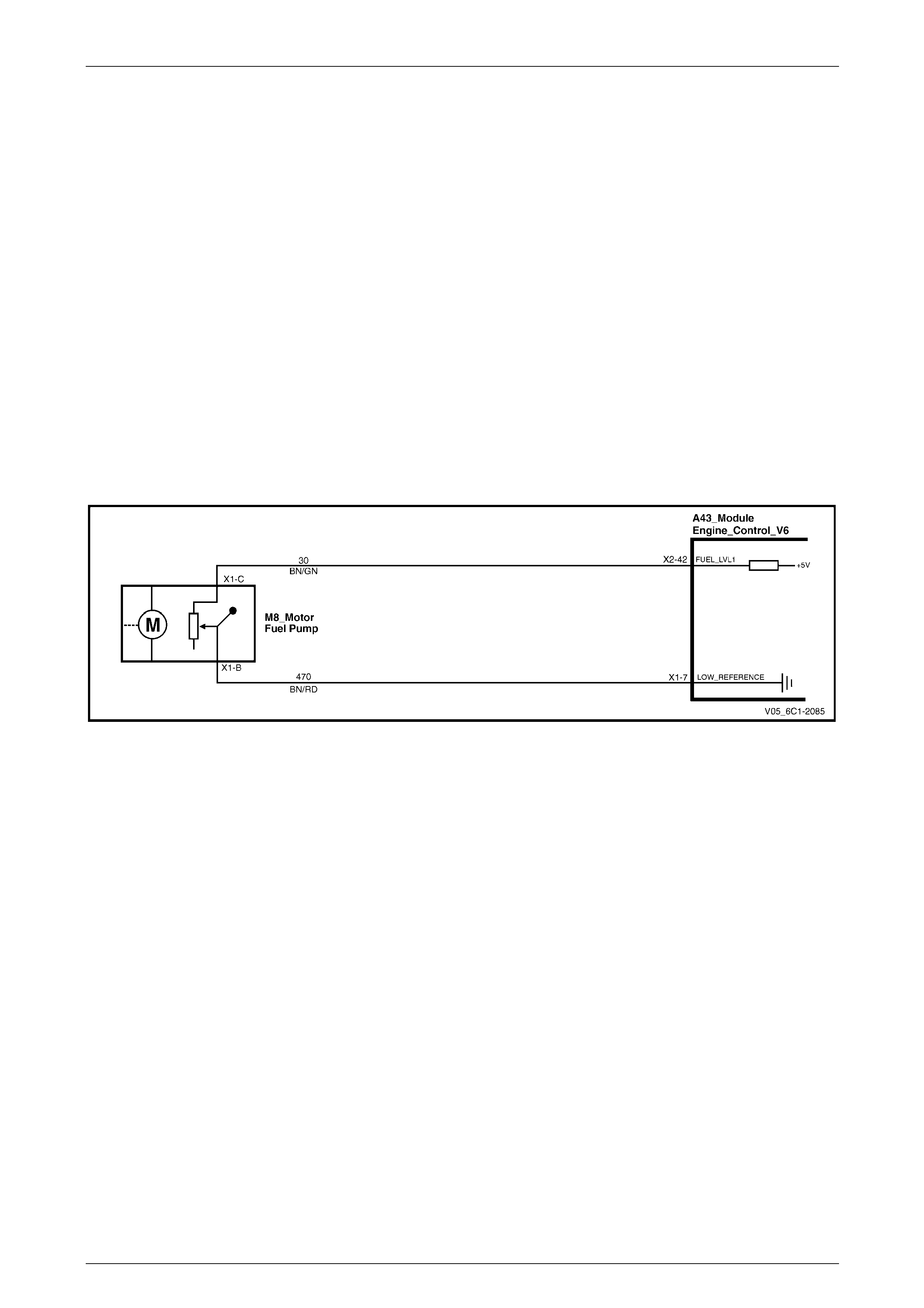
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–231
Page 6C1-2–231
5.52 DTC P0461 to P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor
Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0461 – Fuel Level Sensor Range / Performance
• DTC P0462 – Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage
• DTC P0463 – Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage
Circuit Description
The fuel level sensor changes resistance based on the fuel level in the fuel tank. The engine control module (ECM)
monitors changes in the resistance of the sensor to determine the fuel level. This information is then sent to the
instrument cluster via the GM Lan serial data circuit.
When the fuel tank is full, the sensor resistance is high and the ECM senses high signal voltage. When the fuel tank is
empty, the sensor resistance is low and the ECM senses a low signal voltage.
When the ECM senses a signal voltage outside the normal operating range of the sensor, a fuel level sensor DTC will
set.
Figure 6C1-2 – 52
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 12C Instrumentation for further information on the fuel gauge system.
• Depending on the current fuel level, it may be difficult to locate a malfunctioning sending unit. The malfunction may
only occur when the fuel level is full or near empty. The fuel sender unit may need to be removed for further
diagnosis. A fuel level sensor that has an intermittent condition may cause a DTC to set. Remove the fuel level
sensor to test the resistance of the sensor, refer to Section 8A1 Fuel System for this procedure. Replace the sensor
if the resistance is not within the specified range.
• The following may occur with a fuel level sensor DTC set:
• The vehicle fuel gauge displays empty.
• The Instrument Multi-function Display (MFD) displays a fuel condition message.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The ignition is on.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–232
Page 6C1-2–232
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0461
The ECM detects that greater than 170 km have been accumulated and the fuel level in the fuel tank has not changed by
at least 3.0 litres.
DTC P0462
The ECM detects the fuel level signal voltage is less than 0.5 V for 20 seconds.
DTC P0463
The ECM detects the fuel level signal voltage is greater than 4.5 V for 20 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The fuel level sensor circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when Type
C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
DTC P0461, P0462 or P0463 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC or
road test the vehicle under various driving condition.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0461, P0462, P0463 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the fuel level sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the fuel
level signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter indicate 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse F29 from the engine compartment fuse and
relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
fuel level sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse F29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter indicate less than 5 Ω? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–233
Page 6C1-2–233
Step Action Yes No
5 Test the fuel level sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to
Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
6 Test the fuel level sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the fuel level sensor. Refer to Section 8A1 Fuel Systems.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 –
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9
–
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Do any fuel level sensor DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
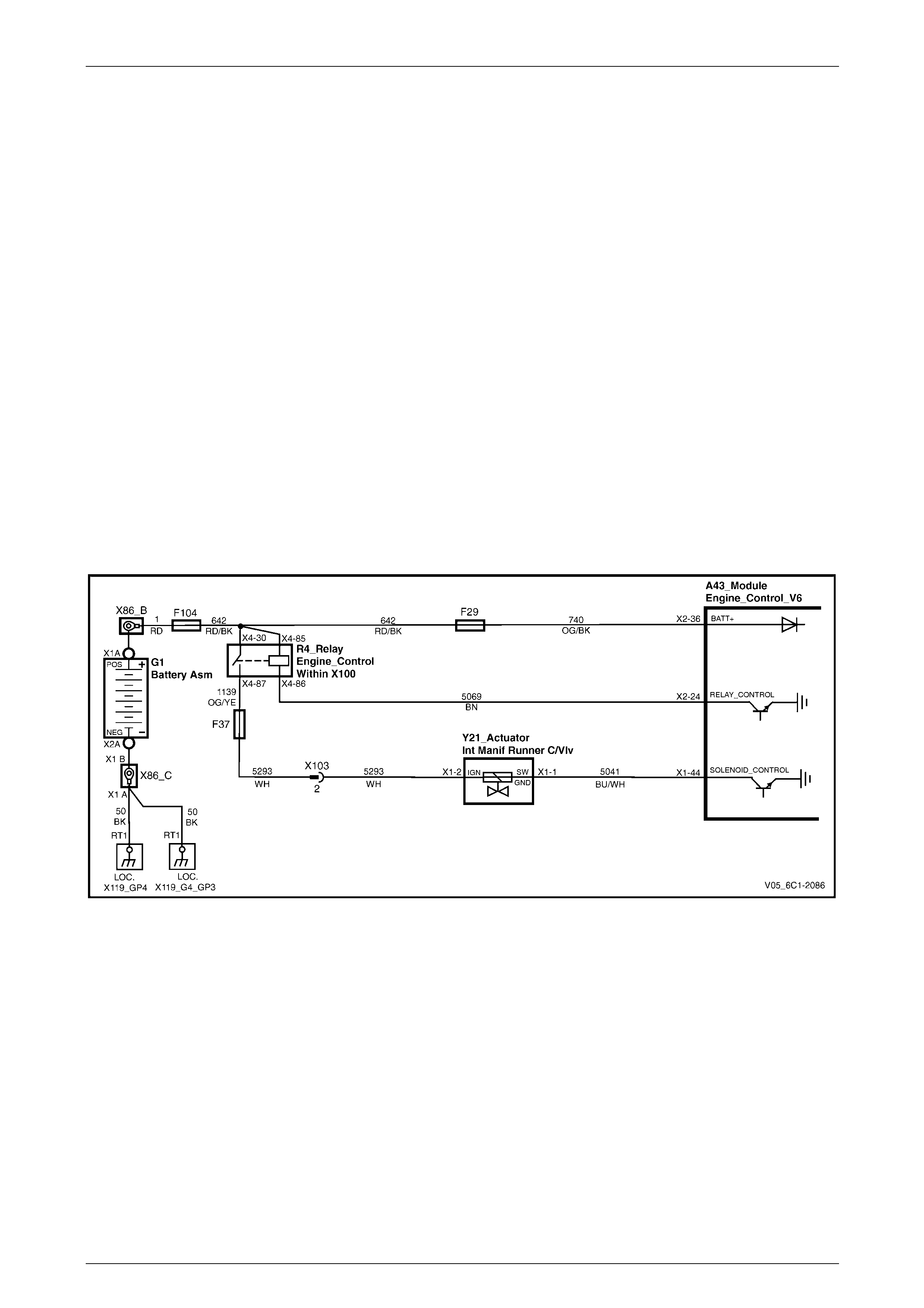
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–234
Page 6C1-2–234
5.53 DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 – Intake
Manifold Runner Control Valve Control
Circuit
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2008 – Intake Manifold Runner Control Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
• DTC P2009 – Intake Manifold Runner Control Solenoid Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P2010 – Intake Manifold Runner Control Solenoid Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies ignition positive battery voltage to the intake manifold runner control (IMRC) solenoid
through the ignition voltage circuit.
Using a device called a driver, the ECM applies a pulse width modulated (PWM) ground to the IMRC solenoid control
circuit to alter the length and volume of the intake manifold runners.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up to a voltage. The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to
determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
An IMRC solenoid circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the voltage on the IMRC solenoid control circuit outside the
predetermined range when the solenoid is commanded off.
Figure 6C1-2 – 53
To aid diagnosis, refer to 2 Wiring Diagrams and Connector Charts for the system wiring diagram and connector charts.
Additional Information
• Refer to Section 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the IMRC solenoid operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 4.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component.
Refer to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–235
Page 6C1-2–235
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The engine speed is greater than 80 r.p.m.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The ECM has commanded the IMRC Solenoid on and off at least once during the ignition cycle.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2008
The ECM detects the voltage on the IMRC solenoid control circuit is between 2.6 – 4.6 V when the solenoid is
commanded off.
DTC P2009
The ECM detects the voltage on the IMRC solenoid control circuit is less than 2.6 V when the solenoid is commanded off.
DTC P2010
The ECM detects the voltage on the IMRC solenoid control circuit is greater than 4.6 V when the solenoid is commanded
on.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The IMRC solenoid control circuit DTCs are Type C DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes for action taken when
a Type C DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 Tests the feedback voltage from the ECM.
DTC P2008, P2009 and P2010 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2
Refer to
3.4 Diagnostic
System Check
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P2008, P2009 or P2010 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3
Refer to Additional
Information in this
Section
3 1 Disconnect the IMRC solenoid wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the IMRC solenoid ignition voltage
circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–236
Page 6C1-2–236
Step Action Yes No
4 1 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
2 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the
IMRC solenoid control circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 2.6 – 4.6 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5 Repair the high resistance, open circuit or short to ground fault
condition at the IMRC solenoid ignition voltage circuit. Refer to Section
12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical wiring repair
procedures
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
6 Test the control circuit of the IMRC solenoid for a high resistance,
open circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer
to Section 12P Wiring Diagrams for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
Was any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the IMRC solenoid. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Was the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the IMRC solenoid control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs?
Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–237
Page 6C1-2–237
6 Tech 2 Data Lists
6.1 Data Display
Data List Parameter Typical Data Description
Actual Intake
Camshaft Bank 1 or 2 Degrees Varies Displays the actual intake cam position in degrees.
Actual Exhaust
Camshaft Bank 1 or 2 Degrees Varies Displays the actual exhaust cam position in degrees.
Actual Gear P/N/R/1 – 5 P/N Displays the current gear selection.
A/C Disengage
1 – 8 History
Reason for A/C
disengagement Varies
Displays the last 8 A/C compressor disengages with 8 the most
recent. There are about 8 possible reasons for the A/C
compressor to disengage.
A/C Pressure Sensor 0 – 3,450 kPa Varies Displays the A/C high side pressure as calculated by the ECM
based on the A/C high side pressure sensor signal.
A/C Pressure Sensor 0 – 5 V Varies Displays the A/C high side pressure signal voltage as received
by the ECM.
A/C Relay Circuit
Status on / off off
Displays the state of the A/C clutch relay control circuit.
Displays (Fault) if the A/C clutch relay control circuit is open,
shorted to ground or shorted to voltage.
A/C Request Signal Yes / No No Displays the state of the A/C request input from the HVAC to
the ECM.
Calculated Pedal
Position 0 – 99 % 0% Displays the accelerator pedal position as calculated by the
ECM based on the APP sensor signal.
APP Sensor 1 0.9 – 4.5 V 1 volt Displays the actual APP sensor 1 signal voltage as measured
by the ECM.
APP Sensor 2 0.45 – 2.25 V 0.5 volt Displays the actual APP sensor 2 signal voltage as measured
by the ECM.
APP Sensor 1 and
Sensor 2 Okay / Fault Okay
Displays the following signal correlation parameters between
APP sensor 1 and 2.
• Agree – normal operating conditions.
• Disagree – APP sensor 1 signal voltage does not
correlate to APP sensor 2 signal voltage.
Barometric Pressure 65 – 104 kPa Varies with
altitude
Displays the barometric pressure as calculated by the ECM
based on the barometric pressure signal.
Brake Lamp Switch Active / Inactive Inactive Displays the brake pedal signal from the brake pedal switch.
Calculated Throttle
Position 0 – 99% Varies Displays the throttle opening percentage value based on the TP
sensor 1 and 2 input to the ECM.
Catalyst Protection
Mode Active / Inactive Inactive Displays Active if the ECM is commanding catalytic converter
protection.
Crank Request Yes / No No Displays Yes if the ignition is switched to the Crank position
requesting the ECM to activate the starter relay.
Cruise Control Active Yes / No No Displays the status of the cruise control system as determined
by the ECM.
Cruise Disengage
1 – 8 History Reason Varies
Displays the last 8 cruise control disengages. There are 33
possible conditions for the cruise control to disengage.
Commanded Intake
Cam Bank 1 or 2 0 – 99% Varies Displays the intake cam position as commanded by the ECM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–238
Page 6C1-2–238
Data List Parameter Typical Data Description
Commanded Exhaust
Cam Bank 1 or 2 0 – 99% Varies Displays the exhaust cam position as commanded by the ECM.
Coolant Temperature -39°C – 140°C 88°C Displays the engine coolant temperature based on the ECT
sensor signal input to the ECM.
Cruise Control Cancel Active/Inactive Active Displays the status of the Cruise Control System.
Cruise Set/Decel
Switch Active/Inactive Inactive Displays the status of the Set / Deceleration switch.
Cruise
Resume/Accelerate Active/Inactive Inactive Displays the status of the Resume / Accelerate switch.
Cruise Control
Disengage on/off off Displays the status of the Cruise Control Disengage.
Decel. Fuel Cut-off Active/Inactive Inactive
Displays Active if the ECM is in deceleration fuel cut-off mode
during certain deceleration conditions.
Desired Exh. CMP
Bank 1 or 2 Degree Varies
Displays the desired exhaust cam angle as commanded by the
ECM.
Desired Engine Idle
Speed 0 – 7,000 r.p.m. 650 r.p.m.
Displays the desired engine idle speed as commanded by the
ECM.
Desired Throttle
Position % 0 – 99% Displays the desired throttle position.
Distance Since DTC
Cleared km Varies
Displays the elapsed mileage since a DTC was cleared from
the ECM.
DTC Set this Ignition DTCs Set / No
DTCs No DTCs Displays DTCs set on the current ignition cycle.
ECU Reset Yes/No No Displays Yes when an internal ECM reset occurs and displays
No under normal operating conditions.
Electronic Throttle
Control System
Learned Counts
Counts Varies Displays the steps
Electronic Throttle
Control System 1 and
2 Circuit Status
Ok/Fault Ok
Displays Fault if the throttle actuator 1 or 2 control circuit is
open, shorted to ground or shorted to voltage.
Engine Load 0 – 99%
0 – 5% @ idle
3 – 7% @
2500 r.p.m.
Displays the engine load in percentage value based on various
sensor inputs to the ECM.
Engine Oil Pressure
Sensor 0 – 5 V Varies Displays the engine oil pressure in voltage value based on the
engine oil pressure sensor input to the ECM.
Engine Run Time 00:00:00 Varies Displays the time elapsed since the engine was started.
Engine Speed r.p.m. 575 – 700
r.p.m.
Displays the engine speed based on the crankshaft position
sensor input to the ECM.
Evap Purge Solenoid
Command 0 – 100% Varies Displays the duty cycle of the EVAP canister purge solenoid as
commanded by the ECM. 0 percent indicates no purge.
Extended Travel
Brake Pedal Switch
Applied/
Released Released Displays the state of the brake pedal based on the extended
travel brake pedal switch input to the ECM.
Fan Relay 1
Command on/off Varies
Displays the state of the fan relay 1 control circuit as
commanded by the ECM.
Fan Relays 2 and 3
Command on/off Varies
Displays the state of the fan relay 2 and 3 control circuit as
commanded by the ECM.
Fuel Level Sensor 0 – 5 V Varies Displays the fuel level sensor signal voltage input to the ECM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–239
Page 6C1-2–239
Data List Parameter Typical Data Description
Fuel Pump Relay on/off on Displays the state of the fuel pump relay as commanded by the
ECM.
Fuel Tank Level
Remaining Litre Varies
Displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank based on the left
and right fuel level sensor input to the ECM.
Fuel Trim Total Bank
1 or 2 % Varies Displays the overall fuel trim.
Fuel Trim Learn Enabled/
Disabled Enabled
Displays Enabled when conditions for enabling long-term fuel
trim corrections are appropriate. This indicates the long-term
fuel trim responds to the short-term fuel trim. Otherwise,
displays Disabled when the long-term fuel trim does not
respond to short term fuel trim.
HO2S Bank 1 or 2
Sensor 1 Lambda 1 Displays the HO2S signal output into the ECM.
HO2S Bank 1 or 2
Sensor 2 0 – 4,998 mV Varies
400 – 700 mV Displays the HO2S signal output into the ECM.
HO2S Sensing
Element Bank 1 or 2,
Sensor 1
Ω 70 – 90Ω Displays the resistance of the HO2S sensing element.
Intake Air
Temperature -39°C – 140°C Varies Displays the intake air temperature based on the IAT sensor
input to the ECM.
Ignition Accessory
Signal on/off on
Displays on when the ECM detects a voltage at the ignition
accessory circuit.
Ignition on Signal on/off on Displays on when the ECM detects a voltage at the ignition on
circuit.
Initial Brake Apply
Command
Applied/
Released Released Displays the state of the brake pedal as transmitted from the
serial data.
Injector Time ms Varies Displays the fuel injector duty cycle.
Knock Retard
Cylinder 1 – 6 Degrees Varies
Displays the amount of spark retard applied to the ignition
control in response to the knock sensor signal input to the
ECM.
KS Signal Bank 1 or 2 V Varies Displays the knock sensor signal input to the ECM.
Loop Status Bank 1
or 2, Sensor 1
Open loop/
Closed loop Closed loop Displays Closed Loop when the ECM controls fuel delivery
based on the HO2Ss.
Loop Status Bank 1
or 2, Sensor 2
Open loop/
Closed loop Open loop Displays Closed Loop when the ECM controls fuel delivery
based on the HO2Ss.
LT FT Bank 1 or 2
Cruise/Acceleration -100% – 100% 0% Displays the ECM commanded long-term fuel trim correction for
bank 1 or 2 cruise and acceleration conditions.
LT FT Bank 1 or 2
Idle/Deceleration -100% – 100% 0% Displays the ECM commanded long-term fuel trim correction for
bank 1 or 2 idle and deceleration conditions.
Malfunction Indicator on / off off Displays the status of the Malfunction Indicator.
Mass Air Flow 0 – 655 g/s 3.4 – 6.3 g/s Displays the quantity of air flowing into the engine based on the
MAF sensor input to the ECM.
Mass Air Flow 0 – 5 V 0.9 – 1.7 V Displays the MAF sensor signal voltage input to the ECM.
Power Enrichment Yes / No No
Displays active if the ECM is in power enrichment mode. The
power enrichment mode increases fuel delivery during certain
acceleration conditions.
Reduced Engine
Power Active/Inactive Inactive
Displays active if the ECM is in reduced engine power mode.
The reduced power mode activates when the ECM detects a
fault in the throttle actuator system.
Requested Torque % 0 – 99% Displays the torque request to the ECM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–240
Page 6C1-2–240
Data List Parameter Typical Data Description
Short Term Fuel Trim
Bank 1 or 2 -25% – +25% 7-3% – +3%
The short-term fuel trim is greater than 0% during lean air/fuel
mixture condition and the HO2S signal voltage averages less
than 450 mV.
The short-term fuel trim is less than 0% during rich air/fuel
mixture condition and the HO2S signal voltage averages
greater than 450 mV.
Spark Advance -20 – +40
Degrees
2 – 10
Degrees
Displays the amount of ignition spark advance as commanded
by the ECM.
Start-up ECT - 39°C – 140°C Varies Displays the engine coolant temperature on start-up based on
the ECT sensor input to the ECM.
Start-up IAT - 39°C – 140°C Varies Displays the intake air temperature on start-up based on the
IAT sensor input to the ECM.
Time Since Engine
off 00:00:00 Varies Displays the amount of time the engine is not running.
Throttle Position 0 – 99% Varies Displays the desired TP angle as commanded by the ECM.
Traction Control Active / Inactive Inactive Displays the status of the traction control functionality of the
ABS/TCS/ESP ECU.
Transmission Gear
Select Valid/Invalid Valid
Displays invalid if the ECM receives an invalid serial data from
the TCM.
TP Sensor 1 0 – 5 V 0.5 – 0.8 V Displays the actual TP sensor 1 signal voltage based on the TP
sensor 1 input to the ECM.
TP 1 Learned Low 0 – 5 V 0 – 0.6 V Displays the learned TP sensor 1 minimum value as recorded
by the ECM during the current ignition cycle.
TP Sensor 2 0 – 5 V 4.7 – 4.1 V Displays the actual TP sensor 2 signal voltage based on the TP
sensor 2 input to the ECM.
TP 2 Learned Low 0 – 5 V 5 – 3.7 V Displays the learned TP sensor 2 minimum value as recorded
by the ECM during the current ignition cycle.
TP Sensor 1 and 2 Agree/Disagree Agree Displays Disagree when the ECM detects the TP sensor 1 and
2 are not within a predetermined value.
Vehicle Speed km/h Varies Displays the vehicle speed as calculated by the TCM based on
the vehicle speed sensor.
Volumetric Efficiency % 5 – 25% Displays the engine volumetric efficiency as calculated by the
ECM.
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–241
Page 6C1-2–241
6.2 Actuator Tests List
Other DTCs may set when the Engine Speed
Control function is used. Disregard those
DTCs that set under this condition.
Actuator Test Description
Camshaft
Actuator Solenoid
Controls the selected camshaft actuator solenoid. The normal commanded state is NONE. This test
increases or decreases the timing angle of the selected camshaft in 5 degree increments up to 50
degrees. Tech 2 initiates this test when the following conditions are met:
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine is at idle speed.
• The transmission is in park or neutral position.
The selected camshaft actuator remains in the commanded state until the command is cancelled.
Engine Speed
Control
Controls the engine idle speed from 600 r.p.m. – 1,700 r.p.m. in 20 r.p.m., 100 r.p.m. and 500 r.p.m.
increments. Tech 2 initiates this test when the following conditions are met:
• The engine speed is less than 1000 r.p.m.
• The transmission is in park or neutral position.
The engine management system remains in this commanded state until the command is cancelled.
Throttle Position
Controls the throttle plate position in 25 percent increments. Tech 2 initiates this test when the
following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on with the engine not running.
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• There are no vehicle speed sensor DTCs set.
• The ECM is not performing a throttle learn procedure.
The engine management system remains in this commanded state until the command is cancelled.
Alternator L
Terminal
Controls the load of the generator on the engine.
Fuel Pump Relay
Controls the fuel pump relay. The normal commanded state is NONE. Tech 2 initiates this test when
the following conditions are met:
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• There are no vehicle speed sensor DTCs set.
If the engine is running and the engine control relay is commanded off, the engine will stall. The
engine management system remains in this commanded state for two seconds or when the
command is cancelled.
A/C Relay Test Controls the A/C relay.
Fan Relay Test Controls the Fan relay.
Starter Relay Test Controls the starter relay.